Abstract. Introduction. Michele Vasso 1 Katia Corona 2 Giuseppe Toro 1 Marco Rossini 1 Alfredo Schiavone Panni 1
|
|
|
- Bertina Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 256 Technical Note THIEME Anatomic Double-Bundle Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction with Autologous Semitendinosus: Aperture Fixation Both at the Femur and the Patella Michele Vasso 1 Katia Corona 2 Giuseppe Toro 1 Marco Rossini 1 Alfredo Schiavone Panni 1 1 Multidisciplinary Department of Medico-Surgical and Dentistry Specialties, Luigi Vanvitelli University, Naples, Italy 2 Department of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Molise, Campobasso, Italy Address for correspondence Katia Corona, MS, Department of Medicine and Health Sciences, University of Molise, Via Francesco De Sanctis, 86100, Campobasso, Italy ( katiacorona@tiscali.it). Joints 2017;5: Abstract Keywords medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction double-bundle aperture fixation semitendinosus Medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) represents the main restraint against lateral patellar displacement. The MPFL insertion at the patella is up to 30 mm wide and is located along the upper half of the medial patellar rim. The femoral insertion of the MPFL is approximately 10 mm distal to the apex of the adductor tubercle and 16 mm proximal to the medial epicondyle. Since most of the patients suffer from MPFL rupture just after the first patellar dislocation, MPFL reconstruction results necessarily in all cases of chronic objective patellar instability to reestablish the primary passive patellofemoral stabilizer. Over time, different techniques of MPFL reconstruction have been proposed with promising results in terms of patient satisfaction and redislocation rate. However, each of these techniques may present peculiar problems and/or complications. An anatomic double-bundle MPFL reconstruction through an aperture fixation both at the femur and at the patella is here presented. The anatomic double-bundle MPFL reconstruction could allow recreating the fan-shape and biomechanics of original MPFL, whereas aperture fixation could provide a strong and safe fixation without risk of loosening or slackening of the graft. Introduction The medial patellofemoral complex consisting of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) and the medial patellotibial ligament represents the main passive stabilizer of the patellofemoral (PF) joint. In particular, the MPFL represents the main restraint against lateral patellar displacement. 1 The MPFL insertion at the patella is up to 30 mm wide and is located along the upper half of the patella. Proximal fibers are mainly attached to the vastus intermedius, without tight adhesion to the vastus medialis. Distal fibers are interdigitated with the deep layer of the medial retinaculum. 2 The femoral insertion of the MPFL is approximately 10 mm distal to the apex of the adductor tubercle and 16 mm proximal to the medial epicondyle. 3 MPFL is located in layer 2 of the medial soft-tissue structures between medial retinaculum (layer 1) and knee capsule (layer 3). Clinically, up to 94 to 100% of patients suffer from MPFL rupture just after the first patellar dislocation, and approximately half of these patients will develop recurrent dislocations. 4 For this reason, MPFL reconstruction is necessary in all cases of chronic objective patellar instability, to reestablish the primary passive PF stabilizer. However, MPFL reconstruction should be supplemented with additional procedures to address various aspects of PF dysplasia when present: severe trochlear dysplasia, patella alta, patellar tilt, and lateralization of the tibial tuberosity. Numerous techniques for MPFL reconstruction have been described, and they all aim to supply tendon graft from the medial aspect of the patella to the femoral insertion site of the native MPFL. Numerous graft sources for reconstruction published online October 4, 2017 DOI /s ISSN Copyright 2017 Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart New York
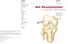
2 Double-Bundle MPFL Reconstruction Vasso et al. 257 are described in the literature, including semitendinosus, gracilis, partial quadriceps, partial patellar tendon, partial adductor tendon, vastus medialis retinaculum, allografts or artificial grafts. Similarly, different techniques and devices for fixing the graft have been used, especially at the patellar MPFL attachment site: bone tunnels, transosseous sutures, small interference screws and suture anchors. However, each of these techniques could present peculiar problems and complications, and biomechanical alterations on the PF joint. Anatomical restoration of MPFL should be the main goal of every reconstruction technique. In this regard, double-bundle MPFL reconstruction at the patellar side could restore native MPFL morphology and biomechanics, therefore, providing more patellar stability, both in extension and up to the first 60 to 70 degrees of flexion. 2 Likewise, direct aperture fixation could provide firm fixation, thus reducing the risk of loosening or slackening of the graft. 5 This technical note aimed to present an anatomical double-bundle MPFL reconstruction through an aperture fixation both at the femur and at the patella. The autologous semitendinosus was always chosen for this procedure. The anatomical double-bundle reconstruction with aperture fixation described here represents a modification of the technique initially introduced by Schöttle et al. 6 Surgical Technique Before the surgery, an examination under anesthesia is performed to confirm the diagnosis of patellar instability and hypermobility. Arthroscopy is routinely performed to treat, if necessary, any intra-articular lesions and evaluate patellar tracking throughout knee motion. Semitendinosus Graft Preparation A 2-cm vertical skin incision is made over the insertion site of the pes anserinus. After incising the sartorius aponeurosis, the semitendinosus tendon is harvested. The two ends of the tendon graft are each sutured with no. 2 absorbable sutures using a whipstitch technique up to approximately 2 cm from each end. We routinely use the semitendinosus graft, since in patients with a short gracilis this tendon may not be long enough to reach the anatomical femoral insertion. MPFL Insertion at the Patella A 2-cm medial parapatellar skin incision is performed along the proximal half of the patella, where the patellar MPFL insertion is located. Retinaculum and periosteum of the medial patella rim are incised longitudinally and elevated off the bone. Two guidewires are drilled into the patella at the proximal and distal ends of the upper half of the medial edge; the two guidewires slightly converge laterally The guidewires are subsequently overdrilled with a cannulated 4-mm drill to a depth of 20 mm. The tails of one graft end are passed through the eyelet of the first 4.75-mm fully threaded, knotless anchor (SwiveLock; Arthrex, Naples, Florida, United States) and the graft/anchor is pushed into the proximal drill hole until the eyelet is fully seated. While maintaining tension on the suture limbs, the SwiveLock anchor is screwed into the patella. After removal of the driver, the SwiveLock suture should be removed or tied to the graft sutures to reinforce the fixation. This procedure is then repeated for the second graft end. The two free sutured graft ends are thus fixed into the patellar holes achieving an anatomical graft fixation. A double-bundle direct aperture fixation at the patellar side is thus achieved leaving the graft loop free ( Fig. 1). After successive fixation of the graft at the femoral MPFL insertion, the reflected periosteum and medial retinaculum were sutured on top of the graft for additional fixation. MPFL Insertion at the Femur For an anatomical femoral insertion of the graft, the medial epicondyle and adductor tubercle are palpated. A 1-cm longitudinal incision is made in this area, and a 2-mm guidewire with an eyelet is placed at the correct femoral MPFL insertion point. The guidewire placement is controlled by an image intensifier on a straight lateral view to obtain and identify the anatomical femoral insertion point. It has been shown 7 to be located 1 mm anterior to an elongation of the posterior femoral cortex in between the posterior articular border of the medial femoral condyle and the most proximal point of the Blumensaat line ( Fig. 2). At this point, the isometry of the MPFL may be evaluated by maintaining adequate tension on the graft and cycling the knee through the full range of motion (ROM). When the isometry Fig. 1 The graft sutures are pulled through the eyelet of the SwiveLock (Arthrex, Naples, Florida, United States) (A), and pushed into the drill holes (B). Keeping the suture under tension, the graft ends are fixed with the SwiveLock anchor leaving the graft loop free (C).
