SUMMMARY INTRODUCTION
|
|
|
- Ellen Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article EVALUATION OF BOSTON QUESTIONNAIRE APPLIED AT LATE POST-OPERATIVE PERIOD OF CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME OPERATED WITH THE PAINE RETINACULATOME THROUGH PALMAR PORT Lia Miyamoto Meirelles 1, João Baptista Gomes dos Santos 2, Luciana Leonel dos Santos 3, Marco Aurelio Branco 4, Flavio Faloppa 5, Vilnei Mattioli Leite 6, Carlos Henrique Fernandes 7 SUMMMARY Between the years of 1995 and 1998, 112 surgeries were performed for treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) using the technique of palmar incision employing the Paine retinaculum. With the objective of analyzing results in the long-term, the patients were called for review. Forty four patients returned. From these, three patients were excluded due to associated diseases, thus resulting in a total of 53 hands assessed. Here we present the results of the subjective evaluation achieved by applying a self-assessment test called Boston questionnaire. This questionnaire consists of questions evaluating symptoms severity and functional status at the moment of its application. By applying this questionnaire, we found a score of 1.41 ± 0.57 for symptoms severity and of 1.59 ± 0.93 for functional status. As this questionnaire was not applied at the pre-operative period for those patients assessed, its scores were thus compared to those found in pertinent literature. The achieved results show that post-operative scores are similar to those described in literature, even when reported in different postoperative follow-up times, thereby concluding that when symptoms are improved, the Boston questionnaire is sensitive to that clinical change. Keywords: Questionnaires; Carpal tunnel syndrome; Disability evaluation. INTRODUCTION Carpal tunnel is the anatomical region where flexor tendons of fingers and the median nerve are found. Tunnel s roof is formed by flexors retinaculum, also called carpal transverse ligament. The retinaculum is a fibrous band, mm thick and 3 4 cm large, immediately above the median nerve. The carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is characterized by median nerve compression on the area in which it crosses the carpal region. Compression may occur due to a reduction of tunnel s inner diameter or due to an increased volume of the structures comprised in it. Anatomical studies show that the narrowest region of the tunnel is distal to the level of the hamate hamulus and that during wrist flexion, nerve compression occurs through the proximal margin of flexors retinaculum (1,2). Many publications about CTS surgical treatment report excellent results and low complication rates (3,4), while others report many kinds of complications, such as the recurrence of the carpal tunnel syndrome (5,6,7). In the last few years, an increasing use of endoscopic methods for carpal tunnel release is noticed, intending to reduce morbidity and hasten the return to work (8,9). Because there are many treatments and surgical techniques, it was required to develop studies evaluating those results. Among the several instruments proposed, the Boston questionnaire was developed, designed Study conducted at the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Federal University of São Paulo UNIFESP. Correspondences to: Avenida Leôncio de Magalhães 1021 Jardim São Paulo São Paulo - Cep: emeirelles@directnet.com.br 1 Physical Therapist, expert in hand therapy, Medical College, USP. 2 Master, PhD, Head of the Discipline of Hand and Upper Limb Surgery, UNIFESP. 3 Resident Doctor of the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, UNIFESP. 4 Resident Doctor of the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, UNIFESP. 5 Chairman of the Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, UNIFESP. 6 Full Professor, Head of the Discipline of Hand and Upper Limb Surgery, UNIFESP. 7 Master, PhD, Doctor of the Discipline of Hand and Upper Limb Surgery, UNIFESP. Received in: 07/25/05; approved in:09/29/05 126
2 to be applied in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome, with the purpose of evaluating the severity of symptoms and the degree of manual skill (10). This evaluation instrument was recognized as reproducible, valid, with internal consistency and able to respond to clinical changes, with a transcultural adaptation being performed and validated in our country by means of a study conducted at UNIFESP in 2003 (11). The objective is to evaluate Boston questionnaire applied at the late postoperative period of carpal tunnel syndrome operated by means of Paine s retinaculatome through palmar port. MATERIALS AND METHODS The present material comprehends 44 patients, totaling 57 hands submitted to surgical release of the carpal tunnel through palmar port and Paine retinaculatome, with follow up of at least 5 years postoperatively. Regarding related diseases, it was observed that 3 (5.2%) patients had other diseases such as stroke, AR and scleroderma, which were excluded in order to not to cause bias in the Order # Age Gender Dom. Hand Affected hand Oper. Hand Table 1 Patients Data. Surgery Date F-up time (months) 1 62 F R Bilateral R 04/03/ F L Bilateral L 01/04/ F R Bilateral R 26/ F R Bilateral L 30/06/ F R Bilateral L 17/07/ F R Bilateral R 26/09/ F R R R 29/09/ F R R R 02/10/ F R Bilateral R 17/10/ F R R R 14/11/ F R Bilateral R 20/11/ F R Bilateral L 19/12/ F R Bilateral R 22/01/ F Bilateral Bilateral R 24/01/ F Bilateral Bilateral L 09/02/ F R Bilateral L 11/03/ F R Bilateral R 12/03/ F R Bilateral L 12/03/ F R Bilateral L 15/03/ F R Bilateral R 27/03/ F R Bilateral R 16/04/ F R Bilateral L 17/04/ F R Bilateral R 08/05/ F R Bilateral R 18/06/ F R Bilateral R 21/06/ F R R R 26/06/ F R Bilateral R 10/07/ F R Bilateral L 19/07/ F R Bilateral L 22/07/ F R Bilateral L 02/08/ F R Bilateral R 13/09/ F R Bilateral R 07/10/ F R R R 09/10/ F R Bilateral R 09/10/ F R Bilateral R 28/10/ F R Bilateral R 20/11/ F R Bilateral R 27/01/ F R Bilateral R 31/01/ F R Bilateral L 19/02/ F R Bilateral L 28/02/ F Bilateral Bilateral R 18/03/ F Bilateral Bilateral R 19/03/ F Bilateral Bilateral L 22/04/ F R Bilateral L 06/05/ F R Bilateral R 21/05/ F R R R 07/07/ F R Bilateral R 30/07/ F R