Managing acromial fractures: prevention and treatment, both nonoperative and operative
|
|
|
- Percival Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Page 1 of 8 Managing acromial fractures: prevention and treatment, both nonoperative and operative Christopher D. Joyce, Adam J. Seidl Department of Orthopaedics, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, USA Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative support: None; (III) Provision of study materials or patients: None; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: None; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: None; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Adam J. Seidl. Department of Orthopaedics, University of Colorado, E. 17 th Avenue, Aurora, CO 80045, USA. adam.seidl@ucdenver.edu. Abstract: Acromial and scapular spine fractures are a known complication in 3.1% to 11.2% of reverse shoulder arthroplasties and can cause significant functional impairment. Acromial and scapular spine fractures often present as increased shoulder pain and may have unremarkable plain radiographs and thus require further imaging for diagnosis. A number of risk factors for these fractures have been proposed in the literature with varying level of evidence. Risk factors may be grouped into patient comorbidities, preoperative acromial pathology, surgical technique, and surgical indications. Ideally, acromial and scapular spine fractures in reverse shoulder arthroplasty patients can be prevented by identifying and addressing risk factors pre-operatively and intra-operatively. Treatment of acromion and scapular spine fractures after reverse shoulder arthroplasty depends on the fracture location, displacement, and patient factors and includes both non-surgical management and surgical fixation. This article aims to serve as a comprehensive review of the available literature on acromial and scapular spine fractures in reverse shoulder arthroplasty patients and suggested methods of prevention and treatment. Keywords: Reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA); acromion; scapular spine; fractures Received: 16 October 2018; Accepted: 23 November 2018; Published: 02 January doi: /aoj View this article at: Introduction The utilization of total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) and specifically reverse shoulder arthroplasty (RSA) has increased steadily over the past decades (1-3). As the indications for RSA have continued to expand, so has the prevalence of this procedure. While traditionally RSA was reserved for patients with end stage rotator cuff arthropathy, indications have expanded to also include many other pathologies (4,5). As the number of RSAs being performed increases, inevitably so will the number of complications. A number of intra-operative and post-operative complications have been described in RSA, with overall complication rates estimated at 19 percent for primary RSA and up to 69 percent for revision RSA procedures (6,7). Some of the more common complications include scapular notching, glenoid component loosening, infection, instability, and fracture (8). Periprosthetic fractures of the humeral shaft, greater tuberosity, coracoid, acromion, and scapular spine have all been described (9,10). Acromial and scapular spine fractures have been associated with significantly worse functional outcomes after RSA and are a major cause of post-operative dysfunction and/or pain in these patients (11-13). Acromial and scapular spine fractures occur in 3.1% to 11.2% of all patients undergoing RSA (Table 1) (11-18,20). While a number of risk factors have been proposed, there is a relative paucity of quality evidence in the literature on the cause of this complication. The purpose of this article is
2 Page 2 of 8 Annals of Joint, 2019 Table 1 Rates of acromial and scapular spine fractures in patients undergoing reverse shoulder arthroplasties in the literature Author Year Patient number to highlight the risk factors for scapular spine and acromial fractures in patients undergoing RSA and discuss treatment and prevention options based on current literature. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and classification Acromion/scapular spine fracture rate (%) Lópiz (13) Dubrow (11) Teusink (12) , Levy (14) Hamid (15) Crosby (16) Hattrup (17) Walch (18) Boileau (19) Frankle (20) Werner (21) Acromial fractures and scapular spine fractures may occur intra-operatively or post-operatively in association with RSA. Intra-operative fractures are rare and may be treated conservatively or with acute fixation depending on location and displacement of the fracture as well as implant stability. Post-operative fractures present differently, and may be due to a direct trauma or a chronic fatigue type of mechanism (17). Patients with a traumatic mechanism often report a fall or an event requiring them to reach out and grab something to prevent a fall. This mechanism suggests that the mechanism for these types of fractures may be from rapid deltoid contraction. Patients with acromial stress fractures often present with a period of initial pain relief post-operatively followed by an increase in pain and poor function (22). It is well established that RSA patients who sustain acromial or scapular spine fractures have worse outcomes compared to patients without fractures. Lópiz et al. showed a significant decreased in Constant scores, lower quality of life scores, and an average decrease of 39 degree of forward flexion and 34 degrees of abduction compared to control patients (13). Similarly, Teusink et al. showed a higher revision surgery rate, less overall improvement in American Shoulder and Elbow Surgeons (ASES) score (58.0 compared to 74.2), and worse range of motion improvement (26 degrees compared to 76 degrees) (12). The success of an RSA is reliant on a functional deltoid, and significant deltoid dysfunction and loss of tension may occur with displaced fractures of the deltoid origin on the acromion or scapular spine. The time period in which these fractures occur varies anywhere from 1 to 94 months post-operatively, with the average typically between 3 and 12 months (12-14). Many patients with acromion fractures are a diagnostic challenge as their clinical exam is ambiguous and radiographs are normal or have subtle findings. Routine shoulder plain radiographs are the initial diagnostic imaging tool but only have a sensitivity of 79% and poor interobserver reliability (14,23). Therefore, early advanced imaging is indicated in patients presenting with a high clinical suspicion for scapula fractures. Computed tomography is the advanced image study that best identifies fractures not apparent on plain radiographs, but magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or bone scans can be helpful for stress fractures or stress reactions. Figures 1 and 2 demonstrate radiographs and advanced imaging in two case examples. Crosby et al. proposed a classification for acromion fractures after RSA after retrospectively reviewing 400 patients, 22 of which sustained acromion or scapular spine fractures. Type I fractures are small anterior fractures at the level of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint and were hypothesized to be secondary to deltoid avulsion from a weakened acromion. Type II fractures are posterior to the AC joint and were thought to be due to fatigue failure of the acromion. Type III fractures are in the posterior acromion or scapular spine and were all related to a traumatic event in their series (16). Levy et al. has also proposed another classification system based on the amount of deltoid origin involvement that is depicted in Table 2 (14). Risk factors The first step in appropriately managing and preventing acromion fractures in RSA patients is to mitigate possible risk factors. Risk factors can be classified into surgical indication, patient comorbidities, acromial pathology, and surgical technique.