3 258 Double-Bundle MPFL Reconstruction Vasso et al. Fig. 2 Straight lateral view of the knee is obtained intraoperatively with an image intensifier. The radiographic landmark of the femoral attachment site is determined by three lines: an elongation of the posterior femoral cortex (continuous line) and two lines perpendicular to this line (dashed lines), one passing through the posterior articular border of the medial femoral condyle and one passing through the most proximal aspect of the Blumensaat line. The landmark is just anterior (1 mm) to the continuous line, in the midpoint between the dashed lines (asterisk). Fig. 3 As the MPFL is situated in the second layer of the medial patellofemoral complex, a tunnel between the superficial medial retinaculum and the joint capsule is created, and an angled clamp is brought into this space and directed toward the femoral MPFL insertion, cautiously avoiding any injury to the joint. A suture loop is then inserted into this tunnel using the angled clamp. MPFL, medial patellofemoral ligament. is respected, then the guidewire is drilled (directed slightly anterior to avoid posterior soft-tissue injuries) and pushed outside the lateral side of the knee. At this point, a halftunnel with a diameter 1 mm larger than that of the double semitendinosus is created with a cannulated drill. The length of the femoral half-tunnel depends on the length of the double semitendinosus. The guidewire is maintained in the femur, as it will be used to pass the graft into the femur. At this point, a blunt dissection is performed to create a soft-tissue tunnel in layer 2 of the medial soft-tissue structures from the patellar insertion point to the femoral insertion point, deep to the superficial medial retinaculum (layer 1) but superficial to the synovium (layer 3), being careful to leave the capsule intact. A no. 2 suture loop is passed from the femoral side to the patellar one through this space using an angled clamp ( Fig. 3). The suture loop is used to carry the graft from the patellar side to the femoral insertion point ( Fig. 4). The suture shuttle used to pull the graft is then inserted into the eyelet of the femoral guidewire ( Fig. 5), and the graft is successively passed through the femoral tunnel by pulling the guidewire and the suture shuttle out of the lateral side of the knee. Equal tension on both graft bundles is maintained during graft passage into the femoral half-tunnel. Femoral fixation is achieved with a biodegradable interference screw 1 mm larger than the graft, which is passed over a nitinol guidewire. Femoral fixation is performed in 30 degrees of knee flexion 8 with the lateral patellar edge positioned in line with the lateral trochlear border. A traditional skin closure is thus performed. Postoperative Care Rehabilitation involves a knee brace for protection. Flexion is restricted to 60 degrees for the first two postoperative weeks and to 90 degrees for the third postoperative week; successively, a full ROM is allowed. Partial weight-bearing with crutches is allowed during the first 3 weeks, then full weight-bearing without crutches is regained. Leg raising and quadriceps isometric strength exercises are immediately performed. Noncontact sports are allowed after 3 months, while contact sports can be resumed 6 months after surgery. Discussion This technical note aimed to describe the procedure for an anatomical double-bundle reconstruction of the MPFL, respecting not only the original ligament shape but also the anatomical patellar and femoral insertion areas. Moreover,
4 Double-Bundle MPFL Reconstruction Vasso et al. 259 Fig. 4 Thesutureloopiscarriedbythecurvedclampatthemedial patellar border and used to pull the graft from the patellar side to the femoral insertion point. an aperture fixation was assured both at the femur and at the patella. The procedure presented here represents a modification of the technique initially introduced by Schöttle et al. 6 The main difference of this procedure compared with the Schöttle s one was that semitendinosus was used instead of gracilis, since in patients with a short gracilis this tendon Fig. 5 The suture shuttle used to pull the graft from the patellar to the femoral side is inserted into the eyelet of the femoral guidewire andusedtopullthegraftthroughthefemoraltunnel. may not be long enough to reach the anatomical femoral insertion, especially when an anatomic double-bundle reconstruction with aperture fixation devices are performed. Also, after graft harvesting, the proximal half of the patella is immediately prepared to fix the two free ends of the graft with the SwiveLock anchors; only at this point, the detection and the dissection of the layer 2 of the medial soft tissues is performed, being that facilitated by a better visualization of the structures of the medial retinaculum due to the previous medial patellar side preparation. Finally, by fixing the graft to the patella before preparing the femoral insertion site, the isometry of the MPFL may be assessed to detect the most anatomical femoral insertion. During years, multiple grafts and fixation techniques have been proposed to reconstruct the MPFL with promising clinical results and low redislocation rate, but each of these techniques may present potential problems and/or complications. The tendon transfer procedure with patellar or quadriceps grafts presents the clear disadvantage of being a single-bundle reconstruction, with the evident risk of increasing the rotational moment of the patella during knee motion. Moreover, when using the patellar tendon transfer procedure, the patella insertion cannot be reconstructed at its anatomical insertion. Also, the transferred muscle may be weakened in its original strength. 8 Finally, the single-bundle MPFL reconstruction could not restore normal patellar tracking at any flexion angle. 9 Although no previous studies confirmed that double-bundle MPFL reconstruction is better in morphology and biomechanics than quadriceps tendon transfer, it is widely recognized how the patellar attachment of the MPFL could vary, from the proximal half of the patella to even the upper two-thirds of the patella. 2 Therefore, sometimes quadriceps tendon cannot restore the anatomy of the native MPFL. Furthermore, Mochizuki et al 2 recently demonstrated the presence of two bundles in the patellar attachment of MPFL (proximal and distal fibers), thus concluding that MPFL reconstruction by recreating both bundles might better restore ligament function and improve patellar stability. We primarily performed a double-bundle MPFL reconstruction with two divergent transverse tunnels on the patella. 10 However, it has been largely proven that most of the techniques using transverse patellar tunnels increase the risk of patellar fracture. 11 Anatomical patellar fixation by looping the graft through short bone tunnels at the medial edge of the patella, without using fixation devices, has been proposed to reduce the risk of fracture; however, tunnel widening might occur in the long-term, thus causing graft loosening. In general, nonapertured fixation techniques could cause loosening, slippage or slackening of the graft. Patellar graft fixation into a bony rim with suture anchors or by tying graft sutures at the lateral patellar edge may potentially result in graft slippage and/or loosening. 6 Similarly, fixing the graft to the surrounding soft tissues might cause graft loosening and/or slackening. Looping the graft through a single small patellar tunnel has been proposed to avoid fractures, with promising results. 12 However, if micromotion in the patellar tunnels develops it may lead to graft
