Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient: Facilitating the Transition to Enteral Nutrition
|
|
|
- Lucy Ross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient: Facilitating the Transition to Enteral Nutrition Ana Abad-Jorge, EdD, MS, RDN, CNSC Program Director, Bachelor of Professional Studies in Health Sciences Management School of Continuing and Professional Studies, University of Virginia Food & Nutrition Conference & Expo October 20 th 2014 Presentation Objectives Describe current practice guidelines for timing and provision of enteral nutrition in critically ill children Identify common barriers to the delivery of optimal EN in the PICU setting. Discuss specific strategies to optimize EN delivery in the challenging PICU setting. Select appropriate formula for EN in critically ill children based on age, clinical status and GI function. Discuss the literature with regards to the use of immune enhancing formulas in pediatric patients. I. Introduction a. Optimal nutrition plays a key role in sustaining organ function b. Also helps to prevent dysfunction of the cardiovascular, respiratory and immune system until the acute phase inflammatory response resolves. c. Requires energy balance to prevent both: Overfeeding can lead to...increased CO 2 production leading to difficulties in weaning from the ventilator and hepatic complications Underfeeding (more prevalent in PICU) leads to: reduced wound healing & increased sepsis d. Despite numerous advances in both technology and formulations, malnutrition in the PICU has remained relatively unchanged for the past 20 years. e. Studies indicate that 24% - 55% of patients present with acute or chronic malnutrition on admission. II. Goals of Nutrition Support in Critically Ill Children a. Provision of nutrition screening in a timely manner to identify those with existing malnutrition or those nutritionally at risk. b. Comprehensive nutritional assessment with the development of a nutrition care plan. Use of the Nutrition Care Process c. Assessment of energy & protein needs throughout the course of illness to prevent overfeeding and underfeeding while providing adequate calories & protein to minimize catabolic response. d. Provision of nutrition support in a timely manner: within hours in children < 2 years old and at nutrition risk, within hours in children > 2 or those previously well-nourished and not at risk. e. Using indirect calorimetry (IC) to assess energy expenditure is preferred; however, if IC is not feasible or available, initial guidelines may be based on published formulas with adjustments as needed, based on clinical status. f. Use of EN as the preferred modality of nutrition support for critically ill children.
2 g. Optimization of EN to meet needs while identifying potential barriers and avoidable interruptions. III. Nutrition Support Guidelines in Peds Critical Care: Enteral (Mehta & Compher, JPEN 2009) IV. Pediatric Patients Most at Nutrition Risk in the PICU Clinical Conditions a. Hypermetabolic states: trauma, head injury, spinal cord injury, thermal injury b. Cardiorespiratory illness: congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease c. Post-surgical patients (particularly non-elective) d. GI disease and dysfunction: short gut syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease with h/o PEM, biliary atresia, pancreatitis e. Neurologic, muscular disease: genetic syndromes, muscular dystrophy, history of CP/MR requiring G-tubes Other Factors a. Underweight: BMI < 5th%-ile for age b. Overweight: BMI > 95th%-ile for age c. Children with either significant weight loss (>10%) or weight gain (>10%) during PICU admission d. Failure to consistently meet prescribed energy and protein requirements e. Failure to wean off the ventilator f. Need for muscle relaxants for > 7days V. Enteral Nutrition: Benefits, Timing, Common Barriers, Optimal Routes & Methods a. Benefits More physiological Maintains physiologic and functional integrity of gut mucosa by nourishing the gut first May prevent or decrease risk of bacterial translocation Decreased infectious complications Often easier to manage fluid and electrolyte balance
3 May have anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing cytokine production, i.e. TNF-α, interleukin-6 More cost effective than parenteral nutrition (PN): $20-$30/day vs. > $200/day b. Optimal early EN guidelines, particularly for infants < 2 and children at nutritional risk : within hours of PICU admission. Study: Mikhailov et al. Early Enteral Nutrition is Associated with Lower Mortality in Critically Ill Children. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, May Design: Multicenter retrospective cohort study in 12 PICUs, Results: 5105 patient within 12 centers; 5.3% mortality with EEN; Children on EEN were less likely to die than those who did not (OR, 0.51). c. Intestinal Dysfunction in the PICU Dysmotility due to hypoperfusion, sedation & paralysis, minimal EN stim. Malabsorption poor nutritional status, minimal EN stimulation Loss of GI Barrier Function Hypoperfusion, toxins & cytokines d. Common Barriers to Initiation & Advancement of EN in the PICU Severe fluid restrictive policies Hemodynamic instability with use of high doses of vasoactive medication, i.e. epinephrine, vasopressin Severe deterioration in respiratory status, requiring endotracheal intubation Surgical post-operative orders Patient is perceived as being too ill to feed Frequent procedures requiring NPO status e. Optimal Site of EN: Gastric vs. Post-Pyloric? Insufficient data to make recommendations regarding the optimal site for EN Study: Meert el al. Chest, 2004.Studied 74 critically ill Randomized to receive either gastric or post-pyloric; EN interrupted frequently Unblinded RCT no differences in microaspiration, EN device displacement and feeding intolerance. f. Optimal Method for EN in the PICU: Continuous or Intermittent? Study: Horn et al. American Journal of Critical Care, children admitted to PICU randomized to receive either continuous or intermittent gastric feeds (every 2 hrs); measured tolerance to enteral feedings Results: number of daily stools and diarrheal or vomiting episodes was similar between the two groups g. Common Challenges and Barriers to Optimal EN in the PICU Study: Mehta et al. JPEN, 2010 Prospective observational study in a 29 bed PICU over a 4 week period Measurements: daily nutrient intake & factors causing avoidable interruptions Clinical characteristics, time to reach calorie goals, and PN use were compared in patients with and without avoidable EN interruptions Objectives: identify risk factors associated with avoidable interruptions to EN in PICU Results: EN was interrupted in 24 patients (30%) at times per patient (88 episodes = 1483 hours); of the 88 episodes, 51 (58%) were deemed avoidable. VI. Enteral Nutrition for PICU Patient: a. Strategies for Minimizing Interruptions:
4 1. Careful attention to procedure times to prevent prolonged fasting and undue delays in resuming EN 2. Clear communications between PICU team members to ensure timely re-initiation of EN following procedures, i.e. following extubation. 3. Active role of the RD in the education of PICU physicians, residents and nursing staff on optimizing EN, troubleshooting GI intolerance to determine alternate causes other than formula intolerance. b. Use of Algorithms and Protocols 1. Use clinical practice guidelines or algorithms for initiation and advancement of EN based on acuity level, age, GI function, intolerance. 2. Four prospective cohort studies from have shown that enteral feeding guidelines or protocols can improve caloric delivery and decrease time to full feeds. 3. Question EN practices which lack evidence 4. Study: Martinez et al. Nutrition Algorithms in PICUs, Nutr Clin Pract, June 2014 A minority of PICUs use EN algorithms only 29% of sample Recommendations varied greatly and did not follow national guidelines Optimal EN was achieved in < 1/3 of the study s cohort 5. Consider starting with trophic feedings: on POD #1or #2 - providing at least 10-15% of calorie needs via EN has been demonstrated to prevent or minimize gut atrophy and potential translocation (Okada et al., 1988). VII. Enteral Formula Choices for the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient: Formulas a. Selection is based on: Patient Factors age, diagnosis, nutritional problems, specialized needs Formula Factors osmolality, renal solute load, caloric density, viscosity, nutrient composition, immunonutrients? b. Immune-Enhancing Formulas Use in Pediatrics? Key Nutrients arginine, glutamine, omega-3 fatty acids, nucleotides, antioxidants Adult Studies - > 30 studies 1. ASPEN Guidelines - use of immunonutrition in critically ill adults, McClave et al. JPEN, 2009:
