Olof Wolf, MD, PhD, Per Mattsson, MD, PhD, Jan Milbrink, MD, PhD, Sune Larsson, MD, PhD, and Hans Mallmin, MD, PhD
|
|
|
- Myra Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Rehabil Med 2013; 45: ORIGINAL REPORT Effects of Postoperative Weight-Bearing on Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density after Uncemented Total Hip Arthroplasty Olof Wolf, MD, PhD, Per Mattsson, MD, PhD, Jan Milbrink, MD, PhD, Sune Larsson, MD, PhD, and Hans Mallmin, MD, PhD From the Department of Orthopaedics, Uppsala University Hospital, Uppsala, Sweden Objective: To investigate whether a postoperative weightbearing regimen affects changes in bone mineral density and body composition after uncemented total hip arthroplasty, and to investigate the changes over a 5-year period after the surgical procedure. Design: Secondary analysis of a previous randomized controlled trial. Methods: A total of 39 patients were randomized to immediate full weight-bearing or partial weight-bearing for 3 months. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry was used to measure bone mineral density of the contralateral hip and both heels and to measure body composition. Results: The weight-bearing regimen had no effect on change in bone mineral density or body composition after 3 and 12 months. At 5 years, there was a decrease in bone mineral density of 3% in the total body and 2 3% in the contralateral hip regions. At 5 years we found a decrease in total body bone mineral content of 5%, but no changes in fat mass or lean mass compared with preoperative values. Conclusion: The postoperative weight-bearing regimen had no effect on changes in body composition or bone mineral density. Five years after total hip arthroplasty there was a decrease in bone mineral content and bone mineral density, but no changes in lean mass or fat mass. Key words: osteoarthritis of the hip; uncemented total hip arthroplasty; DXA; weight-bearing; body composition; bone mineral density. J Rehabil Med 2013; 45: Correspondence address: Olof Wolf, Department of Orthopaedics, Uppsala University Hospital, SE Uppsala, Sweden. olof.wolf@surgsci.uu.se Accepted Dec 19, 2012; Epub ahead of print Apr 10, 2013 Introduction Osteoarthritis of the hip (OAH) results in pain, which, in advanced OAH, limits everyday physical function, reduces walking ability and distance, makes walking aids necessary, and consequently limits the patient in several ways. Total hip arthroplasty (THA) is one of the most effective surgical procedures regarding physical function and pain relief. The benefits of THA are well documented, through the use of disease-specific and generic health-related quality of life instruments, e.g. the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index and the Short-Form 36 (1, 2). Several randomized studies have reported no adverse effects on implant stability with early rehabilitation and full weight-bearing following uncemented THA (3 6). This is supported by a recent review of postoperative weight-bearing regimens after uncemented THA (7). There are several reports of periprosthetic bone loss after uncemented THA (5, 8, 9). The bone loss is apparent around the whole stem, but is most marked in the calcar region. There is usually a restoration towards baseline values around the stem after 12 months; however, the calcar area continuously loses bone even in stems designed for proximal load transfer, regardless of postoperative weight-bearing regimen (5). To our knowledge there are no reports on body composition and bone body mineral density (BMD) changes following THA. A return to a more active daily life would theoretically lead to changes in body composition, or at least counteract inactivity changes induced by disease, e.g. OAH. Fatty infiltration into muscle increases with age (10), but can be diminished with regular physical activity (11). High-resistance training has been shown to have a positive effect on muscle mass (12), strength, size and function in patients as old as 90 years (13). We have previously conducted a randomized controlled trial (RCT) on full vs partial weight-bearing after THA with femoral stem stability assessed with radiostereometry as the primary outcome and periprosthetic BMD changes as the secondary outcome (5). The aim of this paper was to make a secondary analysis of body composition and BMD changes following uncemented THA. Our aim was to investigate: whether the postoperative weight-bearing regimen made a difference in body composition changes; and to follow the changes over a 5-year period after the THA procedure. We also examined the impact of the surgical procedure and/or the implant on the baseline measurements. Patients and methods A total of 42 patients were included in this RCT at the visit to the pre-assessment clinic by the senior authors (PM, JM and HM). Inclusion criteria were strictly unilateral radiographically verified hip osteoarthritis, age between 25 and 65 years (age group in which we 2013 The Authors. doi: / Journal Compilation 2013 Foundation of Rehabilitation Information. ISSN
2 Effects of weight-bearing after THA 499 would routinely use an uncemented THA), and weight less than 110 kg. Exclusion criteria were: patients receiving steroids or other medication known to affect bone metabolism; malignancy; previous hip surgery; body mass index (BMI) above 35; patients living outside the Uppsala municipality. All patients gave informed consent before entering the study, which was approved by the local ethics committee (Ups 99242). Enrolment took place between April 2000 and April 2003, prior to the start of the randomized controlled trial registration. Directly after the operation the patients were randomized, with consecutively numbered sealed envelopes, to either full weight-bearing (FWB) or partial weight-bearing (PWB). The patients in the FWB group were instructed to bear full weight directly after surgery and, in addition, were enrolled in a strictly controlled and active physiotherapeutic programme, with exercises to be performed at home after instruction by the study physiotherapist. The home exercises were intensified after 4 weeks by adding training in a pool twice a week for 4 7 weeks postoperatively. Subsequently, 7 weeks intensive training in the physiotherapist s gym was added and this