USER GUIDE. Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! USERGUIDE
|
|
|
- Christiana Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USER GUIDE USERGUIDE Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! Amino acid analysis kits for: Sample Prep Derivatization GC or LC Analysis 1
2 USERGUIDE Table of Contents Obstacles in Current... 3 Amino Acid Protocols Physiological & Hydrolysate... Amino Acid Testing 50 + Amino Acids... 5 and Related Compounds Quantified in 15 Minutes Eight Simple Steps... 6 in 15 minutes 8 Minutes of Sample Prep... 8 Accurate Analysis... 9 Amino Acid Sample Prep and Analysis in 15 Minutes Accurate Quantitation Applications EZ:faast Kit Components Evaluate an EZ:faast kit in Frequently Asked Questions your lab for 30 days. If you are not completely satisfied with the performance, return it for a full refund. Ordering Information
3 USERGUIDE EZ:faast kits provide reagents and supplies for sample preparation, derivatization and GC/FID, GC/NPD, GC/MS and LC/MS analysis of over 50 amino acids and di-peptides in complex matrices and protein hydrolysates. Additionally the EZ:faast method offers: A standard 8 minute procedure for sample preparation and derivatization Elimination of labor-intensive protein and urea removal procedures Excellent method reproducibility (RSD <1%) and quantitation down to 1nmol/mL Established methods for amino acid analysis in serum, urine, beer, wine, feeds, fermentation broths, foodstuffs and protein hydrolysates Obstacles in Current Amino Acid Protocols Ion-exchange chromatography using ninhydrin derivatization or reversed phase chromatography have traditionally been used on dedicated instruments for amino acid analysis. Current ion-exchange methods originated in the late 190s and are known for lengthy minute runtimes along with extensive sample preparation to remove interfering components (such as proteins or urea). Ion-exchange methods typically use expensive, dedicated instruments that are difficult to maintain and operate. Other methods, relying on reversed-phase HPLC, have been developed that can be run on any HPLC system saving the expense of purchasing and maintaining a dedicated amino acid analyzer. However, reversed phase HPLC methods can suffer from numerous deficiencies including: long analysis times, laborious sample preparation protocols, poor peak resolution, marginal quantification, and limited stability of derivatized amino acids. Laboratories needing a rapid and simple method to process high volumes of samples may find traditional amino acid analysis laborious and costly. EZ:faast Amino Acid analysis kits has been developed to overcome these obstacles with a simple kit containing reagents and supplies to perform sample preparation, derivatization and improved quantitation using any GC/FID, GC/NPD, or GC/MS system in 15 minutes or by LC/MS in 2 minutes. 3
4 USERGUIDE Economical, Hassle-Free Amino Acid Analysis Protein and Peptide Hydrolysates Free (Physiological) Amino Acids Free amino acids are routinely analyzed in physiological fluids, feeds, fermentation broths and other sources for basic research, nutritional labeling and more recently for patient diagnosis. Metabolic deficiencies are diagnosed based on the levels of particular amino acids in body fluids. While some protocols may provide adequate chromatographic methods and derivatization procedures, sample throughput remains slow due to lengthy sample cleanup and preparation requirements. Using the EZ:faast Free (Physiological) Amino Acid GC and LC/MS kits, sample preparation time is only 7 minutes regardless of sample matrix. Blood, plasma, urine, cerebral spinal fluid, wine or grain samples contain interfering proteins, urea and other impurities that can lead to poor chromatographic results. In 7 minutes, EZ:faast can remove interfering components leaving a highly pure and derivatized amino acid sample ready for injection. Analysis time is dramatically reduced and quantitation significantly improved over traditional methods; this makes for a rapid and sensitive method for any lab (Figure 1). For labs with a large number of samples, EZ:faast truly provides rapid throughput. Without the need for lengthy sample preparation, labor cost is dramatically decreased, making EZ:faast a much more economical method. Figure 1 Free Amino Acid Standards Analyzed by EZ:Faast pa ALA SAR GLY ABA VAL ß-ALA IS LEU aile ILE SER THR PRO ASN MET TPR ASP HYP Numerous labs perform quality control assays of both natural and synthetic proteins and peptides by quantifying the hydrolyzed amino acid composition of their final protein product. Protein