Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine. Foisor Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Osteoarticular TBC Clinical Hospital, Bucharest, Romania
|
|
|
- Charles Beasley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2018; 13(1): Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine Review Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following Total Knee Arthroplasty a Systematic Review. Part II Bogdan Stefan CRETU a, Calin DRAGOSLOVEANU a, Stefan CRISTEA b, Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a a Foisor Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Osteoarticular TBC Clinical Hospital, Bucharest, Romania Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania b Sf. Pantelimon Emergency Clinical Hospital, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT The aim of this second part is to review the existing described methods for measuring postoperative total knee arthroplasty (TKA) alignment in sagital and axial plane as well as the existing literature regarding the axial plane evaluation with the use of computer tomography. Given that the most frequent mistakes when positioning the total knee arthroplasty components are made in the axial plane, it is necessary to know what are the limits of radiographic evaluation, for which CT scan is the most valuable tool in assessing the rotation of the components. Keywords: TKA alignment, sagital plane, axial plane, rotational analysis, CT evaluation. INTRODUCTION The sagital and axial preoperative and postoperative evaluations of total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are essential steps in improving the surgical outcome. Precise positioning of the patient is crucial for obtaining correct radiological images. In the sagital plane, the anatomical and mechanical axis of both the femur and tibia, the femoral offset evaluation, patellar height, the joint line height and the patellar tendon angle are important factors for the preoperative planning and also for evaluating the positioning of TKA components. In the axial plane, we can only evaluate the femur. The axial plane evaluation for TKA may be done by using CT scan or MRI. Computer tomography is the most valuable examination in assessing the rotation of the components. 1. Evaluation of the knee in sagital plane (lateral) 1.1 Patient positioning The precise positioning of the patient is crucial for obtaining the radiological image in sagittal Address for correspondence: Serban Dragosloveanu, PhD, MD Foisor Orthopaedics, Traumatology and Osteoarticular TBC Clinical Hospital, Bucharest, Romania Tel.: serbandrago@gmail.com Article received on the 2 nd of February 2018 and accepted for publication on the 23 rd of May
2 plane. This image can be obtained with or without weight bearing of the lower limb. The knee is flexed at 30, with the patella perpendicular to the cassette and with the lower limb parallel to the radiological table. The contralateral limb is positioned in a slightly posterior rotation, allowing enough lateral space for the affected knee (1). For the lateral weight bearing radiography, the knee is flexed at 30 and the contralateral lower limb is positioned posterior, with the patient in a semi-flexed knee position. Both images are likely to be obtained after a fluoroscopically guided exploration which certifies the good position of the knee. After a good positioning of the knee on the sagittal plane, the condyles will appear overlapped. The curve of the femur and tibia must be included in the image as much as possible, obtained with a 24x30 cm image (10x12 inch). The patella must be tangent to the beam to determine the height relative to the joint (1, 2). The fluoroscopically guided examination helps obtaining the femoral condyles overlap for a correct measurement of the position of the components. If fluoroscopy is not available, an external rotation of 3-5 can be done to try to obtain femoral condyles overlap (3). This image is obtained u sing a 24x30 cm film (10x12 inch), the beam is on 5 cranial direction, placed at 97 cm (39 inch) from the cassette and centered between the patellar apex and 1 cm distal from the medial condyle. Paley proposed the use of a 71 or 91 cm cassette with the beam centered knee joint at 305 cm (10 feet) distance from the patient for the la teral weight-bearing image of the lower limb. Chung et al. created a new technique for obtaining a lateral image of the whole femur in which the femoral head is viewed clearly and both femoral condyles are overlapped. The thigh of the patient is positioned on a 17x17 inch digital detector and the x-ray beam is angled at 15 cranial. 1.2 Axis evaluation The femoral anatomical and mechanical axis The sagittal plane radiology in KS evaluation is based on data obtained on lateral short film (14x17 inch). In KS form, the sagittal anatomical angle of the femoral component is named femoral flexion (gamma angle). The value of this angle is given by the sagittal anatomical axis of the femur and the sagittal axis of the femoral component. The sagittal anatomical axis of the femur on the lateral view is obtained uniting the furthest point from the middle of the femoral shaft with a second point placed at 10 cm proximal to the joint line in the middle of the femoral shaft. The sagittal axis of the femoral component is perpendicular to the distal condylar plane of the implant that can be represented by either distal resection of the femur or intercondylar notch of the implant. The sagittal mechanical axis of the femur is an axis drawn from the center of the femoral head, identified using the Mose circles, and the center of the femoral component on the sagittal plane (4, 5). There are two possibilities for identifying the sagittal mechanical axis of the femur by the distal points: - Mechanical axis 1 is a line that goes from the center of the femoral head to a point that is placed 1 cm anterior to the Blumensaat line (a line which goes through the intercondylar notch on the lateral view) - Mechanical axis 2 is defined as a line that goes from the center of the femoral head to a point identified 65% posterior on a line between the anterior cortex and the most prominent point from the posterior medial condyle. The sagittal anatomical axis of the femur is obtained by drawing a line through the proximal, middle and distal centers of the femoral shaft on a full lateral lower limb radiography (3, 6). This produces a segmented line which considers the sagittal femoral curve (between 4 and 9 ) (7, 8). The distal sagittal anatomical axis of the femur: - Distal anterior cortex axis is defined as a line that connects two points on the anterior cortex at 5cm and 10 cm proximal to the joint line; - Distal medullary axis. A Korean study found an angular difference average of 2 (0-4 ) between the mechanical axis and the sagittal anatomical axis of the distal femur. Far as 1 of anterior femoral curve, the angular deviation between those two axes grows for about 0.5 (7). The anterior cortical axis has an average value to the mechanical axis of 4 (0-11 ) (8). The position evaluation in the sagittal plane of the femoral component must consider the anatomy of the distal third of the femur and, according 106