5 260 Double-Bundle MPFL Reconstruction Vasso et al. slackening; moreover, if the graft is not long enough, the femoral insertion cannot be reached. For all these reasons, we adopted the abovementioned anatomical double-bundle MPFL reconstruction through aperture fixation both at the femur and at the patella. This technique could not only recreate the fan-shape of MPFL but also respect the anatomical patellar and femoral insertion areas. Also, the direct aperture fixation both at the femoral and patellar sides could provide firm fixation and minimize the risk of patella fracture. 5 Finally, although different knee flexion angles have been described for MPFL graft fixation, varying from 20 to 70 degrees, 13 several studies showed that MPFL has its maximal length and restraint against patella lateralization at 30 degrees of knee flexion. For this reason, we fixed the graft at 30 degrees of knee flexion and given the strength of aperture fixation we allowed a gradual regaining of knee flexion up to 90 degrees within the first 3 weeks, without reporting any complication. References 1 Panni AS, Cerciello S, Vasso M. Patellofemoral instability: surgical treatment of soft tissues. Joints 2013;1(01): Mochizuki T, Nimura A, Tateishi T, Yamaguchi K, Muneta T, Akita K. Anatomic study of the attachment of the medial patellofemoral ligament and its characteristic relationships to the vastus intermedius. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2013;21(02): Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ, LaPrade RF, et al. Radiographic identification of the primary medial knee structures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2009;91(03): Panni AS, Vasso M, Cerciello S. Acute patellar dislocation. What to do? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2013;21(02): Hapa O, Akşahin E, Özden R, et al. Aperture fixation instead of transverse tunnels at the patella for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2012; 20(02): Schöttle PB, Hensler D, Imhoff AB. Anatomical double-bundle MPFL reconstruction with an aperture fixation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2010;18(02): Schöttle PB, Romero J, Schmeling A, Weiler A. Technical note: anatomical reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament using a free gracilis autograft. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008; 128(05): Amis AA, Firer P, Mountney J, Senavongse W, Thomas NP. Anatomy and biomechanics of the medial patellofemoral ligament. Knee 2003;10(03): Parker DA, Alexander JW, Conditt MA, Uzodinma ON, Bryan WJ. Comparison of isometric and anatomic reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament: a cadaveric study. Orthopedics 2008;31(04): Panni AS, Alam M, Cerciello S, Vasso M, Maffulli N. Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with a divergent patellar transverse 2-tunnel technique. Am J Sports Med 2011;39(12): Schiphouwer L, Rood A, Tigchelaar S, Koëter S. Complications of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using two transverse patellar tunnels. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2017;25(01): Zanon G, Marullo M, Benazzo F. Double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with a single patellar tunnel. Arthrosc Tech 2013;2(04):e401 e Kang HJ, Cao JH, Pan S, Wang XJ, Yu DH, Zheng ZM. The horizontal Y-shaped graft with respective graft tension angles in anatomical two-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2014;22(10):
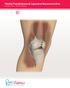
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique
 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique Medial Patellofemoral Ligament The medial patellofemoral complex, consisting of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) and the medial patellotibial
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament (MPFL) Surgical Technique Medial Patellofemoral Ligament The medial patellofemoral complex, consisting of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) and the medial patellotibial
Jia Li 1, Yongqian Li 1, Jingchao Wei 2, Jianzhao Wang 1, Shijun Gao 1 and Yong Shen 1*
 Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:66 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A simple technique for reconstruction of medial patellofemoral ligament with bone-fascia tunnel fixation at
Li et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research 2014, 9:66 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A simple technique for reconstruction of medial patellofemoral ligament with bone-fascia tunnel fixation at
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PREPARED BY MEDSHAPE, INC. IN CONJUNCTION WITH JACK FARR, M.D. MPFL RECONSTRUCTION
 ! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PREPARED BY MEDSHAPE, INC. IN CONJUNCTION WITH JACK FARR, M.D. LATERAL PATELLOFEMORAL INSTABILITY AND THE MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL COMPLEX Lateral patellofemoral instability is characterized
! SURGICAL TECHNIQUE PREPARED BY MEDSHAPE, INC. IN CONJUNCTION WITH JACK FARR, M.D. LATERAL PATELLOFEMORAL INSTABILITY AND THE MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL COMPLEX Lateral patellofemoral instability is characterized
Surgical treatment of patellar instability can be
 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Using a Modified Reverse-Loop Technique Nels E. Sampatacos, M.D., and Mark H. Getelman, M.D. Abstract: Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction is a commonly
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Using a Modified Reverse-Loop Technique Nels E. Sampatacos, M.D., and Mark H. Getelman, M.D. Abstract: Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction is a commonly
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contributing Surgeons R. Justin Mistovich, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Cleveland, OH USA Nirav Pandya, MD
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contributing Surgeons R. Justin Mistovich, MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine Cleveland, OH USA Nirav Pandya, MD
Patellofemoral Pathology
 Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Patellofemoral Pathology Matthew Murray, MD UT Health Science Center/UT Medicine Sports Medicine and Arthroscopic Surgery I have disclosed that I am a consultant for Biomet Orthopaedics. Anterior Knee
Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using dual patella docking technique
 2018; 4(3): 298-304 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 298-304 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-05-2018 Accepted: 25-06-2018 Dr. Ullas Mahesh Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Bangalore,
2018; 4(3): 298-304 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(3): 298-304 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-05-2018 Accepted: 25-06-2018 Dr. Ullas Mahesh Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Bangalore,
10/30/18. Disclosures. Recurrent Patellar Instability. Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability
 Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability Miho J. Tanaka, MD Associate Professor Director, Women s Sports Medicine Program ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Disclosures None Recurrent Patellar Instability Lack of
Management of Recurrent Patellar Instability Miho J. Tanaka, MD Associate Professor Director, Women s Sports Medicine Program ORTHOPAEDIC SURGERY Disclosures None Recurrent Patellar Instability Lack of
Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using the Bio-TransFix femoral fixation device. with an anteromedial portal technique.