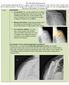
3 Annals of Joint, 2019 Page 3 of 8 A B A B C D C D Figure 1 Radiographs of an 80-year-old male who sustained Figure 2 A 52-year-old female with rheumatoid arthritis presented an acromial base fracture 3 months after RSA. Immediate (A), with a scapular base nonunion and recurrent instability 10 years 3 months (B), and 4 months (C,D) post-operative radiographs after RSA. The nonunion is visible on AP and axillary plain are shown. Note the nondisplaced fracture (arrow) at 3 months radiographs (A,B) and CT scan (C). The patient underwent (B), which displaced with increased inferior tilt of the acromion revision to hemiarthroplasty (D) with improved functional results. at 4 months (C). After conservative management, he went on to RSA, reverse shoulder arthroplasty; AP, anteroposterior. painless union at 7 months post-operative. Table 2 Levy classification for postoperative acromial fractures after reverse shoulder arthroplasty (14) Type Location Deltoid origin involvement Type I Acromion anterior to posterolateral acromial corner Anterior and portion of middle deltoid Type II Mid acromion between base and posterolateral corner Entire middle deltoid Type III Acromial base Entire middle and posterior deltoid Surgical indication The indications for RSA have been expanded over the past decades, and with this more complicated patients are getting reverse shoulder arthroplasties (4,5). One particular example is locked anterior shoulder with static instability and anterior glenoid bone loss. This group of Annals of Joint. All rights reserved. patients develop soft tissue contractures that may place an increased load on the acromion, and have a higher fracture incidence at 21 percent (24). Rheumatoid arthritis patients have a higher risk of intra-operative fractures during RSA; however, post-operative acromial fracture rate appears to be similar to non-rheumatoid patients (10,25,26). aoj.amegroups.com
4 Page 4 of 8 Annals of Joint, 2019 Comorbidities Certain medical comorbidities may increase the risk of acromial fractures in RSA patients. One retrospective case-control study looked at comorbidities in relation to acromial fractures and found the osteoporosis significantly increased the risk; however, no increased risk of fracture existed in patient with osteopenia, endocrine disease, autoimmune disease, smoking, alcohol abuse, or steroid use (23). Definitive conclusions are difficult to make based on such a rare complication, and it is likely that all medical comorbidities that cause decreased bone strength or bone metabolic changes increase the risk of acromion fractures to some degree. Additionally, patients at an increased risk of falling are at higher risk of sustaining an acromial or scapular spine fracture after RSA. Acromial pathology Pre-operative pathology in the acromion such as os acromiale, acromial thickness, acromial tilt, or prior acromioplasty may weaken the bone, theoretically putting it at an increased risk of fracture (18,27). Several retrospective series have studied these particular risk factors. Walch et al. compared 23 patients with os acromiale and 17 patients with pre-operative acromion fracture or fragmentation to patients without these lesions and found no significant difference in outcomes nor an increased risk of postoperative fractures (18). Otto et al. studied 53 RSA patients that sustained post-operative scapular fractures and found no differences in acromial thickness or acromial tilt when compared to non-fractured RSA patients (23). Crosby et al. proposed AC joint stiffness as a predisposing factor for acromial fractures, specifically in type II fractures (16). AC joint stiffness has only been evaluated critically in one study by Dubrow et al. The authors found no significant difference in radiographic presence of AC degenerative changes in patients with acromial fractures and those without (11). The applicability of these results is difficult to assess due to the low sample size and subjective nature of assessing AC stiffness radiographically. Therefore, it is uncertain if the presence of AC arthritis or stiffness is a risk factor for acromial fractures in RSA patients. Surgical technique Several intra-operative factors may also increase the risk of acromial fractures in RSA patients. Several studies have related displaced fractures of the base of the scapular spine to the superior glenoid baseplate screw. The screw being too long or exiting at the scapular spine base may cause increased stress in the scapular spine causing a fracture (16,22,23). Another factor that may contribute is placing excessive tension on the deltoid by distalizing the center of rotation and lengthening the arm. Biomechanically this gives the deltoid a better lever arm for elevation and was one of the original goals in RSA (28). This effectively lengthens the arm and the deltoid, placing increased stress on the acromion and scapular spine. Studies have used objective radiographic measurements such as glenoid-to-tuberosity distance, acromion-to-tuberosity or acromiohumeral distance, and arm length to quantify and reproduce this. However, to date no study has shown that increased arm lengthening or increasing deltoid tension does put the acromion at an increased risk of fracture (11,23,29). Furthermore, inadequate deltoid tension is associated with increased risk of prosthetic instability (29). Several other surgical factors have been reported as a risk for post-operative acromial fractures in RSA. Phadnis et al. compared results in cemented vs. uncemented humeral stems and found that cemented humeral stems were associated with more acromion fractures in a retrospective review (30). In another retrospective series, Molé et al. demonstrated a higher fracture rate in the deltopectoral approach compared to the anterosuperior approach (5.6% vs. 2.2%) (31). However, without randomized controlled trials, the true risk associated with cementation and approach is unknown. Prevention A number of risk factors have been identified as being associated with post-operative acromial spine fractures (Table 3). As this is a relatively infrequent complication in RSA, the evidence in support of each risk factor is generally poor, making prevention of acromion fractures difficult. Prevention strategies can be grouped into mitigation of patient factors and surgical technique. Patient factors are difficult to control. As RSA is typically an end-stage treatment, other lower risk procedures have already been attempted or are not indicated. Surgeons should carry a high index of suspicion when offering RSA to patients presenting with a chronic locked anterior shoulder dislocation, as the incidence of acromial fractures is higher
5 Annals of Joint, 2019 Page 5 of 8 Table 3 List of risk factors for post-operative acromial and scapular spine fractures in reverse shoulder arthroplasty patients Variables With supportive evidence Risk factors Without supportive evidence Acromial pathology AC joint stiffness Os acromiale Acromioplasty or acromial thickness Increased acromial tilt Surgical technique Superior glenoid baseplate screw placement Glenosphere inferiorization Deltopectoral approach Humeral stem cementation Surgical indications Locked anterior shoulder Rheumatoid arthritis Comorbidities Osteoporosis Osteopenia Endocrine disease Smoking Steroid use in this group. Optimization of bone health in osteoporotic individuals with appropriate medical management and bisphosphonate use may help mitigate risk in this patient population. Abnormal pre-operative acromial morphology such as decreased acromial thickness, acromial tilt, AC joint stiffness, or os acromiale has not been shown to increase risk of post-operative fractures and therefore should not preclude patients from getting surgery. Surgical technique may play a role in preventing acromial and scapular spine fractures during and after RSA. The superior glenoid baseplate screw has been shown to be associated with scapular spine fractures, especially those occurring at the base of the scapular spine (16,22,23). This may be prevented by ensuring this screw is of appropriate length and trajectory with a maximum length of 24 mm and avoiding a posterior trajectory (22). It may also be prevented by not placing the superior screw at all as long as the remaining screws have adequate purchase (32). Regarding surgical approach, while one study demonstrated that the anterosuperior approach may have a lower rate of acromial fractures and post-operative instability, the rate of implant loosening and scapular notching was higher with this approach (31). It is recommended that the surgeon utilizes the approach that he or she is most comfortable with. While deltoid lengthening has been shown to improve post-operative function in RSA patients, this may also predispose patients to acromial fractures or deltoid fatigue from overlengthening (33-35). While no definitive evidence has shown that increasing the deltoid tension may predispose RSA patients to acromial fractures, it is still recommended to limit arm lengthening to 2.5 centimeters to mitigate the risk of possible acromion fracture, neurologic injury, or deltoid weakening (29,33,36). This may be achieved by avoiding excessive inferior placement of the baseplate/glenosphere and choosing a humeral component design that does not excessively distalize the humerus (37). Treatment Treatment of scapular spine and acromial fractures in RSA patients can be generally grouped into conservative treatment and operative fixation. Conservative management is the standard treatment for acute, non-displaced fractures of the scapula, with a recent survey of ASES members demonstrating that 74 percent prefer conservative management (15). Nonsurgical treatment involves a period of immobilization for six weeks, followed by progressive range of motion (12-15,22). During this period, gentle pendulum exercises may be allowed, but no active motion due to high risk of fracture displacement (16). Conservative management has yielded nonunion rates as high as 50 to 75 percent, calling into question this treatment modality
