GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR MD IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE
|
|
|
- Megan Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR MD IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE Preamble: The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care and advance the cause of science through research & training. Nuclear medicine is a multi-disciplinary practice and the training of medical doctors is critical to the performance of a Nuclear Medicine department. Successful post graduate students are awarded a final certificate, degree or diploma that is recognized by the government, local health authority and hospital employer as an assurance of specialist competence in Nuclear Medicine. Post graduate training programme in Nuclear Medicine consists of an integrated training course of three years duration and would enable the post graduate student to practice nuclear medicine safely. The purpose of this document is to provide teachers and learners illustrative guidelines to achieve defined outcomes through learning and assessment. This document was prepared by various subject-content specialists. The Reconciliation Board of the Academic Committee has attempted to render uniformity without compromise to purpose and content of the document. Compromise in purity of syntax has been made in order to preserve the purpose and content. This has necessitated retention of domains of learning under the heading competencies. SUBJECT SPECIFIC LEARNING OBJECTIVES The objective of the programme is to enable the post graduate student s to perform Nuclear Medicine practice, teaching and research independently and fulfill the manpower needs of ever expanding new branch of diagnostic and therapeutic medicine. Post Graduate Training will consist of Theoretical and Practical Training: SUBJECT SPECIFIC COMPETENCIES By the end of the course, the student should have acquired knowledge (cognitive domain), professionalism (affective domain) and skills (psychomotor domain) as given below: A. Cognitive domain 1
2 1. Should have knowledge of basic principles of radiation physics and its subsequent applications. 2. Should have knowledge of radiation protection principles. 3. Safe handling of radionuclides and their disposal. 4. Should have knowledge of International Commission for Radiological Protection (ICRP) and National Regulatory guidelines pertaining to nuclear medicine practice. 5. Should have knowledge of diagnostic tests, interpretation of results and pitfalls. 6. Good clinical practice of therapeutic nuclear medicine and dosimetry. 7. Should be able to conduct clinical research and write a thesis/dissertation under supervision. 8. Should develop good working relationship with user specialties and handling inter-specialty referrals B. Affective domain: 1. Should be able to function as a part of a team, develop an attitude of cooperation with colleagues, and interact with the patient and the clinician or other colleagues to provide the best possible diagnosis or opinion. 2. Always adopt ethical principles and maintain proper etiquette in dealings with patients, relatives and other health personnel and to respect the rights of the patient including the right to information and second opinion. 3. Develop communication skills to word reports and professional opinion as well as to interact with patients, relatives, peers and paramedical staff, and for effective teaching. C. Psychomotor domain At the end of the course, the student should have acquired the following skills: A) Basic Sciences Experiment: 1. Practicals related to Physics, Instrumentation and its quality Control. 2. Preparation of radiopharmaceuticals and their quality control. 3. Detection of contamination in various workplaces. 4. Characterization of unknown isotopes. 5. Management of accidental spillage. B) Clinical Experiment: 1. GFR Estimation. 2. Esophageal transit time. 3. Gastric emptying time. 4. Renal transplant evaluation. 2
3 5. Determination of Ejection Fraction and RWMA (wall motion). Course contents: Syllabus The syllabus is divided into the following four parts: 1. Basic Science aspects of Radiation Physics and its application to diagnostic/ therapeutic Nuclear Medicine 2. Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine and its applications 3. Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine and its applications 4. Recent Advances in Nuclear Medicine At the end of the course, the student should have acquired knowledge in the following: Part I: Basic Science related to Nuclear Medicine 1.1 Radiation Physics and Instrumentation a. Structure of atom, Natural and artificial radioactivity. b. Modes of Radioactive decay. c. Interaction of radiation with matter. d. Principles of radiation detection and detectors. e. Basic principles of production of radionuclides by reactors and cyclotrons. f. Nuclear Medicine Instrumentation including Gamma Cameras, Single Photon Computed Tomography (SPECT), Positron Emission Tomography (PET), Hybrid Imaging Systems like SPECT/CT, PET/CT and PET/MR g. Counting Systems: Well counters, liquid scintillation counters, spectrometers, Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) probe and radiation monitoring devices. h. Quality control of Nuclear Instruments, as in (f and g). i. Collimation of radiation detectors and the characteristics of various collimators, their response to point, line and plane sources. j. Electronic instruments, such as pulse amplifiers, pulse height analyzer, count rate meters and computer interfaces including gating devices. k. Software and hardware fusion technology, Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) technology and Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS). 1.2 Mathematics, Statistics and Computer Sciences. 3
4 a. Basic Mathematical concepts, counting statistics, probability distribution, Baysian and McNemmar statistics, parametric and nonparametric statistics. b. Compartmental analysis and mathematical models of physiologic systems. c. Basic aspects of computer structure, function and programming. d. Computer applications with emphasis on digital image acquisition, analysis, processing and enhancement, tomographic reconstruction, display and recordings of findings. e. Fundamental of filters, their applications and uses. 1.3 Radiation Biology a. The biological effects of radiation exposure with emphasis on the effects of low level exposure. b. Methods of reducing unnecessary radiation exposure to patients, personnel and environment. c. ICRP recommendations and their amendments from time to time and other international recommendations, environmental regulationsregarding limits of radiation exposure, handling of radioactive patients, transport of radioactivity material and disposal of radioactive wastes. d. The diagnosis, evaluation and treatment of radiation over exposure in any form. Part 2: Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine 2.1 Radiopharmaceuticals The chemical, physical and biological properties of radiopharmaceuticals used in Nuclear Medicine investigations; production, Quality Control and Regulations of hospital based-nuclear Pharmacy. The emphasis will be on: a. Physical and chemical characteristics of radionuclide used in diagnostic Nuclear Medicine b. Criteria for selection of radionuclide for diagnostic purposes c. Biological behavior of radiopharmaceuticals d. Quality control e. Mechanism of localization f. Positron Emitting radionuclides, target reactions and their radiopharmaceuticals chemistry, various synthetic modules. 4