3 to the KS protocol, the neutral position of the femoral component has the distal condyles perpendicular on the anatomical axis of the distal femur (2) The sagittal anatomical and mechanical axis of the tibia Regarding the tibia, the angle also known as tibial angle is the equivalent of the so-called tibial sloping and, as described in the KS protocol, it is an anatomical angle on that sagittal plane which is formed between a tangent line at the base of the tibial component and a sagittal tibial anatomical line that is formed by connecting the furthest point of the center of the tibial shaft with a point located 10 cm under the knee joint, in the middle of the tibial shaft (3, 9, 10-13). There are five anatomical landmarks described for the sagittal anatomical line of the tibia (14): - the anterior cortical line of the tibia (acl), which connects two points on the tibial cortex that are placed proximal and anterior at 5 and 15 cm distally from the joint line; - the proximal anatomical axis (paa); - the central anatomical axis (caa); - the posterior cortical line (pcl) of the proximal tibia, which connects two points of the posterior cortex of the tibia that are placed on the posterior cortex at 5 cm and 15 cm distally from the joint line; - the fibular shaft axis a line that connects the distal and proximal parts of the fibular shaft. The normal tibial sloping is between 5 and 11 (15, 16). 1.3 The femoral offset evaluation The posterior condylar offset It is the maximal thickness of the posterior condyles, projected posteriorly by the posterior cortical tangent of the femoral shaft for the anatomical knee and knee prosthesis (17). There is a tight correlation between regaining the posterior condylar offset (PCO) and the maximum flexion the more PCO decreases after surgery, the more flexion is reduced. For every 2 mm decrease in PCO, flexion is reduced by about Regaining the PCO is important in TKA with preserving the posterior cruciate ligament. Soda et al. propose a new parameter called PCO rate (18). Arabori et al. found a correlation between PCO and flexion only in cases with TKA with preserved posterior cruciate ligament (19) The anterior condylar offset It is the maximum thickness of the anterior condyles, projected anterior by the anterior cortical tangent of the femoral shaft for the normal knee but also for the knee prosthesis (20, 21). After intraoperative measurements in TKA, the standard anterior condylar offset (ACO) value represented by the anterior resection was 10.9 mm for males and 10.1 mm for females (22). If ACO increases postoperatively, excessive pressure may appear in the patellofemoral joint, with a limitation of postoperative movement (23). If ACO increases, this can lead to a raise of the trochlear groove height in the anterior compartment; as a result, the extension arc of the knee increases and in the end, flexion decreases. Miller et al. discovered that, after a TKA, the lateral and medial flanges increased by 1.1±2.6 mm and 0.5±2.2 mm, respectively, and the trochlear groove by 0±1.1 mm (24). They calculated that, following an increase of the anterior cortex between 2 and 4 mm, the flexion decreases by 1.8 and 4.4, respectively. The modification of the shape of the anterior femur has few consequences on passive flexion but the clinical implications on patient s symptoms remain unidentified (24). 1.4 Patellar height Of all indexes used for patellar measurement after TKA, just those that are related to the tibia can be used (IS, CD, BP) (25-27). Referring to the femur, it is not possible after arthroplasty (Blumennsatt, Bernageau) (28, 29) Insall Salvati Index is the ratio between the length of the patellar tendon, measured on the posterior surface from de distal pole of the patella to the insertion on the tibial tubercle, and the length of the patella measured on the longest diagonal line drawn across the patella. A normal value is 1.02, with a variation of less than 20%. A ratio greater than 1.2 indicates a patella alta, and a ratio lower than 0.8 indicates a patella baja (27) Blackbourne Peel Index is the ratio between A line, represented by the perpendicular distance from the inferior articular edge of the patella and the joint line, and B line represented by the length of the articular surface of the patella. The normal value 107
4 is 0.8 ( ). A ratio greater than 1.2 indicates a patella alta, and under 0.6 suggests a patella baja (25) Caton Deschamps Index is the ratio between the distance from the inferior margin of the articular surface of the patella to the superior margin of the tibial plateau (A) and the length of the patellar articular surface (B). The normal value is 1.0 ( ). A ratio higher than 1.3 indicates a patella alta, and lower than 0.7 suggests a patella baja (26). The Insall-Salvati (IS) has some disadvantages: the tibial insertion of the tendon is hard to identify and the length of the patella does not show the length of the articular surface. The modified Caton index was proposed by Aglietti et al., being considered the most suitable for the measurement of patellar height in the prosthetic knee (30). 1.5 The joint line height It is defined as a line that passes distally by the femoral condyles. The level of the condylar surfaces depends by the spontaneous flexion of the articulation. The position of the joint line is the distance (average of 2.2 cm) from the proximal edge of the tibial tuberosity to the joint line (10, 18). After TKA, the modification of the joint line position is measured as a difference between the preoperative and postoperative status of the joint line. This value is negative if the joint line is lower and positive if the joint line is higher (31). For the cases when the tibial tubercle is not well defined, the usage of the tip of the peroneal head would be a proper method (8). Usually, the joint line is found 15.4±5.4 mm above the head of the peroneus in the sagittal plane and 13.9±5.8 mm in the coronal plane (32, 33). The position of the joint line is a complex tridimensional concept and for a correct evaluation it needs a CAT scan. 1.6 The patellar tendon angle The value of this angle allows us to analyse the knee kinetics in weight bearing position with or without sagittal plane (24). It is an angle represented by the patellar tendon and the tibial axis. There is a correlation between this angle and the flexion angle of the knee that may be quantified (24). With this angle, we can make a good analysis of the patellofemoral and tibiofemoral kinetics. Major modifications of these angles are due to some abnormalities between the tibia and the femur. The angle value is increased by anterior subluxation of the femur and decreased by posterior subluxation. In a normal knee, the patellar tendon angle has an average of 20 in extension position, while in flexion it decreases in a linear fashion: 0 at 80 of flexion and 10 at 120 of flexion (24, 34, 35). 