6 Page 6 of 8 Annals of Joint, 2019 (12,13,15). Some surgeons advocate that patients may go on to a painless nonunion and have acceptable results (15). Certain fracture patterns are better treated with operative management. Displaced fractures and fractures at the base of the scapular spine are prone to poor outcomes due to the larger amount of deltoid insertion involvement. A fracture at the base of the scapular spine will involve roughly two thirds of the deltoid origin. When a fracture in this region displaces, deltoid tension is lost and function of the RSA suffers significantly (23,38). A variety of surgical fixation methods have been described in the literature for acromial fractures in RSA patients. While tension band wiring is a described technique, the deltoid muscle is not a simple single plane tension force vector which may contribute to failure of this technique (18,22,39). Some fractures of the lateral acromion have little area for screw purchase, in which case a tension band construct may be the only feasible option. Most surgeons favor rigid plate fixation when treating these fractures operatively. Rouleau et al. described a technique of dual orthogonal plating of a scapular spine base fracture with excellent results (40). Hess et al. described a technique of bending a cruciform pilon plate over the acromion to place a retrograde lag screw across the fracture (41). Hill et al. described a series of 13 patients with acromion or scapular spine fractures in native scapulae that underwent fixation with a 2.7- or 3.5-mm lag screw and a neutralization reconstruction plate with 100 percent union rate and good overall outcomes (42). A consensus treatment plan for acromial and scapular spine fractures in RSA patients does not exist as no studies have been published comparing fixation techniques or operative and nonoperative management. The majority of literature includes case series of less than five patients, from which little clinical judgement can be made. In the absence of any comparative trials, our institution recommends treating nondisplaced fractures of the acromion and scapular spine conservatively with six weeks of immobilization followed by progressive shoulder motion. In the setting of painful nonunion or displaced fractures, we recommend surgical fixation with dual orthogonal plating when possible. Conclusions Scapular spine and acromial fractures after RSA can be difficult to diagnose and are challenging to treat. We recommend early advanced imaging with a CT scan if the clinical suspicion for a fracture exists despite normal radiographs. It is important for the surgeon to be cognizant of potential risk factors and certain patient characteristics that may contribute to acromial and scapular spine fractures such as osteoporosis, locked anterior shoulder dislocations, inflammatory arthritis, and severe AC joint arthrosis and stiffness. Surgical techniques to prevent these fractures include avoiding aberrant placement of the superior glenoid baseplate screw and avoiding implant placement that may excessively distalize the humerus. Treatment of acromial and scapular spine fractures in RSA patients is typically conservative with shoulder immobilization except in cases of displaced fractures or painful nonunions. In these cases, rigid fixation offers the best chance of achieving union. Future comparative studies are needed to guide management in acromial and scapular spine fractures associated with RSA. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: CD Joyce or any immediate family members have received any financial payments or other benefits related to the subject of this article; AJ Seidl or any immediate family members have received any financial payments or other benefits related to the subject of this article. References 1. Day JS, Lau E, Ong KL, et al. Prevalence and projections of total shoulder and elbow arthroplasty in the United States to J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2010;19: Westermann RW, Pugely AJ, Martin CT, et al. Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty in the United States: A Comparison of National Volume, Patient Demographics, Complications, and Surgical Indications. Iowa Orthop J 2015;35: Schairer WW, Nwachukwu BU, Lyman S, et al. National utilization of reverse total shoulder arthroplasty in the United States. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2015;24: Hyun YS, Huri G, Garbis NG, et al. Uncommon Indications for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg 2013;5: Urch E, Dines JS, Dines DM. Emerging Indications for Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect 2016;65:
7 Annals of Joint, 2019 Page 7 of 8 6. Wall B, Nové-Josserand L, O Connor DP, et al. Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review of Results According to Etiology. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89: Saltzman BM, Chalmers PN, Gupta AK, et al. Complication rates comparing primary with revision reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2014;23: Farshad M, Gerber C. Reverse total shoulder arthroplastyfrom the most to the least common complication. Int Orthop 2010;34: Cheung E, Willis M, Walker M, et al. Complications in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2011;19: Young AA, Smith MM, Bacle G, et al. Early Results of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93: Dubrow S, Streit JJ, Muh S, et al. Acromial Stress Fractures: Correlation With Acromioclavicular Osteoarthritis and Acromiohumeral Distance. Orthopedics 2014;37:e Teusink MJ, Otto RJ, Cottrell BJ, et al. What is the effect of postoperative scapular fracture on outcomes of reverse shoulder arthroplasty? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2014;23: Lópiz Y, Rodríguez-González A, García-Fernández C, et al. Fracturas de estrés de la escápula tras artroplastia invertida en artropatía de manguito: cuál es su repercusión funcional? Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol 2015;59: Levy JC, Anderson C, Samson A. Classification of postoperative acromial fractures following reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2013;95:e Hamid N, Connor PM, Fleischli JF, et al. Acromial fracture after reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2011;40:E Crosby LA, Hamilton A, Twiss T. Scapula Fractures After Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Classification and Treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2011;469: Hattrup SJ. The Influence of Postoperative Acromial and Scapular Spine Fractures on the Results of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty. Orthopedics 2010;33. doi: / Walch G, Mottier F, Wall B, et al. Acromial insufficiency in reverse shoulder arthroplasties. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2009;18: Boileau P, Watkinson D, Hatzidakis AM, et al. Neer Award 2005: The Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: Results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2006;15: Frankle M, Siegal S, Pupello D, et al. The Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis for Glenohumeral Arthritis Associated with Severe Rotator Cuff Deficiency: A Minimum Two- Year Follow-up Study of Sixty Patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: Werner CM, Steinmann PA, Gilbart M, et al. Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2005;87: Mayne IP, Bell SN, Wright W, et al. Acromial and scapular spine fractures after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Shoulder Elbow 2016;8: Otto RJ, Virani NA, Levy JC, et al. Scapular fractures after reverse shoulder arthroplasty: evaluation of risk factors and the reliability of a proposed classification. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2013;22: Kurowicki J, Triplet JJ, Momoh E, et al. Reverse shoulder prosthesis in the treatment of locked anterior shoulders: a comparison with classic reverse shoulder indications. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2016;25: Jauregui JJ, Paul Hovis J, Ashfaq Hasan S. Characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Rheumatol 2018;37: Gee ECA, Hanson EK, Saithna A. Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Open Orthop J 2015;9: Mottier F, Wall B, Nové-Josserand L, et al. Reverse prosthesis and os acromiale or acromion stress fracture. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 2007;93: Grammont P, Trouilloud P, Laffay J. Concept study and realization of a new total shoulder prosthesis. Rhumatologie 1987;39: Lädermann A, Williams MD, Melis B, et al. Objective evaluation of lengthening in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2009;18: Phadnis J, Huang T, Watts A, et al. Cemented or cementless humeral fixation in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty? Bone Joint J 2016;98-B: Molé D, Favard L. Excentered scapulohumeral osteoarthritis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 2007;93: James J, Allison MA, Werner FW, et al. Reverse shoulder arthroplasty glenoid fixation: is there a benefit in using four instead of two screws? J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2013;22: Lädermann A, Walch G, Lubbeke A, et al. Influence
8 Page 8 of 8 Annals of Joint, 2019 of arm lengthening in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012;21: Jobin CM, Brown GD, Bahu MJ, et al. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy: the clinical effect of deltoid lengthening and center of rotation medialization. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012;21: Sabesan VJ, Lombardo D, Josserand D, et al. The effect of deltoid lengthening on functional outcome for reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Musculoskelet Surg 2016;100: Wright J, Potts C, Smyth MP, et al. A quantitative analysis of the effect of baseplate and glenosphere position on deltoid lengthening in reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Int J Shoulder Surg 2015;9: Onstot BR, Jacofsky MC, Hansen ML. Muscle force and excursion requirements and moment arm analysis of a posterior-superior offset reverse total shoulder prosthesis. Bull Hosp Jt Dis (2013) 2013;71 Suppl 2:S Levy JC, Blum S. Postoperative acromion base fracture resulting in subsequent instability of reverse shoulder replacement. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012;21:e Wahlquist TC, Hunt AF, Braman JP. Acromial base fractures after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: report of five cases. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011;20: Rouleau DM, Gaudelli C. Successful treatment of fractures of the base of the acromion after reverse shoulder arthroplasty: Case report and review of the literature. Int J Shoulder Surg 2013;7: Hess F, Zettl R, Smolen D, et al. Anatomical reconstruction to treat acromion fractures following reverse shoulder arthroplasty. Int Orthop 2018;42: Hill BW, Anavian J, Jacobson AR, et al. Surgical Management of Isolated Acromion Fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2014;28:e doi: /aoj Cite this article as: Joyce CD, Seidl AJ. Managing acromial fractures: prevention and treatment, both nonoperative and operative..
Immediate post surgical findings of soft tissue swelling, subcutaneous emphysema, and skin staples for reverse total shoulder arthroplasty.
 Immediate post surgical findings of soft tissue swelling, subcutaneous emphysema, and skin staples for reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY WITH FRACTURED ACROMION Above:
Immediate post surgical findings of soft tissue swelling, subcutaneous emphysema, and skin staples for reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY WITH FRACTURED ACROMION Above:
"Stability and Instability of RTSA"
 Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Orthopedics Update «Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty» Stability and Instability of RTSA A. LÄDERMANN Orthopaedics and Traumatology, La Tour Hospital, Meyrin, Switzerland Orthopaedics and Traumatology,
Radiology Case Reports. Scapular Spine Stress Fracture as a Complication of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Radiology Case Reports Volume 2, Issue 2, 2007 Scapular Spine Stress Fracture as a Complication of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Kimberly J. Burkholz, Catherine C. Roberts, and Steven J. Hattrup We report
Radiology Case Reports Volume 2, Issue 2, 2007 Scapular Spine Stress Fracture as a Complication of Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Kimberly J. Burkholz, Catherine C. Roberts, and Steven J. Hattrup We report
Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement. «Shoulder Course» Day 1. Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern. 11. Sept.
 Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern First total shoulder prosthesis Jules Emile Péan, 1830-1898 Monobloc prostheses Charles Neer, 1917-2011
Biomechanical concepts of total shoulder replacement Richard W. Nyffeler Orthopädie Sonnenhof Bern First total shoulder prosthesis Jules Emile Péan, 1830-1898 Monobloc prostheses Charles Neer, 1917-2011
Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: An Analysis of the First 40 Cases
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:213-217 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.213 Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty:
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:213-217 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.213 Clinical Outcomes and Complications during the Learning Curve for Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty:
SSSR. 1. Nov Shoulder Prosthesis. Postoperative Imaging. Florian M. Buck, MD
 Shoulder Prosthesis Postoperative Imaging Florian M. Buck, MD Shoulder Prosthesis Surgical Approach Findings Imaging Modalities Postoperative Problems Shoulder Prosthesis What are we talking about Anatomical
Shoulder Prosthesis Postoperative Imaging Florian M. Buck, MD Shoulder Prosthesis Surgical Approach Findings Imaging Modalities Postoperative Problems Shoulder Prosthesis What are we talking about Anatomical
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Introduction
 Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Why are these shoulder replacements called a reverse prosthesis?
 PATIENT GUIDE TO REVERSE PROSTHESIS Edward G. McFarland MD The Division of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery The Department of Orthopaedic Surgery The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore MD Why are these
PATIENT GUIDE TO REVERSE PROSTHESIS Edward G. McFarland MD The Division of Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery The Department of Orthopaedic Surgery The Johns Hopkins University Baltimore MD Why are these
Matthew D. Saltzman, MD a, Deana M. Mercer, MD c, Winston J. Warme, MD b, Alexander L. Bertelsen, PA-C b, Frederick A. Matsen III, MD b, *
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2010) 19, 1028-1033 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse A method for documenting the change in center of rotation with reverse total shoulder arthroplasty and its application to a consecutive
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2010) 19, 1028-1033 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse A method for documenting the change in center of rotation with reverse total shoulder arthroplasty and its application to a consecutive
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications)
 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications) Emilie Cheung, MD Associate Professor Chief Shoulder Elbow Svc Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A New Frontier (of Complications) Emilie Cheung, MD Associate Professor Chief Shoulder Elbow Svc Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes
Shoulder Arthroplasty. Valentin Lance 3/24/16
 Shoulder Arthroplasty Valentin Lance 3/24/16 Outline Background Pre-operative imaging assessment Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Standard and Reverse Complications Other shoulder hardware Hemiarthroplasty
Shoulder Arthroplasty Valentin Lance 3/24/16 Outline Background Pre-operative imaging assessment Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Standard and Reverse Complications Other shoulder hardware Hemiarthroplasty
)532( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )532( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE The Midterm Results of the Delta Xtend Reverse Shoulder System: A Five-Year Outcome Study John G. Horneff, MD; Thema A. Nicholson,
)532( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE The Midterm Results of the Delta Xtend Reverse Shoulder System: A Five-Year Outcome Study John G. Horneff, MD; Thema A. Nicholson,
Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study.
 Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study. Byron F. Stephens, MD 1, Casey T. Hebert 2, Thomas W. Throckmorton, MD 1,
Optimal Baseplate Rotational Alignment in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Three-Dimensional Computer-Aided Design Study. Byron F. Stephens, MD 1, Casey T. Hebert 2, Thomas W. Throckmorton, MD 1,
Both anatomic (atsa) and reverse (rtsa) total
 S101 Comparison of Outcomes Using Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Yann Marczuk, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., Joseph Zuckerman, M.D., and
S101 Comparison of Outcomes Using Anatomic and Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D., Yann Marczuk, M.D., Martin Janout, M.D., Thomas W. Wright, M.D., Joseph Zuckerman, M.D., and
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
D Degenerative joint disease, rotator cuff deficiency with, 149 Deltopectoral approach component removal with, 128
 Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Index A Abduction exercise, outpatient with, 193, 194 Acromioclavicular arthritis, with, 80 Acromiohumeral articulation, with, 149 Acromio-humeral interval (AHI), physical examination with, 9, 10 Active
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Influence of Glenosphere Design on Outcomes and Complications of Reverse Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:288-297 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.288 Influence of Glenosphere Design on Outcomes and Complications of Reverse Arthroplasty: A Systematic
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:288-297 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.3.288 Influence of Glenosphere Design on Outcomes and Complications of Reverse Arthroplasty: A Systematic
The use of the Lima reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of fracture sequelae of the proximal humerus
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:141 147 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0185-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of the Lima reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of fracture sequelae of the proximal humerus Angel Antonio
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:141 147 DOI 10.1007/s00776-011-0185-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of the Lima reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of fracture sequelae of the proximal humerus Angel Antonio
Management of arthritis of the shoulder. Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
 Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Management of arthritis of the shoulder Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Diagnosis Pain - with activity initially. As disease progresses night pain is common and sleep difficult Stiffness trouble
Revision of reversed total shoulder arthroplasty. Indications and outcome
 Farshad et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012, 13:160 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Revision of reversed total shoulder arthroplasty. Indications and outcome Mazda Farshad *, Marion Grögli, Sabrina
Farshad et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2012, 13:160 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Revision of reversed total shoulder arthroplasty. Indications and outcome Mazda Farshad *, Marion Grögli, Sabrina
An evaluation of the radiological changes around the Grammont reverse geometry shoulder arthroplasty after eight to 12 years
 UPPER LIMB An evaluation of the radiological changes around the Grammont reverse geometry shoulder arthroplasty after eight to 12 years B. Melis, M. DeFranco, A. Lädermann, D. Molé, L. Favard, C. Nérot,
UPPER LIMB An evaluation of the radiological changes around the Grammont reverse geometry shoulder arthroplasty after eight to 12 years B. Melis, M. DeFranco, A. Lädermann, D. Molé, L. Favard, C. Nérot,
Scapular notching in reverse shoulder arthroplasties: The influence of glenometaphyseal angle
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97S, S131 S137 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scapular notching in reverse shoulder arthroplasties: The influence of glenometaphyseal angle V. Falaise a, C. Levigne
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97S, S131 S137 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Scapular notching in reverse shoulder arthroplasties: The influence of glenometaphyseal angle V. Falaise a, C. Levigne
Scapular Notching. Recognition and Strategies to Minimize Clinical Impact. Gregory P. Nicholson MD, Eric J. Strauss MD, Seth L.
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-010-1720-y SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Scapular Notching Recognition and Strategies to Minimize Clinical Impact Gregory P. Nicholson MD, Eric
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-010-1720-y SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Scapular Notching Recognition and Strategies to Minimize Clinical Impact Gregory P. Nicholson MD, Eric
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD
 Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
ANATOMIC TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT:
 The Shoulder Replacement A total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is a surgery to replace the damaged parts of the ball and socket shoulder joint with an artificial prosthesis. The damage to the shoulder can
The Shoulder Replacement A total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA) is a surgery to replace the damaged parts of the ball and socket shoulder joint with an artificial prosthesis. The damage to the shoulder can
Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design
 S37 Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Phong Diep,
S37 Optimizing Deltoid Efficiency with Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Using a Novel Inset Center of Rotation Glenosphere Design Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Phong Diep,
Assessment of Scapular Morphology and Surgical Technique as Predictors of Notching in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
 An Original Study Assessment of Scapular Morphology and Surgical Technique as Predictors of Notching in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Vani Sabesan, MD, Mark Callanan, MD, Vinay Sharma, BA, and J. Michael
An Original Study Assessment of Scapular Morphology and Surgical Technique as Predictors of Notching in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Vani Sabesan, MD, Mark Callanan, MD, Vinay Sharma, BA, and J. Michael
MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS POLICY STATEMENT. Page: 1 of 6
 Page: 1 of 6 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY (TOTAL, PARTIAL AND REVERSE) Policy Number 7.01.95 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 6/21/18 Revised
Page: 1 of 6 MEDICAL POLICY MEDICAL POLICY DETAILS Medical Policy Title SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY (TOTAL, PARTIAL AND REVERSE) Policy Number 7.01.95 Category Technology Assessment Effective Date 6/21/18 Revised
Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Shoulder Arthroplasty Nathan G. Everding, MD Specializing in Hand, Wrist, Elbow & Shoulder Surgery Syracuse Orthopedic Specialists SJH Family Practice Refresher course 3/8/19 Shoulder Arthroplasty Rate
Shoulder Arthroplasty Nathan G. Everding, MD Specializing in Hand, Wrist, Elbow & Shoulder Surgery Syracuse Orthopedic Specialists SJH Family Practice Refresher course 3/8/19 Shoulder Arthroplasty Rate
Assessment of Approximate Glenoid Size in Thai People
 Assessment of Approximate Glenoid Size in Thai People J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (Suppl. 2): S14-S18 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Pason Phonphok MD*, Nattha Kulkamthorn MD* * Division
Assessment of Approximate Glenoid Size in Thai People J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (Suppl. 2): S14-S18 Full text. e-journal: http://www.jmatonline.com Pason Phonphok MD*, Nattha Kulkamthorn MD* * Division
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD
 General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH)
General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Shawn Hennigan, MD Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH)
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of three and four part fractures of the proximal humerus in patients older than 75 years old
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 99-105 ORIGINAL STUDY Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of three and four part fractures of the proximal humerus in patients older than 75 years old Aristotelis
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 99-105 ORIGINAL STUDY Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of three and four part fractures of the proximal humerus in patients older than 75 years old Aristotelis
Making sense of all our measures-inclination, version, subluxation, reaming depth & implant seating
 Thursday - ANATOMIC SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY 7:00-7:15a Welcome and Introduction of Faculty Athwal, Keener, 7:15-7:22a The ABC s of the Walch Classification Walch 7:22-7:32a How I use x-rays, CT +/- MRI for
Thursday - ANATOMIC SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY 7:00-7:15a Welcome and Introduction of Faculty Athwal, Keener, 7:15-7:22a The ABC s of the Walch Classification Walch 7:22-7:32a How I use x-rays, CT +/- MRI for
0 Introduction (20.9%) [7]
![0 Introduction (20.9%) [7] 0 Introduction (20.9%) [7]](/thumbs/92/108991709.jpg) Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research www.crter.org ( 443000) DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0187 ORCID: 0000-0003-0005-1839() 60 120 2 60 1980 2015 443000 :R318 :A 2017-12-05 3 4 120 60 () 3 (P
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research www.crter.org ( 443000) DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0187 ORCID: 0000-0003-0005-1839() 60 120 2 60 1980 2015 443000 :R318 :A 2017-12-05 3 4 120 60 () 3 (P
what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you
 TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
TOTAL shoulder REPLACEMENT what you is back within LOVE arm s reach find out why the exactech shoulder may be right for you how does your shoulder work? The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body.
