Simultaneous Surgical Treatment in Congenital Scoliosis and/or Kyphosis Associated With Intraspinal Abnormalities
|
|
|
- Gavin Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Simultaneous Surgical Treatment in Congenital Scoliosis and/or Kyphosis Associated With Intraspinal Abnormalities SPINE Volume 32, Number 25, pp , Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Azmi Hamzaoglu, MD,* Cagatay Ozturk, MD,* Mehmet Tezer, MD,* Mehmet Aydogan, MD,* Mercan Sarier, MD,* and Ufuk Talu, MD Study Design. Retrospective clinical study. Objective. To show retrospective analysis of 21 consecutive patients who underwent simultaneous surgical treatment for progressive spinal deformity and coexisting intraspinal pathologies (tethered cord and/or diastematomyelia). Summary of Background Data. The classic advocated approach in patients with congenital spine deformity associated with intraspinal anomalies is first to perform surgery for the intraspinal pathologies and then surgery for correction and stabilization of the deformity 3 to 6 months later. To our knowledge, there is no study on simultaneous surgical treatment for these 2 associated conditions. Methods. In the surgery; after the exposure of the determined levels, placement of all pedicle screws was performed as the initial part of surgical procedure. Then surgical treatment for intraspinal pathology was performed by the neurosurgical team and then followed by completion of instrumentation and correction of the deformity. Additional anterior surgery was done later to prevent pseudarthrosis and crankshaft phenomenon. Results. The mean age of the patients at presentation ranged from 3 to 19 years (mean, 13 years). There were 17 female patients and 4 male patients. Four patients had neurologic deficits at the time of presentation, and all 4 had associated kyphosis. The mean operation time was 9.3 hours (range, 7 12 hours) and the mean blood loss was 1980 ml (range, ml). The average follow-up was 6.8 years (2 12 years). None of the patients experienced deterioration in their neurologic status after surgery. None of the patients had infection, pseudarthrosis, or loss of correction during the follow-up visits. Conclusion. The simultaneous surgical treatment for congenital deformity and intraspinal abnormality does not involve significant complications and seems to be an alternative and safe treatment option. Key words: intraspinal abnormality, congenital scoliosis, congenital kyphosis, surgical treatment. Spine 2007; 32: From the *Istanbul Bilim University Medical School, Istanbul Spine Center, Florence Nightingale Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey; and Istanbul University Medical School Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Istanbul, Turkey. Acknowledgment date: January 9, Revision date: May 5, Acceptance date: May 7, The manuscript submitted does not contain information about medical device(s)/drug(s). No funds were received in support of this work. No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Cagatay Ozturk, MD, Istanbul Bilim University, Istanbul Spine Center, Florence Nightingale Hospital, Abide-i Hurriyet Caddesi, No: 290, 80220, Sisli, Istanbul, Turkey; cgtyztrk@yahoo.com Congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis occurs as a result of either a failure of formation or a failure of segmentation, or both. 1 This most frequently occurs in the first 8 weeks of prenatal development. During this time, the bony elements of the spine are forming, and the neuraxis is completing its infolding, closing the neural tube. 2 These events are closely related, and any intrauterine event that causes congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis could also be associated with an intraspinal anomaly. These anomalies include tethering of the cord, diastematomyelia, lipoma and lipomeningocele, teratomas, and syringomyelia. The intraspinal anomalies can cause progressive neural loss with growth and curve progression. In addition, they greatly increase the risk of neurologic injury during surgical correction of the deformity. 3 6 McMaster 7 reported intraspinal abnormality in 18% of 251 patients with myelography. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is noninvasive and more sensitive in detecting the intraspinal abnormalities. Using MRI, Bradford et al 6 reported that 38% of the 42 patients in their study had an intraspinal anomaly. Congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis due to the presence of vertebral anomalies cause an imbalance in the longitudinal growth of the spine. Being a developmental anomaly, it is often associated with intraspinal, genitourinary, cardiovascular, and other general abnormalities. 7 9 Congenital deformities of the spine are relatively rigid with a concurrent danger of neurologic complications. 10 All these factors, including the presence of intraspinal abnormalities, are important in decisionmaking and the management of congenital scoliosis. The classic advocated approach in such patients is first to perform surgery for the intraspinal pathologies and then surgery for correction and stabilization of the deformity 3 to 6 months later. 7,9 To our knowledge, there is no study on simultaneous surgical treatment for these 2 associated conditions. In the current study, we have retrospectively analyzed 21 consecutive patients who underwent simultaneous surgical treatment for progressive spinal deformity and coexisting intraspinal pathologies (tethered cord and/or diastematomyelia). Materials and Methods We retrospectively reviewed the records of 21 consecutive patients with congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis associated with intraspinal abnormalities treated by simultaneous surgery between the years 1994 and
2 Scoliosis and Intraspinal Abnormalities Hamzaoglu et al 2881 team, then followed completion of instrumentation and correction of the deformity (posterior shortening wedge osteotomy or subtotal vertebrectomy if needed) (Figure 1). Posterior instrumentation for correction of the deformity was short segment in 7 patients and long segment in the remaining 14 patients. Also, vertebrectomy via posterior approach was performed in 5 patients and 3 patients had additional anterior surgery later to prevent pseudarthrosis and crankshaft phenomenon. A combination of autograft and allograft was used for achieving fusion in all patients (Figures 2, 3). The operation time, blood loss, postoperative complications, and the hospitalization time were noted and recorded. Figure 1. The surgical treatment for intraspinal pathology (release of tethered cord and/or excision of diastematomyelic bone spur) was performed by the neurosurgical team. The age at presentation, sex, presence of associated kyphosis, and the neurologic status were documented. All the patients had standing anteroposterior and lateral views of the spine from C5 to sacrum. All patients were subjected to neural axis MRI from brainstem to sacrum to detect the associated intraspinal anomalies. Ultrasonography was used as a screening procedure to detect genitourinary anomalies. A cardiovascular evaluation was done of all the patients by both clinical examination and echocardiography to exclude cardiac anomalies. All patients also underwent assessment by a pediatrician. In the surgery, after the exposure of the determined levels, placement of all pedicle screws was performed as the initial part of surgical procedure. Then surgical treatment for intraspinal pathology (release of tethered cord and/or excision of diastematomyelic bone spur) was performed by the neurosurgical Results The mean age of the patients at presentation ranged from 3 to 19 years (mean, 13 years). There were 17 female patients and 4 male patients. The congenital vertebral anomalies were classified using standard terminology as either failure of formation, failure of segmentation, or mixed defects. 11 There were 16 cases of congenital scoliosis (including kyphoscoliosis) and 5 cases of congenital kyphosis due to hemivertebra. Of the 16 cases of congenital scoliosis, there were 7 classified as failure of formation, 3 as failure of segmentation, and 6 as mixed defects. The MRI showed the intraspinal pathologies as 7 patients with tethered cord, 1 patient with retethering, and 13 patients with diastematomyelia with tethered cord. Four patients had neurologic deficits at the time of presentation, and all 4 had associated kyphosis. Bilateral weakness of toe extensors with absent ankle jerk was seen in 2 patients. In the remaining 2, there was hypoesthesia at L5, S1 dermatome and weakness of toe extensors as well as flexors. Genitourinary anomalies were seen in 5 patients (unilateral agenesis of the kidney in 3 patients and ectopic kidney in 2 patients). None of them had clinical features suggestive of genitourinary anomalies but Figure 2. A 3-year-old female patient with congenital kyphosis associated with tethered cord. The patient had neurologic deficit at presentation. The following surgical procedures were performed in order: placement of pedicle screws, release of tethered cord, posterior total hemivertebrectomy, correction and fusion with titanium mesh cage. At postoperative 2 years, she is free from any neurologic symptoms.