Bilateral R 09/10/ F R Bilateral R 14/10/ F R Bilateral L 14/10/ F R Bilateral R 09/12/ M R Bilateral R 16/12/ F R Bilateral L 03/02/98 80 results, therefore, with 41 patients and 53 hands being analyzed. Time elapsed from surgery to evaluations ranged from 80 to 117 months, with an average of 97 months. In Table 1, data concerning those 41 patients are described and chronologically listed from surgery day, according to the order number, age in years, gender, dominant side, affected side, operated side, surgery date and current follow-up time in months. The evaluation routine consisted of calling patients by telegram or phone. Reaching to the infirmary, the patient was re-evaluated by the doctor. The Boston questionnaire, Annex 1, properly translated and validated into Portuguese, was applied to all patients returning for evaluation. The Boston questionnaire is self-applied and evaluates the severity of symptoms and the functional status of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. The symptoms severity scale (SSS) evaluates symptoms regarding severity, frequency, time and kind. The functional status scale (FSS) evaluates how the syndrome affects daily life. Questions concerning symptoms severity scale are composed of
3 questions addressing: pain intensity during daytime and nighttime, time of pain during the day, dormancy, weakness, tingling sensation at night, frequency of that night tingling sensation, and skill. Each question has five answers numbered from 1 to 5, arranged in an increasing order of symptoms severity. Therefore, 1 means no symptoms, 2 mild symptoms, 3 moderate symptoms, 4 intense symptoms, and 5 severe symptoms. Questions concerning functional status are composed of 8 questions, where each one corresponds to a functional activity (writing, buttoning clothes, holding a book while reading, holding a telephone hang, housekeeping, opening a glass vial cap, carrying market bags, bathing and dressing). Each activity has five difficulty degrees, labeled according to a table shown at the end of the question, where degree 1 corresponds ANNEX 1 SELF-EVALUATION PROTOCOL BOSTON PROTOCOL Name:... RGHSP:... Hand: ( ) Right ( ) Left Evaluation Date:.../.../... Surgery Date:.../.../... THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS REFER TO YOUR SYMPTOMS WITHIN A TYPICAL PERIOD OF 24 HOURS, DURING THE LAST TWO WEEKS. (Choose one answer in each question) 1) How strong is the pain on your hand or wrist at night? 1- I feel no pain on hand or wrist at night. 2- little pain 3- moderate pain 4- intense pain 5- severe pain 2) How many times did your hand or wrist pain wake you up in a typical night for the last two weeks? 1- never 2- once 3- twice or three times 4- four to five times 5- more than five times 3) Do you usually feel hand or wrist pain during the day? 1- I never feel pain during the day 2- I feel little pain during the day 3- I feel moderate pain during the day 4- I feel intense pain during the day 5- I feel severe pain during the day 4) How often do you feel hand or wrist pain during the day? 1- never 2- once or twice a day 3- three to five times a day 4- more than five times a day 5- constant pain 5) In average, how long do daytime pain episodes last? 1- I never feel pain during the day 2- less than 10 minutes 3- from 10 to 60 minutes 4- more than 60 minutes 5- I feel constant pain during the day 6) Do you feel your hand dormant (lost sensitiveness)? 1- no 2- I feel little dormancy 3- I feel moderate dormancy 4- I feel intense dormancy 5- I feel severe dormancy 7) Do you feel weakness on your hand or wrist? 1- no weakness 2- little weakness 3- moderate weakness 4- intense weakness 5- severe weakness 8) Do you feel a tingling sensation on your hand? 1- no tingling sensation 2- little tingling sensation 3- moderate tingling sensation 4- intense tingling sensation 5- severe tingling sensation 9) How strong is dormancy (lost sensitivity) or tingling sensation at night? 1- I never feel dormancy or tingling sensation at night 2- little 3- moderate 4- intense 5- severe 10) How often did dormancy or tingling sensation wake you up during a typical night for the last two weeks? 1- never 2- once 3- twice to three times 4- four to five times 5- more than five times 11) How difficult do you feel in taking and using small objects, such as keys or pens? 1- not difficult 2- a little difficult 3- moderately difficult 4- very difficult 5- severely difficult IN A TYPICAL DAY FOR THE LAST TWO WEEKS, HAVE YOUR HAND OR WRIST SYMPTOMS BROUGHT ANY DIFFICULTY IN PERFORMING THE ACTIVITIES LISTED BELOW? Please, circle the number that best describes your ability to perform the activity. ACTIVITy DEGREE OF DIFFICULTY Writing Buttoning clothes Holding a book while reading Holding the telephone hang Housekeeping Opening a glass vial cap Carrying market bags Bathing and dressing No difficulty... 1 Little difficulty... 2 Moderate difficulty... 3 Intense difficulty... 4 Cannot perform the activity at all due to hands and wrists symptoms... 5 Investigator s opinion:
4 to no difficulty, degree 2 little difficulty, degree 3 moderate difficulty, degree 4 intense difficulty, and degree 5 cannot perform the activity at all due to hands and wrists symptoms. All answers should be concerned to the symptoms within a typical period of 24 hours, for the last two weeks. For the self-appraisal, patients were guided into a room, where they received a copy of the questionnaire. After a brief explanation of what the questions were about and how to answer those questions, patients were left on their own to answer the questionnaire. The patients should answer to the 11 first questions choosing only one alternative. Regarding the last eight questions, they should select the degree of difficulty felt in each activity described, according to the label on the questionnaire itself. In case a patient had both hands operated, two questionnaires should be applied, one for each hand. From answers, two scores were calculated. The symptoms severity score (SSS) refers to the first 11 questions. The functional status score (FSS) refers to the last 8 questions. This calculation is the sum of answers divided by the number of questions. Unanswered questions were excluded from calculation. Answers were listed and analyzed (Table 2). An average of the answers for each question was calculated, aiming a careful analysis of results for each question (Table 3). RESULTS By applying the Boston questionnaire, we found a symptoms severity score (SSS) of 1.41 ± 0.57 and a functional status score (FSS) of 1.59 ± In the analysis by question, the highest averages were found for symptoms severity in questions number 4, 5 and 7 (S4, S5, and S7), and, for functional status, in questions number 5, 6, and 7 (F5, F6 and F7). (Table 3, Graphs 1 and 2). DISCUSSION By analyzing the age group affected, we see that the mean age ranges from 44 years old (12), 46 years old (13), 56 years old (14) and 57 years old (10). In this study group, ages ranged from 45 to 70 years old, with an average of 57. In our study, the incidence of females is higher, as reported in other studies (12,14). The condition affected bilaterally 47 (88.67%) patients, followed by 6 (11.32%) on the right hand, and 0 on the left hand. This order is consistent to findings of other authors (15,16). In comparative studies, postoperative follow-up time using the Boston questionnaire as an evaluation instrument was 1 6 months in a study (14) and 3 6 months in another study (12). Patients follow-up ranged from 80 to 117 months, with an average of 97 months. No long-term follow-up studies were found. Many instruments are used to evaluate the results of carpal tunnel treatment. Among them, the nervous conduction study, symptom inspection, sensitivity test, tweezing and prehension strength measurement, complication rates, pain and skill degree evaluation, return to work and functional ability (17). Studies on carpal tunnel release usually get to outcomes where patients report symptoms relief and functional improvement (18), but, until not so long ago, subjective results were not standardized or properly measured. Quality of life measurement instruments were developed, based on patient s opinion, in order to scientifically evaluate subjective results in a surgical intervention. Initially, generic questionnaires were developed, such as, for example, the SF-36 (short form 36), which consists of 36 questions comprehending physical, mental and social aspects as well as a person s welfare as a whole, with few specific questions. Over time, the need for specific questionnaires became evident. In 1995, a questionnaire was developed to measure upper limb results DASH (Disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand). It consists of 30 items measuring function, symptoms, and quality of life relative to pathologies of the upper limb (19). Among others, we can also find the PRWE (patient-rated wrist evaluation), which consists of 15 questions evaluating pain and functional disability, where the patient evaluates his/ her own ability and degree of domain in personal care, work, housekeeping and leisure. Some authors demonstrated that those scientific me- 129
5 S1 to S11 = symptom 1 to symptom 11; F1 to F8 = function 1 to function 8 Table 2 Answers to Boston questionnaire. BOSTON PROTOCOL S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 1,28 1,3 1,43 1,51 1,55 1,34 1,74 1,32 1,34 1,26 1, ,4 1,45 1,42 1,43 1,75 1,85 2,06 1, Table 3 Answers Averages. 130
6 asurements of a patient s opinion are more sensitive to clinical changes after treatment than data provided by physical examination performed by the surgeon him/herself (17,20,21,23). The Boston questionnaire was employed, which also provided a standardization of those subjective outcomes, due to its reproducibility, coherence, validity and sensitiveness to clinical changes. We noticed that there are scarce studies in literature making a long-term postoperative evaluation employing the Boston questionnaire. In one of the comparative studies, the Boston questionnaire was used to compare electrophysiological results in a carpal tunnel syndrome postoperative follow-up (14). A similar study was published in 2002 by another author (12). Both could not find any correlation between nervous sensitive conduction speed and the Boston questionnaire. One hundred fourteen patients were assessed, by comparing the Katz-Stirrat (25) hand diagram, in which the patient him/ herself marks the areas of symptoms distribution on a diagram, classifying the disease into Classic or Probable, possible and unlikely, with the results of the Boston questionnaire. Patients categorized as Classic or Probable achieved a symptoms severity score higher than the scores for possible and unlikely categories (24). We conducted a comparative study on scores found in other studies, including the results by Levine, regarding postoperative follow-up Graph 1 Analysis of Questions - Symptoms. Graph 2 Analysis of Questions - Functions. EGS periods, using the Boston questionnaire (Table 4). Only three studies meeting the requirements for such comparison were found (10,12,14). When a careful analysis of the questionnaire was performed, we saw that questions concerning the major CTS symptoms such as tingling sensation, nighttime pain, dormancy and skills had lower scores. When the averages for each question were calculated, we found the highest scores concerning symptoms severity for questions related to pain (pain frequency during the day S4, time of pain episodes during the day S5) and muscle weakness (presence of muscular weakness S7), and, concerning the functional status, activities related to strength (housekeeping F5, open a glass vial cap F6, and carry market bags F7). Anyway, scores were overall low, indicating a non-severe picture. During questionnaire application, we observed that the patients were in doubt to answer questions especially regarding pain, because, in the majority of the cases, they experienced other kinds of pain, such as arthrosis, trigger or tendonitis, which could confuse answers. In our study, a lot of difficulty was seen on understanding the labels of the functional status evaluation, requiring the investigator to repeat the explanation many times. Another important difficulty seen was in the moment of evaluating the degree of difficulty for 131 EEF Padua et al. 1,5±0,6 1,5±0,6 Mumcu et al. 2,1±0,7 1,9±1,0 Levine et al. 1,9±1,0 2,0±1,1 Meirelles et al. 1,41±0,59 1,59±0,93 Table 4 Comparison of studies. SSS D.P. EEF D.P.