Convertibilité. Ph. Valenti. Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France)
 Convertibilité Ph. Valenti Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties Arthroscopy Consultant : Zimmer Biomet Arthrex In Last
Convertibilité Ph. Valenti Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties Arthroscopy Consultant : Zimmer Biomet Arthrex In Last
AJO DO NOT COPY. The low grade of the intrinsic stability of the shoulder. Total Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: European Lessons and Future Trends
 A Review Paper Total Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: European Lessons and Future Trends Ludwig Seebauer, MD Abstract In the late 1980s, Grammont introduced a new reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA),
A Review Paper Total Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty: European Lessons and Future Trends Ludwig Seebauer, MD Abstract In the late 1980s, Grammont introduced a new reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (TSA),
S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r T i b l e S h o u l d e r S y S T e m
 S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m A n a t o m i c Aequalis Ascend Flex - UDZF131 One System. Two Solutions.
S h o u l d e r Solutions by Tornier C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m C o n v e r t i b l e s h o u l d e r s y s t e m A n a t o m i c Aequalis Ascend Flex - UDZF131 One System. Two Solutions.
SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY (TOTAL, HEMI, REVERSE)/ARTHRODESIS
 evicore healthcare. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
evicore healthcare. Clinical Decision Support Tool Diagnostic Strategies This tool addresses common symptoms and symptom complexes. Imaging requests for patients with atypical symptoms or clinical presentations
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Early Outcome and Complication Report
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 17, No. 2, June, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2014.17.2.68 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Early Outcome
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 17, No. 2, June, 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2014.17.2.68 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Early Outcome
Objectives. Coracoid Fractures in Football: Evaluation and Management. Objectives. Introduction 5/8/2017
 Objectives Coracoid Fractures in Football: Evaluation and Management Discuss operative and non-operative management of coracoid fractures Chris Warrell, M.D. Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Fellow Andrews
Objectives Coracoid Fractures in Football: Evaluation and Management Discuss operative and non-operative management of coracoid fractures Chris Warrell, M.D. Orthopaedic Sports Medicine Fellow Andrews
Orthopedics - Dr. Ahmad - Lecture 2 - Injuries of the Upper Limb
 The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
The shoulder and the upper arm Fractures of the clavicle 1. Fall on the shoulder. 2. Fall on outstretched hand. In mid shaft fractures, the outer fragment is pulled down by the weight of the arm and the
Reverse Total Shoulder. Dr. Minoo Patel
 Reverse Total Shoulder Dr. Minoo Patel AOA VIC, Lorne, 2011 The role of the rotator cuff Depress and humeral head (against the force of the deltoid) Keep the humeral head co-apted in the glenoid Initiate
Reverse Total Shoulder Dr. Minoo Patel AOA VIC, Lorne, 2011 The role of the rotator cuff Depress and humeral head (against the force of the deltoid) Keep the humeral head co-apted in the glenoid Initiate
Effect of Prosthesis Design on Muscle Length and Moment Arms in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 S31 Effect of Prosthesis Design on Muscle Length and Moment Arms in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Pierre- Henri Flurin,
S31 Effect of Prosthesis Design on Muscle Length and Moment Arms in Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Matthew A. Hamilton, Ph.D., Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Pierre- Henri Flurin,
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Improves Function in Cuff Tear Arthropathy
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2011) 469:2476 2482 DOI 10.1007/s11999-010-1683-z SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Improves Function in Cuff Tear Arthropathy Betsy
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2011) 469:2476 2482 DOI 10.1007/s11999-010-1683-z SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Improves Function in Cuff Tear Arthropathy Betsy
Bulletin of the Hospital for Joint Diseases 2013;71(4):284-93
 284 Impact of Inferior Glenoid Tilt, Humeral Retroversion, Bone Grafting, and Design Parameters on Muscle Length and Wrapping in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong
284 Impact of Inferior Glenoid Tilt, Humeral Retroversion, Bone Grafting, and Design Parameters on Muscle Length and Wrapping in Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
 Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Use of a partial humeral head resurfacing system for management of an osseous mechanic... Page 1 of 12 Int J Shoulder Surg. 2011 Jan-Mar; 5(1): 17 20. doi: 10.4103/0973-6042.80465. PMCID: PMC3109768 Copyright
Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini
 Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Open Access Case report Posterolateral elbow dislocation with entrapment of the medial epicondyle in children: a case report Juan Rodríguez Martín* and Juan Pretell Mazzini Address: Department of Orthopaedic
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis
 Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis Effective January 1, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit
Cigna Medical Coverage Policies Musculoskeletal Shoulder Arthroplasty (Total, Hemi, Reverse)/Arthrodesis Effective January 1, 2016 Instructions for use The following coverage policy applies to health benefit
Reverse shoulder arthroplasty : Does reduced medialisation improve radiological and clinical results?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 158-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Reverse shoulder arthroplasty : Does reduced medialisation improve radiological and clinical results? Ibrahim KALOUCHE, Nuno SEVIVAS, Abhijeet WAHEGAONKER,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 158-166 ORIGINAL STUDY Reverse shoulder arthroplasty : Does reduced medialisation improve radiological and clinical results? Ibrahim KALOUCHE, Nuno SEVIVAS, Abhijeet WAHEGAONKER,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
RCR or rtsa? Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair? JESSE W. ALLERT, MD THOMAS SELLERS, MD PETER SIMON, PHD RACHEL CLARK,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis in Patients Older than 65 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty or Rotator Cuff Repair? JESSE W. ALLERT, MD THOMAS SELLERS, MD PETER SIMON, PHD RACHEL CLARK,
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX. Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW
 TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
TORNIER AEQUALIS FX Shoulder System SYSTEM OVERVIEW Simple in design, but used for the most complex fractures Each year, approximately 4 million people in the United States seek medical care for shoulder
Not relevant to this presentation.