5 g. Specific topics on Radiopharmaceuticals: Bone seeking, hepatobiliary, brain and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), renal, thyroid, parathyroid, infection imaging, Tumor Seeking, cardiac imaging etc. h. Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Laws pertaining to in-house manufacturing of Radiopharmaceuticals. i. Radiopharmaceuticals for Research. 2.2 In vivo Diagnostic Imaging a. General clinical indications for organ imaging; normal and altered anatomy, physiology, biochemistry and metabolism of various organs. Must learn the technical aspects of performing the procedures including proper patient preparation and patient management before, during and after the procedure. b. In vivo imaging and/or functional studies including brain Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT), tracing of cerebrospinal fluid pathways, thyroid imaging, salivary glands, lungs, heart, gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary system, spleen, kidney, prostate, adrenal, bone and joints, bone marrow evaluation etc. c. The use of physiologic gating techniques for functional studies and patient monitoring during intervention, both physical exercise and using pharmacological stress agents d. Cellular kinetics, absorption and excretion analysis, nuclear hematology and metabolic balance studies using radiotracers. e. Comparative analysis of Nuclear Medicine procedures with X-ray, Ultrasound, Echo, MRI, CT and angiography etc. f. Nuclear Cardiology: Stress and redistribution studies using Thallium 201 and other technetium-based myocardial perfusion agents; myocardial viability, Gated SPECT studies, etc. g. Positron Emission Tomography (PET): All indications for use of PET imaging in oncology, cardiology, neurosciences and psychiatric disorders. 2.3 In vitro Studies a. Principles of Radioimmunoassay (RIA), quality control and data analysis for various hormones and drugs assays. b. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) estimation, Red Cell Survival, Red Cell Mass using chromium and C 14 urea Breath test. Part 3: Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine 5
6 3.1 Principles of Internal Dosimetry: Calculation of the radiation dose from internally administered radionuclide 3.2 Characteristics of Radionuclides/Radiopharmaceuticals for radionuclide therapy 3.3 Radiation protection in therapeutic set up: Design of Isolation ward as per the norms of Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) 3.4 Principles of OPD and in-door therapy administration 3.5 Therapy in thyroid disorders; benign thyroid diseases, aetiology of hyperthyroidism, various modalities of treatment and follow up strategy, long-term outcome and various national and international regulations pertaining to therapeutic administration of radionuclides. Therapy in thyroid disorders; aetiopathology, classification and diagnosis of thyroid nodules and malignancies- various modalities of treatment and follow-up strategies, long-term outcome and various national and international regulations pertaining to therapeutic administration of radionuclides. 3.6 Bone pain palliation using various radionuclides such as P 32, Sr 89, Y 90, Sm 153, Ra 223, Lu 177 etc. 3.7 Radiosynevectomy 3.8 Radiopeptide therapy and Radioconjugate therapy 3.9 Radioimmunotherapy 3.10 Locoregional internal radiation therapy 3.11 Research agents in radionuclide therapy Part 4: Recent Advances in Nuclear Medicine Covering all aspects of the following areas: 4.1 Instrumentation 4.2 Radiopharmaceuticals 4.3 Diagnostic procedures 4.4 Therapeutic procedures TEACHING AND LEARNING METHODS Teaching methodology should consist of: 1. Didactic lectures in Physics related to Nuclear Medicine, radiopharmacy, radioisotopes techniques, instrumentation, data processing and quality control. 2. Participation in the daily routine work of the department including work rounds of patients admitted for radionuclide therapy. 6
7 3. The postgraduate students shall be required to participate in the teaching and training programme of undergraduate students and interns. 4. Presentation of cases in the reporting sessions of the department. 5. Log book: Log book will be maintained meticulously to record all training done and Log books shall be checked and assessed periodically by the faculty members imparting the training. 6. A postgraduate student of a postgraduate degree course in broad specialities/super specialities would be required to present one poster presentation, to read one paper at a national/state conference and to present one research paper which should be published/accepted for publication/sent for publication during the period of his postgraduate studies so as to make him eligible to appear at the postgraduate degree examination. 7. Active participation in the combined clinical meetings with other departments for case discussions. 8. Regular participation in department journal clubs, Seminars and other periodical CME programmes. 9. Participation in the Seminars and CME programme of allied departments. 10. Department should encourage e-learning activities. 11. Rotation: Apprenticeship/Rotation in: a) Radio-diagnosis 03 months [CT 2 mo and MR 1 mo] b) Cardiac stress lab 02 months c) Immunoassay lab 01 month During the training programme, patient safety is of paramount importance; therefore, skills are to be learnt initially on the models, later to be performed under supervision followed by performing independently; for this purpose, provision of skills laboratories in medical colleges is mandatory. The year-wise schedule of training would be as follows: Year 1 (a) Scientific principles: Basic physics and mathematics, Instrumentation, Principles of computing, Basic radiation biology and radiation protection, Basic radiopharmacy and radiochemistry, Principles of tracer technology. 7
8 (b) Clinical Nuclear Medicine: Diagnostic: Normal and abnormal appearances of images, mode of pharmaceutical uptake; normal variants and common artifacts in bone, heart, lung, kidney, brain, thyroid, tumour and infection images. Therapeutic: Basic principles of radionuclide therapy; treatment of hyperthyroidism, thyroid cancer and metastatic bone pain. Principles of radiation protection: ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) ALARP (as low as reasonably practicable). Year 2 (a) Requirements of Year 1 in greater depth: Tracer kinetics; Computing and image processing; Radiobiology including the biological effects of high and low level radiation; Linear hypothesis and the threshold hypothesis of the biological response to low level radiation; The effective dose equivalent and the calculation of radiation dose from radiopharmaceuticals. (b) Radiopharmacy: Properties of commonly used diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals; Production of radionuclides by reactors, cyclotrons and radionuclide generators; Quality assurance and quality control of radiopharmaceuticals. Year 3 (a) Requirements of Year 2 in greater depth: Principles of radiology including ultrasound, computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Co-registration of nuclear medicine images and those from other imaging techniques. Diagnostic: special investigations in cardiology, lung disease, gastroenterology, hepato-biliary diseases, nephro-urology, neurology and psychiatry, endocrinology, haematology, oncology and infection. (b) Therapeutic applications: Treatment of bone metastases, neural crest tumors, prostate malignancies, solid malignancies; Use of radionuclide monoclonal antibodies and radionuclide labeled peptides for tumor therapy. 8
