Stenosing flexor tenosynovitis (trigger finger) is
|
|
|
- Barry Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An Original Study Recalcitrant Trigger Finger Managed With Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Resection Sohail N. Husain, MD, Sylvan E. Clarke, MD, Glenn A. Buterbaugh, MD, and Joseph E. Imbriglia, MD Abstract Although trigger finger is a condition commonly treated by orthopedic surgeons, we have not found sufficient studies in the literature addressing the treatment of trigger finger that persists following A1 pulley release. We identified 12 fingers in 11 patients with symptoms of trigger finger following A1 pulley release who subsequently underwent resection of 1 or both slips of the flexor digitorum superficialis tendon. Ten patients (11 fingers) presented for follow-up at a mean of 21 months after surgery. All patients had resolution of their symptoms with a mean visual analog score of 1.5 and a mean DASH score of 17. Grip and pinch strength were comparable to the contralateral side. Mean total active range of motion of the affected digit was 252. Resection of 1 or both slips of the flexor digitorum superficialis is an effective method for treatment of recalcitrant trigger finger. Stenosing flexor tenosynovitis (trigger finger) is commonly seen in orthopedic surgery practices. It may be caused by thickening of the pulley (most commonly A1) or of the tendon. The diagnosis can be made from a history of finger stiffness, locking, and catching. Physical examination reveals visible catching as well as tenderness over the A1 pulley. Trigger finger often is initially managed with steroid injection. When this conservative approach fails, the condition can be managed surgically, typically with A1 pulley release performed with open or percutaneous methods. In most patients who undergo A1 pulley release, symptoms resolve. Dr. Husain is Hand Surgeon, Essex Orthopaedics & Optima Sports Medicine, Salem, New Hampshire. Dr. Clarke is Hand Surgeon, The South Bend Clinic, South Bend, Indiana. Dr. Buterbaugh is President, Hand & UpperEx Center, Wexford, Pennsylvania. Dr. Imbriglia is Clinical Professor, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Pittsburgh Medical School, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, and Chairman of the Board, Hand & UpperEx Center. Address correspondence to: Sohail N. Husain, Essex Orthopaedics & Optima Sports Medicine, 16 Pelham Rd, Salem, NH (tel, ; fax, ; , snhusain@yahoo.com). Am J Orthop. 2011;40(12): Copyright Quadrant HealthCom Inc All rights reserved. Despite the high success rate of A1 pulley release, trigger finger sometimes requires revision surgery. There is a paucity of literature on this topic. Review of our clinic s billing records over a 26-month period revealed 12 fingers (11 patients) that had persistent symptoms of locking, catching, or stiffness after open A1 pulley release and were subsequently managed with excision of 1 or both slips of the flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) tendon of the involved finger. Methods Patients Billing records from January 2006 through February 2008 (26 months) were reviewed to identify patients who had undergone resection of a tendon from the hand or fingers. Clinic notes and operative records were reviewed to identify patients who had undergone complete or partial FDS tendon resection after prior A1 pulley release. Surgical Technique All procedures had been performed by 1 of 2 hand surgeons with the assistance of either a fellow or a resident. Each procedure was performed with local anesthesia, intravenous sedation, and a forearm tourniquet. Dissection was performed, using the prior incision for A1 pulley release, until the flexor tendons were identified. A Brunner incision centered at the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint was then made to expose the A3 pulley, which was incised. In 2 patients who demonstrated clicking in the region of the proximal phalanx and PIP joint during the office visit before revision surgery, the approach to the A3 pulley was made before the approach to the A1 pulley. The FDS tendon was identified, and either or both slips of it were transected at the level of the middle phalanx (Figure 1). The decision to transect both slips, or only one, was made by the attending surgeon during the operation, and was based on the condition and size of the FDS tendon. The 2 slips of the FDS tendon were then separated from each other to the level of the Camper chiasm. Traction was applied to deliver the FDS tendon into the palmar wound, and the transected portion of the tendon was resected (Figure 2). The finger was passively brought through a range of motion (ROM) to ensure there was no catching. PIP contracture release was performed as necessary by incising the proximal aspect of the volar plate, though the volar plate was not formally evaluated for laxity before the FDS excision. Skin closure 620 The American Journal of Orthopedics