core labs will find the EZ:faast kits excellent for confirming protein identity and purity quickly. Using an EZ:faast GC kit, results are obtainable in about 15 minutes and in 2 minutes when using the EZ:faast LC/MS kit. For labs analyzing large number of samples the short analysis time dramatically increases productivity and reduces the cost of sample analysis. Proteins are long linear strings of amino acids connected to each other by peptide bonds. Hydrolysis of the peptide bonds releases the individual amino acids. The EZ:faast system allows rapid purification and derivatization of the released amino acids. Composition and quantity of hydrolyzed amino acids can then be determined quickly and accurately (Figure 2). The overall system provides both a rapid and simple sample preparation and analysis procedure, and is amenable to limited automation. More samples can now be analyzed over a given amount of time for less money as labor cost is dramatically decreased by this simple and rapid procedure. GLU PHE AAA APA GLN ORN GPR LYS HIS HLY TYR TRP PHP CTH App ID 133 C-C 0 Figure 2 Protein Amino Acids Standards Analyzed by EZ:faast 2 3 LEU PRO HYP PHE GLY ALA VAL NORV ILE SER ASP MET LYS TYR 5 6 min THR GLU App ID 137 C-C HIS HYL AAA min
5 USERGUIDE Table 1 Analyze Over 50 Amino Acids Abbreviation Alt. Abbreviation: Chemical Name SIM ALA A Alanine 130, 70 SAR SA Sarcosine 130, 58 GLY G Glycine 116, 7 ABA α-aminobutyric acid 1, 102 VAL V Valine 158, 72 ß-ALA ß-Alanine 217, 129, 116 ß-AIB BAIBA ß-Aminoisobutyric acid 172, 13, 8 ß-ABA ß-Amino-n-butyric acid 216, 172, 1 NORV Norvaline 158, 72 LEU L Leucine 172, 86 ILE I Isoleucine 172, 130 aile Allo-Isoleucine 172, 130 pglu Pyroglutamic acid 8 HSER Homoserine 101, 128, 13 NLE Norleucine 172, 86 THR T Threonine 160, 101 SER S Serine 16, 203 PRO P Proline 156, 23 GABA γ-amino-n-butyric acid 130, 1, 17 ASN N Asparagine 155, 69 TPR Thiaproline 17, 17 ASP D Aspartic acid 216, 130 MET M Methionine 203, 277 SME Seleno-L-Methionine 230, 188, 12 HYP OHPro -Hydroxyproline 172, 86 GLU E Glutamic acid 230, 170 PHE F Phenylalanine 206, 190 AAA α-aminoadipic acid 2, 98 CAD Cadaverine (1,5 Diaminopentane) 116, 170, 215 CYS C Cysteine 28, 162, 206 PABA -Aminobenzoic acid 265, 206, 163 HCYS Homocysteine 12, 203 APA α-aminopimelic acid 198, 258, 286 HA Histamine 180, 168, 9 GLN Q Glutamine 8, 187 DABA 2,-Diamino-n-butyric acid 203, 12, 25 GLY-GLY Glycine-glycine (dipeptide) 117, 1, 201 ORN O Ornithine 156, 70 GPR Glycine-proline (dipeptide) 70, 300 LYS K Lysine 170, 128 THR-ASP Threonine-aspartic acid (dipeptide) 218, 360, 130 HIS H Histidine 282, 168 HLY OHLys Hydroxylysine (2 isomers) 129, 169 TYR Y Tyrosine 206, 107 DAP Diaminopimelic acid 256, 168, 196 PHP Proline-hydroxyproline (dipeptide) 156, 11 TRP W Tryptophan 130 LYS-ALA Lysine-alanine (dipeptide) 170, 22, 153 DA Dopamine 179, 136, 123 CTH Cystathionine 203, 272 DOPA 3,-Dihydroxyphenylalanine 222, 123 C-C (Cys)2 Cystine 28, 216 HC-HC (Hcys)2 Homocystine 230, 188, 128 ARG-SUC Arginino-succinic acid 1, 326 Et(OH)NH2 Ethanolamine 116, 117 ETH Ethionine 203, 291, 13 SRO Serotonin 16, 159, Amino Acids & Related Compounds Quantified in 15 Minutes The EZ:faast method is currently designed to analyze over 50 amino acids and related compounds (Table 1). All peaks can be accurately and reproducibly quantified. Additional amino acids can be analyzed with little to no modification of the standard methodology. Please contact Phenomenex for additional amino acids analyzed using the EZ:faast method. Additional Amino Acids analyzed by the EZ:faast LC/MS kit Abbreviation Alt. Abbreviation: Chemical Name SIM ARG Arginine 303 CIT Citrulline 287 1MHIS 1-Methyl-histidine 298 3MHIS 3-Methyl-histidine 298 5
6 USERGUIDE Colors added for illustration purposes only. 2S P 00:01:00 1P 1S 00:00:00 Step 2. 1 min Pipette sample through SPE sorbent tip. Advantage: No lengthy protein or urea removal. Step 1. 0 min Pipette sample and combine internal standard (yellow). 8 Simple Steps TYR TRP App ID :00:00 ndh. Spannung [mv] GLY ALA ABA BAIB VAL IS THR ILE LEU SER PRO ASN ASP MET HYP PHE GLU CYS AAA GLN APA HCY ORN GPR LYS HIS HYL PHP CTH C-C HC-HC 800:15 : min Step min Analyze the chromatogram Advantage: Full resolution of over 50 amino acids and related compounds in a 7 minute GC run. * 15 minute sample prep and analysis time applies to GC kits only. Sample prep and analysis time by LC/MS is 2 minutes. 00:00:00 ndh. 7S P 00: 0 7:00 6 Step 7. 7 min Sample preparation complete inject onto GC/FID, GC/NPD or GC/MS system. Advantage: Very stable derivatized sample reduces losses due to degradation.