9 (c) Further practice and experience of work accomplished in years 1 to 3: Legal and regulatory requirements, Audit, Departmental management, Research techniques and evaluation, Teaching and training. Practical training The post graduate students are obliged to play an active in-service role in the practice of Nuclear Medicine to familiarize themselves with all the techniques required as a nuclear medicine practitioner, such as: Protocols of in vivo and therapeutic procedures; Data acquisition and processing with various equipments, quality control of instruments and labeled agents; Interventional procedures, including physiological, pharmacological, and mental stress for diagnostic application, and all therapeutic interventions; In vitro protocols and procedures, if appropriate. Since post graduate students will take on the responsibilities of a nuclear physician, they must pass a qualifying test that covers both theoretical knowledge and practical abilities in the daily practice of nuclear medicine. SUGGESTED SCHEDULE FOR POST-GRADUATE TRAINING Subject Duration (hrs) Suggested content of teaching Recommended practice and time period Nuclear physics 40 Decay features, spectrum, Radioisotope production & detection Radiochemistry 40 Labelling, technical design & quality control, interaction, kinetics Radiobiology 40 Dosimetry, bio-modelling, tracer technology, radiation protection Instrumentation 100 Scintillating camera, SPECT, imaging procedure, computer Related fields 50 Medical imaging modalities, epidemiology, statistics Reactor-cyclotron generator, Radioisotope identification (5-7 days) Synthesis, labelling, quality control, animal test (3-4 wks) Dosage-effect, molecular biology, radiation injury (4 wks) Daily operation and quality control, trouble shooting (4 wks) Short round (6 wks) 9
10 Subject Duration (hrs) Suggested content of teaching Recommended practice and time period Clinical use Cardiology, neurology, GI tract, respiratory, endocrine, bones, haematology, tumour and infection Clinical practice, image interpretation etc. (12-18 months) In-vitro use 10 RAIU, RBC mass, survival, hypersplenism GFR measurements RAIU practice (2 wks) GFR estimation (4 weeks) Therapy 60 RIT, palliation, Ward duty (3-4 months) Posting in CT scan and MRI rooms is recommended as an aid to PET Scan imaging. ASSESSMENT FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT, during the training programme Formative assessment should be continual and should assess medical knowledge, patient care, procedural & academic skills, interpersonal skills, professionalism, self directed learning and ability to practice in the system. General Principles Internal Assessment should be frequent, cover all domains of learning and used to provide feedback to improve learning; it should also cover professionalism and communication skills. The Internal Assessment should be conducted in theory and practical/clinical examination. Quarterly assessment during the MD training should be based on: 1. Journal based / recent advances learning 2. Patient based /Laboratory or Skill based learning 3. Self directed learning and teaching 4. Departmental and interdepartmental learning activity 5. External and Outreach Activities / CMEs The student to be assessed periodically as per categories listed in postgraduate student appraisal form (Annexure I). SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT, i.e., namely assessment at the end of the training The summative examination would be carried out as per the Rules given in POSTGRADUATE MEDICAL EDUCATION REGULATIONS, Post Graduate Examination will be in three parts: 1. Thesis: 10
11 Every post graduate student shall carry out work on an assigned research project under the guidance of a recognised Post Graduate Teacher, the result of which shall be written up and submitted in the form of a Thesis. Work for writing the Thesis is aimed at contributing to the development of a spirit of enquiry, besides exposing the post graduate student to the techniques of research, critical analysis, acquaintance with the latest advances in medical science and the manner of identifying and consulting available literature. Thesis shall be submitted at least six months before the Theory and Clinical / Practical examination. The thesis shall be examined by a minimum of three examiners; one internal and two external examiners, who shall not be the examiners for Theory and Clinical examination. A post graduate student shall be allowed to appear for the Theory and Practical/Clinical examination only after the acceptance of the Thesis by the examiners. 2. Theory Examination: The examinations shall be organised on the basis of Grading or Marking system to evaluate and to certify post graduate student's level of knowledge, skill and competence at the end of the training. Obtaining a minimum of 50% marks in Theory as well as Practical separately shall be mandatory for passing examination as a whole. The examination for M.D. shall be held at the end of 3rd academic year. An academic term shall mean six month's training period. There will be 4 theory papers: Paper I: Paper II: Paper III: Paper IV: Basic Sciences related to Nuclear Medicine Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine Therapeutic Nuclear Medicine Recent advances in Nuclear Medicine 3. Practical/Clinical and Oral Examination Practical examination shall consist of carrying out special investigative techniques for diagnosis and therapy. Oral examination shall be comprehensive enough to test the post graduate student s overall knowledge of the subject. There shall be: 1. One long case and two short cases. 2. Two practicals consisting of one in basic science and one in clinical science. 3. Spots 4. Oral/viva-voce examination & scan reading Recommended Reading: Books (latest edition) 11
12 1. Neuro PET, by Herholz 2. Molecular anatomic Imaging, by Von Schulthess 3. Principles and Practice of Nuclear Medicine,by Paul, J. Early, D. Bruce Sodee 4. Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine, by Sandler and Gottchalk 5. Nuclear Medicine in Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment, by Ell and Gambhir 6. Positron Emission Tomography, by Valk, Bailey, Townsend 7. Practical FDG Imaging A teaching File, by Debelke, Martin, Patton, Sandler. 8. Functional Cerebral SPECT and PE Imaging 9. CT and MR Imaging of the whole body, Haaga, Lanzieri, Gilkeson 10. Multidetector CT : Principle Techniques and Clinical Applications, by Fishman Jeffrey Normal Lymph node Topography 11. CT atlas, by Richter Feyerabind Journals international Journals and 02 national (all indexed) journals 12
13 Postgraduate Students Appraisal Form Pre / Para /Clinical Disciplines Name of the Department/Unit : Name of the PG Student : Period of Training Sr. No. PARTICULARS 1. Journal based / recent advances learning 2. Patient based /Laboratory or Skill based learning 3. Self directed learning and teaching 4. Departmental and interdepartmental learning activity 5. External and Outreach Activities / CMEs 6. Thesis / Research work 7. Log Book Maintenance : FROM TO Not Satisfactory Satisfactory More Than Satisfactory Annexure I Remarks Publications Yes/ No Remarks* *REMARKS: Any significant positive or negative attributes of a postgraduate student to be mentioned. For score less than 4 in any category, remediation must be suggested. Individual feedback to postgraduate student is strongly recommended. SIGNATURE OF ASSESSEE SIGNATURE OF CONSULTANT SIGNATURE OF HOD 13