2 S. N. Husain et al Figure 1. Identification of ulnar slip of flexor digitorum superficialis tendon, clamped in hemostat. was performed with nylon horizontal mattress sutures. A soft dressing was applied and the patient was allowed immediate finger motion as tolerated. Outcomes All patients were invited to return for evaluation at the clinic. They were questioned about symptom resolution, residual pain, and other problem reports. Scores on the DASH (Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand) questionnaire and on a visual analog scale (VAS) for pain were recorded. Active ROM of the involved finger was measured with a small joint goniometer (Baseline, Irvington, New York). Grip strength was measured with a dynamometer (Baseline). Tip pinch strength between the thumb and the affected finger was measured with a pinch gauge (B&L Engineering, Tustin, California). All measurements were compared with those of the uninvolved, contralateral hand. Statistical Analysis Values for joint ROM and grip and pinch strength on both sides were compared using a 2-sample t test and the statistical analysis package on Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, Washington). Figure 2. Delivery of ulnar slip of flexor digitorum superficialis tendon through palmar incision. Part of tendon is noticeably thickened. Results Over a 26-month period, open A1 pulley release was performed on 936 trigger fingers. During the same period, 11 of the patients (12 fingers) had all or part of the FDS tendon resected because of locking, catching, or stiffness after prior A1 pulley release. Of these 11 patients, 10 (11 fingers) presented to our clinic for follow-up and measurements to be used in this study. Mean (SD) age of these 10 patients was 55.5 (12.9) years (range, years). Medical comorbidities included diabetes (3 patients), hypothyroidism (3), and rheumatoid arthritis (1). No patient had prior significant trauma to the finger. No patient had preoperative hyperlaxity with swan-neck deformity or extensor mechanism subluxation, which would mimic a snapping trigger; 5 fingers had preoperative PIP flexion contractures of less than 30, a sixth patient had a mild metacarpophalangeal contracture, and a seventh had generalized finger stiffness. The patient who had the procedure performed on 2 fingers was examined 7 months after the contralateral hand underwent thumb carpometacarpal arthroplasty with flexor carpi radialis graft. Table I lists the patient demographics. There were 6 female and 4 male patients. Six right hands and 4 left hands were involved. The long finger was affected in 7 cases and the ring finger in 4 cases. Ten fingers had 1 prior surgery for the trigger finger, and 1 finger had 3 prior surgeries. Of the 11 fingers, 2 had triggering recur after a period without symptoms (6 months in 1 case, 10 years in the other). The other 9 fingers were recalcitrant, and there was no significant resolution of symptoms between FDS resection and most recent previous surgery. Five of the initial procedures were performed at our practice, and 6 were referrals from other centers. Three of the 11 fingers received steroid injections at our practice before the FDS resection was performed; in each case, symptoms did not improve. Mean (range) time from first procedure to FDS resection was 21 ( ) months. Mean (range) follow-up was 8 (2-15) months. The ulnar slip of the FDS was excised in 4 fingers (3 patients), the radial slip in 2 fingers (2 patients), and both slips in 5 fingers (5 patients). Mean follow-up was 3.9 months for patients who had both slips excised and 12.4 months for patients who had a single slip excised. At the office visit before the FDS resection, 6 patients had symptoms or signs (eg, pain, swelling, tenderness, clicking, catching, nodules) over the proximal December
3 Recalcitrant Trigger Finger Table I. Patient Demographics and Intraoperative Findings Patient Age, Hand Involved Involved Changes in Excised Portion of No. y Sex Dominance Side Finger FDS Tendon FDS Tendon 1 60 F R R Middle Partial rupture Ulnar 2 60 M R R Middle None Both 3 60 F R R Middle None Radial 4 a 62 F R R Middle Partial rupture Ulnar 4 a 62 F R R Ring Degeneration Ulnar 5 48 F R R Middle Partial rupture Ulnar 6 29 F R L Middle Partial rupture Both 7 54 M R L Ring Partial rupture Radial 8 80 M R L Ring Degeneration Both 9 51 M R R Middle Degeneration Both F L L Ring Scarring Both Abbreviation: FDS, flexor digitorum superficialis. a Patient 4 had two fingers involved Table II. Range of Motion and Strength Involved Side Contralateral Side P Value Joint range of motion, Metacarpophalangeal Proximal interphalangeal Distal interphalangeal Total Strength, kg Grip Pinch Table III. Range of Motion and Strength: Single vs Both Slip Excision Excision of: Single Slip (Contralateral) Both Slips (Contralateral) Joint range of motion, Metacarpophalangeal 87 (88) 91 (98) Proximal interphalangeal 97 (97) 88 (108) Distal interphalangeal 65 (66) 71 (72) Total 249 (250) 250 (278) Strength, kg Grip 21.6 (19.3) 26.5 (32.1) Pinch 3.18 (2.73) 4.09 (5.18) phalanx and PIP joint. Three of these 6 patients had undergone initial A1 release at our practice, and in each case, symptoms prior to initial release were noted over the A1 pulley; these symptoms included tenderness, clicking, catching, and nodular masses. In 9 fingers, significant scar tissue was noted in the A1 pulley region at time of index surgery, though a well-defined pulley structure was not identified. This scar tissue precluded evaluation of the adequacy of the prior A1 pulley release. Evaluation during index surgery revealed partial FDS rupture in 5 fingers (in 1 case accompanied by significant flexor digitorum profundus [FDP] degeneration in a rheumatoid patient with pulley attrition), significant degenerative changes without rupture in 3 fingers, and FDS scarring in 1 finger (Table I). One finger, which