7 USERGUIDE 3S P 00:02:00 Step 3. 2 min Draw wash solution (blue) through SPE sorbent tip. Advantage: Outstanding sample purity for less contamination and better quantitation. in 15 Minutes! The EZ:faast procedure s greatest benefit is the rapid sample preparation and derivatization method. For complex matrices like plasma, urine, fermentation broths or feeds this procedure can provide results equal to traditional protein and urea removal methods in less time. Even for relatively clean samples like protein hydrolysates, this method shows improvement in quantitation due to cleaner samples and more stable amino acid derivatives. Shorter sample preparation times cut labor time and cost, making this a highly cost effective assay for amino acid analysis (less than $ a sample). Below is a simplified diagram illustrating each of the major steps within the EZ:faast protocol. S 00: 03: 00 Step. 3 min Expel amino acids (blue) with SPE sorbent from tip with Eluting Medium (clear). Advantage: Almost no loss of amino acids. 55P 00: 0 :00 6S P 00: 06: 00 Step 5. min Add organic derivatizing reagent (orange). Advantage: Derivatization is complete in 1 min and can be done in aqueous phase. Step 6. 6 min Extract amino acid derivatives from aqueous layer (light green) into organic layer (orange). Advantage: Additional purification step. 7
8 USERGUIDE 8 minutes of Sample Prep No Protein or Urea Removal Required The analysis of free amino acids in physiological fluids, grains, fermentation broths and other complex matrices differs from the analysis of protein hydrolysates due to the high concentration of interfering compounds. A relatively large amount of proteins, peptides, urea and other matrix components have to be removed prior to free amino acid analysis by GC or HPLC, otherwise columns deteriorate rapidly, quantitation is poor, and analysis results are not reproducible. Current procedures for de-proteinization and urea removal are labor intensive and recoveries are low for some amino acids. Also, reagents used for de-proteinization can interfere in the amino acid profile. The EZ:faast method, however, does not require traditional de-proteinization or urea removal methods to be followed; proteins are excluded from the sample as it is passes through an SPE sorbent tip. The SPE sorbent binds amino acids while proteins and urea are washed away leaving only the free amino acids. A comparison of the EZ:faast method to other common de-proteinization methods shows as good or better results using the EZ:faast method. EZ:faast translates into major cost and time savings. Hydrolyzed protein samples are often in a clean sample matrix. Hydrolysis under strong acidic conditions at elevated temperatures causes proteins and peptides to breakdown into their component amino acids. Other components like hydrolyzed carbohydrates and lipids, are excluded from the sample as it passes through the SPE sorbent tip. With purer samples and better derivative stability quantitation and method reproducibility can be improved. Table 2: Data representing a series of comparative tests on the same plasma sample with and without protein removal; analysis of all samples was performed using the EZ:faast kit. The data represents the calculated amino acid concentration in µmol/l after the sample has undergone three common de-proteinization procedures (SSA = sulfosalicylic acid; TCA = trichloroacetic acid; ORG = acetonitrile:ethanol 2:1) compared to the EZ:faast procedure. The comparative data (mean values for 12 measurements) is presented in the table below. Results for amino acid content show no significant difference between samples with or without protein removal. Table 2 Without SSA TCA ORG De-proteinization (Recommended for OPA (Recommended for PITC (Standard EZ:faast method) derivatized samples) derivatized samples) Procedure Time: 7 minutes 3 hours 3 hours 3 hours GLY 290 ( ) 288 ( ) 259 ( ) 261 ( ) ALA 21 (15-27) 22 (17-27) 380 (357-02) 393 (365-21) ABA 23 (22-2) 23 (20-26) 22 (21-22) 22 (21-23) LEU 165 ( ) 16 ( ) 162 ( ) 163 ( ) ILE 7 (72-75) 70 (69-72) 71 (69-72) 73 (72-73) MET 30 (29-30) 32 (31-33) 31 (30-31) 30 (29-30 PRO 209 ( ) 207 (20-210) 212 ( ) 206 (197-21) ASP 18 (17-19) 16 (15-17) 16 (1-17) 19 (18-20) GLU 0 (38-1) 35 (25-) 35 (29-0) 35 (30-39) THR 176 ( ) 166 ( ) 153 (15-161) 177 ( ) SER 12 (136-17) 133 ( ) 129 ( ) 136 ( ) HYP 1 (13-1) 12 (11-12) 13 (12-13) ASN 3 (32-35) 3 (33-35) 31 (27-3) 31 (28-33) GLN 50 (95-58) 588 ( ) 553 (51-592) 569 (55-58) C-C 1 (39-2) 1 (39-2) 5 (1-9) 30 (21-39) PHE 58 (56-60) 58 (56-59) 63 (59-67) 60 (57-63) TYR 62 (59-6) 62 (58-66) 63 (59-66) 60 (57-63) TRP 8 (6-9) (1-7) 5 (2-8) 50 (3-56) ORN 60 (58-61) 68 (62-73) 6 (60-67) 6 (3-9) LYS 179 ( ) 200 ( ) 18 ( ) 118 ( ) HIS 8 (78-89) 89 (82-96) 90 (85-95) 82 (73-91) 8
