Effects of osteoformin in the rapid distraction osteogenesis of rabbit mandibles
|
|
|
- Reynard Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 135 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of osteoformin in the rapid distraction osteogenesis of rabbit mandibles Ezher Hamza Dayisoylu, Alper Pampu, Figen Cizmeci Senel, Ercument Önder, Dogan Dolanmaz, Nuray Yilmaz Altintas, Mustafa Cihat Avunduk Abstract Objective: To evaluate the effects of osteoformin on mineralisation and quality of the new bone formation during rapid distraction osteogenesis. Methods: This multi-centre study was conducted at the Karadeniz Technical University, Middle East Technical University and Selcuk University. The experimental study was conducted from January 2010 to September 2012 and comprised New-Zealand rabbits that were randomly divided into three groups. In group I distraction rate was 1 mm/day while in groups II and III distraction rates were 2mm/day and 1 mm/day. In groups I and II 100µg/kg osteoformin was injected after the latency period. Distraction region was evaluated by radiological, histomorphometrical and dual energy X-ray absorptiometry analyses. SPSS 17 was used for statistical analysis. Results: There were 18 rabbits with each of three groups having 6(33.3%). Accelerated bone healing was noted in groups I and II compared with group III (p<0.05). No significant differences were indicated between groups I and II (p>0.05). Conclusion: Local injection of osteoformin was effective in the craniomaxillofacial distraction osteogenesis in rabbits. Further experimental studies are recommended before using osteoformin on humans. Keywords: Distraction osteogenesis, Bone healing, Negatively-charged peptide, Distraction rate, Animal model. (JPMA 66: 135; 2016) Introduction Distraction osteogenesis (DO) is a widely used procedure in oral and maxillofacial deformities. Although its principles in orthopaedic surgery have been successfully applied, the rate, rhythm and consolidation period are common problems for craniomaxillofacial DO. 1,2 Prolonged distraction and consolidation period may lead to some other problems such as pin tract-soft tissue or bone infection, patient discomfort and related social problems. 2 Shortening the consolidation period via accelerated bone formation is one of the most emphasised points in DO. For this purpose agents such as zoledronic acid, electric and ultrasound stimulation, matrix metalloproteinase-1, bone morphogenetic protein-2 and hyperbaric oxygen with different rate and rhythm protocols have been investigated. 3-7 In the healing of fractured bones, electrical environment surrounding the injured area is an evident fact. Earlier studies showed negatively-charged resins increased bone formation whereas positively-charged resins had negative response to osteogenesis with inflammatory and fibroblastic activity 4,8,9 Osteoformin (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis MO), a polymer polyaspartate, is one of the Baskent University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Bahcelievler, Ankara, Turkey. Correspondence: Ezher Hamza Dayisoylu. edayisoylu@gmail.com negatively-charged resins. Osteoformin has been suggested to decrease healing time with improved bone quality with increased alkaline phosphotase activity and mineralisation. 10 Osteoformin, which was claimed to accelerate healing in femoral fractures, was also administered successfully to the craniomaxillofacial DO. In a previous in vivo study it was found that osteoformin increased maturation and healing rate of the new bone formation during DO in the craniomaxillofacial region. 11 The present study was planned to investigate the behaviour of osteoformin during rapid DO, which was proven to increase maturation and healing rate during bone lengthening in mandible. Materials and Methods The experimental study was conducted from January 2010 to September 2012 with the ethical approval of Karadeniz Technical University Animal Research Ethics Committee. This multi-centre study was conducted at the Karadeniz Technical University, Middle East Technical University and Selcuk University. It comprised male 20- week-old New Zealand white rabbits, each weighting between 2.2 and 3.2kg, that were randomly divided into three experimental groups. The surgical procedure was performed in line with a previous study. 12 All animals were administered intramuscular IM) penicillin G for the postoperative 5 days, given a soft diet and water ad libitum, and kept alone in single cages during the study.