continued until 3 months after surgery. The patients in the PWB group were instructed to bear weight partially, approximately 15 kg, for 3 months, which was the routine at the department at that time. In addition, they received a short written home-exercise programme, based on mobility through supported flexion and extension exercises. Typically, the patients in both groups were treated as in-patients for 7 days following surgery. In order to evaluate compliance with the instructions regarding weight-bearing, snapshots of weight-bearing were assessed at every visit to the outpatient clinic, using the F-scan system (Tekscan TM Inc., South Boston, USA). Mean weight-bearing, expressed as peak load in kilograms, was calculated on the basis of 3 recordings, each of which included 5 steps. This was carried out by the same physiotherapist and with the same equipment before surgery and 1 week, and 3, 6, 12, and 24 months after surgery, as described previously (14). Three of the initial 42 patients had undergone contralateral THA because of OAH within the follow-up period and were thus excluded from the present study (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials; CONSORT, Fig. 1). Thus, 39 patients (20 men, 19 women) with strictly unilateral OAH were available for the present study. All patients received an uncemented total hip replacement with the grit-blasted titanium CLS hip stem (Centerpulse/Zimmer Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA). The design, described as a press fit stem, allows proximal load transfer and is thought to give no stress shielding (15). The original study included the uncemented Interop acetabular cup. For reasons of manufacturing problems with oil-contaminated shells (16), the product was withdrawn from the market. Thus, only 15 Interop acetabular cups were inserted. The remaining patients were operated on with an uncemented Allofit acetabular cup without screw holes (n = 23), or an uncemented Trilogy cup with cluster holes (n = 1) (all cups by Centerpulse, Bern, Switzerland, acquired by Zimmer Inc., Warsaw, IN, USA). All 3 cups are press fit cups and no additional screws were used for stability. All patients received a modular 28-mm cobalt-chrome femoral head. Five experienced surgeons performed the operations in a standardized manner in accordance with the manufacturer s manual, using an anterolateral approach with the patient in the lateral position. Total body composition measurements and areal bone densitometry at the proximal femur on the unaffected side (preoperatively bilaterally) were performed with a pencil-beam total body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scanner, DPX-L (Lunar Co., Madison, WI, USA). The heels were measured with a cone-beam DXA-equipment, PIXI (Lunar Co.). The same DXA machines were used throughout the study. The baseline DXA measurement was performed 1 2 weeks before surgery for 35 patients, according to the initial study protocol. After study onset the suspicion arose that the implant and/or the surgery itself might artificially alter the baseline values. Hence, 22 patients were also scanned within 1 week after surgery. The follow-up DXA measurements were carried out after 3, 12, 24 and 60 months. The heels were followed to 24 months. A spine phantom was scanned regularly during the study period and the long-term precision, expressed as coefficient of variance (CV%) for L2 L4 BMD, was < 1.5%. Body composition The total body scan was manually adjusted for regions of interest (ROI), i.e. head, trunk, spine, arms and legs (Fig. 2). The DXA scan measured fat mass (FM), lean mass (LM) (i.e. muscle mass) and bone mineral content Enrollment Assessed for eligibility (n=42) Excluded (n=3) Not meeting inclusion criteria (n=3) Randomized (n=39) Allocated to full weight bearing (n=19) Received allocated intervention (n=19) Allocation Allocated to partial weight bearing (n=20) Received allocated intervention (n=20) Lost to follow-up (2 died, 1 stem revision) (n=3) Follow- up 5 years Lost to follow-up (1 cup revision) (n=1) Analysed at 5 years (n=15 prox femur/14 total body) Excluded from analysis (1 with only proximal femur scan, 1 attended but DXA not running) (n=2) Analysis Analysed at 5 years (n=18) Excluded from analysis (1 did not want to attend) (n=1) Fig. 1. Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) flow diagram. DXA: dual x-ray absorptiometry.
3 500 O. Wolf et al. procedure and the implant on the distribution of tissues compared with the preoperative values (19 patients had both pre- and post-operative scans). Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed with Statistica 9.1 (StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). Study groups were compared with Student s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test, depending on whether they were normally distributed. Likewise, within-group comparisons were made using paired t-test or Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Differences were considered significant when p < Values are given as means with standard deviations (SD). The primary study parameter of this RCT was the effect of FWB on the stability of an uncemented femoral stem, Thus, the power analysis for this study was made for radiostereometric analysis (RSA) (3, 5, 17) to estimate the sample size necessary to detect a significant difference in linear micromotion along the y-axis, i.e. subsidence, between the two groups with alpha 0.05 and beta 0.20 (i.e. a power of 0.8), and groups of 20 patients were found sufficient. The aim of this paper was to make a secondary analysis on the effects of weight-bearing and changes in body composition and BMD. Results Fig. 2. Total body DXA scan displaying the manually adjusted regions for measurement of body composition, i.e. fat mass, lean mass, and bone mineral content. (BMC) in grams. Regional analyses gave us the operated and non-operated leg s figures. In order to allow for comparisons between FWB and PWB groups, the FM, LM and BMC proportion of each leg s total weight was calculated, i.e. the FM%, LM%, and BMC% in each leg. By using the proportions rather than the absolute values we minimized the possible difficulties in this longitudinal study with manually adjusted ROIs. The mean age of the 39 patients (20 men, 19 