9 USERGUIDE Derivatization Simplified After the very short sample cleanup procedure, the amino acids are quickly derivatized at room temperature with the addition of two reagents. The proprietary reagents modify both the carboxyl and amino groups of the amino acids forming derivatives stable at room temperature for several hours and stable at ºC for several days. With good derivative stability, amino acid quantitation is more accurate and reliable; almost no amino acid sample is lost in sample preparation or through sample degradation. Reagents and supplies for sample preparation allow for the analysis of 38 samples per kit. Reagents, when stored according to label directions, are guaranteed for up to 12 months. Rapid Chromatographic Analysis Traditional ion exchange and reversed phase methods for the analysis of amino acids utilize long minute runtimes. The EZ:faast method takes advantage of the fast separation capability and high resolution of GC/FID, GC/NPD, GC/MS to analyze over 50 amino acids in about 8 minutes. The LC/MS chromatographic runtime is a quick 12 minutes. High column efficiencies and resolution provides complete baseline separation for easy quantitation. Interfering compounds such as drug metabolites, proteins and urea that can be present in the sample matrix have been removed during sample preparation. With traditional methods, a large number of potential interfering compounds, like drugs and drug metabolites may co-migrate with amino acids thus affecting quatitation. The high resolution GC method also allows for additional rare amino acids not listed in Table 1 to be analyzed without compromising throughput or resolution of other amino acids. In traditional HPLC based methods, rare amino acids may be analyzed but often results in a substantial increase of the analysis times this is not the case with EZ:faast. The GC protocol allows for adjustments in carrier gas flow, oven temperature and the temperature gradient to ensure for the analysis of additional amino acids with a minor increase to the very short analysis time. High separation power and speed of the GC protocol also ensures method flexibility for the rapid analysis of additional amino acids with only slight (<5 min) increases in runtime. Figure 3 Simplified diagram illustrating EZ:faast derivatization reactions N H 2 R OH O Cl O R OR' + 2 cat. + 2HCl + CO OR' OR' NH O O 2 9
10 USERGUIDE EZ:faast kits provide reliable and accurate quantitation of over 50 fully baseline resolved amino acids. The lower limit of detection for EZ:faast is 1 nmol/ml and the precision in quantitation is <10% for most amino acids (a few amino acids show precisions in quantitation of +/- 15%). Sample loss and method precision is illustrated in the comparison of 5 injections of free amino acids extracted from plasma by a traditional ion exchange (IEX) method run on a dedicated amino acid analyzer and by the EZ:faast method (Table 3). EZ:faast provides improved quantitation due to several factors. Both sensitivity and reproducibility are improved with EZ:faast. Full baseline resolution accounts for some of the improvement, and the sample preparation procedure insures nearly all interfering compounds are removed without sacrificing amino acid recovery. Once derivatized, amino acids are stable for several hours at room temperature and for several days if refrigerated, preventing sample loss by degradation. Table 3. Comparative data for the analysis of plasma free amino acids by ion exchange chromatography (on a dedicated amino acid analyzer with ninhydrin detection), and by GC/FID (EZ:faast). Concentrations are given in nmol/ml (statistical evaluation by Horn). P L stands for mean, L L is lower limit; L U is upper limit; IEX is ion exchange chromatography. Table 3 GLY ALA ABA VAL LEU ILE MET PRO IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast P L L L L U THR SER ASP GLU GLN C-C PHE TYR IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast P L L L L U TRP ORN LYS HIS Accuracy and Precision IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast IEX EZ:faast P L L L L U Detection Limit 1nmol/mL by GC/FID 1nmol/mL by GC/MS Precision in Quantitation, %RSD +/-15% (<10% for most amino acids) Reproducibility of Retention Time, % RSD <1%
11 USERGUIDE Sample: Derivatized amino acids in human serum (0.1mL), Norvaline is the internal standard added at a concentration of 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 9. Serine 10. Proline 17. Glutamine 18. Ornithine Free Amino Acids in Human Serum by GC/FID 3. α-aminobutyric acid. Valine 5. Norvaline (IS) 6. Leucine 7. Isoleucine 8. Threonine 11. Asparagine 12. Aspartic Acid 13. Methionine 1. -Hydroxyproline 15. Glutamic Acid 16. Phenylalanine 19. Lysine 20. Histidine 21. Tyrosine 22. Tryptophan 23. Cystine Kit: Order No.: EZ:faast GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit KG App ID 1169 Injection: Split 250 C, 2.5µL 200 Carrier Gas: Pressure Rise: Oven Program: Helium 1.5mL/minute ( C 6 kpa/min 30 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 for 1 minute Detector: 320 C [mv] min 11
12 USERGUIDE Free Amino Acids in Human Urine by GC/FID Sample: Derivatized amino acids in human urine (0.1mL). Norvaline is the internal standard added at a concentration of 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 9. Serine 10. Proline 17. Lysine 18. Histidine 3. Valine. ß-Aminoisobutyric acid 5. Norvaline (IS) 6. Leucine 7. Isoleucine 8. Threonine 11. Asparagine 12. Aspartic Acid 13. Glutamic Acid 1. Phenylalanine 15. α-aminoadipic acid 16. Glutamine 19. Tyrosine 20. Proline hydroxyproline (dipeptide) 21. Tryptophan 22. Cystine App ID 1170 Kit: EZ:faast GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit Order No.: Injection: KG Split 250 C, 2.5µL Carrier Gas: Helium 1.5mL/minute ( C Pressure Rise: 6 kpa/min Oven Program: 30 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 for 1 minute Detector: 320 C [mv] min 12
