Epidemiological characteristics of varicella from 2000 to 2008 and the impact of nationwide immunization in Taiwan
|
|
|
- Erica McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Epidemiological characteristics of varicella from 2 to 28 and the impact of nationwide immunization in Taiwan Luan-Yin Chang *, Li-Min Huang, I-Shou Chang 2 and Fang-Yu Tsai 2 Abstract Background: Varicella has an important impact on public health. Starting in 2 in Taiwan, nationwide free varicella vaccinations were given to -year-old children. Methods: Our study investigated the epidemiological characteristics of varicella from 2 to 28, and assessed the change of varicella epidemiology after the mass varicella immunization. ICD-9-CM codes related to varicella or chickenpox (52, 52., 52.2, 52., 52.8, 52.9) were analyzed for all young people under 2 years of age through the National Health Insurance database of Taiwan from 2 to 28. Results: s of varicella or chickenpox significantly declined after the nationwide immunization in 2. Winter, particularly January, was the epidemic season of varicella. We found a significant post-vaccination decrease in incidence among preschool children, especially 3 to 6 year-old children the peak incidence was 66 per thousand for and 5 year-old children before the nationwide immunization (2 to 23), and the peak incidence was 23 per thousand for 6 year-old children in 28 (p <.). Varicella-related hospitalization also significantly decreased in children younger than 6 years after the nationwide immunization. Conclusion: The varicella annual incidence and varicella-related hospitalization markedly declined in preschool children after nationwide varicella immunization in 2. Keywords: varicella, chickenpox, epidemiology, incidence, vaccine, prevention Background Varicella is the primary disease caused by the varicellazoster virus. It is a common and highly contagious disease and has a significant health impact on children. Although the clinical course of varicella is usually mild and self-limiting, varicella does cause complications and mortality resulting in financial expense [-3]. Chickenpox or varicella now has been considered one of the most common vaccine-preventable diseases in many countries [-]. In Taiwan, some areas including Taipei City, Taichung City and Taichung County gave the public free varicella vaccinations for -2 year-old children before 2. Taipei City started the free varicella vaccination from 998 and * Correspondence: lychang@ntu.edu.tw Department of Pediatrics, National Taiwan University Hospital, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article Taichung City and Taichung County from 999. Other areas did not provide free varicella vaccination, but people could receive varicella vaccination at their own expense before 2. Since 2, free mass varicella immunization has been given to all one year-old children throughout Taiwan. Since the implementation of National Health Insurance (NHI) in 995, there has been a healthcare database in Taiwan. Taiwan has a population of 22.9 million people and the land area of 3688 Km 2. Its population density is 633/Km 2. Taiwan s NHI covered most of the health care costs for 98% of its population in 26 [8]; the remaining 2% of it population are living in the foreign countries or in families with monthly household incomes less than US dollars. Taiwan s NHI database includes health care data collected from over 95% of the hospitals in Taiwan for more than 96% of the population receiving health care. We evaluated the disease burden and epidemiological 2 Chang et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Page 2 of characteristics of varicella by using the NHI database to find out the age-specific incidences, seasonal distribution and varicella-related hospitalization from 2 to 28 the period covering pre- and post-public free vaccination so we could compare the epidemiological characteristics of varicella before and after the mass immunization. Methods Vaccination The administration of a live attenuated varicella vaccine was licensed in Taiwan in 99. Both Merck and GlaxoSmithKline, pharmaceutical companies, provided the varicella vaccines in Taiwan. In 2 the varicella vaccine was incorporated into Taiwan s national immunization program, and all -year-old children could receive the varicella vaccine for free. The varicella coverage rate for -year-old children was 9% for the 23 birth cohort, 95% for the 2 cohort, and 9% for the 25, 26, and 2 birth cohorts according to Taiwan s National Immunization Information System which was developed in the early 99s [9]. When a child received a vaccine, his or her vaccination would not only be recorded in a child s vaccination handbook but would also be reported to the National Immunization Information System. Data collection Taiwan s National Health Insurance (NHI) covered most of the health care costs for 98% of its population. Taiwan s NHI database includes health care data collected from over 95% of the hospitals in Taiwan for more than 98% of the population receiving health care. From this database, hospitalization and outpatient healthcare records were collected from 2 to 28, and International Classifications of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes related to varicella or chickenpox were analyzed for all the population. The age-specific annual incidence and hospitalization rate were calculated. For calculating the annual populationbased incidence, the annual incidence was calculated by dividing the number of varicella-related diseases by the population, which was obtained from Department of Statistics, Ministry of the Interior, Taiwan from 2 to 28 []. Definitions ICD-9-CM codes for chickenpox or varicella include the following: 52 chickenpox; 52. post-varicella encephalitis, post-chickenpox encephalitis; 52. varicella (hemorrhagic) pneumonitis; 52. with other specified complications; 52.8 with unspecified complication; 52.9 varicella without mention of complication. For complications, we define varicella or chickenpox patients to have complications in cases where the patients had both ICD-9-CM codes for varicella or chickenpox (52 and the other related codes) and also ICD-9-CM codes for varicella-related complications which include the following: central nervous system including 32 meningitis, 322 cerebellitis, 323 encephalitis, 38 encephalopathy, 35 facial palsy, 33.8 Reye s syndrome, 8.3 febrile convulsion/seizure; skin and soft tissue including cellulites and abscess, 35 erysipela, 28 pyomyositis and necrotizing fasciitis, 33 & 36. blepharitis, 3 & scarlet fever and streptococcal or staphylococcal infection; skeletal system including arthritis, 3-33 osteomyelitis; lower respiratory tract infection including 8-8 pneumonia, 5-59 pneumonitis, 66 & 9 bronchitis; hematological system- 28 thrombocytopenia, 283 & 285 anemia, 288 neutropenia; 38 & 9 & for sepsis and bacteremia; - for other bacterial infection; 22 cardiomyopathy, 25 myocarditis;.5 &.9 & 53 for hepatitis. Statistics In univariate analysis, categorical variables were compared with chi-square or Fisher s exact test; continuous variables were analyzed with Student s t test. The difference of annual incidence among various age groups, the difference of annual incidences in different years, and the difference in seasonal distribution were measured with appropriate c 2 test. A p value of <.5 was considered to be statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed with SAS software, version 9.. Results Number of cases before and after the mass immunization The monthly distribution of case numbers from 2 to 28 is demonstrated in Figure. s markedly declined after the mass immunization in 2, the highest monthly number was 236 in January 2, and the lowest was 26 in September 28. The peak of varicella usually occurred during winter, especially in January. distribution Overall age-specific case numbers and the cumulative percentage of varicella in children from 2 to 28 are shown in Figure 2, those of 2 in Figure 3, and those of 28 in Figure. Children younger than years old represented 89% of all the cases and the peak age was 3 to 6 years from 2 to 28 (Figure 2). However, the age distribution changed significantly after the mass immunization (p <.): 3% of varicella cases were children less than 6 years of age in 2 (before the mass immunization, Figure 3) but only 2% of the cases were children younger than 6 years of age in 28 ( years after the mass immunization, Figure ). In comparison with age-specific case numbers of 2 (Figure 3), those
3 Page 3 of Case Number Mass immunization Figure Monthly distribution of varicella case number from 2 to 28. of 28 were significantly lower (Figure ) (p <.). In 28, school children had more varicella cases than the kindergarteners. -specific annual incidence Figure 5 demonstrates the age-specific annual incidence of varicella before and after the nationwide immunization. In 2 to 23 (before the nationwide immunization), the peak incidence was in and 5-year-old children with annual incidence of 66 per thousand while in 28, the peak incidence occurred in 6-year-old children with annual incidence of 23 per thousand (p <.). After the nationwide immunization in 2, the annual incidence significantly decreased among children younger than 6 % 9% % % 6% 5% % 3% 2% % Figure 2 -specific case number and cumulative percentage of varicella in children from 2 to 28. %
4 Page of 3 % % 8% % 6% 5% % 3% Cumulative percenatge 5 2% % % Figure 3 -specific case number and cumulative percentage of varicella in children in 2, before the nationwide immunization. 3 % Case Number Cumulative Percentage 9% 8% % 6% 5% % 3% 2% % % Figure -specific case number and cumulative percentage of varicella in children in 28, years after the nationwide immunization.