7 ANNEX 2 COMPARISON BETWEEN BOTH LABELS (A AND B) ACTIVITy DEGREE OF DIFFICULTY Writing Buttoning clothes Holding a book while reading Holding the telephone hang Housekeeping Opening a glass vial cap Carrying market bags Bathing and dressing No difficulty...1 Little difficulty...2 Moderate difficulty...3 Intense difficulty...4 Cannot perform the activity at all due to hands and wrists symptoms...5 A Validated by Campos et al. B - Original by Levine et.al item writing, because, when the dominant hand was not to be evaluated, it was impossible to answer, with two patients leaving the answer in blank and the others giving random answers. In this last question concerning functional status, the questionnaire originally describes the label above each number, while at validation, the label was exhibited at the end of the question, which, in our opinion, made its comprehension difficult (Annex 2). CONCLUSION Patients operated through palmar port technique using the Paine retinaculatome remain happy with their surgical outcomes, even after a long follow-up time, according to the results of the Boston questionnaire. The last portion of the questionnaire was shown to be confused and difficult to understand in what concerns to functional status. REFERENCES 1. Tanzer RC. The carpal - túnel syndrome:a clinical and anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959; 41: Cobb TK; Dalley BK; Posterapo RH,Lewis, RC. Anatomy of the flexor retinaculum. J Hand Surg Am. 1993; 18: Phalen GS.The carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1966; 48: Omer GE Jr. Median nerve compreesion at the wrist. Hand Clin. 1992; 8: Seradge H, Seradge E. Piso-triquetral paqin syndrome after carpal tunnel release. J Hand Surg Am. 1989;14: Zumiotti AV, Ohno PE, Prada FS, Azze RJ. Complicações do tratamento cirúrgico da síndrome do túnel do carpo. Rev. Bras Ortop 1996; 31: KlugeW, Simpson RG, Nicol AC. Late complications after open carpal tunnel decompressiom. J Hand Surg Br. 1996; 21: Agee JM, McCarrol HR, Tortosa RD, Berry DA, Szabo, RM, Peimer CA. Endoscopic release of the carpal tunnel:a randomized prospective multicenter study. J Hand Surg Am. 1992; 17: Chow JCY. Endoscopic release of the carpal ligament: a new techinique for carpal tunnel syndrome. Arthroscopy. 1989; 5: Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, et al. A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symtoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993; 75: Campos CC, Manzano GM, Andrade LB, Castelo A, Nóbrega JAM. Tradução e validação do questionário de avaliação de gravidade dos sintomas e do estado funcional da síndrome do túnel do carpo. Arq Neuropsiq. 2003; 61: Mumcu EF, Heybeli N, Kutluhan S, Demirci S, Kerman M. Assessment of outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome: a com parison of eletrophysiological findings and a selfadministered boston questionnaire. J Hand Surg Br. 2002; 27: You H, Simmons Z, Freivalds A, Kothari MJ, Naidu SH. Relationship between 132 clinical symptom severity scales and nerve conduction measures in carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve. 1999; 22: Padua L, Mondelli M, Reale F, Sicurelli F. Relationship between the self-administered boston questionnaire and eletrophysiological findings in follow-up of surgically-treated carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Br. 2000; 25: Cseuz KA, Thomas JE, Lambert EH, Love JG, Lipscomb PR. Long-term results of operation for carpal tunnel syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966; 41: Paine KWE, Polyzoidis KS.Carpal tunnel syndrome:decompression using the paine retinaculotome. J Neurosurg. 1983; 59: Amadio PC, Silverstein MD, Ilstrup DM, Schleck CD, Jensen LM. Outcome after Colles fracture: the relative responsiveness of three questionnaires and physical examination measures. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21: Glowacki KA, Breen CJ, Sachar K, Weiss AP. Eletrodiagnostic testing and carpal tunnel release outcome. J Hand Surg Am. 1996; 21: Hudak PL, Amadio PC, Bombardier C. The upper extremety collaborative group. Development of na upper extremety outcome measure: the DASH ( disabilities of the arm, sholder, and head (sic) ). Am J Ind Med. 1996; 29: Lohr KN. Advances in health status assessment: overview of the conference. Med Care. 1989; 27 (Suppl.): Katz JN, Gelberman RH, Wright EA, Lew RA, Liag MH. Responsiveness of selfreported and objective measures of disease severity in carpal tunnel syndrome. Med Care. 1994; 32: Atroshi I, Johnsson R, Sprinchorn A. Self administered outcome instrument evaluated in carpal tunnel syndrome. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998; 69: Atroshi I, Breidenbach WC, McCabe SJ. Assessment of the carpal tunnel outcome instrument in patients with nerve-compression symptoms. J Hand Surg Am. 1997; 22: Katz JN, Stirrat CR. A self-administered hand diagram for the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Am. 1990; 15:360-3.
CORTICOID INJECTION AS A PREDICTIVE FACTOR OF RESULTS OF CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.190/11-782201202009 Original Article CORTICOID INJECTION AS A PREDICTIVE FACTOR OF RESULTS OF CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Giselly Veríssimo de Miranda 1, Carlos Henrique Fernandes 1,
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.190/11-782201202009 Original Article CORTICOID INJECTION AS A PREDICTIVE FACTOR OF RESULTS OF CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Giselly Veríssimo de Miranda 1, Carlos Henrique Fernandes 1,
Comparison of the results of open
 1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
1131 Original Article Singapore Med.1 27; 48 (12) : Comparison of the results of open carpal tunnel release and KnifeLight carpal tunnel release Yeo K Q, Yeo E M N Yeo Orthopaedic Centre, Mount Elizabeth
Heecheon You Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802
 PROCEEDINGS of ihe HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 42nd ANNUAL MEETING-1998 841 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CLINICAL SCALES ON SEVERITY OF SYMPTOMS AND ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEASURES ON ABNORMALITY OF NERVE
PROCEEDINGS of ihe HUMAN FACTORS AND ERGONOMICS SOCIETY 42nd ANNUAL MEETING-1998 841 RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN CLINICAL SCALES ON SEVERITY OF SYMPTOMS AND ELECTRODIAGNOSTIC MEASURES ON ABNORMALITY OF NERVE
Responsiveness of the Korean Version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (K-DASH) after Carpal Tunnel Release
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:147-151 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.2.147 Responsiveness of the Korean Version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (K-DASH)
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:147-151 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.2.147 Responsiveness of the Korean Version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand Questionnaire (K-DASH)
Clinical Case Report Competition
 Massage Therapists Association of B.C. Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy June, 2009 Honourable Mention Janet Lee The Effects of Massage Therapy in Pain Management of
Massage Therapists Association of B.C. Clinical Case Report Competition West Coast College of Massage Therapy June, 2009 Honourable Mention Janet Lee The Effects of Massage Therapy in Pain Management of
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION The use of an othosis has been shown to decrease symptoms in carpal tunnel syndrome, but which type of orthosis (cock up or lumbrical) with which type
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) FOCUSED QUESTION The use of an othosis has been shown to decrease symptoms in carpal tunnel syndrome, but which type of orthosis (cock up or lumbrical) with which type
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome)
 A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
A Patient s Guide to Ulnar Nerve Entrapment at the Wrist (Guyon s Canal Syndrome) Introduction The ulnar nerve is often called the funny bone at the elbow. However, there is little funny about injury to
Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: a cost-effectiveness analysis Chung R C, Walters M R, Greenfield M L, Chernew M E
 Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: a cost-effectiveness analysis Chung R C, Walters M R, Greenfield M L, Chernew M E Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