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN SPORTS MEDICINE Preamble: Sports Medicine is a multi-disciplinary field, which caters to a large number of subspecialities
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN SPORTS MEDICINE Preamble: Sports Medicine is a multi-disciplinary field, which caters to a large number of subspecialities
Postgraduate Diploma in Health Sciences in Medical Imaging (Nuclear Medicine Pathway)
 Postgraduate Diploma in Health Sciences in Medical Imaging (Nuclear Medicine Pathway) Introduction The Nuclear Medicine pathway of the Postgraduate Diploma in Health Sciences (Medical Imaging) provides
Postgraduate Diploma in Health Sciences in Medical Imaging (Nuclear Medicine Pathway) Introduction The Nuclear Medicine pathway of the Postgraduate Diploma in Health Sciences (Medical Imaging) provides
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals
 Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
Clinical Radiation Sciences (CLRS) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES (CLRS) CLRS 101. Introduction to Clinical Radiologic Sciences. 1 Hour. Semester course; 1 lecture hour. 1 credit. Presentation and discussion
Nuclear Medicine and PET. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
45 Hr PET Registry Review Course
 45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
Harlem Hospital Center Department of Radiology. Residency Training Program
 Harlem Hospital Center Department of Radiology Residency Training Program NUCLEAR MEDICINE: Goals and Objectives The Nuclear Radiology Core Curriculum is designed to provide the Radiology foundation for
Harlem Hospital Center Department of Radiology Residency Training Program NUCLEAR MEDICINE: Goals and Objectives The Nuclear Radiology Core Curriculum is designed to provide the Radiology foundation for
General Nuclear Medicine
 General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS)
 Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
Kent State University Catalog 2017-2018 1 RADIOLOGIC AND IMAGING SCIENCE (RIS) RIS 34001 INTRODUCTION TO DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY 1 Credit Provides an introduction to diagnostic medical sonography.
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POST GRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN RADIODIAGNOSIS
 GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POST GRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN RADIODIAGNOSIS Preamble: The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POST GRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR DIPLOMA IN RADIODIAGNOSIS Preamble: The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care
Department of Nuclear Medicine with Positron Emission Tomography
 (PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
(PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION THERAPY (SECOND MODALITY)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiation therapy (second modality) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiation therapy (second modality) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION
Radiopharmacy. Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL. CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı
 Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY (SECOND MODALITY)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in nuclear medicine technology (second modality) CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in nuclear medicine technology (second modality) CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOGRAPHY (DEGREE COMPLETION)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiography (degree completion) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOGRAPHY
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiography (degree completion) 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOGRAPHY
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOLOGIST ASSISTANT (SECOND MODALITY)
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiologist assistant (second modality) CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOLOGIST
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiologist assistant (second modality) CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIOLOGIST
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Adult and Pediatric Neurology
 Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Adult and Pediatric Neurology INTRODUCTION 2011 A university wishing to have an accredited program in adult Neurology must also sponsor an
Specific Standards of Accreditation for Residency Programs in Adult and Pediatric Neurology INTRODUCTION 2011 A university wishing to have an accredited program in adult Neurology must also sponsor an
Dr Alfred O Ankrah FCNP
 Dr Alfred O Ankrah FCNP Outline Introduction Brief history of Nuclear Medicine in Ghana Current situation of Nuclear Medicine in Ghana Use of Nuclear medicine in various disciplines Future of Nuclear Medicine
Dr Alfred O Ankrah FCNP Outline Introduction Brief history of Nuclear Medicine in Ghana Current situation of Nuclear Medicine in Ghana Use of Nuclear medicine in various disciplines Future of Nuclear Medicine
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging. Danielle Wilson
 Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Molecular Imaging and Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes
 Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION THERAPY
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiation therapy 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION THERAPY The
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in radiation therapy 1 CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN RADIATION THERAPY The
Catalog Addendum
 Catalog Addendum - 2018 Day Class RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (Levittown) HEGIS CODE: 5207.00 Radiologic Technologies (X-Ray) Day Program - 2005 Hours (16 mos./67 wks.) Diploma Program Hunter Business School
Catalog Addendum - 2018 Day Class RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (Levittown) HEGIS CODE: 5207.00 Radiologic Technologies (X-Ray) Day Program - 2005 Hours (16 mos./67 wks.) Diploma Program Hunter Business School
Atoms for Health. Atoms for Health The. Atoms for Health - Division of Nuclear Health - Dept of Nuclear Aplications P Andreo DIR-NAHU 1
 International Atomic Energy Agency Atoms for Health The human side of nuclear applications NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS IN HEALTH A UNIQUE MANDATE OF THE UN SYSTEM The Agency shall seek to accelerate and enlarge
International Atomic Energy Agency Atoms for Health The human side of nuclear applications NUCLEAR APPLICATIONS IN HEALTH A UNIQUE MANDATE OF THE UN SYSTEM The Agency shall seek to accelerate and enlarge
CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE TECHNOLOGY
 Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in nuclear medicine technology CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Clinical Radiation Sciences, Bachelor of Science (B.S.) with a concentration in nuclear medicine technology CLINICAL RADIATION SCIENCES, BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.S.) WITH A CONCENTRATION IN NUCLEAR MEDICINE