demonstrated synovitis and fraying of the FDS tendon, had a persistent click at the PIP joint despite smooth FDP gliding after excision of both FDS slips. This click resolved after PIP arthrotomy with synovectomy as well as excision of an osteophyte and the most dorsal portion of the adjacent collateral ligament. Pathologic analysis revealed abnormalities of the tendon slips in all but 2 fingers; 1 of these 2 fingers had a single FDS slip excised, and the other had both slips excised. The pathologic changes included fibrosis and chronic inflammation. All patients felt relief of locking or catching symptoms. One patient, treated with resection of both FDS slips after 3 prior surgeries elsewhere, developed a mild swan-neck deformity. Mean (range) DASH score was 17 (0-45). Mean (range) VAS score for pain was 1.5 (0-5). Mean (range) ROM for the PIP joint of the affected finger was 93 ( ). Mean (range) ROM for the entire finger was 252 ( ). Mean (range) grip 622 The American Journal of Orthopedics
4 S. N. Husain et al strength was 112% (63%-200%) of the contralateral side, and mean (range) tip pinch strength was 101% (40%- 200%) of the contralateral side. Table II compares the active ROM, grip and pinch strength of the involved and contralateral sides, and lists the P values from the 2-sample t test. Finger ROM and grip and pinch strength were not statistically different between sides when all patients were pooled together. A trend of decreased grip and pinch strength was found for the 5 fingers that had both FDS slips excised compared with the 6 fingers that had a single FDS slip excised. The number of cases, however, was too small for meaningful statistical analysis (Table III). Discussion Open surgical treatment of trigger digits has been reported to have a success rate of 97% to 98%. 1,2 The need for revision surgery after A1 pulley release is rare. Lim and colleagues 3 did not find any recurrence of triggering among 483 digits that underwent open A1 pulley release. Four patients had postoperative stiffness that resolved with therapy. Le Viet and colleagues 4 noted 19 cases over a 17-year period but did not discuss these separately from the primary cases in their series. Blyth and Ross 5 reported only 1 revision surgery among 142 A1 pulley releases and did not specify which type of reoperation. Turowski and colleagues 1 described 1 reoperation for persistent triggering among 59 patients who underwent open A1 pulley release. Complete excision of the A1 pulley led to complete resolution of symptoms. In our practice, over a 26-month period, 936 open A1 pulley releases were performed, and 5 revision procedures (0.5%) with FDS resection were required for patients initially treated at our practice. The etiology of the symptoms that led to revision surgery were not consistent among our patients. Degenerative FDS changes, including partial ruptures, were noted during surgery in 8 of the 11 fingers, while pathologic analysis revealed abnormalities in 9 fingers. Although these changes are more substantial than those noted by other authors, 4 tendon ruptures without triggering may be seen in other conditions, such as inflammatory tenosynovitis. Two fingers in our series had persistent intraoperative triggering with no clear source after revision A1 release; partial FDS excision resolved the triggering. We could not identify any English-language articles on revision surgery after open A1 pulley release. Most review articles do not offer a protocol for what to do in case of recurrent triggering. 6,7 Some authors have advocated partial release of the A2 pulley if A1 pulley release alone does not completely relieve triggering when tested during surgery. 8,9 The effect of this release on ROM or strength has not been described. Although symptoms of triggering may resolve, joint ROM may remain decreased in the presence of a PIP joint flexion contracture. Resection of part of the FDS tendon has been suggested in several circumstances. Ferlic and Clayton 10 advocated resection of the ulnar slip of the FDS with preservation of the A1 pulley to prevent worsening of ulnar drift in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Le Viet and colleagues 4 described their results with ulnar slip resection of the FDS in 228 fingers with PIP flexion contracture over a 17-year period. Nineteen patients had a prior A1 pulley release. ROM was described, but there was no comment on the effects of FDS resection on pinch or grip strength, nor any report of patient-based outcome scores. Marcus and colleagues 11 described excision of the ulnar slip of the FDS with and without A1 pulley release for triggering in 37 diabetic fingers. They reported postoperative active ROM of 218. Although no quantitative analysis was offered, they noted consistently equal pinch strength. Excision of a slip of the FDS has also been recommended for treatment of trigger finger in the pediatric patient population. 