5 Page 5 of Annual incidence per thousand Figure 5 -specific annual incidence of varicella before (2-23) and after the nationwide immunization (2, 25, 26, 2 and 28). years of age. In 28, the annual incidence (6.8 per thousand) of infants who could not receive the varicella vaccine was even higher than that (3.2 to 5.9 per thousand) of to -year-old children. Children beyond years had similar annual incidence before and after the mass immunization. -specific varicella-related hospitalization incidence The proportion of the number of varicella-related hospitalization to the number of overall varicella cases was the highest in infants and declined with age in children. Figure 6 shows that the annual incidence of varicellarelated hospitalization was the highest in infants. In comparison with the annual incidence of 2 to 23 (before the nationwide immunization), the annual incidence of hospitalization significantly declined in children younger than 6 years of age from 2 to 28 (p <.). From 2 to 28, the annual incidence of preschool children decreased obviously with the year. Complications Among the 2829 hospitalized cases, 56 (2.5%) had central nervous system complications, 22 (2.%) had skin or soft tissue infections, (2.%) had lower respiratory tract infections, 93 (2.26%) had hematological complications, 28 (.29%) had septicemia or bacteremia, and 2 (3.3%) had hepatitis. Twelve children died and Table lists the demography and complications of the 2 fatal varicella cases. Five of them had underlying diseases including 2 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, with severe combined immunodeficiency, with enzymopathy, and with pulmonary vascular anomaly. Most of them had complications of septicemia, skin or soft tissue infections, or encephalitis, and had Reye syndrome. Discussion Nationwide varicella immunization has resulted in a marked reduction of varicella incidence and varicellarelated hospitalization in children younger than 6 years of age in Taiwan. The impact of mass varicella immunization has so far made it possible for most preschool children to be free of varicella and varicella-related hospitalization in Taiwan. However, children beyond years of age had similar annual incidence before and after the mass immunization. As Figure 3 shows the age distribution before the mass immunization in 2, the peak age of varicella was 3 to 6 years, which was also the age group of kindergarteners. Kindergarteners might have more exposure to varicella and also their hand hygiene and sanitation levels are generally not as high as adults or older school children s, who may in turn lead to more varicella cases in kindergarteners without mass immunization (Figure 3). However, after the mass immunization, we observed more varicella cases in the school children than those in 3 to -year-old kindergarteners (Figure ), who were supposed to have received the free varicella vaccine at year of age. Therefore, mass immunization has changed the age distribution of varicella cases significantly and the peak age has subsequently moved to older children without previous immunization.
6 Page 6 of Annual incidence per thousand Figure 6 -specific annual incidence of varicella-related hospitalization before (2-23) and after the nationwide immunization (2, 25, 26, 2 and 28). Similar results were also reported by Lian et al who found that the greatest decrease in varicella incidence occurred in children aged below 6 and the incidence of varicella shifted to older age groups after implementation of the one-dose varicella vaccination policy []. Lian et al also found that the incidence in early launch areas was significantly lower than that in the other areas in Taiwan []. Our study additionally reported the seasonality, varicellarelated hospitalization and complications from 2 to 28 in Taiwan. Moreover, our data in this study is nationwide rather than the selected sample size like that of Lian et al s study. We found that the annual incidence of children beyond years of age was similar before and after mass immunization. It s because most of the school children were not allowed to receive the free varicella vaccine. Thus, the varicella incidence of the school children did not change significantly after the mass immunization in this study. We suppose that the annual incidence of school children may decrease several years later if the immunized children grow up to be 6 to 2 years old. However, we have to follow up on the impact of mass immunization on school children to prove the above assumption several years later. Table Demography and complications of 2 fatal varicella cases Year Sex Underlying disease Complications 2 F Nil Encephalitis, septic shock 2 M Unspecified Enzymopathy Pseudomonas septicemia 2 F Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Septicemia 2 5 F Nil Encephalitis, septicemia 2 6 F Nil Sudden death 22 3 F Nil Respiratory failure 22 3 M Acute lymphoblastic leukemia Not mentioned 23 2 F Nil Skin/soft tissue infections, streptococcal septicemia 2 6 M Nil Skin/soft tissue infections, pneumonia, septicemia 25 F Nil Reye s syndrome 26 M Severe combined immunodeficiency Acute and subacute hepatic necrosis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage 2 M Pulmonary vascular anomaly Hemoptysis, acute respiratory failure
7 Page of The infants had the highest annual incidence of varicella-related hospitalization both before and after the mass immunization (Figure 6). Infants cannot receive the varicella vaccine and they have a higher chance of severe varicella and more complications [2], so their varicella-related hospitalization was significantly higher than the other children. There were 2 cases of fatality, of which 5 of them had underlying diseases. Children with underlying diseases such as acute leukemia are more susceptible to getting severe varicella with complications and have a significantly higher mortality rate [2]. Therefore, the varicella vaccine may be administered to children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are in remission, or, high-titer anti-varicella-zoster virus immune globulin as post-exposure prophylaxis is recommended for immunocompromised children and newborns that are exposed maternally to varicella [2]. Currently, the varicella vaccine program consists of a single-dose vaccination in Taiwan, as it is in Canada, Korea and Australia [3]. However, both varicella outbreaks and breakthrough infections have occurred after the single-dose varicella vaccine program was initiated []. These might be related to a loss of immunity or to primary vaccine failure. Although the reports are limited, varicella vaccine effectiveness may be higher when two doses are administered than when a single-dose is administered. In 26, the United States changed its immunization policy by stipulating that 2 doses be administered, once at year of age and another administered between the ages of 3 and years old [5]. In Taiwan, boosters in -6 year-old children to reduce the breakthrough infection or amend the primary vaccine failure may be considered if further epidemiology reveals frequent outbreaks or breakthrough infections in kindergarteners. The major limitation of this study is that we could not verify the diagnoses because we could just analyze the NHI database rather than detailed medical charts. However, at the very least the nationwide database can let us outline the comprehensive picture of varicella epidemiology in Taiwan and sketch the impact of nationwide immunization. Conclusions In conclusion, nationwide varicella immunization significantly decreased the varicella annual incidence and varicella-related hospitalization in preschool children in Taiwan. The impact of the varicella vaccine on schoolchildren may be followed up on several years later. Acknowledgements and Funding This study is based in part on data from the National Health Insurance Research Database provided by the Bureau of National Health Insurance, Department of Health and managed by National Health Research Institutes. The interpretation and conclusions contained herein do not represent those of the Bureau of National Health Insurance, Department of Health or National Health Research Institutes. This research was supported by the grants, NSC -232-B-2-2 from National Science Council and DOH 98-CD- from Centers for Disease Control, Taiwan. The funding institutes did not have any role in study design, data collection/analysis, the writing of the manuscript and the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Author details Department of Pediatrics, National Taiwan University Hospital, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan. 2 National Institute of Cancer Research and Division of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, National Health Research Institute, Miaoli, Taiwan. Authors contributions LYC, LMH and ISC designed the study. LYC and FYT analyzed the data. LYC wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Received: 9 June 2 Accepted: 6 December 2 Published: 6 December 2 References. Carapetis JR, Russell DM, Curtis N: The burden and cost of hospitalised varicella and zoster in Australian children. Vaccine 2, 23: Poulsen A, Cabral F, Nielsen J, Roth A, Lisse I, Aaby P: Growth, morbidity and mortality after chickenpox infection in young children in Guinea- Bissau. J Infect 25, 5: Rivest P, Bedard L, Valiquette L, Mills E, Lebel MH, Lavoie G, et al: Severe complications associated with varicella: Province of Quebec, April 99 to March 996. Can J Infect Dis 2, 2:2-6.. Patrick D: Prevention strategies: experience of varicella vaccination programmes. Herpes 2, (Suppl 2): Asano Y: Varicella vaccine: the Japanese experience. J Infect Dis 996, (Suppl 3):S Macartney KK, Beutels P, McIntyre P, Burgess MA: Varicella vaccination in Australia. J Paediatr Child Health 25, : Getsios D, Caro JJ, Caro G, De Wals P, Law BJ, Robert Y, et al: Instituting a routine varicella vaccination program in Canada: an economic evaluation. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22, 2: Burea of National Health Insurance, Department of Health, Executive Yuan, Taiwan ROC: Statistical annual reports., (Accessed at tw/statistic/%a5%fe%a5%c%b%b%abo/95.htm). 9. Taiwan Center for Disease Control, Department of Health, Executive Yuan, Taiwan: National Immunization Information System (NIIS).[ gov.tw/public/data/ doc].. Department of Statistics MotI, Taiwan: Population by Single Year of. Department of Statistics, Taiwan;[ Lian IB, Chien YZ, Hsu PS, Chao DY: The changing epidemiology of varicella incidence after implementation of the one-dose varicella vaccination policy. Vaccine 2, 29(): Myers MG, Seward JF, LaRussa FS: Varicella-zoster virus. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, Heininger U, Seward JF: Varicella. Lancet 26, 368: Galil K, Lee B, Strine T, et al: Outbreak of varicella at a day-care center despite vaccination. N Engl J Med 22, 3(2): Marin M, Meissner HC, Seward JF: Varicella prevention in the United States: a review of successes and challenges. Pediatrics 28, 22:e-5. Pre-publication history The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: /prepub doi:.86/ Cite this article as: Chang et al.: Epidemiological characteristics of varicella from 2 to 28 and the impact of nationwide immunization in Taiwan. BMC Infectious Diseases 2 :352.
Complications of varicella infection in children in southern Taiwan
 Varicella J Microbiol infection Immunol in children Infect 2006;39:402-407 Complications of varicella infection in children in southern Taiwan Chia-Yu Chi 1,2, Shih-Min Wang 3, Hui-Chen Lin 2, Ching-Chuan
Varicella J Microbiol infection Immunol in children Infect 2006;39:402-407 Complications of varicella infection in children in southern Taiwan Chia-Yu Chi 1,2, Shih-Min Wang 3, Hui-Chen Lin 2, Ching-Chuan
Varicella Vaccination in Australia and New Zealand
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Varicella Vaccination in Australia and New Zealand Kristine K. Macartney 1 and Margaret A. Burgess 2 1 National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance, The Children s Hospital
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Varicella Vaccination in Australia and New Zealand Kristine K. Macartney 1 and Margaret A. Burgess 2 1 National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance, The Children s Hospital
Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi
 1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
1 Prof Dr Najlaa Fawzi is an acute highly infectious disease, characterized by vesicular rash, mild fever and mild constitutional symptoms. is a local manifestation of reactivation of latent varicella
Decline in Mortality Due to Varicella after Implementation of Varicella Vaccination in the United States
 The new england journal of medicine original article Decline in Mortality Due to Varicella after Implementation of Varicella Vaccination in the United States Huong Q. Nguyen, M.P.H., Aisha O. Jumaan, Ph.D.,
The new england journal of medicine original article Decline in Mortality Due to Varicella after Implementation of Varicella Vaccination in the United States Huong Q. Nguyen, M.P.H., Aisha O. Jumaan, Ph.D.,
Group B Streptococcus
 Group B Streptococcus (Invasive Disease) Infants Younger than 90 Days Old DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail
Group B Streptococcus (Invasive Disease) Infants Younger than 90 Days Old DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail
2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine. Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC
 2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC National Influenza Vaccine Summit April 19, 2007 Recommendation Changes for Influenza Vaccination:
2007 ACIP Recommendations for Influenza Vaccine Anthony Fiore, MD, MPH Influenza Division, NCIRD, CDC National Influenza Vaccine Summit April 19, 2007 Recommendation Changes for Influenza Vaccination:
Progress in varicella vaccine research
 40 1, 1, 1, 2 1., 230032; 2., 10032 : - ( VZV) VZV 1995,, Oka,,, VZV : - ; Oka ; Progress in varicella vaccine research GAN Lin 1, WANG Ming-Li 1, Jason Chen 1, 2 1. Department of Microbiology, Anhui Medical
40 1, 1, 1, 2 1., 230032; 2., 10032 : - ( VZV) VZV 1995,, Oka,,, VZV : - ; Oka ; Progress in varicella vaccine research GAN Lin 1, WANG Ming-Li 1, Jason Chen 1, 2 1. Department of Microbiology, Anhui Medical
Routine Adult Immunization: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement, updated 2002
 Routine Adult Immunization: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement, updated 2002 Ann R. Fingar, MD, MPH, and Byron J. Francis, MD, MPH Burden of suffering Vaccines are available
Routine Adult Immunization: American College of Preventive Medicine Practice Policy Statement, updated 2002 Ann R. Fingar, MD, MPH, and Byron J. Francis, MD, MPH Burden of suffering Vaccines are available
Current Incident Status of Vaccine-Preventable Bacterial and Viral Infectious Diseases in Japan
 Research and Reviews Current Incident Status of Vaccine-Preventable Bacterial and Viral Infectious Diseases in Japan JMAJ 53(2): 106 110, 2010 Hajime KAMIYA,* 1 Tomoe SHIMADA,* 2 Nobuhiko OKABE* 3 Abstract
Research and Reviews Current Incident Status of Vaccine-Preventable Bacterial and Viral Infectious Diseases in Japan JMAJ 53(2): 106 110, 2010 Hajime KAMIYA,* 1 Tomoe SHIMADA,* 2 Nobuhiko OKABE* 3 Abstract
Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection
 Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection Lyn Finelli, DrPH, MS Lead, Influenza Surveillance and Outbreak Response Epidemiology and Prevention Branch Influenza Division
Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection Lyn Finelli, DrPH, MS Lead, Influenza Surveillance and Outbreak Response Epidemiology and Prevention Branch Influenza Division
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES EPIDEMIOLOGIC REPORT
 NEW BRUNSWICK COMMUNICABLE DISEASES EPIDEMIOLOGIC REPORT 2004 COMMUNICABLE DISEASES EPIDEMIOLOGIC REPORT 2004 2 The New Brunswick Communicable Diseases Epidemiologic Report is published by Public Health
NEW BRUNSWICK COMMUNICABLE DISEASES EPIDEMIOLOGIC REPORT 2004 COMMUNICABLE DISEASES EPIDEMIOLOGIC REPORT 2004 2 The New Brunswick Communicable Diseases Epidemiologic Report is published by Public Health
Hospitalization due to varicella in the Netherlands
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hospitalization due to varicella in the etherlands Alies van Lier 1*, icoline AT van der Maas 1, Gerwin D Rodenburg 2, Elisabeth AM Sanders 2 and Hester E de Melker 1 Abstract
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hospitalization due to varicella in the etherlands Alies van Lier 1*, icoline AT van der Maas 1, Gerwin D Rodenburg 2, Elisabeth AM Sanders 2 and Hester E de Melker 1 Abstract
Influenza in the pediatric population
 Influenza in the pediatric population Annual attack rates 10%-40% in children Hospitalization Increased risk in children
Influenza in the pediatric population Annual attack rates 10%-40% in children Hospitalization Increased risk in children
Persistence of Immunity to Live Attenuated Varicella Vaccine in Healthy Adults
 MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunity to Live Attenuated Varicella Vaccine in Healthy Adults Krow Ampofo, 1 Lisa Saiman, 1,2 Philip LaRussa, 1 Sharon Steinberg, 1 Paula Annunziato, 1 and Anne Gershon 1
MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunity to Live Attenuated Varicella Vaccine in Healthy Adults Krow Ampofo, 1 Lisa Saiman, 1,2 Philip LaRussa, 1 Sharon Steinberg, 1 Paula Annunziato, 1 and Anne Gershon 1
Florida Department of Health - Polk County Weekly Morbidity Report - Confirmed and Probable cases * Week #9 (through March 3, 2018)
 Florida Department of Health - Polk County Weekly Morbidity Report - Confirmed and Probable cases * Week #9 (through March 3, 2018) Weekly Cumulative (YTD) Annual Totals ICD 9 code Disease Category 2018