Children's (Pediatric) Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Nuclear Medicine Children s (pediatric) nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and a computer
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Nuclear Medicine Children s (pediatric) nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and a computer
Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine
 Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists and the American College of
Basic Standards for Osteopathic Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine American Osteopathic Association and the American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists and the American College of
(See also General Regulations and Regulations for Taught Postgraduate Curricula)
 D.67/316-i REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF DENTAL SURGERY IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY [MDS(OralMaxFacSur)] These regulations apply to candidates admitted in 2016-2017 and thereafter. (See
D.67/316-i REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF DENTAL SURGERY IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY [MDS(OralMaxFacSur)] These regulations apply to candidates admitted in 2016-2017 and thereafter. (See
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526)
 RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
RADIOLOGIC TECHNOLOGY (526) 526-133 DMS General Procedures 2 Radiologic Technology (526) 1 526-130 Introduction to Diagnostic Medical Sonography This course introduces the student to the history of ultrasound
DEPARTMENT OF RADIATION SCIENCES
 Department of Radiation Sciences 1 DEPARTMENT OF RADIATION SCIENCES Jeffrey S. Legg, Ph.D., RT(R)(CT)(QM) Associate professor and chair sahp.vcu.edu/departments/radsci (http://sahp.vcu.edu/departments/
Department of Radiation Sciences 1 DEPARTMENT OF RADIATION SCIENCES Jeffrey S. Legg, Ph.D., RT(R)(CT)(QM) Associate professor and chair sahp.vcu.edu/departments/radsci (http://sahp.vcu.edu/departments/
Medical Use of Radioisotopes
 Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
RADS Radiologic Sciences
 RADS Radiologic Sciences 1 RADS Radiologic Sciences RADS 2000 Terminology Of Imag & Rad Sci Exploration of medical terms related to Radiologic Sciences. Also includes terminology and track specific content
RADS Radiologic Sciences 1 RADS Radiologic Sciences RADS 2000 Terminology Of Imag & Rad Sci Exploration of medical terms related to Radiologic Sciences. Also includes terminology and track specific content
SPECIFIC AIMS PROGRAM IMAGING. V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS
 V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS SANTONI R. COORDINATOR MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Santoni Riccardo 1 MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Manenti Guglielmo 1 MED/36
V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS SANTONI R. COORDINATOR MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Santoni Riccardo 1 MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Manenti Guglielmo 1 MED/36
ENDOCRINOLOGY, DIABETES AND METABOLISM
 ENDOCRINOLOGY, DIABETES AND METABOLISM (I) OBJECTIVES 1 To provide a broad training and in-depth experience at a level sufficient for trainees to acquire competence and professionalism required of a specialist
ENDOCRINOLOGY, DIABETES AND METABOLISM (I) OBJECTIVES 1 To provide a broad training and in-depth experience at a level sufficient for trainees to acquire competence and professionalism required of a specialist
Fellows on this rotation are expected to attend nuclear conferences and multimodality imaging conference.
 Rotation: Imaging 1 Imaging 1 provides COCATS Level 1 experience for nuclear cardiology (including SPECT and PET) and cardiac CT. Fellows will administer, process, and read cardiac nuclear studies with
Rotation: Imaging 1 Imaging 1 provides COCATS Level 1 experience for nuclear cardiology (including SPECT and PET) and cardiac CT. Fellows will administer, process, and read cardiac nuclear studies with
Basic Standards for Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine
 Basic Standards for Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists and American College of Osteopathic Internists
Basic Standards for Fellowship Training in Sleep Medicine American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists and American College of Osteopathic Internists
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Guideline & Reports 医学物理学会教育委員会資料
 Guideline & Reports 医学物理学会教育委員会資料 2017/11 更新 report title year keyword 1 keyword 2 AAPM TG211 Classification and evaluation strategies of auto-segmentation approaches for PET 2017 PET autosegmentation
Guideline & Reports 医学物理学会教育委員会資料 2017/11 更新 report title year keyword 1 keyword 2 AAPM TG211 Classification and evaluation strategies of auto-segmentation approaches for PET 2017 PET autosegmentation
Revised: 8/05; 9/08; 9/09; 8/11; 8/12; 1/13 Reviewed: 3/10
 DCH RADIOGRAPHY PROGRAM CURRICULUM 17 Hours of Pre-requisites are required before entering into the professional phase of the Radiography Program. Pre-requisites English Comp I Intermediate College Algebra
DCH RADIOGRAPHY PROGRAM CURRICULUM 17 Hours of Pre-requisites are required before entering into the professional phase of the Radiography Program. Pre-requisites English Comp I Intermediate College Algebra
WN MEDICAL IMAGING. RADIOTHERAPY. MEDICAL PHYSICS. NUCLEAR MEDICINE. RADIOACTIVITY
 WN MEDICAL IMAGING. RADIOTHERAPY. MEDICAL PHYSICS. NUCLEAR MEDICINE. RADIOACTIVITY Definitions : (from various online encyclopaedias/dictionaries) Medical Imaging/Radiology/ Diagnostic imaging: the use
WN MEDICAL IMAGING. RADIOTHERAPY. MEDICAL PHYSICS. NUCLEAR MEDICINE. RADIOACTIVITY Definitions : (from various online encyclopaedias/dictionaries) Medical Imaging/Radiology/ Diagnostic imaging: the use
International Conference on Clinical PET and Molecular Nuclear Medicine (IPET 2011)
 IAEA-CN-185 International Conference on Clinical PET and Molecular Nuclear Medicine (IPET 2011) Trends in Clinical PET and Radiopharmaceutical Development 8 11 November 2011 Vienna, Austria Announcement
IAEA-CN-185 International Conference on Clinical PET and Molecular Nuclear Medicine (IPET 2011) Trends in Clinical PET and Radiopharmaceutical Development 8 11 November 2011 Vienna, Austria Announcement
Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 2017 Imaging Inventory
 Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 207 Imaging Inventory Computed Tomography Computed tomography (CT) employs X-rays as a source of ionizing radiation,
Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 207 Imaging Inventory Computed Tomography Computed tomography (CT) employs X-rays as a source of ionizing radiation,
PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015)
 PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015) Course Description: This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce
PHYS 383: Applications of physics in medicine (offered at the University of Waterloo from Jan 2015) Course Description: This course is an introduction to physics in medicine and is intended to introduce
Approved by the Study Board of Biomedical Engineering on 1 April 2012 and approved by the Dean on 1 April Exam and assessment
 Approved by the Study Board of Biomedical Engineering on 1 April 2012 and approved by the Dean on 1 April 2012 This document contains descriptions of the courses and exams of the Master's Degree Programme