12,13 Other authors have reported cases in which either the FDP or the FDS tendon was debulked, but none have reported quantitative measurements on the effects on ROM or grip strength. One weakness of our study is its small number of patients (trigger finger after A1 pulley release is an infrequent outcome). In addition, there was no formal process for deciding whether the radial slip, the ulnar slip, or the entire FDS tendon should be excised. The senior hand surgeon based this decision on intraoperative findings. All patients who had a single slip excised were treated by one attending hand surgeon, and, with the exception of 1 patient with a prior single-slip excision, all patients who had both slips excised were treated by the other attending hand surgeon. During analysis, we pooled our data for patients who had 1 or both slips resected. A larger patient population may have allowed analysis for a difference in outcomes between patients with 1 slip excised and those with both slips excised. Complete FDS resection should be performed with caution because of the potential for postoperative grip and pinch weakness. Complete FDS resection also has the potential to lead to a swan-neck deformity. We noted this deformity in only 1 patient who underwent complete FDS resection. The follow-up of this subgroup of patients was short, and, potentially, more patients could have developed the deformity over time. On the other hand, development of the deformity may have been limited by the presence of PIP contractures, which occur in some patients with chronic trigger fingers and in some patients who undergo surgical treatment. Lim and colleagues 3 reported that 14% of patients who underwent open trigger release had PIP flexion contractures before surgery. Le Viet and colleagues 4 noted that 214 of 883 patients seen for trigger finger over a 17-year period demonstrated preoperative PIP contractures, and 87 of these 214 patients had PIP contractures of more than 5 after A1 pulley release, with or without resection of the ulnar slip of the FDS. In another study, PIP flexion contractures were noted in 2 of 46 patients who were examined after surgical trigger finger release. 1 Marcus and colleagues 11 noted PIP flexion contractures in 3 of 11 diabetic patients treated December
5 Recalcitrant Trigger Finger with ulnar FDS excision with or without A1 pulley release. They also noted no swan-neck deformities in these patients a mean of 48 months after partial FDS resection. The stiffness from PIP contractures may limit development of swan-neck deformities in FDS-absent surgically released trigger fingers. Conversely, although PIP volar plate tightness is one of the main causes of PIP joint stiffness, partial or complete FDS excision may help address a PIP flexion contracture in a trigger finger. Le Viet and colleagues 4 reported a mean gain of 26 in passive PIP extension with this technique. When managing persistent symptoms of trigger finger, the physician should carefully examine the wrist and palm, as masses at this proximal level can cause the same symptoms. 14,15 We believe that, if there is no evidence of pathology proximal to the finger, resection of all or part of the FDS should be the procedure of choice after failure of open A1 pulley release to resolve symptoms. Patients with triggering after surgery often report of persistent locking or catching, but they may also feel a grating sensation as the FDP and FDS tendons rub against each other in the tendon sheath. The examiner can appreciate this if the finger is palpated while the patient actively flexes the finger. Resection of a slip of the FDS will alleviate symptoms originating from the level of the A1, A2, A3, or A4 pulley. Authors Disclosure Statement The authors report no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this article. References 1. Turowski GA, Zdankiewicz PD, Thomson JG. The results of surgical treatment of trigger finger. J Hand Surg Am. 1997;22(1): Gilberts EC, Beekman WH, Stevens HJ, Wereldsma JC. Prospective randomized trial of open versus percutaneous surgery for trigger digits. J Hand Surg Am. 2001;26(3): Lim MH, Lim KK, Rasheed MZ, Narayanan S, Beng-Hoi Tan A. Outcome of open trigger digit release. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007;32(4): Le Viet D, Tsionos I, Boulouednine M, Hannouche D. Trigger finger treatment by ulnar superficialis slip resection (U.S.S.R.). J Hand Surg Br. 2004;29(4): Blyth MJ, Ross DJ. Diabetes and trigger finger. J Hand Surg Br. 1996;21(2): Ryzewicz M, Wolf JM. Trigger digits: principles, management, and complications. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31(1): Saldana MJ. Trigger digits: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9(4): Al-Qattan MM. Trigger fingers requiring simultaneous division of the A1 pulley and the proximal part of the A2 pulley. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007;32(5): Nagaoka M, Yamaguchi T, Nagao S. Triggering at the distal A2 pulley. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2007;32(2): Ferlic DC, Clayton ML. Flexor tenosynovectomy in the rheumatoid finger. J Hand Surg Am. 1978;3(4): Marcus AM, Culver JE Jr, Hunt TR III Treating trigger finger in diabetics using excision of the ulnar slip of the flexor digitorum superficialis with or without A1 pulley release. Hand (N Y). 2007;2(4): Bae DS, Sodha S, Waters PM. Surgical treatment of the pediatric trigger finger. J Hand Surg Am. 2007;32(7): Cardon LJ, Ezaki M, Carter PR. Trigger finger in children. J Hand Surg Am. 1999;24(6): Carneiro RS, Velasquez L, Tietzman A. Trigger wrist caused by a tumor of the tendon sheath in a teenager. Am J Orthop. 2001;30(3): Kernohan JG, Benjamin A, Simpson D. Trigger wrist due to anomalous flexor digitorum profundus muscle in association with fibroma of tendon sheath. Hand. 1982;14(1): The American Journal of of Orthopedics
Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley.
 TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
TRIGGER DIGITS Definition: This problem generally is caused by a size mismatch between the flexor tendon and the first annular (A-1) pulley. Abstract Primary stenosing tenosynovitis is usually idiopathic
Trigger Finger Release
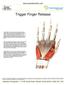 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
RHEUMATOID HAND. History Pain Loss of function Neck pain. Diminished ADL assessment:
 RHEUMATOID HAND History Pain Loss of function Neck pain Diminished ADL assessment: Using toothbrush, hairbrush, knife, fork Dressing bra, Pulling up trousers / stockings Operating remote control Hobbies
RHEUMATOID HAND History Pain Loss of function Neck pain Diminished ADL assessment: Using toothbrush, hairbrush, knife, fork Dressing bra, Pulling up trousers / stockings Operating remote control Hobbies
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management. Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics
 + The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
+ The Rheumatoid Hand Deformities & Management Dr. Anirudh Sharma Resident Department of Orthopedics + Why is Rheumatoid Arthritis important? + RA is a very debilitating disease median life expectancy
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Interesting Case Series. Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy
 Interesting Case Series Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy Leyu Chiu, BA, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, a,b and Paul A. Luce, MD, a,b,c a Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids,
Interesting Case Series Swan-Neck Deformity in Cerebral Palsy Leyu Chiu, BA, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, a,b and Paul A. Luce, MD, a,b,c a Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids,
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries. Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013
 Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Trigger Digits, Mallet Finger & Metacarpal Injuries Joseph P. McCormick, M.D. Affinity Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 2013 Overview Trigger Digits: diagnosis and treatment Bonus: approach in children Mallet
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity. Mark Tait MD
 Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment
 Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
Dupuytren's Contracture Assessment Link to guidance: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ bedfordshire-and-hertfordshire-priorities-forum Dupuytren's contracture - clinical presentation for patients History Examination
FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND
 Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Basrah Journal of Surgery FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MANAGEMENT OF THE FLEXOR TENDON INJURIES IN THE HAND Avadis F.I.C.M.S. Lecturer in Orthopaedic, Department of Surgery, College of Medicine, and specialist
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL
 Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
Andrew McNamara, MD The Orthopaedic and Fracture Clinic 1431 Premier Drive Mankato, MN 56001 507-386-6600 Metacarpophalangeal Joint Implant Arthroplasty REHABILITATION PROTOCOL Patient Name: Date: Diagnosis:
FINGER INJURIES. Chapter 24, pgs ,
 FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal Radius Fracture
 60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
60 pissn : 1226-2102, eissn : 2005-8918 Case Report J Korean Orthop Assoc 2015;50: 60-65 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2015.50.1.60 www.jkoa.org Acute Rupture of Flexor Tendons as a Complication of Distal
Ascension. Silicone MCP surgical technique. surgical technique Ascension Silicone MCP
 Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Ascension Silicone MCP surgical technique WW 2 Introduction This manual describes the sequence of techniques and instruments used to implant the Ascension Silicone MCP (FIGURE 1A). Successful use of this
Examination of the Hand
 1 Examination of the Hand R E Page History 3 Examination 4 Movement 8 Features of Specific Conditions Affecting the Hand and Special Tests 8 Examination of the Hand 3 History General Establish important
1 Examination of the Hand R E Page History 3 Examination 4 Movement 8 Features of Specific Conditions Affecting the Hand and Special Tests 8 Examination of the Hand 3 History General Establish important
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks
 Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Swan-Neck Deformity. Introduction. Anatomy
 Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
10/10/2014. Structure and Function of the Hand. The Hand. Osteology of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
Structure and Function of the Hand 19 bones and 19 joints are necessary to produce all the motions of the hand The Hand Dorsal aspect Palmar aspect The digits are numbered 1-5 Thumb = #1 Little finger
A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the Little Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2013;5:138-144 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.138 A New Examination Method for Anatomical Variations of the Flexor Digitorum Superficialis in the
Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Common Hand Conditions Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives POLICY TRAIL AND VERSION CONTROL SHEET: Policy Reference:
IMPLANT ARTHROPLASTY OF the proximal interphalangeal
