Foundations in Microbiology
|
|
|
- Blaise Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 20
2 The Gram Negative Bacilli of Medical Importance Chapter 20 2
3 3
4 Aerobic Gram Negative Bacilli Pseudomonas an opportunistic pathogen Brucella & Francisella zoonotic pathogens Bordetella & Legionella mainly human pathogens Alcaligenes opportunistic pathogen 4
5 Pseudomonas small gram negative rods with a single polar flagellum, produce oxidase & catalase highly versatile metabolism 5
6 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 6
7 Pseudomonas aeruginosa common inhabitant of soil & water intestinal resident in 10% normal people resistant to soaps, dyes, quaternary ammonium disinfectants, drugs, drying frequent contaminant of ventilators, IV solutions, anesthesia equipment opportunistic pathogen 7
8 Pseudomonas aeruginosa common cause of nosocomial infections in hosts with burns, neoplastic disease, cystic fibrosis complications include pneumonia, UTI, abscesses, otitis, & corneal disease endocarditis, meningitis, bronchopneumonia grapelike odor greenish blue pigment (pyocyanin) multidrug resistant cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, carbenicillin, polymixin, quinolones, & monobactams 8
9 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 9
10 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 10
11 Bordetella pertussis minute, encapsulated coccobacillus causes pertussis or whooping cough, a communicable childhood affliction acute respiratory syndrome often severe, life threatening complications in babies reservoir apparently healthy carriers transmission by direct contact or inhalation of aerosols 11
12 Bordetella pertussis virulence factors receptors that recognize & bind to ciliated respiratory epithelial cells toxins that destroy & dislodge ciliated cells loss of ciliary mechanism leads to buildup of mucus & blockage of the airways vaccine DTaP acellular vaccine contains toxoid & other Ags 12
13 Pertussis 13
14 Legionella pneumophila widely distributed in water live in close association with amebas 1976 epidemic of pneumonia afflicted 200 American Legion members attending a convention in Philadelphia & killed 29 Legionnaires disease & Pontiac fever prevalent in males over 50 nosocomial disease in elderly patients fever, cough, diarrhea, abdominal pain, pneumonia fatality rate of 3 30% azithromycin 14
15 Legionella pneumophilia 15
16 Legionella pneumophilia 16
17 Enterobacteriaceae Family enterics large family of gram negative bacteria many members inhabit soil, water, & decaying matter & common occupants of large bowel of humans & animals all members are small, non sporing rods facultative anaerobes, grow best in air cause diarrhea through enterotoxins divided into coliforms (lactose fermenters) and non coliforms (non lactose fermenters) 17
18 18
19 19
20 20
21 Antigens & virulence factors H flagellar Ag K capsule &/or fimbrial Ag O somatic or cell wall Ag all have endotoxin exotoxins 21
22 22
23 Escherichia coli: the most prevalent enteric bacillus most common aerobic & non fastidious bacterium in gut enterotoxigenic E. coli causes severe diarrhea due to heat labile toxin & heat stable toxin stimulate secretion & fluid loss; also has fimbrae enteroinvasive E. coli causes inflammatory disease of the large intestine enteropathogenic E. coli linked to wasting from infantile diarrhea; O157:H7 strain causes hemorrhagic syndrome & kidney damage 23
24 Escherichia coli pathogenic strains frequent agents of infantile diarrhea greatest cause of mortality among babies causes ~70% of traveler s diarrhea causes 50 80% UTI indicator of fecal contamination in water 24
25 Other coliforms Klebsiella pneumoniae normal inhabitant of respiratory tract, has large capsule, cause of nosocomial pneumonia, mennigitis, bacteremia, wound infections & UTIs Enterobacter UTIs, surgical wounds Serratia marcescens produces a red pigment; causes pneumonia, burn & wound infections, septicemia & meningitis Citrobacter opportunistic UTIs & bacteremia 25
26 26
27 27
28 Noncoliform lactose negative enterics Proteus Salmonella & Shigella 28
29 Proteus Swarm on surface of moist agar in a concentric pattern Cause UTI, wound infections, pneumonia, septicemia, & infant diarrhea 29
30 30
31 Salmonella motile; ferments glucose resistant to chemicals bile & dyes S. typhi typhoid fever ingested bacilli adhere to small intestine, cause invasive diarrhea that leads to septicemia 2 new vaccines S. cholerae suis pigs S. enteritidis 1,700 serotypes salmonellosis zoonotic gastroenteritis 2 5 days 31
32 32
33 33
34 Shigella shigellosis incapacitating dysentery S. dysenteriae, S. sonnei, S. flexneri & S. boydii produce H 2 S or urease invades villus of large intestine, can perforate intestine or invade blood enters Peyer s patches instigates inflammatory response; endotoxin & exotoxins treatment fluid replacement & ciprofloxacin & sulfa trimethoprim 34
35 35
36 Yersinia pestis nonenteric tiny, gram negative rod, unusual bipolar staining & capsules virulence factors capsular & envelope proteins protect against phagocytosis & foster intracellular growth coagulase, endotoxin, murine toxin 36
37 Yersinia pestis 37