13 USERGUIDE Sample: Derivatized amino acids in potato tissue (0.1mL). Norvaline is the internal standard added at a concentration of 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 12. Aspartic Acid 13. Methionine Free Amino Acids in Potato Tissue by GC/FID 3. α-aminobutyric Acid. Valine 5. Norvaline (IS) 6. Leucine 7. Isoleucine 8. Threonine 9. Serine 10. Proline 1. Glutamic Acid 15. Phenylalanine 16. Glutamine 17. Ornithine 18. Lysine 19. Histidine 20. Tyrosine 21. Tryptophan 11. Asparagine Kit: Order No.: Injection: EZ:faast GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit KG Split 250 C, 2.5µL App ID 13 Carrier Gas: Helium 1.5mL/minute ( C Pressure Rise: Constant pressure Oven Program: 30 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 for 1 minute Detector: 320 C pa min 13
14 USERGUIDE Free Amino Acids in Corn Meal by GC/FID Sample: Derivatized amino acids in corn meal (0.1mL). Norvaline is the internal standard added at 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 3. Valine. Norvaline (IS) 5. Leucine 6. Isoleucine 7. Threonine 11. Aspartic Acid 12. Glutamic Acid 13. Phenylalanine 1. Lysine 15. Histidine 16. Tyrosine 17. Tryptophan 8. Serine 9. Proline 10. Asparagine App ID 135 Kit: Order No.: EZ:faast GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit KGO-7165 Injection: Split 250 C 2.5µL Carrier Gas: Helium 8psi (60 kpa) Pressure Rise: Constant pressure Oven Program: 32 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 C for 1 minute Detector: 320 C min 1
15 USERGUIDE Sample: Derivatized amino acids in wine (0.1mL). Norvaline is the internal standard added at a concentration of 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 11. Aspartic Acid Free Amino Acids in Wine by GC/MS 2. Glycine 3. Valine. β-aminoisobutyric acid 5. Norvaline (IS) 6. Leucine 7. Isoleucine 8. Threonine 9. Proline 12. Methionine 13. -Hydroxyproline 1. Glutamic Acid 15. Phenylalanine 16. Ornithine 17. Lysine 18. Tyrosine 19. Tryptophan 10. Asparagine Kit: Order No.: EZ:faast GC/MS Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit KGO-7166 App ID 1610 Injection: Carrier Gas: Pressure Rise: Split 250 C, 2.5µL Helium 1.1mL/ minute@110 C 6 kpa/min 9 Oven Program: 30 C/min from 110 to 320 C 1 Detector: 300 C min 15
16 USERGUIDE Free Amino Acids in Beer by GC/FID Sample: Derivatized amino acids in beer. Norvaline is the internal standard added at 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 3. Valine. Norvaline (IS) 5. Leucine 6. Isoleucine 7. Serine 8. Proline 9. Asparagine 10. Aspartic Acid 11. Glutamic Acid 12. Phenylalanine 13. Ornithine 1. Histidine 15. Tyrosine 16. Tryptophan App ID 1623 Kit: Order No.: EZ:faast GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Kit KGO-7165 Injection: Split 250 C 2.5µL 8 Carrier Gas: Pressure Rise: Helium 8psi (60 kpa) Constant pressure Oven Program: 32 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 C for 1 minute 1 Detector: 320 C min 16
17 USERGUIDE Sample: Derivatized amino acids from a corn meal hydrolysate sample. Norvaline is the internal standard added at 200 µmol/l 1. Alanine 2. Glycine 3. Valine. Norvaline (IS) 5. Leucine 6. Isoleucine 7. Threonine 8. Serine 10. Aspartic Acid 11. Methionine 12. Hydroxyproline 13. Glutamic Acid 1. Phenylalanine 15. Lysine 16. Histidine 17. Tyrosine Amino Acids in Corn Meal Hydrolysate by GC/FID 9. Proline Kit: Order No.: Injection: EZ:faast GC/FID Protein Hydrolysate Kit KG Split 250 C, 2.5µL App ID 136 Carrier Gas: Pressure Rise: Helium 1.5mL/ minute ( C 6kPa/min 5 Oven Program: 30 C/min from 110 to 320 C, hold at 320 for 1 minute Detector: 320 C min 17
18 USERGUIDE Internal Standard Washing Solution (Reference Sample Clean-up) Eluting Medium I (Sample Clean-up) Eluting Medium II (Sample Clean-up) Organic Solution I (Derivatization) Organic Solution II (Derivatization) Acid Solution (Derivatization) Amino Acids Standard Solution 00 Sample Preparation Vials 0.6mL Syringe for SPE amino acid elution Vial Rack for Sample Preparation Microdispenser for Organic Reagents and 5 Zebron ZB-AAA GC Columns or AAA HPLC Column 1.5mL Syringe for SPE loading & washing SPE Sorbent Tips SGE GC FocusLiners (Not Shown)
19 USERGUIDE Frequently Asked Questions Q: For how long are the derivatized amino acids stable? A: Amino acids derivatized by the EZ:faast method are stable for up to a day at room temperature and for several days if refrigerated. Q: How many samples can be analyzed with the EZ:faast kits? A: 38 samples can be analyzed with the reagents and supplies of one kit. Q: How long will the EZ:faast GC and LC column last? A: We have found that the GC and LC columns will last for the duration of the kit. For best results columns should be replaced with each new kit. Q: What is the shelf life of the reagents? A: EZ:faast reagents have a guaranteed shelf life of 12 months if properly stored as indicated on the bottle in a refrigerator or freezer. Q: What are the derivatization reagents and reaction? A: The derivatization reagents and reaction are proprietary. The reaction derivatizes both the amine and carboxyl groups of the amino acids forming a highly stable derivative. Amino Acid Analysis Kits Each kit includes: ZB-AAA GC column, or AAA LC column, sample prep and derivatization reagents, sample prep vials, AA standards, SPE pipette tips, vial rack, and microdispenser. Order No. Description Unit Price KG l GC/FID Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Analysis Kit l ea l KG GC/MS Free (Physiological) Amino Acid Analysis Kit ea KG GC/FID Protein Hydrolysate Kit ea KG GC/MS Protein Hydrolysate Kit ea CG ZB-AAA 10m x 0.25mm ID Amino Acid Analysis GC Column ea KH LC/MS Free (Physiological) Amino Acids Kit with 250 x 2.0mm column ea KH LC/MS Free (Physiological) Amino Acids Kit with 250 x 3.0mm column ea KH LC/MS Protein Hydrolysates Kit with 250 x 2.0mm column ea KH0-730 LC/MS Protein Hydrolysates Kit with 250 x 3.0mm column ea AG0-718 Physiological Amino Acid Standards (SD1, 2, 3) 2mL/vial x 2 ea AG Protein Hydrolysate Standard (SD) 2mL/vial x 2 ea EZ:faast is a registered trademark of Phenomenex, Inc. copyright 2003, all rights reserved. 19