3 2882 Spine Volume 32 Number Figure 3. A, A 15-year-old female patient with congenital scoliosis associated with diastematomyelia and tethered cord. After exposure and posterior placement of pedicle screws, tethered cord was released and bony spur was excised. Then, we performed posterior shortening wedge osteotomy at T10 T11 to correct severe frontal imbalance. Two weeks later, anterior fusion was done to prevent pseudarthrosis. At fifth postoperative year, she is free of any symptoms. B, MRI scans showing the diastematomyelia. were incidental findings detected on screening. Cardiovascular anomalies were seen in 6 patients with mitral valve prolapse being the commonest anomaly (in 4 of 6 patients). The mean operation time was 9.3 hours (range, 7 12 hours) and the mean blood loss was 1980 ml (range, ml). All patients spent at least 1 day in intensive care unit and the mean hospitalization time (excluding 3 patients needing additional anterior surgery) was 7.3 days (range, 5 12 days). The mean correction in the deformity (either kyphosis or scoliosis or both) was 23%, and the correction loss at the end of follow-up was less than 10%. The average follow-up was 6.8 years (range, 2 12 years). None of the patients experienced deterioration in their neurologic status after surgery. For the patients with preoperative neurologic deficit, the recovery was complete in 2 patients, neurologic status was better in 1 patient and unchanged in the other. In 1 patient who had associated myelomeningocele, postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leakage was observed, and it was repaired successfully in a second surgical procedure. None of the patients had infection, pseudarthrosis, or loss of correction during the follow-up visits. Discussion In patients with congenital spinal deformity, the prevalence of intraspinal anomalies that are detected with magnetic resonance imaging has been reported to be 20% to 58%. 3,12,13 MRI is superior to either radiography or myelography for the identification and evaluation of early developmental conditions of the neural axis because it provides more information and is less invasive. In the current study, the most common intraspinal anomalies diagnosed with MRI were tethered spinal cord and diastematomyelia. These findings corroborate those of previous MRI studies of congenital scoliosis that have demonstrated that the most common intraspinal anomalies were tethered spinal cord (prevalence, 13% 29%) and diastematomyelia (prevalence, 3% 12%). 3,4,6,13,14 The median age at presentation was 13 years. This may support the hypothesis that, although the vertebral anomalies are present at birth, they may manifest as a visible deformity only much later. However, socioeconomic factors may have also contributed to this delay in presentation. Neurologic involvement at the time of presentation may indicate the underlying occult intraspinal
4 Scoliosis and Intraspinal Abnormalities Hamzaoglu et al 2883 anomaly. 15 It is therefore essential to exclude underlying spinal cord anomalies if a patient presents with a neurologic deficit, which would then dictate the treatment options. Neurologic deficit at the time of presentation was seen in 4 patients. All of them had associated kyphosis and all were found to have diastematomyelia with tethered cord. Congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis is frequently associated with congenital anomalies in other systems, especially those formed from mesenchymal tissue. These anomalies are often asymptomatic and may remain undetected until the patient is fully assessed following the diagnosis of congenital spinal deformity. 7,16 Genitourinary anomalies that can cause obstruction are silent and, if not searched for, may cause serious damage before they are diagnosed. The incidence of genitourinary anomalies was found to be 23.8% in the current study. This is similar to frequencies seen in other studies Cardiovascular anomalies were the most common of the associated systemic anomalies in our study. They were seen in 28.5% of patients with mitral valve prolapse being the commonest anomaly. According to Winter, the incidence of congenital heart disease in congenital scoliosis was 7%. 8 The study done by Roth et al 19 showed that the overall incidence of scoliosis inpatients with congenital heart disease was 12%. The cause of our high rate may be the small size of the patient group. As decision-making in congenital scoliosis and/or kyphosis depends on the natural history of progression, clinical and radiologic assessment is essential. Detection of inherent problems in the spinal cord and other associated anomalies become relevant in choosing the appropriate surgical management. According to Winter et al, 9 the classic advocated approach in patients having congenital spine deformity associated with intraspinal abnormality is first to perform surgery for the intraspinal pathologies and then surgery for correction and stabilization of the deformity 3 to 6 months later in a different session. However, this different session surgical treatment carries some disadvantages. First, it contains more than 1 surgery and expose the patients to the risks of surgery more than once. Difficult surgical exposure, increased bleeding, adhesion formation, and less clear anatomic landmarks make the later corrective surgery more difficult. Also, after primary neurosurgical procedure, there is a risk of retethering and it often necessitates another neurosurgical procedure before corrective surgery. In addition, more complicated reconstructive procedures like osteotomy, hemivertebrectomy, etc., can be done with difficulty due to preformed adhesion in the surgical site. There is also increased risk of iatrogenic neural element injury during such approaches. From the year 1994, our surgical approach for the treatment of these patients is the simultaneous surgery for the intraspinal pathology and corrective surgery for the congenital spinal deformity via posterior approach. If needed, we perform anterior surgery 2 to 3 weeks later to prevent pseudarthrosis and crankshaft phenomenon. According to our knowledge, there is no study in the English literature involving simultaneous corrective surgical treatment for congenital spinal deformity and neurosurgical procedure for the surgical treatment of the coexisting intraspinal abnormality. It does not increase the surgical time, blood loss, and hospitalization time too much. Although our patient number is not too big, simultaneous surgical treatment for congenital deformity and intraspinal abnormality does not involve significant complications and seems to be an attractive and safe treatment option. Our decision-making procedure in choosing of shortor long-segment fusion is that in patients having severe, sharp angular kyphosis or kyphosis and/or scoliosis due to a single hemivertebra; the posterior instrumentation and short-segment fusion was done together with hemivertebra resection or with corrective osteotomies. On the other hand, in patients with severe thoracolumbar or lumbar scoliosis even associated with pelvic tilt, posterior instrumentation and long segment fusion was preferred. In patients with severe sagittal and coronal imbalance, transpedicular osteotomy and/or vertebral column resection together with long-segment instrumentation was done. This was especially considered in patients with severely disturbed coronal balance, severe kyphoscoliosis, and presence of trunk shift due to the deformity. Decision whether to do fusion in situ or to do correction has arisen during the operation according to the last form of the deformity after neurosurgical approach finished and/or corrective osteotomies were done. The flexibility of the deformity is the major concern in those situations. This study reports on a retrospective study of a small series of patients with congential scoliosis and/or kyphosis associated with intraspinal abnormalities treated surgically for the intraspinal abnormality and the spinal deformity at the same sitting. There were no significant complications, showing that the 1-stage procedure can give comparable results to 2-stage procedures adopted by other workers in the past. This situation is valid only in the presence of the following: surgical team experienced in spinal deformity surgery well preoperative surgical planning neurosurgical team experience in intramedullary abnormalities field use of intraoperative neurophysiologic studies (neuromonitorization). We are routinely using neuromonitorization for last 2 years in our all deformity cases anesthesiology department experienced in caring both intraoperative and early postoperative phases of these patients well working pediatric intensive care unit and also, clear explanation of advantages and disadvantages of
