Dry Needling in Sports Medicine: Is There a Role in Your Practice?
|
|
|
- Bertram Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dry Needling in Sports Medicine: Is There a Role in Your Practice? Sue Falsone, PT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS, COMT, RYT Owner, Structure & Function Education Associate Professor, A.T. Still University, DAT Program
2 Conflicts of Interest Owner: Structure & Function Education, PLLC Teaches dry needling Advisory Board Member Meyer PT
3 Acu- -Puncture Acu = sharp, needle Puncture- to pierce a surface
4 Traditional Acupuncture Originating from China 2000 years ago Balancing ying and yang Clearing up meridians Includes tongue evaluation, pulse readings, palpation, and more Western Medical Acupuncture is a form of TA (TA) Dry Needling vs. Acupuncture: the Ongoing Debate; Zhou 2015
5 Western Medical Acupuncture (WMA) Modern adaptation to traditional acupuncture Based on anatomy, physiology and pathology Different Types Dry Needling (DN) Earliest reports of dry needling are 1979 in Lewit paper Interest has risen in the US with health care professionals in the 2000 s Superficial and deep techniques Peripheral Neuromodulation Stimulates somatic nerves to influence autonomic nerves via somatovisceral reflex IMS Using electrical stimulation Trigger Point Dry Needling 95% overlap with ah shi points Dry Needling vs. Acupuncture: the Ongoing Debate; Zhou 2015
6 Tools in the Tool Box No one discipline owns a specific technique Homeopathic and Naturopathic physicians and acupuncturists all prescribe herbs Physical Therapists, Chiropractors, and Osteopaths all perform manipulation Athletic Trainers, Physical Therapists, and Chiropractors all use tape, exercise and physical agent modalities The Dry Needling Issue, Dommerholt, 2008
7 PAIN AND DRY NEEDLING MECHANISMS
8 Nerve Fibers Diameter And Velocity A Alpha Somatic Motor Propriception Muscle Spindle Ia GTO Ib A Beta Touch/ Pressure II A Gamma Motor to muscle spindles A Delta Pain/ cold / touch III Mylinated B Pregangliotic Sympathetic C Dorsal Root- Pain/ hot/ IV other mechanoreceptors Sympathetic Postgangliotic Unmylinated
9 A Beta, A Delta and C fibers A Beta- Touch and pressure Type II, mylinated A Delta- FAST pain Larger diameter so conducts impulses faster than C fibers Signal gets to brain fast for acute, sharp pain C fibers- SLOW pain Smaller diameter so conducts impulses slower than A Delta fibers Signal gets to brain later and accounts for the dull pain that follows initial sharp sensation
10 Pain Cell damage and pain sensation Releases bradykinin, CGRP, histamine, substance P, nerve growth factor, etc. These can cause pain and inflammation, vasodilation Needle insertion stimulates A Beta, A Delta and C Fibers CGRP, NO, Adenosine locally Vasodilators and pain modulators Dry Needling for Manual Therapists, Gyer, 2016 Physiological Effects of Dry Needling, Cagnie, 2013
11 Pain Pathway- Ascending A Beta, A delta and C fibers go to the dorsal horn and connect to secondary neurons Glutamate and substance P are released here Segmental effect Dry Needling for Manual Therapists, Gyer, 2016 Physiological Effects of Dry Needling, Cagnie, 2013
12 Physiological Effects of Dry Needling, Cagnie, 2013 Pain Pathway- Ascending Ascend via the contralateral lateral spinothalamic tract to the thalamus and PAG Third order neurons go to the somtaosensory cortex Spinoreticular tract goes to the brainstem before the thalamus and hypothalamus, with further projections into the cortex. This is the emotional aspects of pain
13 Pain Pathway- Descending PAG is high in concentration of opioid receptors and opioids causing analgesia Descending pathways go to dorsal horn and inhibit pain transmission Glycine and GABA are inhibitory neurotransmitters Noradrenaline and serotonin as well as dopamine are released Electroacupuncture specifically (Chou, 2012) Enkephlins and Beta-endorphins are released Dry Needling for Manual Therapists, Gyer, 2016 Physiological Effects of Dry Needling, Cagnie, 2013
14 PAIN THEORIES
15 Specificity Theory Specific pain receptors transmit signals to the brain Motor response is elicited Does NOT account for any psychological aspect of pain or previous experience Theories of pain: from specificity to gate control, Moayedi, 2013