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Surface Replacement Arthroplasty of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Using a Volar Approach: Case Series Holbrook H. Stoecklein, BA, Rohit Garg, MBBS, Scott W. Wolfe, MD Purpose To
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Surface Replacement Arthroplasty of the Proximal Interphalangeal Joint Using a Volar Approach: Case Series Holbrook H. Stoecklein, BA, Rohit Garg, MBBS, Scott W. Wolfe, MD Purpose To
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View
 Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Wrist & Hand Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The hand can be divided
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures:
 Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System John M. Agee M.D. Reversing PIP Joint Contractures: Applicability of the Digit Widget External Fixation System
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report
 CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
CASE REPORT 41 OPEN ACCESS A novel method of treating isolated unicondylar fracture of the head of the proximal phalanx: A case report Aysha Rajeev, John Harrison ABSTRACT Introduction: The phalangeal
Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Total distal radioulnar joint replacement for symptomatic joint instability or arthritis Instability of
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
NEUFLEX MCP/PIP FINGER JOINT IMPLANT SYSTEMS This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MCP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Summary provided by designing surgeon Arnold-Peter C.
11/13/2017. Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair. Brandon E. Earp, M.D. How do we best get there?
 Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair Brandon E. Earp, M.D. Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Vice-Chair of Clinical Operations Brigham and Women s Hospital Frontiers in
Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair Brandon E. Earp, M.D. Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Vice-Chair of Clinical Operations Brigham and Women s Hospital Frontiers in
Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or Percutaneous Release for Trigger Thumb
 Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or for Trigger Thumb Hui-Kuang Huang, MD; Jung-Pan Wang, MD, PhD; Chin-Jung Lin, MD; Yi-Chao Huang, MD; Tung-Fu Huang, MD; Ming-Chau Chang, MD abstract Good
Short-term Versus Long-term Outcomes After Open or for Trigger Thumb Hui-Kuang Huang, MD; Jung-Pan Wang, MD, PhD; Chin-Jung Lin, MD; Yi-Chao Huang, MD; Tung-Fu Huang, MD; Ming-Chau Chang, MD abstract Good
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
Chapter 24. Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty. Introduction. Operative Technique. Patient Preparation and Positioning
 Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2012;4:263-268 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2012.4.4.263 The Efficacy of Steroid Injection in the Treatment of Trigger Finger Benan M. Dala-Ali, MBBS, Amir
Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures
 Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Andrew B. Stein, MD Boston University Medical Center May 2 & 3, 2016
 Andrew B. Stein, MD Boston University Medical Center andrew.stein@bmc.org Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Tendon injuries may be obvious or subtle History (mechanism of injury)
Andrew B. Stein, MD Boston University Medical Center andrew.stein@bmc.org Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Tendon injuries may be obvious or subtle History (mechanism of injury)
Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release V Singh, S Chong, S Marriapan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Trigger Finger: Comparative Study between Corticosteroid Injection and Percutaneous Release V Singh, S Chong, S Marriapan Citation
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside
 Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Trapezium is by the thumb, Trapezoid is inside Intercarpal Jt Radiocarpal Jt Distal Middle Proximal DIP PIP Interphalangeal Jts Metacarpalphalangeal (MCP) Jt Metacarpal Carpometacarpal (CMC) Jt Trapezium
Wrist and Hand Anatomy
 Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
Wrist and Hand Anatomy Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium Capitate Hamate Wrist Articulations Radiocarpal Joint Proximal portion Distal portion Most surface contact found
TRIGGER DIGIT, OR stenosing tenosynovitis, isa
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Multiple Pulley Rupture Following Corticosteroid Injection for Trigger Digit: Case Report Cassie Gyuricza, MD, Eva Umoh, BA, Scott W. Wolfe, MD We report a case of pulley rupture following
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Multiple Pulley Rupture Following Corticosteroid Injection for Trigger Digit: Case Report Cassie Gyuricza, MD, Eva Umoh, BA, Scott W. Wolfe, MD We report a case of pulley rupture following
A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty
 A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty (active-assistive therapy, post-operative splinting, rheumatoid arthritis) Barbara M. Johnson Mary Jean Gregory Flynn Robert D. Beckenbaugh Total
A Dynalllic Splint for U se After Total Wrist Arthroplasty (active-assistive therapy, post-operative splinting, rheumatoid arthritis) Barbara M. Johnson Mary Jean Gregory Flynn Robert D. Beckenbaugh Total
Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex)
 Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex) Finger Joint Arthroplasty Operative Technique Silicone PIP Silicone MCP Silicone PreFlex (MCP-X) Stryker Disclaimer This publication sets forth detailed recommended
Silicone PIP, MCP & MCP-X (PreFlex) Finger Joint Arthroplasty Operative Technique Silicone PIP Silicone MCP Silicone PreFlex (MCP-X) Stryker Disclaimer This publication sets forth detailed recommended
Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers A Ogbemudia, A Bafor, E Edomwonyi Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Results Of Tenosynovectomy And Intralesional Steroid In The Management Of Trigger Fingers A Ogbemudia, A Bafor, E Edomwonyi Citation
Integra. Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 Integra Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Assessment... 3 Step 1: Initial
Integra Silicone PIP Implant SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Table of Contents Indications For Use...2 Contraindications...2 Warnings and Precautions...2 Surgical Technique Preoperative Assessment... 3 Step 1: Initial
Failed Extensor Indicis Proprius Tendon Transfer for Extensor Pollicis Longus Tendon Rupture after Distal Radial Fracture
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2015;20(1):23-27. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2015.20.1.23 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Failed Extensor
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis
 AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment
 10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
10 Classification of Established Volkmann s Ischemic Contracture and the Program for Its Treatment In spite of the advances made in preventive treatment of muscular ischemia at the forearm and hand, there
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension
 Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension Elani Muller Corrianne van Velze Tania Buys 24 May 2018 Introduction MP joints should
Occupational therapy guidelines for conditions in which the metacarpophalangeal joints could be splinted in extension Elani Muller Corrianne van Velze Tania Buys 24 May 2018 Introduction MP joints should
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon. sheath
 Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
Multicentric localized giant cell tumor of the tendon sheath Toshihiro Akisue, Tetsuji Yamamoto ( ), Teruya Kawamoto, Toshiaki Hitora, Takashi Marui, Tetsuya Nakatani, Takafumi Onga, and Masahiro Kurosaka.
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
The Stiff Hand: Boutonniere & Sylvia Dávila, PT, CHT San Antonio, Texas Extensor Mechanism Central slip inserts into base of the middle phalanx Lateral bands lie dorsal to the PIP joint center of rotation
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture
 A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Dupuytren s Contracture Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Ascension PIP Post-Operative therapy protocol
 Ascension PIP Post-Operative therapy protocol This brochure summarizes post-operative care guidelines for the Ascension PIP. HUMANITARIAN DEVICE: The Ascension PIP is authorized by Federal law for use
Ascension PIP Post-Operative therapy protocol This brochure summarizes post-operative care guidelines for the Ascension PIP. HUMANITARIAN DEVICE: The Ascension PIP is authorized by Federal law for use
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist. Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury
 Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Prosser, R., Hancock, M. J., Nicholson, L., Merry, C., Thorley, F., & Wheen, D. (2014). Rigid versus semi-rigid orthotic use following TMC arthroplasty: A randomized controlled
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Prosser, R., Hancock, M. J., Nicholson, L., Merry, C., Thorley, F., & Wheen, D. (2014). Rigid versus semi-rigid orthotic use following TMC arthroplasty: A randomized controlled
Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University. May 2 & 3, 2016
 Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Exertional??? Webster- precipitated by
Andrew L Terrono, MD Chief Hand Surgery Service NEBH Clinical Professor Orthopaedics Tufts University Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Exertional??? Webster- precipitated by
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Clinical Examination of the Hand and Wrist
 Clinical Examination of the Hand and Wrist OBJECTIVES Review the clinical anatomy and physical exam of the wrist and hand Formulate a pathoanatomic diagnosis in the clinical setting Discuss common clinical
Clinical Examination of the Hand and Wrist OBJECTIVES Review the clinical anatomy and physical exam of the wrist and hand Formulate a pathoanatomic diagnosis in the clinical setting Discuss common clinical
Complications of Distal Radius Fractures. How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx 11/13/2017. Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago
 Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx Need to restore motion, begin with uninvolved parts Need to reduce an unreduced
Complications of Distal Radius Fractures Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Loyola University Chicago How to Treat a Distal Radius Fx Need to restore motion, begin with uninvolved parts Need to reduce an unreduced
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain,
 1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, 2016 2 de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain, Swiss surgeon, 1895 Stenosing tendinosis, 1st dorsal compartment