2. Axial plane knee evaluation 2.1 Patient positioning for patellar views There are a multitude of positions described by different authors (Laurin, Ficat, Merchant) (36-38): 1. Ficat and Hungerford: The patient s knees are flexed at the end of the radiological table. The tube is positioned at the legs of the patient and the cassette on the anterior thigh. In this position, the knee is perpendicular on the beam. It can be made at 30, 60 and Laurin: The patient is positioned on the radiological table with the legs close to the edge. The beam is parallel with the anterior aspect of the tibia and the knee is flexed at 20. The cassette is holed by the patient at 90 against the beam. 3. Merchant s: The patient stays in supination on the radiological table with the knees flexed at 90 and the cassette is placed proximal from the shins. Both knees are exposed simultaneously with the beam directed to the legs, tilted at 30 from the horizontal. 2.2 The patellofemoral incidence in axial plane with or without weight bearing The previously described views are done without weight bearing. The outcome of the extensor mechanism to the patellofemoral alignment is not taken into account in this radiological view. An axial weight bearing position that incorporates all Merchant s incidence parameters is described and approved (39). This is achieved with the patient standing against a wall (in front of the mobile radiological support) at 25.4 m (10 inch) distance to the wall. The beam source is brought to the level of the patient s head. The 18x43 cm cassette is positioned on the dorsal aspect of the legs, which will stay parallel one 108
5 against the other. The knee is flexed 45, with the tibia at 15 from the beam. This radiological view shows the patellofemoral maltracking, comparing with the standard Merchant s view: the lateral tilt and subluxation of the substituted patella are reduced significantly, the prevalence of the uncovered patella towards femoral trochlear impingement is significantly increased and the patellar maltracking is much easier to correlate with the clinical symptoms. Using the weight bearing axial view for the evaluation of TKA offers additional information over standard radiography. 2.3 Patellofemoral axis evaluation The patellofemoral alignment, measured according to the KS guide takes into account the following: the thickness, width, tilt, and mediolateral tracking of the patella as well as the patellar prosthesis angle to the patellar bone. Those measurements are calculated according to Gomes and Gustilo (40). 1. The preoperative patellar tilt or for the unsurfaced patella is formed by a line dragged anterior to the condylar or prosthetic limit in the axial line and a line which connects the ape of the patellar articular surface with the lateral edge of the lateral facet of the patella. If the angle is positive, this is considered normal, while if it is 0 or negative, the patellar tilt is abnormal. A small or negative angle indicates a subluxation or a dislocation. The patellar tilt after patellar prosthesis is an angle formed by a line that passes anterior to the femoral condyles and a line along the bone/prosthesis interface. 2. The thickness of the patella pre- and postoperatively is the vertical distance from the anterior cortex of the patella to the patellar femoral sulcus. Scott s study on cadavers showed that the flexion decreased by 3 for every 2 mm incrementation of the patellar thickness (41). 3. The mediolateral position of the patella is the horizontal distance between two vertical lines perpendicular to a line that goes through the femoral condyles. A line is formed by the middle of the patella and another one by the patellar femoral sulcus. 2.4 The axial femoral incidence Besides patellofemoral evaluation, an axial view offers information on the position of the femoral component in axial plane. The femoral component rotation is calculated after the condylar twisted angle (CTA), angle formed between the posterior condylar axis and the clinical epicondylar axis. This angle can be obtained using either a CAT scan or a simple radiography (42, 43). Preoperative using of such incidence may anticipate the grades of external rotation from the posterior condyles, which the surgeon can use for obtaining a correct positioning, identical with the one obtained using the trans epicondylar axis (TEA). 1. The Takai view The patient positioning must be in such way that the affected knee is bent at 80 and holed by a support (chair). The x-ray beam is perpendicular to the tibial shaft. The radiology resulted after this positioning is a posterior-lateral view of a flexed knee. 2. Kanekasu view The patient is position on a framework with the lower limbs suspended and the knees flexed at 90. The authors of this view have modified the original position, adding a 1.5 kg distraction on the affected leg, being able to evaluate the tibiofemoral space configuration preoperative and postoperative (44). 3. CT protocol The axial plane evaluation for TKA may be done by using a CT scan (most frequently) or a MRI. Berger created a protocol for evaluation of the transversal (axial) plane rotation (45, 46). 3.1 The Berger protocol The patient stays in supination, with the examined limb in full extension, so the scanning will go perpendicular on the anatomical axis of the knee. In the lateral, scout view, CT incidences are done perpendicular to the femoral axis for the femoral scanning and perpendicular to the tibial axis for the tibial scanning. The 1.5 mm thickness CT sections are necessary in four locations: through the epicondylar axis of the femur, through the tibial tubercle, through the upper edge of the plateau and through the tibial component. The femoral component rotation The optimal level to view both femoral epicondyles is at 30 mm proximal from the joint line (47). Two lines are drawn at this level: one tangent to the posterior condyles and another one connecting 109
