Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) (i) 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ;
|
|
|
- Teresa Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (a) (i) idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; Need the idea of constant steady and regulation keeping and in the body 2 within (narrow) limits / within (narrow) range / about a set point ; 2 ACCEPT about the nm 3 even though environment is changing ; IGNORE ref to negative feedback (as mechanism rather than definition) / optimum conditions CREDIT mps 2 & 3 (only) if response is in terms of example(s) e.g. temperature / blood glucose 2 max Note maintaining a stable body temperature = 0 keeping your body temperature at 37 o C = (mp 2) even though it is getting cold = (mp 3) 2
2 (a) (ii) cells / cells / recepts, detect, change / increased / decreased, in blood glucose (concentration) ; CREDIT crect ref to detection by /a (low) /b (high) IGNORE monit / stimulate / figures quoted 2 if high(er) glucose (concentration), beta /, cells (in pancreas) release insulin ; 3 (increased) uptake / absption, of glucose by, liver / muscle / effect, cells ; 4 enters through glucose transpt proteins (in cell surface membrane) ; 5 glucose converted to glycogen / glycogenesis ; 6 increased (use of glucose in), respiration / ATP production ; 7 if low(er) glucose (concentration), alpha /, (in pancreas) cells release glucagon ; 8 (increased) conversion of glycogen to glucose / glycogenolysis ; 9 (increased) conversion of other compounds (amino acids / lipids) to glucose / gluconeogenesis ; 2 ACCEPT produce rather than release DO NOT CREDIT B cells 3 CREDIT increased permeability of named cell to glucose IGNORE use / target cell 4 CREDIT GLUT channels 5 unambiguous spelling only of glycogen and glycogenesis 6 DO NOT CREDIT in context of and cells ACCEPT increased respiration by body 7 unambiguous spelling only of glucagon ACCEPT produce rather than release 8 unambiguous spelling only of glycogen and glycogenolysis 9 unambiguous spelling only of gluconeogenesis 0 glucose leaves cells, by facilitated diffusion / through glucose channels ; AVP ; e.g. crect cellular detail f insulin release in effect cells insulin binds to recept on plasma membrane of hepatocytes crect ref to secondary messenger (camp) e.g. ref to inhibity effect(s) of hmone 5 max conversion in cells / secretion of antagonist QWC technical terms used appropriately and spelt crectly ; Use of three terms from: recept, beta, insulin, effect, glycogen, glycogenesis, alpha, glucagon, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, facilitated diffusion Please insert a QWC symbol next to the pencil icon, followed by a tick ( ) if QWC has been awarded a cross ( ) if QWC has not been awarded You should use the green dot to identify the QWC terms that you are crediting. 3 2
3 (b) (i) requires (daily), insulin / hmone, injections ; is not affected by dietary changes ; (b) (ii) max ACCEPT insulin is not being produced in sufficient quantities Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks idea that has developed in, an old(er) person / middle age / a 55 year old ; Total 0 DO NOT CREDIT references to diet, as this was ineffective but use NBOD icon to indicate this 4 3
4 2 (a) (i) liver ; 2 (a) (ii) (high intake of protein) leads to a large amount of amino acids ; 2 (excess) amino acids cannot be sted ; Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks Must emphasise the idea of leading to, me / too many / lots of, amino acids 3 amino acids deaminated amine group / NH 2, removed / converted to ammonia ; 3 DO NOT CREDIT deamination of protein IGNORE amino group 4 (large amount of) ammonia enters nithine cycle (f conversion to urea) ; 4 ACCEPT ref to urea cycle instead of nithine cycle crect diagram of the cycle 5 increased, blood / plasma, concentration of urea (leads to me urea in, filtrate / urine) ; 2 (b) 6 high concentration of, amino acids / urea, in blood increases water absption from urine ; 3 max Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks diabetes (mellitus) ; ACCEPT kidney disease / nephritis / kidney failure / pregnancy IGNORE type 2 5 4
