Do small changes in rotation affect measurements of lower extremity limb alignment?
|
|
|
- Lindsay Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Do small changes in rotation affect measurements of lower extremity limb alignment? Amir A. Jamali 1*, John P. Meehan 2, Nathan M. Moroski 3, Matthew J. Anderson 4, Ramit Lamba 5 and Carol Parise 6 Abstract Background: The alignment of the lower extremity has important implications in the development of knee arthritis. The effect of incremental rotations of the limb on common parameters of alignment has not been studied. The purpose of the study was to (1) determine the standardized neutral position measurements of alignment and (2) determine the effect of rotation on commonly used measurements of alignment. Methods: Eighty-seven full length CT angiography studies (49 males and 38 females, average age 66 years old) were included. Three-dimensional models were created using a rendering software program and placed on a virtual plane. An image of the extremity was obtained. Thirty scans were randomly selected, and those models were rotated in 3 intervals around the longitudinal axis and additional images were obtained. Results: In the neutral position, the mechanical lateral distal femoral articular angle (mldfa) was 85.6 ± 2.3, medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) was 86.1 ± 2.8, and mechanical tibiofemoral angle (mtfa) was 0.7 ± 3.1. Females had a more valgus alignment with a mtfa of 0.5 ± 2.9 while males had a more varus alignment with a mtfa of 1.7 ± 2.9. The anatomic tibiofemoral angle (atfa) was 4.8 ± 2.6, the anatomic lateral distal femoral angle (aldfa) measured 80.2 ± 2.2, and the anatomical-mechanical angle (AMA) was 5.4 ± 0.7. The prevalence of constitutional varus was 18%. The effect of rotation on the rotated scans led to statistically significant differences relative to the 0 measurement for all measurements. These effects may be small, and their clinical importance is unknown. Conclusions: This study provides new information on standardized measures of lower extremity alignment and the relationship between discreet axial rotations of the entire lower extremity and these parameters. Keywords: Alignment, Lower extremity, Osteotomy, Rotation, Constitutional varus, Total knee replacement Background The alignment of the lower extremity has been an area of ongoing study for decades. Standard have been used to determine the normal parameters of alignment of the lower extremity. These are prone to technical errors based on distance from the cassette and rotation of the lower extremity around the longitudinal axis. Deviations from normal have been broadly categorized at malalignment although a clear definition of normal alignment has not been established. One can define normal on a statistical basis as lying within some arbitrarily defined range relative to the mean or on * Correspondence: contact@hipandknee.net 1 Joint Preservation Institute, 2825 J Street, Suite 440, Sacramento, CA 95816, USA Full list of author information is available at the end of the article a pathological basis according to the risk of the joint undergoing degeneration secondary to the deformity. Malalignment of the native lower extremity has been associated in previous studies with a higher risk of osteoarthritis [1 4]. Accurate preoperative and postoperative alignment parameters are required for planning and prediction of outcome for both osteotomies and total knee replacement [5 11]. Thus, the assessments of both the lower extremity alignment in native knees and those that have undergone replacement depend on an accurate definition of native lower extremity alignment [12, 13]. In spite of increased sophistication in imaging and computer generated reconstructions, most surgeons still depend on two-dimensional in planning The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 2 of 8 operations such as osteotomy, unicompartmental knee replacement, or total knee replacement. The objectives of this study were twofold. We sought to (1) determine the standardized neutral position measurements of alignment and (2) determine the effect of rotation on commonly used measurements of alignment. We prepared three-dimensional models of the lower extremity in a standardized position and rotated the models in 3 increments in each direction, taking digital photographs in each position. Methods A total of 221 full lower extremity CT angiography studies for vascular disease workup were performed at our institute between July 8, 2008, and May 14, Of these, 87 patients (49 males and 38 females) were included in the present study. The average age was 66 years old (range years old) Exclusion criteria included advanced osteoarthritis of the hip, knee, or ankle, radiographic evidence of previous realignment surgery or fracture, irregular positioning in the scanner, or any type of lower extremity joint prosthesis. Normal values of coronal alignment of the lower extremities with the femur placed on a virtual flat table The first portion of the study was the determination of the normal values of coronal alignment of the lower extremity without the effect of rotation and in a neutral position. Three-dimensional models were created from the CT data using a commercially available and previously validated three-dimensional rendering software program (Mimics, Materialise, Ann Arbor, MI) [14]. These models were then placed on a virtual flat table in the computer environment. The femora rested with the virtual table plane passing through the posterior most point of the greater trochanter and the posterior most points of both the medial and lateral femoral condyles. In this neutral position, a high resolution image of the femur and the tibia from anterior to posterior was obtained. Next, 30 scans were randomly selected, and using the software, the entire lower extremity model was rotated in discreet 3 intervals in both internal and external rotation around the virtual axis from the femoral head to the center of distal femur up to 12 in each direction. After each rotation, a new anterior to posterior image of the now rotated lower extremity was obtained. The image files were then analyzed using a custom measurement analysis program written in Matlab (Mathworks, Natick, MA, USA). The analysis was performed in this fashion to optimize speed and precision and minimize risk of observer bias. The independent variable was the degree of rotation. The dependent variables were the alignment parameters measured. Definitions for image analysis, points, axes, and angular measurements Points The convention used by Moreland et al. was utilized to define the center of the femoral trochlea as the center point of the knee [15]. Moreland et al. had described taking a visual midpoint among a total of five points to define the center of the knee. These included the center of the femoral notch (trochlea), center of tibial spines, center of femoral condyles, center of soft tissue, and center of the tibia. They found that all points were within 5 mm of one another. Based on the high consistency of the center of the femoral trochlea, we chose that point as the center of the knee. The center of the ankle was defined visually as the center of the distal tibial articular surface. The other points selected on lower extremity images obtained were the center of the femoral head, the most distal points of the distal medial and lateral femoral condyles, and the most proximal point of the medial and lateral tibial plateaus. The proximal femoral shaft center (PFSC) was defined by selecting two lateral points and two medial points in the subtrochanteric region of the femur and allowing the software to calculate the geometric center of those four points located centrally within the femoral shaft in the subtrochanteric region. Axes Mechanical axes The mechanical axis of the femur was defined as a line drawn from the center of the femoral head to the center of the knee. The mechanical and anatomical axes of the tibia were both defined in an identical fashion as the line connecting the center of the knee and the center of the ankle. Anatomical axes The line connecting the PFSC and the center of the femoral trochlea was used to define the anatomical axis of the femur. The line connecting the center of the femoral trochlea and the center of the ankle was used to define the anatomical and mechanical axes of the tibia as noted above. Articular axes The distal femoral articular axis was defined by the line connecting the distal most points of the medial and lateral femoral condyles. The proximal tibial articular axis was defined as the line connecting the two most proximal points of the tibial plateaus.
