Preventative Measures for Common Musculoskeletal Disorders Found in the Office Environment. by: Teresa A. Bellingar, Ph.D., AEP
|
|
|
- Augustine Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preventative Measures for Common Musculoskeletal Disorders Found in the Office Environment by: Teresa A. Bellingar, Ph.D., AEP
2 Although working in an office environment might seem like it should be risk free, there are still opportunities for workers to become injured or to develop illnesses. A company that is proactive in eliminating risks and hazards can reduce the likelihood of injuries and illnesses occurring. One way to do this is to embrace ergonomics. Ergonomics studies the relationship between people and their working environment. It is concerned with fitting the job to the worker, not the worker to the job. In this respect, ergonomics plays an important role in ensuring that the risk factors associated with developing musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are recognized and eliminated. MSDs are injuries and disorders of the muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, joints, cartilage, and spinal discs. Examples of physical signs associated with MSDs are decreased range of motion or grip strength, and examples of physical symptoms are numbness, burning, pain, tingling, cramping, and stiffness. The Need to Reduce MSDs Despite an overall decrease in the number of MSDs occurring each year, they still account for one-third of all lost workday injuries and illnesses (BLS, 2003; Chao, 2002). MSD cases in 2001 accounted for 522,500 lost workday cases with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) having the highest median days (25) away from work (BLS, 2003). Data collected by the California Department of Health Services found that of those who had been diagnosed with CTS, 49 percent reported using a computer (NIOSH, 2000). Specifically, injuries and illnesses caused by typing or key entry resulted in a median of 16 days away from work (BLS, 2003). What s more, MSDs cost businesses $15 to $20 billion dollars in workers compensation costs each year. Indirect costs may run as high as $45 to $60 billion dollars (OSHA, 2000). The average total cost per claim for a cumulative trauma disorder is $15,301, and the average cost per claim for a carpal tunnel injury is $16,308 (NSC, 2002). MSDs, Risk Factors, and Work Association Reviews of epidemiological research have provided reliable evidence that there is an association between MSDs and certain work environment risk factors. The probability of an MSD occurring is even greater when there are high levels of exposure and when individuals are exposed to a combination of more than one risk factor (Bernard, 1997; NRC, 2001). Specific work-related risk factors that have been identified as causing MSDs are: Awkward, deviated, or static postures Excessive force Highly repetitive work Contact stress or pressure Vibration Environmental factors cold or hot temperature extremes, noise, lighting, etc. Evidence has also been found that factors such as age, gender, smoking, physical activity, and obesity can be related to the development of MSDs. Nonoccupational activities might also increase the risk for developing MSDs because an individual is continuing exposure to risk factors for longer periods of the day (Bernard, 1997; NRC, 2001). That being said, it is a reality that people are exposed to risk factors at work that could result in developing MSDs. It is important to be able to identify those risk factors in order to reduce or eliminate workers exposure to them. MSDs and the Office Environment Parts of the body commonly affected by MSDs are the eyes, neck, shoulders, arms, wrists, hands, fingers and thumb, back, and legs. Several epidemiologic studies of physical exposures (force, repetition) and psychosocial exposure (perceived stress, job demands) have found a relation between computer-related tasks and the development of MSDs (NRC, 2001). In one study, 20 to 25 percent of employees who performed data entry tasks had almost daily discomfort in the upper torso (Sauter, et al., 1991). Besides discomfort in the upper torso, computer users are experiencing more vision-related symptoms as the time they spend on computers continues to rise. It has been reported that 50 percent or more of individuals who use computers experience at least occasional eye strain (Lim, et al., 1998). Additionally, these studies have found the development of MSDs by computer users to be partially explained by user posture, workstation ergonomics, repeated work measurements, and keyboard and monitor positioning. (Sauter, et al., 1991; Bergqvist, et al., 1995). 2