16 Cartesian Model Theories of pain: from specificity to gate control, Moayedi, 2013
17 Theories of pain: from specificity to gate control, Moayedi, 2013 Gate Control Theory OPEN GATE CLOSED GATE Strong Signal to Brain Weak Signal to Brain Inhibitory Interneuron C-Fiber Pain Stimulus C- Fiber Pain Stimulus Touch from skin (A Beta Fiber)
18 Neuromatrix Theory of Pain Pain is produced in the brain and spinal cord, not peripheral tissue Several parts of the central nervous system work together to produce pain Shifts focus from peripheral tissue and peripheral nervous system to the central nervous system Explains things such as phantom limb pain, fibromylagia, NSLBP, etc. Pain and the neuromatrix in the brain, Melzack 2001
19 Conditioned Pain Modulation CPM is a pain- inhibits pain theory Two noxious stimuli are applied at the same time The second in the area, but not in the same spot as the first The second stimulus gets processed by the dorsal horn and can inhibit the first noxious stimuli Could be why dry needling near the area is helpful Give cause to why we do not have to be in an exact location to see good results Physiologic Effects of Dry Needling, Cagnie, 2013
20 PHYSIOLOGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
21 Effects on Blood Flow When A Delta and C fibers are stimulated, CGRP, NO and SP are released Associated with inflammation Vasodialtors Increased blood flow locally Unclear as to if this is a local response or has more diffuse effects Peripheral and Spinal Mechanisms, Butts, 2016 CGRP Produces Skeletal Muscle Vasodialation Sato, 2000
22 Effects on Nervous System Needling will increase beta-endordphin release and inhibit pain Needling will activate A Beta, Delta and C fibers, decreasing pain via counter-irritation or hyperstimulation analgesia Gate Control Theory Cagnie, 2013 DN may stimulate inhibitory dorsal horn interneurons via enkephalin, GABA, and Glycine Peripheral and Spinal Mechanisms, Butts, 2016 CGRP Produces Skeletal Muscle Vasodialation Sato, 2000
23 BIOMECHANICAL CONSIDERATIONS
24 Needle Manipulation Pistoning Winding Winding + Pistoning Periosteal Pecking With or without estim
25 Trigger Points Tenderness is the only moderately reliable identification of a trigger point, and only in the upper trap (Myburgh, 2008) Experts were unable to identify taut bands, trigger points or twitches when blinded to patient condition (Wolfe and Simons, 1992) Injection of botox into trigger point in infraspinatus decreases end plate activity but does not influence pain (Qerama, 2006)
26 Effectiveness of trigger point dry needling Boyles, R,., Pistoning TrP TDN appears to be an effective treatment intervention for relief of trigger point-associated pain, regardless of body region Outcome measures related to pain reduction TDN is more effective than stretching and percutaneous electric nerve stimulation (PENS) At least equally as clinically effective as manual MTrP release and other needling treatments More research is needed to determine the role of the local twitch response (LTR) and other protocol-related variables
27 Muscle Twitch 2 of the 14 most common points treated by Lewit were not muscle tissue Lewit 1979 Superficial (not in muscle tissue) needling is effective Itoh 2011, Ceccherelli 2002, Baldry 2002
28 Conclusion- Muscle Twitch We do NOT need a twitch in order to be effective
29 Needle Grasp of Tissue 60 human subjects US guided for same depth NO/ BI/ Uni Conditions Biomechanical response to acupuncture needling in humans. Langevin, 2001
30 Needle Grasp of Tissue Evidence to show physical winding of the tissue around the needle May include skin and subcutaeous tissue, muscle, fascia, etc. Collagen, elastic fibers, fibroblast, adipocytes, and mast cells, CGRP + nerve fibers have all been found histologically on the needle after removal Kimura et al, 1992 Biomechanical response to acupuncture needling in humans. Langevin, 2001
31 Needle Grasp and Pistoning Because of this winding of tissues around the needle, pistoning may be more effective if winding is done first Evidence to show tissue movement occurred 4 cm away from needle Evidence that after 5 minutes, there was a loosening of the tissue/ needle bond Tissue displacements during acupuncture Langevin, 2004.