5 2. Immune-modulating enteral formulations should be used for the appropriate patient populations (major elective surgery, trauma, burns, heads and neck cancer, and critically ill patients on mech. ventilation), with caution in patients with severe sepsis. 3. While meta-analyses found reduced infection rates, Sub-group analysis conducted by the Heyland et al. meta-analysis showed no differences in mortality between treatment and control groups. 4. Study limitations: only 25% of the studies used intention to treat analysis. As such, there could have been an overestimation of the treatment effect. Pediatric Studies 1. Briassoulis et al. Nutrition, a. Blinded RCT in PICU patients (n=50, 25 in each group) b. Patients randomized to an adult Immune (I) formula which included glutamine, arginine, omega-3 FA and antioxidants or conventional (C) pediatric formulas for children < or > 6 years. c. Results: Nitrogen balance in 64% of patients in I group vs. 40% in C group, no changes in mortality, trend towards decrease in nosocomial infections rates and positive gastric culture rates, transient diarrhea in the I group. d. Limitations: adult formulation used, formulas NOT isonitrogenous, two separate formulas for the control group. 2. Briassoulis et al. Pediatr Crit Care Med, a. Blinded RCT in PICU pts with severe head injury (n=40). Age: months b. Patients received adult immune enhancing formula (IE) vs. regular formula. IE formula much higher in protein. c. Results: Improved nitrogen balance and decreased interleukin-8 levels in the IE group, less gastric cultures were positive in the IE group. d. No differences in rates of nosocomial infections, length of stay, length of mechanical ventilation or survival. 3. Summary - May be beneficial in older pediatric patients (>15 years or >50 kg) with the following criteria: trauma, malnourished adolescent undergoing surgery or consider use of the product upon which most studies were based, i.e. Impact (higher arginine levels, nucleotides, omega-3 FA) VIII. Enteral Case Study: Adolescent Trauma a. 15 year old male who sustained closed head injury, skull fracture, splenic laceration, and femur fracture following a skiing accident is admitted to the PICU. b. Anthropometrics: Previously well-nourished Weight: 64 kg (75th%-ile) Height: 177 cm (75th 90th%-ile): BMI: 19.4 c. Clinical Considerations: Clinical Status: Increased ICP, on mechanical ventilator Current medications: epinephrine, fentanyl, versed, IV phenytoin Surgery on Hospital Day #1 for craniotomy Clinical status stabilizing with decreased ICPs and weaning on ventilator d. Estimating Nutrition Requirements: Calories & Protein If available, order indirect calorimetry Alternative: BEE (for weight & sex) X stress factor (limited data)
6 1793 kcal (initial goal) for first 1-2 days, then Move towards factor of ; endpoint goal of kcal. Protein: gm protein/kg or gm protein e. Enteral Nutrition Management Possible Approach Use standard formula with fiber, i.e. Jevity OR Use calorically dense/ high protein formula if fluid restricted Formula Options: Promote, Jevity 1.5 Alternative: May consider immunonutrition formula, i.e Impact with Glutamine Begin at 20 ml/hr, advance by 20 ml/hr every 6-8 hours, to goal ml/hr. Jevity 1.0 will provide = 2798 kcal, 116 gm protein. Monitor GI tolerance, obtain prealbumin initially and weekly (measure of disease acuity to gauge transition from catabolism to anabolism). Some PICUs are also measuring CRP. Reference List 1. Abad-Jorge, A. Chapter 12 Critical Care. In Kane-Alves, V. and Tarrant, S. (eds): The Nutrition Care Process in Pediatric Practice. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Pediatric Nutrition Dietetic Practice Group, September Abad-Jorge, A. Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient: Minimizing Barriers to Optimal Nutrition Support, J Infant, Child & Adolescent Nutrition, 2013; 5(4): Abad-Jorge, A., Roman, B., Perks, P., Hubbard, A. and Buck, M. Pediatric Nutrition Support Handbook, University of Virginia Health System, Briassoulis, G., Filippou, O., Kanarious, M., Hatzi, E., Hatzis, T. and Papassotiriou, I. Temporal nutritional and inflammatory changes in children with severe head injury fed a regular or an immune-enhancing diet: A randomized, controlled trial. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2006; 7(1): Cook, R.C. and Blinman, T.A. Nutritional support of the pediatric trauma patient. Seminars in Pediatric Surgery, 2010; 19: Horn, D., Chalboyer, W. Gastric feeding in critically ill children: a randomized controlled trial. Am Journal of Crit Care 2003; 12: Meert,, K.L., Daphtary, K.M., Metheny, N.A. Gastric vs. small-bowel feeding in critically ill children receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomized controlled trial. Chest 2004; 126: Mehta, N.M. and Compher, C. ASPEN Clinical Guidelines: Nutrition support of the Critically Ill Child. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition, 2009; 33(3): Mehta, N.M. Approach to enteral feeding in the PICU. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2009; 24(3): Mehta, N., McAleer, D., Hamilton, S., Naples, E., Leavitt, K. Mitchell, P. and Duggan, C. Challenges to optimal enteral nutrition in a multidisciplinary pediatric intensive care unit. J Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2010; 34: Mikhailov, T.A., Kuhn, E.M., Manzi, J. et al. Early enteral nutrition is associated with lower mortality in critically ill children. J Parenteral & Enteral Nutrition, 2014; 38(4): Tume, I., Latten, I., Darbyshire, A. An evaluation of enteral feeding practices in critically ill children. Nurs Crit Care. 2010; 15: Zamberlain, P., Delgado, AF, Leone C. et al. Nutrition therapy in a pediatric intensive care unit: indications, monitoring and complications. J Parenter & Enter Nutr, 2011; 35:
Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: ASPEN-SCCM 2017
 Number of Patients Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: ASPEN-SCCM 2017 Jorge A. Coss-Bu, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics
Number of Patients Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: ASPEN-SCCM 2017 Jorge A. Coss-Bu, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics
L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang
 L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang 14 15 AUG ASMIC 2015 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the importance of nutrition support in ICU 2. To know the right time to feed 3. To understand the indications
L.Mageswary Dietitian Hospital Selayang 14 15 AUG ASMIC 2015 Learning Objectives 1. To understand the importance of nutrition support in ICU 2. To know the right time to feed 3. To understand the indications
10/3/2012. Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition A Comprehensive Review
 Critical Care Nutrition Foundation for Moving Forward Justine Turner MD PhD Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition University of Alberta I have the following financial relationships to
Critical Care Nutrition Foundation for Moving Forward Justine Turner MD PhD Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition University of Alberta I have the following financial relationships to
NO DISCLOSURES 5/9/2015
 Annette Stralovich-Romani, RD, CNSC Adult Critical Care Nutritionist UCSF Medical Center NO DISCLOSURES Incidence & consequences of malnutrition Underfeeding in the ICU Causes/ consequences Nutrition intervention
Annette Stralovich-Romani, RD, CNSC Adult Critical Care Nutritionist UCSF Medical Center NO DISCLOSURES Incidence & consequences of malnutrition Underfeeding in the ICU Causes/ consequences Nutrition intervention
Nutrition and Sepsis
 Nutrition and Sepsis Todd W. Rice, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University 2017 DNS Symposium June 2, 2017 Case 55 y.o. male COPD, DM, HTN, presents with pneumonia and septic shock.