2 Effects of osteoformin in the rapid distraction osteogenesis of rabbit mandibles 136 In group I distraction rate was 1mm/day, while in groups II and III distraction rates were 2mm/day and 1mm/day respectively. After a latency period of 5 days, in groups I and III the left mandibles were lengthened 0.5mm every 12 hours for 10days. In group II the left mandibles were lengthened 1.0 mm every 12 hours for 5 days. In groups I and II, 100µg/kg osteoformin in 100µL/kg phosphatebuffered saline (PBS) was injected into the central zone of distraction gap at the 1st and 7th days after the latency period as described in literature. 9,10 In group III only 100µL/kg PBS was injected on the same days. The distraction apparatus was kept 42 days for consolidation. On postoperative day 42, the animals were sacrificed with high dose of sodium pentothal injection. The mandibles were dissected and placed in 10% buffered formalin solution. Plain radiographs were taken using Trophy X-ray unit (Kodak Co. France). Specimens were placed on an occlusal film, and X-ray was directed from the buccal side of the mandibles. Radiography procedure was performed under a standard condition of 3.2-mA and a tube-to-film distance of 10cm. All radiographic evaluations were performed by the same blinded radiologist. Sections were examined for the union or non-union in the field of distraction gap. New bone formation was evaluated by 0-2+ scale as follows; (0): Non- union of the specimen;(1): Bone formation less than 30% of the specimen; and (2): Bone formation more than 30% of the specimen. After radiological examination the specimens were evaluated using Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to determine bone mineral density (BMD; g) and bone mineral content (BMC;g/cm 2 ) values in the distraction area. Lunar DPX-IQ (Digital Picture Exchange - Image Quality) device (Madison, WI) equipped with small animal software used for measurement of DEXA. The appendicular programme was used and the measurements were performed in 0.032mm 2 space in the distraction gap. Following DEXA measurements of the distraction gaps, specimes were fixed in 10% buffered paraformaldehyde for 48 hours and decalcified in ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution. Tissue specimens were prepared in an autotechnicon, embedded in paraffin and sectioned with microtome. The sections (5µm) were stained with Haematoxylin & Eosin (H&E). Stained specimens were investigated by a Nikon Eclipse E400 (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) light microscope. For each specimen, the same area was photographed after staining by using a Nikon Coolpix 5000 photograph attachment. The photograph of Nikon micrometer microscope slide was also taken during the procedure. All photographs were then transferred into computer environment and analysed using Clemex Vision Lite 3.5 Image Analysis programme (Clemex Technologies, Longueuil, Quebec, Canada). The length was calibrated by comparing the photograph of specimen with the photograph of Nikon micrometer microscope slide, which was taken under the same magnification. Areas of mm 2 (square micrometre) areas was designated with using Clemex Vision Lite 3.5 Image Analysis programme. Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, capillaries, fibroblasts and collagen fibres were marked with the same image analysis programme in mm 2 area. New bone forming area and cartilaginous area were measured, but damaged cells were not evaluated. The marked cells were counted automatically with the same image analysis programme. The reader was masked to the origin of the specimen. SPSS 17 was used for the statistical analysis. Kruskal-Wallis analysis followed by Mann Whitney U test with Bonferroni correction were applied. Results Initially 21 rabbits were included, but 3(14%) were excluded before the end of the latency period. Of them 2(66%) removed the pins of the distractors, and 1(33.3%) rabbit underwent unexpected weight loss. Groups I, II and III lost 1(14%) rabbit each, leaving a total of 18(86%) rabbits each with a mean weight 2.6±0.23 kg for Table-1: Radiological evaluation of bone formation in distraction gaps Group I 0% 16.6% A 83.3% C Group II 0% 33.3% A 66.6% C Group III 33.3% 50% B 16.6% D *In each column different superscript capital letters indicate significant differences between the groups (p<0.05). Table-2: Mean values of BMC and BMD in the distraction gap with DEXA. BMC (g/cm 2 ) BMD (g) Group I 0,008±0,001 A 0,264±0,025 A Group II 0,009 ±0,001 A 0,287±0,037 A Group III 0,005 ±0,000 B 0,156±0,018 B *In each column different superscript capital letters indicate significant differences between the groups (p<0,05). DEXA: Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry BMC: Bone mineral content BMD: Bone mineral density. Vol. 66, No. 2, February 2016
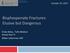
3 137 E. H. Dayisoylu, A. Pampu, F. C. Senel, et al Figure: Histological (left) and radiological (right) view of the specimens. Note the newly-formed bone area in groups (Haematoxylin-eosin) a: Osteoblast b: Osteoclast c: Vessel e: Fibroblast f: Kollagen g: Newly-formed bone. evaluation, with each of the three groups having 6(33.3%) animals. All rabbits recovered uneventfully from surgery and none experienced post-operative complications, and distractors were stable until sacrifise. Obvious crossbite and overgrowth of the lower incisor developed in all rabbits. A statistically significant difference between the groups for new bone formation was observed during radiological evaluation (p=0.037). Increased bone formation was noted in groups I and II compared with group III (p= and p=0.01). On the other hand, intergroup analysis indicated no significant differences between the groups I and II (p=0.523) (Table-1). Evident osteoblastic activity with new bone formation was noted in groups I and II compared with group III (Figure). A statistically significant difference between the groups
4 Effects of osteoformin in the rapid distraction osteogenesis of rabbit mandibles 138 Table-3: Mean values of newly-formed bone area, vessels, number of osteoblasts, osteoclasts, collagen fibres and fibroblasts in the distraction area. Group I Group II Group III Newly formed bone area (mm 2 ) ± A ±171769,3 A ± B Vessels 18.2±4.1 A 16.8±5,3 A 14.6±5.4 B Osteoblasts 63.1±22.5 A 51.4±12,6 A 37.6±4.2 B Osteoclasts 8.7± ±4,1 7.5±2.5 Collagen fibers 14.9±3.8 A 14.6±14,9 A 12.3±7.3 B Fibroblasts 36.5±13.8 A 34.2±3,9 A 31.0±6.9 B *In each line different superscript capital letters indicate signficant differences between the groups (p<0,05). The mean difference is significant at the <0.05 level. regarding BMC and BMD values were observed during DEXA analysis (p=0.043). Increased BMC and BMD values were noted in groups I and II compared with group III (p= and p= 0.043). Intergroup analysis indicated no significant differences between groups I and II (p=0.152) (Table-2). Histomorphometrical analysis comparing bone formation, number of vessels, number of osteoblasts and number of collagen fibres and fibroblasts showed that groups I and II had significantly greater values than group III (p=0.002; p=0.033; p=0.042; p=0.020; p=0.005, respectively). Intergroup analysis indicated no significant differences between groups I and II (p>0.05). No significant differences were noted between the groups regarding the number of osteoclasts (p=0.054) (Table-3). Discussion The application of DO for adjusting congenital deformities occurring in craniomaxillofacial area became a popular technique and many operations have been performed all around the world. 