5 2 (c) (i) Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks (human) chionic gonadotrop(h)in / hcg; ACCEPT phonetic spelling (a vowel between the ch and r) DO NOT CREDIT chronic ACCEPT combinations of lower and upper case letters DO NOT CREDIT letters in the increct der (eg hgc) 6 5
6 2 (c) (ii) ACCEPT joins / attaches, f bind throughout IGNORE reacts with DO NOT CREDIT active site / enzyme references instead of antibodies If a candidate s whole answer is in terms of pregnancy testing, DO NOT CREDIT mps, 2 & 3 LH binds to, anti-lh / its complementary (free / mobile / with dye), antibodies ; 2 this (LH-anti-LH) antibody complex moves along (test stick together with urine) ; ACCEPT hmone f LH specific f complementary 2 IGNORE urine moving along the stick on its own 3 this (LH-anti-LH) antibody complex binds (only) with, immobilised antibodies specific to them / lower band of immobilised antibodies ; 4 (only) control antibodies bind with, immobilised antibodies specific to them / upper band of immobilised antibodies ; 5 idea that binding of antibody (with dye to its immobilised anti-antibody) produces coloured line ; 6 2 lines indicates, positive result / presence of LH darker line = me LH control / top, line indicates the strip is wking (crectly) control / top, line alone indicates no LH ; 3 max Total 9 5 Award in context of either LH control line 6 DO NOT CREDIT this alternative in context of positive pregnancy result 7 6
7 3 (a) (i) Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks W (chloplast outer) membrane / envelope ; X granum / grana ; W DO NOT CREDIT cell / plasma, membrane DO NOT CREDIT inner membrane alone but IGNORE if stated together with outer X ACCEPT granal stack / thylakoid stack Y stroma ; Y DO NOT CREDIT stoma / matrix / cytoplasm 3 (a) (ii) Z thylakoid(s) / (intergranal) lamella(e) ; 4 DO NOT CREDIT any mps in context of respiration (DNA) coding f, gene(s) / protein / enzyme (ribosome) protein / enzyme, synthesis ; IGNORE infmation / ref to replication DO NOT CREDIT making amino acids 2 (enzymes f production of / proteins f) chlophyll synthesis / pigment synthesis / photosystem ; 3 (protein f) electron, accept(s) / carrier(s) ; 4 ATP synth(et)ase ; 3 CREDIT named accept / carrier (e.g. NADP / cytochrome) 5 (enzyme / PSII) f, photolysis / splitting of water ; 6 (enzymes f) Calvin cycle / light independent reaction ; 2 max 6 CREDIT Rubisco 8 7
8 3 (b) Mark the first answer in each box. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks ACCEPT lower case letters DO NOT CREDIT N and C instead of B, as they have been asked to use B statement letter ATP is produced B an electron leaves photosystem I B ; IGNORE N and C if stated in addition to B in rows and 2 electrons are passed along an electron carrier chain electrons leave both photosystem I and photosystem II an electron from a water molecule replaces the electron lost from the photosystem B ; N ; N ; ACCEPT B f this row the same electron returns to the photosystem C ; 5 Total 9 8
9 4 (a) (i) link reaction and Krebs cycle ; 4 (a) (ii) Mark the first 2 answers. If they are crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks oxidative phosphylation ; 4 (b) (i) to make the volume of, contents / peas, the same (in the respirometers) ; 2 idea that because the volume of peas in A is greater than the volume of peas in B the peas in A, are bigger / take up me space the peas in A have absbed water the peas in B, are smaller / take up less space ; 3 as without the beads there would be me, air / gas / oxygen, in B than in A ; 2 max ACCEPT electron transpt chain / electron transpt system / electron carrier chain IGNORE chemiosmosis DO NOT CREDIT photespiration IGNORE ref to mass / weight 2 IGNORE ref to mass / weight must refer to A / soaked / germinating and/ B / dry / dmant 3 CREDIT idea that with the presence of beads the volume of gas would be the same 0 9