32 Efficacy of periosteal stimulation therapy for the treatmtment of OA Weiner et al, 2007 Periosteal Pecking Aka periosteal stimulation therapy (PST) Aka osteopuncture Pain in OA of the knee was significantly reduced with use of PST with e-stim in a study with 88 people who were in pain for longer than 3 months Touched bone (med and lat femoral condyle, fibular head and tibial flare), stimulated with 100 Hz for 30 minutes Improvements in pain for 1 month post treatment
33 Periosteal Pecking 144 patients received intramuscular acupuncture, periosteal pecking or control (nothing) Both groups were more effective in decreasing neck and low back pain than the control, but there was no significant difference between PP and intramuscular acupuncture Intramuscular and periosteal acupuncture,hansson 2008
34 CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
35 Contraindications Patients with known HIV Hepatitis B and C If you have a known BBP you should not dry needle your patients until consulting with an infectious disease control professional Cancerous tissue Pregnancy
36 Contraindications Metal allergy Blood diseases, including but not limited to: Leukemia and lymphoma Severe aplastic anemia True needle phobia Specific to the LB Moderate scoliosis Spina bifida
37 Precautions Patient on blood thinners Coumadin, Aspirin, Plavix and more Cancer Discuss with patient and MD Uncontrolled diabetes diabetic ulcers and foot/ ankle dry needling Disease that compromises your bony safety block Ex: osteoporosis and the scapula
38 ADVERSE EVENTS
39 Safety of Acupuncture Kim, Medicine, 2016 Adverse Events Retrospectively reviewed electronic medical records in a Korean hospital Dec 2010 to Oct 2014 Classified as: Mild: no follow up medical attention needed and does not affect ADL s Moderate: significant impact on ADL s; may require additional medical attention but resolves after Severe: requires intense medical intervention and leaves post event symptoms Casualty: causes death
40 Safety of Acupuncture Kim, Medicine, 2016 Adverse Events 80,523 patients were treated with acupuncture AE N Severity Forgotten Needle 47 Mild- 47 Presyncope 4 Mild-2 Moderate-2 Pneuomothorax 4 Mild-1 Moderate-3 Infection 2 Severe- 2 (inpatients)
41 Adverse Events Prospective questionnaire (Ireland) Form A for mild events Form B for severe events 39 physiotherapists voluntarily participated Sept 2011 to June 2012 Focused on SDN or DDN DDN was trigger point DN Adverse events following trigger point dry needling Brady et al, J. Man Manip, 2014
42 Adverse events following trigger point dry needling Brady et al, J. Man Manip, 2014 Results 1463 adverse events were recorded in 7629 treatments per 100 treatments (20%)
43 Results No Form B s were returned, indicating no serious events occurred forgotten needles, pneumothorax, fainting, vomiting, prolonged aggravation; or other significant events Adverse events following trigger point dry needling Brady et al, J. Man Manip, 2014
44 COMMON REACTIONS TO NEEDLING
45 Common Reactions to Dry Needling UK Based members of the British Acupuncture Council 1955 members 638 clinicians agreed to participate 9408 patients answered survey Did you experience during or immediately afterward any of the following Short term reactions to acupuncture, MacPherson 2005
46 Results 94.7% of patients reported at least one short term reaction Average per patient was 1.8 reactions Short term reactions to acupuncture MacPherson 2005
47 Short term reactions to acupuncture MacPherson 2005
48 In Conclusion We have theories about the mechanism by which dry needling works, but exact mechanisms are unknown Many schools of thought regarding the use of needle manipulation Pistoning, winding, combo, periosteal pecking We do not know the most effective parameters for dosing dry needling Placement, intensity, frequency, use of needle manipulation
49 In Conclusion Dry needling can cause serious side effects, especially if performed by an untrained person Pneumothorax, organ puncture Dry needling is a safe treatment when administered by someone with proper training