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 497 501 TECHNICAL NOTE DOI 10.1007/s00167-005-0705-y Michael E. Hantes Zoe Dailiana Vasilios C. Zachos Sokratis E. Varitimidis Anterior cruciate ligament
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2006) 14: 497 501 TECHNICAL NOTE DOI 10.1007/s00167-005-0705-y Michael E. Hantes Zoe Dailiana Vasilios C. Zachos Sokratis E. Varitimidis Anterior cruciate ligament
Extensor Mechanism Rupture
 Extensor Mechanism Rupture Repair or Augmentation Michael J. Stuart MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Michael J. Stuart MD February 25, 2018 Financial Relationships Consultant & Royalties- Arthrex Research
Extensor Mechanism Rupture Repair or Augmentation Michael J. Stuart MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN Michael J. Stuart MD February 25, 2018 Financial Relationships Consultant & Royalties- Arthrex Research
AFX. Femoral Implant. System. The AperFix. AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide. with the. The AperFix System with the AFX Femoral Implant
 The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
The AperFix System AFX with the Femoral Implant AM Portal Surgical Technique Guide The Cayenne Medical AperFix system with the AFX Femoral Implant is the only anatomic system for soft tissue ACL reconstruction
ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique
 ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique Surgical Technique Lonnie E. Paulos, MD Salt Lake City, Utah 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 201 831 5000 www.stryker.com A surgeon should always rely on
ACL Reconstruction Cross-Pin Technique Surgical Technique Lonnie E. Paulos, MD Salt Lake City, Utah 325 Corporate Drive Mahwah, NJ 07430 t: 201 831 5000 www.stryker.com A surgeon should always rely on
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Technical Note
 Technical Note Hybrid Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Introduction of a New Technique for Anatomic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Darren A. Frank, M.D., Gregory T. Altman, M.D., and
Technical Note Hybrid Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Introduction of a New Technique for Anatomic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Darren A. Frank, M.D., Gregory T. Altman, M.D., and
Double Bundle ACL Reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew Outside-In Anatomic ACL Guide System
 Knee Series Technique Guide Double Bundle ACL Reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew Outside-In Anatomic ACL Guide System Luigi Adriano Pederzini, MD Massimo Tosi, MD Mauro Prandini, MD Luigi Milandri,
Knee Series Technique Guide Double Bundle ACL Reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew Outside-In Anatomic ACL Guide System Luigi Adriano Pederzini, MD Massimo Tosi, MD Mauro Prandini, MD Luigi Milandri,
*smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL. Knee Series Technique Guide. Fixation System
 Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Double Bundle ACL Reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew ACUFEX Director Set for Anatomic ACL Reconstruction French Anatomic ACL-R
Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Double Bundle ACL Reconstruction using the Smith & Nephew ACUFEX Director Set for Anatomic ACL Reconstruction French Anatomic ACL-R
Surgical treatments of patellar instability have been
 Reconstruction of the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament With Gracilis Tendon Autograft in Transverse Patellar Drill Holes Svend Erik Christiansen, M.D., Bent W. Jacobsen, M.D., Bent Lund, M.D., and Martin
Reconstruction of the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament With Gracilis Tendon Autograft in Transverse Patellar Drill Holes Svend Erik Christiansen, M.D., Bent W. Jacobsen, M.D., Bent Lund, M.D., and Martin
Hong-De Wang, Jiang-Tao Dong and Shi-Jun Gao *
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:138 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0473-z TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using a bone groove and a suture
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:138 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0473-z TECHNICAL NOTE Open Access Medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction using a bone groove and a suture
Figure 3 Figure 4 Figure 5
 Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
MPFL positioning on the femoral side
 MPFL positioning on the femoral side Stephen et al AJSM 2012 Prof Dr med Jacques Menetrey, MD, PhD Dr med Philippe Tscholl, MD Centre de médecine de l appareil moteur et du sport - HUG Swiss Olympic medical
MPFL positioning on the femoral side Stephen et al AJSM 2012 Prof Dr med Jacques Menetrey, MD, PhD Dr med Philippe Tscholl, MD Centre de médecine de l appareil moteur et du sport - HUG Swiss Olympic medical
Why does it matter? Patellar Instability 7/23/2018. What is the current operation de jour? Common. Poorly taught. Poorly treated
 Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Patellar Instability It s Really Not That Difficult! David Shneider MD East Lansing, MI www.patellamdcom Detroit Sports Medicine Foundation July 2018 Why does it matter? Common Poorly taught Poorly treated
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Instability Using a Gracilis Autograft without Bone Tunnel
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:457-464 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.4.457 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Instability Using a Gracilis
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2015;7:457-464 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.4.457 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction for Recurrent Patellar Instability Using a Gracilis
Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation
 Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation American Medical Society for Sports Medicine April 6, 2014 Beth E. Shubin Stein, MD Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery Beth E. Shubin
Patella Instability 1 st Time Dislocation American Medical Society for Sports Medicine April 6, 2014 Beth E. Shubin Stein, MD Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery Hospital for Special Surgery Beth E. Shubin
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery
 Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
Anatomy Anterior Cruciate Ligament Surgery Roger Ostrander, MD Andrews Institute Anatomy Anatomy Function Primary restraint to anterior tibial translation Secondary restraint to internal tibial rotation
In Vivo Positioning Analysis of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
 In Vivo Positioning Analysis of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Elvire Servien,* y MD, PhD, Brett Fritsch, z MD, Sébastien Lustig, y MD, Guillaume Demey, y Romain Debarge, y MD, Carole Lapra,
In Vivo Positioning Analysis of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Elvire Servien,* y MD, PhD, Brett Fritsch, z MD, Sébastien Lustig, y MD, Guillaume Demey, y Romain Debarge, y MD, Carole Lapra,
Doron Sher. 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick Burwood Rd, Concord. MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA
 Doron Sher MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick 47 49 Burwood Rd, Concord www.kneedoctor.com.au www.orthosports.com.au Medial PatelloFemoral (MPFL) And AnteroLateral Ligament (ALL) Reconstruction
Doron Sher MBBS, MBiomedE, FRACS FAOrthA 160 Belmore Rd, Randwick 47 49 Burwood Rd, Concord www.kneedoctor.com.au www.orthosports.com.au Medial PatelloFemoral (MPFL) And AnteroLateral Ligament (ALL) Reconstruction
ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and. ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System. *smith&nephew. Knee Series Technique Guide ENDOBUTTON CL
 Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Thomas D. Rosenberg, MD ACL Reconstruction
Knee Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System ACL reconstruction with the ACUFEX Director Drill Guide and ENDOBUTTON CL Fixation System Thomas D. Rosenberg, MD ACL Reconstruction
Human ACL reconstruction
 Human ACL reconstruction current state of the art Rudolph Geesink MD PhD Maastricht The Netherlands Human or canine ACL repair...!? ACL anatomy... right knees! ACL double bundles... ACL double or triple
Human ACL reconstruction current state of the art Rudolph Geesink MD PhD Maastricht The Netherlands Human or canine ACL repair...!? ACL anatomy... right knees! ACL double bundles... ACL double or triple
Anterolateral Ligament. Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine
 Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
Anterolateral Ligament Bradd G. Burkhart, MD Orlando Orthopaedic Center Sports Medicine What in the world? TIME magazine in November 2013 stated: In an age filled with advanced medical techniques like
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction 1. Defined a. Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in an effort to restore medial patellar stability and reduce chances of lateral dislocation.
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction 1. Defined a. Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament in an effort to restore medial patellar stability and reduce chances of lateral dislocation.
CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL
 CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL INTRODUCTION The RIGIDFIX Curve Cross Pin System is designed specifically for use with the anteromedial (AM) portal approach to achieve a more anatomic soft tissue
CROSS PIN TECHNOLOGY FOR AN ANATOMIC ACL INTRODUCTION The RIGIDFIX Curve Cross Pin System is designed specifically for use with the anteromedial (AM) portal approach to achieve a more anatomic soft tissue
Meniscus cartilage replacement with cadaveric
 Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Technical Note Meniscal Allografting: The Three-Tunnel Technique Kevin R. Stone, M.D., and Ann W. Walgenbach, R.N.N.P., M.S.N. Abstract: This technical note describes an improved arthroscopic technique
Computational Evaluation of Predisposing Factors to Patellar Dislocation
 Computational Evaluation of Predisposing Factors to Patellar Dislocation Clare K. Fitzpatrick 1, Robert Steensen, MD 2, Jared Bentley, MD 2, Thai Trinh 2, Paul Rullkoetter 1. 1 University of Denver, Denver,
Computational Evaluation of Predisposing Factors to Patellar Dislocation Clare K. Fitzpatrick 1, Robert Steensen, MD 2, Jared Bentley, MD 2, Thai Trinh 2, Paul Rullkoetter 1. 1 University of Denver, Denver,
7/20/14. Patella Instability. Alignment. PF contact areas. Tissue Restraints. Pain. Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint
 Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
Patella Instability Acute Blunt force trauma Disorders of the Patellafemoral Joint Evan G. Meeks, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgery Sports Medicine The University of Texas - Houston Pivoting action Large effusion
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation
 Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
Knee Preservation System
 Knee Preservation System Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System
Knee Preservation System Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Anatomic Patellar Tendon ACL Reconstruction using the Bullseye Cruciate System
Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016
 Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016 With many thanks to Beth Shubin Stein, MD What is the Problem??? THIS IS THE PROBLEM Patella Stability Factors contributing to stability Articular
Patellofemoral Instability Jacqueline Munch, MD April 23, 2016 With many thanks to Beth Shubin Stein, MD What is the Problem??? THIS IS THE PROBLEM Patella Stability Factors contributing to stability Articular
Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for treatment of patellar instability
 354 Acta Orthopaedica 2008; 79 (3): 354 360 Review Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for treatment of patellar instability Martin Lind, Bent W Jakobsen, Bent Lund, and Svend Erik Christiansen
354 Acta Orthopaedica 2008; 79 (3): 354 360 Review Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for treatment of patellar instability Martin Lind, Bent W Jakobsen, Bent Lund, and Svend Erik Christiansen
The AperFix II System
 The AperFix II System A Complete Anatomic Solution Transtibial Surgical Technique 2 AperFix II System Transtibial Surgical Technique Figure 1 A Complete Anatomic Solution The Cayenne Medical AperFix and
The AperFix II System A Complete Anatomic Solution Transtibial Surgical Technique 2 AperFix II System Transtibial Surgical Technique Figure 1 A Complete Anatomic Solution The Cayenne Medical AperFix and
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery
 Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
Minimally Invasive ACL Surgery KOCO EATON, M.D. T A M P A B A Y R A Y S ( 1 9 9 5 P R E S E N T ) T A M P A B A Y B U C C A N E E R S ( 2 0 1 5 2 0 1 6 ) T A M P A B A Y R O W D I E S ( 2 0 1 4 2 0 1 7
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH PINN-ACL CROSSPIN SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The ConMed Linvatec Pinn-ACL CrossPin System
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE VISUALIZE FEMORAL FIXATION 360 GRAFT TO BONE CONTACT INCREASED PULL-OUT STRENGTH PINN-ACL CROSSPIN SYSTEM SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION The ConMed Linvatec Pinn-ACL CrossPin System
Minimally Invasive Quad Tendon Harvest System Surgical Technique
 Minimally Invasive Quad Tendon Harvest System Surgical Technique Quad Tendon Harvest System Quadricep tendon grafts offer unique benefits for cruciate ligament reconstruction such as a predictably large
Minimally Invasive Quad Tendon Harvest System Surgical Technique Quad Tendon Harvest System Quadricep tendon grafts offer unique benefits for cruciate ligament reconstruction such as a predictably large
MPFL reconstruction with autologous gracilis tendon using the two bone tunnel technique
 *smith&nephew Knee Technique Guide MPFL reconstruction with autologous gracilis tendon using the two bone tunnel technique Prof. Elvire Servien, MD, PhD Prof. Philippe Neyret, MD Knee Hip Shoulder Extremities
*smith&nephew Knee Technique Guide MPFL reconstruction with autologous gracilis tendon using the two bone tunnel technique Prof. Elvire Servien, MD, PhD Prof. Philippe Neyret, MD Knee Hip Shoulder Extremities