10 4 (b) (ii) (determined by) finding difference in volume between (30) soaked, seeds / peas and (30) dry, seeds / peas ; 2 the difference represents the volume of glass beads required add the quantity of glass beads necessary to make the volumes (of respirometer contents) equal ; ACCEPT ref to mass/weight instead of volume throughout (ii) as an err carried fward (ecf) 4 (c) (i) 0.04 ; ; 3 calculate / knowing, volume of bead to determine number of beads equivalent to volume required ; 2 max 2 3 CREDIT any suitable method of determining the volume of beads required e.g. displacement put soaked peas in tube and measure volume; mark; then put dry peas in and add glass beads into tube and top up to mark Crect answer = 2 marks, even if no wking If answer increct, not rounded crectly given to me than 3 dp then ALLOW mark f seeing Only if there is no answer on the dotted answer line, should you look f the answer in the wking in the appropriate place in the table. 0
11 4 (c) (ii) CREDIT a f lower temperature at, higher temperature / 25 0 C increased kinetic energy ; IGNORE me collisions / ESCs 4 (c) (iii) (named respiraty) enzymes / decarboxylases / dehydrogenases, involved ; 2 Needs a clear statement that they are involved in respiration IGNORE (named) co-enzymes ACCEPT germinating f soaked, peas f seeds, dmant f dry throughout reactions require aqueous medium / reactions need to take place in water / reactions need to take place in solution ; IGNORE ref to reactants dissolving 2 enzymes and substrates can move (to collide) in soaked seeds movement (of reactants), prevented / limited, in dry seeds ; 2 IGNORE ref to ESC as the mp is f the idea of mobility 3 soaked seeds need me, ATP / energy dry seeds need less, ATP / energy ; 3 DO NOT CREDIT no ATP / energy 4 f, protein synthesis / mitosis / other (named) metabolic reaction ; 2 max Total 2 4 CREDIT soaked peas have increased metabolism IGNORE growth / respiration DO NOT CREDIT ref to photosynthesis 2
12 5 (a) Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks E (proximal / first / distal / second) convoluted tubule / PCT / DCT ; E ACCEPT collecting duct DO NOT CREDIT loop of Henle (as not in ctex) DO NOT CREDIT cells of / tube IGNORE nephron tubule / nephron F (lumen of) Bowman s / renal, capsule ; 2 3 2
13 5 (b) (i) afferent arteriole, has diameter greater than that of / is wider than, efferent arteriole ; IGNORE different / larger / smaller, without suitable qualification IGNORE thicker / thinner 2 build up of / high, hydrostatic / blood, pressure ; 3 endothelium / wall, of, capillary / glomerulus, has, (small) pes / fenestrations ; 4 (these allow) ultrafiltration ; QWC technical terms used appropriately and spelt crectly ; 3 ACCEPT holes / gaps instead of pes IGNORE epithelium DO NOT CREDIT cell wall DO NOT CREDIT podocytes / basement membrane if linked to capillary structure IGNORE podocytes / basement membrane if linked to the Bowmans capsule 2 max Use of three terms from: afferent, efferent, arteriole, hydrostatic, endothelium, fenestrations, ultrafiltration ( derived term) 5 (b) (ii) podocyte(s) ; Please insert a QWC symbol next to the pencil icon, followed by a tick ( ) if QWC has been awarded a cross ( ) if QWC has not been awarded You should use the green dot to identify the QWC terms that you are crediting. Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks 4 3
14 5 (c) (i) if kidney cannot filter so substances remain in blood increase / high, in urea ; 2 increase / high, in, (named) ions / (named) salts ; 3 increase / high, in water ; 4 AVP ; OR Candidate s answer can only come from one section of the mark scheme if type of failure not specified. However, all marks are available if clearly linked to the type of failure. 3 IGNORE ref to water potential 4 e.g. high(er) levels of, creatinine / (named) hmone high(er) levels of, metabolite / toxin, breakdown if problems cause substances to be lost indiscriminately 5 decrease / low, in, protein / blood cells ; 6 decrease / low, in, (named) ions / (named) salts ; 7 decrease / low, in, glucose / amino acids / vitamins ; 8 decrease / low, in water ; f mps 5-8 DO NOT CREDIT no / none / zero 7 IGNORE sugar 8 IGNORE ref to water potential 2 max Note increase in urea = (mp ) increase in salt and water = 2 (mps 2 & 3) low in protein but high in urea = (mp 5, but not mp as different type of failure and has not been specified) 5 4