38 Yersinia pestis humans develop plague through contact with wild animals (sylvatic plague) or domestic or semidomestic animals (urban plague) or infected humans found in 200 species of mammals rodents without causing disease flea vectors bacteria replicates in gut, coagulase causes blood clotting that blocks the esophagus; flea becomes ravenous 38
39 Yersinia pestis 39
40 Pathology of plague 3 50 bacilli bubonic bacillus multiplies in flea bite, enters lymph, causes necrosis & swelling called a bubo in groin or axilla septicemic progression to massive bacterial growth; virulence factors cause intravascular coagulation subcutaneous hemorrhage & purpura black plague pneumonic infection localized to lungs, highly contagious; fatal without treatment treatment: streptomycin, tetracycline or chloramphenicol Killed or attenuated vaccine 40
41 41
42 Pasteruella multocida zoonotic genus opportunistic infections animal bites or scratches cause local abscess that can spread to joints, bones, & lymph nodes treatment: penicillin & tetracycline 42
43 Hemophilus tiny gram negative pleomorphic rods fastidious, sensitive to drying, temperature extremes, & disinfectants none can grow on blood agar without special techniques chocolate agar require hemin, NAD or NADP some species are normal colonists of upper respiratory tract or vagina (H. aegyptius, H. parainfluenzae, H ducreyi) others are virulent species responsible of conjunctivitis, childhood meningitis, & chancroid 43
44 Hemophilus H. influenzae acute bacterial meningitis, epiglottitis, otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia, & bronchitis Subunit vaccine Hib H. aegyptius conjunctivitis, pink eye H. ducreyi chancroid STD H. parainfluenzae & H. aphrophilus normal oral & nasopharyngeal flora; infective endocarditis 44
45 45
46 46
47 47
Gram Negative Bacilli. ASSIST. PROF. Dr. Abdulameer Abdullah University of Basra College of Nursing
 Gram Negative Bacilli ASSIST. PROF. Dr. Abdulameer Abdullah University of Basra College of Nursing 2017-2018 1 2 Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli O O Pseudomonas - aeruginosa, cepacia, pituita Brucella -
Gram Negative Bacilli ASSIST. PROF. Dr. Abdulameer Abdullah University of Basra College of Nursing 2017-2018 1 2 Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli O O Pseudomonas - aeruginosa, cepacia, pituita Brucella -
Gram negative rods and cocci
 Gram negative rods and cocci 1 Endotoxin: Lipid A, the superantigen Part of LPS of the Gram negative outer membrane Causes an over-stimulation of macrophages with production of various cytokines Fever,
Gram negative rods and cocci 1 Endotoxin: Lipid A, the superantigen Part of LPS of the Gram negative outer membrane Causes an over-stimulation of macrophages with production of various cytokines Fever,
Chapter 38 Pt. II. Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria
 Chapter 38 Pt. II Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria Arthropod-Borne Diseases generally rare some are of historical interest some newly emerged Yersinia pestis nonenteric tiny, gram-negative rod, unusual
Chapter 38 Pt. II Human Diseases Caused by Bacteria Arthropod-Borne Diseases generally rare some are of historical interest some newly emerged Yersinia pestis nonenteric tiny, gram-negative rod, unusual
I. Enterobacteriaceae (enteric = intestine) Enterics
 I. Enterobacteriaceae (enteric = intestine) Enterics Enterics are ubiquitous in nature Except for few, most are present in the intestinal tract of animals and humans as commensal flora; therefore, they
I. Enterobacteriaceae (enteric = intestine) Enterics Enterics are ubiquitous in nature Except for few, most are present in the intestinal tract of animals and humans as commensal flora; therefore, they
Gram-Negative rods Introduction to
 Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
Lec 5 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Gram-Negative rods Introduction to Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics: جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Small gram-negative rods (2-5 by 0.5 microns) Most motile with peritrichous
True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella
 Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
Lec. 6 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Salmonella General Characteristics of Salmonella جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان Coliform bacilli
Yersinia pestis. Yersinia and plague. Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Yersinia pestis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Yersinia species Short, pleomorphic gram-negative rods that can exhibit bipolar staining. Catalase positive, and microaerophilic or facultatively anaerobic. Animals
Manal AL khulaifi. Enterobacteriaceae
 Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
Enterobacteriaceae Characteristics E.coli Most significant species in the genus Important potential pathogen in humans Common isolate from colon flora Dry, pink (lactose positive) pink colony with area
Shigella and salmonella
 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Microbiology Lec. 9 & 10 Shigella and salmonella Dr. Abdullah Ahmed Hama PhD. Microbiology/Molecular Parasitology abdullah.hama@spu.edu.iq 1 Shigella Shigella species
