Use of a Caged, Bone Ingrowth, Glenoid Implant in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
|
|
|
- Sibyl Elisabeth Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S41 Use of a Caged, Bone Ingrowth, Glenoid Implant in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Technique and Early Results Sean G. Grey, M.D. Abstract Shoulder arthroplasty represents one of the fastest growing orthopaedic procedures in the USA. In comparison to hemiarthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty has higher patient satisfaction and lower revision rates. Aseptic glenoid loosening remains a concern for longevity of total shoulder arthroplasties. Cement fixation on the glenoid side represents the primary and only mode of fixation in the majority of implants in the USA. Metal backed glenoid designs have demonstrated higher failure rates, primarily due to thinning of the polyethylene bearing surface. We reviewed our early experience and results with a novel glenoid design. Long-term fixation in this design is provided by a central metallic bone ingrowth cage, without the need for metal backing. Improved techniques along with an aging patient population have led to a significant increase in the number of total shoulder arthroplasties being performed in the USA. 1 When compared to hemiarthroplasty, total shoulder arthroplasty results in better range of motion, pain relief, and patient satisfaction. 2 While the overall success rate for total shoulder arthroplasty has been quite satisfactory, glenoidsided loosening remains the most common complication. 3 Radiographic evidence of lucent lines has been reported to range from 22% to 95% in various types of glenoid implants. 3-9 While radiolucent lines are common, clinical failures, defined as revision surgeries, are much less common in studies evaluating intermediate term follow-up. 10 Although a variety of glenoid designs exist in the USA at this time, the all-polyethylene cemented peg glenoid design Sean G. Grey, M.D., is at the Orthopaedic Center of the Rockies, Fort Collins, Colorado. Correspondence: Sean G. Grey, M.D., Orthopaedic Center of the Rockies, 2500 East Prospect Road, Fort Collins, Colorado 80525; sgrey1@msn.com. remains the gold standard. 4,6-8,10 In these pegged all-polyethylene glenoid components, radiolucent lines are common, and aseptic glenoid loosening has remained a concern for the long-term survival of the implant. This has led to interest in a variety of metal-backed and bone in-growth devices, 6,10,12-14 with the primary goal being to move to either noncemented or limitedly cemented implants with the hope of decreasing the likelihood of aseptic glenoid loosening. A number of metal-backed noncemented designs have been or are currently available in the USA and Europe. In comparison to cemented all-polyethylene glenoids, previous metal-backed designs have shown higher failure rates. Failure of previous metal-backed designs has been primarily related to three mechanisms 6,10,12-14 : 1. Metal backing requires a relatively thin layer of polyethylene in order to avoid overstuffing of the joint. The decreased polyethylene thickness in combination with increased contact pressures lead to higher polyethylene wear rates, osteolysis, and loosening A number of metal-backed designs have no bone ingrowth surface. Initial fixation was usually obtained with screws. Lack of in-growth led to eventual loosening or fatigue failure of the screws under repetitive loading Trabecular metal (highly porous metal foam) designs, in which the trabecular substrate is molded to the polyethylene, have shown excellent bone in-growth but have had problems with dissociation of the trabecular metal from the polyethylene. 11 This has been accompanied by higher early revisions for aseptic loosening. Lack of peripheral pegs to control rotational forces between the trabecular metal and polyethylene may be a contributing factor. 11 Limited cemented, all-polyethylene designs have shown some promise In this design, early fixation is obtained with a combination of peripheral peg cementation combined Grey SG. Use of a caged, bone ingrowth, glenoid implant in anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty: technique and early results. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(Suppl 2):S41-5.
2 S42 Figure 1 Equinoxe cage glenoid (Exactech, Inc.; Gainesville, FL). with the interference fit of the central peg. Long-term fixation is supplemented with bone in-growth around the flanges of the all-polyethylene central peg. Studies have shown successful bone in-growth around the flanges of the central peg. 17 Some studies, however, have shown radiolucencies around the central peg, and there is concern that the flanges may not represent the best long-term bone in-growth surface. 18 The genesis of the current cage glenoid design developed from the success of the Equinoxe (Exactech, Inc., Gainesville, Florida) reverse shoulder arthroplasty s baseplate, which utilizes a central peg. With its release in March 2007, the glenoid baseplate showed minimal aseptic loosening on early and intermediate follow-up. In addition, early retrieval studies have shown excellent bone in-growth in as little as 6 months. Additional intraoperative observation demonstrated stable fixation of the baseplate with interference fit of the central peg alone, prior to screw placement in most bone densities. These concepts were incorporated into a cemented nonmetal-backed glenoid implant with an interference-fit plasma coated cage peg and titanium peripheral pegs (Fig 1). The potential advantages of this implant are as follows: 1. This novel glenoid design provides the possibility of bone in-growth without any metal backing. 2. By maintaining a monolithic 4 mm thick polyethylene bearing surface without a metal backing, concerns of polyethylene failure due to insufficient thickness, backside wear, and joint overstuffing are all mitigated. 3. Initial intraoperative fixation is obtained with interference fit of the oversized cage peg in the central hole, eliminating the need for stabilizing the implant until the cement sets. Not only does this decrease operative time, but the secure immediate fixation prevents the micromotion that is often seen when stabilizing the implant manually during cement curing. Early short-term fixation is obtained by a combination of central peg interference fit and peripheral peg cementation. The addition of the peripheral pegs allows for better control of rotational forces. Long-term fixation is achieved with a combination of peripheral peg cementation and bone in-growth through the central cage. When compared to an all-polyethylene center peg with flanges, the central titanium cage is considered a superior bone in-growth surface. Gritblasted peripheral pegs may allow for fully uncemented technique in the future; however, at the time of this writing, the device is only cleared by the Food and Drug Administration for cemented use. The glenoid bone preparation is identical for the cage design and the all-polyethylene peg design, and this allows the surgeon to choose between either implant, based upon bone quality or other factors, prior to opening the component to be implanted. Finally, even in the face of adequate bone in-growth, the system is designed to be revision friendly. The central cage and peg can be removed with little damage or loss to underlying glenoid bone. Technique The overall surgical technique for the cage glenoid varies little from the standard anatomical total shoulder arthroplasty