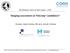
3 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 3 of 8 Angular measurements Mechanical angle measurements The mechanical lateral distal femoral articular angle (mldfa) was defined as the lateral angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the distal femoral articular axis [16] (Fig. 1a). The medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) was unique among the measurements in that it was included in both the mechanical parameters and the anatomical parameters and was defined as the medial angle between the mechanical (as well as anatomical) axis of the tibia and the proximal tibial articular axis (Fig. 1b). The mechanical tibiofemoral angle (mtfa) [16] was defined as the angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the tibial mechanical axis with a positive value indicative of a valgus alignment and a negative value indicative of a varus alignment of the lower extremity (Fig. 1c). The joint line convergence angle (JLCA) was defined as the angle between the proximal tibial and distal femoral articular axes with a negative value indicative of convergence laterally and a positive value indicative of convergence medially (Fig. 1d). Anatomical angle measurements The anatomic tibiofemoral angle (atfa) [16] was defined as the angle between the anatomical axis of the femur and the anatomical-mechanical axis of the tibia (Fig. 1e). Once again, a positive value was indicative of a valgus and a negative value indicative of a varus alignment of the lower extremity. The angle between the mechanical and anatomical axes of the femur was defined as the anatomical-mechanical angle (AMA) [16] (Fig. 1f). The anatomical lateral distal femoral angle (aldfa) was defined as the angle between the anatomical axis of the femur and the distal femoral articular axis [16] (Fig. 1g). The anatomical medial proximal tibial angle was by convention defined to be equivalent to the medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) due to the equivalence of the mechanical and anatomical tibial axes as noted above. Effect of 3 rotational intervals on coronal alignment The rotated anterior to posterior (AP) images of the 3D models of 30 randomly selected specimens were analyzed in the same fashion as the neutral AP images described above. By convention, negative measurements indicated the lower extremity to be internally rotated and positive measurements externally rotated around the longitudinal axis of the femur. Statistical analysis Inter- and intraobserver reliability analysis was performed for each parameter using intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) for intraobserver reliability analysis for observer 1 (AAJ) at two time points 4 weeks apart and interobserver reliability between the two observers (AAJ and MA) for a total of 20 of subjects. All ICCs were Fig. 1 Measurement methods of common parameters of lower extremity alignment studied in this paper. a mldfa. b MPTA. c mtfa. d JLCA. e atfa. f AMA. g aldfa
4 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 2 Histogram of mechanical tibiofemoral angle (mtfa) in patients in the series subcategorized by gender greater than 0.94 indicating excellent reliability with the exception of the measurements of JLCA with ICC of 0.18 and 0.68 for inter- and intraobserver reliability respectively. The effect of rotation of each parameter was analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance (RMANOVA) with Bonferroni correction as appropriate. The prevalence of constitutional varus based on gender was analyzed using the chi-squared test. All analyses were performed with SPSS (IBM, Chicago, IL), Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA), and StatView software (SAS, Cary, NC). Statistical significance was set at p < Results Mechanical measurements The mldfa was 85.6 ± 2.3. The MPTA was 86.1 ± 2.8. The JLCA angle was 1.2 ± 1.7. The mechanical tibiofemoral angle (mtfa) was 0.7 ± 3.1. Females had a more valgus alignment with a mtfa of 0.5 ± 2.9 while males had a more varus alignment with a mtfa of 1.7 ± 2.9 (Fig. 2) (Table 1). Constitutional varus The prevalence of constitutional varus defined as mtfa of more than 3 varus was 16/87, or 18%. There was a statistically significant difference (p = 0.005) in the prevalence based on gender with 2/38, or 5% of females, and 14/49, or 29% for males, being classified as constitutional varus. Anatomical measurements The anatomic tibiofemoral angle (atfa) was 4.8 ± 2.6. The anatomic lateral distal femoral angle (aldfa) measured 80.2 ± 2.2. The medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) was 86.1 ± 2.8. The anatomical-mechanical angle (AMA) was 5.4 ± 0.7. Effect of rotation The effect of rotation in 3 increments led to a statistically significant difference in measurements for all measurements except for aldfa and mldfa. For aldfa and mldfa, there was no significant difference in spite of rotation of the images. For the remaining parameters, the effect of rotation varied. Measurements taken with the lower extremity rotated as little as 3 leading to significant differences (Fig. 3). For the mtfa, atfa, and AMA measurements, pairwise comparisons indicated that all rotated measurements were significantly different from the neutral, 0, rotational position. This indicated that even a 3 rotational variation in these parameters leads to a statistically significant difference in the measured value. For MPTA, measurements at the 3 and 6 positions were not significantly different than those at the neutral position while all others were significantly different than the neutral position value. JLCA was not analyzed due to the low interobserver reliability of that measurement. Table 1 Summary of lower extremity alignment measurements from this study (n=87) Mechanical alignment parameters Mechanical lateral distal femoral articular angle (mldfa) 85.6 ± 2.3 Medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) 86.1 ± 2.8 Mechanical tibiofemoral angle 0.7 ± 3.1 The joint line convergence angle (JLCA) 1.2 ± 1.7 Anatomical alignment parameters Anatomic tibiofemoral angle (atfa) 4.8 ± 2.6 Lateral distal femoral angle (aldfa) 80.2 ± 2.2 Medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) 86.1 ± 2.8 Other Anatomical-mechanical angle (AMA). 5.4 ± 0.7
5 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 5 of 8 Fig. 3 a f Effect of rotation on various measured parameters of lower extremity alignment (n = 30). Degrees for each parameter ±S.D. (Green indicates no significant difference relative to baseline or 0 measurement) Discussion The objective of this study was to twofold. The first goal was to obtain commonly performed measurements of alignment using standardized three-dimensional lower extremity models in a neutral position and to compare those values to data previously reported in the literature. Based on our analysis of the available literature, the measurements obtained in the study were comparable to those of the previous literature (Table 2) [1, 15, 17 20]. Our second goal was to determine the effect of rotation of the lower extremity, even in as little as 3 intervals, on these commonly performed measurements of alignment. We found that small amounts of rotation did lead to statistically significant differences for a number of parameters analyzed including mtfa, atfa, and AMA and to a limited degree for MPTA. Bellemans et al. performed a study using standard positioned according to the methodology of Paley [16]. The study consisted of 250 volunteers, 125 male and 125 female. They measured many of the same parameters as in our study. Their main finding of their study was that 32% of males and 17% of females fit the