5 2884 Spine Volume 32 Number the same sitting surgery to the patients parents is mandatory before all such kind of procedures. Key Points The classic advocated approach in patients with congenital spine deformity associated with intraspinal abnormalities is first to perform surgery for the intraspinal pathologies and then surgery for correction and stabilization of the deformity 3 to 6 months later. There is no study in the literature related to simultaneous surgical treatment for these 2 associated conditions. The separate session surgical treatment carries some disadvantages related to the patient s general medical condition and surgical site. The simultaneous surgical treatment for congenital deformity and intraspinal abnormality does not involve significant complications and seems to be an alternative and safe treatment option. References 1. Winter RB. Congenital spinal deformity. In: Lonstein JE, ed. Moe s Textbook of Scoliosis and Other Spinal Deformities, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1995: Tsou PM, Yau A, Hodgson AR. Embryogenesis and prenatal development of congenital vertebral anomalies and their classification. Clin Orthop 1980; 152: Belmont PJ, Kuklo TR, Taylo KF, et al. Intraspinal anomalies associated with isolated congenital hemivertebra: the role routine magnetic resonance imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86: Prahinski JR, Polly DW, McHale K, et al. Occult intraspinal anomalies in congenital scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop 2000;20: Basu PS, Elsebaie H, Noordeen MHH. Congenital spinal deformity: a comprehensive assessment at presentation. Spine 2002;27: Bradford DS, Heithoff KB, Cohen M. Intraspinal anomalies and congenital scoliosis: a radiographic and MRI study. J Pediatr Orthop 1991;11: McMaster MJ. Occult intraspinal anomalies and congenital scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984;66: Winter RB. Congenital scoliosis. Clin Orthop 1973;93: Winter RB, Haven JJ, Moe JH, et al. Diastematomyelia and congenital spine deformities. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1974;56: McMaster MJ, Ohtsuka K. The natural history of congenital scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1982;64: McMaster M. Congenital scoliosis caused by a unilateral failure of vertebral segmentation with contralateral hemivertebrae. Spine 1998;23: Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Boachie-Adjei O. Congenital spinal deformity. Instr Course Lect 1996;45: Reckles LN, Peterson HA, Weidman WH, et al. The association of scoliosis and congenital heart defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1975;57: Suh SW, Sarwak JF, Vora A, et al. Evaluating congenital spine deformities for intraspinal anomalies with magnetic resonance imaging. J Pediatr Orthop 2001;21: Mohanty S, Kumar N. Patterns of presentation of congenital scoliosis. J Orthop Surg 2000;9: Gillespie R, Faithfull DK, Roth A, et al. Intraspinal anomalies in congenital scoliosis. Clin Orthop 1973;93: Tori JA, Dickson JH. Association of congenital anomalies of the spine and kidneys. Clin Orthop 1980;148: Winter RB. Congenital scoliosis. Orthop Clin North Am 1988;19: Roth A, Rosenthal A, Hall JE, et al. Scoliosis and congenital heart disease. Clin Orthop 1973;93:
Tethered cord syndrome is a rare intraspinal anomaly, Pediatric tethered cord syndrome: response of scoliosis to untethering procedures
 J Neurosurg Pediatrics 4:000 000, 4:270 274, 2009 Pediatric tethered cord syndrome: response of scoliosis to untethering procedures Clinical article Ma t t h e w J. McGi r t, M.D., 1 Vi v e k Me h ta,
J Neurosurg Pediatrics 4:000 000, 4:270 274, 2009 Pediatric tethered cord syndrome: response of scoliosis to untethering procedures Clinical article Ma t t h e w J. McGi r t, M.D., 1 Vi v e k Me h ta,
Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence
 Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence Comparison of Clinical, Radiographic, and Health-Related Quality of Life
Hemivertebra Resection Combined With Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Severe Rigid Congenital Kyphoscoliosis in Adolescence Comparison of Clinical, Radiographic, and Health-Related Quality of Life
The Incidence and Interrelationship of Concomitant Anomalies in Congenital Scoliosis
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.24429-18.2 Received: 25.07.2018 / Accepted: 17.09.2018 Published Online: 26.11.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation The Incidence and Interrelationship of Concomitant
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.24429-18.2 Received: 25.07.2018 / Accepted: 17.09.2018 Published Online: 26.11.2018 Turk Neurosurg, 2018 Original Investigation The Incidence and Interrelationship of Concomitant
Posterior Convex Wedge Resection in the Management of Advanced Congenital Scoliosis Caused by Hemivertebra
 WSJ. 2006;1(2):75-78 74 Posterior Convex Wedge Resection in the Management of Advanced Congenital Caused by Hemivertebra Surya Prakash Rao Voleti, MS, Dnb Department Of Orthopaedics, Nizam s Institute
WSJ. 2006;1(2):75-78 74 Posterior Convex Wedge Resection in the Management of Advanced Congenital Caused by Hemivertebra Surya Prakash Rao Voleti, MS, Dnb Department Of Orthopaedics, Nizam s Institute
Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 344-348 Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease Teoman ATICI, Ufuk AYDINLI, Burak AKESEN, Rasim ŠERIFOĞLU
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 344-348 Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease Teoman ATICI, Ufuk AYDINLI, Burak AKESEN, Rasim ŠERIFOĞLU
Radiographic characteristics in congenital scoliosis associated with split cord malformation: a retrospective study of 266 surgical cases
 Feng et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:420 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1782-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic characteristics in congenital scoliosis associated with split cord malformation:
Feng et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:420 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1782-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic characteristics in congenital scoliosis associated with split cord malformation:
Congenital scoliosis results from abnormal vertebral
 SPINE Volume 41, Number 21, pp E1271 E1278 ß 2016 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved Pediatric Posterior Vertebral Column Resection (PVCR): Before and After Ten Years of Age Greater Than 10-Year
SPINE Volume 41, Number 21, pp E1271 E1278 ß 2016 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved Pediatric Posterior Vertebral Column Resection (PVCR): Before and After Ten Years of Age Greater Than 10-Year
Laterally positioned hemivertebrae and the resultant. Dorsal midline hemivertebra at the lumbosacral junction: report of 2 cases.