6 the lateral epicondyle prominence to the medial epicondyle sulcus (surgical TEA=transepicondylar axis). The angle formed by the two lines is the posterior condylar angle (PCA). The value of this angle must be as close as possible 0. Romero et al. suggest the use of TEA, which connects the lateral epicondyles to the edge of the medial epicondyle, being a much easier landmark to find (47). This axis is helpful to calculate the CTA (condylar twist angle) (the angle between the posterior condylar axis and the clinical transepicondylar axis) that has 3-4 of external rotation by the PCA (47). The tibial component rotation For the evaluation of tibial component rotation, it is necessary to determine the geometrical center of the proximal tibial and its axial transposition above the tibial tubercle (48). After that, the geometric center of the proximal tibial component and the junction between the medial edge and the medial third of the tibial tubercle are connected, defining the tubercle orientation. The anteroposterior axis of the tibial component is evaluated on the axial view through the tibial component. The rotation of the tibial component is calculated in relationship with the tibial tubercle orientation and the anteroposterior axis of the tibial component (48). The Akagi line The line, which goes from the insertion center of the posterior cruciate ligament towards the medial aspect of the patellar ligament, must be perpendicular to the surgical transepicondylar axis of the femur, on the transversal plane CT image (49). The Insall line The central anteroposterior axis of the tibial component has to coincide the line, which connect the PCL insertion to the junction between 1/3 medial to 2/3 lateral of the patellar ligament. q CONCLUSION Sagital and axial roentgenographic analysis for the preoperative planning and after TKA are important steps; however, they have a limit: they are bidimensional. Only when 3D evaluation of the entire lower limb will become feasible on a routine basis, it will be possible to understand rotational assessment of components, combined component position under load, and kinematics relationships between components and between bones. q Conflicts of interest: none declared. Financial support: none declared. References 1. Pavlov H. Lower Extremity. Knee. Lateral view. In: Pavlov H, Burke M, Giesa M, et al (Eds). Orthopaedist s guide to plain film imaging. New York: Thieme, Berquist TH. The Knee. In: Berquist TH (Ed). Imaging of Orthopaedic Fixation Devices and Prostheses. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2009, pp Paley D. Radiographic Assessment of Lower Limb Deformities. In: Paley D (Ed). Principles of Deformity Correction. New York: Springer, Minoda Y, Kobayashi A, Iwaki H, et al. TKA sagittal alignment with navigation system and conventional technique vary only few degrees. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009;467: Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE, et al. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: Just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 2009;24(6, suppl): Yehyawi TM, Callaghan JJ, Pedersen DR, et al. Variances in Sagittal Femoral Shaft Bowing in Patients Undergoing TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2007;464: Chung BJ, Kang YG, Chang CB, et al. Differences between sagittal femoral mechanical and distal reference axes should be considered in navigated TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009;467: Seo JG, Kim BK, Moon YW, et al. Bony landmarks for determining the mechanical axis of the femur in the sagittal plane during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg 2009;1: Balakrishnan V, De Steigert R, Lowe A. Radiographic assessment of alignment following TKA: outline of standardized protocol and assessment of a newly devise trigonometric method of analysis. ANZ J Surg 2010;80: Hankemeier S, Gosling T, Richter M, et al. Computer assisted analysis of lower limb geometry: higher intra obserever reliability compared to conventional method. Comput Aided Surg 2006;11: Hinman RS, May RL, Crossley KM. Is there an alternative to the full leg radiograph for determining knee joint alignment in osteoarthritis? Arthritis Rheum 2006;55: Yin L, Chen K, Guo L, et al. Knee alignment in the transverse plane during weight-bearing activity and its implication for the tibial rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 2015;6: Maderbacher G, Baier C, Benditz A, et al. Presence of rotational errors in long leg radiographs after total knee arthroplasty and impact on measured lower limb and component alignment. Int Orthop 2017;8:
7 14. Yoo JH, Chang CB, Shin KS, et al. Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: a comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J Arthroplasty 2008; 23: Denis K, Van Ham G, Bellemans J, et al. How correctly does an intramedullary rod represent the longitudinal tibial axes? Clin Orthop Related Res 2002;397: Singh G, Tan JH, Sng BY, et al. Restoring the anatomical tibial slope and limb axis may maximise post-operative flexion in posterior-stabilised total knee replacements. Bone Joint J 2013;95-B(10): Bellemans J, Banks S, Victor J, et al. Fluoroscopic analysis of the kinematics of deepflexion in total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2002;84: Soda Y, Oishi J, Nakasa T, et al. New parameter of flexion after posterior stabilized total knee arthroplasty: posterior condylar offset ratio on X-ray photographs. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2007;127: Arabori M, Matsui N, Kuroda R, et al. Posterior condylar offset and flexion in posterior cruciate-retaining an posterior stabilized TKA. J Orthop Sci 2008;13: Clarke HD, Hentz JG. Restoration of femoral anatomy in TKA with unisex and gender-specific components. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008;466: Fehring TK, Odum SM, Hughes J, et al. Differences between the sexes in the anatomy of the anterior condyle of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91: Poilvache PL, Insall JN, Scuderi GR, et al. Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1996;331: Weissman BN. Radiographic evaluation of total joint replacement. In: Sledge CB, Ruddy S, Harris ED Jr, et al. (Eds.), Arthritis Surgery, Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders, 1994, pp Miller RK, Goodfellow JW, Murray DW, et al. In vitro measurement of patellofemoral force after three types of knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1998;80: Caton JH, Prudhon JL, Aslanian T, et al. Patellar height assessment in total knee arthroplasty: a new method. Int Orthop 2016;12: Lin CF, Wu JJ, Chen TS, et al. Comparison of the Insall-Salvati ratio of the patella in patients with and without an ACL tear. 2005;1: Allen AM, Ward WG, Pope TL, et al. Imaging of the total knee arthroplasty. Radiol Clin North Am 1995;33: Eshnazarov KE, Seon JK, Song EK. Comparison of Radiological Assessments Patellar Resurfacing with Retention for Grade IV Osteoarthritis in Patellofemoral Joint accomplished Total Knee Arthroplasty. Vestn Rentgenol Radiol 2016;1: Malo M, Vince KG. The unstable patella after total knee arthroplasty: Etiology, prevention, and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2003;5: Aglietti P, Baldini A, Buzzi R, et al. Patella resurfacing in total knee replacement: functional evaluation and complications. 