BioRCI Screw System. Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts
 BioRCI Screw System Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Using the BioRCI Screw System The Smith & Nephew BioRCI cruciate
BioRCI Screw System Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Surgical Technique for Hamstring and Patellar Tendon Grafts Using the BioRCI Screw System The Smith & Nephew BioRCI cruciate
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Principles of ACL graft fixation. Ph. Landreau Aspetar Doha Qatar
 Principles of ACL graft fixation Ph. Landreau Aspetar Doha Qatar Introduction The success of ACL surgery relies on patient selection, graft selection, fixation method, surgical technique (position, tensioning
Principles of ACL graft fixation Ph. Landreau Aspetar Doha Qatar Introduction The success of ACL surgery relies on patient selection, graft selection, fixation method, surgical technique (position, tensioning
Original Article A biomechanical study of different techniques in medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15235-15242 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0023348 Original Article A biomechanical study of different techniques in medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction Junhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15235-15242 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0023348 Original Article A biomechanical study of different techniques in medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction Junhang
Anatomical Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in Management of Cases of Patellar Instability
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, September: 145-151, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Anatomical Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in Management of Cases of Patellar Instability
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 2, September: 145-151, 2016 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Anatomical Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction in Management of Cases of Patellar Instability
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction
 53 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Hany Elrashidy, Joseph Carney, Najeeb Khan, and Donald C. Fithian CHAPTER DEFINITION Stability of the patellofemoral joint (PFJ) is multifactorial as it
53 Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Hany Elrashidy, Joseph Carney, Najeeb Khan, and Donald C. Fithian CHAPTER DEFINITION Stability of the patellofemoral joint (PFJ) is multifactorial as it
MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD
 MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD Professor and Team Physician: Orthopaedic Surgery University of Kentucky School of Medicine Disclosure Institution: Research/Education Smith-Nephew
MCL Injuries: When and How to Repair Scott D. Mair, MD Professor and Team Physician: Orthopaedic Surgery University of Kentucky School of Medicine Disclosure Institution: Research/Education Smith-Nephew
Patellofemoral Joint. Question? ANATOMY
 Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Doug Elenz is a paid Consultant/Advisor for the Biomet Manufacturing Corporation. Doug Elenz, MD Team Orthopaedic Surgeon The University of Texas Men s Athletic Department Question? Patellofemoral Joint
Chronic patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 11 Chronic patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for chronic dislocation? Which is the best imaging modality for documentation? How can we treat it? Table CS11 Patellofemoral joint
Aperture fixation instead of transverse tunnels at the patella for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2012) 20:322 326 DOI 10.1007/s00167-011-1582-1 KNEE Aperture fixation instead of transverse tunnels at the patella for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2012) 20:322 326 DOI 10.1007/s00167-011-1582-1 KNEE Aperture fixation instead of transverse tunnels at the patella for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction
Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no
 Patellar subluxa,on Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no. 4 472-479 History taking is important: a. Trivial or significant injury b. Requires Hospital or self reducion c. Bilateral,
Patellar subluxa,on Acute Trauma,c Disloca,on Am J Sports Med July 2000 vol. 28 no. 4 472-479 History taking is important: a. Trivial or significant injury b. Requires Hospital or self reducion c. Bilateral,
Disclosures. Outline. The Posterior Cruciate Ligament 5/3/2016
 The Posterior Cruciate Ligament Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. PCL Basic
The Posterior Cruciate Ligament Christopher J. Utz, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Cincinnati Disclosures I have no disclosures relevant to this topic. Outline 1. PCL Basic
PCL Reconstruction Utilizing the TightRope /GraftLink Technique Juxtaposed to posterior horn
 Tibial & Femoral PCL Footprints PCL Reconstruction Utilizing the TightRope /GraftLink Juxtaposed to posterior horn Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UCONN Health Team Physician, Orthopaedic
Tibial & Femoral PCL Footprints PCL Reconstruction Utilizing the TightRope /GraftLink Juxtaposed to posterior horn Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UCONN Health Team Physician, Orthopaedic
Graft choice for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
 Technical Note Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Using Quadriceps Tendon Autograft and Bioabsorbable Cross-Pin Fixation Emmanuel Antonogiannakis, M.D., Christos K. Yiannakopoulos,
Technical Note Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction Using Quadriceps Tendon Autograft and Bioabsorbable Cross-Pin Fixation Emmanuel Antonogiannakis, M.D., Christos K. Yiannakopoulos,
Extracapsular Repair Monofilament Nylon Suture
 Extracapsular Repair Monofilament Nylon Suture Management of the ruptured Cranial Cruciate Ligament (CCL) by placing a non-absorbable suture between the lateral fabella and the proximal, cranial tibia
Extracapsular Repair Monofilament Nylon Suture Management of the ruptured Cranial Cruciate Ligament (CCL) by placing a non-absorbable suture between the lateral fabella and the proximal, cranial tibia
Technique Guide. VersiTomic. ReelX STT Double-Row Achilles G-Lok. J. Martin Leland III, M.D. J. Martin Leland III, M.D. Proximal Biceps Tenodesis
 Technique Guide VersiTomic ReelX STT Double-Row Achilles G-Lok Tendon Sub-Pectoral Repair Proximal Biceps Tenodesis J. Martin Leland III, M.D. J. Martin Leland III, M.D. The opinions expressed are those
Technique Guide VersiTomic ReelX STT Double-Row Achilles G-Lok Tendon Sub-Pectoral Repair Proximal Biceps Tenodesis J. Martin Leland III, M.D. J. Martin Leland III, M.D. The opinions expressed are those
Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique
 Surgical Technique Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique for Lateral Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique for Lateral Ankle Ligament Reconstruction
Surgical Technique Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique for Lateral Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Modified Brostrom-Gould Technique for Lateral Ankle Ligament Reconstruction