women) was 54 years (SD 9) (range 25 63). Their mean weight (DXA derived for 35 patients with preoperative scan) was 79 kg (SD 13), mean height 172 cm (SD 9) and mean body mass index 27 (SD 3). Four patients were lost to follow-up. One patient died of pulmonary embolism 3 months postoperatively; 1 patient (PWB) had a cup revision within 20 months because of loosening (no data after 1 year); 1 patient (FWB) had a stem revision after 1.5 years because of aseptic loosening (no data after 1 year); and 1 patient died of unrelated causes after 2 years (no data at 5 years). At 5 years 3 patients could not attend the follow-up examination (1 only had the proximal femur scan). Thirty-two of the 39 patients completed a total body scan at 5 years, 33 completed a proximal femur scan, and 36 patients had their heels scanned after 2 years. Nineteen of the 38 patients were scanned both pre- and post-operatively. Compliance with weight-bearing Bone mineral density The proximal femur was scanned bilaterally preoperatively, and the unaffected contralateral hip was followed for 5 years. Three ROIs at the proximal femur were analysed for areal bone mineral density (g/ cm 2 ), i.e. femoral neck (FN), total hip (TH), and trochanter region (TR). A manufacturer-defined ROI of the heels was analysed for areal BMD (g/cm 2 ) of the calcaneus bilaterally (followed for 2 years). In order to assess the effect of postoperative weight-bearing regimen we compared: changes in body composition proportions from baseline to 3 and 12 months; Effect of postoperative weight-bearing effects on BMD at 3 and 12 months. In order to assess the changes over 5 years following the unilateral THA procedure we pooled the data for both groups and analysed: total body composition of FM% (TB FM%), LM% (TB LM%) and BMC% (TB BMC%); changes in the operated and non-operated leg s FM%, LM% and BMC%; BMD of the contralateral hip, and BMD of the heels (for 2 years after surgery); total body weight assessed by DXA. Twenty-two patients were also scanned within a few days after the operation. This allowed for assessment of the influence of the surgical As previously reported, the patients in the PWB group put almost twice the recommended weight on the operated side (26 kg at 1 week and 32 kg at 3 months) (14). The PWB group, however, put substantially less load on the operated leg at 1 week and 3 months than the FWB group (14). Not surprisingly, the FWB group was unable to perform full weight-bearing during the first postoperative week. The prescribed postoperative weight-bearing regimen had no effect on either the change of FM%, LM% or BMC% in either leg at 3 months (Table I) or at 12 months (data not shown) or on the BMD at the contralateral hip or heels from baseline to 3 months (Table I) or 12 months (data not shown). Changes over 5 years following unilateral total hip arthroplasty (Table II) There was a 5% decrease in TB BMC% at 5 years. The TB FM% and TB LM% did not change during the 5 years. There
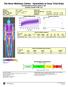
4 Effects of weight-bearing after THA 501 Table I. Changes in body composition of the legs and bone mineral density (BMD) of the heels and the contralateral hip from baseline to 3 months. Full weight-bearing (FWB) vs partial weight-bearing (PWB) after uncemented total hip arthroplasty Change in percentage from baseline to 3 months FWB PWB Fat mass, % Op +11 (12) +16 (21) /18 Non-op +9 (13) +10 (17) 0.8 Lean mass, % Op 4 (5) 4 (4) 0.6 Non-op 3 (4) 2 (6) 0.9 BMC, % Op 13 (5) 9 (7) 0.06 Non-op 2 (6) 0 (8) 0.6 BMD, g/cm 2 FN 0 (3) 1 (3) /20 TR +1 (3) 1 (4) 0.1 TH +1 (2) 1 (2) 0.07 Heels op 1 (4) 1 (4) /20 Heels non-op 1 (5) +1 (2) /20 p = body composition changes compared with Mann-Whitney U test, BMD compared with t-test. n = patients in FWB/PWB. Non-op: non-operated side; BMC: bone mineral content; FN: femoral neck; TR: trochanter; TH: total hip. p n % of leg's weight Lean Fat BMC Fat Mass, Lean Mass and Bone Mineral Content 5 year follow up after THA. FM% op LM% op BMC% op FM% non op LM% non op BMC% non op Preop 1 yr 2 yr 5 yr Time Fig. 3. Body weight and distribution of fat mass (FM), lean mass (LM) and bone mineral content (BMC) (operated vs non-operated leg) following total hip arthroplasty. Preoperative to 5-year follow-up. was a decrease of 9% in BMC% in the operated leg and of 4% in the non-operated leg from baseline, and the decrease was larger on the operated side (p < 0.01). FM% reaches its highest value, and LM% its lowest, at 3 months (Fig. 3). From then on the values normalized towards the baseline values and there was no change from baseline to 5 years. There was a decrease in BMD of the contralateral hip by 3% at the FN, by 3% at the TH, and by 2% at TR, and also a decrease of 3% in total body BMD at 5 years. There was no change in BMD of the heels at 2 years. The 29 patients with both preoperative and 5 years examinations showed no change in body weight (+1% over 5 years, p = 0.5). Timing of baseline examination (19 pre- vs post-operative scans) The operated hip displayed a 13% decrease in BMC% (4.87 vs 4.25; p < 0.05) after surgery. There was no difference in FM% or LM% when comparing the 19 pre- and post-operative examinations (data not shown). Table II. Baseline, 5-year values, and changes in total body composition, weight, and bone mineral density (BMD) from pre-operative to 5 years (2 years for heels) after unilateral uncemented total hip arthroplasty Baseline n 5-year n Change, % n p p a Total body FM% 32.9 (7.8) (8.9) 32 2 (14) LM% 63.3 (7.4) 62.5 (8.5) 1 (7) 0.7 BMC% 3.8 (0.5) 3.6 (0.5) 5 (6) < Weight, kg 78.8 (13) 79.8 (13) 1 (6) 0.5 BMD, g/cm 2 TB (0.1) (0.1) 3 (3) < FN (0.1) (0.1) 33 3 (6) 33 < 0.01 TH (0.1) (0.1) 3 (4) < TR (0.1) (0.1) 2 (5) < 0.05 Regional analysis of lower extremities, operated and non-operated side FM, % Op 32.3 (11) (11) (16) Non-op 31.7 (11) 32.6 (11) +3 (17) LM, % Op 63.1 (10) 62.6 (11) 0 (7) 0.8 Non-op 63.6 (10) 62.9 (10) 0 (7) BMC, % Op 4.6 (0.8) 4.2 (0.7) 9 (8) < Non-op 4.6 (0.8) 4.4 (0.7) 4 (7) < 0.05 < 0.01 BMD Heels Op (0.1) (0.1) 36 0 (7) Non-op (0.1) (0.1) +1 (6) p = Wilcoxon signed-rank test/paired t-test (DXA) baseline to 5 years ( a between op and non-op side). TB: total body; FN: femoral neck; TH: total hip; TR: trochanter; op: operated side; non-op: non-operated side.