2001;9:S27-S Figgie H, Goldberg V, Heiple K, et al. The influence of tibial-patellofemoral location on function of the knee in patients with posterior stabilized condylar knee prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg 1986;68: Kawamura H, Bourne RB. Factors affecting range of flexion after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci 2001;6: Selvarajah E, Hooper G. Restoration of the joint line in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2009;24: Mihalko WM, Boyle J, Clark LD, et al. The variability of intramedullary alignment of the femoral component during total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2005;20: Price AJ, Rees JL, Beard DJ, et al. Sagittal plane kinematics of a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthropasty at 10 years: a comparative in vivo fluoroscopic analysis. J Arthroplasty 2004;5: Chia SL, Merican AM, Devadasan B, et al. Radiographic features predictive of patellar maltracking during total knee arthroplasty. 2009;10: Classen T, Wegner A, Muller RD, et al. Femoral component rotation and Laurin angle after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Belg 2010;1: Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, et al. Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane: a comparison of conventional and computer-assisted surgery in an Asian population. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2011;93: Baldini A, Anderson JA, Cerulli-Mariani P, et al. Patello femoral evaluation after total knee arthroplasty. Validation of a new weight-bearing axial radiographic view. J Bon Joint Surg Am 2007;89: Merican AM, Ghosh KM, Baena FR, et al. Patellar thickness and lateral retinacular release affects patellofemoral kinematics in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2014;3: Bengs BC, Scott RD. The effect of patellar thickness on intraoperative knee flexion and patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2006;21: Kaneka su K, Kondo M, Kadoya Y. Axial radiography of the distal femur to assess rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;434: Takai S, Yoshino N, Isshiki T, et al. Kneeling view: a new roentgenographic technique to assess rotational deformity and alignment of the distal femur. J Arthroplasty 2003;18: Tokuhara Y, Kadoya Y, Kanekasu K, et al. Evaluation of the flexion gap by axial radiography of the distal femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88: Crossett LS, Rubash HE, Berger R. Computerized tomography in total knee arthroplasty. In: Insall JN, Scott WN, Scuderi GR (Eds.), Current Concepts in Primary and Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty, Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott- Raven, 1996, pp Berger RA, Seel MJ, Schleiden M, et al. Determination of femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty using computer tomography. Orthop Trans 1993;17: Suter T, Zanetti M, Schmid M, et al. Reproductibility of measurement of femoral component rotation after total knee arthroplasty using computer tomography. J Arthroplasty 2006;21: De Valk EJ, Noorduyn JC, Mutsaerts EL. How to assess femoral and tibial component rotation after total knee arthroplasty with computed tomography: a systematic review. Review article. 2016;11: Yu HC, Wen H, Zhang Y, et al. Research on the reliability of the Akagi line as a reference axis to guide for rotational alignment of the proximal tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2015;10:
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement
 Knee Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement A COMPUTER-SIMULATION STUDY W.-Q. Cui, Y.-Y. Won, M.-H. Baek, K.-K. Kim, J.-H. Cho From Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon City,
Knee Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement A COMPUTER-SIMULATION STUDY W.-Q. Cui, Y.-Y. Won, M.-H. Baek, K.-K. Kim, J.-H. Cho From Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon City,
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an increasingly. Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
)122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Distal Femoral Rotational Alignment with Spiral CT Scan before Total Knee Arthroplasty (A Study in Iranian
)122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Distal Femoral Rotational Alignment with Spiral CT Scan before Total Knee Arthroplasty (A Study in Iranian
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Influence of the Rotational Alignment of the Femoral and Patellar Components on Patellar Tilt in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;273):163-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.3.163 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Influence of the Rotational Alignment
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;273):163-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.3.163 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Influence of the Rotational Alignment
LAMINA SPREADER SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 LAMINA SPREADER SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Balanced and appropriate external rotation of the femoral component is important for tibio-femoral stability in flexion and patello-femoral tracking/function. Depending
LAMINA SPREADER SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Balanced and appropriate external rotation of the femoral component is important for tibio-femoral stability in flexion and patello-femoral tracking/function. Depending
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability
 CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability Poster No.: C-2157 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Ruef, C. Edgar, C. Lebedis, A. Guermazi, A. Kompel, A. Murakami; Boston, MA/US Keywords:
CT Evaluation of Patellar Instability Poster No.: C-2157 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Ruef, C. Edgar, C. Lebedis, A. Guermazi, A. Kompel, A. Murakami; Boston, MA/US Keywords:
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
ANATOMIC. Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0
 ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique
 ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
ANTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Anterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees INTRODUCTION
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION. Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique
 POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
POSTERIOR REFERENCE NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION Multi-Reference 4-in-1 Femoral Instrumentation Posterior Reference Surgical Technique For NexGen Cruciate Retaining & Legacy Posterior Stabilized Knees
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