1 Comprehensive Orthopaedic Review Hand and Wrist Tendinopathies Bernard F. Hearon, MD September 2, 2016 2 de Quervain Disorder Fritz de Quervain, Swiss surgeon, 1895 Stenosing tendinosis, 1st dorsal compartment
Management of Chronic Elbow Pain
 Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Interesting Case Series. Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries
 Interesting Case Series Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries Evgenios Evgeniou, MBBS, MRCS, a and Harriet Walker, MBBS, MRCS b a North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol, United Kingdom, b Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust,
Interesting Case Series Zone I Flexor Tendon Injuries Evgenios Evgeniou, MBBS, MRCS, a and Harriet Walker, MBBS, MRCS b a North Bristol NHS Trust, Bristol, United Kingdom, b Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust,
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II
 Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
Upper Limb- Sports Medicine II I. Palpation A. With patient sitting, supine, & prone, palpate for pain, specific tenderness, swelling, effusion, local hyperthermia B. Bony Palpation 1. Carpal Bones (8)
1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely:
 CHAPTER 50 HAND 2 OCTOBER 2013 1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely: A. He is a gamer and
CHAPTER 50 HAND 2 OCTOBER 2013 1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely: A. He is a gamer and
SWAN'S NECK DEFORMITY OF THE FINGERS
 SWAN'S NECK DEFORMITY OF THE FINGERS By STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S.R.C.S.(Edin.) The Mount Vernon Centre of Plastic Surgery, Northwood, Middlesex, and the Windsor Group of Hospitals HYPEREXTENSION
SWAN'S NECK DEFORMITY OF THE FINGERS By STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S.R.C.S.(Edin.) The Mount Vernon Centre of Plastic Surgery, Northwood, Middlesex, and the Windsor Group of Hospitals HYPEREXTENSION
Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 451-455 ORIGINAL STUDY Proximal row carpectomy : A volar approach Eline A. VAN AMERONGEN, Arnold H. SCHUURMAN From the University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger Flaps and Vigorous Postoperative Exercises
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.4.574 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(4):574-578, 2010 Correction of Long Standing Proximal Interphalangeal Flexion Contractures with Cross Finger
Phase 1 Maximum Protection 0-4 Weeks
 Dr. Schmidt CMC Arthroplasty When conservative treatment of thumb osteoarthritis fails to control pain surgical treatment may be indicated. The most common surgical technique involves complete resection
Dr. Schmidt CMC Arthroplasty When conservative treatment of thumb osteoarthritis fails to control pain surgical treatment may be indicated. The most common surgical technique involves complete resection
Key Points for Success:
 SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
SELF WRIST & HAND 1 2 All of the stretches described in this chapter are detailed to stretch the right side. Key Points for Success: Sit comfortably in a position where you can straighten or fully extend
Rehabilitation Protocol: Primary Flexor Tendon Repair LHMC Protocol for Zone 1 & 2
 Rehabilitation Protocol: Primary Flexor Tendon Repair LHMC Protocol for Zone 1 & 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington 781-744-8650 Lahey Outpatient Center, Lexington
Rehabilitation Protocol: Primary Flexor Tendon Repair LHMC Protocol for Zone 1 & 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington 781-744-8650 Lahey Outpatient Center, Lexington
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Fracture and Dislocation of the Carpus ( 1-Jan-1985 )
 In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
In: Textbook of Small Animal Orthopaedics, C. D. Newton and D. M. Nunamaker (Eds.) Publisher: International Veterinary Information Service (www.ivis.org), Ithaca, New York, USA. Fracture and Dislocation
Kokko Wrist 3/11/17. Updates in General Internal Medicine for Primary Care Wrist Pain
 Updates in General Internal Medicine for Primary Care 2017 Wrist Pain Kyle P. Kokko, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Hand, Wrist, and Microvascular Surgeon MUSC Department of Orthopaedics Disclosures I pulled
Updates in General Internal Medicine for Primary Care 2017 Wrist Pain Kyle P. Kokko, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Hand, Wrist, and Microvascular Surgeon MUSC Department of Orthopaedics Disclosures I pulled
MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES. Mary C. Burns & Brian Derby & Michael W. Neumeister
 HAND (2013) 8:17 22 DOI 10.1007/s11552-012-9488-z MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES Wyndell merritt immediate controlled active motion (ICAM) protocol following extensor tendon repairs in zone IV VII: review of literature,
HAND (2013) 8:17 22 DOI 10.1007/s11552-012-9488-z MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES Wyndell merritt immediate controlled active motion (ICAM) protocol following extensor tendon repairs in zone IV VII: review of literature,
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First Carpometacarpal Arthritis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:372-376 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.3.372 Results of Abductor Pollicis Longus Suspension Ligamentoplasty for Treatment of Advanced First
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