Nutrition and Sepsis Todd W. Rice, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Vanderbilt University 2017 DNS Symposium June 2, 2017 Case 55 y.o. male COPD, DM, HTN, presents with pneumonia and septic shock.
Division of Acute Care Surgery Clinical Practice Policies, Guidelines, and Algorithms: Enteral Nutrition Algorithm Clinical Practice Guideline
 Division of Acute Care Surgery Clinical Practice Policies, Guidelines, and Algorithms: Enteral Nutrition Algorithm Clinical Practice Guideline Original Date: 08/2011 Purpose: To promote the early use of
Division of Acute Care Surgery Clinical Practice Policies, Guidelines, and Algorithms: Enteral Nutrition Algorithm Clinical Practice Guideline Original Date: 08/2011 Purpose: To promote the early use of
The Meat and Potatoes of Critical Care Nutrition ROSEMARY KOZAR MD PHD SHOCK TRAUMA UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND
 The Meat and Potatoes of Critical Care Nutrition ROSEMARY KOZAR MD PHD SHOCK TRAUMA UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND 2013 Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines www.criticalcarenutrition.com NEJM March 27, 2014 Use
The Meat and Potatoes of Critical Care Nutrition ROSEMARY KOZAR MD PHD SHOCK TRAUMA UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND 2013 Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines www.criticalcarenutrition.com NEJM March 27, 2014 Use
Timing of Parenteral Nutrition
 Timing of Parenteral Nutrition Arun Bansal; MD, FCCM, MRCPCH Professor Pediatric Critical Care PGIMER, Chandigarh, INDIA drarunbansal@gmail.com Malnutrition in Critically Ill Incidence: from 19 32% Associated
Timing of Parenteral Nutrition Arun Bansal; MD, FCCM, MRCPCH Professor Pediatric Critical Care PGIMER, Chandigarh, INDIA drarunbansal@gmail.com Malnutrition in Critically Ill Incidence: from 19 32% Associated
Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient
 vol. 5 no. 4 ICAN: Infant, Child, & Adolescent Nutrition Evidence-Based Practice Reports Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient Minimizing Barriers to Optimal Nutrition Support Ana
vol. 5 no. 4 ICAN: Infant, Child, & Adolescent Nutrition Evidence-Based Practice Reports Nutrition Management of the Critically Ill Pediatric Patient Minimizing Barriers to Optimal Nutrition Support Ana
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition
 Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
Current concepts in Critical Care Nutrition Dr.N.Ramakrishnan AB (Int Med), AB (Crit Care), MMM, FACP, FCCP, FCCM Director, Critical Care Services Apollo Hospitals, Chennai Objectives Why? Enteral or Parenteral
Providing Optimal Nutritional Support on the ICU common problems and practical solutions. Pete Turner Specialist Nutritional Support Dietitian
 Providing Optimal Nutritional Support on the ICU common problems and practical solutions Pete Turner Specialist Nutritional Support Dietitian ICU Nutritional Support ACCEPT study showed improved ICU survival
Providing Optimal Nutritional Support on the ICU common problems and practical solutions Pete Turner Specialist Nutritional Support Dietitian ICU Nutritional Support ACCEPT study showed improved ICU survival
Enteral Nutrition in the Critically Ill Child: Challenges and Current Guidelines
 Enteral Nutrition in the Critically Ill Child: Challenges and Current Guidelines 1 Presented on January 24, 2017 Jorge A. Coss-Bu, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Section of Critical Care Baylor College
Enteral Nutrition in the Critically Ill Child: Challenges and Current Guidelines 1 Presented on January 24, 2017 Jorge A. Coss-Bu, MD Associate Professor of Pediatrics Section of Critical Care Baylor College
Oklahoma Dietetic Association. Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSD April, 16, 2008 Permissive Underfeeding: What, Where and Why? Mt.
 The What, Why and When of Permissive Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, CNSD Nutrition Support Team Mt. Carmel West Hospital Mt. Carmel West 500 bed academic center Non-physician based NST Dietitian, pharmacist and
The What, Why and When of Permissive Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, CNSD Nutrition Support Team Mt. Carmel West Hospital Mt. Carmel West 500 bed academic center Non-physician based NST Dietitian, pharmacist and
Enteral Nutrition: Whom, Why, When, What and Where to Feed?
 Meier RF, Reddy BR, Soeters PB (eds): The Importance of Nutrition as an Integral Part of Disease Management. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 82, pp 53 59, (DOI: 10.1159/000382002) Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S.
Meier RF, Reddy BR, Soeters PB (eds): The Importance of Nutrition as an Integral Part of Disease Management. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 82, pp 53 59, (DOI: 10.1159/000382002) Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S.
Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses
 Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses Case Male, 60 - No PMH - L 1.74 m and W 85 kg Pneumococcal pneumonia Stable hemodynamics - No AKI MV in prone position (PEEP 16 - FiO2 60%)
Feeding the septic patient How and when? Masterclass ICU nurses Case Male, 60 - No PMH - L 1.74 m and W 85 kg Pneumococcal pneumonia Stable hemodynamics - No AKI MV in prone position (PEEP 16 - FiO2 60%)
A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines: Pediatric Critical Care. Nilesh M. Mehta MD, DCH
 1 A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines: Pediatric Critical Care Nilesh M. Mehta MD, DCH Division of Critical Care Medicine Children s Hospital Boston 300 Longwood Avenue / Bader 634 Boston, Massachusetts 02115
1 A.S.P.E.N. Clinical Guidelines: Pediatric Critical Care Nilesh M. Mehta MD, DCH Division of Critical Care Medicine Children s Hospital Boston 300 Longwood Avenue / Bader 634 Boston, Massachusetts 02115
Pharmaconutrition in PICU. Gan Chin Seng Paediatric Intensivist UMMC
 Pharmaconutrition in PICU Gan Chin Seng Paediatric Intensivist UMMC Pharmaconutrition in Critical Care Unit Gan Chin Seng Paediatric Intensivist UMMC Definition New concept Treatment with specific nutrients
Pharmaconutrition in PICU Gan Chin Seng Paediatric Intensivist UMMC Pharmaconutrition in Critical Care Unit Gan Chin Seng Paediatric Intensivist UMMC Definition New concept Treatment with specific nutrients
PICUs have a larger operating budget than many other departments within the hospital
 به نام خدا Nutrition In PICU 2 A pediatric intensive care unit (also paediatric), usually abbreviated to PICU is an area within a hospital specializing in the care of critically ill infants, children,
به نام خدا Nutrition In PICU 2 A pediatric intensive care unit (also paediatric), usually abbreviated to PICU is an area within a hospital specializing in the care of critically ill infants, children,
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers
 WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
WHEN To Initiate Parenteral Nutrition A Frequent Question With New Answers Ainsley Malone, MS, RD, LD, CNSC, FAND, FASPEN Dubai International Nutrition Conference 2018 Disclosures No commercial relationship
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University
 ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
ICU NUTRITION UPDATE : ESPEN GUIDELINES 2018 Mirey Karavetian Assistant Professor Zayed University http://www.espen.org/files/espen- Guidelines/ESPEN_Guideline_on_clinical_nutrition_in_-ICU.pdf Medical
Nutrition care plan. Components and development
 Nutrition care plan Components and development Objectives To define the nutrition care plan To present the components of the nutrition care plan To discuss the different approaches in determining the contents
Nutrition care plan Components and development Objectives To define the nutrition care plan To present the components of the nutrition care plan To discuss the different approaches in determining the contents
ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL
 ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL 1 Ebb phase Flow phase acute response (catabolic) adoptive response (anabolic) 2 3 Metabolic Response to Stress (catabolic phase) Glucose and Protein Metabolism
ENTERAL NUTRITION IN THE CRITICALLY ILL 1 Ebb phase Flow phase acute response (catabolic) adoptive response (anabolic) 2 3 Metabolic Response to Stress (catabolic phase) Glucose and Protein Metabolism
Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor
 Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor Lynch.Scott@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Nutrition in the Hospital Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development 2nd Annual Inpatient Medicine for
Scott A. Lynch, MD, MPH,FAAFP Assistant Professor Lynch.Scott@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Nutrition in the Hospital Mayo School of Continuous Professional Development 2nd Annual Inpatient Medicine for
3.2 Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Enhanced Dose of Enteral Nutrition May 2015
 . Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Enhanced Dose of Enteral Nutrition May 015 015 Recommendation: Based on 1 level 1 study, level studies and cluster randomized controlled trials, when starting
. Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Enhanced Dose of Enteral Nutrition May 015 015 Recommendation: Based on 1 level 1 study, level studies and cluster randomized controlled trials, when starting
2.0 Early vs. Delayed Nutrient Intake May 2015
 2.0 Early vs. Delayed Nutrient Intake May 2015 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2013 update and hence there are no changes to the following summary of evidence. 2013 Recommendation:
2.0 Early vs. Delayed Nutrient Intake May 2015 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2013 update and hence there are no changes to the following summary of evidence. 2013 Recommendation:
Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy
 LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
LOGO Metabolic Control in Critical Care: Nutrition Therapy ผศ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาขาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล 2016 SCCM/ASPEN Guidelines Nutrition Therapy in the ICU
Intensive Care Nutrition. Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA
 Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Intensive Care Nutrition Dr Alan Race BSc(Hons) PhD FRCA Objectives 1. What examiners say 2. Definition 3. Assessment 4. Requirements 5. Types of delivery 6. CALORIES Trial 7. Timing 8. Immunomodulation
Nutrition Support. John Cha Department of Surgery DHMC/UCHSC
 Nutrition Support John Cha Department of Surgery DHMC/UCHSC Overview Why? When? How much? What route? Fancy stuff: enhanced nutrition Advantages of Nutrition Decreased catabolism Improved wound healing
Nutrition Support John Cha Department of Surgery DHMC/UCHSC Overview Why? When? How much? What route? Fancy stuff: enhanced nutrition Advantages of Nutrition Decreased catabolism Improved wound healing
Nutrition. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Nutrition ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Critical Care MCQ s Nasogastric (NG) and nasojejunal (NJ) feeding tubes: A. Enteral nutrition is associated with a reduced risk of bacterial and toxin translocation.
Nutrition ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Critical Care MCQ s Nasogastric (NG) and nasojejunal (NJ) feeding tubes: A. Enteral nutrition is associated with a reduced risk of bacterial and toxin translocation.
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
IS THERE A PLACE IN THE ICU FOR PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING AND WHERE? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION: PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING No clear definition in literature Permissive underfeeding definition prior to
ICU ENTERAL FEEDING GUIDELINES
 DISCLAIMER: These guidelines are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care practices based upon the available medical literature and clinical expertise at the time of
DISCLAIMER: These guidelines are intended to serve as a general statement regarding appropriate patient care practices based upon the available medical literature and clinical expertise at the time of
Nutrition Support in Critically Ill Cardiothoracic Patients
 Nutrition Support in Critically Ill Cardiothoracic Patients อ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาชาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Outline Malnutrition in cardiothoracic patients Nutritional
Nutrition Support in Critically Ill Cardiothoracic Patients อ.นพ.พรพจน เปรมโยธ น สาชาโภชนาการคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Outline Malnutrition in cardiothoracic patients Nutritional
Clinical Guidelines for the Hospitalized Adult Patient with Obesity
 Clinical Guidelines for the Hospitalized Adult Patient with Obesity 1 Definition of obesity: Obesity is characterized by an excess storage of adipose tissue that is related to an imbalance between energy
Clinical Guidelines for the Hospitalized Adult Patient with Obesity 1 Definition of obesity: Obesity is characterized by an excess storage of adipose tissue that is related to an imbalance between energy
Nutrition and GI. How much?