Gram-negative rods Ferment glucose with acid production Reduce nitrates into nitrites Oxidase negative Facultative anaerobic
 Enterobacteriaceae Lecture -17 Dr.Baha,H. AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Characters of Enterobacteriaceae EnterobacteriaciaeAll Gram-negative rods Ferment glucose with
Enterobacteriaceae Lecture -17 Dr.Baha,H. AL-Amiedi Ph. D.Microbiology Gram-negative rods Enterobacteriaceae Characters of Enterobacteriaceae EnterobacteriaciaeAll Gram-negative rods Ferment glucose with
[The following notes organizes the various genera based on their oxygen requirements (aerobic vs. anaerobic).]*
![[The following notes organizes the various genera based on their oxygen requirements (aerobic vs. anaerobic).]* [The following notes organizes the various genera based on their oxygen requirements (aerobic vs. anaerobic).]*](/thumbs/72/67000058.jpg) Chapter 20 Medically Important Gram-Negative Bacilli* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. [I. Gram-Negative
Chapter 20 Medically Important Gram-Negative Bacilli* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. [I. Gram-Negative
Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio د. حامد الزعبي
 Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio د. حامد الزعبي Enterobacteriaceae Escherichia coli, proteus and klebsiella... Shigella Salmonella Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are: small Gram negative straight rods. Some
Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio د. حامد الزعبي Enterobacteriaceae Escherichia coli, proteus and klebsiella... Shigella Salmonella Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are: small Gram negative straight rods. Some
Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio
 Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio حامد الزعبي د. Enterobacteriaceae Escherichia coli, proteus and klebsiella... Shigella Salmonella Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are: small Gram negative straight rods. Some
Enterobacteriaceae Vibrio حامد الزعبي د. Enterobacteriaceae Escherichia coli, proteus and klebsiella... Shigella Salmonella Members of the Enterobacteriaceae are: small Gram negative straight rods. Some
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 13 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella 1 Haemophilus "loves heme" Small gram-negative coccobacilli Non-spore forming Non-motile Growth is enhanced in CO2 Present
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella
 DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 Obgectives: GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 Obgectives: GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS:
 DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella OBJECTIVES Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
DR. HUDA ABO- ALEES 214-2-15 GRAM-NEGATIVE BACILLI THE ENTERICS: Family Enterobacteriaceae: Genus Escherichia & Genus Klebsiella OBJECTIVES Describe the morphology & physiology for E.coli & Klebsiella
GENERAL CHARACTERS OF MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
 GENERAL CHARACTERS OF MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Presented by: Dr: lamiaa adel Assistant professor of Medical Microbiology and Immunology Intended Learning Outcomes By the end
GENERAL CHARACTERS OF MEDICALLY IMPORTANT BACTERIA THE ENTEROBACTERIACEAE Presented by: Dr: lamiaa adel Assistant professor of Medical Microbiology and Immunology Intended Learning Outcomes By the end
Gram-negative rods: Enterobacteriaceae Part II Common Organisms. Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli. CLS 418 Clinical Microbiology I
 Gram-negative rods: Enterobacteriaceae Part II Common Organisms Karen Honeycutt, M.Ed., MLS(ASCP) CM SM CM Session Enterobacteriaceae Antigens O somatic, part of cell wall (serogroup) Stimulates earliest
Gram-negative rods: Enterobacteriaceae Part II Common Organisms Karen Honeycutt, M.Ed., MLS(ASCP) CM SM CM Session Enterobacteriaceae Antigens O somatic, part of cell wall (serogroup) Stimulates earliest
Enteric bacteria(pseudomonas+salmonella) Dr.Asem shihabi. Jumanah Nayef Abu Asbeh
 15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
15 Microbiology sheet #15 1. Gram-negative facultative anaerobic rapidly growing bacteria are divided into 2 major Lactose fermenter group which is represented by the Coliforms. 2. Lactose non-fermenter
#sheet (15) PART.1 Enterobacteriaceae
 1Page #sheet (15) PART.1 Enterobacteriaceae Made by: marah al-hiary corrected by: Mohammad al-momani date: 10/11/2016 1 2Page *in this lecture we will talk about a big family which is Enterobacteriaceae:
1Page #sheet (15) PART.1 Enterobacteriaceae Made by: marah al-hiary corrected by: Mohammad al-momani date: 10/11/2016 1 2Page *in this lecture we will talk about a big family which is Enterobacteriaceae:
YERSINIA MODULE 26.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 26.2 YERSINIA PESTIS. Notes
 MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
MODULE Yersinia 26 YERSINIA 26.1 INTRODUCTION Genus Yersinia belongs to tribe Yersinieae of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Yersinia are Gram-negative rod shaped bacteria and are facultative anaerobes.