Florida Department of Health - Polk County Weekly Morbidity Report - Confirmed and Probable cases * Week #9 (through March 3, 2018) Weekly Cumulative (YTD) Annual Totals ICD 9 code Disease Category 2018
Varicella among Adults: Data from an Active Surveillance Project,
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Varicella among Adults: Data from an Active Surveillance Project, 1995 2005 Mona Marin, 1 Tureka L. Watson, 1 Sandra S. Chaves, 1 Rachel Civen, 2 Barbara M. Watson, 3 John X. Zhang,
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Varicella among Adults: Data from an Active Surveillance Project, 1995 2005 Mona Marin, 1 Tureka L. Watson, 1 Sandra S. Chaves, 1 Rachel Civen, 2 Barbara M. Watson, 3 John X. Zhang,
HEPATITIS B VACCINATION IN TAIWAN AND THE INCIDENCE OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA IN CHILDREN
 UNIVERSAL HEPATITIS B VACCINATION IN TAIWAN AND THE INCIDENCE OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA IN CHILDREN MEI-HWEI CHANG, M.D., CHIEN-JEN CHEN, SC.D., MEI-SHU LAI, M.D., HSU-MEI HSU, M.P.H., TZEE-CHUNG WU,
UNIVERSAL HEPATITIS B VACCINATION IN TAIWAN AND THE INCIDENCE OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA IN CHILDREN MEI-HWEI CHANG, M.D., CHIEN-JEN CHEN, SC.D., MEI-SHU LAI, M.D., HSU-MEI HSU, M.P.H., TZEE-CHUNG WU,
Varicella and varicella vaccination An update
 THEME: School contagions Varicella and varicella vaccination An update John Litt, Margaret Burgess BACKGROUND Although varicella is generally mild in children, it is often more severe in adults and overall
THEME: School contagions Varicella and varicella vaccination An update John Litt, Margaret Burgess BACKGROUND Although varicella is generally mild in children, it is often more severe in adults and overall
TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH
 TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH SERIES 95 IMMUNIZATION REQUIRMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NEW SCHOOL ENTERERS 64-95-1. General. 1.1. Scope.
TITLE 64 INTERPRETIVE RULE DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN RESOURCES BUREAU FOR PUBLIC HEALTH SERIES 95 IMMUNIZATION REQUIRMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR NEW SCHOOL ENTERERS 64-95-1. General. 1.1. Scope.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is an important. Brief Communication
 Brief Communication Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Children and Adolescents in a Hyperendemic Area: 15 Years after Mass Hepatitis B Vaccination Yen-Hsuan Ni, MD, PhD; Mei-Hwei Chang, MD; Li-Min Huang,
Brief Communication Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Children and Adolescents in a Hyperendemic Area: 15 Years after Mass Hepatitis B Vaccination Yen-Hsuan Ni, MD, PhD; Mei-Hwei Chang, MD; Li-Min Huang,
Influenza Backgrounder
 Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
Influenza Backgrounder Influenza Overview Influenza causes an average of 36,000 deaths and 200,000 hospitalizations in the U.S. every year. 1,2 Combined with pneumonia, influenza is the seventh leading
The Northern Kentucky Health Department advises that you take the following actions:
 February 5, 2019 Dear Parent or Guardian, This letter is to inform you that your child s school, Assumption Academy, is currently experiencing an outbreak of an illness that is accompanied by a blister-like
February 5, 2019 Dear Parent or Guardian, This letter is to inform you that your child s school, Assumption Academy, is currently experiencing an outbreak of an illness that is accompanied by a blister-like
HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE
 23 Annual Morbidity Report HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE CRUDE DATA 35 Annual Incidence a LA County.37 California b. United States c.2 Age at Diagnosis Mean 4. years Median 36. years Range Birth
23 Annual Morbidity Report HAEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE INVASIVE DISEASE CRUDE DATA 35 Annual Incidence a LA County.37 California b. United States c.2 Age at Diagnosis Mean 4. years Median 36. years Range Birth
APPENDIX A. Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2
 APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
APPENDIX A Comparability Ratios for the Major Causes of Death in North Carolina Vital Statistics, Volume 2 The comparability ratio is an adjustment factor that is applied to the number of deaths coded
Diphtheria. Vaccine Preventable Childhood Diseases. General information
 Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Current Swine Influenza Situation Updated frequently on CDC website 109 cases in US with 1 death 57 confirmed cases aroun
 Swine Flu Olga Emgushov, MD, MPH Director Epidemiology/Public Health Preparedness Brevard County Health Department April 30, 2009 Current Swine Influenza Situation Updated frequently on CDC website http://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/
Swine Flu Olga Emgushov, MD, MPH Director Epidemiology/Public Health Preparedness Brevard County Health Department April 30, 2009 Current Swine Influenza Situation Updated frequently on CDC website http://www.cdc.gov/swineflu/
RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF EPIDEMIOLOGY IN JAPAN Infectious Disease Surveillance System of Infectious Diseases in Japan
 Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 6, No. 3 (Supplement) August RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF EPIDEMIOLOGY IN JAPAN Infectious Disease Surveillance System of Infectious Diseases in Japan Hitoshi Ohshiro, Kyoko Kawamoto,
Journal of Epidemiology Vol. 6, No. 3 (Supplement) August RESEARCH ACTIVITIES OF EPIDEMIOLOGY IN JAPAN Infectious Disease Surveillance System of Infectious Diseases in Japan Hitoshi Ohshiro, Kyoko Kawamoto,
Introduction and overview of the program; new vaccine pipeline and prioritization process
 Immunization for the Modern Family: Western Canada Immunization Forum 2011 Introduction and overview of the program; new vaccine pipeline and prioritization process Monika Naus, MD, MHSc, FRCPC, FACPM
Immunization for the Modern Family: Western Canada Immunization Forum 2011 Introduction and overview of the program; new vaccine pipeline and prioritization process Monika Naus, MD, MHSc, FRCPC, FACPM
Usa Thisyakorn and Chule Thisyakorn
 CHILDHOOD DENGUE DISEASES: A TWENTY YEARS PROSPECTIVE STUDY Usa Thisyakorn and Chule Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. Dengue
CHILDHOOD DENGUE DISEASES: A TWENTY YEARS PROSPECTIVE STUDY Usa Thisyakorn and Chule Thisyakorn Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand Abstract. Dengue
Health economic evaluation of vaccine: the example of varicella-zoster virus
 Health economic evaluation of vaccine: the example of varicella-zoster virus Benoît DERVAUX, CNRS, Catholic University of Lille Advances in infectious diseases modelling Annecy, Les Pensières, December
Health economic evaluation of vaccine: the example of varicella-zoster virus Benoît DERVAUX, CNRS, Catholic University of Lille Advances in infectious diseases modelling Annecy, Les Pensières, December
MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR)
 MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST MEASLES, MUMPS OR RUBELLA? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! MMR VACCINE
MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST MEASLES, MUMPS OR RUBELLA? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! MMR VACCINE
Situation Update Pandemic (H1N1) August 2009
 Situation Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 31 August 2009 Timeline pandemic (H1N1) 2009 April 12: an outbreak of influenza-like illness in Veracruz, Mexico reported to WHO April 15-17: two cases of the new
Situation Update Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 31 August 2009 Timeline pandemic (H1N1) 2009 April 12: an outbreak of influenza-like illness in Veracruz, Mexico reported to WHO April 15-17: two cases of the new
Tables e1a-d. Diagnostic and drug codes for the identification of the multiple sclerosis population, DMT exposures, and study outcomes
 Appendix Tables e1a-d. Diagnostic and drug codes for the identification of the multiple sclerosis population, DMT exposures, and study outcomes Table e-1a Multiple sclerosis and demyelinating disease related
Appendix Tables e1a-d. Diagnostic and drug codes for the identification of the multiple sclerosis population, DMT exposures, and study outcomes Table e-1a Multiple sclerosis and demyelinating disease related
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS AND
 TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
TABLE I-1: RESIDENT INFANT DEATHS PER 1,000 LIVE BIRTHS, BY RACE AND ETHNICITY, FLORIDA AND UNITED STATES, CENSUS YEARS 1970-2000 AND 2004-2014 FLORIDA 1 UNITED STATES 1 YEAR WHITE2 BLACK2 HISPANIC3 WHITE2
A DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF VARICELLA INFECTIONS AMONG PATIENTS PRESENTING TO EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS IN NORTH CAROLINA. Jennifer K.