5 502 O. Wolf et al. Discussion To our knowledge, the present paper is the first to investigate the effect of postoperative weight-bearing on changes in body composition and BMD. Most studies of FWB vs PWB following THA compare periprosthetic BMD and we have previously reported our data on that (5). In this paper we focus on a secondary analysis of changes in body composition of the lower extremities and BMD of the heels and contralateral hip following a unilateral THA procedure. Our patients were randomized to partial weight-bearing for 3 months (PWB group) with the instruction to load 15 kg on the operated leg, or to full immediate weight-bearing (FWB group) combined with intensive supervised physiotherapy. Compliance with the weight-bearing instruction was measured at visits to the physiotherapist, using the F-scan system. The PWB group had problems in complying with the set weightbearing limits, which is in line with other findings of difficulties in staying within the prescribed weight-bearing limits (18). Others have used an auditory feedback device calibrated to between 10% of body weight to 30 kg of loading to instruct the patients (4, 19). Effect of postoperative weight-bearing The 2 different weight-bearing regimens had no effect on the change in FM%, LM% or BMC% in either leg 3 and 12 months after the surgical procedure. There was no difference in the change in BMD of either the operated or non-operated side s heels or of the contralateral hip. This could be in line with previous studies showing no adverse effect on the stability of femoral implants (3 5, 17) or on the periprosthetic BMD (5, 19) regarding the postoperative weight-bearing regimens after uncemented THA. Changes over 5 years following unilateral total hip arthroplasty Body composition. Five years after a unilateral THA we found no change in TB FM% or TB LM%, nor did we find any change in FM% or LM% in either leg. The percentage of body fat increases in both men and women with normal ageing, with higher values in women (20, 21). Our results are in contrast with the findings of an annual increase in TB FM of 2.4% for women and 7% for men older than 50 years, and a decrease of 1% and 1.9% in TB LM, in a cross-sectional study of 273 ethnic Swedish individuals re-measured after 3 4 years (22). The different findings might reflect the different study designs in terms of a selected OAH group in our case, and also perhaps be a matter of sample size. In our patients, however, there was a decrease in TB BMC% of 5%, as well as a decrease in BMC% in both legs. The BMC% decrease in the operated side was larger at 5 years than in the non-operated side, but there might be no real difference in loss of BMC with the extraction of the femoral head in mind. Bone mineral density. The OAH patients displayed a decrease in BMD in all ROIs of the contralateral hip, as well as a decrease in total body BMD, which probably reflects the expected age-related reductions. At 5 years, the decrease in FN BMD was 3% in our OAH patients, i.e. an annual loss of 0.6%. This is in line with cross-sectional and longitudinal studies with reported annual losses of % in FN BMD (22 24). We found no change in BMD at the heels 2 years after THA. Body weight. Pain resulting from OAH prevents ordinary physical activities and may therefore be a factor in weight gain. A decrease in pain following THA would be beneficial for these patients and could therefore lead to more physical activity and promote weight loss. On the contrary, we found no change in weight during the 5 years following THA. Contrary to our finding, the median annual weight loss was 1 kg in a cohort study of 4,800 former male civil servants (age years) from England with a median follow-up of 28 years (25). However, the patients in the latter study were younger at inclusion, and were all men. Our results are in line with the finding of no weight gain in a large cohort study of more than 6,000 men and women, who were older than 60 years and healthy at inclusion, from 6 European countries during a median follow-up of years (26). However, both weight loss and weight gain (in the obese subjects only) of more than 1 kg per year was associated with increased mortality in a nested case-control analysis in this study population. Does timing of baseline examination matter? Since we became aware of the possible artificial effect of the implant and the surgical procedure on the total body scan, 22 patients were also scanned postoperatively. Comparisons between the preoperative and postoperative examinations clearly show a 13% decrease in BMC% of the operated side. This probably reflects the effect of the surgical procedure with extraction of a considerable amount of BMC, i.e. the femoral head. In addition, the software excluded the BMC anterior and posterior to the implant. We found no difference in FM% or LM%. Visser et al. (27) chose to use the results of only the non-fractured leg in a study of muscle mass and muscle strength after hip fracture, since the swelling after the surgical procedure would be measured as lean mass, and hence theoretically overestimate the muscle mass at baseline. With our findings at hand, we chose to use the preoperative examination as the baseline, but with the decrease in BMC in mind. For comparisons of soft tissues and weight the preoperative examinations offer a more reliable baseline; we found no differences in FM% and LM% between the pre- and postoperative examinations. Our study has both strengths and limitations. We used a randomized design to study the effect of postoperative weightbearing on body composition and BMD of the contralateral hip and of both heels. We used DXA to measure the proportion of FM, LM and BMC, which has been described as a method with excellent long-term precision (28). We also investigated the potential effect of the surgical procedure on the baseline values of body composition in half of the study group after study onset. Compliance with the prescribed weight-bearing was controlled with the F-scan system, although only at visits
6 Effects of weight-bearing after THA 503 to our PT. The sample size in our study was much smaller than the cross-sectional studies on age-related BMD changes. Power analysis in this RCT was performed for the stability of the femoral implant assessed by RSA. We might lack the power to find small differences in BMD and body composition. In conclusion, we found no differences between the varying postoperative weight-bearing regimens regarding effect on change in body composition or BMD of the legs after an uncemented THA. Five years after THA there was a decrease in BMC and BMD, but no changes in fat mass or lean mass (muscle) distribution in the total body or legs. Acknowledgements This study could not have been performed without the strenuous work of our late colleague Dr. Håkan Ström. The authors are grateful to Marja Gustafsson and Monika Gelotte for skilful DXA measurements. We thank Lisa Wernroth, Uppsala Clinical Research Center, for valuable statistical assistance. Financial support. Zimmer Inc. sponsored the study financially. However, they had no influence on the design of the study, collection of data, or writing of the manuscript. References 1. Cushnaghan J, Coggon D, Reading I, Croft P, Byng P, Cox K, et al. Long-term outcome following total hip arthroplasty: a controlled longitudinal study. Arthritis Rheum 2007; 57: Nilsdotter AK, Aurell Y, Siosteen AK, Lohmander LS, Roos HP. Radiographic stage of osteoarthritis or sex of the patient does not predict one year outcome after total hip arthroplasty. Ann Rheum Dis 2001; 60: Ström H, Nilsson O, Milbrink J, Mallmin H, Larsson S. Early migration pattern of the uncemented CLS stem in total hip arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2007; 454: Thien TM, Ahnfelt L, Eriksson M, Stromberg C, Karrholm J. Immediate weight-bearing after uncemented total hip arthroplasty with an anteverted stem: a prospective randomized comparison using radiostereometry. Acta Orthop 2007; 78: Wolf O, Mattsson P, Milbrink J, Larsson S, Mallmin H. Periprosthetic bone mineral density and fixation of the uncemented CLS stem related to different weight bearing regimes. A randomized study using DXA and RSA in 38 patients followed for 5 years. Acta Orthopaedica 2010; 81: Bottner F, Zawadsky M, Su EP, Bostrom M, Palm L, Ryd L, et al. Implant migration after early weightbearing in cementless hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005; Hol AM, van Grinsven S, Lucas C, van Susante JL, van Loon CJ. Partial versus unrestricted weight bearing after an uncemented femoral stem in total hip arthroplasty: recommendation of a concise rehabilitation protocol from a systematic review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2010; 130: Boden HS, Skoldenberg