 spine case report J Neurosurg Spine 22:84 89, 2015 Dorsal midline hemivertebra at the lumbosacral junction: report of 2 cases Shaheryar F. Ansari, MD, 1 Richard B. Rodgers, MD, 2 and Daniel H. Fulkerson,
spine case report J Neurosurg Spine 22:84 89, 2015 Dorsal midline hemivertebra at the lumbosacral junction: report of 2 cases Shaheryar F. Ansari, MD, 1 Richard B. Rodgers, MD, 2 and Daniel H. Fulkerson,
of thoracolumbar angular kyphosis.
 spine clinical article J Neurosurg Spine 23:42 48, 2015 Expanded eggshell procedure combined with closing-opening technique (a modified vertebral column resection) for the treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar
spine clinical article J Neurosurg Spine 23:42 48, 2015 Expanded eggshell procedure combined with closing-opening technique (a modified vertebral column resection) for the treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar
Formation defects Scoliosis Deformities I 07 1
 What is congenital scoliosis? Congenital scoliosis is a spinal deformity with lateral deviation and rotation of the spinal column, where congenital dysfunctions in embryonal vertebra development cause
What is congenital scoliosis? Congenital scoliosis is a spinal deformity with lateral deviation and rotation of the spinal column, where congenital dysfunctions in embryonal vertebra development cause
Wh e n idiopathic adolescent scoliosis involves 2
 J Neurosurg Spine 10:000 000, 10:214 219, 2009 Shoulder balance after surgery in patients with Lenke Type 2 scoliosis corrected with the segmental pedicle screw technique Clinical article *Mi n g Li, M.D.,
J Neurosurg Spine 10:000 000, 10:214 219, 2009 Shoulder balance after surgery in patients with Lenke Type 2 scoliosis corrected with the segmental pedicle screw technique Clinical article *Mi n g Li, M.D.,
Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity
 Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
Hemivertebra Resection for the Treatment of Congenital Lumbarspinal Scoliosis With Lateral-Posterior Approach
 SPINE Volume 33, Number 18, pp 2001 2006 2008, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Hemivertebra Resection for the Treatment of Congenital Lumbarspinal Scoliosis With Lateral-Posterior Approach Xiangdong Li,
SPINE Volume 33, Number 18, pp 2001 2006 2008, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Hemivertebra Resection for the Treatment of Congenital Lumbarspinal Scoliosis With Lateral-Posterior Approach Xiangdong Li,
Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives
 Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives Scott B. Rosenfeld, MD Division of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 8:26:24 AM I have no disclosures Disclosures
Scoliosis: Orthopaedic Perspectives Scott B. Rosenfeld, MD Division of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 8:26:24 AM I have no disclosures Disclosures
Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma
 Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma a* a a a b a a b ʼ 2 ʼ August 2012 Spinal Deformity with
Segmental Pedicle Screw Fixation for a Scoliosis Patient with Post-laminectomy and Post-irradiation Thoracic Kyphoscoliosis of Spinal Astrocytoma a* a a a b a a b ʼ 2 ʼ August 2012 Spinal Deformity with
What Every Spine Surgeon Should Know About Neurosurgical Issues
 What Every Spine Surgeon Should Know About Neurosurgical Issues Amer Samdani, MD Chief of Surgery Shriners Hospitals for Children Philadelphia, PA Objectives Main intraspinal lesions Chiari malformation
What Every Spine Surgeon Should Know About Neurosurgical Issues Amer Samdani, MD Chief of Surgery Shriners Hospitals for Children Philadelphia, PA Objectives Main intraspinal lesions Chiari malformation
WHICH FACTORS PREDICT SHOULDER ASYMMETRY IN PATIENTS WITH LENKE TYPE 1 AND 3 CURVES FOLLOWING PEDICLE SCREW INSTRUMENTATION?