 A DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF VARICELLA INFECTIONS AMONG PATIENTS PRESENTING TO EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS IN NORTH CAROLINA by Jennifer K. MacFarquhar July 13, 2006 A Master's paper submitted to the faculty of
A DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF VARICELLA INFECTIONS AMONG PATIENTS PRESENTING TO EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS IN NORTH CAROLINA by Jennifer K. MacFarquhar July 13, 2006 A Master's paper submitted to the faculty of
Epidemiology of EV71 in Taiwan, Kow-Tong Chen, MD, Ph.D. Shiing-Jer Twu, MD, Ph.D. Chin-Yun Lee, MD. Monto Ho, MD.
 Epidemiology of EV71 in Taiwan, 1998-2001 Kow-Tong Chen, MD, Ph.D. Shiing-Jer Twu, MD, Ph.D. Chin-Yun Lee, MD. Monto Ho, MD. Introduction Enterovirus Poliovirus Coxsackie A virus Coxsackie B virus Echovirus
Epidemiology of EV71 in Taiwan, 1998-2001 Kow-Tong Chen, MD, Ph.D. Shiing-Jer Twu, MD, Ph.D. Chin-Yun Lee, MD. Monto Ho, MD. Introduction Enterovirus Poliovirus Coxsackie A virus Coxsackie B virus Echovirus
Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis
 SEVENTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A70/13 Provisional agenda item 12.2 13 April 2017 Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis Report by the Secretariat 1. The Executive Board
SEVENTIETH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A70/13 Provisional agenda item 12.2 13 April 2017 Improving the prevention, diagnosis and clinical management of sepsis Report by the Secretariat 1. The Executive Board
Immunization and Vaccines
 Immunization and Vaccines A parental choice Dr. Vivien Suttorp BSc, MPH, MD, CCFP, FCFP Lead Medical Officer of Health South Zone, Alberta Health Services November 7, 2013 Overview Facts about vaccines
Immunization and Vaccines A parental choice Dr. Vivien Suttorp BSc, MPH, MD, CCFP, FCFP Lead Medical Officer of Health South Zone, Alberta Health Services November 7, 2013 Overview Facts about vaccines
Downloaded from:
 Granerod, J; Davison, KL; Ramsay, ME; Crowcroft, NS (26) Investigating the aetiology of and evaluating the impact of the Men C vaccination programme on probable meningococcal disease in England and Wales.
Granerod, J; Davison, KL; Ramsay, ME; Crowcroft, NS (26) Investigating the aetiology of and evaluating the impact of the Men C vaccination programme on probable meningococcal disease in England and Wales.
Infectious DISEASE Report
 Infectious DISEASE 2014 Report Introduction For an electronic copy of the 2014 Disease Report ramseycounty.us The 2014 Disease Report provides final numbers, rates and trends for selected reportable diseases
Infectious DISEASE 2014 Report Introduction For an electronic copy of the 2014 Disease Report ramseycounty.us The 2014 Disease Report provides final numbers, rates and trends for selected reportable diseases
Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran
 Short Communication Iran J Pediatr Dec 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:359-363 Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran Khadijehsadat Najib 1, MD; Ebrahim Fallahzadeh *2, MD; Mohammad
Short Communication Iran J Pediatr Dec 2007; Vol 17 ( No 3), Pp:359-363 Disease Spectrum and Mortality in Hospitalized Children of Southern Iran Khadijehsadat Najib 1, MD; Ebrahim Fallahzadeh *2, MD; Mohammad
Maternal influenza immunisation
 Maternal influenza immunisation Cheryl Cohen Centre Head Centre for Respiratory Disease and Meningitis, National Institute for Communicable Diseases cherylc@nicd.ac.za Global causes of death in children
Maternal influenza immunisation Cheryl Cohen Centre Head Centre for Respiratory Disease and Meningitis, National Institute for Communicable Diseases cherylc@nicd.ac.za Global causes of death in children
Shabir A. Madhi. Global Overview of Maternal Immunisation
 Shabir A. Madhi Global Overview of Maternal Immunisation National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand, South Africa Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Research Unit, & DST/NRF:
Shabir A. Madhi Global Overview of Maternal Immunisation National Institute for Communicable Diseases & University of Witwatersrand, South Africa Respiratory and Meningeal Pathogens Research Unit, & DST/NRF:
VARICELLA EPIDEMIOLOGY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF UNIVERSAL VARICELLA VACCINATION PROGRAM IN TAIWAN
 VARICELLA EPIDEMIOLOGY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF UNIVERSAL VARICELLA VACCINATION PROGRAM IN TAIWAN HF Tseng 1, HF Tan 2 and CK Chang 3 1 Institute of Medical Research, Chang-Jung Christian University,
VARICELLA EPIDEMIOLOGY AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS ANALYSIS OF UNIVERSAL VARICELLA VACCINATION PROGRAM IN TAIWAN HF Tseng 1, HF Tan 2 and CK Chang 3 1 Institute of Medical Research, Chang-Jung Christian University,
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS INFECTIONS IN NSW CHILDREN,
 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS INFECTIONS IN NSW CHILDREN, 1992 1997 Susan Lister * and Peter McIntyre National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance of Vaccine Preventable
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF RESPIRATORY SYNCYTIAL VIRUS INFECTIONS IN NSW CHILDREN, 1992 1997 Susan Lister * and Peter McIntyre National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance of Vaccine Preventable
Pedro Plans-Rubió 1,4 Encarna Navas. Angela Domínguez 3,4 Mireia Jané
 PharmacoEconomics Open https://doi.org/10.1007/s41669-018-0081-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reduction of Direct Health Costs Associated with Pertussis Vaccination with Acellular Vaccines in Children Aged
PharmacoEconomics Open https://doi.org/10.1007/s41669-018-0081-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Reduction of Direct Health Costs Associated with Pertussis Vaccination with Acellular Vaccines in Children Aged
Incidence per 100,
 Group B Streptococcus Surveillance Report 2005 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services Updated: January 2007 Background
Group B Streptococcus Surveillance Report 2005 Oregon Active Bacterial Core Surveillance (ABCs) Office of Disease Prevention & Epidemiology Oregon Department of Human Services Updated: January 2007 Background
Trends in Pneumonia and Influenza Morbidity and Mortality
 Trends in Pneumonia and Influenza Morbidity and Mortality American Lung Association Research and Program Services Epidemiology and Statistics Unit September 2008 Table of Contents Trends in Pneumonia and
Trends in Pneumonia and Influenza Morbidity and Mortality American Lung Association Research and Program Services Epidemiology and Statistics Unit September 2008 Table of Contents Trends in Pneumonia and