OG, Salemyr MO, Lundberg HJ, Adolphson PY. Continuous bone loss around a tapered uncemented femoral stem: a long-term evaluation with DEXA. Acta Orthop 2006; 77: Panisello JJ, Herrero L, Canales V, Herrera A, Martinez AA, Mateo J. Long-term remodeling in proximal femur around a hydroxyapatite-coated anatomic stem: ten years densitometric follow-up. J Arthroplasty 2009; 24: Borkan GA, Hults DE, Gerzof SG, Robbins AH, Silbert CK. Age changes in body composition revealed by computed tomography. J Gerontol 1983; 38: Goodpaster BH, Chomentowski P, Ward BK, Rossi A, Glynn NW, Delmonico MJ, et al. Effects of physical activity on strength and skeletal muscle fat infiltration in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. J Appl Physiol 2008; 105: Campbell WW, Joseph LJ, Davey SL, Cyr-Campbell D, Anderson RA, Evans WJ. Effects of resistance training and chromium picolinate on body composition and skeletal muscle in older men. J Appl Physiol 1999; 86: Fiatarone MA, Marks EC, Ryan ND, Meredith CN, Lipsitz LA, Evans WJ. High-intensity strength training in nonagenarians. Effects on skeletal muscle. JAMA 1990; 263: Ström H, Huss K, Larsson S. Unrestricted weight bearing and intensive physiotherapy after uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Scand J Surg 2006; 95: Spotorno L, Romagnoli S, Ivaldo N, Grappiolo G, Bibbiani E, Blaha DJ, et al. The CLS system. Theoretical concept and results. Acta Orthop Belg 1993; 59 Suppl 1: Blumenfeld TJ, Bargar WL. Early aseptic loosening of a modern acetabular component secondary to a change in manufacturing. J Arthroplasty 2006; 21: Ström H, Nilsson O, Milbrink J, Mallmin H, Larsson S. The effect of early weight bearing on migration pattern of the uncemented CLS stem in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2007; 22: Tveit M, Karrholm J. Low effectiveness of prescribed partial weight bearing. Continuous recording of vertical loads using a new pressure-sensitive insole. J Rehabil Med 2001; 33: Boden H, Adolphson P. No adverse effects of early weight bearing after uncemented total hip arthroplasty: a randomized study of 20 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 2004; 75: Kehayias JJ, Fiatarone MA, Zhuang H, Roubenoff R. Total body potassium and body fat: relevance to aging. Am J Clin Nutr 1997; 66: Pierson RN Jr, Wang J, Heymsfield SB, Russell-Aulet M, Mazariegos M, Tierney M, et al. Measuring body fat: calibrating the rulers. Intermethod comparisons in 389 normal Caucasian subjects. Am J Physiol 1991; 261: E103 E Karlsson MK, Obrant KJ, Nilsson BE, Johnell O. Changes in bone mineral, lean body mass and fat content as measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry: a longitudinal study. Calcif Tissue Int 2000; 66: Jones G, Nguyen T, Sambrook P, Kelly PJ, Eisman JA. Progressive loss of bone in the femoral neck in elderly people: longitudinal findings from the Dubbo osteoporosis epidemiology study. BMJ 1994; 309: Sheu Y, Cauley JA, Wheeler VW, Patrick AL, Bunker CH, Ensrud KE, et al. Age-related decline in bone density among ethnically diverse older men. Osteoporos Int 2011; 22: Breeze E, Clarke R, Shipley MJ, Marmot MG, Fletcher AE. Cause-specific mortality in old age in relation to body mass index in middle age and in old age: follow-up of the Whitehall cohort of male civil servants. Int J Epidemiol 2006; 35: Bamia C, Halkjaer J, Lagiou P, Trichopoulos D, Tjonneland A, Berentzen TL, et al. Weight change in later life and risk of death amongst the elderly: the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition-Elderly Network on Ageing and Health study. J Intern Med 2010; 268: Visser M, Harris TB, Fox KM, Hawkes W, Hebel JR, Yahiro JY, et al. Change in muscle mass and muscle strength after a hip fracture: relationship to mobility recovery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2000; 55: M434 M Blake GM, Fogelman I. The clinical role of dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Eur J Radiol 2009; 71:
The optimal timing of baseline radiostereometric analysis of uncemented press fit cups
 Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 99: 244 249, 2010 The optimal timing of baseline radiostereometric analysis of uncemented press fit cups O. Wolf, J. Milbrink, S. Larsson, P. Mattsson, H. Mallmin Department
Scandinavian Journal of Surgery 99: 244 249, 2010 The optimal timing of baseline radiostereometric analysis of uncemented press fit cups O. Wolf, J. Milbrink, S. Larsson, P. Mattsson, H. Mallmin Department
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi
 DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
DXA When to order? How to interpret? Dr Nikhil Tandon Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi Clinical Utility of Bone Densitometry Diagnosis (DXA)
Metha Short Hip Stem System
 Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
Metha Short Hip Stem System Accuracy That Stands Alone Aesculap Orthopaedics Metha Short Hip Stem System Designed For Anatomic Accuracy The Metha Short Hip Stem is designed for anatomic accuracy to restore
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
TITLE: Unrestricted Weight-Bearing after Hip Arthroplasty or Hip Fracture Surgery. DATE: 25 June 2007 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Unrestricted Weight-Bearing after Hip Arthroplasty or Hip Fracture Surgery DATE: 25 June 2007 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Total Hip Arthroplasty: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) generally involves replacing
TITLE: Unrestricted Weight-Bearing after Hip Arthroplasty or Hip Fracture Surgery DATE: 25 June 2007 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES: Total Hip Arthroplasty: Total hip arthroplasty (THA) generally involves replacing
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302)
 PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
76 F: Plays tennis, lives independently, told she has weak bone
 Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Femoral Neck Fractures In the ELDERLY What to do, when and why Frank Liporace, MD Chairman & VP, Dept of Orthopaedics Chief of Trauma & Adult Reconstruction Jersey City Medical Center / RWJ Barnabas Health
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/38039 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Embden, Daphne van Title: Facts and fiction in hip fracture treatment Issue Date:
Preoperative dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and FRAX in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis
 Bergh et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:253 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0964-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preoperative dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and FRAX in patients with
Bergh et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:253 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0964-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Preoperative dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and FRAX in patients with
Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery
 Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery Satoru Fujita, Masamichi Tanaka, Sigeaki Hirota, and Takeshi Fuji Since 1988, Fuji Computed Radiography (FCR) system (Fuji Medical Systems,
Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery Satoru Fujita, Masamichi Tanaka, Sigeaki Hirota, and Takeshi Fuji Since 1988, Fuji Computed Radiography (FCR) system (Fuji Medical Systems,
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients. Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist
 Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Use of DXA / Bone Density in the Care of Your Patients Brenda Lee Holbert, M.D. Associate Professor Senior Staff Radiologist Important Websites Resources for Clinicians and Patients www.nof.org www.iofbonehealth.org
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Gerald Friedl 1 ; Roman Radl 1 ; Peter Rehak 2, Reingard Aigner 3, and Reinhard Windhager 1
 Viability of a single infusion of zoledronic acid (ZOL) to reduce implant failure rate in THA Results from a randomized, double-blind, blind, controlled trial Gerald Friedl 1 ; Roman Radl 1 ; Peter Rehak
Viability of a single infusion of zoledronic acid (ZOL) to reduce implant failure rate in THA Results from a randomized, double-blind, blind, controlled trial Gerald Friedl 1 ; Roman Radl 1 ; Peter Rehak
Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE
 Design Rationale Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Design Rationale Approach Patients with CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult
 2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
Reaching new heights. Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple.
 Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Reaching new heights Comprehensive. Efficient. Simple. Various acetabular cup choices Compatible with the different head and liner options including VERILAST Technology Reach for proven OR efficient Instrumentation
Effect of Precision Error on T-scores and the Diagnostic Classification of Bone Status
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Measurement of Periprosthetic Bone Density in Hip Arthroplasty Using Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Reproducibility of Measurements
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 11 No. 4 1996 Measurement of Periprosthetic Bone Density in Hip Arthroplasty Using Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Reproducibility of Measurements R. C. Smart, BSc, MSc,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 11 No. 4 1996 Measurement of Periprosthetic Bone Density in Hip Arthroplasty Using Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry Reproducibility of Measurements R. C. Smart, BSc, MSc,
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(2): 78-85, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.78 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(2): 78-85, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.78 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
Relative Osteopenia After Femoral Implant Removal in Children and Adolescents
 Relative Osteopenia After Femoral Implant Removal in Children and Adolescents L. Johnson Patman, MD; Elizabeth A. Szalay, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search: 20130327-24
Relative Osteopenia After Femoral Implant Removal in Children and Adolescents L. Johnson Patman, MD; Elizabeth A. Szalay, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search: 20130327-24
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
BONE FLUORIDE IN PROXIMAL FEMUR FRACTURES
 Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 4 227-235 2001 Research Report 227 BONE FLUORIDE IN PROXIMAL FEMUR FRACTURES A Bohatyrewicz a Szczecin, Poland SUMMARY: Bone fluoride concentration and bone mineral density (BMD) were
Fluoride Vol. 34 No. 4 227-235 2001 Research Report 227 BONE FLUORIDE IN PROXIMAL FEMUR FRACTURES A Bohatyrewicz a Szczecin, Poland SUMMARY: Bone fluoride concentration and bone mineral density (BMD) were
Fall-related risk factors and osteoporosis in older women referred to an open access bone densitometry service
 Age and Ageing 05; 34: 67 71 Age and Ageing Vol. 34 No. 1 British Geriatrics Society 04; all rights reserved doi:10.1093/ageing/afh238 Published electronically 15 November 04 Fall-related risk factors
Age and Ageing 05; 34: 67 71 Age and Ageing Vol. 34 No. 1 British Geriatrics Society 04; all rights reserved doi:10.1093/ageing/afh238 Published electronically 15 November 04 Fall-related risk factors
Dual Mobility Cups. Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium
 Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
Dual Mobility Cups Kris Govaers, MD, PhD Dendermonde Belgium Introduction Indications Limitations Conclusions All good things in life come from France Gilles Bousquet 1979 + Rambert (SERF) Inventions Bousquet
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Totally Hip Preservation to Revision. Gothenburg, Sweden 29 March - 1 April 2017 WEDNESDAY 29 MARCH. Arrivals THURSDAY 30 MARCH
 Totally Hip 2017 Preservation to Revision Gothenburg, Sweden 29 March - 1 April 2017 WEDNESDAY 29 MARCH Arrivals THURSDAY 30 MARCH 08:00 08:30 Welcome from the Chairmen, Co Chairmen and technical intro
Totally Hip 2017 Preservation to Revision Gothenburg, Sweden 29 March - 1 April 2017 WEDNESDAY 29 MARCH Arrivals THURSDAY 30 MARCH 08:00 08:30 Welcome from the Chairmen, Co Chairmen and technical intro
The Bone Densitometry Examination
 The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
The Bone Densitometry Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologist (ARRT ) Bone Densitometry Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section
 9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
DISCLOSURE FNFX ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? 11/21/2016 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET
 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
A Proven Concept. Alloclassic Zweymüller Stem
 A Proven Concept Alloclassic Zweymüller Stem Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i. e. physicians in particular, and is expressly not for the information of laypersons.
A Proven Concept Alloclassic Zweymüller Stem Disclaimer This document is intended exclusively for experts in the field, i. e. physicians in particular, and is expressly not for the information of laypersons.
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
M-SERIES. Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME
 M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
M-SERIES Modular Femoral Stem AN ACCURATE MATCH EVERY TIME 54 Extension 114 Flexion High How do you ensure optimal post-operative joint stability? MECHANICAL RANGE OF MOTION Cup Position: 45 degrees abduction,
ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
E C H E L O N P R I M A R Y H I P S Y S T E M P R O D U C T R A T I O N A L E ADDRESSING CLINICAL ISSUES OF CEMENTLESS HIP ARTHROPLASTY Echelon Primary Total Hip System HIGH OFFSET STANDARD OFFSET Cementless
ACTIS. TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE
 ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
ACTIS TOTAL HIP SYSTEM Approach Active Patients with Confidence DESIGN RATIONALE APPROACH ACTIVE PATIENTS WITH CONFIDENCE The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes Companies of Johnson & Johnson
Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis: results of a 1-year study
 Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
Rheumatol Int (2006) 26: 427 431 DOI 10.1007/s00296-005-0004-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE J. D. Ringe Æ H. Faber Æ P. Farahmand Æ A. Dorst Efficacy of risedronate in men with primary and secondary osteoporosis:
Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
Bone Densitometry. Total 30 Maximum CE 14. DXA Scanning (10) 7
 STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
STRUCTURED SELF ASSESSMENT CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS SSA LAUNCH DATE: JANUARY 1, 2018 Bone Densitometry The purpose of continuing qualifications requirements (CQR) is to assist registered technologists in
Oral risedronate increases Gruen zone bone mineral density after primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis
 Li and Xu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0794-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Oral risedronate increases Gruen zone bone mineral density after primary total
Li and Xu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0794-1 REVIEW ARTICLE Oral risedronate increases Gruen zone bone mineral density after primary total
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication?
 CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
CASE REPORT Open Access Femoral neck fracture during physical therapy following surface replacement arthroplasty: a preventable complication? A case report Timothy R Judkins, Michael R Dayton * Abstract
Osteoporosis International. Original Article. Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures in Men
 Osteoporos Int (1999) 10:265 270 ß 1999 International Osteoporosis Foundation and National Osteoporosis Foundation Osteoporosis International Original Article Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures
Osteoporos Int (1999) 10:265 270 ß 1999 International Osteoporosis Foundation and National Osteoporosis Foundation Osteoporosis International Original Article Bone Mineral Density and Vertebral Fractures
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
R/F. Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? 1. Abstract
 R/F Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? Professor and Chair Dept. of Adult Reconstructive Surgery Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the 4th Clinical College of PKU
R/F Can T-smart Tomosynthesis Improve Diagnostic Accuracy on THA Component Stability? Professor and Chair Dept. of Adult Reconstructive Surgery Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, the 4th Clinical College of PKU
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS Bone Densitometry The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome after total knee arthroplasty.
 Reference number to be mentioned by correspondence : ORTHO/- Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 83, 00-00 ORIGINAL STUDY Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome
Reference number to be mentioned by correspondence : ORTHO/- Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 83, 00-00 ORIGINAL STUDY Vitamin D deficiency is associated with longer hospital stay and lower functional outcome
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem
 Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta
 Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Technical: Patient positioning Performance of the scan Analysis of the data Theoretical: Identification
Adina Alazraki, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor, Radiology and Pediatrics Emory University School of Medicine Technical: Patient positioning Performance of the scan Analysis of the data Theoretical: Identification
Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Standard Operating Procedure TCRC Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
 1. RELEVANCE a. This SOP outlines the instructions to completing Duel Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) including: scanning, analysis, review and filing. 2. SCOPE a. This SOP applies to all TCRC RDs. 3.
1. RELEVANCE a. This SOP outlines the instructions to completing Duel Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) including: scanning, analysis, review and filing. 2. SCOPE a. This SOP applies to all TCRC RDs. 3.
Smith & Nephew. R3 Cementless Cup
 Implant Smith & Nephew Comprising PRIMARY hips implanted up to: 09 September 2018 NJR Database extract: 08 November 2018 Produced on: Licenced for use until: 18 November 2018 18 March 2019 Contents Recorded
Implant Smith & Nephew Comprising PRIMARY hips implanted up to: 09 September 2018 NJR Database extract: 08 November 2018 Produced on: Licenced for use until: 18 November 2018 18 March 2019 Contents Recorded
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know
 Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Bone Densitometry Radiation dose: what you need to know John Damilakis, PhD Associate Professor and Chairman University of Crete, Iraklion, Crete, GREECE Estimation of bone status using X-rays Assessment
Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training.
 Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training. Mau-Moeller, A. 1,2, Behrens, M. 2, Finze, S. 1, Lindner,
Effectiveness of passive and active knee joint mobilisation following total knee arthroplasty: Continuous passive motion vs. sling exercise training. Mau-Moeller, A. 1,2, Behrens, M. 2, Finze, S. 1, Lindner,
Comparison of Bone Density of Distal Radius With Hip and Spine Using DXA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Bone Density of Distal Radius With Hip and Spine Using DXA Leila Amiri 1, Azita Kheiltash 2, Shafieh Movassaghi 1, Maryam Moghaddassi 1, and Leila Seddigh 2 1 Rheumatology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Bone Density of Distal Radius With Hip and Spine Using DXA Leila Amiri 1, Azita Kheiltash 2, Shafieh Movassaghi 1, Maryam Moghaddassi 1, and Leila Seddigh 2 1 Rheumatology
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006
 The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
The arc of pelvic motion has been shown to be as great as 70 through sit to stand activities 1 DiGioia CORR 2006 Overview Every patient moves differently 1 and their total hip replacement should be optimised
CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS
 CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
CASE REPORT CIRCUMFERENTIAL PROXIMAL FEMORAL ALLOGRAFTS IN REVISION SURGERY ON TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: CASE REPORTS WITH A MINIMUM FOLLOW-UP OF 20 YEARS Bruno Dutra Roos 1, Milton Valdomiro Roos 2, Antero
Klinische und radiologische Ergebnisse einer «isoelastischen» Pfanne
 Klinische und radiologische Ergebnisse einer «isoelastischen» Pfanne Martin Beck, Prof. Dr.med. Klinik für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie Luzerner Kantonsspital resorption of acetabular bone can be observed
Klinische und radiologische Ergebnisse einer «isoelastischen» Pfanne Martin Beck, Prof. Dr.med. Klinik für Orthopädie und Unfallchirurgie Luzerner Kantonsspital resorption of acetabular bone can be observed
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
Design Rationale. ECHELON Primary Hip System
 Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
Design Rationale ECHELON Primary Hip System ECHELON Primary Total Hip System Addressing clinical issues of cementless hip arthroplasty Cementless total hip arthroplasty has provided a proven method of
5A* ODEP. Conserving bone. Preserving soft tissue. Restoring biomechanics. rating
 MiniHip is designed to give patients the advantages of a traditional hip replacement whilst also preserving the natural anatomy. MiniHip potentially allows for future revisions and so provides a pre-primary
MiniHip is designed to give patients the advantages of a traditional hip replacement whilst also preserving the natural anatomy. MiniHip potentially allows for future revisions and so provides a pre-primary
Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 21 No. 2 2006 Painful Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Cambize Shahrdar, MD,* Pat Campbell, PhD,y Joseph Mirra, MD,y and Lawrence D. Dorr, MD* Abstract: Two patients
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS ARRT BOARD APPROVED: JANUARY 2017 IMPLEMENTATION DATE: JULY 1, 2017
 EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
EXAMINATION CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS Bone Densitometry The purpose of the bone densitometry examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive skills underlying the intelligent performance of the tasks
Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen
 Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen Christian Muschitz II. Medizinische Abteilung mit Rheumatologie, Osteologie & Gastroenterologie Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus
Diagnostische Präzision von DXL im Vergleich zu DXA bei pmp Frauen mit Frakturen Christian Muschitz II. Medizinische Abteilung mit Rheumatologie, Osteologie & Gastroenterologie Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus
Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up.
 Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up. Olsson, Christian; Petersson, Claes; Nordquist, Anders Published in:
Increased mortality after fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus: a case-control study of 253 patients with a 12-year follow-up. Olsson, Christian; Petersson, Claes; Nordquist, Anders Published in:
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Surgical Technique Approach Patients with Confidence The ACTIS Total Hip System is the first DePuy Synthes stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior
Shunsaku Nishihara 1, Nobuhiko Sugano 1, Takashi Nishii 1, Hisashi Tanaka 2, Hideki Yoshikawa 1, and Takahiro Ochi 1
 J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
J Orthop Sci (2003) 8:352 360 Comparison of the fit and fill between the Anatomic Hip femoral component and the VerSys Taper femoral component using virtual implantation on the ORTHODOC workstation Shunsaku
Changes in bone mineral density of the distal femur after revision total knee arthroplasty with metaphyseal press-fit stem
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2010) 11:143 148 DOI 10.1007/s10195-010-0098-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes in bone mineral density of the distal femur after revision total knee arthroplasty with metaphyseal press-fit
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2010) 11:143 148 DOI 10.1007/s10195-010-0098-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Changes in bone mineral density of the distal femur after revision total knee arthroplasty with metaphyseal press-fit
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
CLS Spotorno Hip Stem A Milestone in the History of Hip Replacements
 CLS Spotorno Hip Stem A Milestone in the History of Hip Replacements 2 The Original CLS Cementless Spotorno Hip Stem The Creation of CLS Marked a Milestone in the History of Hip Replacements Until the
CLS Spotorno Hip Stem A Milestone in the History of Hip Replacements 2 The Original CLS Cementless Spotorno Hip Stem The Creation of CLS Marked a Milestone in the History of Hip Replacements Until the
Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 23, 79, 667-67 ORIGINAL STUDY Effect of surgical approach on the early outcome of total hip replacement for femoral neck fractures Ahmed M. Mohamed, Daoud Makki, James Gibbs From the
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
DXA Best Practices. What is the problem? 9/29/2017. BMD Predicts Fracture Risk. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry: DXA
 BMD Predicts Fracture Risk Ten Year Fracture Probability (%) 50 40 30 20 10 Age 80 70 60 50 E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Director, New Mexico Clinical Research & Osteoporosis Center Director, Bone TeleHealth
BMD Predicts Fracture Risk Ten Year Fracture Probability (%) 50 40 30 20 10 Age 80 70 60 50 E. Michael Lewiecki, MD Director, New Mexico Clinical Research & Osteoporosis Center Director, Bone TeleHealth
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
Body Mass Index as Predictor of Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women in India
 International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.3, No.4, December 2014, pp. 276 ~ 280 ISSN: 2252-8806 276 Body Mass Index as Predictor of Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women in India
International Journal of Public Health Science (IJPHS) Vol.3, No.4, December 2014, pp. 276 ~ 280 ISSN: 2252-8806 276 Body Mass Index as Predictor of Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women in India
MINIMUM TEN-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY BASED, CUSTOM CEMENTLESS STEM AFTER INTERTROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY FOR DYSPLASTIC HIPS
 (65) MINIMUM TEN-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY BASED, CUSTOM CEMENTLESS STEM AFTER INTERTROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY FOR DYSPLASTIC HIPS YOSHIHIDE MASUDA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara Prefecture
(65) MINIMUM TEN-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY BASED, CUSTOM CEMENTLESS STEM AFTER INTERTROCHANTERIC OSTEOTOMY FOR DYSPLASTIC HIPS YOSHIHIDE MASUDA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara Prefecture
Approach Patients with Confidence
 Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Approach Patients with Confidence The is the first stem specifically designed to be utilized with tissue sparing approaches, such as the anterior approach, as well as traditional approaches. The implant
Collars on Cementless Femoral Stems Make More of a Contribution to Primary Stability When Subjected to Adverse Mechanical Environments
 Collars on Cementless Femoral Stems Make More of a Contribution to Primary Stability When Subjected to Adverse Mechanical Environments Mark Taylor, PhD 1, Scott Brumby, MD 2, David Beverland, MD 3, Clare
Collars on Cementless Femoral Stems Make More of a Contribution to Primary Stability When Subjected to Adverse Mechanical Environments Mark Taylor, PhD 1, Scott Brumby, MD 2, David Beverland, MD 3, Clare
REVISION. Zimmer Biomet All Trabecular Metal Cups vs. All non-tm cementless cups
 REVISION Bespoke Implant Report for: Zimmer Biomet vs. All non-tm cementless cups Comprising REVISION hips implanted up to: 01 August 2015 NJR Database extract: 30 September 2015 Produced on: 05 November
REVISION Bespoke Implant Report for: Zimmer Biomet vs. All non-tm cementless cups Comprising REVISION hips implanted up to: 01 August 2015 NJR Database extract: 30 September 2015 Produced on: 05 November
Restoration Modular Revision Hip System. Choice Matters
 Restoration Modular Revision Hip System Choice Matters Restoration Modular Revision Hip System The Restoration Modular Revision Hip System combines successful designs with the latest technology to answer
Restoration Modular Revision Hip System Choice Matters Restoration Modular Revision Hip System The Restoration Modular Revision Hip System combines successful designs with the latest technology to answer
Continuing the Tradition. VerSys Heritage Hip System
 Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
Continuing the Tradition VerSys Heritage Hip System Heritage Following the Tradition The low-friction hip prosthesis developed by Sir John Charnley has more than a 20-year history of outstanding results.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedures overview of minimally invasive two-incision surgery for total hip replacement Introduction This
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Recently Reviewed and Updated CAT: May 2018
 1 Short Question: Specific Question: Does standing a patient on the day of surgery following a primary unilateral total hip or knee replacement reduce the length of hospital stay? Clinical bottom line
1 Short Question: Specific Question: Does standing a patient on the day of surgery following a primary unilateral total hip or knee replacement reduce the length of hospital stay? Clinical bottom line
Are there limits for a cementless short hip stem?
 Are there limits for a cementless short hip stem? Results after 2 year follow up Dr. Sabine Mai Consulting Surgeon Vitos Orthopädische Klinik Kassel Germany Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus der Universität
Are there limits for a cementless short hip stem? Results after 2 year follow up Dr. Sabine Mai Consulting Surgeon Vitos Orthopädische Klinik Kassel Germany Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus der Universität