50 Stay In Touch FB: Sue Falsone / Structure & Function /@structureandfunction LinkedIn: Sue Falsone sue@suefalsone.com
Alternative Therapies in Sports Medicine
 Alternative Therapies in Sports Medicine Sue Falsone PT,MS,SCS,ATC,CSCS,COMT,RYT Owner, Structure & Function Education Owner, Falsone Consulting Associate Professor, Athletic Training, A.T. Still University
Alternative Therapies in Sports Medicine Sue Falsone PT,MS,SCS,ATC,CSCS,COMT,RYT Owner, Structure & Function Education Owner, Falsone Consulting Associate Professor, Athletic Training, A.T. Still University
9/2/2014. System Dry Needling for Athletes
 SYSTEMIC DRY NEEDLING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT AND SPORTS MEDICINE Sue Falsone PT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS, COMT President and Founder, S&F: Structure and Function President and Founder, Dr. Ma s Systemic Dry Needling
SYSTEMIC DRY NEEDLING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT AND SPORTS MEDICINE Sue Falsone PT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS, COMT President and Founder, S&F: Structure and Function President and Founder, Dr. Ma s Systemic Dry Needling
Dry Needling: Interventions and Clinical Application
 Dry Needling: Interventions and Clinical Application Craig A. Voll, Jr. PhD, ATC, PT Jessica Gillespie, PT, DPT Lafayette Area Sports Symposium February 7, 2018 Objectives: Define Dry Needling (DN) Utilization
Dry Needling: Interventions and Clinical Application Craig A. Voll, Jr. PhD, ATC, PT Jessica Gillespie, PT, DPT Lafayette Area Sports Symposium February 7, 2018 Objectives: Define Dry Needling (DN) Utilization
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Chapter 16. Sense of Pain
 Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
Chapter 16 Sense of Pain Pain Discomfort caused by tissue injury or noxious stimulation, and typically leading to evasive action important /// helps to protect us lost of pain in diabetes mellitus = diabetic
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Pain. Pain. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Pain: One definition. Psyc 2906: Sensation--Introduction 9/27/2006
 Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Pain Pain Pain: One Definition Classic Paths A new Theory Pain and Drugs According to the international Association for the Study (Merskey & Bogduk, 1994), Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience
Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain
 Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain Uncovering the Central Map of Physiological Homeostasis Joseph F. Audette, M.A., M.D. Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Department of PM&R, Harvard Medical School INTRODUCTION
Acupuncture & Myofascial Pain Uncovering the Central Map of Physiological Homeostasis Joseph F. Audette, M.A., M.D. Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Department of PM&R, Harvard Medical School INTRODUCTION
11/23/16. Advanced Arm Care for Baseball. Pain Generator. How Does Kinesiology Tape work? Kinesiology Tape
 Advanced Arm Care for Baseball Examination Sue Falsone PT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS, COMT, RYT Owner, S&F: Structure and Function Education Associate Professor, Athletic Training, A.T. Still University Examination
Advanced Arm Care for Baseball Examination Sue Falsone PT, MS, SCS, ATC, CSCS, COMT, RYT Owner, S&F: Structure and Function Education Associate Professor, Athletic Training, A.T. Still University Examination
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
TRIGGER POINT DRY NEEDLING
 TRIGGER POINT DRY NEEDLING Sadie Newman PT DPT Cox Health What is it? 1 A skilled intervention that uses a thin filiform needle to penetrate the skin and stimulate underlying myofascial trigger points,
TRIGGER POINT DRY NEEDLING Sadie Newman PT DPT Cox Health What is it? 1 A skilled intervention that uses a thin filiform needle to penetrate the skin and stimulate underlying myofascial trigger points,
Sensory Analgesia. Pain Definitions a distressing feeling due to disease, bodily injury or organic disorder. uneasiness of mind or grief.