3 Being proactive and using ergonomic principles to design workstations and select furniture from the outset of a project is the most cost-effective approach companies can take to reduce MSDs in the work environment. However, sometimes a company must take a reactive approach to ergonomics when workers develop MSDs. The table that follows identifies and discusses some of the MSDs that are commonly experienced in the office environment and identifies commonly recommended preventive measures that may help alleviate a worker s symptoms. Fortunately, solutions to ergonomic problems in the workplace are quite often simple and inexpensive (Bellingar, 2001). Workstation Seating Provide ergonomic chair or stool. Ensure chair is properly adjusted. Worksurfaces and Workstation Layout Properly adjust worksurface height. Position input devices at approximately the same height and distance from the user as the keyboard. Position supplies and equipment within easy reach. Lay out workstation to reduce or eliminate reaching above the shoulder. For example, don t place overhead storage units behind computer monitors. Ensure workstation has proper task lighting to reduce eye strain. Computer Monitors Ensure the top line of the screen is slightly below eye level with the user in an upright posture. This may be different for individuals that wear bifocals/trifocals. Ensure that the monitor is placed between 18 and 30 inches from the user. Provide a flat-panel monitor for work surfaces that are less than 30 deep. Reduce glare on the monitor screen. Keyboards Place keyboard directly in front of the user. Ensure keyboard or keyboard tray is at the appropriate height and angle for the user. Input Devices (Mouse/Trackball/ Touch Pad) Place the input device directly to the side of the keyboard. Ensure user s mouse is clean. Workstation Accessories Provide document holders. Provide footrests. Provide telephone headsets. Work Practices and Tasks Encourage individuals to vary tasks. Ensure individuals take breaks this is important for the eyes as well as the body. Laptop Computers Provide an external keyboard and mouse or monitor when using a laptop computer in the office. Conclusion Embracing ergonomics and making ergonomic changes to the work environment will improve the safety and health of workers, as well as reduce the company s costs and productivity or quality issues. Being able to recognize the risk factors workers can be exposed to in the work environment and the resulting MSDs that can develop will go a long way toward ensuring that workers do not develop work-related MSDs. However, recognizing them is just one step in the process. Evaluating workstations to determine which risk factors users are being exposed to, making the necessary changes, and training workers in how to adjust furniture and accessories cannot be overlooked. It s also important to consider the differences between people so that a proactive approach to ergonomics is taken when designing workstations and purchasing furniture and equipment. The following table has been designed to help identify commonly recommended preventive measures that may aid in alleviating a worker s symptoms. It is not meant to be used as a tool to diagnose a musculoskeletal disorder. Anyone suffering from symptoms should seek medical attention from a physician. At any time, if an individual continues to experience discomfort after changes have been made to their workstation, or if you are unsure how to best apply these suggestions to the work environment, please consult an ergonomist. 3
4 Disorder (Body Part Affected) Bursitis (Joints) Bursitis Shoulder (Shoulder/Upper Arm) Description Symptoms Contributing Factors Commonly Recommended Preventive Measures filled sac beneath the tendons (bursa). of the bursa, located in the shoulder between the tendons and the head of the humerus bone. Pain and stiffness aggravated by movement. Pain and stiffness aggravated by movement. Injury or overuse during work or play. Often occurs in individuals who are poorly conditioned, have bad posture, or use the affected limb in an awkward posture. Arm elevation, adduction, and rotation. Reduce or avoid the activity that caused the issue. Use proper positioning during the activity to prevent reoccurrence. Reduce work done above shoulder level. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (Hand/Wrist) Compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel of the wrist. Numbness, tingling, and pain in the wrist, thumb, index, middle the little finger. Early symptoms often wake people in the middle of the night. May also include swelling, weakness or clumsiness in the hand. Rapid, often repeated finger movements, excessive wrist deviations, excessive or repeated forceful pinching and grasping. Swelling from adjacent problems may also aggravate or bring on carpal tunnel syndrome. Reduce or eliminate repetitive work, wrist deviations, and forceful pinching and grasping. Avoiding or reducing the activity that is causing the symptoms often alleviates symptoms in mild cases. Computer Vision Syndrome (Eyes) Eye and vision problems related to near work, experienced during or related to computer use. Eyestrain, blurred near or distant vision, headache, dry or irritated eyes, neck or back aches, light sensitivity, or double vision. Improper workplace conditions. Work habits. Vision characteristics. Make a conscious effort to blink while working and to take breaks away from your work. Refer to Dry Eye Syndrome for specifics related to it. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (Elbow/Ring and Little Fingers) Compression of the ulnar nerve below the notch of the elbow. Often occurs in combination with medial epicondylitis. Numbness, tingling and pain in the ring and little fingers. May include clumsiness and weakness in the hand. Also often results in elbow pain on the inside of the arm. Resting the elbow on hard surfaces or sharp of the elbow creating tension on the nerve. Avoid or reduce contact stressors or prolonged pressure on the nerve. Avoid direct trauma to the nerve. 4
5 DeQuervain's Disease/ Tenosynovitis (Wrist and Forearm) Dry Eye Syndrome (Eyes) Epicondylitis Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer s Elbow) Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Lumbosacral Strain/ Sprain (Spine) Sciatica (Lower Back/ Legs) Tendonitis (Joints) Irritation of the tendons on the side of the wrist which moves the thumb, and at the base of thumb. The decline in the quality or quantity of tears that bathe the eye. Irritation or inflammation of the bumps (epicondyles) on either the outside or inside of the elbow or surrounding tissues. Medial is on the inside of elbow and lateral on the outside of the elbow. Abnormal deviations of alignment that cause compression to the bony structures and tension on muscles and ligaments. Pain along the course of the sciatic nerve, which runs from the lower back down the back of the legs. Inflammation or irritation of a tendon. Tendons attach muscles to bones. Occurs most often in the flexor and extensor tendons of the fingers, thumb, forearm, elbow, or shoulder. Pain and swelling on the side of the wrist and forearm just above the thumb. Dry, red, or irritated eyes, contact lens discomfort, or excessive reflex tearing. Tenderness and pain at the affected site. May also include pain in the forearm muscles. Low back pain and possible pain in the legs. Pain extends down the posterior thigh and lower leg to the sole of the foot and along the lateral aspect of the lower leg to the dorsum of the foot. Symptoms can range from specific aching, stiffness, tightness, and burning sensations to a deep, nonspecific pain. Grasp can be impaired. Combined forceful gripping and hand twisting. Decreased blink rate. High gaze angle. Dry office environment. Unaccustomed strenuous activity or excessive stress of the forearm muscles or tendons that bend or straighten the wrist and hand. Faulty alignment, standing for long periods, unguarded forward bending, sudden forceful movement. Also poor conditioning, improper use, obesity, and smoking. Pressure on one or more of the nerve roots contributing to the sciatic nerve. Mechanical factor of compression or tension. Pain often occurs following an unusual movement or exertion that causes a tear in one or more of the intevertebral discs. Injury or overuse during work or play. Often occurs in individuals who are poorly conditioned, have bad posture, or use the affected limb in an awkward posture. Reduce force to hands. Keep hands in neutral postures. Take a break every 30 minutes and look 30 feet away for 30 seconds. Reduce or avoid activities that require use of the flexor muscles in a bending motion or grasping with the hand. Reduce static loading, carrying, manual material handling, and poor back postures. When lifting, use correct lifting and moving techniques and get help if an object is too heavy or an awkward size or shape. Reduce or avoid manual material handling. Avoid lifting and twisting at the same time. Avoid sitting in a slouched posture. Reduce or avoid the activity that caused the issue. Use proper positioning during the activity to prevent reoccurrence. 5
6 Tendonitis (Elbow) Tendonitis (Wrist) Tension Neck Syndrome (Neck) Elbow tendon inflammation. Inflammation and thickening of the tendons in the wrist. Irritation of the levator scapulae and trapezium, all muscles of the neck. Causes tightening of the muscles in the neck. See tendonitis. See tendonitis. Neck stiffness as well as headaches. Headaches are often described as a pressure sensation around the head. Pain may build and intensify at the end of day. Repetitive forceful exertions of forearm, rotations around elbow joint. Forceful ulnar deviation and thumb pressure, repetitive wrist motion, forceful wrist extension, and pronation. Lateral, static movement of the head and neck flexion or extension of the neck. Reduce hand fasteners. Reduce repetitions, poor postures, and forceful motions. Ensure proper neck postures, correct working heights, and adjust visual cues. 6