Correlation between Knee Kinematics and Patello-femoral Contact Pressure in Total Knee Arthroplasty Takuya Konno, MD 1, Tomohiro Onodera, MD, PhD 1, Yasuhiko Kasahara, MD, PhD 1, Daisuke Takahashi 1, Norimasa
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS
 STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
STIFFNESS AFTER TKA PRE, PER AND POST OPERATIVE CAUSING FACTORS Patrick DJIAN INTRODUCTION Stiffness is one of the most common complications following TKR, causing frustration to both the surgeon and the
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy
 Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy LATERAL RELEASE IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY FOR A FIXED VALGUS DEFORMITY J. Brilhault, S. Lautman, L. Favard, P. Burdin From Trousseau University Hospital of Tours, France
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing?
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 287 291 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing? G. Kamei a,,
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 287 291 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Is patella eversion during total knee arthroplasty crucial for gap adjustment and soft-tissue balancing? G. Kamei a,,
Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 16 Number 2 Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty V Chester, E Biden, T Barnhill Citation V Chester,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 16 Number 2 Noninvasive Assessment of Sagittal Knee Kinematics After Total Knee Arthroplasty V Chester, E Biden, T Barnhill Citation V Chester,
Gap Balancing vs. Measured Resection Technique in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:1-8 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.1 Gap Balancing vs. Measured Resection Technique in Total Knee Arthroplasty Brian K. Daines, MD, Douglas
Review Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:1-8 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.1 Gap Balancing vs. Measured Resection Technique in Total Knee Arthroplasty Brian K. Daines, MD, Douglas
Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design. Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman
 Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman History: The Total Condylar knee represented a significant advance in
Retrospective Study of Patellar Tracking in an Anatomical, Motion Guided Total Knee Design Adam I. Harris, M.D. & Michelle Ammerman History: The Total Condylar knee represented a significant advance in
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement
 Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Results and Techniques Alexander P. Sah, MD California Orthopaedic Association Meeting Laguna Niguel, CA May 20th, 2011 Overview Why partial knee replacement? - versus
Zhe Du 1, Shichang Chen 2, Mengning Yan 2, Bing Yue 1, Yiming Zeng 2 and You Wang 1*
 Du et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1374-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Do size, shape, and alignment parameters of the femoral condyle affect the trochlear groove
Du et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1374-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Do size, shape, and alignment parameters of the femoral condyle affect the trochlear groove
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
 Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia?
 Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Nirav Joshi 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California
Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Nirav Joshi 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California
Rotational landmarks of the distal femur in Indian population: A MRI-based study
 Raju et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:186 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0333-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Rotational landmarks of the distal femur in Indian population: A MRI-based
Raju et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2015) 10:186 DOI 10.1186/s13018-015-0333-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Rotational landmarks of the distal femur in Indian population: A MRI-based
Zimmer FuZion Instruments. Surgical Technique (Beta Version)
 Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
Zimmer FuZion Surgical Technique (Beta Version) INTRO Surgical Technique Introduction Surgical goals during total knee arthroplasty (TKA) include establishment of normal leg alignment, secure implant fixation,
Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population
 Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population Mehdi Moghtadaei1,
Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population Mehdi Moghtadaei1,
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
Think isometry Feel balance
 Think isometry Feel balance Learning from the experience of over 40 years of total knee development, Unity Knee is the latest evolution in total knee arthroplasty, unifying key design technologies with
Think isometry Feel balance Learning from the experience of over 40 years of total knee development, Unity Knee is the latest evolution in total knee arthroplasty, unifying key design technologies with
The Posterior Condylar Cartilage Affects Rotational Alignment of the Femoral Component in Varus Knee Osteoarthritis
 24 ORIGINAL The Posterior Condylar Cartilage Affects Rotational Alignment of the Femoral Component in Varus Knee Osteoarthritis Daisuke Hamada 1, Keizo Wada 1, Hiroshi Mikami 2, Shunichi Toki 2, Tomohiro
24 ORIGINAL The Posterior Condylar Cartilage Affects Rotational Alignment of the Femoral Component in Varus Knee Osteoarthritis Daisuke Hamada 1, Keizo Wada 1, Hiroshi Mikami 2, Shunichi Toki 2, Tomohiro
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes
 Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no
 Patellar subluxa,on Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no. 4 472-479 History taking is important: a. Trivial or significant injury b. Requires Hospital or self reducion c. Bilateral,
Patellar subluxa,on Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no. 4 472-479 History taking is important: a. Trivial or significant injury b. Requires Hospital or self reducion c. Bilateral,
OrthoMap Express Knee Product Guide. OrthoMap Express Knee Navigation Software 2.0
 OrthoMap Express Knee Product Guide OrthoMap Express Knee Navigation Software 2.0 Product Guide 1 Introduction Introduction The Stryker OrthoMap Express Knee Navigation System is providing surgeons with
OrthoMap Express Knee Product Guide OrthoMap Express Knee Navigation Software 2.0 Product Guide 1 Introduction Introduction The Stryker OrthoMap Express Knee Navigation System is providing surgeons with
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
Patellofemoral Pathology
 Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Single Axis Revision Knee System
 Orthopaedics Scorpio TS Single Axis Revision Knee System Scorpio TS Trial Cutting Guide Surgical Protocol Orthopaedics Scorpio TS Single Axis Revision Knee System Scorpio TS Trial Cutting Guide Surgical
Orthopaedics Scorpio TS Single Axis Revision Knee System Scorpio TS Trial Cutting Guide Surgical Protocol Orthopaedics Scorpio TS Single Axis Revision Knee System Scorpio TS Trial Cutting Guide Surgical
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Evolution. Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee. Key Aspects
 Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Evolution Medial-Pivot Knee System The Bi-Cruciate-Substituting Knee Key Aspects MicroPort s EVOLUTION Medial-Pivot Knee System was designed to recreate the natural anatomy that is lost during a total
Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 331, pp 35-46 0 1996 Lippincott-Raven Publishers Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty Pascal L. Poilvache, MD*;
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 331, pp 35-46 0 1996 Lippincott-Raven Publishers Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty Pascal L. Poilvache, MD*;
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Ye-Ran Li, Yu-Hang Gao, Xin Qi *, Jian-Guo Liu, Lu Ding, Chen Yang, Zheng Zhang and Shu-Qiang Li
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing
 A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
How to Minimize Rotational Conflict between Femoral & Tibial Component in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.454 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 56(2):454-459, 2015 How to Minimize Rotational Conflict between Femoral & Tibial Component in
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2015.56.2.454 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 56(2):454-459, 2015 How to Minimize Rotational Conflict between Femoral & Tibial Component in
Tibial Base Design Factors Affecting Tibial Coverage After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Bases
 Tibial Base Design Factors Affecting Tibial Coverage After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Bases Chadd Clary, PhD I Staff Engineer I DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Daren Deffenbaugh,
Tibial Base Design Factors Affecting Tibial Coverage After Total Knee Arthroplasty: Symmetric Versus Asymmetric Bases Chadd Clary, PhD I Staff Engineer I DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction Daren Deffenbaugh,
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Mako Partial Knee Patellofemoral
 Mako Partial Knee Patellofemoral Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Surgical reference guide Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative implant planning... 4 Intra-operative planning....
Mako Partial Knee Patellofemoral Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Surgical reference guide Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative implant planning... 4 Intra-operative planning....
TKA Gap Planning. Supporting healthcare professionals
 TKA Gap Planning The NAVIO TKA Gap Planning stage helps you adjust the plan based on gap information between the femur and tibia implants. Supporting healthcare professionals Interactive Views Four interactive
TKA Gap Planning The NAVIO TKA Gap Planning stage helps you adjust the plan based on gap information between the femur and tibia implants. Supporting healthcare professionals Interactive Views Four interactive
Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1): pissn eissn Knee Surgery & Related Research
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based comparison of varus and valgus knees
 Cohen et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:92 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1133-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based
Cohen et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2019) 14:92 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1133-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access How coronal alignment affects distal femoral anatomy: an MRI-based
Case Report. Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology
 Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Case Report Antegrade Femur Lengthening with the PRECICE Limb Lengthening Technology S. Robert Rozbruch, MD Hospital for Special Surgery New York, NY, USA ABSTRACT This is a case illustrating a 4.5 cm
Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee
 Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee By Mark C. Komosa Submitted to the graduate degree program in Bioengineering and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas in partial fulfillment
Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee By Mark C. Komosa Submitted to the graduate degree program in Bioengineering and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas in partial fulfillment
Anterior referencing versus posterior referencing in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective observational study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Choudhary P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jan;3(1):66-70 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164789
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Choudhary P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jan;3(1):66-70 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164789
Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff),
 Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff), Consultant Knee Surgeon NHS: The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital & Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham MRI Knee:
Mr. S. Tanweer Ashraf MS, MRCS (Ed), FRCS (Eng). FRCS (Tr&Orth) MSc Ortho Engineering (Cardiff), Consultant Knee Surgeon NHS: The Royal Orthopaedic Hospital & Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham MRI Knee:
Calculating position of joint line of knee using various radiological parameters based on Indian population
 2017; 3(3): 1118-1123 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 1118-1123 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-05-2017 Accepted: 02-06-2017 R Amarnath Senior Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic
2017; 3(3): 1118-1123 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(3): 1118-1123 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-05-2017 Accepted: 02-06-2017 R Amarnath Senior Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedic
Zimmer Gender Solutions Natural-Knee Flex System
 Zimmer Natural-Knee Flex System Because Men and Women are Different Two distinct shapes for men and women. Two distinct shapes for men and women. Industry-leading technology. The proven success of the