PROTEUS-PROVIDENCIA-MORGANELLA GENERA
 Gram-negative rods Proteus & Pseudomonas DR. HUDA ABO-ALEES 2014-2015 Objectives: Describe the morphology & physiology for Proteus & Pseudomonas. Determine the virulence factors of proteus and pseudomonas.
Gram-negative rods Proteus & Pseudomonas DR. HUDA ABO-ALEES 2014-2015 Objectives: Describe the morphology & physiology for Proteus & Pseudomonas. Determine the virulence factors of proteus and pseudomonas.
Bio 119 PLAGUE 7/21/ Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague.
 PLAGUE Reading in BOM-12: 35.7 Plague p. 1017 Discussion Questions 1. Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague. 2. Describe the Hemin Storage Phenotype (Hms) phenotype and
PLAGUE Reading in BOM-12: 35.7 Plague p. 1017 Discussion Questions 1. Distinguish between sylvatic, bubonic, septicemic, and pneumonic plague. 2. Describe the Hemin Storage Phenotype (Hms) phenotype and
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15
 Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Medical Bacteriology Lecture 15 Gram Negative Coccobacilli Haemophilus Bordetella pertussis Haemophilus "loves heme" small gram-negative coccobacilli, non-spore forming, non-motile, require enriched media
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7. Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods. Bacillus
 Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Medical Bacteriology - Lecture 7 Spore- forming Gram Positive Rods Bacillus 1 Bacillus Characteristics - Gram positive - Large rod. - Arranged in long chain - Spore forming - Aerobic or facultative anaerobic
Pathogenic bacteria. Lab 6: Taxonomy: Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum: Proteobacteria Class: Gammaproteobacteria Order: Enterobacteriales
 Level 5 Pathogenic bacteria Lab 6: Family: Enterobacteriaceae Taxonomy: Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum: Proteobacteria Class: Gammaproteobacteria Order: Enterobacteriales Family: Enterobacteriaceae The prefix
Level 5 Pathogenic bacteria Lab 6: Family: Enterobacteriaceae Taxonomy: Kingdom: Bacteria Phylum: Proteobacteria Class: Gammaproteobacteria Order: Enterobacteriales Family: Enterobacteriaceae The prefix
Enterobacteriaceae & Vibrios. Stijn van der Veen
 Enterobacteriaceae & Vibrios Stijn van der Veen Enterobacteriaceae Enterobacteriaceae are a family of gram-negative rod-shaped (bacilli) enteric bacteria that cause a wide variety of diseases, including
Enterobacteriaceae & Vibrios Stijn van der Veen Enterobacteriaceae Enterobacteriaceae are a family of gram-negative rod-shaped (bacilli) enteric bacteria that cause a wide variety of diseases, including
SERRATIA. and primary pathogen species in the genus is Serratia marcescens.
 SERRATIA Serratia species are opportunistic gram-negative bacteria classified in Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia are widespread in the environment, but are not a common members of the human fecal flora. The
SERRATIA Serratia species are opportunistic gram-negative bacteria classified in Enterobacteriaceae. Serratia are widespread in the environment, but are not a common members of the human fecal flora. The
Host Parasite Relationship. Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU
 Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter
 1 Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Salmonella and enteritis Salmonellae are often pathogenic for humans or animals when acquired by the oral route. They are transmitted from
1 Salmonella, Shigella, and Campylobacter Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Salmonella and enteritis Salmonellae are often pathogenic for humans or animals when acquired by the oral route. They are transmitted from
Rods Gram Negative Rods Enteric Rods Enterobacteriacease,Vibrio, Campylobacter,Helicobacter
 Rods Gram Negative Rods Enteric Rods Enterobacteriacease,Vibrio, Campylobacter,Helicobacter Enterobacteriacease General Characters of Enterobacteriacease (1) Numerous interrelated bacteria flora of intestine
Rods Gram Negative Rods Enteric Rods Enterobacteriacease,Vibrio, Campylobacter,Helicobacter Enterobacteriacease General Characters of Enterobacteriacease (1) Numerous interrelated bacteria flora of intestine
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي. Enterobacteriaceae
 ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي Bacteriology Genus Salmonella Enterobacteriaceae - Pathogenic for human and animals - They are gram negative rods, motile with peritrichous flagella except Gallinarum-pullorum - Ferment
ا.م.د.هيفاء الحديثي Bacteriology Genus Salmonella Enterobacteriaceae - Pathogenic for human and animals - They are gram negative rods, motile with peritrichous flagella except Gallinarum-pullorum - Ferment
Ayman Musleh. Osama Hussein, Saba Massimi ... Dr.Anas
 14 Ayman Musleh Osama Hussein, Saba Massimi... Dr.Anas Enterobacteriaceae: *General properties: 1. Enterobacteriaceae are moderate-sized (0.3 to 1.0 1.0 to 6.0 μm). 2. non spore-forming. 3. gram-negative
14 Ayman Musleh Osama Hussein, Saba Massimi... Dr.Anas Enterobacteriaceae: *General properties: 1. Enterobacteriaceae are moderate-sized (0.3 to 1.0 1.0 to 6.0 μm). 2. non spore-forming. 3. gram-negative
Microbiological aspects of Salmonella including morphology, culture characters, virulence factors, carrier state and prevention.