6 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 6 of 8 Table 2 Literature review Reference Number of normal subjects Present study 87 patients undergoing CT angiography Mean age Gender Technique aldfa mldfa MPTA AMA mtfa JLCA N/A 49M, 38F 3D CT reconstructions with computer assisted analysis ± ± ± ± ± ± healthy volunteers 38 52M, 67F Standard full length N/A ± 2.33 N/A 0.97 ± ± male volunteers 30 25M, 0F Standard full length N/A N/A (varus) N/A healthy Chinese adult volunteers 23-year-old females, 24-year-old males 25M, 25F Standard full length N/A N/A 85.1 (males), 84.6 (females) 3.6 males, 3.1 females 2.2 (males and females) N/A healthy Caucasian adult volunteers range M, 60F Standard full length N/A ± ± 2.2 N/A healthy Iranian adult volunteers range M, 50F Standard full length 83.2 ± 3 N/A ± (varus) 1 ± healthy female Korean volunteers range F Standard full length N/A ± ± ± ± 2.04 N/A
7 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 7 of 8 criteria of constitutional varus defined as a hip-kneeankle (HKA, equivalent to mtfa in this study) angle of 3 or greater varus. They further postulated that correcting such patients to a neutral mechanical axis through total knee replacement may lead to unfavorable outcomes. The authors noted one of the weaknesses of their study was the use of plain. They indicated that the rotational position of the extremities was controlled by positioning the subjects standing barefoot with the feet together and standing at attention with the patella oriented forward. Although this is a widely used technique, it is clear that all studies that use this methodology are at best estimating at the degree of rotation of the extremities. They considered the use of CT scans but were concerned about increased radiation. Our study addressed the issues discussed by Bellemans et al. By using CT scan generated models using preexisting scans, we avoided any additional radiation to patients. We also addressed the rotational variability of the positioning by placing the models on virtual planes and taking images in this position for the semiautomatic analysis. Song et al. explored the incident of constitutional varus in a controlled population of normal volunteers demonstrating a 20% incidence of constitutional varus in a group of Korean female volunteers [21]. Our data demonstrated a lower incidence of constitutional varus than both of these studies. This may reflect the different methodologies used (CT generated 3D models vs standard ) as well as a different population (Belgian and Korean populations compared to a population from the USA). A number of studies have evaluated the effect of rotation on lower extremity alignment parameters. Oswald et al. performed a cadaveric study on 38 lower extremity specimens using standard and analyzed the effect of rotation on the anatomic mechanical angle (AMA) [22]. At neutral, the AMA was 6.3. They noted a change in this angle from 6.8 in 15 of internal rotation to 5.7 in 15 of external rotation for an average decrease in the AMA of per degree of rotation. Radtke et al. performed a limited study on one lower extremity saw bone model in which a total knee replacement was implanted [23]. They then took five series of X-rays of that specimen measuring the AMA in various rotations from 20 of internal rotation (6.83 ) to 20 of external rotation (4.63 ) for an average decrease of per degree of rotation. In our series, the AMA in the rotated studies was 5.33 at neutral and decreased from 5.43 to 5.08 between 12 of internal rotation and 12 of external rotation for an average decrease of per degree of rotation. This study has a number of important weaknesses. The population included in this study was a random sample of patients undergoing CT angiography for vascular disease. As a result, the majority of the subjects were elderly with an average age of 66 years old. Furthermore, the characteristics of the population based on factors such as weight, height, or race could not be determined. In spite of our efforts to rule out patients with osteoarthritis of the knee, undoubtedly some degree of degeneration may have been present in this population. Second, we standardized the position of the femur relative to the coronal plane. However, there is some variability of the position of the tibia relative to that of the femur. We chose to standardize the femur since the methods for doing so are more reproducible based on the three points of contact of the femur on the coronal plane, namely the medial and lateral posterior condyles and the posterior greater trochanter. We operated under the assumption that the tibia would be relatively consistent in relation to the femur. Third, the software output was a three-dimensional reconstruction rather than a radiograph. These images do not demonstrate typical physical distortions such as parallax seen in standard, potentially limiting their comparisons to the traditional methods of alignment measurement used in previous publications. Fourth, in spite of our use of large monitor computer workstations, there is a possibility of some degree of inaccuracy of the measurements of the most distal aspect of each condyle and most proximal aspect of each tibial plateau due to the relatively low magnification of these regions relative to the entire image of the lower extremity. The number of patients included in the study was relatively low compared to some other population based studies. Another limitation of this study is that although there is a statistically significant error introduced with rotation of the leg for some of the parameters such as MPTA, the size of this error may not be clinically significant. It rests upon the reader to determine for themselves the clinically relevant range of error acceptable to them from a clinical perspective for the analysis or operation being considered. Some procedures may be more sensitive to variabilities in alignment than others. In spite of these weaknesses, this study is one of the first to provide rotationally controlled values for commonly performed measurements of coronal alignment and one of the few studies that indicates the sensitivity of commonly performed measurements of coronal alignment to discreet small rotations of the entire lower extremity. Conclusions In conclusion, the current study validates the lower extremity alignment measurements that are commonly used in the fields of rheumatology and orthopedics with a more robust methodology that standardizes the rotational position of the lower extremity using three-dimensional models in a virtual environment. The study indicates that for some parameters, even a 3 rotational deviation can lead to a statistically significantly different value.