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction
 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Repair and Reconstruction The knee consists of four bones that form three joints. The femur is the large bone
Jae-Ang Sim 1, Jin-Kyu Lim 2 and Byung Hoon Lee 2*
 Sim et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:346 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2261-x TECHNICAL ADVANCE Open Access Anatomic double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with
Sim et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:346 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2261-x TECHNICAL ADVANCE Open Access Anatomic double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction with
ACL Athletic Career. ACL Rupture - Warning Features Intensive pain Immediate swelling Locking Feel a Pop Dead leg Cannot continue to play
 FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
FIMS Ambassador Tour to Eastern Europe, 2004 Belgrade, Serbia Montenegro Acute Knee Injuries - Controversies and Challenges Professor KM Chan OBE, JP President of FIMS Belgrade ACL Athletic Career ACL
Acute patellar dislocation in adults
 CASE STUDY 14 Acute patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for the first acute dislocation? How can we document the pathoanatomy? What is our treatment concept? Table CS14 Patellofemoral joint
CASE STUDY 14 Acute patellar dislocation in adults What are the reasons for the first acute dislocation? How can we document the pathoanatomy? What is our treatment concept? Table CS14 Patellofemoral joint
Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction
 Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects
Torn ACL - Anatomic Footprint ACL Reconstruction The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four ligaments that are crucial to the stability of your knee. It is a strong fibrous tissue that connects
SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
 Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Copyright 2016 NGD. All rights reserved Neil Embleton, B.Sc., DVM and Veronica Barkowski, DVM Helivet Mobile Surgical Services, Sundre, AB, Canada July 2016 SIMITRI STABLE IN STRIDE SURGICAL PROCEDURE
Incidence. Avoiding Complications of ACL Surgery. ACL Complications 6/10/2011. Not if, but when
 Avoiding Complications of ACL Surgery Thomas J. Gill, MD Chief, MGH Sports Medicine Service Dept of Orthopedic Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical
Avoiding Complications of ACL Surgery Thomas J. Gill, MD Chief, MGH Sports Medicine Service Dept of Orthopedic Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
The medial side of the knee has been relatively overlooked
 REVIEW ARTICLE Medial and Posteromedial Instability of the Knee: Evaluation, Treatment, and Results James P. Stannard, MD Abstract: Medial-sided knee ligament injuries are complex and require a thorough
REVIEW ARTICLE Medial and Posteromedial Instability of the Knee: Evaluation, Treatment, and Results James P. Stannard, MD Abstract: Medial-sided knee ligament injuries are complex and require a thorough
FIXED PERFORMANCE. Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction
 ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System is an innovative technology
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction Surgical Technique The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System The RIGIDLOOP Adjustable Cortical System is an innovative technology
HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES
 HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES Written by Philippe Landreau, Qatar The treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries remains challenging in young athletic populations. A residual
HISTORY AND INDICATIONS OF LATERAL TENODESIS IN ATHLETES Written by Philippe Landreau, Qatar The treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries remains challenging in young athletic populations. A residual
Patella Fracture and Extensor Mechanism Injuries
 Patella Fracture and Extensor Mechanism Injuries Kyle T. Judd MS, MD, FACS David J. Hak MD, MBA, FACS Updated February 2016 1 Anatomy Patella Largest sesamoid bone Triangular shape (apex distal) Distal
Patella Fracture and Extensor Mechanism Injuries Kyle T. Judd MS, MD, FACS David J. Hak MD, MBA, FACS Updated February 2016 1 Anatomy Patella Largest sesamoid bone Triangular shape (apex distal) Distal
Alternative Design Report
 Alternative Design Report Novel Polysaccharide-derived Fixation Device for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Team 13 Derek Holyoak Alexander Werne Benjamin Roberts Clients: Dr. Krystyna Gielo-Perczak
Alternative Design Report Novel Polysaccharide-derived Fixation Device for Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Reconstruction Team 13 Derek Holyoak Alexander Werne Benjamin Roberts Clients: Dr. Krystyna Gielo-Perczak
Fibular collateral ligament reconstruction of knee using titanium button: a new fixation technique and an outcome of 35 cases
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rai SK et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 May;3(3):573-577 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20171904
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rai SK et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 May;3(3):573-577 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20171904
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Technique Guide. *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System
 Technique Guide *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System N8TIVE ACL System The N8TIVE ACL Anatomic Reconstruction System provides a novel and simple approach to ACL repair. The N8TIVE
Technique Guide *smith&nephew N8TIVE ACL Anatomic ACL Reconstruction System N8TIVE ACL System The N8TIVE ACL Anatomic Reconstruction System provides a novel and simple approach to ACL repair. The N8TIVE
Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing?
 Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing? 1. Presentation (4 x approx. 5min.) i. Mitsuo Ochi ii. Freddie Fu, iii. Takeshi Muneta iv. Rainer Siebold, 2. Debate (approx. 10 min.) 1 ACL
Remnant Preservation in ACL Reconstruction: Is it Worth Doing? 1. Presentation (4 x approx. 5min.) i. Mitsuo Ochi ii. Freddie Fu, iii. Takeshi Muneta iv. Rainer Siebold, 2. Debate (approx. 10 min.) 1 ACL
John J Christoforetti, MD Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
 ARTHROSCOPIC ASSISTED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR WITH HUMAN ACELLULAR DERMAL ALLOGRAFT PATCH AUGMENTATION FOR REVISION OF FAILED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR: SHORT TERM CLINICAL AND MRI RESULT John J Christoforetti,
ARTHROSCOPIC ASSISTED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR WITH HUMAN ACELLULAR DERMAL ALLOGRAFT PATCH AUGMENTATION FOR REVISION OF FAILED PROXIMAL HAMSTRINGS REPAIR: SHORT TERM CLINICAL AND MRI RESULT John J Christoforetti,
Retinacular tear knee
 P ford residence southampton, ny Retinacular tear knee The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) helps to keep the kneecap centered along the front of the knee, so that it tracks well during knee movements.