Endoscopic versus open carpal tunnel release: a cost-effectiveness analysis Chung R C, Walters M R, Greenfield M L, Chernew M E Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.7.1095 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1095-1099 Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Korean Version of the Boston Carpal Tunnel
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Musculoskeletal Disorders http://dx.doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2013.28.7.1095 J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 1095-1099 Cross-Cultural Adaptation of the Korean Version of the Boston Carpal Tunnel
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi: /bmj f (published 15 June 2006)
 Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.38863.632789.1f (published 15 June 2006) BMJ Outcomes of endoscopic surgery compared with open surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome among employed patients: randomised
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.38863.632789.1f (published 15 June 2006) BMJ Outcomes of endoscopic surgery compared with open surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome among employed patients: randomised
Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release
 Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Technique Centerline Carpal Tunnel Release Centerline Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgical Set Up The patient is positioned supine on the operating
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a problem that affects the wrist and hand. If you have CTS, tingling and numbness
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP)
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Horng, Y. S., Hsieh, S. F., Tu, Y. K., Lin, M. C., Horng, Y. S., & Wang, J. D. (2011). The comparative effectiveness of tendon and nerve gliding exercises in patients with
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Horng, Y. S., Hsieh, S. F., Tu, Y. K., Lin, M. C., Horng, Y. S., & Wang, J. D. (2011). The comparative effectiveness of tendon and nerve gliding exercises in patients with
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery
 Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
Initial experience with endoscopic carpal tunnel release surgery Craig H. Rabb, M.D., and Todd Kuether, M.D. Division of Neurosurgery, Oregon Health Sciences University, Portland, Oregon; and Portland
carpal tunnel get back to life Patient information about Endoscopic Surgery for the treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 carpal tunnel get back to life Patient information about Endoscopic Surgery for the treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome what is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a medical condition
carpal tunnel get back to life Patient information about Endoscopic Surgery for the treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome what is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a medical condition
TRANSVERSE MINI-INCISION FOR CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 Original Article TRANSVERSE MINI-INCISION FOR CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Marcelo de Pinho Teixeira Alves ABSTRACT Objective: To compare two incisions used for the surgical treatment of CTS: the classic longitudinal
Original Article TRANSVERSE MINI-INCISION FOR CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Marcelo de Pinho Teixeira Alves ABSTRACT Objective: To compare two incisions used for the surgical treatment of CTS: the classic longitudinal
Carpal Tunnel Release
 Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Carpal Tunnel Release Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition in the hand and wrist caused by excessive pressure on the median nerve in the wrist. Compression of the nerve typically causes numbness and tingling
Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Japanese version of the patient-rated elbow evaluation
 J Orthop Sci (2013) 18:712 719 DOI 10.1007/s00776-013-0408-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Japanese version of the patient-rated elbow evaluation Tadamasa Hanyu Mikihiko
J Orthop Sci (2013) 18:712 719 DOI 10.1007/s00776-013-0408-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reliability, validity, and responsiveness of the Japanese version of the patient-rated elbow evaluation Tadamasa Hanyu Mikihiko
Simultaneous Median Radial Nerve Electrical Stimulation Revisited: An Accurate Approach to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis and Severity METHODS
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Simultaneous Median Radial Nerve Electrical Stimulation Revisited: An Accurate Approach to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis and Severity Thaís Rodrigues,* Pablo B. Winckler,* Vitor Félix-Torres,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Simultaneous Median Radial Nerve Electrical Stimulation Revisited: An Accurate Approach to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Diagnosis and Severity Thaís Rodrigues,* Pablo B. Winckler,* Vitor Félix-Torres,
Hand numbness and carpal tunnel syndrome after volar plating of distal radius fracture
 HAND (2011) 6:34 38 DOI 10.1007/s11552-010-9283-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and carpal tunnel syndrome after volar plating of distal radius fracture Angela Wing Hang Ho & S. T. Ho & S. C. Koo & K. H. Wong
HAND (2011) 6:34 38 DOI 10.1007/s11552-010-9283-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and carpal tunnel syndrome after volar plating of distal radius fracture Angela Wing Hang Ho & S. T. Ho & S. C. Koo & K. H. Wong
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release ECTR Christophe MATHOULIN Paris, France Historics Paget, 1854 Putnam, 1893 Hunt, 1909 Marie et Foix, 1913 Recommanded surgical release Learmonth, 1933 First reported release
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Sudqi A. Hamed 1, Falah Z. Harfoushi 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate prospectively the
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE VIA MINI-OPEN WRIST CREASE INCISION: PROCEDURE AND RESULTS OF FOUR YEARS CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Sudqi A. Hamed 1, Falah Z. Harfoushi 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate prospectively the
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Acute Services Division. Information for patients. Carpal Tunnel. Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary
 Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
Acute Services Division Information for patients Carpal Tunnel Physiotherapy Department Glasgow Royal Infirmary Introduction Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) can cause the symptoms of pain, pins and needles
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
eplasty: Vol. 8 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Louisville,
Anatomic Distribution of Sensory Symptoms in the Hand and Their Relation to Neck Pain, Psychosocial Variables, and Occupational Activities
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 2003 by the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 157, No. 6 Printed in U.S.A. DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwf225 Anatomic Distribution
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
British Journal of Rheumatology 1991; 30:468-470 CASE REPORT CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME COMPLICATED BY REFLEX SYMPATHETIC DYSTROPHY SYNDROME BY M.-A. FITZCHARLES AND J.M. ESDAILE Rheumatic Disease Unit, McGill
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Carpal tunnel decompression advice
 Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Externally Applied Forces to the Palm Increase Carpal Tunnel Pressure
 Externally Applied Forces to the Palm Increase Carpal Tunnel Pressure Tyson K. Cobb, MD, Kai-Nan An, PhD, William P. Cooney, MD, Rochester, MN Change in carpal tunnel pressures that result from externally
Externally Applied Forces to the Palm Increase Carpal Tunnel Pressure Tyson K. Cobb, MD, Kai-Nan An, PhD, William P. Cooney, MD, Rochester, MN Change in carpal tunnel pressures that result from externally
Effects of Wrist Splinting for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Motor Nerve Conduction Measurements
 Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences ISSN: 0300-9734 (Print) 2000-1967 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iups20 Effects of Wrist Splinting for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Motor Nerve
Upsala Journal of Medical Sciences ISSN: 0300-9734 (Print) 2000-1967 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iups20 Effects of Wrist Splinting for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Motor Nerve
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Interesting Case Series. The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve
 Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a relatively common complaint in individuals
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. Nerve anatomy. Pathophysiology 6/14/2014. Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Experience at King Hussein Medical Center
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Experience at King Hussein Medical Center Issam A. Dahabra MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To describe the results of the endoscopic carpal tunnel release using the MicroAire Carpal
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Experience at King Hussein Medical Center Issam A. Dahabra MD* ABSTRACT Objective: To describe the results of the endoscopic carpal tunnel release using the MicroAire Carpal
Shared Decision Making
 Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
Deciding what to do about carpal This short decision aid is to help you decide what to do about your carpal. You can use it on your own, or with your doctor, to help you make a decision about what's right
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release A Prospective Study of Functional Outcome
 Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release A Prospective Study of Functional Outcome T Ravindran, MS Ortho, T Sara, FRCS, YC Loh, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, University Malaya Medical Centre, Kuala Lumpur,
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release A Prospective Study of Functional Outcome T Ravindran, MS Ortho, T Sara, FRCS, YC Loh, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics, University Malaya Medical Centre, Kuala Lumpur,
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Revised review: 30/04/2018 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Information for patients Therapy Services Phone no: 01625 661481 www.eastcheshire.nhs.uk @eastcheshirenhs Ref: 11437 Review: 06/2015 Revised review: 30/04/2018 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet. Under review. Page 1
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common problem which affects the hand and wrist. Symptoms are caused
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a common problem which affects the hand and wrist. Symptoms are caused
Carpal Tunnel Release: Analysis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Rehabilitation. Michael Commesso, Nicholas Francisco, and Maritza Rodriguez
 Carpal Tunnel Release: Analysis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Rehabilitation Michael Commesso, Nicholas Francisco, and Maritza Rodriguez PHYT 625: Movement Analysis & Patient/Client Management I Abstract
Carpal Tunnel Release: Analysis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and Rehabilitation Michael Commesso, Nicholas Francisco, and Maritza Rodriguez PHYT 625: Movement Analysis & Patient/Client Management I Abstract
1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)
 Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is an upper extremity disability. It
Midwifery Management Process for Common Health Problems 1. Common Health Problem/Condition: MSK Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is an upper extremity disability. It
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects nerves in the wrist and hand. CTS causes tingling and numbness
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects nerves in the wrist and hand. CTS causes tingling and numbness
Disclosure. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 11/9/15
 Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
Michael S. Bednar, M.D. Chief, Hand Surgery Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery and Rehab Loyola University - Chicago Disclosure No conflicts for this talk Carpal Tunnel Syndrome AKA Corporal tunnel
The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release
 The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release Zlatko Kolic, M.D., Vladimir Micovic, M.D., Gordana Zamolo, Ph.D., Vesna Golubovic, M.D., Ph.D., Miljenko Uravic,
The anatomy of the Berrettini branch: implications for endoscopic carpal tunnel release Zlatko Kolic, M.D., Vladimir Micovic, M.D., Gordana Zamolo, Ph.D., Vesna Golubovic, M.D., Ph.D., Miljenko Uravic,
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique
 Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
Assessment of the Distal Extent of the A1 Pulley Release: A New Technique Ron Hazani, MD, Nitin J. Engineer, MD, Linda L. Zeineh, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, School of Medicine,
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome & Thread Carpal Tunnel Release (TCTR) The Guo Technique. Minimally Invasive Procedure for CTR. Danzhu Guo, MD 10.4.
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome & Thread Carpal Tunnel Release (TCTR) The Guo Technique Minimally Invasive Procedure for CTR Danzhu Guo, MD 10.4.18 CTS has the longest average disability duration among the top
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome & Thread Carpal Tunnel Release (TCTR) The Guo Technique Minimally Invasive Procedure for CTR Danzhu Guo, MD 10.4.18 CTS has the longest average disability duration among the top
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS)
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME (CTS) CTS: why does it matter? Fairly prevalent Early detection may prevent permanent impairment 1 To review: Learning Objectives Signs/symptoms Causes Management prevention treatment
Clinical experience of open carpal tunnel release and Camitz operation in elderly Chinese patients
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical experience of open carpal tunnel release and Camitz operation in elderly Chinese patients SH Wan TC Wong TH Yip FK Ip Objective To report preliminary experience on
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical experience of open carpal tunnel release and Camitz operation in elderly Chinese patients SH Wan TC Wong TH Yip FK Ip Objective To report preliminary experience on
Shohei Omokawa Toshihiko Imaeda Takuya Sawaizumi Toshimitsu Momose Hiroyuki Gotani Yukio Abe Hisao Moritomo Fuminori Kanaya
 J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:551 555 DOI 10.1007/s00776-012-0265-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Responsiveness of the Japanese version of the patient-rated wrist evaluation (PRWE-J) and physical impairment measurements
J Orthop Sci (2012) 17:551 555 DOI 10.1007/s00776-012-0265-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Responsiveness of the Japanese version of the patient-rated wrist evaluation (PRWE-J) and physical impairment measurements
A New Neurological Sign Shows Severity of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Open Journal of Modern Neurosurgery, 2014, 4, 38-42 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmn) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmn.2014.41009 A New Neurological Sign Shows Severity of
Open Journal of Modern Neurosurgery, 2014, 4, 38-42 Published Online January 2014 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmn) http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmn.2014.41009 A New Neurological Sign Shows Severity of
Instrument set for endoscopically assisted decompression of the ulnar nerve. Arthroscopy
 Instrument set for endoscopically assisted decompression of the ulnar nerve Arthroscopy Instrument set for endoscopically assisted decompression of the ulnar nerve Introduction The compression of the ulnar
Instrument set for endoscopically assisted decompression of the ulnar nerve Arthroscopy Instrument set for endoscopically assisted decompression of the ulnar nerve Introduction The compression of the ulnar
How effective is chiropractic for chronic carpal tunnel syndrome?