Varicella (Chickenpox) and Varicella Vaccines
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Varicella (Chickenpox) and Varicella Vaccines September 2018 Photographs and images included in this
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Varicella (Chickenpox) and Varicella Vaccines September 2018 Photographs and images included in this
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
EXANTHEMATOUS ILLNESS 1 DEFINITIONS Exanthema eruption of the skin Exanthema eruption of mucosae Macule flat nonpalpable lesion Papule small palpable lesion Nodule large palpable lesion Vesicle small fluid
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE METHODS
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Varicella Vaccination among Health Care Providers Participating in the Varicella Active Surveillance Project, Antelope Valley, California,
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices Regarding Varicella Vaccination among Health Care Providers Participating in the Varicella Active Surveillance Project, Antelope Valley, California,
Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants
 Helen Y. Chu, MD MPH Division of Allergy & Infectious Diseases University of Washington Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants June 2, 2015 Midwives Association of Washington State Conference Financial
Helen Y. Chu, MD MPH Division of Allergy & Infectious Diseases University of Washington Prevention of Infections in Mothers & Infants June 2, 2015 Midwives Association of Washington State Conference Financial
Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease (igas) in British Columbia 2017 Annual Summary
 Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease (igas) in British Columbia 2017 Annual Summary Background In 2016, BC experienced a higher incidence of igas than observed in 2009 through 2015, with a rate surpassing
Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease (igas) in British Columbia 2017 Annual Summary Background In 2016, BC experienced a higher incidence of igas than observed in 2009 through 2015, with a rate surpassing
FORECASTING THE DEMAND OF INFLUENZA VACCINES AND SOLVING TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING
 National Cheng Kung University Institute of International Management Business Decision Methods FORECASTING THE DEMAND OF INFLUENZA VACCINES AND SOLVING TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING HOLLY
National Cheng Kung University Institute of International Management Business Decision Methods FORECASTING THE DEMAND OF INFLUENZA VACCINES AND SOLVING TRANSPORTATION PROBLEM USING LINEAR PROGRAMMING HOLLY
The Ministry of Health recommends measles vaccines for all child care providers, children and parents to ensure they are protected against measles.
 Since January 1, 2014, there have been several cases of measles reported in Saskatchewan. Because measles is a highly contagious vaccine-preventable disease and there are a number of unvaccinated children
Since January 1, 2014, there have been several cases of measles reported in Saskatchewan. Because measles is a highly contagious vaccine-preventable disease and there are a number of unvaccinated children
ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE
 ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, 1 Wen-Chen Tsai, 2 Wei-Hsiung Hu, and Dar-Yu Yang Department of Emergency
ANALYSIS OF EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT UTILIZATION BY ELDERLY PATIENTS UNDER NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE Jin-An Huang, Rhay-Hung Weng, 1 Wen-Chen Tsai, 2 Wei-Hsiung Hu, and Dar-Yu Yang Department of Emergency
Recommendations for VZV management in. Dan Engelhard, Pierre Reusser, Rafael de la Camara, Hermann Einsele, Jan Styczynski, Kate Ward, Per Ljungman
 Recommendations for VZV management in patients Cas cliniques with leukemia Dan Engelhard, Pierre Reusser, Rafael de la Camara, Hermann Einsele, Jan Styczynski, Kate Ward, Per Ljungman Introduction Acute
Recommendations for VZV management in patients Cas cliniques with leukemia Dan Engelhard, Pierre Reusser, Rafael de la Camara, Hermann Einsele, Jan Styczynski, Kate Ward, Per Ljungman Introduction Acute
CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS
 CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE What immunizations should be administered? NCQA ACCEPTED CODES DOCUMENTATION
CHILDHOOD IMMUNIZATIONS APPLICATIONS OBJECTIVE Purpose of Measure: ELIGIBLE POPULATION Which members are included? STANDARD OF CARE What immunizations should be administered? NCQA ACCEPTED CODES DOCUMENTATION
SUBJECT: ISOLATION PRECAUTIONS REFERENCE #6003 PAGE: 1 DEPARTMENT: REHABILITATION SERVICES OF: 6 EFFECTIVE:
 PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
PAGE: 1 STANDARD PRECAUTIONS: Precautions which are designed for care of all patients, regardless of diagnosis or presumed infection status to reduce the risk of transmission from both recognized and unrecognized
Invasive Bacterial Diseases in the Arctic. Tom Hennessy, MD, MPH Arctic Investigations Program October 2, 2015 Copenhagen
 Invasive Bacterial Diseases in the Arctic Tom Hennessy, MD, MPH Arctic Investigations Program October 2, 2015 Copenhagen Outline Introduction to Alaska International Circumpolar Surveillance Invasive bacterial
Invasive Bacterial Diseases in the Arctic Tom Hennessy, MD, MPH Arctic Investigations Program October 2, 2015 Copenhagen Outline Introduction to Alaska International Circumpolar Surveillance Invasive bacterial
Methods. Linking three datasets BRIEF COMMUNICATION
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Changes in Causes of Death and Associated Conditions Among Persons with HIV/AIDS After the Introduction of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Taiwan Tsung-Hsueh Lu, Hong-Jen Chang,
BRIEF COMMUNICATION Changes in Causes of Death and Associated Conditions Among Persons with HIV/AIDS After the Introduction of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy in Taiwan Tsung-Hsueh Lu, Hong-Jen Chang,
ARF & RHD Primordial and Primary Prevention
 ARF & RHD Primordial and Primary Prevention Bart Currie Infectious Diseases Department, Royal Darwin Hospital Global and Tropical Health Division, Menzies Northern Territory Medical Program, Flinders &
ARF & RHD Primordial and Primary Prevention Bart Currie Infectious Diseases Department, Royal Darwin Hospital Global and Tropical Health Division, Menzies Northern Territory Medical Program, Flinders &
INSTRUCTOR S NOTE. Copyright 2018, The Johns Hopkins University and Teaching Vaccine Economics Everywhere.