 Dr. Waleed Eldars Microbiological aspects of Salmonella including morphology, culture characters, virulence factors, carrier state and prevention. Microbiological aspects of Brucella including morphology,
Dr. Waleed Eldars Microbiological aspects of Salmonella including morphology, culture characters, virulence factors, carrier state and prevention. Microbiological aspects of Brucella including morphology,
SHIGELLA. Bacillary dysentery is caused by genus Shigella, named after Shiga who isolated them.
 24 SHIGELLA 24.1 INTRODUCTION Bacillary dysentery is caused by genus Shigella, named after Shiga who isolated them. OBJECTIVES After reading this lesson, you will be able to: describe the characteristics
24 SHIGELLA 24.1 INTRODUCTION Bacillary dysentery is caused by genus Shigella, named after Shiga who isolated them. OBJECTIVES After reading this lesson, you will be able to: describe the characteristics
True Pathogens. Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia
 True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Anatomy of Digestive Tract Digestive tract is a tube (from mouth to anus); technically outside
True Pathogens of the Enterobacteriaceae: ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ Salmonella, Shigella & Yersinia Anatomy of Digestive Tract Digestive tract is a tube (from mouth to anus); technically outside
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity -Pathogenicity - ability of pathogen to cause disease by overcoming the defenses of the host -Virulence - degree of pathogenicity
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOLOGY Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity -Pathogenicity - ability of pathogen to cause disease by overcoming the defenses of the host -Virulence - degree of pathogenicity
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS
 PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
Rapid and progressive necrosis of the tissue underlying epidermis (cellulitis)
 Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Table 1. Infections of the Skin, Eyes and Ears Folliculitis Furuncles (boils) & Carbuncles Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Scald Skin Syndrome Peeling skin on infants Staphylococcus aureus (G+) Impetigo Lesions
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
Bacterial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 st Lecture Introduction Infection and Disease A. Definitions B. Generalized Stages of Infection C. Virulence Factors and Toxins A. Definitions Disease and Infectious
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE
 THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES FINAL YEAR EXAMINATION
THE KENYA POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY COLLEGE SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY DIPLOMA IN MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES FINAL YEAR EXAMINATION
Medical Microbiology
 Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
Lecture 5!!!!!!ƒš!!Œ!!! š!!œ!! Œ!!!! Dr. Ismail I. Daood Medical Microbiology!! Systematic Bacteriology Gram-Positive Cocci : GENUS : Staphylococcus : The general properties of Staphylococcus are Gram-
FINAL. Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know. Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Page No. Know term "diphtheroids"...
 10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
10 th Edition Tortora FINAL Microbiology Etiologic Agents & Related Information to Know Chapter 21: Microbial Diseases of Skin and Eyes Know term "diphtheroids"................. 586 Agents of boils and
Microbial Hazard. Microorganisms. Microbial Hazard. Some microorganisms can be pathogenic (concerns food processors and public health officials).
 Lecture Material - Food Safety Inneke Hantoro Microbial Hazard Microbial Hazard Microbial foodborne illness, also commonly called food poisoning, is illness caused by eating food contaminated with specific
Lecture Material - Food Safety Inneke Hantoro Microbial Hazard Microbial Hazard Microbial foodborne illness, also commonly called food poisoning, is illness caused by eating food contaminated with specific
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students. Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan
 URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS 3 rd Y Med Students Prof. Dr. Asem Shehabi Faculty of Medicine, University of Jordan Urinary Tract Infections-1 Normal urine is sterile.. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products,
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Lecture (14) Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology
 AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
AEROBIC BACILLUS Lecture (14) Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus 60 species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um) Most
FAECAL WELL D-ONE. System for the presumptive identification and antibiotic susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms of the intestinal tract.