 WHICH FACTORS PREDICT SHOULDER ASYMMETRY IN PATIENTS WITH LENKE TYPE 1 AND 3 CURVES FOLLOWING PEDICLE SCREW INSTRUMENTATION? Meric ENERCAN, MD Sinan KAHRAMAN, MD Bahadır GÖKÇEN, MD Tunay SANLI, MA Cagatay
WHICH FACTORS PREDICT SHOULDER ASYMMETRY IN PATIENTS WITH LENKE TYPE 1 AND 3 CURVES FOLLOWING PEDICLE SCREW INSTRUMENTATION? Meric ENERCAN, MD Sinan KAHRAMAN, MD Bahadır GÖKÇEN, MD Tunay SANLI, MA Cagatay
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine
 Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine A. I. Tsirikos, M. J. McMaster From The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, Scotland We report five children
Infantile developmental thoracolumbar kyphosis with segmental subluxation of the spine A. I. Tsirikos, M. J. McMaster From The Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Edinburgh, Scotland We report five children
Scoliosis is considered to be the most common skeletal
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 19:96 101, 2017 Posterior-only surgical correction of dystrophic scoliosis in 31 patients with neurofibromatosis Type 1 using the multiple anchor point method Ang Deng,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 19:96 101, 2017 Posterior-only surgical correction of dystrophic scoliosis in 31 patients with neurofibromatosis Type 1 using the multiple anchor point method Ang Deng,
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis S Harwant, FRSCSEd., rthopaedic Unit, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 8 th Floor, Grand Seasons Avenue,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Influencing the Outcome of Arthrodesis for Congenital Kyphosis and Kyphoscoliosis S Harwant, FRSCSEd., rthopaedic Unit, Universiti Putra Malaysia, 8 th Floor, Grand Seasons Avenue,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Congenital Spine Deformity: Surgical Treatment Options. Spine Masters. Fri May , 4:10-4:25 Paul Sponseller MD
 Congenital Spine Deformity: Surgical Treatment Options Spine Masters Fri May19 2017, 4:10-4:25 Paul Sponseller MD Disclosures Medical Education Reviews JBJS Depuy Synthes Spine: Research, royalties Globus:
Congenital Spine Deformity: Surgical Treatment Options Spine Masters Fri May19 2017, 4:10-4:25 Paul Sponseller MD Disclosures Medical Education Reviews JBJS Depuy Synthes Spine: Research, royalties Globus:
Delayed treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
 spine clinical article J Neurosurg Spine 22:194 198, 2015 Posterior-only spinal release combined with derotation, translation, segmental correction, and an in situ rod-contouring technique for treatment
spine clinical article J Neurosurg Spine 22:194 198, 2015 Posterior-only spinal release combined with derotation, translation, segmental correction, and an in situ rod-contouring technique for treatment
Keith Bachmann, MD UVA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Keith Bachmann, MD UVA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Definition Spinal deformity secondary to either neurologic or muscle pathology. Etiology Imbalance of muscle forces Lack of truncal support Similar
Keith Bachmann, MD UVA Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Definition Spinal deformity secondary to either neurologic or muscle pathology. Etiology Imbalance of muscle forces Lack of truncal support Similar
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
SCIENTIFIC PROGRAMME
 SCIENTIFIC PROGRAMME LEARNING OUTCOMES: SESSION 1 PRINCIPLES OF SPINAL DEFORMITY Scoliosis: Aetiology & Prognostic Factors Describe the aetiology and prognostic factors associated with o idiopathic scoliosis
SCIENTIFIC PROGRAMME LEARNING OUTCOMES: SESSION 1 PRINCIPLES OF SPINAL DEFORMITY Scoliosis: Aetiology & Prognostic Factors Describe the aetiology and prognostic factors associated with o idiopathic scoliosis
May have excessive movement in the unfused segment to compensate. Flexion extension better preserved than lateral bend or rotation
 IV CONGENITAL SPINE KLIPPEL FLAIL SYNDROME Prevalence 0.60% Mainly around upper 3 vertebrae [75%] Commonest: C2 3 Lower Cervical spine fusion may be associated with syndromes: Fetal alcohol syndrome Goldenhar
IV CONGENITAL SPINE KLIPPEL FLAIL SYNDROME Prevalence 0.60% Mainly around upper 3 vertebrae [75%] Commonest: C2 3 Lower Cervical spine fusion may be associated with syndromes: Fetal alcohol syndrome Goldenhar
Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur
 Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Long segment composite split cord malformation with double bony spur Anand Sharma, Achal Sharma, R.S. Mittal SMS Medical College, Jaipur, India Abstract: A composite type of SCM is very rare and only a
Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity
 Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1703 1710 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1771-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity Yan Wang Lawrence G. Lenke Received:
Eur Spine J (2011) 20:1703 1710 DOI 10.1007/s00586-011-1771-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral column decancellation for the management of sharp angular spinal deformity Yan Wang Lawrence G. Lenke Received:
Complications in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery
 Complications in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery Jacob M. Buchowski, M.D., M.S. Professor of Orthopaedic and Neurological Surgery Director, Washington University Spine Fellowship Director, Center for Spinal
Complications in Adult Spinal Deformity Surgery Jacob M. Buchowski, M.D., M.S. Professor of Orthopaedic and Neurological Surgery Director, Washington University Spine Fellowship Director, Center for Spinal
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center:
 Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center: --Dose monitoring truly detect all spinal cord abnormalities and improve
Comparison of outcomes between patients using SSEP/TcMEP monitoring during PVCR procedure and no monitoring in a single center: --Dose monitoring truly detect all spinal cord abnormalities and improve
Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique
 Case Report Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique Shaishav Bhagat 1, Alexander Z. E. Durst
Case Report Simultaneous anterior vertebral column resection-distraction and posterior rod contouring for restoration of sagittal balance: report of a technique Shaishav Bhagat 1, Alexander Z. E. Durst
Sinan Kahraman, 1 Meriç Enercan, 1 Özkan Demirhan, 2 Türker Fengül, 3 Levent Dalar, 4 and Azmi HamzaoLlu Introduction
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 987578, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/987578 Case Report Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema, and Tracheal Tear in the Early Postoperative
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 987578, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/987578 Case Report Pneumomediastinum, Subcutaneous Emphysema, and Tracheal Tear in the Early Postoperative
Surgical treatment of congenital kyphosis in patients older than 10 years
 M.V. Mikhaylovskiy et al., 2016 Surgical treatment of congenital kyphosis in patients older than 10 years M.V. Mikhaylovskiy 1, V.V. Novikov 1, A.S. Vasyura 1, I.G. Udalova 1, T.N. Sadovaya 2 1 Novosibirsk
M.V. Mikhaylovskiy et al., 2016 Surgical treatment of congenital kyphosis in patients older than 10 years M.V. Mikhaylovskiy 1, V.V. Novikov 1, A.S. Vasyura 1, I.G. Udalova 1, T.N. Sadovaya 2 1 Novosibirsk
Spinal deformities, such as increased thoracic
 An Original Study Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Sagittal Imbalance: A New Radiographic Assessment Hossein Elgafy, MD, MCh, FRCS Ed, FRCSC, Rick Bransford, MD, Hassan Semaan, MD, and Theodore
An Original Study Clinical and Radiographic Evaluation of Sagittal Imbalance: A New Radiographic Assessment Hossein Elgafy, MD, MCh, FRCS Ed, FRCSC, Rick Bransford, MD, Hassan Semaan, MD, and Theodore
Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:137 143 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0400-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Bradley P. Jaquith
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:137 143 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0400-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Bradley P. Jaquith