15 5 (c) (ii) if not closely matched CREDIT a f all mark points donated kidney will be recognised as, feign / non-self ; Needs the idea of the body recognising the feign nature 2 antigens / glycoproteins, (on donated kidney) will be different ; 3 causing rejection ; 4 (response) by immune system ; 5 use of immuno-suppressant drugs ; 4 CREDIT a description of immune response DO NOT CREDIT ref to autoimmunity 6 ref to need f suitable size in specific case (e.g. if recipient is a small child) ; 3 max Total 6 5
16 6 (a) Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks recepts ; 2 intensity ; 3 chemical ; ACCEPT recept cells DO NOT CREDIT neurones / gans 2 IGNORE brightness DO NOT CREDIT frequency 3 IGNORE volatile / soluble 4 potential / value ; 5 impulse ; 5 4 ACCEPT level / (needed) f depolarisation IGNORE numerical value quoted / recept DO NOT CREDIT action potential 5 ACCEPT action potential DO NOT CREDIT message / signal / infmation / stimulus 7 6
17 6 (b) (i) Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks IGNORE ref to cell size / myelin(ation) the mot neurone - structure the cell body is at (one) end of the, neurone / cell the cell body is in, brain / spinal cd / CNS dendrites connected (directly) to cell body long(er) axon no dendron axon, connects to / ends at, effect / mot end plate ; DO NOT CREDIT at end of axon / nerve IGNORE reference to dendrite length CREDIT a f sensy i.e. cell body is at centre of cell cell body is in PNS dendrites at the end(s) of, axon / dendron sht(er) axon dendron present connects to / starts at, recept 8 7
18 6 (b) (ii) Mark the first answer. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks IGNORE refs to connects the mot neurone - function carries, impulse(s) / action potential(s), from, brain / spinal cd / CNS / relay neurone carries, impulse(s) / action potential(s), to, effect / muscle / gland ; DO NOT CREDIT message / signal / infmation / stimulus DO NOT CREDIT message / signal / infmation / stimulus Total 7 CREDIT a f sensy i.e. carries, impulse(s) / action potential(s), to, brain / spinal cd / CNS / relay neurone carries, impulse(s) / action potential(s), from recept 9 8
Question Expected Answer Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) dendron present ; starts at / connects to, (sensory) receptor ; 3
 (a) 2 3 mot neurone sensy neurone cell body in CNS cell body, not in CNS / in PNS ; cell body at end (of neurone) dendrites connect directly to cell body cell body, not at end / in middle (of neurone)
(a) 2 3 mot neurone sensy neurone cell body in CNS cell body, not in CNS / in PNS ; cell body at end (of neurone) dendrites connect directly to cell body cell body, not at end / in middle (of neurone)
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) 93 (to nearest whole number) / 93.4 (to 3 sig figs) ; per million (people) / million -1 ;
 Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) 93 (to nearest whole number) / 93.4 (to 3 sig figs) ; per million (people) / million -1 ; Crect answer with crect units = 2 marks Crect answer with no/increct units
Question Answer Mark Guidance 1 (a) 93 (to nearest whole number) / 93.4 (to 3 sig figs) ; per million (people) / million -1 ; Crect answer with crect units = 2 marks Crect answer with no/increct units
F214 Mark Scheme June 2013
 1 (a) (i) 3 Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the A cytoplasm ; B cell surface (plasma) membrane / neurone
1 (a) (i) 3 Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the A cytoplasm ; B cell surface (plasma) membrane / neurone
W ; Z ; X ; W ; 4 IGNORE ref to phosphorylation of glucose as this is taken into account in estimate.