 System for the presumptive identification and antibiotic susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms of the intestinal tract. 1. INTRODUCTION Intestinal and gastrointestinal infections are a fairly common
System for the presumptive identification and antibiotic susceptibility of pathogenic microorganisms of the intestinal tract. 1. INTRODUCTION Intestinal and gastrointestinal infections are a fairly common
Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease:
 Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
Infectious Diseases Pathogens: Microorganisms that are capable of causing disease Infection: Results when a pathogen invades and begins growing within the host Disease: Results only if and when normal
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic contaminants or normal flora
 AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
AEROBIC BACILLUS (Lecture (15 Dr. Baha,H,AL-Amiedi Ph.D.Microbiology General Characteristics of Bacillus species; Gram-positive or Gram-variable bacilli 60 (Large (0.5 x 1.2 to 2.5 x 10 um Most are saprophytic
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
The Gram-negative coccobacilli Prof. dr hab. Beata M. Sobieszczańska Department of Microbiology University of Medicine
 The Gram-negative coccobacilli Prof. dr hab. Beata M. Sobieszczańska Department of Microbiology University of Medicine The Gram-Negative Coccobacilli This group includes: Haemophilus Neisseria Bordetella
The Gram-negative coccobacilli Prof. dr hab. Beata M. Sobieszczańska Department of Microbiology University of Medicine The Gram-Negative Coccobacilli This group includes: Haemophilus Neisseria Bordetella
GI Bacterial Infections (part-1)
 GI Bacterial Infections (part-1) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (Gastroenterology & Hepatology) Acute diarrhea and vomiting Acute diarrhea, sometimes with vomiting, is the predominant
GI Bacterial Infections (part-1) Mohammed Abdulla Mehdi FIBMS (internal medicine), FIBMS (Gastroenterology & Hepatology) Acute diarrhea and vomiting Acute diarrhea, sometimes with vomiting, is the predominant
KOMAR UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KUST) Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016
 Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
V. A. Bacterial Diseases
 V. A. Bacterial Diseases A. Airborne Bacterial Diseases B. Foodborne & Waterborne Bacterial Diseases C. Soilborne Bacterial Diseases D. Arthropodborne Bacterial Diseases E. Sexually Transmitted Bacterial
V. A. Bacterial Diseases A. Airborne Bacterial Diseases B. Foodborne & Waterborne Bacterial Diseases C. Soilborne Bacterial Diseases D. Arthropodborne Bacterial Diseases E. Sexually Transmitted Bacterial
ONE STEP (Lemon, Mint, Pine) Detergent for Cleaning, Disinfecting and Deodorizing
 SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY ONE STEP (Lemon, Mint, Pine) Detergent for Cleaning, Disinfecting and Deodorizing Description One Step is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically
SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY ONE STEP (Lemon, Mint, Pine) Detergent for Cleaning, Disinfecting and Deodorizing Description One Step is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
Chapter 13. Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology
 Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
Chapter 13 Topics - Human Host - Progress of an Infection - Epidemiology 1 Human Host Acquire resident flora New born exposure 2 Acquire resident flora The human body supports a wide range of habitats
1/9/ :00:00AM 1/9/ :40:15AM 6/9/2017 9:19:16AM A/c Status. Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Nasal Swab
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091523 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 114015AM 6/9/2017 91916AM Ref By Final RESIRATORY COMREHENSIVE ANEL (33 ATHOGENS) RESIRATORY ANEL 1 #
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091523 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 114015AM 6/9/2017 91916AM Ref By Final RESIRATORY COMREHENSIVE ANEL (33 ATHOGENS) RESIRATORY ANEL 1 #
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Bacterial infections Diphtheria, Pertussis and Enteric fever Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University Gram negative: Diplococci Bacilli Coccobacilli Gram Positive: Diplococci Chains
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa
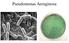 Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative
Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 18 Cocci of Medical Importance Chapter 18 2 Cocci of Interest Staphylococcus aureus S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S. capitis S. saprophyticus Streptococcus
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 18 Cocci of Medical Importance Chapter 18 2 Cocci of Interest Staphylococcus aureus S. epidermidis, S. hominis, S. capitis S. saprophyticus Streptococcus
Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner
 SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner Description Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically designed for hospitals,
SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner Description Fresh Citrus Disinfectant Cleaner is an effective economical 4 ounce per gallon disinfectant, specifically designed for hospitals,
SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY
 SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY ELEMENTS Neutral Disinfectant/Cleaner Neutral Disinfectant & Detergent Description ELEMENTS Neutral Disinfectant/Cleaner is a broad spectrum, neutral ph, hard surface