12,13 The reduced necessity of bone grafting and donor-site morbidity and the concomitant adaptation of the soft-tissue, called distraction histogenesis, are the main advantages of craniomaxillofacial DO. 14 The main disadvantage of DO in the craniofacial skeleton is the long distraction and consolidation periods. The latency, rate, rhythm and consolidation periods are common problems because of prolonged distraction time. 2,3 In addition, the risk of injury, fractures in the regenerated bone, bony union with fibrous callus formation and even non-union and associated social problems complicate the application of DO Rapid DO would attenuate the complications associated with the overall treatment time. The intramembranous bones of the craniofacial skeleton, which has a generous blood flow, may permit the rapid distraction procedure. 18 Different rate and rhythm protocols were investigated for rapid distraction, but poor ossification, fibrous or nonunion of the fragments were noted in earlier experimental studies, therefore adjunctive agents and techniques have been used for accelerated DO in order to reduce the time required for optimum consolidation. 3-7,19 The negatively-charged dextran beads have been successfully used for critical-sized defects in the craniofacial area. The negatively-charged beads were found to have bone formation stimulating capacity whereas positively-charged beads were nonosteogenic. 8,9 Osteoformin was suggested to accelerate the rate of fracture healing in a closed femoral fracture. 10 In a study, osteoformin was administered to the craniomaxillofacial DO. It was shown that osteoformin significantly increased maturation and healing rate of new bone formation in rabbits during DO in the mandible. One study noted that osteoformin significantly increased BMD and BMC values in distraction region. 11 In the present study, although there were no significant differences observed between groups I and II, increased BMC and BMD values were noted compared with group III which was consistent with the literature. 11 Histomorphometric results also supported DEXA results; an increased number of the -formed bone area, number of vessels, osteoblasts, collagen fibres and fibroblasts were noted in groups I and II compared with group III. However, there were no significant differences between the groups regarding the number of osteoclasts. In the present study, osteoformin increased mineralisation and quality of the regenerate in the time course of consolidation. Although radiological analysis indicated no significant differences between groups I and II, but increased bone formation was noted in groups I and II compared with group III. In addition, obvious radioopacity was noted across the distraction gap in groups I and II, whereas incomplete union at the central zone of the distraction regenerate was noted in group III. Therefore, adjunctive osteoformin injection may be effective in reducing overall treatment time by increasing the resistance of the regenerated bone in DO. The majority of the complications in DO are related to long duration of therapy, therefore increased efforts were made to shorten the treatment with accelerated bone healing. Adjunctive therapies in DO are usually intended to shorten the duration of consolidation by increasing resistance of the regenerate. Osteoformin was previously suggested to increase BMC and BMD values at a rate of 1mm/day distraction. 11 In our study, osteoformin Vol. 66, No. 2, February 2016
5 139 E. H. Dayisoylu, A. Pampu, F. C. Senel, et al improved healing of regenerate at a rate of 2mm/day distraction that also shortened the duration of distraction period. Prolonged distraction and consolidation periods may result in the failure of the region of regenerate as a result of non-function atrophy, increased risk of infection and osteoporosis in the surrounding bone caused by leaving the external fixator in place for a long time and functional and psychological problems. 20 Therefore, osteoformin may encourage the rapid DO protocol with accelerated bone healing. Conclusion Histomorphometrical analysis and DEXA results indicated that local injection of osteoformin during DO was effective in the craniomaxillofacial region in rabbits. DEXA results also supported the idea that the administration of osteoformin may allow 2mm/day instead of 1mm/day elongation. Further experimental studies are needed to be conducted before using osteoformin on humans. References 1. McCarthy JG, Stelnicki EJ, Mehrara BJ, Longaker MT. Distraction osteogenesis of the craniofacial skeleton. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2001;107: Cheung LK, Zheng LW. Effect of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on mandibular distraction at different rates in an experimental model. J Craniofac Surg. 2006; 17: Tekin U, Tuz HH, Onder E, Ozkaynak O, Korkusuz P. Effects of alendronate on rate of distraction in rabbit mandibles. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008; 66: Kawamoto K, Kim WC, Tsuchida Y, Tsuji Y, Fujioka M, Horii M et al. Effects of alternating current electrical stimulation on lengthening callus. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2005; 14: Eberson CP, Hogan KA, Moore DC, Ehrlich MG. Effect of lowintensity ultrasound stimulation on consolidation of the regenerate zone in a rat model of distraction osteogenesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2003; 23: Cheung LK, Zheng LW. Effect of recombinant human tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in mandibular distraction osteogenesis in rabbits: a computed tomographic study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006; 44: Salgado CJ, Raju A, Licata L, Patel M, Rojavin Y, Wasielewski S, et al. Effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy on an accelerated rate of mandibular distraction osteogenesis. J Plast Rec Aest Surg. 2009; 62: Snyders RV Jr, Eppley BL, Krukowski M, Delfino JJ. Enhancement of repair in experimental calvarial bone defects using calcium sulfate and dextran beads. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993; 51: Krukowski M, Shively RA, Osdoby P, Eppley BL. Stimulation of craniofacial and intramedullary bone formation by negatively charged beads. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1990; 48: Bi LX, Mainous EG, Zeng Y, Buford WL. Osteoformin accelerates fresh fracture healing in rats. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65: Pampu AA, Ozkaynak O, Senel FC, Cankaya M, Dolanmaz D, Ersoz S, et al. The effects of osteoformin on mineralisation and quality of newly formed bone during mandibular distraction osteogenesis in rabbits. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 108: Franco J, Coppage J, Carstens MH. Mandibular distraction using bone morphogenic protein and rapid distraction in neonates with Pierre Robin syndrome. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21: Miloro M. Mandibular distraction osteogenesis for pediatric airway management. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 68: Apaydin A, Yazdirduyev B, Can T, Keklikoglu N. Soft tissue changes during distraction osteogenesis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011; 40: Heidari P, Abbaspour A, Baghdadi T, Espandar R, Farzan M, Amanpour S, et al. Effect of risedronate on bone resorption during consolidation phase of distraction osteogenesis: a rabbit model. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010; 18: Cho BC, Park JW, Baik BS, Kwon IC, Kim IS. The role of hyaluronic acid, chitosan, and calcium sulfate and their combined effect on early bony consolidation in distraction osteogenesis of a canine model. J Craniofac Surg. 2002; 13: Long J, Tang W, Fan YB, Tian WD, Feng F, Liu L, et al. Effects of rapid distraction rate on new bone formation during mandibular distraction osteogenesis in goats. Injury. 2009; 40: Farhadieh RD, Gianoutsos MP, Dickinson R, Walsh WR. Effect of distraction rate on biomechanical, mineralization, and histologic properties of an ovine mandible model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000; 105: Park BH, Yoon SJ, Jang KY, Kim MR, Lee HS, Kim KB et al. COMPangiopoietin-1 accelerates bone formation during distraction osteogenesis. Bone. 2010; 46: Ilizarov GA. Clinical application of the tension-stress effect for limb lengthening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990; 8-26.