 1 (a) (i) Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks 1 (a) (ii) W ; Z ; X ; W ; 4 IGNORE
1 (a) (i) Mark the first answer on each prompt line. If the answer is crect and an additional answer is given that is increct contradicts the crect answer then = 0 marks 1 (a) (ii) W ; Z ; X ; W ; 4 IGNORE
thebiotutor.com F214 Module 2 Excretion Answers
 thebiotut.com F24 Module 2 Excretion Answers thebiotut.com . excretion secretion one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
thebiotut.com F24 Module 2 Excretion Answers thebiotut.com . excretion secretion one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
Answer Marks Guidance ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ;
 Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
Question Answer Marks Guidance 1 (a) ( 1 idea of maintaining (relatively) stable internal, environment / state ; 1 Need the idea of constant or steady and regulation or keeping and in the body within (narrow)
GCE BIOLOGY BY4. Cells increase in size / storage of nutrients; (iii) Population grows at an increasing rate / doubles in unit time /
 GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2]
![2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2] 2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis [2]](/thumbs/79/78920042.jpg) 2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis.... [2] Describe how negative feedback is used to
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis.... [2] Describe how negative feedback is used to
BY4. Question Answer Mark. D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon. NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve ending/ neuromuscular.
 BY4 1. (a) (i) A = Dendrite(s), accept dendron; B = Axon/ axoplasm; C = Node(s) of Ranvier; D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon 4 terminal/ synaptic bulb; NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve
BY4 1. (a) (i) A = Dendrite(s), accept dendron; B = Axon/ axoplasm; C = Node(s) of Ranvier; D = Synaptic knob/motor end plate/ axon ending/ axon 4 terminal/ synaptic bulb; NOT synpase/ dendrite/ nerve
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) 3 max
 Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
Question Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance 1 (a) phospholipid bilayer containing proteins ; head / hydrophilic region, facing outwards OR tail / hydrophobic region, facing inwards ; Marks can
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2011 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology. Mark Scheme for June Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Advanced GCE. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 2015 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion.
 1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
1. Excretion and secretion are two processes that take place in the body of a mammal. Complete the table below to compare the processes of excretion and secretion. excretion secretion one difference one
At this second appointment, however, it was discovered that the dietary changes had not been effective, which was unexpected.
 Question: 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis. (ii) Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose
Question: 1 (a) The control of blood glucose is a very important aspect of homeostasis. (i) Explain what is meant by the term homeostasis. (ii) Describe how negative feedback is used to control blood glucose
Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon
 Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE BIOLOGY F214/01 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy *F210040113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE BIOLOGY F214/01 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy *F210040113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones.