Approved by the Study Board of Biomedical Engineering on 1 April 2012 and approved by the Dean on 1 April 2012 This document contains descriptions of the courses and exams of the Master's Degree Programme
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST
 HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
Nuclear Medicine: Manuals. Nuclear Medicine. Nuclear imaging. Emission imaging: study types. Bone scintigraphy - technique
 Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Hybrid imaging guidance on legislative, reporting and training aspects
 Hybrid imaging guidance on legislative, reporting and training aspects The Royal College of Radiologists Royal College of Physicians of London Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow Royal
Hybrid imaging guidance on legislative, reporting and training aspects The Royal College of Radiologists Royal College of Physicians of London Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Glasgow Royal
Description MRI, TMJ C T Head Without Contrast C T Head With Contrast C T Head Without & With Contrast
 s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
Texas A&M College of Dentistry Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology
 Texas A&M College of Dentistry Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology The college offers a graduate education program in Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (OMR) that is accredited by the Commission on Dental
Texas A&M College of Dentistry Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology The college offers a graduate education program in Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (OMR) that is accredited by the Commission on Dental
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
COMPETENCES REQUIRED FOR APPLICANTS TO ATTAIN HPC REGISTRATION AS CLINICAL SCIENTISTS
 This document comprises a discipline-specific version of the general competence document and provides additional guidance as to how to complete the general document, Appendix 1 of the Guidelines, that
This document comprises a discipline-specific version of the general competence document and provides additional guidance as to how to complete the general document, Appendix 1 of the Guidelines, that
SYLLABUS NEURO & VASCULAR INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY
 SYLLABUS NEURO & VASCULAR INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS A: General Principles: Each Fellowship student is required to possess a comprehensive knowledge of the imaging modalities
SYLLABUS NEURO & VASCULAR INTERVENTIONAL RADIOLOGY DURATION OF THE COURSE : TWO YEARS A: General Principles: Each Fellowship student is required to possess a comprehensive knowledge of the imaging modalities
Course specification
 Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Master of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for men Course specification - Programmers on which
Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Master of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for men Course specification - Programmers on which
CARDIOLOGY. 3 To develop in the trainees the humanistic, moral and ethical aspects of medicine.
 CARDIOLOGY (I) OBJECTIVES 1 To provide a broad training and in-depth experience at a level sufficient for trainees to acquire competence and professionalism required of a specialist in Cardiology. 2 To
CARDIOLOGY (I) OBJECTIVES 1 To provide a broad training and in-depth experience at a level sufficient for trainees to acquire competence and professionalism required of a specialist in Cardiology. 2 To
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Musculoskeletal Tumor Society Curriculum Guidelines for Clinical Fellowship Programs In Musculoskeletal Oncology
 Musculoskeletal Tumor Society Curriculum Guidelines for Clinical Fellowship Programs In Musculoskeletal Oncology Preamble: The Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS) is committed to excellence in the fellowship
Musculoskeletal Tumor Society Curriculum Guidelines for Clinical Fellowship Programs In Musculoskeletal Oncology Preamble: The Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS) is committed to excellence in the fellowship
Basics of nuclear medicine
 Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
General Nuclear Medicine
 Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
Scan for mobile link. General Nuclear Medicine Nuclear medicine imaging uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers that are typically injected into the bloodstream, inhaled or swallowed.
An investigation of the effect of ionising radiation on nurses and their patients during dialysis
 International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
The European Board of Urology
 Page 1 of 15 The European Board of Urology Sub-specialty certification application: Prostate cancer, A - General information A1 - APPLICATION IDENTIFICATION 1a. Application code blank 1b. EBU internal
Page 1 of 15 The European Board of Urology Sub-specialty certification application: Prostate cancer, A - General information A1 - APPLICATION IDENTIFICATION 1a. Application code blank 1b. EBU internal
Info Packet. Sacramento Ultrasound Institute. AAS Degree in MRI Technology Session: 2016/17
 Sacramento Ultrasound Institute Info Packet Admissions: (916) 484-7666 admissions@sui.edu For more information abour the MRI Technology program, please visit www.sui.edu AAS Degree in MRI Technology Session:
Sacramento Ultrasound Institute Info Packet Admissions: (916) 484-7666 admissions@sui.edu For more information abour the MRI Technology program, please visit www.sui.edu AAS Degree in MRI Technology Session:
2010 Radiology Prior Authorization List for UnitedHealthcare s HealthChoice Members
 70336 MR TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT 70450 CT, HEAD OR BRAIN; WITHOUT MATERIAL 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ 70480 CT, ORBIT, SELLA, OR POSTERIOR FOSSA OR OUTER, MID 70481 CT ORBIT W/
70336 MR TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT 70450 CT, HEAD OR BRAIN; WITHOUT MATERIAL 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/ 70470 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O & W/ 70480 CT, ORBIT, SELLA, OR POSTERIOR FOSSA OR OUTER, MID 70481 CT ORBIT W/
Specialist List in Special Care Dentistry
 Specialist List in Special Care Dentistry Definition of Special Care Dentistry Special Care Dentistry (SCD) is concerned with providing enabling the delivery of oral care for people with an impairment
Specialist List in Special Care Dentistry Definition of Special Care Dentistry Special Care Dentistry (SCD) is concerned with providing enabling the delivery of oral care for people with an impairment
(See also General Regulations and Regulations for Taught Postgraduate Curricula)
 D.29/817 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF DENTAL SURGERY IN ENDODONTICS [MDS(Endo)] These regulations apply to candidates admitted in 2017-2018 and thereafter (See also General Regulations and Regulations
D.29/817 REGULATIONS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF DENTAL SURGERY IN ENDODONTICS [MDS(Endo)] These regulations apply to candidates admitted in 2017-2018 and thereafter (See also General Regulations and Regulations
OTHER NON-CARDIAC USES OF Tc-99m CARDIAC AGENTS Tc-99m Sestamibi for parathyroid imaging, breast tumor imaging, and imaging of other malignant tumors.
 DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
Basic Standards for Residency Training in General Neurology
 Basic Standards for Residency Training in General Neurology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists Revised 2/2003 Revised 7/2004 Revised 6/2006
Basic Standards for Residency Training in General Neurology American Osteopathic Association and American College of Osteopathic Neurologists and Psychiatrists Revised 2/2003 Revised 7/2004 Revised 6/2006
Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry
 Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY Regular Session. Enrolled. Senate Bill 280
 78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY--2015 Regular Session Enrolled Senate Bill 280 Printed pursuant to Senate Interim Rule 213.28 by order of the President of the Senate in conformance with presession filing
78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY--2015 Regular Session Enrolled Senate Bill 280 Printed pursuant to Senate Interim Rule 213.28 by order of the President of the Senate in conformance with presession filing
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Hepatic Procedural Hepatic Procedural Purpose: Prerequisites: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Hepatic Procedural Hepatic Procedural Purpose: Prerequisites: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical
PHARMACY PRACTICE (PHM PRAC)
 Pharmacy Practice (PHM PRAC) 1 PHARMACY PRACTICE (PHM PRAC) PHM PRAC 305 CONSUMER SELF-CARE AND OVER-THE-COUNTER DRUGS Provides learners with information regarding self-care of common, minor health conditions.
Pharmacy Practice (PHM PRAC) 1 PHARMACY PRACTICE (PHM PRAC) PHM PRAC 305 CONSUMER SELF-CARE AND OVER-THE-COUNTER DRUGS Provides learners with information regarding self-care of common, minor health conditions.
HIP RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LISTS
 EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
EFFECTIVE OCTOBER 1, 2012 70336 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING TMJ 70450 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT 70460 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITH 70470 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY HEAD/BRAIN WITHOUT AND WITH
CLINICAL PRIVILEGE WHITE PAPER
 Vascular Procedure ultrasound 57 Procedure 57 CLINICAL PRIVILEGE WHITE PAPER Vascular ultrasound Background Vascular ultrasound is a noninvasive procedure used to diagnose and locate disorders of the vascular
Vascular Procedure ultrasound 57 Procedure 57 CLINICAL PRIVILEGE WHITE PAPER Vascular ultrasound Background Vascular ultrasound is a noninvasive procedure used to diagnose and locate disorders of the vascular
Programme Specification
 Programme Specification Title: Forensic Science Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Master of Science (MSc) Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) To be
Programme Specification Title: Forensic Science Final Award: Master of Science (MSc) With Exit Awards at: Master of Science (MSc) Postgraduate Certificate (PG Cert) Postgraduate Diploma (PG Dip) To be
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR MD IN PSYCHIATRY
 GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR MD IN PSYCHIATRY Preamble The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care and advance
GUIDELINES FOR COMPETENCY BASED POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME FOR MD IN PSYCHIATRY Preamble The purpose of PG education is to create specialists who would provide high quality health care and advance
Program Admissions Requirements:
 ASSOCIATE OF APPLIED SCIENCE IN DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY (DMS AAS) 2,160 clock hours / 84 weeks (Total time to complete the program may vary based on school holidays and breaks) 60 weeks Theory/Lab
ASSOCIATE OF APPLIED SCIENCE IN DIAGNOSTIC MEDICAL SONOGRAPHY (DMS AAS) 2,160 clock hours / 84 weeks (Total time to complete the program may vary based on school holidays and breaks) 60 weeks Theory/Lab
Volume 14 - Issue 4, Management Matrix
 Volume 14 - Issue 4, 2014 - Management Matrix The Modern Radiology Department Prof. Christoph Becker ******@***hcuge.ch R -?pitaux Universitaires Key Points A central, integrated radiology department offers
Volume 14 - Issue 4, 2014 - Management Matrix The Modern Radiology Department Prof. Christoph Becker ******@***hcuge.ch R -?pitaux Universitaires Key Points A central, integrated radiology department offers
Last Updated: 2/10/2017 Implementation date: 4/3/2017 Radiology & Cardiology Prior Authorization / Utilization Management Procedure List
 Last Updated: 2/10/2017 Implementation date: 4/3/2017 Radiology & Cardiology Prior Authorization / Utilization Management Procedure List Deal Sheet Group Product Category CPT CPT Description 3D Imaging
Last Updated: 2/10/2017 Implementation date: 4/3/2017 Radiology & Cardiology Prior Authorization / Utilization Management Procedure List Deal Sheet Group Product Category CPT CPT Description 3D Imaging
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey
 Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey A. M. Bomben, C. A. Chiliutti Autoridad Regulatoria
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in Argentine: Results of a National Survey A. M. Bomben, C. A. Chiliutti Autoridad Regulatoria
PROGRAMME OVERVIEW Saturday, October 13, 2018
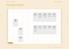 Saturday, October 13, 2018 Plenary Hall Meeting Room 26 Hall 1 Hall 2 Hall 3 Hall X Hall Y Hall 28 - - - - - - - - - - Advisory Council Meeting Delegates Assembly 1 Radiopharmacy/ Drug Development Trial
Saturday, October 13, 2018 Plenary Hall Meeting Room 26 Hall 1 Hall 2 Hall 3 Hall X Hall Y Hall 28 - - - - - - - - - - Advisory Council Meeting Delegates Assembly 1 Radiopharmacy/ Drug Development Trial
EUROPASS DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT
 EUROPASS DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT TITLE OF THE DIPLOMA (ES) Técnico Superior en Imagen para el Diagnóstico y Medicina Nuclear TRANSLATED TITLE OF THE DIPLOMA (EN) (1) Higher Technician in Diagnostic Imaging
EUROPASS DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT TITLE OF THE DIPLOMA (ES) Técnico Superior en Imagen para el Diagnóstico y Medicina Nuclear TRANSLATED TITLE OF THE DIPLOMA (EN) (1) Higher Technician in Diagnostic Imaging
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine
 Name: Date: 1. This question is about radiation dosimetry. Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine Define exposure. A patient is injected with a gamma ray emitter. The radiation from the source creates
Name: Date: 1. This question is about radiation dosimetry. Medical Physics 4 I3 Radiation in Medicine Define exposure. A patient is injected with a gamma ray emitter. The radiation from the source creates
REGULATIONS FOR THE POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN MOLECULAR AND DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY (PDipMDPath)
 REGULATIONS FOR THE POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN MOLECULAR AND DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY (PDipMDPath) (See also General Regulations and Regulations for Taught Postgraduate Curricula) M.129 Admission requirements
REGULATIONS FOR THE POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN MOLECULAR AND DIAGNOSTIC PATHOLOGY (PDipMDPath) (See also General Regulations and Regulations for Taught Postgraduate Curricula) M.129 Admission requirements
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region. Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
THESE STANDARDS ARE DORMANT.