 Sensory Analgesia Anesthesia- Analgesia- Partial or complete loss of sensation with or without loss of consciousness Relieving pain, being in a state without pain Pain Definitions a distressing feeling
Sensory Analgesia Anesthesia- Analgesia- Partial or complete loss of sensation with or without loss of consciousness Relieving pain, being in a state without pain Pain Definitions a distressing feeling
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL NERVE STIMULATION (TENS) Dr. Mohammed TA, Omar, PhD, PT Rehabilitation Science Department CAMS-KSU
 TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL NERVE STIMULATION (TENS) Dr. Mohammed TA, Omar, PhD, PT Rehabilitation Science Department CAMS-KSU momarar@ksu.edu.sa Definition of TENS and current specifications Modes of TENS
TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL NERVE STIMULATION (TENS) Dr. Mohammed TA, Omar, PhD, PT Rehabilitation Science Department CAMS-KSU momarar@ksu.edu.sa Definition of TENS and current specifications Modes of TENS
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
SomeFacts... Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture. Overview. Some Figures. Primary (Idiopathic) OA. Primary (Idiopathic) OA
 Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Dr Panos Barlas Research Fellow p.barlas@shar.keele.ac.uk Applications of acupuncture Principles of acupuncture
Joint pain and its treatment with acupuncture Overview Physiological considerations of joint pain Dr Panos Barlas Research Fellow p.barlas@shar.keele.ac.uk Applications of acupuncture Principles of acupuncture
Pain. Types of Pain. Types of Pain 8/21/2013
 Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling
 Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling JILL THEIN-NISSENBAUM, PT, DSC, SCS, ATC ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UW-MADISON SMPH STAFF PT, BADGER SPORTSMEDICINE THEIN@PT.WISC.EDU No Conflict of Interest
Let s get to the point: Therapeutic Dry Needling JILL THEIN-NISSENBAUM, PT, DSC, SCS, ATC ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UW-MADISON SMPH STAFF PT, BADGER SPORTSMEDICINE THEIN@PT.WISC.EDU No Conflict of Interest
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S
 The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
The Nervous System S P I N A L R E F L E X E S Reflexes Rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to a stimulus Spinal Reflexes Spinal somatic reflexes Integration center is in the spinal cord Effectors
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
The anatomy and physiology of pain
 The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture. Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs
 Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva, February 2009 A misunderstanding
Neurobiological Basis of Acupuncture Dr Marc Petitpierre Association Genevoise des Médecins Acupuncteurs Training Course in Sexual and Reproductive Health Research Geneva, February 2009 A misunderstanding
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways.
 Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
MYOFASCIAL PAIN. Dr. Janet Travell ( ) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare providers.
 Myofascial Trigger Points background info Laurie Edge-Hughes BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT History lesson Dr. Janet Travell (1901 1997) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare
Myofascial Trigger Points background info Laurie Edge-Hughes BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT History lesson Dr. Janet Travell (1901 1997) credited with bringing MTrPs to the attention of healthcare
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
OSHA education & Not OSHA compliant!! Precautions, contraindications and safety of dry needling. For employers the must:
 OSHA education & Precautions, contraindications and safety of dry needling Bloodborne pathogens are infectious micro-organisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include,
OSHA education & Precautions, contraindications and safety of dry needling Bloodborne pathogens are infectious micro-organisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include,
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile
 Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
Ch. 47 Somatic Sensations: Tactile and Position Senses (Reading Homework) - Somatic senses: three types (1) Mechanoreceptive somatic senses: tactile and position sensations (2) Thermoreceptive senses:
*Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord.