Changes in the temporomandibular joint after mandibular lengthening with different rates of distraction
 Shujuan Zou, DDS, MS Department of Orthodontics Jing Hu, DDS, MS, PhD Dazhang Wang, DDS, FICD Jihua Li, DDS, MS Zhenglong Tang, DDS, MS Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Huaxi School of Stomatology
Shujuan Zou, DDS, MS Department of Orthodontics Jing Hu, DDS, MS, PhD Dazhang Wang, DDS, FICD Jihua Li, DDS, MS Zhenglong Tang, DDS, MS Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Huaxi School of Stomatology
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Intraoral mandibular distraction osteogenesis in facial asymmetry patients with unilateral temporomandibular joint bony ankylosis
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002; 31: 544 548 doi:10.1054/ijom.2002.0297, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Intraoral mandibular distraction osteogenesis in facial asymmetry patients
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002; 31: 544 548 doi:10.1054/ijom.2002.0297, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Intraoral mandibular distraction osteogenesis in facial asymmetry patients
Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 1014 1019 CASE REPORT Use of internal callus distraction in the treatment of congenital brachymetatarsia Naoto Yamada*, Yoshihiro Yasuda, Nobuko Hashimoto,
The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia
 The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity
The Effect of Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) during Distraction Osteogenesis of the Tibia Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity
Differences in mandibular distraction osteogenesis after corticotomy and osteotomy
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002; 31: 185 189 doi:10.1054/ijom.2001.0193, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Differences in mandibular distraction osteogenesis after corticotomy and osteotomy
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002; 31: 185 189 doi:10.1054/ijom.2001.0193, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Differences in mandibular distraction osteogenesis after corticotomy and osteotomy
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins during Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
 Experimental Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins during Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis Paolo Campisi, M.D., Reggie C. Hamdy, M.D., Dominique Lauzier, Masatoshi Amako, M.D., Frank Rauch, M.D.,
Experimental Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins during Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis Paolo Campisi, M.D., Reggie C. Hamdy, M.D., Dominique Lauzier, Masatoshi Amako, M.D., Frank Rauch, M.D.,
Tobacco and Bone Health
 Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Tobacco and Bone Health Prof. Dr. Alok Chandra Agrawal MS Orthopaedics, DNB Orthopaedics, PhD Orthopaedics MAMS All India Institute of Medical Sciences Raipur CG Cigarette smoking is commonly identified
Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2005, 71, 577-581 ORIGINAL STUDY Prophylactic surgical correction of Crawford s type II anterolateral bowing of the tibia using Ilizarov s method Hani EL-MOWAFI, Mazen ABULSAAD, Wael
Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis CASE REPORT
 Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis Peter J. Taub, MD* James P. Bradley, MD* Henry K. Kawamoto, MD, DDS* Los Angeles, California Pittsburgh,
Closure of an Oronasal Fistula in an Irradiated Palate by Tissue and Bone Distraction Osteogenesis Peter J. Taub, MD* James P. Bradley, MD* Henry K. Kawamoto, MD, DDS* Los Angeles, California Pittsburgh,
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ultrasound_accelerated_fracture_healing_device 12/1994 2/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: ultrasound_accelerated_fracture_healing_device 12/1994 2/2017
Case Reports Pediatric Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis: The Present and the Future
 Case Reports Pediatric Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis: The Present and the Future Samuel T. Rhee, MD, and Steven R. Buchman, MD Ann Arbor, Michigan Pediatric mandibular distraction osteogenesis (MDO)
Case Reports Pediatric Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis: The Present and the Future Samuel T. Rhee, MD, and Steven R. Buchman, MD Ann Arbor, Michigan Pediatric mandibular distraction osteogenesis (MDO)
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Effect of Strontium Citrate on Bone Consolidation During Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis
 The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Effect of Strontium Citrate on Bone Consolidation During Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis Benjamin A.
The Laryngoscope VC 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Effect of Strontium Citrate on Bone Consolidation During Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis Benjamin A.
Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/383 Assessment of Regenerate in Limbs by Ilizarov External Fixation T Suresh Kumar 1, Swagat Mahapatra 2 1 Assistant
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1
 Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1 20-2 From: Al-Tayyar Basic Biomechanics Bending Axial Loading Tension Compression Torsion Bending Compression Torsion 20-3 From: Le Fracture Mechanics Figure
Section 20: Fracture Mechanics and Healing 20-1 20-2 From: Al-Tayyar Basic Biomechanics Bending Axial Loading Tension Compression Torsion Bending Compression Torsion 20-3 From: Le Fracture Mechanics Figure
GENERAL DISCUSSION & SUMMARY
 GENERAL 9 DISCUSSION & SUMMARY 139 140 Chapter 9 The aim of this thesis was to investigate problems, obstacles, and complications arising from treatment using mandibular DO. Further specification for various
GENERAL 9 DISCUSSION & SUMMARY 139 140 Chapter 9 The aim of this thesis was to investigate problems, obstacles, and complications arising from treatment using mandibular DO. Further specification for various
First Issued: 12/19/2007 Revisions: 8/12/2009, 11/09/2010, 3/1/2015
 U n i t e d H e a l t h C a r e G u i d e l i n e Division UnitedHealthcare Departments Community Plan Products Children s Rehabilitative Services (CRS) State :Arizona Title: CRS Maxillo Mandibular Osteodistraction
U n i t e d H e a l t h C a r e G u i d e l i n e Division UnitedHealthcare Departments Community Plan Products Children s Rehabilitative Services (CRS) State :Arizona Title: CRS Maxillo Mandibular Osteodistraction
Subject: Non-Invasive Electrical Bone Growth Stimulators (EBGS)
 09-E0000-22 Original Effective Date: 06/15/00 Reviewed: 04/28/16 Revised: 05/15/16 Subject: Non-Invasive Electrical Bone Growth Stimulators (EBGS) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
09-E0000-22 Original Effective Date: 06/15/00 Reviewed: 04/28/16 Revised: 05/15/16 Subject: Non-Invasive Electrical Bone Growth Stimulators (EBGS) THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Callus formation during healing of the repaired tendon-bone junction
 Callus formation during healing of the repaired tendon-bone junction A RAT EXPERIMENTAL MODEL N. Hibino, Y. Hamada, K. Sairyo, K. Yukata, T. Sano, N. Yasui From University of Tokushima Graduate School,
Callus formation during healing of the repaired tendon-bone junction A RAT EXPERIMENTAL MODEL N. Hibino, Y. Hamada, K. Sairyo, K. Yukata, T. Sano, N. Yasui From University of Tokushima Graduate School,
Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 214-218 TECHNICAL NOTE Management of a large post-traumatic skin and bone defect using an Ilizarov frame Pieter D HOOGHE, Koen DEFOORT, Johan LAMMENS, Jos STUYCK From the
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis
 In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
Article in press. Distraction Osteogenesis: Role and Clinical Application in the Maxillofacial Region. Case Report
 Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis: Role and Clinical Application in the Maxillofacial Region Thongchai Nuntanaranont 1, Wipapan Ritthagol 2 and Butsakorn Akarawatcharangura 1 1 Department of Oral and
Case Report Distraction Osteogenesis: Role and Clinical Application in the Maxillofacial Region Thongchai Nuntanaranont 1, Wipapan Ritthagol 2 and Butsakorn Akarawatcharangura 1 1 Department of Oral and
Research Article. Abstract
 Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Research Article Assessment of Bone Healing During Antegrade Intramedullary Rod Femur Lengthening Using Radiographic Pixel Density Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/jaaos by BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3XGJiJSDa6kLdjliRzOOsR+bI3gZWJ99prwiH9JOuTYY=
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Promoting Fracture Healing Through Systemic or Local Administration of Allogeneic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Gang Li Dept. of Orthopaedics and Traumatology School of Biomedical Sciences, The Chinese University
Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI Procedure. Subtalar arthrodesis
 OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Subtalar Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report SUBTALAR NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries and Dr. Brandon M. Scharer Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic,
Ankle and subtalar arthrodesis
 OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Ankle Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report ANKLE NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI
OSTEOAMP Allogeneic Morphogenetic Proteins Ankle Nonunions OSTEOAMP Case Report ANKLE NONUNIONS Dr. Jason George DeVries Orthopedic & Sports Medicine, Bay Care Clinic, 501 N. 10th Street, Manitowoc, WI
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring Fixator
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Stress Fracture Of The Supracondylar Region Of The Femur Induced By The Weight Of The Tibial Ring S Dhar, M Mir Citation S Dhar, M
The Function Effect of Botulimun Toxin A (BtX-A) at the Calf Muscle in Lower Limb Lengthening Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD
 The Function Effect of Botulimun Toxin A (BtX-A) at the Calf Muscle in Lower Limb Lengthening Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction Service Department of Orthopaedic
The Function Effect of Botulimun Toxin A (BtX-A) at the Calf Muscle in Lower Limb Lengthening Dong Hoon Lee, MD, Ph.D, Keun Jung Ryu MD Limb Lengthening and Deformity Correction Service Department of Orthopaedic
Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery
 Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Brief Communication Circumferential skin defect - Ilizarov technique in plastic surgery Vrisha Madhuri, Shankar R. Kurpad, Manasseh Nithyananth, Thilak S Jepegnanam, V. T. K. Titus, Prema Dhanraj Department
Large Experimental Segmental Bone Defects Treated By Bone Transportation With Monolateral External Distractors
 Large Experimental Segmental Bone Defects Treated By Bone Transportation With Monolateral External Distractors Julio De Pablos, M.D., Carlos Barrios, M.D., Carmen Alfaro, M.D., and Jose Cañadell, M.D.