technique. The primary distinction of the cage glenoid technique is that it requires straight line glenoid insertion. Unlike a standard all-polyethylene implant, in which the prosthesis can be rolled into the glenoid, the cage implant must be inserted directly perpendicular to the face of the glenoid from the time the central cage peg engages the drilled glenoid bone holes until it is fully seated. This straight line insertion requires better surgical glenoid exposure, and caution should be carried out in patients with difficult exposure or significant glenoid deformity. Exposure is obtained through a standard deltopectoral approach. Care should be taken to release an appropriate amount of pectoralis major tendon to allow for relaxation and posterior translation of the humerus during glenoid preparation. Humeral capsular releases should be performed past the six o clock position and distally on the neck to the superior border of the latissimus dorsi tendon. I prefer a slight increase in humeral head retroversion (cutting into the bare area). This is generally well tolerated on the humeral side with use of the replicator plate. In addition, the removal of an additional 5 mm to 7 mm of posterior humeral bone results in significantly better glenoid exposure. After preparation of the humerus, attention is turned to glenoid exposure. Capsular releases should be performed circumferentially on the glenoid. Labrum and all soft tissue debris should be removed from the glenoid face (Fig. 2). As mentioned previously, glenoid preparation is identical for the all-polyethylene peg system and the cage design. Two orthogonal lines are drawn, dividing the anterior-posterior and superior-inferior halves of the glenoid face (Fig. 3). The proper position of the central peg hole is consistently just anterior to the intersection of these two lines. The position is confirmed with the glenoid drill guide. The central hole can be drilled either through the guide or in a freehand method. Sequential reaming is carried out to the appropriate size.
3 S43 Figure 2 Removal of surrounding soft tissue. Figure 3 Identification of the center of the glenoid. Figure 4 Drill Preparation of the peg holes in the glenoid. Figure 5 Drilled central and peripheral peg holes. Figure 6 Straight-line impaction of the cage glenoid. Figure 7 Fully seated cage glenoid. Care is taken to remove minimal subchondral bone. The peripheral peg drill guide is placed in the central hole, and the peripheral three peg holes are drilled (Figs. 4 and 5). Attention is then turned toward trialing. The option of either an all-polyethylene component or cage glenoid component still exists. After identifying the appropriate sized trial glenoid, the trial and the glenoid insertion tool are used. If straight line insertion is possible and bone density is adequate, a cage glenoid component is selected; however, if straight line insertion is not possible, either further releases are performed, or the all-polyethylene pegged implant is selected. A depth gauge is available to ascertain if the drilled holes are of sufficient depth to permit for full insertion of the pegs. The central hole may require repeat drilling, especially if additional reaming was performed. The glenoid is cemented in place by placing cement in the peripheral holes. The peripheral holes are irrigated free of blood and debris. A provisional peg is placed in the central drilled hole to prevent cement from entering. In a doughy state, cement is pressurized into the peripheral holes using the instruments. The cage glenoid is then impacted until seated with one of a variety of supplied insertion tools. Straight line insertion is paramount, as off-line insertion may lead to damage to the locking mechanism that fixes the
4 S44 metal pegs to the polyethylene articular body (Fig. 6). Care should be taken to assess full seating of the entire glenoid (Fig. 7). Attention can then be turned to completion of the arthroplasty, as the central cage peg will prevent micromotion as the cement cures in the peripheral holes. Results At the time of this writing, the investigator has performed 127 total shoulder arthroplasties with the cage glenoid technique since December It has become the preferred implant for anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty in patients without significant bone deformity. In the presence of large glenoid deformity (greater than 12 of posterior erosion), typically we use a posterior augmented glenoid design. In the majority of osteoarthritis patients, bone quality has not been an issue for central peg fixation. We remain more cautious in patients with inflammatory and crystalline arthropathies; however, many of these patients also have adequate bone density for cage glenoid placement. At the time of this writing, we have not undertaken a formal review of the patients. This will be done when greater than 2-years follow-up is available. However, at this point we have made the following observations: 1. Operative time has been significantly reduced relative to total shoulder arthroplasty cases using an allpolyethylene cemented glenoid, as 5 to 13 minutes are eliminated by removing the need to hold the implant while the cement sets. 2. Given that all four pegs have a metallic component, postoperative radiographs allow for more critical review of multi-planar glenoid position. We feel this has improved our overall glenoid placement, as recent studies have suggested that small changes in glenoid position have implications on long-term survival of the implant. Short-term clinical results in terms of range of motion, function, and pain relief do not appear to vary significantly from our anatomic total shoulder arthroplasties using allpolyethylene glenoids. A short-term review of our 6 and 12 month x-rays have shown good position of the implants, signs of early bone in-growth, and no obvious signs of progressive lucency in all but three patients (discussed below). We have not altered our postoperative care or changed our short- and long-term activity restrictions based on the bone in-growth implant. We have observed radiographic evidence of loosening in three patients, two of which required revision. The first patient had the initial design of the implant (no longer available) in which the central cage had a thicker plasma coating and was more oversized in relationship to the drilled center peg hole in the glenoid. This thicker peg resulted in greater interference and more difficult insertion/impaction into dense bone. Complete seating may have been the issue with this patient. This resulted in damage to the mechanism connecting the polyethylene to the central peg, which was identified on the first postoperative x-ray. The patient subsequently developed pain and went on to have a revision approximately 10 months after the index procedure. She was converted to an all-polyethylene pegged implant with good results. The implant has since been modified. Decreasing the thickness of the plasma spray coating on the cage peg has improved the ease of insertion into dense bone. With this thinner coating, we have found that the vast majority of patients get excellent initial interference fixation with the bone cage into the central hole on the glenoid. A second patient developed postoperative subscapularis insufficiency. Loosening of the central peg locking mechanism was observed between 3 and 6 months postoperatively. She was revised to a reverse shoulder arthroplasty without complication. In both of the above patients, at the time of revision surgery, the central peg was found to have excellent bone in-growth. Despite this in-growth, the revision was uncomplicated, and the cage could be removed with minimal glenoid bone loss. In each revision, the polyethylene articular surface was separated from the underlying cage with an osteotome. When the cage was noted to be well fixed, a 3.2 mm drill bit was used to remove bone from the central cage. A slap hammer extraction device was then threaded into the central cage, and with slight rotational force, the implant was removed without difficulty. Summary Early experience with a novel cage glenoid implant design appears to hold promise for a minimally cemented, bone in-growth implant, with a potential to decrease long-term aseptic glenoid loosening. Longer term follow-up is necessary to confirm these promising early results. Disclosure Statement Sean G. Grey, M.D., is a consultant for Exactech, Inc., Gainesville, Florida, and receives royalties on products related to this article. References 1. Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, et al. Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthropasty in the United States to J Shoulder Elbow Surg Dec;19(8): doi: /j.jse Epub 2010 Jun Radnay CS, Setter KJ, Chambers L, et al. Total shoulder replacement compared with humeral head replacement for the treatment of primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis. a systemic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg JulAug;16(4): Castagna A, Randelli M, Garofalo R, et al. Mid-term results of a metal-glenoid component in total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br Oct;92(10): doi: / X.92B Norris BL, Lachiewicz PF. Modern cement technique and the survivorship of a total shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res Jul;(328): Bohsali KI, Wirth MA, Rockwood CA Jr. Complications
5 S45 of total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am Oct;88(10): Boileu P, Avidor C, Krishnan SC, et al. Cemented polyethelene versus uncemented metal-backed glenoid components in total shoulder arthroplasty: a prospective double-blind, randomized study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Jul-Aug;11(4): Boyd AD Jr, Thomas WH, Scott RD, et al. Total shoulder arthroplasty versus hemiarthroplasty. Indications for glenoid resurfacing. J Arthroplasty Dec;5(4): Brenner BC, Ferlic DC, Clayton ML, Dennis DA. Survivorship of unconstrained total shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am Oct;71(9): Cofield RH. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am Jul;66(6) Fox TJ, Cil A, Sperling JW, et al. Survival of the glenoid component in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Nov-Dec;18(6): doi: /j.jse Epub 2009 Mar Budge MD, Kurdziel MD, Baker KC, Wiater JM. A biomechanical analysis of initial fixation options for poroustantalum-backed glenoid components. J Shoulder Elbow Surg May;22(5): doi: /j.jse Epub 2012 Sep Fucentese SF, Costouros JG, Kühnel SP, Gerber C. Total shoulder arthroplasty with an uncemented soft-metal-backed-glenoid component. J Shoulder and Elbow Surg Jun;19(4): doi: /j.jse Epub 2010 Apr Tammachote N, Sperling JW, Vathana T, et al. Long term results of cemented metal-backed glenoid components for osteoarthritis of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am Jan;91(1): doi: /JBJS.F Wallace Al, Phillips RL, MacDougal GA, et al. Resurfacing of the glenoid in total shoulder arthroplasty: a comparison, at a mean of five years, of prostheses inserted with and without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am Apr;81(4): Groh GI. Survival and radiographic analysis of a glenoid component with a cementless fluted central peg. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Dec;19(8): doi: /j.jse Epub 2010 Jun Churchill RS, Zellmer C, Zimmers HJ, Ruggero R. Clinical and radiographic analysis of a partially cemented glenoid implant:five year minimum follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Oct;19(7): doi: /j.jse Epub 2010 Apr De Wilde L, Dayerizadeh N, De Neve F, et al. Fully uncemented glenoid component in total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Apr 22. pii: S (13) doi: /j.jse [Epub ahead of print] 18. Vidil A, Valenti P, Guichoux F, Barthas JH. Ct scan evaluation of the glenoid component fixation: a prospective study of 27 minimally cemented shoulder arthroplasties. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol Jul;23(5): doi: /s Epub 2012 Nov 9.
Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 S5 Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Sean G. Grey, M.D., and Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D. Abstract
S5 Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Sean G. Grey, M.D., and Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D. Abstract
Case Report Acute Failure of a Glenoid Component in Anatomic Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 6208294, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6208294 Case Report Acute Failure of a Glenoid Component in Anatomic Shoulder Arthroplasty William E.
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 6208294, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6208294 Case Report Acute Failure of a Glenoid Component in Anatomic Shoulder Arthroplasty William E.
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANCHOR PEG GLENOID DESIGN RATIONALE In total shoulder arthroplasty, most cases of clinical and radiographic loosening involve failure of the fixation of the glenoid
DESIGN RATIONALE AND SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANCHOR PEG GLENOID DESIGN RATIONALE In total shoulder arthroplasty, most cases of clinical and radiographic loosening involve failure of the fixation of the glenoid
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Addressing Glenoid Erosion in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 S46 Addressing Glenoid Erosion in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Richard B. Jones, M.D. Abstract Glenoid wear is common in the setting of shoulder arthritis. Severe glenoid erosion presents a serious
S46 Addressing Glenoid Erosion in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Richard B. Jones, M.D. Abstract Glenoid wear is common in the setting of shoulder arthritis. Severe glenoid erosion presents a serious
SSSR. 1. Nov Shoulder Prosthesis. Postoperative Imaging. Florian M. Buck, MD
 Shoulder Prosthesis Postoperative Imaging Florian M. Buck, MD Shoulder Prosthesis Surgical Approach Findings Imaging Modalities Postoperative Problems Shoulder Prosthesis What are we talking about Anatomical
Shoulder Prosthesis Postoperative Imaging Florian M. Buck, MD Shoulder Prosthesis Surgical Approach Findings Imaging Modalities Postoperative Problems Shoulder Prosthesis What are we talking about Anatomical
Shoulder Arthroplasty. Valentin Lance 3/24/16
 Shoulder Arthroplasty Valentin Lance 3/24/16 Outline Background Pre-operative imaging assessment Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Standard and Reverse Complications Other shoulder hardware Hemiarthroplasty
Shoulder Arthroplasty Valentin Lance 3/24/16 Outline Background Pre-operative imaging assessment Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Standard and Reverse Complications Other shoulder hardware Hemiarthroplasty
what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you
 TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement. «Shoulder Course» Day 1. Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern. 11. Sept.
 Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern First total shoulder prosthesis Jules Emile Péan, 1830-1898 Monobloc prostheses Charles Neer, 1917-2011
Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern First total shoulder prosthesis Jules Emile Péan, 1830-1898 Monobloc prostheses Charles Neer, 1917-2011
Fixed and Variable Geometry Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Fixed and Variable Geometry Total Shoulder Arthroplasty RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total shoulder replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and
Fixed and Variable Geometry Total Shoulder Arthroplasty RECOVERY FUNCTION SURVIVORSHIP DePuy believes in an approach to total shoulder replacement that places equal importance on recovery, function and
Managing Glenoid Bone Deficiency The Augment Experience in Anatomic and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Managing Glenoid Bone Deficiency The Augment Experience in Anatomic and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Publish date: March 5, 2018 Authors: Rowan J. Michael, MD Bradley S. Schoch, MD Joseph J. King, MD
Managing Glenoid Bone Deficiency The Augment Experience in Anatomic and Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Publish date: March 5, 2018 Authors: Rowan J. Michael, MD Bradley S. Schoch, MD Joseph J. King, MD
Surface Replacement for the Active Patient with GH DJD. Disclosures. Popularized by Copeland 3/1/2018
 Surface Replacement for the Active Patient with GH DJD E. Rhett Hobgood, M.D. MS Sports Medicine Jackson, MS Disclosures Consultant for Exactech No royalties from any company Fellowship support from Mitek,
Surface Replacement for the Active Patient with GH DJD E. Rhett Hobgood, M.D. MS Sports Medicine Jackson, MS Disclosures Consultant for Exactech No royalties from any company Fellowship support from Mitek,
Revision of the Loose Glenoid Component in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 S68 Revision of the Loose Glenoid Component in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., and Joseph
S68 Revision of the Loose Glenoid Component in Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., and Joseph
Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Augmented Baseplate
 Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Augmented Baseplate Surgical Technique Addendum FPO 1 Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Augmented Baseplate Surgical Technique Addendum Adaptive Building on the
Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Augmented Baseplate Surgical Technique Addendum FPO 1 Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Augmented Baseplate Surgical Technique Addendum Adaptive Building on the
A novel cementless option. Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Primary Patella Surgical Technique
 A novel cementless option Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Primary Patella Surgical Technique Zimmer Trabecular Metal Primary Patella 1 Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Primary Patella Surgical Technique
A novel cementless option Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Primary Patella Surgical Technique Zimmer Trabecular Metal Primary Patella 1 Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Primary Patella Surgical Technique
Disclosure. General. Total Shoulder Arthroplasty : Results, Outcomes and Expectations 2/8/2016. Consultant for Tornier/Wright, DJO, and Conventus
 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty : Results, Outcomes and Expectations Edwin E Spencer Jr MD Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic Disclosure Consultant for Tornier/Wright, DJO, and Conventus General The literature is
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty : Results, Outcomes and Expectations Edwin E Spencer Jr MD Knoxville Orthopaedic Clinic Disclosure Consultant for Tornier/Wright, DJO, and Conventus General The literature is
Posterior Glenoid Wear in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty:
 Posterior Glenoid Wear in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Eccentric Anterior Reaming is Superior to Posterior Augment Tim Wang MD, Geoffrey Abrams MD, Anthony Behn MS, Emilie Cheung MD Department of Orthopaedic
Posterior Glenoid Wear in Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Eccentric Anterior Reaming is Superior to Posterior Augment Tim Wang MD, Geoffrey Abrams MD, Anthony Behn MS, Emilie Cheung MD Department of Orthopaedic
Revision of the humeral component for aseptic loosening in arthroplasty of the shoulder
 Revision of the humeral component for aseptic loosening in arthroplasty of the shoulder A. Cil, C. J. H. Veillette, J. Sanchez-Sotelo, J. W. Sperling, C. Schleck, R. H. Cofield From the Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Revision of the humeral component for aseptic loosening in arthroplasty of the shoulder A. Cil, C. J. H. Veillette, J. Sanchez-Sotelo, J. W. Sperling, C. Schleck, R. H. Cofield From the Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Technical Tip for Prosthesis of Antibiotic-Loaded Acrylic Cement (PROSTALAC) Use for Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Technical Tip for Prosthesis of Antibiotic-Loaded Acrylic Cement (PROSTALAC) Use for Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty ABSTRACT BACKGROUND Shoulder arthroplasty procedures have
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES Technical Tip for Prosthesis of Antibiotic-Loaded Acrylic Cement (PROSTALAC) Use for Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty ABSTRACT BACKGROUND Shoulder arthroplasty procedures have
Trabecular Metal Primary Patella
 Trabecular Metal Primary Patella NexGen Complete Knee Solution Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Prepare the Patella... 2 Patella Reamer Technique... 3 Insetting Technique... 5 Universal
Trabecular Metal Primary Patella NexGen Complete Knee Solution Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Prepare the Patella... 2 Patella Reamer Technique... 3 Insetting Technique... 5 Universal
Both anatomic (atsa) and reverse (rtsa) total
 S101 Comparison of Outcomes Using Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Yann Marczuk, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., Joseph Zuckerman, M.D., and
S101 Comparison of Outcomes Using Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Yann Marczuk, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., Joseph Zuckerman, M.D., and
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Making sense of all our measures-inclination, version, subluxation, reaming depth & implant seating
 Thursday - ANATOMIC SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY 7:00-7:15a Welcome and Introduction of Faculty Athwal, Keener, 7:15-7:22a The ABC s of the Walch Classification Walch 7:22-7:32a How I use x-rays, CT +/- MRI for
Thursday - ANATOMIC SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY 7:00-7:15a Welcome and Introduction of Faculty Athwal, Keener, 7:15-7:22a The ABC s of the Walch Classification Walch 7:22-7:32a How I use x-rays, CT +/- MRI for
ANATOMIC TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT:
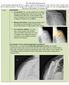 The Shoulder Replacement A total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is a surgery to replace the damaged parts of the ball and socket shoulder joint with an artificial prosthesis. The damage to the shoulder can
The Shoulder Replacement A total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is a surgery to replace the damaged parts of the ball and socket shoulder joint with an artificial prosthesis. The damage to the shoulder can
PRIMARY POROUS PATELLA WITH TRABECULAR METAL. Surgical Technique
 PRIMARY POROUS PATELLA WITH TRABECULAR METAL Surgical Technique 1 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FOR NEXGEN PRIMARY POROUS PATELLA * WITH TRABECULAR METAL CONTENTS PREPARE THE PATELLA............... 2 Patella Reamer
PRIMARY POROUS PATELLA WITH TRABECULAR METAL Surgical Technique 1 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FOR NEXGEN PRIMARY POROUS PATELLA * WITH TRABECULAR METAL CONTENTS PREPARE THE PATELLA............... 2 Patella Reamer
S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r T i b l e S h o u l d e r S y S T e m
 S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m A n a t o m i c Aequalis Ascend Flex - UDZF131 One System. Two Solutions.