Radiographic Outcome and Complications after Single-level Lumbar Extended Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Fixed Sagittal Malalignment:
 Radiographic Outcome and Complications after Single-level Lumbar Extended Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Fixed Sagittal Malalignment: Traditional A PSO Retrospective Analysis of 55 Adult Spinal Deformity
Radiographic Outcome and Complications after Single-level Lumbar Extended Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Fixed Sagittal Malalignment: Traditional A PSO Retrospective Analysis of 55 Adult Spinal Deformity
Diastematomyelia: A Case with Familial Aggregation of Neural Tube Defects
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4, 847 852 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.140 Diastematomyelia: A Case with Familial Aggregation of Neural Tube Defects Nuray Öksüz Kanbur 1, *, Pınar
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4, 847 852 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.140 Diastematomyelia: A Case with Familial Aggregation of Neural Tube Defects Nuray Öksüz Kanbur 1, *, Pınar
Computer-assisted Hemivertebra Resection. For Congenital Spinal Deformity
 Computer-assisted Hemivertebra Resection - 1 - Computer-assisted Hemivertebra Resection For Congenital Spinal Deformity Jun Takahashi, MD 1), Sohei Ebara, MD 2), Hiroyuki Hashidate, MD 1), Hiroki Hirabayashi,
Computer-assisted Hemivertebra Resection - 1 - Computer-assisted Hemivertebra Resection For Congenital Spinal Deformity Jun Takahashi, MD 1), Sohei Ebara, MD 2), Hiroyuki Hashidate, MD 1), Hiroki Hirabayashi,
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy. Case JB. Antonio Castellvi 5/19/2017
 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy John M. Small MD Florida Orthopedic Institute University South Florida Department Orthopedic Surgery Castellvi Spine May 11, 2017 Case JB 66 y/o male 74 235 lbs Retired police
ELY ASHKENAZI Israel Spine Center at Assuta Hospital Tel Aviv, Israel
 nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
nterior cervical decompression using the Hybrid Decompression Fixation technique, a combination of corpectomies and or discectomies, in the management of multilevel cervical myelopathy J ORTHOP TRUM SURG
The Kickstand Rod technique for correction of coronal imbalance in patients with adult spinal deformity: theory and technical considerations
 Case Report The Kickstand Rod technique for correction of coronal imbalance in patients with adult spinal deformity: theory and technical considerations Melvin C. Makhni 1, Meghan Cerpa 2, James D. Lin
Case Report The Kickstand Rod technique for correction of coronal imbalance in patients with adult spinal deformity: theory and technical considerations Melvin C. Makhni 1, Meghan Cerpa 2, James D. Lin
Analysis of instrumentation failures after three column osteotomies of the spine
 Kavadi et al. Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2017) 12:19 DOI 10.1186/s13013-017-0127-x RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of instrumentation failures after three column osteotomies of the spine Niranjan Kavadi
Kavadi et al. Scoliosis and Spinal Disorders (2017) 12:19 DOI 10.1186/s13013-017-0127-x RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of instrumentation failures after three column osteotomies of the spine Niranjan Kavadi
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):21748-21755 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0034462 Original Article Revision surgery outcomes of proximal junctional failure in surgically treated patients with posterior
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):21748-21755 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0034462 Original Article Revision surgery outcomes of proximal junctional failure in surgically treated patients with posterior
Idiopathic scoliosis Scoliosis Deformities I 06
 What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
What is Idiopathic scoliosis? 80-90% of all scolioses are idiopathic, the rest are neuromuscular or congenital scolioses with manifest primary diseases responsible for the scoliotic pathogenesis. This
Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 854151, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/854151 Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 854151, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/854151 Case Report Ipsilateral Hip Dysplasia in Patients with Sacral Hemiagenesis: A Report of Two Cases
A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal imbalance
 Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
Wang et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:538 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1902-9 CASE REPORT Open Access A rare case of osteoblastoma combined with severe scoliosis deformity, coronal and sagittal
Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium
 Original Study Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium Tatsuya Yasuda, Tomohiko Hasegawa, Yu Yamato, Sho Kobayashi, Daisuke Togawa, Shin
Original Study Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity with long spinal fusion from T9/T10 to the ilium Tatsuya Yasuda, Tomohiko Hasegawa, Yu Yamato, Sho Kobayashi, Daisuke Togawa, Shin
Congenital scoliosis : Management and future directions
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 147-160 CURRENT CONCEPTS REVIEW Congenital scoliosis : Management and future directions Sameer BATRA, Sashin AHUJA From Llandough Hospital and University Hospital of Wales,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 147-160 CURRENT CONCEPTS REVIEW Congenital scoliosis : Management and future directions Sameer BATRA, Sashin AHUJA From Llandough Hospital and University Hospital of Wales,
Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection for Spinal Deformity
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 4, pp 257~265, 2012 Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection / 257 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.4.257 Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection for Spinal
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 4, pp 257~265, 2012 Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection / 257 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.4.257 Complications of Posterior Vertebral Resection for Spinal
Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery.
 Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery. G. Saló, PhD, MD. Senior Consultant Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Ass. Prof. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Introduction The management
Management of Bone and Spinal Cord in Spinal Surgery. G. Saló, PhD, MD. Senior Consultant Spine Unit. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Ass. Prof. Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona. Introduction The management
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws
 Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Management of fractures of the pedicle after instrumentation with transpedicular screws A REPORT OF THREE PATIENTS F. Lattig, T. F. Fekete, D. Jeszenszky From the Schulthess Clinic, Zürich, Switzerland
Chiari I Malformation Associated with Syringomyelia and Scoliosis
 Chiari I Malformation Associated with Syringomyelia and Scoliosis A Twenty-Year Review of Surgical and Nonsurgical Treatment in a Pediatric Population James M. Eule, MD,* Mark A. Erickson, MD, Michael
Chiari I Malformation Associated with Syringomyelia and Scoliosis A Twenty-Year Review of Surgical and Nonsurgical Treatment in a Pediatric Population James M. Eule, MD,* Mark A. Erickson, MD, Michael
Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy. Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier**
 Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier** *free spine surgeons of Austria, **SMZ-East, Vienna Conservative therapy in clear cases of progression (2 hemi vertebrae, unilateral
Congenital deformity of the spine-therapy Werner Lack*, Georg Grabmeier** *free spine surgeons of Austria, **SMZ-East, Vienna Conservative therapy in clear cases of progression (2 hemi vertebrae, unilateral
Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management
 THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature.
 Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Kadir KOT L Tamer TUNÇKAYA Turgay B LGE Department of Neurosurgery,
Reduction of High-grade Spondylolisthesis Using a Transvertebral Surgical Approach in a Child. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Kadir KOT L Tamer TUNÇKAYA Turgay B LGE Department of Neurosurgery,
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), or peripheral neurofibromatosis,
 SPINE Volume 38, Number 18, pp 1595 1601 2013, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Does the Presence of Dystrophic Features in Patients With Type 1 Neurofibromatosis and Spinal Deformities Increase the
SPINE Volume 38, Number 18, pp 1595 1601 2013, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Does the Presence of Dystrophic Features in Patients With Type 1 Neurofibromatosis and Spinal Deformities Increase the
A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Profile and Surgical Outcome in Patients with Spinal Dysraphism at Tertiary Care Center
 Original Research Article A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Profile and Surgical Outcome in Patients with Spinal Dysraphism at Tertiary Care Center Premlal KV * Assistant Professor, Department of Neurosurgery,
Original Research Article A Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Profile and Surgical Outcome in Patients with Spinal Dysraphism at Tertiary Care Center Premlal KV * Assistant Professor, Department of Neurosurgery,
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION. DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon
 SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
SPLIT NOTOCHORD SYNDROME ASSOCIATION DR. Hasan Nugud Consultant Paediatric Surgeon CASE PRESENTATION :- New born baby, boy, referred to the paediatric surgical team at the age of 14 hours. Birth History
Modified Vertebral Column Resection Technique for Correcting Congenital Rigid Angular Kyphosis and its Effect on Functional Outcomes
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/21967.8506 Orthopaedics Section Original Article Modified Vertebral Column Resection Technique for Correcting Congenital Rigid Angular Kyphosis and its Effect on Functional Outcomes
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/21967.8506 Orthopaedics Section Original Article Modified Vertebral Column Resection Technique for Correcting Congenital Rigid Angular Kyphosis and its Effect on Functional Outcomes
What is an osteotomy? Bony resection designed to increase flexibility of spine or alteration of alignment
 Spinal osteotomies Nicholas D. Fletcher, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Director of Spinal Quality/Outcomes Emory University Department of Orthopedics Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Atlanta, GA
Spinal osteotomies Nicholas D. Fletcher, MD Assistant Professor of Orthopedics Director of Spinal Quality/Outcomes Emory University Department of Orthopedics Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Atlanta, GA
AOSpine Advances Symposium Spinal Deformity
 AOSpine Advances Symposium Spinal Deformity December 03-04, 2010 Istanbul, Türkiye Proper radiographic evaluation, parameters, clinical relevance and importance Dr. Alpaslan Şenköylü Session: Sagittal
AOSpine Advances Symposium Spinal Deformity December 03-04, 2010 Istanbul, Türkiye Proper radiographic evaluation, parameters, clinical relevance and importance Dr. Alpaslan Şenköylü Session: Sagittal
Case report: Imaging findings in a butterfly vertebra
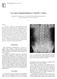 Acta Neurol. Belg., 2011, 111, 344-348 Case report: Imaging findings in a butterfly vertebra Cedric BOULET, Ann SCHIETTECATTE, Johan DE MEY and Michel DE MAESENEER Department of Radiology, UZ Brussel,
Acta Neurol. Belg., 2011, 111, 344-348 Case report: Imaging findings in a butterfly vertebra Cedric BOULET, Ann SCHIETTECATTE, Johan DE MEY and Michel DE MAESENEER Department of Radiology, UZ Brussel,
Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction
 Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction S. Samuel Bederman, MD PhD FRCSC Department of Orthopaedic Surgery California Orthopaedic Association, Indian Wells, CA April 25, 2015 2 3 4 Adult
Adult Spinal Deformity: Principles of Surgical Correction S. Samuel Bederman, MD PhD FRCSC Department of Orthopaedic Surgery California Orthopaedic Association, Indian Wells, CA April 25, 2015 2 3 4 Adult
Spondylolysis. Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down.
 Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
Spondylolysis Lysis (Greek λύσις, lýsis from lýein "to separate") refers to the breaking down. Thomas J Kishen Spine Surgeon Sparsh Hospital for Advanced Surgeries Bangalore Spondylolysis Defect in the
Purpose: To discuss the fatty filum terminale which is incidentally demonstrated on MRI concerning the causes of TCS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 T Iizuka Citation T Iizuka.. The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery. 2006 Volume 3 Number 1. Abstract Background: Fatty filum terminale
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 3 Number 1 T Iizuka Citation T Iizuka.. The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery. 2006 Volume 3 Number 1. Abstract Background: Fatty filum terminale
Corresponding: The 2 nd Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming, Yunnan Province, P.R.
 Incidence and Risk Factors for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis(PJK)Following Posterior Vertebral Column Resection(PVCR)for Patients with Severe and Rigid Spinal Deformities-Minimum 2-Year Follow-up The Medical
Incidence and Risk Factors for Proximal Junctional Kyphosis(PJK)Following Posterior Vertebral Column Resection(PVCR)for Patients with Severe and Rigid Spinal Deformities-Minimum 2-Year Follow-up The Medical
M ASTER S T ECHNIQUES: VCR & GROWING R ODS
 M ASTER S T ECHNIQUES: VCR & GROWING R ODS LAWRENCE G. LENKE, MD The Jerome J. Gilden Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Professor of Neurological Surgery Chief, Spinal Surgery Co-Director,
M ASTER S T ECHNIQUES: VCR & GROWING R ODS LAWRENCE G. LENKE, MD The Jerome J. Gilden Distinguished Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Professor of Neurological Surgery Chief, Spinal Surgery Co-Director,
Prevalance of neural axis abnormalities in patients with infantile idiopathic scoliosis
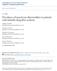 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 12-1-2002 Prevalance of neural axis abnormalities in patients with infantile idiopathic scoliosis Matthew B. Dobbs
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 12-1-2002 Prevalance of neural axis abnormalities in patients with infantile idiopathic scoliosis Matthew B. Dobbs
Cervicothoracic Congenital Scoliosis: Treatment of shoulder balance and head tilt
 Cervicothoracic Congenital Scoliosis: Treatment of shoulder balance and head tilt David L. Skaggs, MD, MMM Professor and Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Southern California Children s Hospital
Cervicothoracic Congenital Scoliosis: Treatment of shoulder balance and head tilt David L. Skaggs, MD, MMM Professor and Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Southern California Children s Hospital
vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in
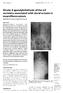 e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
Dorsal resection of a thoracic hemivertebra in a 4-year-old boy with endochondral gigantism. A case report
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 699-705 CASE REPORT Dorsal resection of a thoracic hemivertebra in a 4-year-old boy with endochondral gigantism. A case report Kourosh ZARGHOOni, Rolf SOBOTTKE, Heinrich SCHMiDT,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 699-705 CASE REPORT Dorsal resection of a thoracic hemivertebra in a 4-year-old boy with endochondral gigantism. A case report Kourosh ZARGHOOni, Rolf SOBOTTKE, Heinrich SCHMiDT,