Large Experimental Segmental Bone Defects Treated By Bone Transportation With Monolateral External Distractors Julio De Pablos, M.D., Carlos Barrios, M.D., Carmen Alfaro, M.D., and Jose Cañadell, M.D.
A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral Fracture: Two Case Reports of Curved Femurs
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 213614, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/213614 Case Report Combined Effect of a Locking Plate and Teriparatide for Incomplete Atypical Femoral
Superelastic shape memory alloy (SMA) has
 Transport Distraction Osteogenesis Using Nitinol Spring: An Exploration in Canine Mandible Hong-Zhi Zhou, MD, PhD,* Min Hu, MD, PhD, 1 Kai-Jin Hu, MD, PhD,* Jun Yao, MD, PhD, 1 Liu Yan-Pu, MD, PhD,* Beijing,
Transport Distraction Osteogenesis Using Nitinol Spring: An Exploration in Canine Mandible Hong-Zhi Zhou, MD, PhD,* Min Hu, MD, PhD, 1 Kai-Jin Hu, MD, PhD,* Jun Yao, MD, PhD, 1 Liu Yan-Pu, MD, PhD,* Beijing,
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(2): 78-85, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.78 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 30(2): 78-85, 2018 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2018.30.2.78 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures Following Hip Arthroplasty
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation
 Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
Analysis of Bone Fixation Methods in Digital Replantation Seung Woo Lee, Dong Chul Lee, Jin Soo Kim, Si Young Roh, Kyung Jin Lee Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Gwangmyeong Sungae General
Mechanism of Action. Activating bone healing at every stage
 Mechanism of Action Activating bone healing at every stage Ultrasound Bone Healing System Mechanism of Action The Bone Healing System is a unique fracture healing device that uses low intensity pulsed
Mechanism of Action Activating bone healing at every stage Ultrasound Bone Healing System Mechanism of Action The Bone Healing System is a unique fracture healing device that uses low intensity pulsed
Protocol. Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device
 Protocol Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device (10105) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09, 05/10, 05/11, 01/12,
Protocol Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device (10105) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/15 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09, 05/10, 05/11, 01/12,
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment. William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC
 Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Module 5 - Speaking of Bones Osteoporosis For Health Professionals: Fracture Risk Assessment William D. Leslie, MD MSc FRCPC Case #1 Age 53: 3 years post-menopause Has always enjoyed excellent health with
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Electrical Bone Growth Stimulation File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: electrical_bone_growth_stimulation 4/1981 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Electrical Bone Growth Stimulation File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: electrical_bone_growth_stimulation 4/1981 6/2017 6/2018 6/2017 Description
Abstract. Firas T. Ismaeel, Dept. of Surgery, College of Medicine, Tikrit University
 Bone marrow injection in patients with delayed union and non-union of long Firas T. Ismaeel, Dept. of Surgery, College of Medicine, Tikrit University Abstract In the process of bone formation and healing
Bone marrow injection in patients with delayed union and non-union of long Firas T. Ismaeel, Dept. of Surgery, College of Medicine, Tikrit University Abstract In the process of bone formation and healing
Novel Application of HA-TCP Biomaterials in Distraction Osteogenesis Shortened the Lengthening Time and Promoted Bone Consolidation
 Novel Application of HA-TCP Biomaterials in Distraction Osteogenesis Shortened the Lengthening Time and Promoted Bone Consolidation Yan Wang, 1 Ming Ni, 1 Pei-Fu Tang, 1 Gang Li 2,3 1 Department of Orthopaedic
Novel Application of HA-TCP Biomaterials in Distraction Osteogenesis Shortened the Lengthening Time and Promoted Bone Consolidation Yan Wang, 1 Ming Ni, 1 Pei-Fu Tang, 1 Gang Li 2,3 1 Department of Orthopaedic
Targeting P38 Pathway Regulates Bony Formation via MSC Recruitment during Mandibular Distraction Osteogenesis in Rats
 783 Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2016; 13(10): 783-789. doi: 10.7150/ijms.16663 Targeting P38 Pathway Regulates Bony Formation via MSC Recruitment during Mandibular Distraction
783 Research Paper International Journal of Medical Sciences 2016; 13(10): 783-789. doi: 10.7150/ijms.16663 Targeting P38 Pathway Regulates Bony Formation via MSC Recruitment during Mandibular Distraction
Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis
 Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis Eralp Levent 1, Sen Cengiz 1, Dikmen Goksel 1, Tomak Yılmaz 2, Gulsen Mahir 3,
Comparison of acute compression distraction and segmental bone transport techniques in the treatment of tibia osteomyelitis Eralp Levent 1, Sen Cengiz 1, Dikmen Goksel 1, Tomak Yılmaz 2, Gulsen Mahir 3,
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
DOWNLOAD OR READ : RIGID FIXATION FOR MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : RIGID FIXATION FOR MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 rigid fixation for maxillofacial surgery rigid fixation for maxillofacial pdf rigid fixation for maxillofacial
DOWNLOAD OR READ : RIGID FIXATION FOR MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 rigid fixation for maxillofacial surgery rigid fixation for maxillofacial pdf rigid fixation for maxillofacial
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Protocol. Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device
 Protocol Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device (10105) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/17 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09, 05/10, 05/11, 01/12,
Protocol Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device (10105) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/14 Next Review Date: 01/17 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 09/07, 09/08, 09/09, 05/10, 05/11, 01/12,
We present a series of ten hypertrophic nonunions
 MANAGEMENT OF NONUNION OF FRACTURES BY DISTRACTION WITH CORRECTION OF ANGULATION AND SHORTENING MICHAEL SALEH, SIMON ROYSTON From the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England We present a series of
MANAGEMENT OF NONUNION OF FRACTURES BY DISTRACTION WITH CORRECTION OF ANGULATION AND SHORTENING MICHAEL SALEH, SIMON ROYSTON From the Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, England We present a series of
Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells
 Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Johannes Schneppendahl, MD 1, Jan Grassmann, MD 1, Marcel Betsch, M.D. 2, Michael Wild, MD, PhD 3, Mohssen Hakimi, MD,
Does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Improve Bone Regeneration With Mesenchymal Stem Cells Johannes Schneppendahl, MD 1, Jan Grassmann, MD 1, Marcel Betsch, M.D. 2, Michael Wild, MD, PhD 3, Mohssen Hakimi, MD,
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Skeletal System. The skeletal System... Components
 Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Skeletal System The skeletal System... What are the general components of the skeletal system? What does the skeletal system do for you & how does it achieve these functions? Components The skeletal system
Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
HOW PEMF WORKS. Orthofix Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Technology
 HOW PEMF WORKS Orthofix Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Technology HOW PEMF STIMULATES SPINE FUSION How does PEMF affect spinal fusion? A successful spinal fusion depends on many complex healing processes.