S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m A n a t o m i c Aequalis Ascend Flex - UDZF131 One System. Two Solutions.
Shoulder Replacement Commonly Asked Questions
 Shoulder Replacement Commonly Asked Questions Patrick J Denard, MD Shoulder Specialist 2780 E. Barnett Rd Medford, OR 97530 541-779-6250 Background Information What is the anatomy of the shoulder? The
Shoulder Replacement Commonly Asked Questions Patrick J Denard, MD Shoulder Specialist 2780 E. Barnett Rd Medford, OR 97530 541-779-6250 Background Information What is the anatomy of the shoulder? The
Comparison of conforming and nonconforming retrieved glenoid components
 Comparison of conforming and nonconforming retrieved glenoid components Shane J. Nho, MD, MS, a Owen L. Ala, c Christopher C. Dodson, MD, a Mark P. Figgie, MD, b Timothy M. Wright, PhD, c Edward V. Craig,
Comparison of conforming and nonconforming retrieved glenoid components Shane J. Nho, MD, MS, a Owen L. Ala, c Christopher C. Dodson, MD, a Mark P. Figgie, MD, b Timothy M. Wright, PhD, c Edward V. Craig,
Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
Surgical. Technique. AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid. Shoulder Prosthesis.
 Surgical Technique Shoulder Prosthesis AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid www.tornier.com CONTENTS CONTENTS 1. Subscapularis 2. Anterior capsule 3. Humeral protector 4. Inserting retractors 1. DESIGN FEATURES
Surgical Technique Shoulder Prosthesis AEQUALIS Spherical Base Glenoid www.tornier.com CONTENTS CONTENTS 1. Subscapularis 2. Anterior capsule 3. Humeral protector 4. Inserting retractors 1. DESIGN FEATURES
Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design
 S37 Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Phong Diep,
S37 Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Phong Diep,
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
Aequalis -Glenoid. Keeled and Pegged. Surgical Technique
 Aequalis -Glenoid Keeled and Pegged Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS COMMON OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR THE KEELED AND PEGGED AEQUALIS-GLENOIDS p. 1-3 IMPLANTATION OF THE AEQUALIS KEELED GLENOID p. 4-5
Aequalis -Glenoid Keeled and Pegged Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS COMMON OPERATIVE TECHNIQUES FOR THE KEELED AND PEGGED AEQUALIS-GLENOIDS p. 1-3 IMPLANTATION OF THE AEQUALIS KEELED GLENOID p. 4-5
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
1Acetabular Reaming. 2Shell Sizing and Positioning. Trial Range of Motion. Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System
 Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
Trabecular Metal Natural Cup System 1Acetabular Reaming Use progressively larger reamers to prepare the acetabulum. Hold the reamer steady in the same position in which the cup will be implanted (approximately
The rate of total shoulder arthroplasty. Glenoid Bone Loss in Primary Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Evaluation and Management. Review Article.
 Review Article Glenoid Bone Loss in Primary Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Evaluation and Management Benjamin W. Sears, MD Peter S. Johnston, MD Matthew L. Ramsey, MD Gerald R. Williams, MD Abstract Glenohumeral
Review Article Glenoid Bone Loss in Primary Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Evaluation and Management Benjamin W. Sears, MD Peter S. Johnston, MD Matthew L. Ramsey, MD Gerald R. Williams, MD Abstract Glenohumeral
Results of a new stemless shoulder prosthesis: Radiologic proof of maintained fixation and stability after a minimum of three years follow-up
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2010) 19, 847-852 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Results of a new stemless shoulder prosthesis: Radiologic proof of maintained fixation and stability after a minimum of three years
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2010) 19, 847-852 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Results of a new stemless shoulder prosthesis: Radiologic proof of maintained fixation and stability after a minimum of three years
AEQUALIS PERFORM + Shoulder System
 TORNIER AEQUALIS PERFORM + Shoulder System THE ANATOMIC AUGMENTED GLENOID Decades of Dedication Since the late 1990 s, the Wright Upper Extremities team has partnered with surgeons who have dedicated themselves
TORNIER AEQUALIS PERFORM + Shoulder System THE ANATOMIC AUGMENTED GLENOID Decades of Dedication Since the late 1990 s, the Wright Upper Extremities team has partnered with surgeons who have dedicated themselves
Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Buttress and Shim Augments Surgical Technique
 Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Buttress and Shim Augments Surgical Technique Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Buttress and Shim Augments 1 Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision
Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Buttress and Shim Augments Surgical Technique Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision System Buttress and Shim Augments 1 Trabecular Metal Acetabular Revision
GLENOID SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 UP. EXTREMITY Dual-Platform Shoulder Prosthesis GLENOID SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANATOMICAL REVERSE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE REFERENCE NUMBERS HUMERAL STEM REFERENCE DIAMETER HEIGHT 267 360 Ø 06 100 265 102 Ø 08 120
UP. EXTREMITY Dual-Platform Shoulder Prosthesis GLENOID SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ANATOMICAL REVERSE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE REFERENCE NUMBERS HUMERAL STEM REFERENCE DIAMETER HEIGHT 267 360 Ø 06 100 265 102 Ø 08 120
D Degenerative joint disease, rotator cuff deficiency with, 149 Deltopectoral approach component removal with, 128
 Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DUAL-PLATFORM SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY.