 How effective is chiropractic for chronic carpal tunnel syndrome? Average improvement following a course of chiropractic care. 0% 25% 50% 75% Data taken from: A randomized controlled (intervention) trial
How effective is chiropractic for chronic carpal tunnel syndrome? Average improvement following a course of chiropractic care. 0% 25% 50% 75% Data taken from: A randomized controlled (intervention) trial
Carpal tunnel syndrome
 Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
Condition Carpal tunnel syndrome Carpal tunnel syndrome This booklet provides information and answers to your questions about this condition. Arthritis Research UK produce and print our booklets entirely
Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia)
 Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia) Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The carpal tunnel is a tunnel found
Carpal tunnel decompression (under local anaesthesia) Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4898 All Rights Reserved 2017. Document for issue as handout. Procedure The carpal tunnel is a tunnel found
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. William T. Grant, MD
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Dr. Grant is a talented orthopedic surgeon with more than 30 years of experience helping people return to their quality of life. He and GM Pugh, PA-C pride themselves
Int J Physiother. Vol 2(3), , June (2015) ISSN:
 Int J Physiother. Vol (), 54-5, June (5) ISSN: 48-86 ABSTRACT Vikranth.G.R Vinod Kumar.K.C Lawrence Mathias Background: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a constellation of symptoms associated with compression
Int J Physiother. Vol (), 54-5, June (5) ISSN: 48-86 ABSTRACT Vikranth.G.R Vinod Kumar.K.C Lawrence Mathias Background: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a constellation of symptoms associated with compression
The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.181 The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:181-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.2.181 The Effect of Distal Location of the Volar Short Arm Splint on the Metacarpophalangeal Joint Motion
Functional Tests to Quantify Recovery Following Carpal Tunnel Release BY ROBERT G. RADWIN, PHD, MARY E. SESTO, PHD, PT, AND STEFAN V.
 2614 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Functional Tests to Quantify Recovery Following Carpal Tunnel Release BY ROBERT G. RADWIN, PHD, MARY E. SESTO, PHD, PT, AND STEFAN
2614 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Functional Tests to Quantify Recovery Following Carpal Tunnel Release BY ROBERT G. RADWIN, PHD, MARY E. SESTO, PHD, PT, AND STEFAN
SUSPECTS THE UNUSUAL. Often-Overlooked Muscles. Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis. Flexor pollicis longus.
 THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
THE UNUSUAL SUSPECTS Often-Overlooked Muscles By Joseph E. Muscolino, DC Sternohyoid, longus colli, and longus capitis Flexor pollicis longus Quadratus femoris 52 massage & bodywork november/december 2016
Influence of compensation status on time off work after carpal tunnel release and rotator cuff surgery: a meta-analysis
 de Moraes et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2013, 7:1 SHORT REPORT Open Access Influence of compensation status on time off work after carpal tunnel release and rotator cuff surgery: a meta-analysis Vinícius
de Moraes et al. Patient Safety in Surgery 2013, 7:1 SHORT REPORT Open Access Influence of compensation status on time off work after carpal tunnel release and rotator cuff surgery: a meta-analysis Vinícius
Corticosteroid Injection vs. Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drug and Splinting in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Authors: Reyhan Çeliker, MD Şule Arslan, MD Fatma İnanıcı, MD Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Affiliations: From the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Hacettepe University School of Medicine,
Authors: Reyhan Çeliker, MD Şule Arslan, MD Fatma İnanıcı, MD Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Affiliations: From the Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Hacettepe University School of Medicine,
CARPAL TUNNEL CARPAL TUNNEL. A guide for patients and their family members
 If you have any concerns, contact your neurosurgeon or the hospital and ask for the neurosurgical registrar on-call: Prince of Wales Hospital & Community Services 9382 2222 St George Hospital & Community
If you have any concerns, contact your neurosurgeon or the hospital and ask for the neurosurgical registrar on-call: Prince of Wales Hospital & Community Services 9382 2222 St George Hospital & Community
Jane Case-Smith. The American Journal of Occupational Therapy 499
 Outcomes in Hand Rehabilitation Using Occupational Therapy Services Jane Case-Smith KEY WORDS effects functional performance hand therapy OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to measure functional
Outcomes in Hand Rehabilitation Using Occupational Therapy Services Jane Case-Smith KEY WORDS effects functional performance hand therapy OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to measure functional
The muscular system is like a giant pulley system.
 The muscular system is like a giant pulley system. Muscles work with and against each other in order for you to do all the things you do. Muscle Premium takes a dive into the human muscular system with
The muscular system is like a giant pulley system. Muscles work with and against each other in order for you to do all the things you do. Muscle Premium takes a dive into the human muscular system with
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)
 Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Open versus Endoscopic Release of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 International Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant Biology Volume 5 Number 7 (July-2018) ISSN: 2349-8080 (Online) Journal homepage: www.ijcrbp.com Original Research Article doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrbp.2018.507.005
International Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant Biology Volume 5 Number 7 (July-2018) ISSN: 2349-8080 (Online) Journal homepage: www.ijcrbp.com Original Research Article doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrbp.2018.507.005
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Integra. SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
SafeGuard Mini Carpal Tunnel Release System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE SafeGuard Mini Carpal Release System Contents Surgical Technique...2 Description...2 The SafeGuard System...2 Indications...2 Contraindications...2
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL
 2001 ONWSIAT 2849 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1966 01 [1] This appeal was heard in Sudbury on July 24, 2001, by Tribunal Vice-Chair L.J. Henderson. THE APPEAL PROCEEDINGS
2001 ONWSIAT 2849 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1966 01 [1] This appeal was heard in Sudbury on July 24, 2001, by Tribunal Vice-Chair L.J. Henderson. THE APPEAL PROCEEDINGS
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks
 Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Safe Treatment of Trigger Thumb With Longitudinal Anatomic Landmarks Ron Hazani, MD, Josh Elston, BS, Ryan D. Whitney, BS, Jeremiah Redstone, MD, Saeed Chowdhry, MD, and Bradon J. Wilhelmi, MD Division
Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1807.008 Proposal for a Radiological Classification System for Carpo-Metacarpal Joint Dislocations with or without Fractures Pundkare GT, DNB Orthopaedics, Deshpande
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome
 Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome This leaflet will help answer some of the questions you may have about having surgery to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. It should accompany the leaflet, Surgical Admissions
Immediate and durable clinical improvement in the non-operated hand after contralateral surgery for patients with bilateral Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 HAND (2015) 10:381 387 DOI 10.1007/s11552-014-9719-6 Immediate and durable clinical improvement in the non-operated hand after contralateral surgery for patients with bilateral Carpal Tunnel Syndrome F.