7 References A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Fact Sheet. Available: patient_education/6564/carpal_tunnel_ syndrome.html A Patient s Guide to DeQuervain s Tenosynovitis. Fact Sheet. Available: patient_education/6454/de_quervains_ tenosynovitis.html Anshel, J. (March, 2001). Visual Ergonomics in the Workplace. Presentation - Applied Ergonomics Conference, Orlando, Florida. Bellingar, T.A. (2001). Common Musculoskeletal Disorders. (Available from Haworth, Inc., One Haworth Center, Holland, MI 49423). Bergqvist, B., Wolgast, E., Nilsson, B., Voss, M. (1995). Musculoskeletal disorders among visual display terminal workers: Individual, ergonomic, and work organizational factors. Ergonomics, 38(4), Bernard, B.P. (Ed.). (1997). Musculoskeletal Disorders and Workplace Factors: A Critical Review of Epidemiologic Evidence for Work- Related Musculoskeletal Disorders of the Neck, Upper Extremity, and Low Back [DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 97B141]. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Available: Bureau of Labor Statistics [BLS]. (2003, March 27). Lost Worktime Injuries and Illnesses: Characteristics and Resulting Days away from work, 2001 (Document No. USDL ). Washington, DC: Department of Labor. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Fact Sheet. Available: html Chao, E.L. (2002, December 19). Statement by U.S. Secretary of Labor Elaine L. Chao on 2001 Workplace Injury and Illness Rates (OSHA News Release USDL ). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Labor. Available: www. osha.gov Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. Fact Sheet. Available: htm DeQuervain s Tendinitis. Fact Sheet. Available: hw008.htm Lateral epicondylitis. Fact Sheet. Available: public/patient_education/6472/lateral_ epicondylitis_tennis_elbow.html Lim, S., Sauter, S.L., & Schnorr, T.M. (1998). Occupational health aspects of work with video display terminals. In Rorn, W.N. (Ed.), Environmental and Occupational Medicine (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers. Medial epicondylitis. Fact Sheet. Available: patient_education/6473/medial_ epicondylitis_golfers_elbow.html Musculoskeletal Disorders Anatomy of an Injury. UCLA Ergonomics. Available: Anatomy.html National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health [NIOSH]. (2000). Worker Health Chartbook, 2000 (DHHS [NIOSH] Publication Number ). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. National Research Council [NRC] and the Institute of Medicine. (2001). Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace: Low Back and Upper Extremities. Panel on Musculoskeletal Disorders and the Workplace. Commission on Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. Available: National Safety Council [NSC]. (2002). Injury Facts, 2002 edition, Itasca, IL: National Safety Council. Occupational Safety and Health Administration [OSHA]. (2000). Ergonomics: The Study of Work, Revised Edition (Publication No. 3125). Washington, DC: Department of Labor. Available: Sauter, S.L., Schleifer, L.M., Knutson, S.J. (1991). Work posture, workstation design and musculoskeletal discomfort in a VDT data-entry task. Human Factors, 22(2), Tendinitis/Bursitis. Fact Sheet. Available: factsheets/diseases_and_conditions/ index.asp Tennis Elbow (Lateral epicondylitis). Fact Sheet. Available: hw/hw014.htm Tetro, A.M. and Pichora, D.R. (2000). Cubital Tunnel Syndrome and the Painful Upper Extremity. Available: literature/cubitaltunnelsyndrome/ cubitaltunnelsyndrome.html 7
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY
 CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Work Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Upper Extremity Disorders Carpel tunnel syndrome Cubital tunnel syndrome Thoracic outlet syndrome Raynaud s syndrome (white finger) Rotator cuff syndrome DeQuervain
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
13/02/2011. Ergonomics
 13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
13/02/2011 Ergonomics Workplace Safety Electrical Safety Medical & First Aid Lockout/Tag-out Confined Space Asbestos Control Fire Prevention Personal Protective Equipment Hazard Communication Chemical
Ergonomics in the Laboratory
 instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
Maine. Video Display Terminal Law. Training Program SAFE345
 Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics. WSU-TFREC Safety Training
 Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents
 Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Strains and Sprains. Signs and Symptoms of MSI
 Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Strains and Sprains Strains and sprains (known as musculoskeletal injuries) are the most common type of workrelated injury. Musculoskeletal injury (MSI) is a term used to describe an injury of the muscles,
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST
 PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job
 Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Ergonomics Keeping the Worker on the Job Job Site Analysis WorkRisk Analysis WorkTask Analysis WorkStation Analysis David Raptosh, MA, OTR/L Regional Director of WorkStrategies Job Site Analysis - Identify
Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results. Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC)
 Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC) www.ohiobwc.com Analysis of Injury Data Nineteen organizations received safety grants to incorporate
Office Ergonomics: Best Practices and Results Mike Lampl, MS, CPE Ohio Bureau of Workers Compensation (BWC) www.ohiobwc.com Analysis of Injury Data Nineteen organizations received safety grants to incorporate
Ergonomics in Sonography
 Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics in Sonography Marissa Pentico, MS, OT/L Duke Ergonomics Division Occupational and Environmental Safety Office Janet Ellis, RT(R), RDMS, RVT Duke Radiology Ultrasound What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1
 Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
2/28/2017. EMC Insurance Companies Risk Improvement Department. Ergonomics for School Districts. Objectives. What is Ergonomics?
 Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics for School Districts February 28, 2017 Dave Young, CSP EMC Insurance Companies Objectives Define ergonomics and its effect on the workplace Discuss ergonomic risk factors Review the preferred
Ergonomics 101. Presented by: Macomb Benefits
 Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Muscular Skeletal Disorders
 Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
Alabama Department of REHABILITATION SERVICES "for Alabama's children and adults with disabilities" Muscular Skeletal Disorders Michael Papp, MSE Muscular Skeletal Disorders What are MSDs? Muscles Nerves
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
Ergonomics Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa (515) Copyright
 2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
2408 Wanda Daley Drive Ames, Iowa 50011-3602 (515) 294-5359 www.ehs.iastate.edu Copyright Reviewed 2016 2 Ergonomics Directory of Service and Emergency Providers Services Environmental Health and Safety
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Ergonomics in General Industry
 Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomics in General Industry Any job requires physical movement Some tasks may be repetitious and may require you to stand or sit for extended periods Jobs in the industrial environment can be physically
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations
 Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries. Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist
 Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Risk Factors and Control Measures for Musculoskeletal Injuries Presented by: Gina Vahlas, Ergonomist Chloe Eaton, Ergonomist Agenda Musculoskeletal Injuries Risk factors Risk controls Tools and resources
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop
 Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc
 Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
BOHS-Series. Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
ERGONOMICS in Office.
 ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
ERGONOMICS in Office ก ก. ก What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics ก ก ก ก. ก ergonomic ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก ก Static vs Dynamic muscular effort ก ก vs. ก ก Dynamic Effort Static Effort What are the risks of ignoring
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs
 KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
KEEPING IRONWORKERS HEALTHY: ERGONOMICS AND WMSDs Funded by: With assistance from: WMSDs are preventable! 1 This training is dedicated to the memory of 2 GOALS OF THIS CLASS You will understand: What WMSDs
Feel Better. Stanford University ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE. USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better.
 Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
OPNAVINST G 30 Dec 05
 Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Courtesy of your source for the best ergonomic office furniture.
 Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS)
 Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
The Reasons We Experience Pain
 Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Pain signals can originate in the skin, bone, muscles or nerves. We have all experienced aches and pains from daily activities, work activities, sports activities or accidents and trauma. Our bodies have
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS
 Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
Ergonomics 101: CREATING A PLAYBOOK FOR WORKSTATION ANALYSIS Andy Litchfield Loss Prevention Consultant Gibson Presentation Objectives What Is Ergonomics? What Does OSHA Say? Identifying Problems Hierarchy
To educate employees that they share in the responsibility for their comfort and prevention of injury.