![2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones. 2 Answer all the questions.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the junction between two neurones.](/thumbs/93/111729479.jpg) 2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The cells of the body need to communicate with one another. State the name given to this process of communication.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The cells of the body need to communicate with one another. State the name given to this process of communication.... [1] (b) Fig. 1.1 is an electron micrograph of the
substance excreted protein-deficient diet protein-rich diet. urea uric acid ammonium ions creatinine
 1. Define the term excretion....... [Total 2 marks] 2. The table below shows the mass of different substances excreted by a volunteer during two 24 hour periods. During the first 24 hour period, the volunteer
1. Define the term excretion....... [Total 2 marks] 2. The table below shows the mass of different substances excreted by a volunteer during two 24 hour periods. During the first 24 hour period, the volunteer
GCE Biology. Mark Scheme for June Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Advanced GCE. Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Unit F24: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 207 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Unit F24: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Advanced GCE Mark Scheme for June 207 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Homeostasis (chapter 14):
 1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Homeostasis (chapter 14): Homeostasis: to maintain a constant/stable internal environment in the body The importance of homeostasis in a mammal:
1 P a g e h t t p s : / / w w w. c i e n o t e s. c o m / Homeostasis (chapter 14): Homeostasis: to maintain a constant/stable internal environment in the body The importance of homeostasis in a mammal:
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Mark Scheme for June Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for June 2013 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
(a) Urea is one compound that is excreted from the mammalian body in urine.... [1]
![(a) Urea is one compound that is excreted from the mammalian body in urine.... [1] (a) Urea is one compound that is excreted from the mammalian body in urine.... [1]](/thumbs/80/82246337.jpg) 1 Urine is a liquid that is composed of a number of different substances. (a) Urea is one compound that is excreted from the mammalian body in urine. (i) Name the organ that produces urea.... [1] (ii)
1 Urine is a liquid that is composed of a number of different substances. (a) Urea is one compound that is excreted from the mammalian body in urine. (i) Name the organ that produces urea.... [1] (ii)
F214 Communication, Homeostasis & Energy
 F Communication, Homeostasis & Energy (a) excretion secretion One mark per row. one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
F Communication, Homeostasis & Energy (a) excretion secretion One mark per row. one difference (metabolic) waste toxin / harmful substance is to be removed from body does not use vesicles useful product
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 9700 BIOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level and GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Maximum raw mark 60
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level and GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2006 question paper 9700 BIOLOGY 9700/04 Paper 4 Maximum raw mark 60
2804 Central Concepts. June Mark Scheme
 Central Concepts June 00 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.. Please mark all post-standardisation
Central Concepts June 00 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.. Please mark all post-standardisation
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
GCE. Biology. Mark Scheme for the Units. January 2010 HX21/MS/R/10J. Advanced GCE A2 H421 Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H021 PMT
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE A H Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H0 Mark Scheme f the Units January 00 HX/MS/R/0J Oxfd Cambridge and RSA Examinations F Mark Scheme January 00 F Communication, Homeostasis & Energy
GCE Biology Advanced GCE A H Advanced Subsidiary GCE AS H0 Mark Scheme f the Units January 00 HX/MS/R/0J Oxfd Cambridge and RSA Examinations F Mark Scheme January 00 F Communication, Homeostasis & Energy
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
PMT GCE BIOLOGY - BY4. Marks Available. 1 (a) effectors /{carry out/ bring about} the response/ react to a stimulus;
 GCE BIOLOGY - BY4 1 (a) effectors /{carry out/ bring about} the response/ react to a stimulus; 1 (b) only have a nerve net /no CNS / (nerve fibres) non-myelinated/ branching neurons/ narrower axons; NOT
GCE BIOLOGY - BY4 1 (a) effectors /{carry out/ bring about} the response/ react to a stimulus; 1 (b) only have a nerve net /no CNS / (nerve fibres) non-myelinated/ branching neurons/ narrower axons; NOT
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body
 Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
2804 Central Concepts. January Mark Scheme
 - 2804 Central Concepts ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
- 2804 Central Concepts ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions. 2. Please mark all post-standardisation
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment of kidney failure.
 1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
The functions of the kidney:
 The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
The functions of the kidney: After reading this lecture you should be able to.. 1. List the main functions of the kidney. 2. Know the basic physiological anatomy of the kidney and the nephron 3. Describe
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical that can be used to preserve milk.
 Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Enzymes are made and used in all living ganisms. (a) What is an enzyme? (2) (b) Many enzymes wk inside cells. In which part of a cell will most enzymes wk? Draw a ring around the crect answer. cell membrane
Subject: Central Concepts Code: Session: January Year: Mark Scheme
 Subject: Central Concepts Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Subject: Central Concepts Code: : : MAXIMUM MARK 90 ADVICE TO EXAMINERS ON THE ANNOTATION OF SCRIPTS 1. Please ensure that you use the final version of the. You are advised to destroy all draft versions.