 INSTRUCTOR S NOTE This case study can be used to motivate several learning objectives and can be tied to specific course objectives in the modules. In case studies the students are not spoon-fed. Instead,
INSTRUCTOR S NOTE This case study can be used to motivate several learning objectives and can be tied to specific course objectives in the modules. In case studies the students are not spoon-fed. Instead,
Research Article Epidemiological Patterns of Varicella in the Period of 1977 to 2012 in the Rijeka District, Croatia
 Epidemiology Research International, Article ID 193678, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/193678 Research Article Epidemiological Patterns of Varicella in the Period of 1977 to 212 in the Rijeka District,
Epidemiology Research International, Article ID 193678, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/193678 Research Article Epidemiological Patterns of Varicella in the Period of 1977 to 212 in the Rijeka District,
VARICELLA/ZOSTER (CHICKENPOX/SHINGLES) SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL FOR ONTARIO HOSPITALS
 VARICELLA/ZOSTER (CHICKENPOX/SHINGLES) SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL FOR ONTARIO HOSPITALS Developed by the Ontario Hospital Association and the Ontario Medical Association Joint Communicable Diseases Surveillance
VARICELLA/ZOSTER (CHICKENPOX/SHINGLES) SURVEILLANCE PROTOCOL FOR ONTARIO HOSPITALS Developed by the Ontario Hospital Association and the Ontario Medical Association Joint Communicable Diseases Surveillance
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
 Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
By: Zenessa Morrison and Denise Bailey
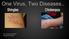 By: Zenessa Morrison and Denise Bailey Shingles which is also known as Herpes Zoster is a painful skin rash caused by the Varicella virus. The Varicella virus belongs to the herpesviridae family. The structure
By: Zenessa Morrison and Denise Bailey Shingles which is also known as Herpes Zoster is a painful skin rash caused by the Varicella virus. The Varicella virus belongs to the herpesviridae family. The structure
2.3 Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease
 2.3 Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease Summary Total number of cases, 2015 = 107 Crude incidence rate, 2015 = 2.3 per 100,000 population Notifications In 2015, 107 cases of invasive group A streptococcal
2.3 Invasive Group A Streptococcal Disease Summary Total number of cases, 2015 = 107 Crude incidence rate, 2015 = 2.3 per 100,000 population Notifications In 2015, 107 cases of invasive group A streptococcal
Steps toward Measles Eradication in Japan A report from Okinawa Prefecture
 Conferences and Lectures Steps toward Measles Eradication in Japan A report from Okinawa Prefecture JMAJ 53(1): 19 23, 2010 Kaoru ASHIMINE* 1 Okinawa, a Measles-endemic Prefecture in Japan In 1998 1999,
Conferences and Lectures Steps toward Measles Eradication in Japan A report from Okinawa Prefecture JMAJ 53(1): 19 23, 2010 Kaoru ASHIMINE* 1 Okinawa, a Measles-endemic Prefecture in Japan In 1998 1999,
Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox
 Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Chickenpox Caused
Spots and Pox: Contact Tracing and Follow Up for Measles and Chickenpox Noelle Bessette, MPH Surveillance Specialist New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Chickenpox Caused
IASR Back Number Vol.35. The Topic of This Month Vol.35 No.3 (No.409) Rotavirus, , Japan. (IASR 35: 63-64, March 2014) Phoca PDF
 The Topic of This Month Vol.35 No.3 (No.409) Rotavirus, 2010-2013, Japan (IASR 35: 63-64, March 2014) Rotavirus belongs to the family Reoviridae, whose genome consists of 11 segments of double-stranded
The Topic of This Month Vol.35 No.3 (No.409) Rotavirus, 2010-2013, Japan (IASR 35: 63-64, March 2014) Rotavirus belongs to the family Reoviridae, whose genome consists of 11 segments of double-stranded
Vaccinations and Vaccine- Preventable Diseases. Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 28, 2019
 Vaccinations and Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 28, 2019 Vaccines prevent a lot of disease. Disease 20 th Century Annual Morbidity* Reported Cases, 2016
Vaccinations and Vaccine- Preventable Diseases Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 28, 2019 Vaccines prevent a lot of disease. Disease 20 th Century Annual Morbidity* Reported Cases, 2016
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN Active substance(s) (INN or common name): Pharmaco-therapeutic group (ATC Code): Name of Marketing Authorisation Holder or Applicant: Haemagglutinin of three strains of influenza virus,
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN Active substance(s) (INN or common name): Pharmaco-therapeutic group (ATC Code): Name of Marketing Authorisation Holder or Applicant: Haemagglutinin of three strains of influenza virus,
Pharmacoepidemiology In Drug and Vaccine Development
 Pharmacoepidemiology In Drug and Vaccine Development Nancy Santanello, MD, MS, FISPE Vice President Epidemiology Department Merck Research Laboratories, MSD ACPE Beijing, China October 29, 2011 Conflict
Pharmacoepidemiology In Drug and Vaccine Development Nancy Santanello, MD, MS, FISPE Vice President Epidemiology Department Merck Research Laboratories, MSD ACPE Beijing, China October 29, 2011 Conflict
Pneumococcal Vaccine in Children: current situation
 Pneumococcal Vaccine in Children: current situation LAU Yu Lung Chair Professor of Paediatrics Doris Zimmern Professor in Community Child Health LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Chairman
Pneumococcal Vaccine in Children: current situation LAU Yu Lung Chair Professor of Paediatrics Doris Zimmern Professor in Community Child Health LKS Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Chairman
Classification: official 1
 NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
NHS public health functions agreement 2018-19 Service specification No.4 Immunisation against diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, pertussis, Hib and HepB programme 1 NHS public health functions agreement
Ageing and the burden of diseases in the elderly. Karl-Heinz Krause Geneva University Hospitals and Medical Faculty
 Ageing and the burden of diseases in the elderly Karl-Heinz Krause Geneva University Hospitals and Medical Faculty - Norwegian Surveillance System for Communicable Diseases (MSIS) - Clinicians and laboratories
Ageing and the burden of diseases in the elderly Karl-Heinz Krause Geneva University Hospitals and Medical Faculty - Norwegian Surveillance System for Communicable Diseases (MSIS) - Clinicians and laboratories
Chickenpox vaccine for all?
 MODERN MEDICINE CPD ARTICLE NUMBER TWO: 1 point Chickenpox vaccine for all? MARK J FERSON, MB BS, MPH, MD, FRACP, FAFPHM A live attenuated varicella vaccine is now available in South Africa; it is approved
MODERN MEDICINE CPD ARTICLE NUMBER TWO: 1 point Chickenpox vaccine for all? MARK J FERSON, MB BS, MPH, MD, FRACP, FAFPHM A live attenuated varicella vaccine is now available in South Africa; it is approved
Unsupervised activity is a major risk factor for traumatic coma and its age-specific
 The assessment of patients in coma is a medical emergency. The cause should be identified and, where possible, corrected and the brain provided with appropriate protection to reduce further damage. It
The assessment of patients in coma is a medical emergency. The cause should be identified and, where possible, corrected and the brain provided with appropriate protection to reduce further damage. It
Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa
 Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa Nigeria Center for Disease Control Federal Ministry of Health Abuja July 2015 Outline 1. Measles disease 2. Progress towards
Introduction to Measles a Priority Vaccine Preventable Disease (VPD) in Africa Nigeria Center for Disease Control Federal Ministry of Health Abuja July 2015 Outline 1. Measles disease 2. Progress towards
BCG vaccine and tuberculosis
 PART 2: Vaccination for special risk groups 2.1 Vaccination for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people historically had a very high burden of infectious
PART 2: Vaccination for special risk groups 2.1 Vaccination for Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people historically had a very high burden of infectious
What are the new active vaccine recommendations in the Canadian Immunization Guide?