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DUAL-PLATFORM SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY www.fhortho.com SURGICAL TECHNIQUE REFERENCE NUMBERS HUMERAL STEMS REFERENCE DIAMETER HEIGHT 267 360 Ø 06 100 265 102 Ø 08 120 265 103 Ø 08 170 265
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DUAL-PLATFORM SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY www.fhortho.com SURGICAL TECHNIQUE REFERENCE NUMBERS HUMERAL STEMS REFERENCE DIAMETER HEIGHT 267 360 Ø 06 100 265 102 Ø 08 120 265 103 Ø 08 170 265
Early To Medium Term Results of the Anatomical Total Shoulder Replacement
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 13 Number 2 Early To Medium Term Results of the Anatomical Total Shoulder Replacement R Sloan, J Young, N Parker, I Nwachukwu Citation R Sloan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 13 Number 2 Early To Medium Term Results of the Anatomical Total Shoulder Replacement R Sloan, J Young, N Parker, I Nwachukwu Citation R Sloan,
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
Convertibilité. Ph. Valenti. Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France)
 Convertibilité Ph. Valenti Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties Arthroscopy Consultant : Zimmer Biomet Arthrex In Last
Convertibilité Ph. Valenti Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties Arthroscopy Consultant : Zimmer Biomet Arthrex In Last
Triathlon Tritanium Knee System
 Triathlon Tritanium Knee System Table of Contents Cementless TKA... 4 Why Cementless TKA?... 4 Cementless TKA - Clinical History... 4 Published RSA Results Comparing Fixation Methods... 5 Biologic Fixation...
Triathlon Tritanium Knee System Table of Contents Cementless TKA... 4 Why Cementless TKA?... 4 Cementless TKA - Clinical History... 4 Published RSA Results Comparing Fixation Methods... 5 Biologic Fixation...
Name of Policy: Shoulder Resurfacing
 Name of Policy: Shoulder Resurfacing Policy #: 366 Latest Review Date: November 2010 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Active policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and update. Background/Definitions:
Name of Policy: Shoulder Resurfacing Policy #: 366 Latest Review Date: November 2010 Category: Surgery Policy Grade: Active policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and update. Background/Definitions:
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Glenoid
 Zimmer Trabecular Metal Glenoid Surgical Technique Interference fit for secure initial fixation Trabecular Metal Glenoid Surgical Technique 1 Table of Contents Glenoid Preparation 2 Determining the Size
Zimmer Trabecular Metal Glenoid Surgical Technique Interference fit for secure initial fixation Trabecular Metal Glenoid Surgical Technique 1 Table of Contents Glenoid Preparation 2 Determining the Size
Locking Radial Head Plates
 Locking Radial Head Plates Locking Radial Head Plates Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy
Locking Radial Head Plates Locking Radial Head Plates Since 1988, Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopaedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients. Our strategy
Outcomes of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with B2 Glenoids
 of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with B2 Glenoids A Systematic Review Colten Luedke, DO Michael J. Kissenberth, MD Stefan J. Tolan, MD Richard J. Hawkins, MD John M. Tokish, MD Investigation performed
of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with B2 Glenoids A Systematic Review Colten Luedke, DO Michael J. Kissenberth, MD Stefan J. Tolan, MD Richard J. Hawkins, MD John M. Tokish, MD Investigation performed
Shoulder DJD in Athletic patient. What is Athletic? McCarty University of Colorado Fall Sports Medicine Symposium. Oct. 3, 2008
 Indications for Shoulder Arthroplasty in Athletic Patients Eric C. McCarty, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Head Team Physician, University of
Indications for Shoulder Arthroplasty in Athletic Patients Eric C. McCarty, M.D. Associate Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedics Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Head Team Physician, University of
Integra. Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5
 Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments (PSI) for Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments (PSI) for Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Ryan Krupp, M.D. Norton Orthopaedic Specialists Louisville, KY Anand Murthi, M.D. MedStar Union Memorial Hospital Baltimore,
Zimmer Patient Specific Instruments (PSI) for Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Ryan Krupp, M.D. Norton Orthopaedic Specialists Louisville, KY Anand Murthi, M.D. MedStar Union Memorial Hospital Baltimore,
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
The Bio-Modular Choice Shoulder System,
 Surgical Technique The Bio-Modular Choice Shoulder System, designed for both total and hemiarthroplasty of the shoulder, has enjoyed nearly two decades of clinical success. The variety of head types and
Surgical Technique The Bio-Modular Choice Shoulder System, designed for both total and hemiarthroplasty of the shoulder, has enjoyed nearly two decades of clinical success. The variety of head types and
Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study.
 Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study. Byron F. Stephens, MD 1, Casey T. Hebert 2, Thomas W. Throckmorton, MD 1,
Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study. Byron F. Stephens, MD 1, Casey T. Hebert 2, Thomas W. Throckmorton, MD 1,
Stability of two versus three peripheral pegs of the glenoid component in modern total shoulder arthroplasty
 International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2017) 41:2345 2351 DOI 10.1007/s00264-017-3599-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stability of two versus three peripheral pegs of the glenoid component in modern total shoulder arthroplasty
International Orthopaedics (SICOT) (2017) 41:2345 2351 DOI 10.1007/s00264-017-3599-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stability of two versus three peripheral pegs of the glenoid component in modern total shoulder arthroplasty
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques
 Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
Conventus CAGE PH Surgical Techniques Conventus Orthopaedics The Conventus CAGE PH (PH Cage) is a permanent implant comprised of an expandable scaffold, made from nitinol and titanium, which is deployed
The glenoid in shoulder arthroplasty
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) 18, 819-833 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse The glenoid in shoulder arthroplasty Eric J. Strauss, MD a, Chris Roche, MS b, Pierre-Henri Flurin, MD c, Thomas Wright, MD d, Joseph
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) 18, 819-833 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse The glenoid in shoulder arthroplasty Eric J. Strauss, MD a, Chris Roche, MS b, Pierre-Henri Flurin, MD c, Thomas Wright, MD d, Joseph
Management of Glenoid and Humeral Bone Loss in Shoulder Instability
 Short Stem and Long Stem Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor, Orthopaedics Today Short Stem
Short Stem and Long Stem Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox and Bulls Chief Medical Editor, Orthopaedics Today Short Stem
Balgrist Shoulder Course 2017
 My approach to failed hemiprosthesis Ernst Wiedemann OCM Clinic Munich Consultant to Arthrex Royalties from Arthrex Consultant to Zimmer Disclosures Pathways Hemi-prosthesis Anatomical prosthesis (HSA
My approach to failed hemiprosthesis Ernst Wiedemann OCM Clinic Munich Consultant to Arthrex Royalties from Arthrex Consultant to Zimmer Disclosures Pathways Hemi-prosthesis Anatomical prosthesis (HSA
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CONTENTS Design Rationale GLOBAL APG+ Instrument Design Rationale...2 Features and Benefits of Instruments...3
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. PRODUCT RATIONALE & SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CONTENTS Design Rationale GLOBAL APG+ Instrument Design Rationale...2 Features and Benefits of Instruments...3
Conflicts of Interest Consulting (C), Royalty (R)
 Principles of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflicts of Interest Consulting
Principles of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflicts of Interest Consulting
System. Humeral Nail. Surgical Technique
 System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
Reverse Shoulder Glenoid Loosening
 S12 Reverse Shoulder Glenoid Loosening An Evaluation of the Initial Fixation Associated with Six Different Reverse Shoulder Designs Nick Stroud, M.S., Matthew J. DiPaola, M.D., Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D.,
S12 Reverse Shoulder Glenoid Loosening An Evaluation of the Initial Fixation Associated with Six Different Reverse Shoulder Designs Nick Stroud, M.S., Matthew J. DiPaola, M.D., Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D.,
Encina Taper Stem. Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA
 Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
Stinson Orthopedics Inc. 303 Twin Dolphin Drive, Suite 600 Redwood City, CA 94065 info@stinsonortho.com www.stinsonortho.com Table of Contents Introduction 3 Features 4 Surgical Technique 5 Preoperative
TORNIER BLUEPRINT. 3D Planning + PSI THE VALUE OF BLUEPRINT
 TORNIER BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI THE VALUE OF BLUEPRINT BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI is a surgeon controlled, automated, D pre-operative planning software with optional patient
TORNIER BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI THE VALUE OF BLUEPRINT BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI BLUEPRINT D Planning + PSI is a surgeon controlled, automated, D pre-operative planning software with optional patient
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Anatomical Shoulder System
 Anatomical Shoulder System Adjustable. Convertible. Compatible. Anatomical Shoulder System by Zimmer This unique system is like an individually produced prosthesis specifically designed for each patient.
Anatomical Shoulder System Adjustable. Convertible. Compatible. Anatomical Shoulder System by Zimmer This unique system is like an individually produced prosthesis specifically designed for each patient.
Optimum implant geometry
 Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Design Rationale Optimum implant geometry Extending the proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 1 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Surgical indications and contraindications Anatomical Considerations: Total shoulder arthroplasty surgery involves the replacement of the humeral head and the glenoid articulating
1 Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Surgical indications and contraindications Anatomical Considerations: Total shoulder arthroplasty surgery involves the replacement of the humeral head and the glenoid articulating
OPTIONAL/ADDITIONAL INSTRUMENTS
 20 Elevated 6320-36-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 36mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-80-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 80mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-42-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 42mm OD x 26mm ID 6320-80-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner,
20 Elevated 6320-36-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 36mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-80-22 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 80mm OD x 22mm ID 6320-42-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner, 42mm OD x 26mm ID 6320-80-26 20 Elevated Rim Liner,
System Overview 3. Anatomic Sizing And Design Features 4. Instrumentation 6. Indications And Contraindications 7. Surgical Technique 8
 Surgical Technique Table of Contents System Overview 3 Anatomic Sizing And Design Features 4 Instrumentation 6 Indications And Contraindications 7 Surgical Technique 8 Implant Information 22 Instrumentation
Surgical Technique Table of Contents System Overview 3 Anatomic Sizing And Design Features 4 Instrumentation 6 Indications And Contraindications 7 Surgical Technique 8 Implant Information 22 Instrumentation
Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique
 Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique Surgical Technique The Comprehensive Fracture System offers a unique tool to evaluate and re-establish humeral height, which can be critical to restoring proper biomechanics
Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique Surgical Technique The Comprehensive Fracture System offers a unique tool to evaluate and re-establish humeral height, which can be critical to restoring proper biomechanics