SUMMARY OF ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY ELEMENTS Neutral Disinfectant/Cleaner Neutral Disinfectant & Detergent Description ELEMENTS Neutral Disinfectant/Cleaner is a broad spectrum, neutral ph, hard surface
Bacteriology cont d. Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi
 Bacteriology cont d Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi Listeria g+ve rods Neisseria -ve Haemophilus influenzae -ve Bordetella -ve Listeria monocytogenes: Differential characteristics: Gram positive, non-spore forming,
Bacteriology cont d Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi Listeria g+ve rods Neisseria -ve Haemophilus influenzae -ve Bordetella -ve Listeria monocytogenes: Differential characteristics: Gram positive, non-spore forming,
Bacteriology cont d. Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi. Listeria g+ve rods Neisseria -ve Haemophilus influenzae -ve Bordetella -ve
 Bacteriology cont d Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi Listeria g+ve rods Neisseria -ve Haemophilus influenzae -ve Bordetella -ve Listeria monocytogenes: Differential characteristics: Gram positive, non-spore forming,
Bacteriology cont d Dr. Hamed Al-Zoubi Listeria g+ve rods Neisseria -ve Haemophilus influenzae -ve Bordetella -ve Listeria monocytogenes: Differential characteristics: Gram positive, non-spore forming,
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
Shigellae. DNA analysis has determined that 4 species of shigella are biogroups within E.coli. Pathogenic species of shigella
 Shigellae DNA analysis has determined that 4 species of shigella are biogroups within E.coli Pathogenic species of shigella S.dysenteriae S.Flexneri S.Boydii S.Sonnei type A type B type C type D shigellae
Shigellae DNA analysis has determined that 4 species of shigella are biogroups within E.coli Pathogenic species of shigella S.dysenteriae S.Flexneri S.Boydii S.Sonnei type A type B type C type D shigellae
General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas
 THE GENUS VIBRIO, CAMPYLOBACTER AND ASSOCIATED BACTERIA (AEROMONAS, HELICOBACTER, PLESIOMONAS) General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas Gram-negative Facultative anaerobes Fermentative
THE GENUS VIBRIO, CAMPYLOBACTER AND ASSOCIATED BACTERIA (AEROMONAS, HELICOBACTER, PLESIOMONAS) General Characteristics of Vibrio, Aeromonas and Plesiomonas Gram-negative Facultative anaerobes Fermentative
Francisella tularensis. Patricia Bolivar MS., CLS, PHM
 Francisella tularensis Patricia Bolivar MS., CLS, PHM Case A 42 year old male hunter presents with a painful, purulent conjunctivitis. Ulcerations were present on the conjunctiva. Cervical lymphadenopathy
Francisella tularensis Patricia Bolivar MS., CLS, PHM Case A 42 year old male hunter presents with a painful, purulent conjunctivitis. Ulcerations were present on the conjunctiva. Cervical lymphadenopathy
The Plague. By Joel Kent. Etiologic Agent: The plague, also known as the Black Death, is caused the bacterium Yersinia pestis.
 The Plague By Joel Kent Etiologic Agent: The plague, also known as the Black Death, is caused the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Transmission: Transmission occurs when a flea from a rodent bites a human. Fleas
The Plague By Joel Kent Etiologic Agent: The plague, also known as the Black Death, is caused the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Transmission: Transmission occurs when a flea from a rodent bites a human. Fleas
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Pathogens of the Digestive System
 Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Pathogens of the Digestive System Chapter 24 (Pages 625-661) 1. Digestive System Review (Pages 627-629) A. Oral Cavity B. Esophagus C. Stomach D. Small Intestine E. Pancreas F. Liver G. Gall Bladder H.
Medical Microbiology Enterobacteriaceae and other gram negative bacilli
 Medical Microbiology Enterobacteriaceae and other gram negative bacilli William H. Benjamin PhD Clinical Pathology E. Coli O157:H7 spinach 204 cases, 103 hospitalizations, 31 HUS, 3 deaths 26 states Since
Medical Microbiology Enterobacteriaceae and other gram negative bacilli William H. Benjamin PhD Clinical Pathology E. Coli O157:H7 spinach 204 cases, 103 hospitalizations, 31 HUS, 3 deaths 26 states Since
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction
 Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
Spore-Forming Gram-Positive Bacilli: Bacillus & Clostridium Species: Introduction The gram-positive spore-forming bacilli are the bacillus and clostridium species. These bacilli are ubiquitous, and because
The Streptococci. Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens
 The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
The Streptococci Diverse collection of cocci. Gram-positive Chains or pairs significant pathogens Strong fermenters Facultative anaerobes Non-motile Catalase Negative 1 Classification 1 2 Classification
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Quiz Student:
 Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4
 Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
Welcome to Pathogen Group 4 Chlamydia trachomatis Trachoma Genital chlamydia Chlamydophila (Chlamydia) psittaci Bacillus anthracis Neisseria meningitidis Haemophilus influenzae, type B Helicobacter pylori
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Anatomy of the Respiratory System Respiratory Infections Respiratory tract can be divided into: Upper Respiratory Tract (URT): Sinuses Nasopharynx,.