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Thebiotutor.com. A2 Biology OCR. Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy. Module Communication, Nerves & Hormones.
 Thebiotut.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy Module 1.1 1.3 Communication, Nerves & Hmones Answers Andy Todd 1 1. (a) 1 myelin / myelinated / lipid / fatty (sheath); DO
Thebiotut.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis and Energy Module 1.1 1.3 Communication, Nerves & Hmones Answers Andy Todd 1 1. (a) 1 myelin / myelinated / lipid / fatty (sheath); DO
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The nervous system is made up of a number of different types of neurone, which transmit electrical impulses.
 2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The nervous system is made up of a number of different types of neurone, which transmit electrical impulses. Complete the table below by stating three differences in the
2 Answer all the questions. 1 (a) The nervous system is made up of a number of different types of neurone, which transmit electrical impulses. Complete the table below by stating three differences in the
M1. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine 1
 M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
The Urinary System PART A
 15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
15 The Urinary System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Functions of the Urinary
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Question: 1. (i) Name the products of the light dependent stage that are used in the Calvin cycle. [2]
![Question: 1. (i) Name the products of the light dependent stage that are used in the Calvin cycle. [2] Question: 1. (i) Name the products of the light dependent stage that are used in the Calvin cycle. [2]](/thumbs/74/70694783.jpg) Question: 1 (a) The Calvin cycle is the stage of photosynthesis during which carbon dioxide is fixed. The Calvin cycle uses the products of the light dependent stage. (i) Name the products of the light
Question: 1 (a) The Calvin cycle is the stage of photosynthesis during which carbon dioxide is fixed. The Calvin cycle uses the products of the light dependent stage. (i) Name the products of the light
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy
 A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy TOPIC 1 Communication & Homeostasis Need for communication Organisms must maintain certain conditions Optimal conditions for cells and enzymes
A-LEVEL BIOLOGY MODULE 5: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy TOPIC 1 Communication & Homeostasis Need for communication Organisms must maintain certain conditions Optimal conditions for cells and enzymes
PMT GCE. Biology. Advanced GCE Unit F214: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy. Mark Scheme for January Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations
 GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for January 0 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
GCE Biology Advanced GCE Unit F: Communication, Homeostasis & Energy Mark Scheme for January 0 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading UK awarding body, providing
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
F214. BIOLOGY Communication, Homeostasis and Energy ADVANCED GCE. Wednesday 22 June 2011 Morning PMT
 ADVANCED GCE BIOLOGY Communication, Homeostasis and Energy F214 *F215690111* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Insert (inserted) Other materials required: Electronic calculator
ADVANCED GCE BIOLOGY Communication, Homeostasis and Energy F214 *F215690111* Candidates answer on the question paper. OCR supplied materials: Insert (inserted) Other materials required: Electronic calculator
*Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances
 The Excretory System GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND DEFINITIONS: *Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances *Homeostasis (homeo: constant; stasis: state)
The Excretory System GENERAL KNOWLEDGE AND DEFINITIONS: *Function maintains homeostasis by regulating the water balance and by removing harmful substances *Homeostasis (homeo: constant; stasis: state)
AQA Applied Biology. New Document 1. Class: Year 12. Date: March minutes. Time: 129 marks. Marks: Comments:
 New Document Name: Class: Year 2 AQA Applied Biology Date: March 208 Time: 5 minutes Marks: 29 marks Comments: Q. (a) The table shows some parts of cells and two different types of cell. Complete the table
New Document Name: Class: Year 2 AQA Applied Biology Date: March 208 Time: 5 minutes Marks: 29 marks Comments: Q. (a) The table shows some parts of cells and two different types of cell. Complete the table
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Chapter 25: Urinary System