 Nolan R. May, MD Kearney, NE Heartland Surgery Center, Kearney NE Not relevant to this presentation. 1 What are the indications for total shoulder arthroplasty? What are the differences between total shoulder
Nolan R. May, MD Kearney, NE Heartland Surgery Center, Kearney NE Not relevant to this presentation. 1 What are the indications for total shoulder arthroplasty? What are the differences between total shoulder
Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 S5 Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Sean G. Grey, M.D., and Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D. Abstract
S5 Biomechanical Impact of Posterior Glenoid Wear on Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Christopher P. Roche, M.S., M.B.A., Phong Diep, B.S., Sean G. Grey, M.D., and Pierre-Henri Flurin, M.D. Abstract
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Shoulder Problems Fractures Instability Impingement Miscellaneous Anatomy Bones Joints / Ligaments Muscles Neurovascular Anatomy Anatomy Supraspinatus Anterior Posterior Anatomy
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Shoulder Problems Fractures Instability Impingement Miscellaneous Anatomy Bones Joints / Ligaments Muscles Neurovascular Anatomy Anatomy Supraspinatus Anterior Posterior Anatomy
Gerald R. Williams, MD
 Reverse Arthroplasty: Is Overutilization a Problem? Gerald R. Williams, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery The Rothman Institute Jefferson Medical College Royalties Conflict
Reverse Arthroplasty: Is Overutilization a Problem? Gerald R. Williams, MD John M. Fenlin, Jr, MD Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery The Rothman Institute Jefferson Medical College Royalties Conflict
Reverse Total Shoulder Protocol
 Marion Herring, M.D. OrthoVirginia PH: (804) 270-1305 FX: (804) 273-9294 www.orthovirginia.com Reverse Total Shoulder Protocol General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed
Marion Herring, M.D. OrthoVirginia PH: (804) 270-1305 FX: (804) 273-9294 www.orthovirginia.com Reverse Total Shoulder Protocol General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed
The Shoulder. By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson
 The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
The Shoulder By Patrick Ryan, Bobby Law, Jack Beaty, Alex Newhouse and Chuck Nelson Learning Objectives/Agenda Review the anatomy of the shoulder Describe the main diseases of the shoulder Describe the
Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA
 Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA Joseph A. Abboud, M.D. Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Senior Vice-President at the Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA Disclosures Joseph A. Abboud, MD Depuy Synthes
Conversion of Anatomic TSA to RSA Joseph A. Abboud, M.D. Professor of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Senior Vice-President at the Rothman Institute Philadelphia, PA Disclosures Joseph A. Abboud, MD Depuy Synthes
What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures?
 NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
NHMI Winter Meeting Stowe, VT January 2015 What s New in the Treatment of Proximal Humerus Fractures? John Bell, M.D., M.S. Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Les séquelles traumatiques. Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz
 Indications et Techniques Les séquelles traumatiques Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties
Indications et Techniques Les séquelles traumatiques Ph. Valenti, J. Kany, D. Katz Paris Shoulder Unit Clinique Bizet (Paris, France) Disclosures Arthroplasty Consultant : FH orthopaedics receive royalties
The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear:
 The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear: Trauma 101: Shoulder Session #2 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 5/10/2018 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Phone Number: 513-558-4516
The Irreparable Rotator Cuff Tear: Trauma 101: Shoulder Session #2 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine 5/10/2018 Brian Grawe, MD Assistant Professor Phone Number: 513-558-4516
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review of Results According to Etiology
 1476 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review of Results According to Etiology By Bryan Wall, MD, Laurent Nové-Josserand, MD,
1476 COPYRIGHT 2007 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Review of Results According to Etiology By Bryan Wall, MD, Laurent Nové-Josserand, MD,
REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT
 REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is designed specifically for the use in shoulders with a deficient rotator cuff and arthritis, as well as other difficult shoulder reconstructive
REVERSE SHOULDER REPLACEMENT The Reverse Shoulder Replacement is designed specifically for the use in shoulders with a deficient rotator cuff and arthritis, as well as other difficult shoulder reconstructive
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol
 General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it
General Information: Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Protocol Reverse or Inverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty (rtsa) is designed specifically for the treatment of glenohumeral (GH) arthritis when it
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
The Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. The Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Frederick A. Matsen, III, Pascal
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. The Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Frederick A. Matsen, III, Pascal
Reverse Prostheses in Arthropathies With Cuff Tear
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2011) 469:2469 2475 DOI 10.1007/s11999-011-1833-y SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Reverse Prostheses in Arthropathies With Cuff Tear Are Survivorship and Function
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2011) 469:2469 2475 DOI 10.1007/s11999-011-1833-y SYMPOSIUM: REVERSE TOTAL SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY Reverse Prostheses in Arthropathies With Cuff Tear Are Survivorship and Function
P V S MEMORIAL HOSPITAL LTD.
 SHOULDER XRAYS Instability Series o True AP (Grashey s) o Axillary o Stryker Notch view o True AP in Internal rotation o Scapular Y view o West Point view for Bony Bankart ( looks like modif axillary view)
SHOULDER XRAYS Instability Series o True AP (Grashey s) o Axillary o Stryker Notch view o True AP in Internal rotation o Scapular Y view o West Point view for Bony Bankart ( looks like modif axillary view)
CLINICAL GUIDELINES. CMM-318: Shoulder Arthroplasty/ Replacement/Resurfacing/ Revision/Arthrodesis. Version Effective October 22, 2018
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES CMM-318: / Replacement/Resurfacing/ Revision/Arthrodesis Version 20.0.2018 Effective October 22, 2018 Clinical guidelines for medical necessity review of speech therapy services. CMM-318:
CLINICAL GUIDELINES CMM-318: / Replacement/Resurfacing/ Revision/Arthrodesis Version 20.0.2018 Effective October 22, 2018 Clinical guidelines for medical necessity review of speech therapy services. CMM-318:
Instability After Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Which Patients Dislocate?
 An Original Study Instability After Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Which Patients Dislocate? Eric M. Padegimas, MD, Benjamin Zmistowski, MD, Camilo Restrepo, MD, Joseph A. Abboud, MD, Mark D. Lazarus,
An Original Study Instability After Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: Which Patients Dislocate? Eric M. Padegimas, MD, Benjamin Zmistowski, MD, Camilo Restrepo, MD, Joseph A. Abboud, MD, Mark D. Lazarus,
3/9/2018. Algorithm for Massive RCT s. Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Introduction 7/14/2014. Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Optimizing Outcomes. Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty. Kim Kraft, PT, DPT, CHT
 Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Optimizing Outcomes Kim Kraft, PT, DPT, CHT Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty How is it different than a normal shoulder replacement? What are the therapy precautions?
Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Optimizing Outcomes Kim Kraft, PT, DPT, CHT Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty How is it different than a normal shoulder replacement? What are the therapy precautions?