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10. Mycobacterium. Actinomycetes. Nocardia
 Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
Medical Bacteriology- Lecture 10 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Nocardia 1 Mycobacterium Characteristics - Large, very weakly gram positive rods - Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes - Catalase positive
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology
 NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
NBCE MOCK BOARD QUESTIONS Microbiology, Public Health, and Immunology 1. What occurs in a primary lymphoid tissue? A. Lymphocytes respond to antigens B. Lymphocytes process antigens C. Lymphocytes produce
Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology
 Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology PSEUDOMONAS BRUCELLA LEGIONELLA CAMPYLOBACTER HELICOBACTER PYLORI (H.PYLORI) Pseudomonas Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia
Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology PSEUDOMONAS BRUCELLA LEGIONELLA CAMPYLOBACTER HELICOBACTER PYLORI (H.PYLORI) Pseudomonas Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia
Disease Transmission Methods
 Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Disease Transmission Methods In epidemiology, transmission simply means any method by which an infectious agent is spread from one host to another. Knowing the type of pathogen often, but not always, identifies
Pathogens of the Respiratory System
 Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
Pathogens of the Respiratory System Chapter 21, Pages 531-567 1. Respiratory System Introduction A. Anatomy (Pages 532-534) i. Upper Respiratory Track a. Nasal Hairs b. Paranasal Sinuses c. Nasal Chonchae
Lori Carpenter - The Plague February 23, 2014
 Lori Carpenter - The Plague February 23, 2014 Causative Agent Plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, nonendospore forming, pleomorphic rod that is a member of the
Lori Carpenter - The Plague February 23, 2014 Causative Agent Plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, nonendospore forming, pleomorphic rod that is a member of the
Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology
 Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology PSEUDOMONAS BRUCELLA LEGIONELLA CAMPYLOBACTER HELICOBACTER PYLORI (H.PYLORI) Pseudomonas Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia
Dr Hamed Al-Zoubi Ass. Prof. / Medical Microbiology PSEUDOMONAS BRUCELLA LEGIONELLA CAMPYLOBACTER HELICOBACTER PYLORI (H.PYLORI) Pseudomonas Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Burkholderia pseudomallei and Burkholderia
College of Medicine Microbiology Medical bacteriology Gram-negative rods related to respiratory tract: Hemophilus:
 College of Medicine Medical bacteriology Microbiology Gram-negative rods related to respiratory tract: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Hemophilus: H.influenzae
College of Medicine Medical bacteriology Microbiology Gram-negative rods related to respiratory tract: ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Hemophilus: H.influenzae
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE 1
 ENTEROBACTERIACEAE 1 Family Enterobacteriaceae often referred to as enterics Enterics are ubiquitous in nature Except for few, most are present in the intestinal tract of animals and humans as commensal
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE 1 Family Enterobacteriaceae often referred to as enterics Enterics are ubiquitous in nature Except for few, most are present in the intestinal tract of animals and humans as commensal
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis. Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017
 320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
320 MBIO Microbial Diagnosis Aljawharah F. Alabbad Noorah A. Alkubaisi 2017 Pathogens of the Urinary tract The urinary system is composed of organs that regulate the chemical composition and volume of
Diphtheria. Vaccine Preventable Childhood Diseases. General information
 Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Diphtheria General information Caused by the bacterium Corynebacterium diphtheria. Transmission is most often person-to-person spread via respiratorydroplets. The word diphtheria comes from Greek and means
Pasteurella, Yersinia, and Francisella
 Pasteurella, Yersinia, and Francisella Frank M. Collins General Concepts Pasteurella Clinical Manifestations In cattle, sheep and birds Pasteurella causes a life-threatening pneumonia. Pasteurella is non-pathogenic
Pasteurella, Yersinia, and Francisella Frank M. Collins General Concepts Pasteurella Clinical Manifestations In cattle, sheep and birds Pasteurella causes a life-threatening pneumonia. Pasteurella is non-pathogenic
Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia
 The Family Enterobacteriaceae 1972: 12 genera and 26 species in the family Enterobacteriaceae 1994: 27 genera and 102 species! Most important genera: Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia Others
The Family Enterobacteriaceae 1972: 12 genera and 26 species in the family Enterobacteriaceae 1994: 27 genera and 102 species! Most important genera: Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Yersinia Others
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 13 13.1 We Are Not Alone The human body exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium Many interactions between human body and microorganisms involve
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 13 13.1 We Are Not Alone The human body exists in a state of dynamic equilibrium Many interactions between human body and microorganisms involve
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13. Mycobacterium Actinomycetes
 Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
Medical Bacteriology- lecture 13 Mycobacterium Actinomycetes Mycobacterium tuberculosis Large, very weakly gram positive rods, Obligate aerobes, related to Actinomycetes, non spore forming, non motile
The Haemophilus Species. By:Dr. Kareema Amine Al-Khafajii,Assistant Professor, Babylon University,College Of Medicine, Department Of Microbiology.
 The Haemophilus Species By:Dr. Kareema Amine Al-Khafajii,Assistant Professor, Babylon University,College Of Medicine, Department Of Microbiology. Haemophilus influenzae This is a group of small, gram-negative,
The Haemophilus Species By:Dr. Kareema Amine Al-Khafajii,Assistant Professor, Babylon University,College Of Medicine, Department Of Microbiology. Haemophilus influenzae This is a group of small, gram-negative,
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