 Nutrition and GI How much? The goal of nutritional supplementation is to meet but not exceed the nutritional requirements of patients with critical illness. Due to the inherent variability between patients
Nutrition and GI How much? The goal of nutritional supplementation is to meet but not exceed the nutritional requirements of patients with critical illness. Due to the inherent variability between patients
3.2 Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Achieving Target Dose of Enteral Nutrition March 2013
 . Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Achieving Target Dose of Enteral Nutrition March 01 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 009 update and hence there are no changes to
. Nutritional Prescription of Enteral Nutrition: Achieving Target Dose of Enteral Nutrition March 01 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 009 update and hence there are no changes to
What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
 1 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition? พ นโทหญ ง ส รกานต เตชะวณ ช MD, MSc, ABPNS ห วหน าหน วยโภชนศาสตร คล น ก กองอาย รกรรม โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า 7 กรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2559 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
1 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition? พ นโทหญ ง ส รกานต เตชะวณ ช MD, MSc, ABPNS ห วหน าหน วยโภชนศาสตร คล น ก กองอาย รกรรม โรงพยาบาลพระมงก ฎเกล า 7 กรกฎาคม พ.ศ. 2559 What s New in Parenteral Nutrition?
Nutritional Issues. Perioperative Nutritional Interventions. A challenging case you are likely familiar with
 Perioperative Nutritional Interventions Lygia Stewart MD, John Maa MD, and Annette Romani RD UCSF Post-Graduate Course Nutritional Issues Who needs nutritional supplementation? Oral, feeding tube, or TPN?
Perioperative Nutritional Interventions Lygia Stewart MD, John Maa MD, and Annette Romani RD UCSF Post-Graduate Course Nutritional Issues Who needs nutritional supplementation? Oral, feeding tube, or TPN?
Disclosures. None. Enteral Nutrition and Vasoactive Therapy! But actually.. Stocks Advisory boards Grants Speakers Bureau. Paul Marik, MD,FCCM,FCCP
 Enteral Nutrition and Vasoactive Therapy! Paul Marik, MD,FCCM,FCCP Disclosures Stocks Advisory boards Grants Speakers Bureau None But actually.. 1 We suggest a determination of nutrition risk (NUTRIC score)
Enteral Nutrition and Vasoactive Therapy! Paul Marik, MD,FCCM,FCCP Disclosures Stocks Advisory boards Grants Speakers Bureau None But actually.. 1 We suggest a determination of nutrition risk (NUTRIC score)
Nutrition Supplementation in the ICU
 Nutrition Supplementation in the ICU ROSEMARY KOZAR MD PHD SHOCK TRAUMA UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines www.criticalcarenutrition.com NEJM March 27, 2014 1 Use of Enteral vs
Nutrition Supplementation in the ICU ROSEMARY KOZAR MD PHD SHOCK TRAUMA UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Canadian Clinical Practice Guidelines www.criticalcarenutrition.com NEJM March 27, 2014 1 Use of Enteral vs
Nutrition in ECMO. Elize Craucamp RD(SA)
 Nutrition in ECMO Elize Craucamp RD(SA) ECMO What now!? KEEP CALM AND FEED THE ECMO PATIENT Despite the fact that little is known about nutritional strategies for adult ECMO patients! Neither overcomplicate
Nutrition in ECMO Elize Craucamp RD(SA) ECMO What now!? KEEP CALM AND FEED THE ECMO PATIENT Despite the fact that little is known about nutritional strategies for adult ECMO patients! Neither overcomplicate
Heather Evans, MD University of Washington Seattle, WA
 Heather Evans, MD University of Washington Seattle, WA 1 American College of Surgeons Division of Education Heather L. Evans, MD, MS, FACS Nothing to disclose 2 Determine nutritional goals Determine when
Heather Evans, MD University of Washington Seattle, WA 1 American College of Surgeons Division of Education Heather L. Evans, MD, MS, FACS Nothing to disclose 2 Determine nutritional goals Determine when
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition. Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health
 Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Pediatric Nutrition Care as a strategy to prevent hospital malnutrition Div Pediatric Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases Dept of Child Health Child is not a miniature adult Specific for child growth and
Jodie R. Orwig, RDN, LDN
 Jodie R. Orwig, RDN, LDN In the first 12-24 hours post injury, the #1goal is stabilizing the patient, not nutrition. Goal #2 is surgery, as indicated, to correct the injury Preservation of organ function
Jodie R. Orwig, RDN, LDN In the first 12-24 hours post injury, the #1goal is stabilizing the patient, not nutrition. Goal #2 is surgery, as indicated, to correct the injury Preservation of organ function
When to start SPN in critically ill patients? Refereeravond IC
 When to start SPN in critically ill patients? Refereeravond IC Introduction (1) Protein/calorie malnutrition is very frequent in critically ill patients Protein/calorie malnutrition is associated with
When to start SPN in critically ill patients? Refereeravond IC Introduction (1) Protein/calorie malnutrition is very frequent in critically ill patients Protein/calorie malnutrition is associated with
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital
 By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
By; Ashraf El Houfi MD MS (pulmonology) MRCP (UK) FRCP (London) EDIC Consultant ICU Dubai Hospital Introduction The significance of nutrition in hospital setting (especially the ICU) cannot be overstated.
Nutrition Services at a glance
 Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
Nutrition Services at a glance Ragini Raghuveer, MS, RD, LD/N Systems Clinical Nutrition Manager Linette De Armas, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian Melissa Lorenzo, RD, LD/N Clinical Dietitian 1 Learning Objectives
VOLUME-BASED VS. RATE-BASED FEEDING
 VOLUME-BASED VS. RATE-BASED FEEDING Amanda Holyk Critical Care Pharmacist Mount Nittany Medical Center Society of Critical Care Medicine Annual Symposium November 10, 2017 0 Disclosure I have no actual
VOLUME-BASED VS. RATE-BASED FEEDING Amanda Holyk Critical Care Pharmacist Mount Nittany Medical Center Society of Critical Care Medicine Annual Symposium November 10, 2017 0 Disclosure I have no actual
Nutrition in critical illness:
 Nutrition in critical illness: from theory to daily practice Aim of the presentation Summarize the guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient.
Nutrition in critical illness: from theory to daily practice Aim of the presentation Summarize the guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient.
The prescription of optimal nutrition support therapy. Challenges to Optimal Enteral Nutrition in a Multidisciplinary Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
 Challenges to Optimal Enteral Nutrition in a Multidisciplinary Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Volume XX Number X Month XXXX 1-8 2009 American Society for Parenteral
Challenges to Optimal Enteral Nutrition in a Multidisciplinary Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Volume XX Number X Month XXXX 1-8 2009 American Society for Parenteral
Feeding the critically ill child
 Feeding the critically ill child Khaw Sia (1913 1984) Lee Jan Hau, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit September 2018 1 2 3 No disclosures Outline Is there a need to optimize enteral nutrition?
Feeding the critically ill child Khaw Sia (1913 1984) Lee Jan Hau, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit September 2018 1 2 3 No disclosures Outline Is there a need to optimize enteral nutrition?