8 Jamali et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:77 Page 8 of 8 Abbreviations aldfa: Anatomical lateral distal femoral articular angle. The angle between the anatomical axis of the femur and the distal femoral articular axis; AMA: Anatomical-mechanical angle. The angle between the mechanical and anatomical axes of the femur; atfa: Anatomic tibiofemoral angle. The angle between the anatomical axis of the femur and the mechanical/anatomical axis of the tibia; CT: Computerized tomography; HKA: Hip-knee-ankle angle. Equivalent to mtfa in this study; ICC: Intraclass correlation coefficients; JLCA: Joint line convergence angle. The angle between the proximal tibial and distal femoral articular axes; mldfa: Mechanical lateral distal femoral articular angle. The lateral angle between the mechanical axis of the femur and the distal femoral articular axis; MPTA: Medial proximal tibial angle. The medial angle between the mechanical/anatomical axis of the tibia and the proximal tibial articular axis; mtfa: Mechanical tibiofemoral angle. The angle between the mechanical axis of the femur and the mechanical/anatomical axis of the tibia; PFSC: Proximal femoral shaft center. The geometric center of four points, two points on the lateral femoral surface and two points on the medial femoral surface in the subtrochanteric region of the femur; RMANOVA: Repeated measures analysis of variance Acknowledgements We would like to acknowledge the staff at the UC Davis Department of Radiology for their assistance with data acquisition protocols. Funding No external sources of funding were used for this study. Availability of data and materials Please contact the author for data requests. Authors contributions AAJ was the principal investigator and was involved in the study conception and manuscript preparation and submission. JPM was the co-principal investigator and was involved in the study conception and manuscript preparation and submission. NMM was the research resident and was involved in a large portion of the data acquisition and analysis as well as manuscript preparation. MJA was the research fellow and was involved in the remaining portion of the data acquisition and analysis as well as manuscript preparation. RL was the musculoskeletal radiologist and was involved in CT image acquisition, analysis, and data presentation. CP was the statistician and was involved in the presentation of the data and the statistical analysis and presentation of the results. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Consent for publication Not applicable Ethics approval and consent to participate This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board, University of California, Davis. Protocol # Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Joint Preservation Institute, 2825 J Street, Suite 440, Sacramento, CA 95816, USA. 2 UC Davis Medical Center, 4860 Y St., #4800, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA. 3 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California, Irvine, 101 The City Drive South, Pavillion III, Building 29A, Orange, CA 92868, USA. 4 UC Davis Department of Orthopaedics, nd Ave, Research 1 Room 2000, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA. 5 UC Davis Department of Radiology, 4860 Y St., #3100, Sacramento, CA 95817, USA. 6 Sutter Institute for Medical Research, 2801 Capitol Ave Suite 400, Sacramento 95816, USA. Received: 15 December 2016 Accepted: 25 April 2017 References 1. Cooke D, Scudamore A, Li J, Wyss U, Bryant T, Costigan P. Axial lower-limb alignment: comparison of knee geometry in normal volunteers and osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1997;5: Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT, Cahue S, Shamiyeh E, Dunlop DD. The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA. 2001;286: Cooke TD, Harrison L, Khan B, Scudamore A, Chaudhary MA. Analysis of limb alignment in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: a comparison of Saudi Arabian and Canadian cases. Rheumatol Int. 2002;22: Brouwer GM, van Tol AW, Bergink AP, Belo JN, Bernsen RM, Reijman M, Pols HA, Bierma-Zeinstra SM. Association between valgus and varus alignment and the development and progression of radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56: Paley D, Herzenberg JE, Tetsworth K, McKie J, Bhave A. Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25: Kettelkamp DB, Wenger DR, Chao EY, Thompson C. Results of proximal tibial osteotomy. The effects of tibiofemoral angle, stance-phase flexion-extension, and medial-plateau force. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1976;58: Rudan JF, Simurda MA. High tibial osteotomy. A prospective clinical and roentgenographic review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;255: Terauchi M, Shirakura K, Kobuna Y, Fukasawa N. Axial parameters affecting lower limb alignment after hightibial osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;317: Insall JN, Binazzi R, Soudry M, Mestriner LA. Total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;192: Collier MB, Engh Jr CA, McAuley JP, Engh GA. Factors associated with the loss of thickness of polyethylene tibial bearings after knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89: Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24: Howell SM, Howell SJ, Kuznik KT, Cohen J, Hull ML. Does a kinematically aligned total knee arthroplasty restore function without failure regardless of alignment category? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471: Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92: Jamali AA, Deuel C, Perreira A, Salgado CJ, Hunter JC, Strong EB. Linear and angular measurements of computer-generated models: are they accurate, valid, and reliable? Comput Aided Surg. 2007;12: Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69: Paley D. Principles of deformity correction. 1st edn. New York: Spinger- Verlag; Chao EY, Neluheni EV, Hsu RW, Paley D. Biomechanics of malalignment. Orthop Clin North Am. 1994;25: Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY. Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82-A: Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J. The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients?: the concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(1): Jabalameli M, Moghimi J, Yeganeh A, Nojomi M. Parameters of lower extremities alignment view in Iranian adult population. Acta Med Iran. 2015;53: Song MH, Yoo SH, Kang SW, Kim YJ, Park GT, Pyeun YS. Coronal alignment of the lower limb and the incidence of constitutional varus knee in Korean females. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2015;27: Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM. Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1993;8: Radtke K, Becher C, Noll Y, Ostermeier S. Effect of limb rotation on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130:451 7.