HOW PEMF WORKS Orthofix Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Technology HOW PEMF STIMULATES SPINE FUSION How does PEMF affect spinal fusion? A successful spinal fusion depends on many complex healing processes.
Pattern of bone resorption after extraction
 Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Introduction: A. Bones are very active, living tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment,
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion. Norbert Wiegand
 Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Bone healing, delayed fracture healing and nonunion Norbert Wiegand 2/3 of traumatology: treatment of fractures We have to understand: Structure of the bone Biology of the bone Bone healing Types of Bone
Simultaneous gap arthroplasty and intraoral distraction and secondary contouring surgery for unilateral temporomandibular joint ankylosis
 Sharma et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:12 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0058-0 CASE REPORT Open Access Simultaneous gap arthroplasty and intraoral distraction and secondary contouring
Sharma et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:12 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0058-0 CASE REPORT Open Access Simultaneous gap arthroplasty and intraoral distraction and secondary contouring
Low Intensity Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device
 Page 1 of 14 Medical Policies - DME Low Intensity Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device Print Number: DME101.030 Effective Date: 01-01-2015 Coverage: Low-intensity ultrasound treatment may be
Page 1 of 14 Medical Policies - DME Low Intensity Ultrasound Accelerated Fracture Healing Device Print Number: DME101.030 Effective Date: 01-01-2015 Coverage: Low-intensity ultrasound treatment may be
Temporal and Spatial Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2, -4, and -7 During Distraction Osteogenesis in Rabbits
 ERRATUM Due to a production error, Figures 2 5 were printed in black and white. The complete article, with color figures, is presented below. Temporal and Spatial Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2,
ERRATUM Due to a production error, Figures 2 5 were printed in black and white. The complete article, with color figures, is presented below. Temporal and Spatial Expression of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2,
Case Study. Micrognathia Secondary to Pierre Robin Sequence. Treated with distraction osteogenesis using an internal mandible distractor.
 Case Study Micrognathia Secondary to Pierre Robin Sequence. Treated with distraction osteogenesis using an internal mandible distractor. Micrognathia Secondary to Pierre Robin Sequence Patient profile
Case Study Micrognathia Secondary to Pierre Robin Sequence. Treated with distraction osteogenesis using an internal mandible distractor. Micrognathia Secondary to Pierre Robin Sequence Patient profile
Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide
 Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide Takuya Uemura, MD, PhD; Mitsuhiro Okada, MD, PhD; Takuya Yokoi, MD; Kosuke Shintani, MD; Hiroaki
Successful Bone Healing of Nonunion After Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy for Smokers Treated With Teriparatide Takuya Uemura, MD, PhD; Mitsuhiro Okada, MD, PhD; Takuya Yokoi, MD; Kosuke Shintani, MD; Hiroaki
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH
 PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous
 Krista Weiss, 2014 Gillian Lieberman, MD October 25, 2013 Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous Krista Weiss, Tufts Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD Presentation Outline Our Patient:
Krista Weiss, 2014 Gillian Lieberman, MD October 25, 2013 Bisphosponate Fractures: Elusive but Dangerous Krista Weiss, Tufts Medical School Year IV Gillian Lieberman, MD Presentation Outline Our Patient:
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC)
 BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) Sept 2015 Review: Sept 2018 Bulletin 227: EXOGEN ultrasound bone healing system used for the management of long bone fractures JPC Recommendations:
BEDFORDSHIRE AND LUTON JOINT PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JPC) Sept 2015 Review: Sept 2018 Bulletin 227: EXOGEN ultrasound bone healing system used for the management of long bone fractures JPC Recommendations:
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS
 ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
ILIZAROV METHOD IN TREATMENT OF TIBIAL AND FEMORAL INFECTED NON-UNIONS IN PATEITNES WITH HIGH-ENERGY TRAUMA AND BATTLE-FIELD WOUNDS M. N. Tahmasebi * and Sh. Jalali Mazlouman Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Radiological and histological analysis of synthetic bone grafts in recurring giant cell tumour of bone: a retrospective study
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(1):63-7 Radiological and histological analysis of synthetic bone grafts in recurring giant cell tumour of bone: a retrospective study Hiroyuki Hattori, Hiroaki Matsuoka,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2010;18(1):63-7 Radiological and histological analysis of synthetic bone grafts in recurring giant cell tumour of bone: a retrospective study Hiroyuki Hattori, Hiroaki Matsuoka,
In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft Putty: Improved Bone Formation
 In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft : Improved Bone Formation ABSTRACT BioSphere is a novel bone graft product that was developed using spherical particles of bioactive glass with a narrow,
In Vivo Evaluation of BioSphere Bioactive Bone Graft : Improved Bone Formation ABSTRACT BioSphere is a novel bone graft product that was developed using spherical particles of bioactive glass with a narrow,