TORNIER BIO-RSA. Bony Increased Offset - Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 TORNIER BIO-RSA Bony Increased Offset - Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 2 Table of Contents: Concept...4 Bony Increased Offset Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty (BIO-RSA ) Concept...4 Surgical
TORNIER BIO-RSA Bony Increased Offset - Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 2 Table of Contents: Concept...4 Bony Increased Offset Reversed Shoulder Arthroplasty (BIO-RSA ) Concept...4 Surgical
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray
 Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique Give Bone A Solid Hold Zimmer NexGen Trabecular Metal Tibial Tray Surgical Technique
Developments in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Developments in Shoulder Arthroplasty Andrew L. Wallace PhD MFSEM FRCS FRACS Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Glenohumeral Joint Arthritis Relatively uncommon Not as common as hip/knee/hand UK National Joint
Developments in Shoulder Arthroplasty Andrew L. Wallace PhD MFSEM FRCS FRACS Consultant Shoulder Surgeon Glenohumeral Joint Arthritis Relatively uncommon Not as common as hip/knee/hand UK National Joint
TRABECULAR METAL ACETABULAR RESTRICTOR AND AUGMENT. Surgical Technique
 TRABECULAR METAL ACETABULAR RESTRICTOR AND AUGMENT Surgical Technique ACETABULAR ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION Intra-operatively, carefully assess any acetabular bone defects present. Note the location, extent,
TRABECULAR METAL ACETABULAR RESTRICTOR AND AUGMENT Surgical Technique ACETABULAR ASSESSMENT AND PREPARATION Intra-operatively, carefully assess any acetabular bone defects present. Note the location, extent,
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications)
 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications) Emilie Cheung, MD Associate Professor Chief Shoulder Elbow Svc Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications) Emilie Cheung, MD Associate Professor Chief Shoulder Elbow Svc Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes
Trilogy Acetabular System
 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Versatility in a proven design Trilogy Acetabular System 1 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Acetabular Reaming 2 Component Sizing
Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Versatility in a proven design Trilogy Acetabular System 1 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Acetabular Reaming 2 Component Sizing
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
Featuring. Technology. Product Rationale
 Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Featuring Technology Product Rationale 2 Optimum implant geometry Extending proven TRI-LOCK heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge
Resurfacing Arthroplasty of the Humerus: Indications, Surgical Technique, and Clinical Results
 8(3):152 160, 2007 Ó 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia R E V I E W Resurfacing Arthroplasty of the Humerus: Indications, Surgical Technique, and Clinical Results Jason J. Scalise, MD, Anthony
8(3):152 160, 2007 Ó 2007 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia R E V I E W Resurfacing Arthroplasty of the Humerus: Indications, Surgical Technique, and Clinical Results Jason J. Scalise, MD, Anthony
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
Index. ESSKA 2018 G. Milano et al. (eds.), Management of Failed Shoulder Surgery,
 A Acromial fractures, 186 Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) instability, 55, 97 case study, 98 100 classification, 85 clinical relevant situations, 86 dislocation, 97 98 insufficient fixation, 87 88 operative
A Acromial fractures, 186 Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) instability, 55, 97 case study, 98 100 classification, 85 clinical relevant situations, 86 dislocation, 97 98 insufficient fixation, 87 88 operative
Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Optimizing Outcomes and Avoiding Complications
 Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Optimizing Outcomes and Avoiding Complications Dr. Ryan T. Bicknell, MD, MSc, FRCSC Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, Departments of Surgery, Mechanical
Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Optimizing Outcomes and Avoiding Complications Dr. Ryan T. Bicknell, MD, MSc, FRCSC Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedic Surgery, Departments of Surgery, Mechanical
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER
 Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
Principles of acetabular fixation in primary and revision hip arthroplasty Piotr Wojciechowski, Damian Kusz, Anna WAGNER Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology Medical University of Silesia Head of
EXACTECH EXTREMITIES. Operative Technique. Platform Shoulder System. Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM
 EXACTECH EXTREMITIES Operative Technique Platform Shoulder System Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM TABLE OF CONTENTS EQUINOXE PLATFORM SHOULDER SYSTEM INTRODUCTION... 3 Primary Shoulder... 3 Reverse
EXACTECH EXTREMITIES Operative Technique Platform Shoulder System Surgeon focused. Patient driven. TM TABLE OF CONTENTS EQUINOXE PLATFORM SHOULDER SYSTEM INTRODUCTION... 3 Primary Shoulder... 3 Reverse
AEQUALIS PERFORM + REVERSED
 TO R N I E R AEQUALIS PERFORM + REVERSED Glenoid WEDGED AUGMENT SURGIC AL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents: AEQUALIS PERFORM + REVERSED Glenoid...3 Overview...3 Indications/Contraindications...4 Pre-Operative
TO R N I E R AEQUALIS PERFORM + REVERSED Glenoid WEDGED AUGMENT SURGIC AL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents: AEQUALIS PERFORM + REVERSED Glenoid...3 Overview...3 Indications/Contraindications...4 Pre-Operative
GLOBAL CAP CTA. Resurfacing Shoulder Systems SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 GLOBAL CAP GLOBAL CAP CTA Resurfacing Shoulder Systems SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The GLOBAL CAP Resurfacing Humeral Head Implant is well suited for osteoarthritic or rheumatoid arthritic patients
GLOBAL CAP GLOBAL CAP CTA Resurfacing Shoulder Systems SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The GLOBAL CAP Resurfacing Humeral Head Implant is well suited for osteoarthritic or rheumatoid arthritic patients
SHOULDER EXTRACTION INSTRUMENTS
 SHOULDER EXTRACTION INSTRUMENTS PRODUCT OVERVIEW Introducing the orthopaedic industry s first dedicated Shoulder Extraction Instrument set. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction has created this set of instruments
SHOULDER EXTRACTION INSTRUMENTS PRODUCT OVERVIEW Introducing the orthopaedic industry s first dedicated Shoulder Extraction Instrument set. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction has created this set of instruments
Trilogy Acetabular System
 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Versatility in a proven design Trilogy Acetabular System 1 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Acetabular Reaming 2 Component Sizing
Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Versatility in a proven design Trilogy Acetabular System 1 Trilogy Acetabular System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Acetabular Reaming 2 Component Sizing