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and Varus Knee Deformity Based on Two-Dimensional Assessment of Side-to-Side Differences
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
)289( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty Hamidreza Yazdi, MD; Ara Nazarian, DrSc; Jim S Wu, MD;
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference?
 Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Kinematic vs. mechanical alignment: What is the difference? In this 4 Questions interview, Stephen M. Howell, MD, explains the potential benefits of 3D alignment during total knee replacement. Introduction
Coronal Alignment of the Lower Limb and the Incidence of Constitutional Varus Knee in Korean Females
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(1):49-55 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.1.49 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Coronal Alignment of the Lower Limb and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(1):49-55 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.1.49 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Coronal Alignment of the Lower Limb and
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY
 2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
2017 Resident Advanced Trauma Techniques Course COMPLICATIONS / CHALLENGES MALUNIONS/DEFORMITY What is a Malunion? Definition: a fracture that has healed in a nonanatomic (i.e. deformed) position Must
Ye-Ran Li, Yu-Hang Gao, Xin Qi *, Jian-Guo Liu, Lu Ding, Chen Yang, Zheng Zhang and Shu-Qiang Li
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:92 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0588-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Analysis of factors that affect the precision of the radiographic lateral femoral
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
)116( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis of the Geometry of the Distal Femur and Proximal Tibia in the Osteoarthritic Knee: A 3D Reconstruction CT Scan Based
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an increasingly. Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 12(3): 214-218 REVIEW Radiographic Evaluation of Alignment Following TKA, a Systematic Review Serban DRAGOSLOVEANU a,
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
Coronal Tibiofemoral Subluxation in Knee Osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy, MD 1,2 * ; Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan, MD 1 ; Meir Liebergall, MD 2; Andrew D. Pearle, MD 1 1Hospital for Special Surgery, Weill Medical
How accurate is anatomic limb alignment in predicting mechanical limb alignment after total knee arthroplasty?
 Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:323 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0756-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE How accurate is anatomic limb alignment in predicting mechanical limb alignment after total knee arthroplasty?
Lee et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2015) 16:323 DOI 10.1186/s12891-015-0756-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE How accurate is anatomic limb alignment in predicting mechanical limb alignment after total knee arthroplasty?
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W.
 University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
University of Groningen Alignment of the femoral component in a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty Kort, N. P.; van Raay, J. J. A. M.; Thomassen, B. J. W. Published in: Knee DOI: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.007
Malrotation can occur following closed intramedullary
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Effects of Femoral Shaft Malrotation on Lower Extremity Anatomy Joseph J. Gugenheim, MD,* Robert A. Probe, MD, and Mark R. Brinker, MD* Objective: To determine how axial rotation around
Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia?
 Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Nirav Joshi 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California
Where Is the Natural Internal-External Rotation Axis of the Tibia? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Nirav Joshi 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California
Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient Instrumentation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 891210, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/891210 Clinical Study Accuracy of Implant Placement Utilizing Customized Patient
Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA)
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22 (1 Suppl): 83-89 Impact of knee varus and valgus deformity on alignment in lower extremities after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) F. TIAN
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ANATOMIC. Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0
 ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
ANATOMIC Navigated Surgical Technique 4 in 1 TO.G.GB.016/1.0 SCREEN LAYOUT Take screenshot Surgical step Dynamic navigation zone Information area and buttons 2 SCREEN LAYOUT Indicates action when yellow
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
A comparative assessment of alternatives to the full-leg radiograph for determining knee joint alignment
 Navali et al. Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation, Therapy & Technology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access A comparative assessment of alternatives to the full-leg radiograph for determining knee
Navali et al. Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation, Therapy & Technology 2012, 4:40 RESEARCH Open Access A comparative assessment of alternatives to the full-leg radiograph for determining knee
Multiapical Deformities p. 97 Osteotomy Concepts and Frontal Plane Realignment p. 99 Angulation Correction Axis (ACA) p. 99 Bisector Lines p.
 Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Normal Lower Limb Alignment and Joint Orientation p. 1 Mechanical and Anatomic Bone Axes p. 1 Joint Center Points p. 5 Joint Orientation Lines p. 5 Ankle p. 5 Knee p. 5 Hip p. 8 Joint Orientation Angles
Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil Dr Murilo Leie MD Mr Joshua Twiggs BEng Dr Brett A Fritsch MBBS FRACS (Orth) FAOrthA.
 A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
A comparison of kinematic and mechanical alignment with regards to bony resection, soft tissue release, and deformity correction in total knee replacement Presented By Dr Vincent VG An MD BSc (Adv) MPhil
Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement
 Knee Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement A COMPUTER-SIMULATION STUDY W.-Q. Cui, Y.-Y. Won, M.-H. Baek, K.-K. Kim, J.-H. Cho From Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon City,
Knee Variations of the grand-piano sign during total knee replacement A COMPUTER-SIMULATION STUDY W.-Q. Cui, Y.-Y. Won, M.-H. Baek, K.-K. Kim, J.-H. Cho From Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon City,
Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients with Proximal Tibia Vara
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:458-464 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.458 Lateralization of Tibial Plateau Reference Point Improves Accuracy of Tibial Resection in Total Knee
Foot and ankle radiographic parameters: validity and reproducibility of biplane imaging system versus conventional radiography
 Foot and ankle radiographic parameters: validity and reproducibility of biplane imaging system versus conventional radiography Chamnanni Rungpai, MD; Jessica E. Goetz, PhD; Marut Arunakul, MD; Yubo, Gao,
Foot and ankle radiographic parameters: validity and reproducibility of biplane imaging system versus conventional radiography Chamnanni Rungpai, MD; Jessica E. Goetz, PhD; Marut Arunakul, MD; Yubo, Gao,
Yu-Hsien Lin 1, Feng-Shuo Chang 1, Kun-Hui Chen 6,7,8, Kui-Chou Huang 2,3* and Kuo-Chih Su 4,5,6
 Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:411 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2335-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mismatch between femur and tibia coronal alignment in the knee joint: classification
Lin et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:411 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2335-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Mismatch between femur and tibia coronal alignment in the knee joint: classification
Institutional review board approval was obtained prior to the start of this study.
 Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
Instructional Course Lecture 2011
 Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
Instructional Course Lecture 2011 Yoon Hae Kwak Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital Hallym University Medical Center Rotational and Angular variations of the lower extremities
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
The coronal hypomochlion
 KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
KNEE The coronal hypomochlion A TIPPING POINT OF CLINICAL RELEVANCE WHEN PLANNING VALGUS PRODUCING HIGH TIBIAL OSTEOTOMIES E. Heijens, P. Kornherr, C. Meister From Gelenkzentrum Rhein-Main, Wiesbaden,
Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick
 Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
Dr Andreas Loefler www.orthosports.com.au 29 31 Dora Street, Hurstville 160 Belmore Road, Randwick Dr Andreas Loefler Joint Replacement & Spine Surgery CAS or Navigation in TKA New Software for a Full
KNEE. T. J. Shelton, A. J. Nedopil, S. M. Howell, M. L. Hull
 T. J. Shelton, A. J. Nedopil, S. M. Howell, M. L. Hull From Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California, Davis, Sacramento, United States T. J. Shelton, MD, MS, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Department
T. J. Shelton, A. J. Nedopil, S. M. Howell, M. L. Hull From Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of California, Davis, Sacramento, United States T. J. Shelton, MD, MS, Orthopaedic Surgeon, Department
Zhe Du 1, Shichang Chen 2, Mengning Yan 2, Bing Yue 1, Yiming Zeng 2 and You Wang 1*
 Du et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1374-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Do size, shape, and alignment parameters of the femoral condyle affect the trochlear groove
Du et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:4 DOI 10.1186/s12891-016-1374-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Do size, shape, and alignment parameters of the femoral condyle affect the trochlear groove
Assessment of Lower Limb Length and Alignment by Biplanar Linear Radiography: Comparison With Supine CT and Upright Full-Length Radiography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Guggenberger et al. Assessment of Lower Limb Length and Alignment Using Different Modalities Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 172.69.22.242 on 8/23/18 from
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Guggenberger et al. Assessment of Lower Limb Length and Alignment Using Different Modalities Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 172.69.22.242 on 8/23/18 from
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Three-dimensional Effect of the Single Plane Proximal Femur Osteotomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(1): 23-29, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Three-dimensional Effect of the Single Plane Proximal Femur Osteotomy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(1): 23-29, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.1.23 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Three-dimensional Effect of the Single Plane Proximal Femur Osteotomy
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
Simulation of Total Knee Arthroplasty in 5 or 7 Valgus: A Study of Gap Imbalances and Changes in Limb and Knee Alignments From Native
 Simulation of Total Knee Arthroplasty in 5 or 7 Valgus: A Study of Gap Imbalances and Changes in Limb and Knee Alignments From Native Yu Gu, 1 Stephen M. Howell, 2,3 Maury L. Hull 2,3,4 1 Mako Surgical
Simulation of Total Knee Arthroplasty in 5 or 7 Valgus: A Study of Gap Imbalances and Changes in Limb and Knee Alignments From Native Yu Gu, 1 Stephen M. Howell, 2,3 Maury L. Hull 2,3,4 1 Mako Surgical
)122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE
 )122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Distal Femoral Rotational Alignment with Spiral CT Scan before Total Knee Arthroplasty (A Study in Iranian
)122( COPYRIGHT 2016 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Distal Femoral Rotational Alignment with Spiral CT Scan before Total Knee Arthroplasty (A Study in Iranian
Masterclass. Tips and tricks for a successful outcome. E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter. September 15th, 2012, Brussels
 Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Masterclass Tips and tricks for a successful outcome September 15th, 2012, Brussels E. Verhaven, M. Thaeter Belgium St. Nikolaus-Hospital Orthopaedics & Traumatology Ultimate Goal of TKR Normal alignment
Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population
 Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population Mehdi Moghtadaei1,
Original Article Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences Computed Tomographic measurement of distal femor rotation in Iranian population Mehdi Moghtadaei1,
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study
 Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Conservative surgical treatments for osteoarthritis: A Finite Element Study Diagarajen Carpanen, BEng (Hons), Franziska Reisse, BEng(Hons), Howard Hillstrom, PhD, Kevin Cheah, FRCS, Rob Walker, PhD, Rajshree
Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity
 ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
ORTHOPEDICS May 2009;32(5):360. Closing Wedge Retrotubercular Tibial Osteotomy and TKA for Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis With Angular Deformity by John P. Meehan, MD; Mohammad A. Khadder, MD; Amir A. Jamali,
Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Correction of Traumatic Ankle Valgus and Procurvatum using the Taylor Spatial Frame: A Case Report by
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA)
 Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Biomechanical Effects of Femoral Component Axial Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) Mohammad Kia, PhD, Timothy Wright, PhD, Michael Cross, MD, David Mayman, MD, Andrew Pearle, MD, Peter Sculco,
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane
 KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
KNEE Total knee replacement in patients with significant femoral bowing in the coronal plane A COMPARISON OF CONVENTIONAL AND COMPUTER-ASSISTED SURGERY IN AN ASIAN POPULATION T.-W. Huang, W.-H. Hsu, K.-T.