Zimmer Natural-Knee Flex System Because Men and Women are Different Two distinct shapes for men and women. Two distinct shapes for men and women. Industry-leading technology. The proven success of the
PIN GUIDE SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 PIN GUIDE SYSTEM with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are
PIN GUIDE SYSTEM with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments System This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pin Guide Surgical Technique The following steps are
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE KNEE, PATELLA, and FEMUR
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE KNEE, PATELLA, and FEMUR KNEE AP Projection Patient Position: Part Position: Leg in Center Femoral condyles Central Ray: - Asthenic patient - if ASIS to tabletop is < 19 cm Sthenic patient
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE KNEE, PATELLA, and FEMUR KNEE AP Projection Patient Position: Part Position: Leg in Center Femoral condyles Central Ray: - Asthenic patient - if ASIS to tabletop is < 19 cm Sthenic patient
FACTORS AFFECTING PATELLAR TRACKING IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 FACTORS AFFECTING PATELLAR TRACKING IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Essay submitted in partial fulfillment of M.Sc. Degree in Orthopaedic surgery Cairo University By Ahmed Ali Ahmed Ali Elsayed M.B.B.Ch Supervised
FACTORS AFFECTING PATELLAR TRACKING IN TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Essay submitted in partial fulfillment of M.Sc. Degree in Orthopaedic surgery Cairo University By Ahmed Ali Ahmed Ali Elsayed M.B.B.Ch Supervised
VARIABILITY OF THE POSTERIOR CONDYLAR ANGLE
 VARIABILITY OF THE POSTERIOR CONDYLAR ANGLE Łukasz Cieliński, Damian Kusz, Michał Wójcik Department of Orthopedics Medical University of Silesia in Katowice Introduction Correct positioning of implants
VARIABILITY OF THE POSTERIOR CONDYLAR ANGLE Łukasz Cieliński, Damian Kusz, Michał Wójcik Department of Orthopedics Medical University of Silesia in Katowice Introduction Correct positioning of implants
Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation
 Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
Surgical Technique Distal Cut First Femoral Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Femoral preparation Contents Introduction...3 DCF femoral highlights...4 Preoperative planning...6
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Resected femoral anthropometry for design of the femoral component of the total knee prosthesis in a Korean population
 Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Resected femoral anthropometry for design of the femoral component of the total knee prosthesis in a Korean population Dai-Soon Kwak 1, Suhyoun Han 2, Chang
Original Article pissn 2093-3665 eissn 2093-3673 Resected femoral anthropometry for design of the femoral component of the total knee prosthesis in a Korean population Dai-Soon Kwak 1, Suhyoun Han 2, Chang
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. 5 in 1. Conventional instrumentation 07/11/2013
 ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
ANATOMIC SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5 in 1 Conventional instrumentation PRO.GB.933/1.0 Octobre 2013 2 Tibial step 3 Intramedullary technique - Based on the preoperative plan, drill the medullary canal with the
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM. TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments
 RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
RESECTION GUIDE SYSTEM TRUMATCH Personalized Solutions Surgical Technique with ATTUNE Knee INTUITION Instruments RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the ATTUNE Knee
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year
 Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
Cementless Oxford unicompartmental knee replacement shows reduced radiolucency at one year H. Pandit, C. Jenkins, D. J. Beard, J. Gallagher, A. J. Price, C. A. F. Dodd, J. W. Goodfellow, D. W. Murray From
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE
 ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Chronic patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental
 Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental Surgical reference guide Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative planning.... 4 Intra-operative planning....
Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental Surgical reference guide Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative planning.... 4 Intra-operative planning....
Are Current Total Knee Arthroplasty Implants Designed to Restore Normal Trochlear Groove Anatomy?
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Are Current Total Knee Arthroplasty Implants Designed to Restore Normal Trochlear Groove Anatomy? Kartik M. Varadarajan, PhD,*y Harry E. Rubash, MD,* and
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Are Current Total Knee Arthroplasty Implants Designed to Restore Normal Trochlear Groove Anatomy? Kartik M. Varadarajan, PhD,*y Harry E. Rubash, MD,* and
Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane
 Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane Yifei Dai, Ph.D., Dwight Todd. Zimmer Inc, Warsaw, IN, USA. Disclosures: Y. Dai: 3A; zimmer inc. 4; zimmer
Impact of Intramedullary Reaming Depth on Establishing Femoral Canal Axis in the Sagittal Plane Yifei Dai, Ph.D., Dwight Todd. Zimmer Inc, Warsaw, IN, USA. Disclosures: Y. Dai: 3A; zimmer inc. 4; zimmer
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Pin Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PIN GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Pin Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PIN GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA High Performance
The Geometry of the Trochlear Groove
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI.07/s11999-009-1156-4 CLINICAL RESEARCH The Geometry of the Trochlear Groove Farhad Iranpour MD, Azhar M. Merican BM, MS(Orth), Wael Dandachli MRCS, Andrew A. Amis DSc(Eng), Justin
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI.07/s11999-009-1156-4 CLINICAL RESEARCH The Geometry of the Trochlear Groove Farhad Iranpour MD, Azhar M. Merican BM, MS(Orth), Wael Dandachli MRCS, Andrew A. Amis DSc(Eng), Justin
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
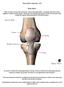 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION S A. Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical. ATechnique
 NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
NEXGEN COMPLETE KNEE SOLUTION ATechnique Tibial Stem Extension & Augmentation Surgical INTRODUCTION The NexGen Complete Knee Solution Intramedullary Tibial Instruments have been designed to provide an
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