 It is the County of Fresno's policy to provide its employees with a safe and healthy workplace. This handbook reflects General Industry Safety guidelines for safe workstation arrangements for employees
It is the County of Fresno's policy to provide its employees with a safe and healthy workplace. This handbook reflects General Industry Safety guidelines for safe workstation arrangements for employees
Ergonomics. MSD Injury Prevention
 Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
Ergonomics MSD Injury Prevention Ergonomics Definition The International Ergonomics Association offers a very comprehensive definition: The scientific discipline concerned with the understanding of interactions
Adjust the chair height so that your feet rest comfortably on the floor, footrest or foot ring.
 Laboratory ergonomics Some tasks performed in research laboratories can lead to joint and muscle strains if done for prolonged periods. The following tips can help you to work effectively and reduce fatigue
Laboratory ergonomics Some tasks performed in research laboratories can lead to joint and muscle strains if done for prolonged periods. The following tips can help you to work effectively and reduce fatigue
Office Ergonomics OSHA Resources. Risk Factors for Developing MSDs taken from OSHA voluntary guidelines. Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Setting up Your Home Office
 Setting up Your Home Office The home office is becoming more and more prevalent. Even those who do not work from home on a regular basis have computer workstations set up in the home for personal activities.
Setting up Your Home Office The home office is becoming more and more prevalent. Even those who do not work from home on a regular basis have computer workstations set up in the home for personal activities.
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics
 Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
Enhancing Safety Through Ergonomics Targeting Risk Factors Definition of Risk Factors: Actions or conditions found to contribute to worker discomfort or development of Musculoskeletal Disorders MAIN RISK
About Humanscale Consulting Service Philosophy Engage Evaluate Plan Implement Measure Support
 About Humanscale Consulting Humanscale Consulting assists organizations with the development and implementation of cost effective ergonomics programs. Our research based training and assessment programs
About Humanscale Consulting Humanscale Consulting assists organizations with the development and implementation of cost effective ergonomics programs. Our research based training and assessment programs
Title: Ergonomics Program Date: July 7, 2008 Revision No.: 0 Page 1 of 17 Prepared by: Darlene Necaster
 Revision No.: 0 Page 1 of 17 I. PURPOSE SUNY Geneseo s ergonomics program has been implemented to reduce the number and severity of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) caused by exposure to hazards in the
Revision No.: 0 Page 1 of 17 I. PURPOSE SUNY Geneseo s ergonomics program has been implemented to reduce the number and severity of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) caused by exposure to hazards in the
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness
 Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
Ergonomics and Risk Factor Awareness PART 1 Objectives To gain an understanding of: What is ergonomics How cumulative trauma disorders develop Ergonomic risk factors Controlling risk factors To gain an
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
Proper Workstation Setup
 Proper Workstation Setup A Step by Step Guide to help you organize your workstation and reduce the risk of injury Step 1 Review Work Habits Working in a stationary position for long periods will increase
Proper Workstation Setup A Step by Step Guide to help you organize your workstation and reduce the risk of injury Step 1 Review Work Habits Working in a stationary position for long periods will increase
Carpal tunnel syndrome
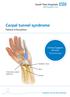 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Computer Ergonomics. Static Efforts
 Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS
 DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
Ergonomics Seminar. Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller
 Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Environmental Health & Safety
 Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
OFFICE ERGONOMICS SELF-ASSESSMENT
 This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
Addressing the Root Cause of Preventable Injuries
 Addressing the Root Cause of Preventable Injuries Ergonomic Consultants of Indiana 11595 N. Meridian Street Suite 140 Carmel, IN 46032 www.eci-in.com Presented by: David Verdeyen MS, ATC/L CEAS II Ergonomic
Addressing the Root Cause of Preventable Injuries Ergonomic Consultants of Indiana 11595 N. Meridian Street Suite 140 Carmel, IN 46032 www.eci-in.com Presented by: David Verdeyen MS, ATC/L CEAS II Ergonomic
ERGONOMIC ASSESSMENT TOOL. Eyes
 This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
Central Office Ergonomics. Marie Robinson SBC Communications
 Central Office Ergonomics Marie Robinson SBC Communications Wire Stripping Use neutral wrist posture while stripping wire Use minimal force on your hands while wire stripping Keep right hand neutral while
Central Office Ergonomics Marie Robinson SBC Communications Wire Stripping Use neutral wrist posture while stripping wire Use minimal force on your hands while wire stripping Keep right hand neutral while
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
Regulatory Requirements
 Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. 5th Edition
 Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
Prepared by the Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety 5th Edition Summary Ergonomics deals with the compatibility between workers and their work. Work is made up of the work environment, workstations,
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre
 Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
Deborah Ruediger, ASAR, DipHlthSc, MHlthSc Manager Non-Invasive Cardiology Lab Heart Centre King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Centre 1 No Disclosures 2 Musculoskeletal Injury (MSI) refers to damage
PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY
 PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY Tobey Village Office Park 140 Office Park Way Pittsford, NY 14534 V: (585)370-7180 www.grpt.com
PROPER ERGONOMICS HOW TO AVOID OVERUSE INJURIES GRETCHEN ROMAN, PT, DPT GREATER ROCHESTER PHYSICAL THERAPY Tobey Village Office Park 140 Office Park Way Pittsford, NY 14534 V: (585)370-7180 www.grpt.com
Repetitive Upper Limb Tasks. Introductions. ' Crown Copyright Health & Safety Laboratory. 1. Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist.
 Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
Repetitive Upper Limb s Dr Lanre Okunribido: HSL Ergonomist Introductions Sessions 1. Why repetitive upper limb tasks? 2. Common Upper Limb Disorders (ULD) and injuries? 3. 4. Introduction to the ART tool
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
BACK SPRAINS AND STRAINS FIRST AID FOR MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES This information sheet is designed to increase your awareness of factors that can contribute to the formation of Musculoskeletal Injuries
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Work Pain & MSD Prevention in the Office. from. SmartCare Physical Therapy
 from. SmartCare Physical Therapy Work Pain & MSD Prevention in the Office Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Doctor of Physical Therapy Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright 2017 Lauren
from. SmartCare Physical Therapy Work Pain & MSD Prevention in the Office Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Doctor of Physical Therapy Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright 2017 Lauren
OFFICE SAFETY Horizon Drive SE Grand Rapids, MI FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 OFFICE SAFETY 2660 Horizon Drive SE Grand Rapids, MI 49546 800-842-0466 www.safetyontheweb.com FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside Overview 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c
OFFICE SAFETY 2660 Horizon Drive SE Grand Rapids, MI 49546 800-842-0466 www.safetyontheweb.com FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside Overview 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist
 Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Ergonomics: Why do workers get injured? Presented by: Steve Bilan Ergonomic Specialist What do you know about Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the study of designing equipment and devices that fit the human body,
Functional Well-Being. Neck, Shoulders and Wrist
 Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
Functional Well-Being Neck, Shoulders and Wrist 1 Neck Definition and Structure Your neck (cervical spine) is made up of 7 vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. 2 Causes of Neck Pain
Learning Objectives ERGO <> NOMICS. Objectives of Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 History of Ergonomics COMPUTER ERGONOMICS AND WORKSTATION DESIGN Presented by: Janet DeLapp, MS, CDMS, CPE Occupational Ergonomist Celeste McLaughlin, BA, CPT www.solutionsnw.com The science was used before
History of Ergonomics COMPUTER ERGONOMICS AND WORKSTATION DESIGN Presented by: Janet DeLapp, MS, CDMS, CPE Occupational Ergonomist Celeste McLaughlin, BA, CPT www.solutionsnw.com The science was used before
BioSafety ERGONOMICS. Abigail Overduin Ergonomics Coordinator. Health Promotion Programs
 BioSafety ERGONOMICS Abigail Overduin Ergonomics Coordinator Health Promotion Programs www.hr.ubc.ca/health/ergonomics WorkSafe BC Statistics (2010): Research Labs Other 59% Injury Cost RSI 16% Overexertion
BioSafety ERGONOMICS Abigail Overduin Ergonomics Coordinator Health Promotion Programs www.hr.ubc.ca/health/ergonomics WorkSafe BC Statistics (2010): Research Labs Other 59% Injury Cost RSI 16% Overexertion
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville
 Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
Ergonomic Risk Factors Resolved in Microelectronics Shop at Naval Air Station Jacksonville Ergonomics is the science of fitting the work task to the worker, instead of requiring the worker to adapt to