1 Introduction. 2 Data and method
 Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART)
 CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
CORRECTIVE OSTEOTOMY BRINGING THE PLAN TO THE BONE (TRIGONOMETERY, GUIDE WIRES, SLA MODELING AND ART) Randy J. Boudrieau, DVM, DACVS, DECVS Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine at Tufts University, North
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT
 ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
ATTUNE KNEE SYSTEM: SOFCAM CONTACT Douglas A. Dennis, MD Medical Director at Porter Center for Joint Replacement Denver, Colorado Historically, sagittal plane instability following Total Knee Arthroplasty
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing
 A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
A Non-CT Based Total Knee Arthroplasty System Featuring Complete Soft-Tissue Balancing Manuela Kunz 1, Matthias Strauss 2, Frank Langlotz 1, Georg Deuretzbacher 2, Wolfgang Rüther 2, and Lutz-Peter Nolte
What Is Normal Femoral Head/Neck Anatomy? An Analysis of Radial CT Reconstructions in Adolescents
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:3581 3587 DOI 10.1007/s11999-013-3166-5 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons BASIC RESEARCH What Is Normal
An In Vivo Study of the Effect of Distal Femoral Resection on Passive Knee Extension
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 7 2010 An In Vivo Study of the Effect of Distal Femoral Resection on Passive Knee Extension Conrad K. Smith, MS,* Justin A. Chen, BS,* Stephen M. Howell, MD,y and
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 7 2010 An In Vivo Study of the Effect of Distal Femoral Resection on Passive Knee Extension Conrad K. Smith, MS,* Justin A. Chen, BS,* Stephen M. Howell, MD,y and
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Total Knee Arthroplasty Following High Tibial Osteotomy a Radiological Evaluation Horia ORBAN, MD, PhD; Emil MARES, MD; Mihaela DRAGUSANU, MD; Gabriel
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
The value of weight-bearing functional CT scans
 The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images
 Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
Memoirs of the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, Vol. 68, No. 1, March 2008 A Kinematic Assessment of Knee Prosthesis from Fluoroscopy Images by Mohammad Abrar HOSSAIN *, Michihiko FUKUNAGA and
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Are varus knees contracted? Reconciling the literature Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Article Are varus knees contracted? Reconciling the literature Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Where Is The Natural Flexion-Extension Axis Of The Knee?
 Where Is The Natural Flexion-Extension Axis Of The Knee? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles,
Where Is The Natural Flexion-Extension Axis Of The Knee? Daniel Boguszewski 1, Paul Yang 2, Keith Markolf 1, Frank Petrigliano 1, David McAllister 1. 1 University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles,
Coronal tibiofemoral subluxation in knee osteoarthritis
 Skeletal Radiol (2016) 45:57 61 DOI 10.1007/s00256-015-2244-z SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Coronal tibiofemoral subluxation in knee osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy 1 & Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan 1 & Ran Thein 1 & Brian
Skeletal Radiol (2016) 45:57 61 DOI 10.1007/s00256-015-2244-z SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Coronal tibiofemoral subluxation in knee osteoarthritis Saker Khamaisy 1 & Hendrik A. Zuiderbaan 1 & Ran Thein 1 & Brian
Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20180422 Tibial deformity correction by Ilizarov method Robert
No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery
 DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00167-014-2849-0 KNEE No radiographic difference between patient-specific guiding and conventional Oxford UKA surgery Bart Kerens Martijn G. M. Schotanus Bert Boonen Nanne P. Kort Received:
Biomechanical Characterization of a New, Noninvasive Model of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture in the Rat
 Biomechanical Characterization of a New, Noninvasive Model of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture in the Rat Tristan Maerz, MS Eng 1, Michael Kurdziel, MS Eng 1, Abigail Davidson, BS Eng 1, Kevin Baker,
Biomechanical Characterization of a New, Noninvasive Model of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Rupture in the Rat Tristan Maerz, MS Eng 1, Michael Kurdziel, MS Eng 1, Abigail Davidson, BS Eng 1, Kevin Baker,
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Treatment of osteochondral defects of the talus van Bergen, C.J.A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van Bergen, C. J. A. (2014). Treatment
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Preoperative Planning. The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to:
 Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
Preoperative Planning The primary objectives of preoperative planning are to: - Determine preoperative leg length discrepancy. - Assess acetabular component size and placement. - Determine femoral component
PROPHECY INBONE. Preoperative Navigation Guides
 PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
PROPHECY INBONE Preoperative Navigation Guides Simple. Fast. Accurate. Simple. Fast. Accurate. Prophecy Envision the Results PROPHECY Preoperative Navigation Guides have ushered in a new era of total ankle
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo 3D study
 Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo D study Hara Y, Ikoma K, Kido M, Imai K, Maki M, Takatori R, Tokunaga D, Inoue N,, Kubo T Department of Orthopaedics,
Load Response of the Hindfoot Bones in patients with the Ankle Osteoarthritis : in vivo D study Hara Y, Ikoma K, Kido M, Imai K, Maki M, Takatori R, Tokunaga D, Inoue N,, Kubo T Department of Orthopaedics,
Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after High Tibial Osteotomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(2):171-175 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.034 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Back out of Locking Pin with Hinge Fracture after
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery. Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D.
 Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
Computer Navigation in TKA The role of Robotic Surgery Christos Yiannakopoulos, M.D., Ph.D. Why are TKA failing? 11.8% Sharkley, CORR, 2005 55.6% of revision occurred early (< 2 years) 32% of patients
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the Varus Deformity after High Tibial Osteotomy?
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 18;3():311-318 https://doi.org/1.579/ksrr.18.35 pissn 3-7 eissn 3-51 Knee Surgery & Related Research Does Coronal Knee and Ankle Alignment Affect Recurrence of the
Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) -, 1-6 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty Heinz R. Hoenecke Jr., MD*, Juan C. Hermida, MD, Cesar
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2009) -, 1-6 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse Accuracy of CT-based measurements of glenoid version for total shoulder arthroplasty Heinz R. Hoenecke Jr., MD*, Juan C. Hermida, MD, Cesar
Bone Preservation Stem
 TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TRI-LOCK Bone Preservation Stem Featuring GRIPTION Coating Surgical Technique Implant Geometry Extending the TRI-LOCK Stem heritage The original TRI-LOCK Stem was introduced in 1981. This implant was
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN VARUS VALGUS ALIGNMENT AND PATELLOFEMORAL OSTEOARTHRITIS
 1874 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 8, August 2000, pp 1874 1880 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN VARUS VALGUS ALIGNMENT AND PATELLOFEMORAL OSTEOARTHRITIS SADAF ELAHI,
1874 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 8, August 2000, pp 1874 1880 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE ASSOCIATION BETWEEN VARUS VALGUS ALIGNMENT AND PATELLOFEMORAL OSTEOARTHRITIS SADAF ELAHI,
Investigation performed at The Center for Problem Fractures and Limb Restoration, Texas Orthopedic Hospital, Houston, Texas
 1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
1229 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Bone Realignment with Use of Temporary External Fixation for Distal Femoral Valgus and Varus Deformities BY JOSEPH J. GUGENHEIM
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular Femoral Deformity and/or Retained Hardware
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 174384, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/174384 Case Report Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for Osteoarthritis with Extra-Articular
Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 331, pp 35-46 0 1996 Lippincott-Raven Publishers Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty Pascal L. Poilvache, MD*;
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 331, pp 35-46 0 1996 Lippincott-Raven Publishers Rotational Landmarks and Sizing of the Distal Femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty Pascal L. Poilvache, MD*;
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Knee kinematics after TKA depends on preoperative kinematics
 ICL #30 Achieving normal kinematics in TKA Knee kinematics after TKA depends on preoperative kinematics Tokifumi Majima, MD, PhD Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery Nippon Medical School 2017 ISAKOS, Shanghai,
ICL #30 Achieving normal kinematics in TKA Knee kinematics after TKA depends on preoperative kinematics Tokifumi Majima, MD, PhD Dept. of Orthopedic Surgery Nippon Medical School 2017 ISAKOS, Shanghai,
Analysis of factors affecting range of motion after Total Knee Arthroplasty
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 9 Ver. II (Sep. 2015), PP 01-10 www.iosrjournals.org Analysis of factors affecting range of
Improving tibial component coronal alignment using clearly defined anatomical structures in total knee arthroplasty
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 694-698 ORIGINAL STUDY Improving tibial component coronal alignment using clearly defined anatomical structures in total knee arthroplasty Masahiko Ikeuchi, Masashi Izumi,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2013, 79, 694-698 ORIGINAL STUDY Improving tibial component coronal alignment using clearly defined anatomical structures in total knee arthroplasty Masahiko Ikeuchi, Masashi Izumi,
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1): pissn eissn Knee Surgery & Related Research
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2013;25(1):13-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2013.25.1.13 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Comparative Study of Two Techniques for
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No. 8 2007 Interobserver and Intra-observer Errors in Obtaining Visually Selected Anatomical Landmarks During Registration Process in Non Image-Based Navigation-Assisted
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 22 No. 8 2007 Interobserver and Intra-observer Errors in Obtaining Visually Selected Anatomical Landmarks During Registration Process in Non Image-Based Navigation-Assisted
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 CORONAL ALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT ROBERT S. JEFFERY, RICHARD W. MORRIS, ROBIN A. DENHAM From Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth Maquet s line passes from the centre of the femoral head to
CORONAL ALIGNMENT AFTER TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT ROBERT S. JEFFERY, RICHARD W. MORRIS, ROBIN A. DENHAM From Queen Alexandra Hospital, Portsmouth Maquet s line passes from the centre of the femoral head to