HAND (2015) 10:381 387 DOI 10.1007/s11552-014-9719-6 Immediate and durable clinical improvement in the non-operated hand after contralateral surgery for patients with bilateral Carpal Tunnel Syndrome F.
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 GENERAL INFORMATION Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most commonly known repetitive strain injury (RSI). It is just one diagnosis under the umbrella heading of repetitive strain injuries. RSIs occur
GENERAL INFORMATION Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most commonly known repetitive strain injury (RSI). It is just one diagnosis under the umbrella heading of repetitive strain injuries. RSIs occur
NEW BRACE FOR CTS. New Splint for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy.
 NEW BRACE FOR CTS Title: New Splint for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy. Authors: Humberto Porrata, M.D. * Alejandro Porrata, M.D. * Julian Sosner, M.D.* ** Affiliation: * Department
NEW BRACE FOR CTS Title: New Splint for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy. Authors: Humberto Porrata, M.D. * Alejandro Porrata, M.D. * Julian Sosner, M.D.* ** Affiliation: * Department
Three-dimensional Analysis of the Attachment and Path of the Transverse Carpal Ligament
 Original Three-dimensional Analysis of the Attachment and Path of the Transverse Carpal Ligament Mitsuhiko Nanno 1, Takuya Sawaizumi 2,NorieKodera 2, Yuji Tomori 2 and Shinro Takai 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic
Original Three-dimensional Analysis of the Attachment and Path of the Transverse Carpal Ligament Mitsuhiko Nanno 1, Takuya Sawaizumi 2,NorieKodera 2, Yuji Tomori 2 and Shinro Takai 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
New Carpal Ligament Traction Device for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy
 SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLES JHT READ FOR CREDIT ARTICLE #046 New Carpal Ligament Traction Device for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy Humberto Porrata, MD Alejandro
SCIENTIFIC/CLINICAL ARTICLES JHT READ FOR CREDIT ARTICLE #046 New Carpal Ligament Traction Device for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Unresponsive to Conservative Therapy Humberto Porrata, MD Alejandro
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare. Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome
 NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
NHS Fylde and Wyre Clinical Commissioning Group Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome 1 Introduction 1.1 This document is part of a suite
Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Is Preferred Over Mini-open Despite Similar Outcome: A Randomized Trial
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:1548 1554 DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2666-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Endoscopic
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2013) 471:1548 1554 DOI 10.1007/s11999-012-2666-z Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons CLINICAL RESEARCH Endoscopic
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM
 TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
Modified mini-incision surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome: Results of 131 interventions
 r l a Re s e a r c h g i O in Modified mini-incision surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome: Results of 131 interventions Ziya Asan Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Ahi Evran University, Kirsehir,
r l a Re s e a r c h g i O in Modified mini-incision surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome: Results of 131 interventions Ziya Asan Department of Neurosurgery, Faculty of Medicine, Ahi Evran University, Kirsehir,
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides
 IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
Shoulder Instability Latarjet Procedure
 Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Anatomy The shoulder is a ball and socket joint and is the most mobile joint of the body. Its plays a major role in positioning your arm and hand in space. Because
Explanation of Procedure and/or Diagnosis Anatomy The shoulder is a ball and socket joint and is the most mobile joint of the body. Its plays a major role in positioning your arm and hand in space. Because
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Lecturer, Dalhousie University School of Nursing, Outpost Nursing Program
 Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Gary R. McGillivary, M.D. Revised: October 1, 2012 Office Address: Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Emory Orthopaedic and Spine Center 59 Executive
Name: McGillivary, Gary R. 1 CURRICULUM VITAE Name: Gary R. McGillivary, M.D. Revised: October 1, 2012 Office Address: Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Emory Orthopaedic and Spine Center 59 Executive
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Background Information for HemaClear Product Specialists
 H E M A C L E A R P R E S S A u g u s t 2 0 1 2 P a g e 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Background Information for HemaClear Product Specialists Edith R. Gavriely Abstract Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is the
H E M A C L E A R P R E S S A u g u s t 2 0 1 2 P a g e 1 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Background Information for HemaClear Product Specialists Edith R. Gavriely Abstract Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is the
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Carpal Tunnel Wrist Exercises Chiropractic Acupuncture
 Carpal Tunnel Wrist Exercises Chiropractic Acupuncture 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Carpal Tunnel Wrist Exercises Chiropractic What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve,
Carpal Tunnel Wrist Exercises Chiropractic Acupuncture 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 Carpal Tunnel Wrist Exercises Chiropractic What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) occurs when the median nerve,
ULTRASOUND GUIDED CTR
 ULTRASOUND GUIDED CTR What Every Clinician Should Know Jay Smith, M.D. Departments of PM&R, Radiology & Anatomy Mayo Clinic Sports Medicine Center UPMC Sports Ultrasound Course September 2018 2015 MFMER
ULTRASOUND GUIDED CTR What Every Clinician Should Know Jay Smith, M.D. Departments of PM&R, Radiology & Anatomy Mayo Clinic Sports Medicine Center UPMC Sports Ultrasound Course September 2018 2015 MFMER
Carpal tunnel syndrome
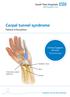 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Carpal Tunnel Decompression Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Originator: G Parsons Date: March 2012 Version: 3 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00648 Contact numbers
Carpal Tunnel Decompression Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Originator: G Parsons Date: March 2012 Version: 3 Date for Review: March 2015 DGOH Ref No: DGOH/PIL/00648 Contact numbers
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
LOW-LEVEL LASER THERAPY AFTER CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marcelo de Pinho Teixeira Alves 1, Gabriel Costa Serrão de Araújo 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Evaluate the post-operative treatment of CTS, using the LLLT. Method: We prospectively evaluated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marcelo de Pinho Teixeira Alves 1, Gabriel Costa Serrão de Araújo 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Evaluate the post-operative treatment of CTS, using the LLLT. Method: We prospectively evaluated