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
RUMAIZI SHAARI D.V.M (UPM), M.V.M (UPM) Thesis submitted for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY (PhD)
 INVESTIGATION OF VERTICAL MANDIBULAR DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS ON THE MASTICATORY MUSCLES IN A UNILATERAL HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA LIKE DEFECT IN THE SHEEP MODEL RUMAIZI SHAARI D.V.M (UPM), M.V.M (UPM) Thesis
INVESTIGATION OF VERTICAL MANDIBULAR DISTRACTION OSTEOGENESIS ON THE MASTICATORY MUSCLES IN A UNILATERAL HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA LIKE DEFECT IN THE SHEEP MODEL RUMAIZI SHAARI D.V.M (UPM), M.V.M (UPM) Thesis
Mechanism of Action. Activating bone healing at every stage
 Mechanism of Action Activating bone healing at every stage EXOGEN Ultrasound Bone Healing System The EXOGEN Bone Healing System is a unique fracture healing device that uses low intensity pulsed ultrasound
Mechanism of Action Activating bone healing at every stage EXOGEN Ultrasound Bone Healing System The EXOGEN Bone Healing System is a unique fracture healing device that uses low intensity pulsed ultrasound
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Downloaded by Guangxi University for Nationalities from online.liebertpub.com at 02/20/18. For personal use only. ABSTRACT
 TISSUE ENGINEERING Volume 6, Number 4, 2000 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Promoted Bone Healing at a Rabbit Skull Gap Between Autologous Bone Fragment and the Surrounding Intact Bone with Biodegradable Microspheres
TISSUE ENGINEERING Volume 6, Number 4, 2000 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Promoted Bone Healing at a Rabbit Skull Gap Between Autologous Bone Fragment and the Surrounding Intact Bone with Biodegradable Microspheres
Of approximately 2 million long bone fractures
 Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
Proceedings S.Z.P.G.M.I vol: 13(1-2) 1999, pp. 71-75. Treatment of Tibial Non-Union with the Ilizarov Method Pervaiz Iqbal, Muhammad Maq, Hamid Qayum Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed Hospital,.
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Interesting Case Series. Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review
 Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
Interesting Case Series Traumatic Thumb Amputation: Case and Review Ryan Engdahl, MD, a and Norman Morrison, MD b a Division of Plastic Surgery, New York Presbyterian Hospital, The University Hospital
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND
 Keio Journal of Medicine 34: 123-128, 1985 CASE REPORT AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND MICROVASCULAR SURGERIES TOYOMI FUJINO,*1 RYUZABURO
Keio Journal of Medicine 34: 123-128, 1985 CASE REPORT AN ELEVEN YEAR FOLLOW-UP CASE OF FACIAL HEMIATROPHY TREATED BY COMBINED APPROACHES OF CRANIOFACIAL AND MICROVASCULAR SURGERIES TOYOMI FUJINO,*1 RYUZABURO
Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna with Distraction Osteogenesis: Three Cases
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 656542, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/656542 Case Report Correction of Length Discrepancy of Radius and Ulna
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Stiffness of callus tissue during distraction osteogenesis
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 155 160 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stiffness of callus tissue during distraction osteogenesis T. Floerkemeier, F. Thorey, C. Hurschler, M. Wellmann, F.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2010) 96, 155 160 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stiffness of callus tissue during distraction osteogenesis T. Floerkemeier, F. Thorey, C. Hurschler, M. Wellmann, F.
Calcium Phosphate Cement
 Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Calcium Phosphate Cement Fast-Setting Bone Graft and AutoGraft Extender. * Ossilix is a high performance next generation calcium phosphate cement indicated for filling bony defects in cancellous bone.
Citation for published version (APA): Schortinghuis, J. (2004). Ultrasound stimulation of mandibular bone defect healing s.n.
 University of Groningen Ultrasound stimulation of mandibular bone defect healing Schortinghuis, Jurjen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Ultrasound stimulation of mandibular bone defect healing Schortinghuis, Jurjen IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING
 Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
Paracrine Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Human Adipose tissue in Bone Regeneration.
 Paracrine Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Human Adipose tissue in Bone Regeneration. By Linero I., Chaparro O., 2014 Suzana Tufegdzic 1 Background 2 Background Stem Cells: undifferentiated
Paracrine Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells derived from Human Adipose tissue in Bone Regeneration. By Linero I., Chaparro O., 2014 Suzana Tufegdzic 1 Background 2 Background Stem Cells: undifferentiated
Fracture and Dislocation of Metacarpal Bones, Metacarpophalangeal Joints, Phalanges, and Interphalangeal Joints ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation
 Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy Mammary adenocarcinoma was induced by administering 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a)
Rat Model of Bone Metastasis Obtained by Mammary Cancer Transplantation ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Cancer Research and Therapy Mammary adenocarcinoma was induced by administering 7, 12-dimethylbenz (a)