Nutrition care plan for surgical patients. Objectives
 Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Slide 1 Nutrition care plan for surgical patients Surgical Nutrition Training Module Level 1 Philippine Society of General Surgeons Committee on Surgical Training In this session we will discuss the most
Vanderbilt University Medical Center Trauma ICU Nutrition Management Guidelines
 Vanderbilt University Medical Center Trauma ICU Nutrition Management Guidelines Trauma Critical Care Nutrition Guidelines Clinical judgment may supersede guidelines as patient circumstances warrant ASSESSMENT
Vanderbilt University Medical Center Trauma ICU Nutrition Management Guidelines Trauma Critical Care Nutrition Guidelines Clinical judgment may supersede guidelines as patient circumstances warrant ASSESSMENT
Malnutrition: An independent Risk Factor for Postoperative Complications
 Malnutrition: An independent Risk Factor for Postoperative Complications Bryan P. Hooks, D.O. University of Pittsburgh-Horizon June 24, 2017 Orthopedic Surgeon-Adult Reconstruction Disclosures: None Objectives:
Malnutrition: An independent Risk Factor for Postoperative Complications Bryan P. Hooks, D.O. University of Pittsburgh-Horizon June 24, 2017 Orthopedic Surgeon-Adult Reconstruction Disclosures: None Objectives:
The Basics of Nutritional Support Terry L. Forrette, M.H.S., RRT
 Presentation Overview The basics of metabolism Methods to measure metabolic rate Using indirect calorimetry Case studies Importance of Nutritional Support Malnutrition occurs in approx.40% of hospitalized
Presentation Overview The basics of metabolism Methods to measure metabolic rate Using indirect calorimetry Case studies Importance of Nutritional Support Malnutrition occurs in approx.40% of hospitalized
Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient. Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC
 Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC Financial Disclosures NONE Declared PROPER NUTRITION Surgical Effects on Nutrition Intake & Status
Surgical Nutrition for the Cardiothoracic Patient Stephanie Kunioki RD, CNSC, LD Memorial Hermann TMC Financial Disclosures NONE Declared PROPER NUTRITION Surgical Effects on Nutrition Intake & Status
patients : review of advances in last five years Dr. Aditya Jindal
 Enteral nutrition in medical ICU patients : review of advances in last five years Dr. Aditya Jindal Our food should be our medicine and our medicine should be our food. Hippocrates Introduction ti Nutritional
Enteral nutrition in medical ICU patients : review of advances in last five years Dr. Aditya Jindal Our food should be our medicine and our medicine should be our food. Hippocrates Introduction ti Nutritional
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Using the gut in acute care patients Permissive underfeeding in practice J.-C. Preiser (BE) PERMISSIVE UNDERFEEDING IN PRACTICE ESPEN congress Jean-Charles Preiser, M.D.,
Int. Med J Vol. 6 No 1 June 2007 Enteral Nutrition In Intensive Care: Tiger Tube For Small Bowel Feeding In Acute Pancreatitis.
 Page 1 of 6 Int. Med J Vol. 6 No 1 June 2007 Enteral Nutrition In Intensive Care: Tiger Tube For Small Bowel Feeding In Acute Pancreatitis. Case Report Mohd Basri bin Mat Nor. Department of Anaesthesiology
Page 1 of 6 Int. Med J Vol. 6 No 1 June 2007 Enteral Nutrition In Intensive Care: Tiger Tube For Small Bowel Feeding In Acute Pancreatitis. Case Report Mohd Basri bin Mat Nor. Department of Anaesthesiology
Indirect Calorimetry: Clinical Implications in Critically Ill Patients
 Indirect Calorimetry: Clinical Implications in Critically Ill Patients Sharla Tajchman, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Critical Care / Nutrition Support Clinical Pharmacy Specialist University of Texas MD Anderson
Indirect Calorimetry: Clinical Implications in Critically Ill Patients Sharla Tajchman, PharmD, BCPS, BCNSP Critical Care / Nutrition Support Clinical Pharmacy Specialist University of Texas MD Anderson
Veeradej Pisprasert, MD PhD
 Immunonutrition: Asian Perspectives Evidence of Immunonutrition in Asia Veeradej Pisprasert, MD PhD Division of Clinical Nutrition Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University pveera@kku.ac.th Outline
Immunonutrition: Asian Perspectives Evidence of Immunonutrition in Asia Veeradej Pisprasert, MD PhD Division of Clinical Nutrition Department of Medicine, Khon Kaen University pveera@kku.ac.th Outline
ICU Acquired Weakness: Role of Specific Nutrients
 ICU Acquired Weakness: Role of Specific Nutrients Dr Jonathan TAN Senior Consultant Dept of Anaesthesiology, Intensive Care & Pain Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Purpose? Healthcare professionals?
ICU Acquired Weakness: Role of Specific Nutrients Dr Jonathan TAN Senior Consultant Dept of Anaesthesiology, Intensive Care & Pain Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Purpose? Healthcare professionals?
[No conflicts of interest]
![[No conflicts of interest] [No conflicts of interest]](/thumbs/86/94144068.jpg) [No conflicts of interest] Patients and staff at: Available evidence pre-calories Three meta-analyses: Gramlich L et al. Does enteral nutrition compared to parenteral nutrition result in better outcomes
[No conflicts of interest] Patients and staff at: Available evidence pre-calories Three meta-analyses: Gramlich L et al. Does enteral nutrition compared to parenteral nutrition result in better outcomes
CLINICAL WORKSHEET #2 Nutrition Support In: Extended Care Facilities, HIV Disease, and Thermal Injury
 Name: Danielle Reschke BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIVERSITY NDFS 466 Clinical Worksheet #2 CLINICAL WORKSHEET #2 Nutrition Support In: Extended Care Facilities, HIV Disease, and Thermal Injury Purpose(s) 1. To complete
Name: Danielle Reschke BRIGHAM YOUNG UNIVERSITY NDFS 466 Clinical Worksheet #2 CLINICAL WORKSHEET #2 Nutrition Support In: Extended Care Facilities, HIV Disease, and Thermal Injury Purpose(s) 1. To complete
SECTION 4: RECRUIT PARTICIPANTS
 SECTION 4: RECRUIT PARTICIPANTS Contents Participant Eligibility & Enrollment... 2 Screening... 2 Study ID Numbers... 2 Inclusion Criteria... 2 Exclusion Criteria... 4 Co-Enrollment... 5 Informed Consent
SECTION 4: RECRUIT PARTICIPANTS Contents Participant Eligibility & Enrollment... 2 Screening... 2 Study ID Numbers... 2 Inclusion Criteria... 2 Exclusion Criteria... 4 Co-Enrollment... 5 Informed Consent
Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal?
 Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal? PD Dr. med. Claudia Heidegger Service des Soins Intensifs Genf/Schweiz Dresden 11. Juni 2016 Nutrition News Nutrition controversy in
Ernährungstherapie des Kritisch Kranken Enteral Parenteral Ganz egal? PD Dr. med. Claudia Heidegger Service des Soins Intensifs Genf/Schweiz Dresden 11. Juni 2016 Nutrition News Nutrition controversy in
THE AUTHOR OF THIS WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE: PARENTERAL NUTRITION (PN)
 WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
WHAT S NEW IN NUTRITION? Alisha Mutch, Pharm.D., BCPS THE AUTHOR OF THIS PRESENTATION HAS NOTHING TO DISCLOSE. OBJECTIVES & OUTLINE MALNUTRITION OBJECTIVES Indicate when parenteral nutrition (PN) is warranted
Optimal nutrition in critically ill children
 Optimal nutrition in critically ill children MODULE 1 Nutritional assessment of critically ill children Developed by The Asia Pacific Middle East Consensus Working Group on Nutrition Therapy in the Paediatric
Optimal nutrition in critically ill children MODULE 1 Nutritional assessment of critically ill children Developed by The Asia Pacific Middle East Consensus Working Group on Nutrition Therapy in the Paediatric
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA)
 STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE ENTERAL FEEDING TOLERANCE. IS IT WORTH IT? ENGELA FRANCIS RD(SA) DEFINITION OF ENTERAL FEEDING INTOLERANCE Gastrointestinal feeding intolerance are usually defined as: High gastric
The speaker has no disclosures relevant to this presentation.
 Etiology driven approach to malnutrition diagnosis Supporting systematic approach to nutrition assessment. Affordable Care Act - opportunities Conclusions Where do we go from here? The speaker has no disclosures
Etiology driven approach to malnutrition diagnosis Supporting systematic approach to nutrition assessment. Affordable Care Act - opportunities Conclusions Where do we go from here? The speaker has no disclosures
5.1 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Feeding Protocols March 2013
 5.1 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Feeding Protocols March 2013 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2009 update and hence there are no changes to the following
5.1 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Feeding Protocols March 2013 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2009 update and hence there are no changes to the following
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 New ESPEN Guidelines Nutrition In The ICU P. Singer (IL) ESPEN Guidelines: Nutrition in the ICU Pierre Singer Annika Reintam Blaser Mette M Berger Waleed Alhazzani Philip C Calder
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 New ESPEN Guidelines Nutrition In The ICU P. Singer (IL) ESPEN Guidelines: Nutrition in the ICU Pierre Singer Annika Reintam Blaser Mette M Berger Waleed Alhazzani Philip C Calder
NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF CHYLOTHORAX. Lekha.V.S Senior Clinical Dietitian HOD- Department Of Dietetics Apollo Children's Hospital
 NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF CHYLOTHORAX Lekha.V.S Senior Clinical Dietitian HOD- Department Of Dietetics Apollo Children's Hospital INTRODUCTION Nutrition therapy is a key component in the care of patients
NUTRITIONAL MANAGEMENT OF CHYLOTHORAX Lekha.V.S Senior Clinical Dietitian HOD- Department Of Dietetics Apollo Children's Hospital INTRODUCTION Nutrition therapy is a key component in the care of patients
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition. in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT. Dzulfikar DLH. Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition in PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Dzulfikar DLH Pediatric Emergency and Intensive Care Unit Department of Child Health, Faculty of Medicine Universitas Padjajaran, Hasan
The provision of optimal nutrition
 Nutritional practices and their relationship to clinical outcomes in critically ill children An international multicenter cohort study* Nilesh M. Mehta, MD; Lori J. Bechard, MEd, RD, LDN; Naomi Cahill,
Nutritional practices and their relationship to clinical outcomes in critically ill children An international multicenter cohort study* Nilesh M. Mehta, MD; Lori J. Bechard, MEd, RD, LDN; Naomi Cahill,
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention?
 Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Who Needs Parenteral Nutrition? 1 Is Parenteral Nutrition An Appropriate Intervention? Key questions to ask with initial consultation Can the gastrointestinal (GI) tract be utilized? Can the GI tract be
Feeding the Critically Ill Obese Patient
 Feeding the Critically Ill Obese Patient Carla Vartanian 1 Critically Ill Obese Patients WHO: Obesity is abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health, or as a BMI 30. The American Medical
Feeding the Critically Ill Obese Patient Carla Vartanian 1 Critically Ill Obese Patients WHO: Obesity is abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health, or as a BMI 30. The American Medical
Acetaminophen recommendations from the Food and Drug Administration Advisory Committee
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Acetaminophen: recommendations from the FDA Advisory Committee 1 Recombinant human erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and mortality in cancer patients Hospital-acquired pneumonia: risks
TABLE OF CONTENTS Acetaminophen: recommendations from the FDA Advisory Committee 1 Recombinant human erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and mortality in cancer patients Hospital-acquired pneumonia: risks
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal pain, enteral therapy in acute pancreatitis and, 812 Abscess(es), pancreatic, nutritional support for, 814 815 Acute Physiology and
Recognize the importance of early nutritional support in the ICU Assessment and monitoring of nutritional status Determine how to estimate specific
 Recognize the importance of early nutritional support in the ICU Assessment and monitoring of nutritional status Determine how to estimate specific nutritional requirements Enteral vs. Parenteral Specific
Recognize the importance of early nutritional support in the ICU Assessment and monitoring of nutritional status Determine how to estimate specific nutritional requirements Enteral vs. Parenteral Specific
Providing adequate nutritional support is a cornerstone
 Enteral Nutrition Practices in Critically Ill Children Requiring Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Matthew K. Leroue, MD 1,2 ; Ryan J. Good, MD 3 ; Heather E. Skillman, MS, RD 4 ; Angela S. Czaja,
Enteral Nutrition Practices in Critically Ill Children Requiring Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Matthew K. Leroue, MD 1,2 ; Ryan J. Good, MD 3 ; Heather E. Skillman, MS, RD 4 ; Angela S. Czaja,
Nutritional Support of the Injured Patient
 Nutritional Support of the Injured Patient A health care practice does not usually attend to severely traumatized, burned, or critically ill patients because they are usually hospitalized for extended
Nutritional Support of the Injured Patient A health care practice does not usually attend to severely traumatized, burned, or critically ill patients because they are usually hospitalized for extended
E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol
 E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol Arthur RH van Zanten, MD PhD Gelderse Vallei Hospital, Ede, The Netherlands Learning objectives Develop an evidence based
E S T A B L I S H I N G N U T R I T I O N I N Y O U R I C U The Need for a Protocol Arthur RH van Zanten, MD PhD Gelderse Vallei Hospital, Ede, The Netherlands Learning objectives Develop an evidence based
Etiology based definitions for adult malnutrition: Role of inflammation A systematic approach to nutrition assessment
 Etiology based definitions for adult malnutrition: Role of inflammation A systematic approach to nutrition assessment Gordon L Jensen, MD, PhD Penn State University University Park, PA Objectives Review
Etiology based definitions for adult malnutrition: Role of inflammation A systematic approach to nutrition assessment Gordon L Jensen, MD, PhD Penn State University University Park, PA Objectives Review
Proteins Amino Acids. K. Georg Kreymann Baxter Healthcare, Deerfield, USA
 Proteins Amino Acids K. Georg Kreymann Baxter Healthcare, Deerfield, USA François Magendie (1783-1855) Manfred Köhnlechner (1925-2002) The Manager Diet Main points Arginine supplemented diets should be
Proteins Amino Acids K. Georg Kreymann Baxter Healthcare, Deerfield, USA François Magendie (1783-1855) Manfred Köhnlechner (1925-2002) The Manager Diet Main points Arginine supplemented diets should be
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points. Ht: 5 11 Current wt: 156 # UBW: 167 # Serum albumin: 3.