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments
 Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
Spinal Deformity Pathologies and Treatments Scoliosis Spinal Deformity 3-dimensional deformity affecting all 3 planes Can be difficult to visualize with 2-dimensional radiographs Kyphosis Deformity affecting
Long lumbar instrumented fusions have been described
 SPINE Volume 37, Number 16, pp 1407 1414 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Upper Instrumented Vertebral Fractures in Long Lumbar Fusions What Are the Associated Risk Factors? Stephen J. Lewis,
SPINE Volume 37, Number 16, pp 1407 1414 2012, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins SURGERY Upper Instrumented Vertebral Fractures in Long Lumbar Fusions What Are the Associated Risk Factors? Stephen J. Lewis,
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table
 35 35 40 The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table Authors Justin Bundy, Tommy Hernandez, Haitao Zhou, Norman Chutkan Institution Orthopaedic Department, Medical
35 35 40 The effect of body mass index on lumbar lordosis on the Mizuho OSI Jackson spinal table Authors Justin Bundy, Tommy Hernandez, Haitao Zhou, Norman Chutkan Institution Orthopaedic Department, Medical
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
MRI of chronic spinal cord injury
 The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Morbidity and radiographic outcomes of severe scoliosis of 90 or more: a comparison of hybrid with total pedicle screw instrumentation
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:345 352 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0604-1 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Morbidity and radiographic outcomes of severe scoliosis of 90 or more: a comparison of hybrid with total pedicle
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:345 352 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0604-1 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Morbidity and radiographic outcomes of severe scoliosis of 90 or more: a comparison of hybrid with total pedicle
Surgical Management of Congenital Cervical Kyphosis
 n Feature Article Surgical Management of Congenital Cervical Kyphosis Zhimin He, MD; Yang Liu, MD; Feng Xue, MD; Haijun Xiao, MD; Wen Yuan, MD; Deyu Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
n Feature Article Surgical Management of Congenital Cervical Kyphosis Zhimin He, MD; Yang Liu, MD; Feng Xue, MD; Haijun Xiao, MD; Wen Yuan, MD; Deyu Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
King II Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (Lenke B and C): Prediction of coronal decompensation
 Original Article King II Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (Lenke B and C): Prediction of coronal decompensation Osmar Avanzi, Elcio Landim, Robert Meves, Maria Fernanda Silber Caffaro, Ricardo Umeta, Jose
Original Article King II Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (Lenke B and C): Prediction of coronal decompensation Osmar Avanzi, Elcio Landim, Robert Meves, Maria Fernanda Silber Caffaro, Ricardo Umeta, Jose
Prevention and management of iatrogenic flatback deformity
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2004 Prevention and management of iatrogenic flatback deformity Benjamin K. Potter Walter Reed Army Medical
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2004 Prevention and management of iatrogenic flatback deformity Benjamin K. Potter Walter Reed Army Medical
L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD
 L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD Wiltse, Newman and Macnab Classification Clin Orthop 1976;117:23-29 Type I: Congenital spondylolisthesis
L5-S1 Spondylolysis/listhesis in children & adolescents: When is surgery indicated? Hubert Labelle, MD Wiltse, Newman and Macnab Classification Clin Orthop 1976;117:23-29 Type I: Congenital spondylolisthesis
A single posterior approach for vertebral column resection in adults with severe rigid kyphosis
 Original Research Medical Journal of Islamic Republic of Iran, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov. 2011, pp. 111-118 A single posterior approach for vertebral column resection in adults with severe rigid kyphosis Seyed
Original Research Medical Journal of Islamic Republic of Iran, Vol. 25, No. 3, Nov. 2011, pp. 111-118 A single posterior approach for vertebral column resection in adults with severe rigid kyphosis Seyed
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 TWO RARE CASES OF DIASTEMATOMYELIA MUTHURAMAN P Department of Neuro Surgery, THANJAVUR MEDICAL COLLEGE Abstract
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialties ISSN 2455-2860 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 TWO RARE CASES OF DIASTEMATOMYELIA MUTHURAMAN P Department of Neuro Surgery, THANJAVUR MEDICAL COLLEGE Abstract
As edited by Dr. Oheneba Boachie-Adjei, Dr. Matthew Cunningham, Dr. John Kostuik, Dr. Raymund Woo and the Complex Spine Study Group et al
 As edited by Dr. Oheneba Boachie-Adjei, Dr. Matthew Cunningham, Dr. John Kostuik, Dr. Raymund Woo and the Complex Spine Study Group et al RANGE Spinal System A fusion of DENALI and MESA, offering a complete
As edited by Dr. Oheneba Boachie-Adjei, Dr. Matthew Cunningham, Dr. John Kostuik, Dr. Raymund Woo and the Complex Spine Study Group et al RANGE Spinal System A fusion of DENALI and MESA, offering a complete
Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy
 REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy Yukihiro Matsuyama Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu
REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Surgical treatment for adult spinal deformity: Conceptual approach and surgical strategy Yukihiro Matsuyama Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu
There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid Construct in the Correction of Lenke Type-1 Curves
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
Posterior spinal fusion in patients with Ehlers Danlos syndrome: a report of six cases
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:131 136 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0393-3 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Posterior spinal fusion in patients with Ehlers Danlos syndrome: a report of six cases Brien Michael Rabenhorst Sumeet
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:131 136 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0393-3 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Posterior spinal fusion in patients with Ehlers Danlos syndrome: a report of six cases Brien Michael Rabenhorst Sumeet
Implementation of Pre-operative Planning:
 Implementation of Pre-operative Planning: 1-Year Results Using Patient-Specific UNiD Rods in Adult Deformity C.J. Kleck, MD 06/16/2017 Pre-operative Planning In the fields of observation chance favors
Implementation of Pre-operative Planning: 1-Year Results Using Patient-Specific UNiD Rods in Adult Deformity C.J. Kleck, MD 06/16/2017 Pre-operative Planning In the fields of observation chance favors
Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note Mehmet Nuri Erdem, Anas
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXII Number 1 2018 January-March Article Surgical treatment of preschool childhood spinal thoracic tuberculosis: two case reports and technical note Mehmet Nuri Erdem, Anas
18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD. July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA
 18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA SCOLIOSIS AND ITS TREATMENT Steven M. Reich, MD Assistant Clinical
18th International Scientific Meeting of the VCFS Educational Foundation Steven M. Reich, MD July 15-17, 2011 New Brunswick, New Jersey USA SCOLIOSIS AND ITS TREATMENT Steven M. Reich, MD Assistant Clinical