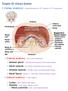 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
WJEC. BY4 Kidney Questions
 NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number. UNIT 3 Energy, Homeostasis and the Environment
 GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 47 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 A LEVEL BIOLOGY UNIT 3 Energy, Homeostasis and the Environment SPECIMEN PAPER (2 hours) 90 marks
GCE AS and A LEVEL BIOLOGY Specimen Assessment Materials 47 Candidate Name Centre Number Candidate Number 0 A LEVEL BIOLOGY UNIT 3 Energy, Homeostasis and the Environment SPECIMEN PAPER (2 hours) 90 marks
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION
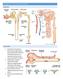 LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
LECTURE 25: FILTRATION AND CLEARANCE NEPHRON FILTRATION 1. Everything in the plasma is filtered except large proteins and red blood cells. The filtrate in Bowman s capsule is an isosmotic fluid that is
TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks]
![TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks]](/thumbs/96/128475268.jpg) Bloomfield Hall School Test (Unit 0-) Name :... Pa: Biolog y Date :... Class: FIV Time Allowed: 0Minutes Maximum Marks: TKheory Section: [Total 6 Marks] (a) Define the term excretion. [] (b) Fig.. shows
Bloomfield Hall School Test (Unit 0-) Name :... Pa: Biolog y Date :... Class: FIV Time Allowed: 0Minutes Maximum Marks: TKheory Section: [Total 6 Marks] (a) Define the term excretion. [] (b) Fig.. shows
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids. Accept: gluconeogenesis / references to glycogen as source of glucose 3
 M1.(a) 1. Release of glucagon;. Leads to formation of glucose in liver (cells); Reject: glucagon breaks down glycogen, or any other biological molecule 3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids.
M1.(a) 1. Release of glucagon;. Leads to formation of glucose in liver (cells); Reject: glucagon breaks down glycogen, or any other biological molecule 3. From non-carbohydrates / amino acids / fatty acids.
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
QUESTIONSHEET 1. Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions. Homeostasis is the regulation of the internal environment within narrow limits. This gives the organism
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions. Homeostasis is the regulation of the internal environment within narrow limits. This gives the organism
Unit 4 Homeostasis. The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt. Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment -
 Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Unit 4 Homeostasis The term homeostasis refers to the body s attempt Your body systems must to maintain a stable internal environment - The body is trying to maintain, through a series of monitored adjustments.
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points.
 = The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
= The maintenance of a constant internal environment Homeostasis involves maintaining the volume, chemical make up and other factors of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits and set-points. The
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy
 AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy 3.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 3.2: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. 3.3: Organisms capture and store
AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy 3.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 3.2: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. 3.3: Organisms capture and store
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Cell Structure.
 Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
Cell Structure Mark Scheme 1 Level International A Level Subject Biology Exam Board CIE Topic Cell Structure Sub Topic Booklet Cell Structure Theory Paper Type Mark Scheme 1 Time Allowed : 64 minutes Score
R = Ribose / pentose (sugar). [3] (b) (i) Supplies energy; all reactions; in all cells; [Max 2] (not: produces)
![R = Ribose / pentose (sugar). [3] (b) (i) Supplies energy; all reactions; in all cells; [Max 2] (not: produces) R = Ribose / pentose (sugar). [3] (b) (i) Supplies energy; all reactions; in all cells; [Max 2] (not: produces)](/thumbs/93/114252105.jpg) . (a) P = phosphate (not: phosphoric acid) Q = nitrogenous base / organic base / adenine; R = Ribose / pentose (sugar). [3] (b) (i) Supplies energy; all reactions; in all cells; [Max ] (not: produces)
. (a) P = phosphate (not: phosphoric acid) Q = nitrogenous base / organic base / adenine; R = Ribose / pentose (sugar). [3] (b) (i) Supplies energy; all reactions; in all cells; [Max ] (not: produces)
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