 154 CCDR 17 April 2014 Volume 40-8 https://doi.org/10.14745/ccdr.v40i08a03 1 What are the new active vaccine recommendations in the Canadian Immunization Guide? Warshawsky B 1 and Gemmill I 2 on behalf
154 CCDR 17 April 2014 Volume 40-8 https://doi.org/10.14745/ccdr.v40i08a03 1 What are the new active vaccine recommendations in the Canadian Immunization Guide? Warshawsky B 1 and Gemmill I 2 on behalf
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title: Trends of Hepatitis A Hospitalization and Risk Factors in Canada Between 1990 and 2003 Authors: Magalie Canuel (magalie.canuel@inspq.gouv.qc.ca) Gaston De Serres (gaston.deserres@ssss.gouv.qc.ca)
Author's response to reviews Title: Trends of Hepatitis A Hospitalization and Risk Factors in Canada Between 1990 and 2003 Authors: Magalie Canuel (magalie.canuel@inspq.gouv.qc.ca) Gaston De Serres (gaston.deserres@ssss.gouv.qc.ca)
CASE SUMMARY: PERTUSSIS IN THE SOUTHERN HEALTH SANTÉ SUD REGION
 CASE SUMMARY: PERTUSSIS IN THE SOUTHERN HEALTH SANTÉ SUD REGION By: Braden Arbuckle Home for the Summer Program, May to August 2017 Portage La Prairie, Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. Finney Introduction Pertussis,
CASE SUMMARY: PERTUSSIS IN THE SOUTHERN HEALTH SANTÉ SUD REGION By: Braden Arbuckle Home for the Summer Program, May to August 2017 Portage La Prairie, Manitoba Supervisor: Dr. Finney Introduction Pertussis,
A Medical Critique of the Varicella Vaccine
 A Medical Critique of the Varicella Vaccine On March 17, 1995 the FDA approved the use of Varivax-the varicella vaccine (i.e., chicken pox vaccine) made by Merck-for use in healthy young children. A review
A Medical Critique of the Varicella Vaccine On March 17, 1995 the FDA approved the use of Varivax-the varicella vaccine (i.e., chicken pox vaccine) made by Merck-for use in healthy young children. A review
MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR)
 MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST MEASLES, MUMPS OR RUBELLA? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! MMR VACCINE
MEASLES, MUMPS, RUBELLA (MMR) WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW ARE YOU SURE YOU USE THE RIGHT MEASURES TO PROTECT YOURSELF AGAINST MEASLES, MUMPS OR RUBELLA? GET INFORMED! GET VACCINATED! GET PROTECTED! MMR VACCINE
Epidemiological surveillance in points of care for refugees/migrants Weekly Report
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (HCDCP) Department of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention Contact information: Tel: 210 5212 054, Fax: 210 8818 868 E-mail: epid@keelpno.gr
MINISTRY OF HEALTH Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (HCDCP) Department of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention Contact information: Tel: 210 5212 054, Fax: 210 8818 868 E-mail: epid@keelpno.gr
A Mathematical Approach to Characterize the Transmission Dynamics of the Varicella-Zoster Virus
 Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2012 Weber State University, Ogden Utah March 29 31, 2012 A Mathematical Approach to Characterize the Transmission Dynamics of the
Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2012 Weber State University, Ogden Utah March 29 31, 2012 A Mathematical Approach to Characterize the Transmission Dynamics of the
Chickenpox Death. West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System
 Chickenpox Death Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program Phone: 304-558-5358 or 800-423-1271 in Fax: 304-558-8736 Investigation
Chickenpox Death Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology Program Phone: 304-558-5358 or 800-423-1271 in Fax: 304-558-8736 Investigation
Epidemiological surveillance in points of care for refugees/migrants Weekly Report
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (HCDCP) Department of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention Contact information: Tel: 210 5212 054, Fax: 210 8818 868 E-mail: epid@keelpno.gr
MINISTRY OF HEALTH Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (HCDCP) Department of Epidemiological Surveillance and Intervention Contact information: Tel: 210 5212 054, Fax: 210 8818 868 E-mail: epid@keelpno.gr
HEALTH ADVISORY: MEASLES EXPOSURES IN NEW YORK STATE
 December 11, 2018 To: Health Care Providers, Hospitals, Emergency Departments, Dental Providers, and Local Health Departments From: New York State Department of Health, Bureau of Immunization HEALTH ADVISORY:
December 11, 2018 To: Health Care Providers, Hospitals, Emergency Departments, Dental Providers, and Local Health Departments From: New York State Department of Health, Bureau of Immunization HEALTH ADVISORY:
10/6/2014. INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? OUTLINE INFLUNZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS INFLUENZA VIRUS
 INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? Baptist Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital J. Milton Gaviria, MD, FACP October 17, 2014 Homestead Hospital Mariners Hospital Baptist Cardiac
INFLUENZA: Why Should We Take The Vaccine? Baptist Hospital Baptist Children s Hospital Doctors Hospital J. Milton Gaviria, MD, FACP October 17, 2014 Homestead Hospital Mariners Hospital Baptist Cardiac
A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY
 A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY Julia Brotherton and Jeremy McAnulty Communicable Diseases Branch NSW Department of Health Pertussis has traditionally been considered
A PERTUSSIS EPIDEMIC IN NSW: HOW EPIDEMIOLOGY REFLECTS VACCINATION POLICY Julia Brotherton and Jeremy McAnulty Communicable Diseases Branch NSW Department of Health Pertussis has traditionally been considered
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT
 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT Quarterly Report Volume 31, Number 1 2014 June Immunization Programs in NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR Routine Immunization Schedule (2 months - 6 years) July 1, 2014 In Newfoundland
COMMUNICABLE DISEASE REPORT Quarterly Report Volume 31, Number 1 2014 June Immunization Programs in NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR Routine Immunization Schedule (2 months - 6 years) July 1, 2014 In Newfoundland
Summary of Key Points. WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017
 Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Summary of Key Points WHO Position Paper on Vaccines against Hepatitis B, July 2017 1 Background l HBV is transmitted by exposure of mucosal membranes or non-intact skin to infected blood, saliva, semen
Measles. Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 7, 2019
 Measles Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 7, 2019 Measles Symptoms Incubation period: ~14 days Prodrome: fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis Rash starts on face or at hairline, spreads
Measles Paul R. Cieslak, MD Public Health Division February 7, 2019 Measles Symptoms Incubation period: ~14 days Prodrome: fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis Rash starts on face or at hairline, spreads
RESPIRATORY DISEASES AND ITS TREATMENT THROUGH AYURVEDIC AND HEBAL MEDICINES
 RESPIRATORY DISEASES AND ITS TREATMENT THROUGH AYURVEDIC AND HEBAL MEDICINES page 1 / 5 page 2 / 5 respiratory diseases and its pdf The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases (GARD) contributes
RESPIRATORY DISEASES AND ITS TREATMENT THROUGH AYURVEDIC AND HEBAL MEDICINES page 1 / 5 page 2 / 5 respiratory diseases and its pdf The Global Alliance against Chronic Respiratory Diseases (GARD) contributes
Increase Hepatitis B Screening and Vaccinations
 17 Increase Hepatitis B Screening and Vaccinations Situation Viral hepatitis is considered to be the most common contagious disease in Japan. Of the estimated three million patients and carriers of viral
17 Increase Hepatitis B Screening and Vaccinations Situation Viral hepatitis is considered to be the most common contagious disease in Japan. Of the estimated three million patients and carriers of viral
Epidemiologic Features of Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan,
 ARTICLE Epidemiologic Features of Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan, 23 26 Wen-Chan Huang, MD a, Li-Min Huang, MD, PhD a, I-Shou Chang, PhD b, Luan-Yin Chang, MD, PhD a, Bor-Luen Chiang, MD, PhD a,c, Pei-Jer
ARTICLE Epidemiologic Features of Kawasaki Disease in Taiwan, 23 26 Wen-Chan Huang, MD a, Li-Min Huang, MD, PhD a, I-Shou Chang, PhD b, Luan-Yin Chang, MD, PhD a, Bor-Luen Chiang, MD, PhD a,c, Pei-Jer