 Name: Wan yi Wang Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from
Name: Wan yi Wang Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Due 2/13/15 60 points Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from
Protein Supplementation in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Jan Hau Lee, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit 28 th July 2017
 Protein Supplementation in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Jan Hau Lee, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit 28 th July 2017 1 Objectives Basis for protein supplementation Challenges in monitoring
Protein Supplementation in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit Jan Hau Lee, MBBS, MRCPCH, MCI Children s Intensive Care Unit 28 th July 2017 1 Objectives Basis for protein supplementation Challenges in monitoring
CASE STUDY ON INPATIENT MALNUTRITION DISCUSSION
 CASE STUDY ON INPATIENT MALNUTRITION Elena Kret-Sudjian MD, PhD, UC Davis Medical Center A 59 year-old white man with a history of diabetes, severe PVD, CKD IV, chronic hepatitis C admitted for non-healing
CASE STUDY ON INPATIENT MALNUTRITION Elena Kret-Sudjian MD, PhD, UC Davis Medical Center A 59 year-old white man with a history of diabetes, severe PVD, CKD IV, chronic hepatitis C admitted for non-healing
A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I
 FEEDING THE OBESE CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I HOSPITAL, EDE,
FEEDING THE OBESE CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT A R T H U R R. H. V A N Z A N T E N, MD PHD I N T E R N I S T - I N T E N S I V I S T H O S P I T A L MEDICAL DIRECTOR G E L D E R S E V A L L E I HOSPITAL, EDE,
Introduction to Clinical Nutrition
 M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
M-III Introduction to Clinical Nutrition Donald F. Kirby, MD Chief, Section of Nutrition Division of Gastroenterology 1 Things We Take for Granted Air to Breathe Death Taxes Another Admission Our Next
IMMUNONUTRITION AND GI SURGERY (UPPER AND LOWER) STUDIES COMPENDIUM
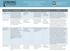 IMMUNONUTRITION AND GI SURGERY (UPPER AND LOWER) Colorectal or gastric cancer Xu 2006 (WJS;30:1284-1289) RCT to determine the effect of preoperative immunonutrition on nutritional status, immunity, and
IMMUNONUTRITION AND GI SURGERY (UPPER AND LOWER) Colorectal or gastric cancer Xu 2006 (WJS;30:1284-1289) RCT to determine the effect of preoperative immunonutrition on nutritional status, immunity, and
DOES IN WITH THE GOOD EQUAL OUT WITH THE BAD? APPLICATION OF NUTRITION SUPPORT RESEARCH
 DOES IN WITH THE GOOD EQUAL OUT WITH THE BAD? APPLICATION OF NUTRITION SUPPORT RESEARCH ANN-MARIE BROWN, PHD, CPNP-AC/PC, CCRN, FCCM ASST PROFESSOR, THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON PICU NURSE PRACTITIONER, AKRON
DOES IN WITH THE GOOD EQUAL OUT WITH THE BAD? APPLICATION OF NUTRITION SUPPORT RESEARCH ANN-MARIE BROWN, PHD, CPNP-AC/PC, CCRN, FCCM ASST PROFESSOR, THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON PICU NURSE PRACTITIONER, AKRON
Second Generation Enteral Nutrition Feeding Protocols: Taking us the the next level of performance
 Second Generation Enteral Nutrition Feeding Protocols: Taking us the the next level of performance Mr CD 47 renal transplant Severe CAP Septic shock, ARDS, MODs Requires vasopressors for days Admitting
Second Generation Enteral Nutrition Feeding Protocols: Taking us the the next level of performance Mr CD 47 renal transplant Severe CAP Septic shock, ARDS, MODs Requires vasopressors for days Admitting
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition
 Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from a severe concussion and lapses of consciousness,
Major Case Study: Enteral and Parenteral Nutrition Mr. R, a 35 yo drug user, is hospitalized after a motor vehicle accident (MVA). He is currently suffering from a severe concussion and lapses of consciousness,
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition for Critically Ill Children
 The Role of Parenteral Nutrition for Critically Ill Children Canadian Critical Care Forum Alejandro Floh MD, MSc Staff Physician, Department of Critical Care Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada
The Role of Parenteral Nutrition for Critically Ill Children Canadian Critical Care Forum Alejandro Floh MD, MSc Staff Physician, Department of Critical Care Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Canada
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
 NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man. By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy
 Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
Small Bowel Obstruction after operation in a severely malnourished man By: Ms Bounmark Phoumesy Normal length of GI tract Normal length(achieved by age 9) Small bowel 600cm (Men: 630 cm; Women: 592 cm)
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetate, in pediatric surgical patients, 525 526 Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), immune-modulating nutrition in, 584 585 Aerobic
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetate, in pediatric surgical patients, 525 526 Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), immune-modulating nutrition in, 584 585 Aerobic
Early enteral nutrition in the major trauma patient requiring intensive care: An overview of the evidence.
 Early enteral nutrition in the major trauma patient requiring intensive care: An overview of the evidence. Dr. Gordon S. Doig Associate Professor in Intensive Care Northern Clinical School Intensive Care
Early enteral nutrition in the major trauma patient requiring intensive care: An overview of the evidence. Dr. Gordon S. Doig Associate Professor in Intensive Care Northern Clinical School Intensive Care
5.2 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Motility Agents May 2015
 5.2 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Motility Agents May 2015 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2009 and 2013 updates and hence there are no changes to the
5.2 Strategies to Optimize Delivery and Minimize Risks of EN: Motility Agents May 2015 There were no new randomized controlled trials since the 2009 and 2013 updates and hence there are no changes to the
A review on enteral nutrition guidelines for traumatic brain injury
 A review on enteral nutrition guidelines for traumatic brain injury According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 1.7 million people suffer from traumatic brain injury (TBI) every
A review on enteral nutrition guidelines for traumatic brain injury According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 1.7 million people suffer from traumatic brain injury (TBI) every