P ford residence southampton, ny Retinacular tear knee The medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) helps to keep the kneecap centered along the front of the knee, so that it tracks well during knee movements.
GASTROCNEMIUS TENDON REPAIR VETLIG USING THE STIF CAT 30 SOFT TISSUE INTERNAL FIXATION VETLIG
 VETLIG SOFT TISSUE INTERNAL FIXATION GASTROCNEMIUS TENDON REPAIR USING THE STIF CAT 30 VETLIG A R T I F I C I A L L I G A M E N T S F O R V E T E R I N A R Y U S E VETLIG MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC GASTROCNEMIUS
VETLIG SOFT TISSUE INTERNAL FIXATION GASTROCNEMIUS TENDON REPAIR USING THE STIF CAT 30 VETLIG A R T I F I C I A L L I G A M E N T S F O R V E T E R I N A R Y U S E VETLIG MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC GASTROCNEMIUS
Transtibial PCL Reconstruction. Surgical Technique. Transtibial PCL Reconstruction
 Transtibial PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Transtibial PCL Reconstruction The Arthrex Transtibial PCL Reconstruction System includes unique safety features for protecting posterior neurovascular
Transtibial PCL Reconstruction Surgical Technique Transtibial PCL Reconstruction The Arthrex Transtibial PCL Reconstruction System includes unique safety features for protecting posterior neurovascular
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Management of Knee Dislocations
 Management of Knee Dislocations Thomas J. Gill, MD Chief, Sports Medicine Service Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical School Complex Challenging Multi-Ligament
Management of Knee Dislocations Thomas J. Gill, MD Chief, Sports Medicine Service Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Orthopedic Surgery Harvard Medical School Complex Challenging Multi-Ligament
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE
 ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE RIGIDLOOP ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL SYSTEM The RIGIDLOOP
ADJUSTABLE CONVENIENCE, FIXED PERFORMANCE Soft Tissue ACL Reconstruction This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE THE RIGIDLOOP ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL SYSTEM The RIGIDLOOP
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS The Advantage of Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction with Autograft from the Tendons of the Semitendinosus Gracilis Muscles for
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS The Advantage of Arthroscopic Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction with Autograft from the Tendons of the Semitendinosus Gracilis Muscles for
Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2013) 23:819 823 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1073-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2013) 23:819 823 DOI 10.1007/s00590-012-1073-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bone patellar tendon bone autograft versus LARS artificial ligament for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction
RIGIDfix. Soft Tissue. Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction PRODUCTS. Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. TISSUE SOFT.
 RIGIDfix A C L C R O S S P I N S Y S T E M Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. Toledo, Ohio SOFT TISSUE Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction Soft Tissue PRODUCTS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RIGIDfix A
RIGIDfix A C L C R O S S P I N S Y S T E M Daniel J. McKernan, M.D. Toledo, Ohio SOFT TISSUE Surgical Technique for Mitek RIGIDfix ACL Reconstruction Soft Tissue PRODUCTS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RIGIDfix A
Dr. Pablo E. Gelber MD PhD Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau and ICATME Hospital Universitari Quirón Dexeus (Barcelona, Spain) Figure 2a-d
 A GUIDE TO MASTERING THE GRAFTMAX BUTTON ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL FIXATION DEVICE An examination of surgical learnings during the first 6 months of clinical usage Dr. Pablo E. Gelber MD PhD Hospital de la Santa
A GUIDE TO MASTERING THE GRAFTMAX BUTTON ADJUSTABLE CORTICAL FIXATION DEVICE An examination of surgical learnings during the first 6 months of clinical usage Dr. Pablo E. Gelber MD PhD Hospital de la Santa
LARS PCL. PCL Reconstruction and Reinforcement Surgical technique
 PCL Reconstruction and Reinforcement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Indications 5 LARS synthetic ligament composition 5 General considerations 5 LARS in PCL reconstruction 6
PCL Reconstruction and Reinforcement Surgical technique Contents Operative summary 4 Overview 5 Indications 5 LARS synthetic ligament composition 5 General considerations 5 LARS in PCL reconstruction 6
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play
 ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
ACL Rehabilitation and Return To Play Seth Gasser, MD Director of Sports Medicine Florida Orthopaedic Institute Introduction Return to Play: the point in recovery from an injury when a person is safely
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes
 Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Is a malady commonly seen in the orthopaedic office. MPFL to be the major medial so: ;ssue stabilizer, providing 53% of the total restraining force.
 Is a malady commonly seen in the orthopaedic office. MPFL to be the major medial so: ;ssue stabilizer, providing 53% of the total restraining force. Symptoms are occasionally preceded by a trauma;c event
Is a malady commonly seen in the orthopaedic office. MPFL to be the major medial so: ;ssue stabilizer, providing 53% of the total restraining force. Symptoms are occasionally preceded by a trauma;c event
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact)
 STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
STATE OF THE ART OF ACL SURGERY (Advancements that have had an impact) David Drez, Jr., M.D. Clinical Professor of Orthopaedics LSU School of Medicine Financial Disclosure Dr. David Drez has no relevant
Xuancheng Zhang, Guoming Xie *, Chengyuan Zhang, Zhaoyi Fang, Jinzhong Zhao * and Xiaoqiao Huangfu *
 Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:53 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2439-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparation and evaluation of the accuracy of the sulcus localization method
Zhang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2019) 20:53 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2439-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparation and evaluation of the accuracy of the sulcus localization method
Patellofemoral Instability
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Patellofemoral Instability. All decisions about the management of Patellofemoral Instability must be made in conjunction
Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee
 Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee By Mark C. Komosa Submitted to the graduate degree program in Bioengineering and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas in partial fulfillment
Assessment of Patellar Laxity in the in vitro Native Knee By Mark C. Komosa Submitted to the graduate degree program in Bioengineering and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas in partial fulfillment
All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes
 All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes William Godfrey, BS Aaron Gebrelul, BA; John Xerogeanes, MD; Ajay
All-Soft Tissue Quadriceps Tendon Autograft for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: Short to Intermediate-Term Clinical Outcomes William Godfrey, BS Aaron Gebrelul, BA; John Xerogeanes, MD; Ajay