20 Phenomenex 11 Madrid Avenue Torrance, CA U.S.A. Printed Matter Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! 187_I
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis
 An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis Lisa Sapp Clinical Research and Forensic Toxicology Product Manager Mass Spectrometry Systems Amino Acid Analysis Using itraq Reagents
An Introduction to the Use of itraq Reagents for Amino Acid Analysis Lisa Sapp Clinical Research and Forensic Toxicology Product Manager Mass Spectrometry Systems Amino Acid Analysis Using itraq Reagents
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization
 ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization VERVIEW We have developed a novel amino acid separation column for LC-MS without
ASMS 2014, (Jun 16, 2014, Baltimore, USA) Development of a novel amino acids analysis column for LC-MS without derivatization VERVIEW We have developed a novel amino acid separation column for LC-MS without
Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400
 Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400 Determination of amino acid of hydrolyzates (food and feed) Column: LG ANB OSTION 3.6x340 12μm Eluents: sodium-citrate buffers, 0.2 M NaOH Aspartic Acid, Threonine, Serine, Glutamic
Amino Acid Analyzer AAA400 Determination of amino acid of hydrolyzates (food and feed) Column: LG ANB OSTION 3.6x340 12μm Eluents: sodium-citrate buffers, 0.2 M NaOH Aspartic Acid, Threonine, Serine, Glutamic
Authors. Abstract. Introduction. Food
 Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
Improved and Simplified Liquid Chromatography/Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry Method for the Analysis of Underivatized Free Ao Acids in Various Foods Application Food Authors
0010 Amino Acids 40 Profile - Plasma
 Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
Accession #: Order #: G1234567 Date Collected: Date Received: 01/22/2013 Reference #: Patient: Date of Birth: 02/05/1962 Date of Report: Telephone: 7704464583 Ordering Physician: 1234 Main St. Anywhere,
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
[ APPLICATION NOTE ] UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of 45 Amino Acids Using the Kairos Amino Acid Kit for Biomedical Research INTRODUCTION APPLICATION BENEFITS
![[ APPLICATION NOTE ] UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of 45 Amino Acids Using the Kairos Amino Acid Kit for Biomedical Research INTRODUCTION APPLICATION BENEFITS [ APPLICATION NOTE ] UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of 45 Amino Acids Using the Kairos Amino Acid Kit for Biomedical Research INTRODUCTION APPLICATION BENEFITS](/thumbs/88/117895443.jpg) UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of 45 Amino Acids Using the Kairos Amino Acid Kit for Biomedical Research Padhraic Rossiter, 1 Jaime Salcedo Dominguez, 1 Jennifer Warren, 1 Norma Breen, 1 Lisa Calton 2 1 Waters Corporation,
UPLC-MS/MS Analysis of 45 Amino Acids Using the Kairos Amino Acid Kit for Biomedical Research Padhraic Rossiter, 1 Jaime Salcedo Dominguez, 1 Jennifer Warren, 1 Norma Breen, 1 Lisa Calton 2 1 Waters Corporation,
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
USER GUIDE. Can You Complete An Amino Acid Analysis In 15:00 Minutes? ...now you can!
 USER GUIDE TM Can You Compete An Amino Acid Anaysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! Patent Pending Amino acid anaysis kits for: Sampe Prep Derivatization GC or LC Anaysis Patent Pending Tabe of Contents
USER GUIDE TM Can You Compete An Amino Acid Anaysis In 15:00 Minutes?...now you can! Patent Pending Amino acid anaysis kits for: Sampe Prep Derivatization GC or LC Anaysis Patent Pending Tabe of Contents
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS
 Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Study of Amino Acids in DDGS Y. Zhang, J. V. Simpson and B. A. Wrenn National Corn-to-Ethanol Research Center Edwardsville, IL 62025 Hans Stein University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Gerald C. Shurson
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS. procedure. S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co.
 Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS procedure S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Jeff Zhu Eurofins Background A considerable number of analytical methods are reported in
Analysis of free amino acids in tobacco with a new LC/MS/MS procedure S. C. Moldoveanu R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Co. Jeff Zhu Eurofins Background A considerable number of analytical methods are reported in
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications - Acids. Data No. Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection Data No.
 GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
MASS SPEC 2017, (Sep 22, 2017, Boston, USA) Amino acids and metabolites/derivatives analysis without derivatization using a novel mixed-mode column
 MASS SPEC 07, (Sep, 07, Boston, USA) Amino acids and metabolites/derivatives analysis without derivatization using a novel mixed-mode column ITRDUCTI Amino acids and derived metabolites/derivatives are
MASS SPEC 07, (Sep, 07, Boston, USA) Amino acids and metabolites/derivatives analysis without derivatization using a novel mixed-mode column ITRDUCTI Amino acids and derived metabolites/derivatives are
Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column
 Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Application Note Pharmaceutical and Food Testing Analysis of Amino Acids Derived Online Using an Agilent AdvanceBio AAA Column Author Lu Yufei Agilent Technologies, Inc. Abstract A liquid chromatographic
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2*
 Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
0010 Amino Acid Analysis - 40 Plasma
 770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
770.446.5483 770.441.2237 This report contains reference range adjustments from routine revalidation procedures. It also contains the following three upgrades: 1) The amino acids have been reorganized
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
High Throughput simultaneous analysis of 39 amino acids in various foods without derivatization using LC-MS/MS
 PO-CON1532E High Throughput simultaneous analysis of 39 amino acids in various foods without derivatization using LC-MS/MS ASMS 2015 ThP 409 Manabu Yukiyama 1, Keiko Matsumoto 1, Jun Watanabe 1, Itaru
PO-CON1532E High Throughput simultaneous analysis of 39 amino acids in various foods without derivatization using LC-MS/MS ASMS 2015 ThP 409 Manabu Yukiyama 1, Keiko Matsumoto 1, Jun Watanabe 1, Itaru
Annual Report ERNDIM-EQAS Quantitative Amino Acids 2002
 Annual Report ERNDIM-EQAS Quantitative Amino Acids 2002 1. Purpose The purpose of the ERNDIM External Quality Assurance Scheme for Quantitative Organic Acids is the monitoring of the analytical quality
Annual Report ERNDIM-EQAS Quantitative Amino Acids 2002 1. Purpose The purpose of the ERNDIM External Quality Assurance Scheme for Quantitative Organic Acids is the monitoring of the analytical quality
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
AbsoluteIDQ Kit: Targeted Metabolomics Identification and Quantification
 AbsoluteIDQ Kit: Targeted Metabolomics Identification and Quantification Accurate, Reproducible, Metabolomics Studies The word metabolome refers to the complete set of small molecule metabolites arising
AbsoluteIDQ Kit: Targeted Metabolomics Identification and Quantification Accurate, Reproducible, Metabolomics Studies The word metabolome refers to the complete set of small molecule metabolites arising
Protein Investigator. Protein Investigator - 3
 Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Protein Investigator Objectives To learn more about the interactions that govern protein structure. To test hypotheses regarding protein structure and function. To design proteins with specific shapes.
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Amino acid metabolism
 Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
Amino acid metabolism The important reaction commonly employed in the breakdown of an amino acid is always the removal of its -amino group. The product ammonia is excreted after conversion to urea or other
2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava 1. Fundamental of Mass Spectrometry Role of MS and basic concepts 2. Ionization Sources 3. Mass Analyzers 4. Tandem Mass Spectrometry 2 1 MS basic concepts Mass spectrometry - technique
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Amino acids. Ing. Petrová Jaroslava. Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, , Ankara. Turkey ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1
 Amino acids Ing. Petrová Jaroslava Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, 6. 7. 12. 2011, Ankara. Turkey 6.12.2011 ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1 Content of this presentation 1. Function of amino acids
Amino acids Ing. Petrová Jaroslava Workshop on Official Controls of Feed AGR 46230, 6. 7. 12. 2011, Ankara. Turkey 6.12.2011 ÚKZÚZ - NRL RO Praha 1 Content of this presentation 1. Function of amino acids
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
High Throughput Extraction of Opiates from Urine and Analysis by GC/MS or LC/MS/MS)
 High Throughput Extraction of Opiates from Urine and Analysis by GC/MS or LC/MS/MS) Michael Rummel, Matthew Trass, Michael Campognone, and Sky Countryman Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Avenue, Torrance,
High Throughput Extraction of Opiates from Urine and Analysis by GC/MS or LC/MS/MS) Michael Rummel, Matthew Trass, Michael Campognone, and Sky Countryman Phenomenex, Inc., 411 Madrid Avenue, Torrance,
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
MS/MS APPROACHES TO CLINICAL TESTING FOR INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM
 MS/MS APPROACHES TO CLINICAL TESTING FOR INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM Tina M. Cowan, PhD Director, Clinical Biochemical Genetics Laboratory Stanford University Medical Center Presented at the 2011 Stanford
MS/MS APPROACHES TO CLINICAL TESTING FOR INBORN ERRORS OF METABOLISM Tina M. Cowan, PhD Director, Clinical Biochemical Genetics Laboratory Stanford University Medical Center Presented at the 2011 Stanford
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
9/16/15. Properties of Water. Benefits of Water. More properties of water
 Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
Properties of Water Solid/Liquid Density Water is densest at 4⁰C Ice floats Allows life under the ice Hydrogen bond Ice Hydrogen bonds are stable Liquid water Hydrogen bonds break and re-form Benefits
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
MS/MS Scan Modes. Eötvös University, Budapest April 16, MS/MS Scan Modes. Árpád Somogyi. Product Ion Scan Select. Scan. Precursor Ion Scan Scan
 MS/MS Modes Árpád Somogyi Eötvös University, Budapest April 16, 2012 MS/MS Modes Product Ion Precursor Ion Neutral Loss Δ ed Reaction Monitoring (SRM) 1 modes in a triple quadrupole (QqQ) (one quadrupole
MS/MS Modes Árpád Somogyi Eötvös University, Budapest April 16, 2012 MS/MS Modes Product Ion Precursor Ion Neutral Loss Δ ed Reaction Monitoring (SRM) 1 modes in a triple quadrupole (QqQ) (one quadrupole
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, & Enzymes General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 21: Amino Acids, Proteins, Enzymes Learning Objectives: q The 20 common, naturally occurring
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood Choyce A. Weatherly 1, Siqi Du 1, Curran Parpia 1, Polan T. Santos 2, Adam
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Level and activity of D-amino acids in mouse brain tissue and blood Choyce A. Weatherly 1, Siqi Du 1, Curran Parpia 1, Polan T. Santos 2, Adam
Application Note. Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated OPA- Derivatization by the Autosampler. Summary. Fig. 1.
 Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
Application Note Determination of Amino acids by UHPLC with automated PA- Derivatization by the Autosampler Category Bio Analysis Matrix - Method UHPLC Keywords Proteinogenic Amino acids, Canonical Amino
Technical Note 55. Screening of Sample Matrices and Individual Matrix Ingredients for Suitability in AAA-Direct INTRODUCTION
 Technical Note 55 Screening of Sample Matrices and Individual Matrix Ingredients for Suitability in AAA-Direct INTRODUCTION All chromatographic techniques are susceptible to chemical interferences. Problems
Technical Note 55 Screening of Sample Matrices and Individual Matrix Ingredients for Suitability in AAA-Direct INTRODUCTION All chromatographic techniques are susceptible to chemical interferences. Problems
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
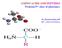 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Amino acid metabolism II
 Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
AA s are the building blocks of proteins
 Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Chamras Chemistry 106 Lecture otes Chapter 24: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins General Formula: () n (') α-amino Acids: (n = 1) Example: Amino Acids and Proteins: Glycine Alanine Valine AA s are the
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE. Authors: J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C.
 EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
EFFECTS OF AMINO ACID SUBSTITUTIONS FOR WHEY PROTEIN CONCENTRATE ON WEANLING PIG PERFORMANCE 1999 Animal Science Research Report Authors: Story in Brief Pages 266-272 J. Chung, S.D. Carter and J.C. Whisenhunt
Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with LC/MS Detection
 Application Note Food Testing, Metabolomics, Agricultural Chemistry, Environmental Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with
Application Note Food Testing, Metabolomics, Agricultural Chemistry, Environmental Quantitative Analysis of Underivatized Amino Acids in Plant Matrix by Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography (HILIC) with
Determination of Unbound Urinary Amino Acids Incorporated with Creatinine Normalization by LC-MS/MS Method with CLAM-2000 Online Sample Pre-treatment
 PO-CON133E Determination of Unbound Urinary Amino Acids Incorporated with Creatinine Normalization by LC-MS/MS Method with CLAM-2000 Online Sample Pre-treatment ASMS 201 WP 34 Zhe Sun 1, Jie Xing 1, Ei
PO-CON133E Determination of Unbound Urinary Amino Acids Incorporated with Creatinine Normalization by LC-MS/MS Method with CLAM-2000 Online Sample Pre-treatment ASMS 201 WP 34 Zhe Sun 1, Jie Xing 1, Ei
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide
 Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide Quantitative Amino acids Plasma Plasma. Container/Tube: Preferred EDTA, Place immediately in ice. Acceptable: lithium heparin, sodium heparin. Patient preparation:
Lab Guide 2019 Metabolic Section Lab Guide Quantitative Amino acids Plasma Plasma. Container/Tube: Preferred EDTA, Place immediately in ice. Acceptable: lithium heparin, sodium heparin. Patient preparation:
Tomoko Tanahashi 1, Yasushi Tsuchihashi 3*, Akiyo K. Sakamiya 1 1, 2. and Takeo Yano
 Metabolomic approach using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Quantitative amino acid analysis and characterization of four species of marine fish, and a cuttlefish Tomoko
Metabolomic approach using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Quantitative amino acid analysis and characterization of four species of marine fish, and a cuttlefish Tomoko
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit
 Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
1 Digestion and absorption. Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval
 1 Digestion and absorption Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval Presentation of Protein 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 2 Lectures plan 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 3 Overview of Protein Metabolism
1 Digestion and absorption Lecture #14 Lecturer: PhD Alexander N. Koval Presentation of Protein 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 2 Lectures plan 12/22/2016 A. Koval (C), 2016 3 Overview of Protein Metabolism
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon. Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011
 Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
Quantitative LC-MS/MS Analysis of Glucagon Veniamin Lapko, Ph.D June 21, 2011 Contents Comparison with small molecule LC-MS/MS LC-MS/MS sensitivity of peptides detection Stability: neat vs. matrix solutions