 *somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
*somatic sensations : PAIN *Anteriolateral spinothalamic tract (STT) : a sensory pathway that is positioned anteriorly and laterally in the spinal cord. *This pathway carries a variety of sensory modalities:
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon
 Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Dendrites Receive impulse from the axon of other neurons through synaptic connection. Conduct impulse towards the cell body Axon Page 22 of 237 Conduct impulses away from cell body Impulses arise from
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL STIMULATION
 TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL STIMULATION Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) Transcutaneous electrical stimulation ; An electronic device that produces electrical signals used to stimulate nerve
TRANSCUTANEOUS ELECTRICAL STIMULATION Transcutaneous electrical stimulation (TENS) Transcutaneous electrical stimulation ; An electronic device that produces electrical signals used to stimulate nerve
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Mechanism of Pain Production
 Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Mechanism of Pain Production Pain conducting nerve fibers are small myelinated (A-delta) or unmyelinated nerve fibers (C-fibers). Cell bodies are in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or sensory ganglia of
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
PAIN MODULATION. numerical value. adjectives. DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH
 PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
Functional Dry Needling for the Orthopedic Patient
 Functional Dry Needling for the Orthopedic Patient By: Stephanie Brandt PT, DPT CKSPT Bandana Square June 15, 2018 Stephanie Brandt PT, DPT Bachelor s of science in kinesiology from the University of Minnesota
Functional Dry Needling for the Orthopedic Patient By: Stephanie Brandt PT, DPT CKSPT Bandana Square June 15, 2018 Stephanie Brandt PT, DPT Bachelor s of science in kinesiology from the University of Minnesota
1. Differences in function of the 3 muscle types: a) Skeletal Muscle b) Cardiac Muscle c) Smooth Muscle
 Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. Energetics of muscle
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
Peripheral Nervous System 1 Sensory Receptors Sensory Receptors and Sensation Respond to changes (stimuli) in the environment Generate graded potentials that can trigger an action potential that is carried
4/28/2017. Treatment Targets for MFDTM. Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes. Trigger Points. Travel and Simons
 Treatment Targets for MFDTM Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes Trigger Points Travel and Simons 1 Trigger Points Lower levels of oxygen, nutrients, blood perfusion Increased levels of
Treatment Targets for MFDTM Trigger Points, Fascial Lines, and Postural Syndromes Trigger Points Travel and Simons 1 Trigger Points Lower levels of oxygen, nutrients, blood perfusion Increased levels of
Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord
 Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
Chapter 13 Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves and Somatic Reflexes Spinal cord Spinal nerves Somatic reflexes Gross Anatomy of Lower Spinal Cord Meninges of Vertebra & Spinal Cord Spina Bifida Congenital defect
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center
 A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
A lecture on PAIN AKA a painful lecture by Colleen Blanchfield, MD Full Circle Neuropsychiatric Wellness Center 1 Overview of the lecture Anatomy of the Pain Tract How a painful stimulus travels from the
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Dry Needling Let s Get To The Point. Maggie Hanna PT, DPT
 Dry Needling Let s Get To The Point Maggie Hanna PT, DPT Clinical Questions: What is Dry Needling (DN)? Are there other names for Dry Needling? What are trigger points and what can cause them to form?
Dry Needling Let s Get To The Point Maggie Hanna PT, DPT Clinical Questions: What is Dry Needling (DN)? Are there other names for Dry Needling? What are trigger points and what can cause them to form?
HEAD AND NECK PART 2
 HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
HEAD AND NECK PART 2 INTEGRATED CURRICULUM = Integrate Basic Science and Clinical Training 1- ENT PATIENT EXAM IN ICS COURSE - Today and next week - Review/Preview Anatomy underlying ENT exam 2- NEUROANATOMY/NEUROLOGY
1. Differences in function of the 3 muscle types: a) Skeletal Muscle b) Cardiac Muscle c) Smooth Muscle
 Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. What influences muscle
Ch 9: Muscle Physiology Objectives: 1. Review 3 muscle types and how they are regulated. 2. Review muscle anatomy. 3. Sliding filament theory of how muscles contract and relax. 4. What influences muscle
GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS ATP Adenosine Triphosphate that helps to promote protein synthesis. Accommodation Becoming accustomed to stimulation resulting in nerve and muscle fatigue. Acute
GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS ATP Adenosine Triphosphate that helps to promote protein synthesis. Accommodation Becoming accustomed to stimulation resulting in nerve and muscle fatigue. Acute
Thermoreceptors (hot & cold fibers) Temperature gated Na+ channels. Adaptation in thermoreceptors
 Thermoreceptors (hot & cold fibers) Temperature gated Na+ channels Adaptation in thermoreceptors Response of a cold receptor Drugs can mimic sensory stimuli Response of taste nerve to cold water or menthol
Thermoreceptors (hot & cold fibers) Temperature gated Na+ channels Adaptation in thermoreceptors Response of a cold receptor Drugs can mimic sensory stimuli Response of taste nerve to cold water or menthol
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts
 Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
PAIN. Physiology of pain relating to pain management
 PAIN Physiology of pain relating to pain management What is pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. (Melzac and Wall) The generation of pain
PAIN Physiology of pain relating to pain management What is pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. (Melzac and Wall) The generation of pain
HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL. Emmanuel Guigon
 HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL Emmanuel Guigon Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS / UMR 7222 Paris, France emmanuel.guigon@upmc.fr e.guigon.free.fr/teaching.html
HUMAN MOTOR CONTROL Emmanuel Guigon Institut des Systèmes Intelligents et de Robotique Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS / UMR 7222 Paris, France emmanuel.guigon@upmc.fr e.guigon.free.fr/teaching.html
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 15! Chapter 15 Sensory Pathways, Somatic Nervous System! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System!
 Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Chapter 15! Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the SECTION 15-2! Sensory receptors connect our internal and external environments with the nervous system! 2 Sensation and Receptors! Transduction!
Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review
 Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review 1) Pain related issues currently account for approximately of doctor s visits. a) 60% b) 70% c) 80% d) 90% 2) Which pain scale is frequently utilized with children?
Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review 1) Pain related issues currently account for approximately of doctor s visits. a) 60% b) 70% c) 80% d) 90% 2) Which pain scale is frequently utilized with children?
Manual Therapy Techniques
 Manual Therapy Techniques manual therapy: the use of hands-on techniques to evaluate, treat, and improve the status of neuromusculoskeletal conditions massage: the systematic and scientific manipulation
Manual Therapy Techniques manual therapy: the use of hands-on techniques to evaluate, treat, and improve the status of neuromusculoskeletal conditions massage: the systematic and scientific manipulation
1 The Physiology of Pain
 1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System. Total 33 points
 Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
Biology 3201 Quiz on Nervous System Total 33 points Name: Circle the best response to the following: (33 points) 1. What do we call the long fibre that carries impulses away from the nerve cell body? A.
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
Meninges. Connective tissue membranes
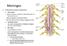 Meninges Connective tissue membranes Dura mater: -outermost layer; continuous with epineuriumof the spinal nerves - dense irregular connective tissue - from the level of the foramen magnum to S2 Arachnoid
Meninges Connective tissue membranes Dura mater: -outermost layer; continuous with epineuriumof the spinal nerves - dense irregular connective tissue - from the level of the foramen magnum to S2 Arachnoid
Chapter 13. The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture
 Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Chapter 13 The Nature of Muscle Spindles, Somatic Reflexes, and Posture Nature of Reflexes A reflex is an involuntary responses initiated by a sensory input resulting in a change in the effecter tissue
Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review
 Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review 1) Pain related issues currently account for approximately of doctor s visits. a) 60% b) 70% c) 80% d) 90% 2) Which pain scale is frequently utilized with children?
Pain Management: A Comprehensive Review 1) Pain related issues currently account for approximately of doctor s visits. a) 60% b) 70% c) 80% d) 90% 2) Which pain scale is frequently utilized with children?