 THESE STANDARDS ARE DORMANT. TO INQUIRE ABOUT AOBA PARTICIPATION IN THE CAQ FOR CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE FOR ANESTHESIOLOGY PLEASE CONTACT THE AOBA aoba@osteopathic.org. BASIC STANDARDS FOR SUBSPECIALTY
THESE STANDARDS ARE DORMANT. TO INQUIRE ABOUT AOBA PARTICIPATION IN THE CAQ FOR CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE FOR ANESTHESIOLOGY PLEASE CONTACT THE AOBA aoba@osteopathic.org. BASIC STANDARDS FOR SUBSPECIALTY
Course specification
 Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Doctorate of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for Men Course specification - Programmers on
Al-Azhar University Faculty of Medicine for Men Course specification For Doctorate of Radiodiagnosis ( 2014 2015 ) University : Al-Azhar Faculty : Medicine for Men Course specification - Programmers on
created by high-voltage devices Examples include medical and dental x-rays, light, microwaves and nuclear energy
 What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
Nuclear Medicine in Australia. Shaun Jenkinson
 Nuclear Medicine in Australia Shaun Jenkinson Landmark Infrastructure for Australian Science OPAL Research Reactor Australian Synchrotron Camperdown Cyclotron Bragg Institute Centre for Accelerator Science
Nuclear Medicine in Australia Shaun Jenkinson Landmark Infrastructure for Australian Science OPAL Research Reactor Australian Synchrotron Camperdown Cyclotron Bragg Institute Centre for Accelerator Science
PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY, MEDICAL ORTHOTICS/PROSTHETICS AND ARTS THERAPY MINIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE TRAINING OF ARTS THERAPISTS
 PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY, MEDICAL ORTHOTICS/PROSTHETICS AND ARTS THERAPY MINIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE TRAINING OF ARTS THERAPISTS INTRODUCTION Arts Therapies is a generic term of convenience
PROFESSIONAL BOARD FOR OCCUPATIONAL THERAPY, MEDICAL ORTHOTICS/PROSTHETICS AND ARTS THERAPY MINIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE TRAINING OF ARTS THERAPISTS INTRODUCTION Arts Therapies is a generic term of convenience
ACRO Scope of Practice Document
 ACRO Scope of Practice Document I. ORGANIZATIONAL AND LEGAL STATEMENT The American College of Radiation Oncology (ACRO) is a nonprofit professional organization whose primary purposes are to advance the
ACRO Scope of Practice Document I. ORGANIZATIONAL AND LEGAL STATEMENT The American College of Radiation Oncology (ACRO) is a nonprofit professional organization whose primary purposes are to advance the
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Hepatic Procedural
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Hepatic Procedural Page 1 of 6 12/18 Hepatic Procedural Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Hepatic Procedural Page 1 of 6 12/18 Hepatic Procedural Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET)
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Nuclear Sciences and Medicine
 Nuclear Sciences and Medicine Rethy Chhem, MD, PhD (Edu), PhD (His), FRCPC Division of Human Health Guest Professor, Medical University of Vienna International Atomic Energy Agency Medical Imaging X-rays
Nuclear Sciences and Medicine Rethy Chhem, MD, PhD (Edu), PhD (His), FRCPC Division of Human Health Guest Professor, Medical University of Vienna International Atomic Energy Agency Medical Imaging X-rays
Medical Diagnostic Imaging
 Medical Diagnostic Imaging Laboratories Medical Diagnostic Imaging Lab Name Location Person in Charge Programs Served Courses Served Patient Care and Management (2) Introduction to MDI Radiographic Technique
Medical Diagnostic Imaging Laboratories Medical Diagnostic Imaging Lab Name Location Person in Charge Programs Served Courses Served Patient Care and Management (2) Introduction to MDI Radiographic Technique
Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Medical Expert
 Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Introduction Medical Expert This is a three month PGY 1-5 rotation in which residents gain exposure in the care and management of patients
Health Sciences Centre, Team A, Dr. L. Bohacek (Endocrine Surgery) Introduction Medical Expert This is a three month PGY 1-5 rotation in which residents gain exposure in the care and management of patients
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING
 RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
RADIOTRACERS FOR MYOCARDIAL PERFUSION IMAGING RAYMOND TAILLEFER, M.D. FRCP(c), ABNM DIRECTOR, DEPARTMENT OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE HOPITAL ST-JEAN-SUR-RICHELIEU Disclosures to Report: Grant Research Support:
Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy
 Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy RCP Medical careers day Dr Sabina Dizdarevic MD MSc PhD FRCP Dr Deena Neriman MBBS FRCR Ms Charlotte Weston CEO BNMS On behalf of the British Nuclear Medicine Society
Nuclear Medicine: Basics to therapy RCP Medical careers day Dr Sabina Dizdarevic MD MSc PhD FRCP Dr Deena Neriman MBBS FRCR Ms Charlotte Weston CEO BNMS On behalf of the British Nuclear Medicine Society