P. Trouilloud M. Gonzalvez P. Martz H. Charles F. Handelberg R. W. Nyffeler E. Baulot DuocentricÒ Group
 DOI 10.1007/s00590-013-1213-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Duocentric Ò reversed shoulder prosthesis and Personal Fit Ò templates: innovative strategies to optimize prosthesis positioning and prevent scapular notching
DOI 10.1007/s00590-013-1213-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Duocentric Ò reversed shoulder prosthesis and Personal Fit Ò templates: innovative strategies to optimize prosthesis positioning and prevent scapular notching
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Shoulder Arthroplasty Review. Gregory P. Nicholson, M.D.
 Shoulder Arthroplasty Review Gregory P. Nicholson, M.D. Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush Rush University Medical Center Chicago, Illinois Etiologies of degenerative joint disease of shoulder: Osteoarthritis
Shoulder Arthroplasty Review Gregory P. Nicholson, M.D. Midwest Orthopaedics at Rush Rush University Medical Center Chicago, Illinois Etiologies of degenerative joint disease of shoulder: Osteoarthritis
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Reverse Shoulder System. Abstracts
 TM Reverse Shoulder System s 2 Contents Introduction 2 Reverse shoulder arthroplasty components and surgical techniques that restore glenohumeralmotion 3 Isometric strength, range of motion, and impairment
TM Reverse Shoulder System s 2 Contents Introduction 2 Reverse shoulder arthroplasty components and surgical techniques that restore glenohumeralmotion 3 Isometric strength, range of motion, and impairment
WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH
 YOUR TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH Nathan Richardson, MD Orthopedics, Shoulder & Elbow Surgeon Board Certified in
YOUR TOTAL SHOULDER REPLACEMENT SURGERY STEPS TO RETURNING TO A LIFESTYLE YOU DESERVE WHAT YOU IS BACK WITHIN ARM S REACH Nathan Richardson, MD Orthopedics, Shoulder & Elbow Surgeon Board Certified in
Disclosures A prospective comparison between reverse and anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty
 Disclosures A prospective comparison between reverse and anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty Tuyen Kiet Micah Naimark, MD Brian T. Feeley, MD Teddy T. Chung Tatiana Gajiu Sarah L. Hall, MA C. Benjamin
Disclosures A prospective comparison between reverse and anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty Tuyen Kiet Micah Naimark, MD Brian T. Feeley, MD Teddy T. Chung Tatiana Gajiu Sarah L. Hall, MA C. Benjamin
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
Integra. Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5
 Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Titan Modular Shoulder System, 2.5 Limit uncertainty with a shoulder implant system that redefines modularity, addresses multiple indications, and allows for reproducible results. Titan Modular Shoulder
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Disclosure. Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability 7/23/2018. Orthopaedics for the Primary Care Practitioner & Rehabilitation Therapist
 Orthopaedics for the Primary Care Practitioner & Rehabilitation Therapist Christopher E. Baker M.D. Sports Medicine Shoulder Reconstruction Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability Disclosure Speaking/Consulting
Orthopaedics for the Primary Care Practitioner & Rehabilitation Therapist Christopher E. Baker M.D. Sports Medicine Shoulder Reconstruction Traumatic Anterior Shoulder Instability Disclosure Speaking/Consulting
Shoulder Revisions: Why Are We Here?
 Shoulder Revisions: Why Are We Here? Indications for Revision to RSA Mark A. Frankle, MD Kaitlyn N. Christmas, BS Peter Simon, PhD DJO Revision Course 2017 June 2-3 Introduction Reverse shoulder arthroplasty(rsa)
Shoulder Revisions: Why Are We Here? Indications for Revision to RSA Mark A. Frankle, MD Kaitlyn N. Christmas, BS Peter Simon, PhD DJO Revision Course 2017 June 2-3 Introduction Reverse shoulder arthroplasty(rsa)
Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris
 Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris Proximal Complex fracture of the humerus Surgeon is not always happy!!!! Reduction is not anatomical!!!! Great tuberosity is not reduced!!!
Fracture complexe ESH Que choisir? Hémi ou Inversée Ph Valenti Paris Proximal Complex fracture of the humerus Surgeon is not always happy!!!! Reduction is not anatomical!!!! Great tuberosity is not reduced!!!
Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) -, 1-6 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty Heinz R. Hoenecke Jr., MD*, Juan C. Hermida, MD, Cesar
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) -, 1-6 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty Heinz R. Hoenecke Jr., MD*, Juan C. Hermida, MD, Cesar
Index. ESSKA 2018 G. Milano et al. (eds.), Management of Failed Shoulder Surgery,
 A Acromial fractures, 186 Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) instability, 55, 97 case study, 98 100 classification, 85 clinical relevant situations, 86 dislocation, 97 98 insufficient fixation, 87 88 operative
A Acromial fractures, 186 Acromioclavicular joint (ACJ) instability, 55, 97 case study, 98 100 classification, 85 clinical relevant situations, 86 dislocation, 97 98 insufficient fixation, 87 88 operative
Bilateral Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Versus Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Bilateral Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Versus Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Vaqar Latif, MD; Patrick J. Denard, MD; Allan A. Young, MD; Jean-Pierre Liotard, MD; Gilles Walch, MD abstract Full article
Bilateral Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Versus Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty Vaqar Latif, MD; Patrick J. Denard, MD; Allan A. Young, MD; Jean-Pierre Liotard, MD; Gilles Walch, MD abstract Full article
)19( COPYRIGHT 2019 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )19( COPYRIGHT 2019 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Failure of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with Revision to Another Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Mihir Sheth,
)19( COPYRIGHT 2019 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Failure of Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with Revision to Another Anatomic Total Shoulder Arthroplasty Mihir Sheth,
Case 61. Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative.
 Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
ASSESMENT OF KEY PARAMETERS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF THE DELTOID MUSCLE IN REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY A MODELING AND SIMULATION BASED STUDY
 ASSESMENT OF KEY PARAMETERS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF THE DELTOID MUSCLE IN REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY A MODELING AND SIMULATION BASED STUDY NAVID ASLANI Department of Design and Engineering, Faculty of
ASSESMENT OF KEY PARAMETERS ON THE PERFORMANCE OF THE DELTOID MUSCLE IN REVERSE SHOULDER ARTHROPLASTY A MODELING AND SIMULATION BASED STUDY NAVID ASLANI Department of Design and Engineering, Faculty of
Reversed Revised : What to do when it goes wrong?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 314-321 ORIGINAL STUDY Reversed Revised : What to do when it goes wrong? Bart Middernacht, Alexander Van Tongel, Lieven De Wilde From Department of Orthopaedics, University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2014, 80, 314-321 ORIGINAL STUDY Reversed Revised : What to do when it goes wrong? Bart Middernacht, Alexander Van Tongel, Lieven De Wilde From Department of Orthopaedics, University
Shoulder Joint Examination. Shoulder Joint Examination. Inspection. Inspection Palpation Movement. Look Feel Move
 Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