D) around, bypassing B) toward
 Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
Nervous System Practice Questions 1. Which of the following are the parts of neurons? A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Physical Therapy Modalities for the Office
 Physical Therapy Modalities for the Office Jeff G. Konin, PhD, PT, ATC, FACSM, FNATA Professor & Chair Physical Therapy Department University of Rhode island Rehabilitation Interventions Manual Therapy
Physical Therapy Modalities for the Office Jeff G. Konin, PhD, PT, ATC, FACSM, FNATA Professor & Chair Physical Therapy Department University of Rhode island Rehabilitation Interventions Manual Therapy
Thursday, January 22, Nerve impulse
 Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
Nerve impulse Transmembrane Potential caused by ions moving through cell membrane at different rates Two main ions of concern Na + - Sodium K + - potassium Cell membrane not freely permeable therefore
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Nervous System IN DEPTH
 The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN
 SYLLABUS NSC 4358 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN SPRING 2011 1 SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC 4358 001 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN Instructor: Aage R. Møller PhD E-mail: AMOLLER@UTDALLAS.EDU Class schedule: Main Campus:
SYLLABUS NSC 4358 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN SPRING 2011 1 SYLLABUS SPRING 2011 COURSE: NSC 4358 001 NEUROBIOLOGY OF PAIN Instructor: Aage R. Møller PhD E-mail: AMOLLER@UTDALLAS.EDU Class schedule: Main Campus:
IMPROVING CHRONIC PAIN PATIENTS QUALITY OF LIFE WITH CUTTING EDGE TECHNOLOGY. Jacqueline Weisbein, DO Napa Valley Orthopaedic Medical Group
 IMPROVING CHRONIC PAIN PATIENTS QUALITY OF LIFE WITH CUTTING EDGE TECHNOLOGY Jacqueline Weisbein, DO Napa Valley Orthopaedic Medical Group Who Am I? Avid equestrian Trained in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
IMPROVING CHRONIC PAIN PATIENTS QUALITY OF LIFE WITH CUTTING EDGE TECHNOLOGY Jacqueline Weisbein, DO Napa Valley Orthopaedic Medical Group Who Am I? Avid equestrian Trained in Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
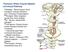 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Powerful Frequencies for Balancing the Brain
 Powerful Frequencies for Balancing the Brain By Darren Starwynn, O.M.D. Ph: 415.888.3891 www.drstarwynn.com Darren@DrStarwynn.com With credit and appreciation to Harry Van Gelder, Carolyn McMakin and Vanessa
Powerful Frequencies for Balancing the Brain By Darren Starwynn, O.M.D. Ph: 415.888.3891 www.drstarwynn.com Darren@DrStarwynn.com With credit and appreciation to Harry Van Gelder, Carolyn McMakin and Vanessa
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
THERAPEUTIC USE OF ULTRASOUND PURPOSE POLICY STATEMENTS INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATIONS. To describe the safe use of ultrasound therapy
 PURPOSE To describe the safe use of ultrasound therapy POLICY STATEMENTS All electrophysical agents must be used in accordance with College of Physical Therapists of BC practice standards. Ultrasound therapy
PURPOSE To describe the safe use of ultrasound therapy POLICY STATEMENTS All electrophysical agents must be used in accordance with College of Physical Therapists of BC practice standards. Ultrasound therapy
Trigger Point Injection. Objectives. What is a Trigger Point (TrP)? 3/19/2019
 Trigger Point Injection Brian Shian, MD, FHM Department of Family Medicine University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Discuss the definition and diagnosis criterial Explore possible pathophysiology
Trigger Point Injection Brian Shian, MD, FHM Department of Family Medicine University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Objectives Discuss the definition and diagnosis criterial Explore possible pathophysiology
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
This Session by Simon Strauss
 This Session by Simon Strauss Myofascial Pain. Part A Myofascial Pain. Part B Pain Assessment Tools. Part C Definitions and Language of Pain Allodynia- 1. A lower than normal pain threshold. 2. A clinical
This Session by Simon Strauss Myofascial Pain. Part A Myofascial Pain. Part B Pain Assessment Tools. Part C Definitions and Language of Pain Allodynia- 1. A lower than normal pain threshold. 2. A clinical
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Stretch reflex and Golgi Tendon Reflex. Prof. Faten zakareia Physiology Department, College of Medicine, King Saud University 2016
 Stretch reflex and Golgi Tendon Reflex Prof. Faten zakareia Physiology Department, College of Medicine, King Saud University 2016 Objectives: Upon completion of this lecture, students should be able to
Stretch reflex and Golgi Tendon Reflex Prof. Faten zakareia Physiology Department, College of Medicine, King Saud University 2016 Objectives: Upon completion of this lecture, students should be able to
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
