Perception Laboratory: Basic Visual Processing
|
|
|
- Natalie Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Perception Laboratory: Basic Visual Processing 1. Ganzfeld Tell me approximately how long it took you for the effect to kick in and describe your perceptual experience when it happened. What does that say about the importance of edges? 2. Mach Bands Explain the role of lateral inhibition in producing the Mach Bands. Focus your explanation on the receptive fields (A-E) illustrated in the figure. For example, how would the ganglion cell connected to Receptive Field A differ in firing from the ganglion cell connected to Receptive Field B? What about D and E? Explain why B would produce less firing than A and D would produce more firing than E? 3. Lightness in Context How might you explain the different perception of identical stimuli (in this case identical gray squares)? What might your experience have to say about the relative nature of perception? Why does your perceptual experience of the gray squares differ in A, B, and C? A B C Basic Visual Processes Lab - 1
2 D E F In D, which four gray squares (on left or right) seem darker? Given the immediate background, which four gray squares should seem darker? In E, which of the two gray lines (on left or right) seems darker? Given the immediate background, which line should seem darker? In both D and E the target lightness that emerges is not driven by the immediately surrounding lightness, so how would you explain the perception of lightness that emerges? In F, do the two gray triangles (on left or right) differ in lightness? Note that the surround of the two triangles is identical (two sides surrounded by black and one side surrounded by white). Some people may not perceive a difference in lightness. For those who do, the effect may not be particularly strong. What do you experience? Why do you think you have the experience of lightness that you do? Basic Visual Processes Lab - 2
3 Why are the two squares (labeled A and B) in Adelson s demonstration perceived as different in lightness, even though they are identical? Why do the gray ellipses in the room appear to differ in lightness? (Of course, they are identical.) Actual depth relations have an impact on perceived lightness (e.g., Gilchrist study, above left). Both Mach s Book and Kersten s demonstration rely on mentally changing the depth relations in a stimulus. Note that the retinal stimulation doesn t change. As a result, one might predict that the lightness perception would not change. However, that s clearly not the case. Can you explain why? Basic Visual Processes Lab - 3
4 4. Lightness/Brightness Illusions and Demonstrations a. R. Beau Lotto Site Illusions Illusion Your explanation C H I L b. Adelson Site Demonstration Explanation Simultaneous Contrast (why does the articulated background enhance the effect?) Craik-O Brien-Cornsweet Effect Vasarely Illusion Based on these experiences, what factors (besides the differences in retinal activity) seem to you to be responsible for our experience of lightness/brightness? Basic Visual Processes Lab - 4
5 5. Hermann Grid, etc. The Hermann Grid provides you with another example of a perceptual experience that is not consistent with the visual stimulus. Why might you be seeing dark spots on the grid when no dark spots are actually present? And why might shrinking the stimulus lead the dark spots to disappear? The "scintillating grid" demonstration was discovered by Elke Lingelbach. It's similar to the Hermann grid, but not identical in its effect. What is your experience like? Why do you think that the stimulus leads to your perception? 6. Filling-In Processes: The Blind Spot As you are already beginning to observe, our visual system is a "value added" system. It takes in stimulation from the outside world, but it processes that input in ways that may lead to perceptual experiences that are quite different from the visual input. What occurs at the blind spot is a great illustration of the contributions of filling-in processes that are ubiquitous in the processing of incomplete stimuli. a. (R eye) b. (L eye) What is your perceptual experience of each stimulus? Why? a. b. Basic Visual Processes Lab - 5
6 c. (R eye) d. (L eye) c. d. e. (R eye) f. (L eye) e. f. (what happens to the vertical and horizontal lines?) g. (R eye) h. (L eye) g. h. Basic Visual Processes Lab - 6
7 i. (L eye) j. (L eye) i. j. k. (R eye) l. (R eye) k. l. m. (R eye) What is your perceptual experience of this stimulus? What does activity at the blind spot tell us about filling-in processes? Basic Visual Processes Lab - 7
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 4: Coding Concepts Chapter 2 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 4: Coding Concepts Chapter 2 Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
What do we perceive?
 THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
THE VISUAL SYSTEM Aditi Majumder What do we perceive? Example: Switch off the light in room What we perceive Not only the property of the scene But also that of the visual system Our perception is filtered
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience. Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3
 Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Psy393: Cognitive Neuroscience Prof. Anderson Department of Psychology Week 3 The Eye: Proof for the existence of God? And then there was light Optics Perception Absorption Eye is receiver not sender Plato
Perceiving the Intensity of Light
 Psychological Review Copyright 2004 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2004, Vol. 111, No. 1, 142 158 0033-295X/04/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0033-295X.111.1.142 Perceiving the Intensity of Light
Psychological Review Copyright 2004 by the American Psychological Association, Inc. 2004, Vol. 111, No. 1, 142 158 0033-295X/04/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0033-295X.111.1.142 Perceiving the Intensity of Light
PSY 310: Sensory and Perceptual Processes 1
 Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
Processing streams PSY 310 Greg Francis Neurophysiology We are working under the following hypothesis What we see is determined by the pattern of neural activity in the brain This leads to several interesting
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
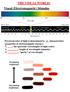 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. : the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color) 2.
IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology
 IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis, PhD email: gfrancis@purdue.edu http://www.psych.purdue.edu/ gfrancis/classes/iie269/index.html Study Guide for Exam 1 Exam Date: 14 July 2008 The exam will include
IIE 269: Cognitive Psychology Greg Francis, PhD email: gfrancis@purdue.edu http://www.psych.purdue.edu/ gfrancis/classes/iie269/index.html Study Guide for Exam 1 Exam Date: 14 July 2008 The exam will include
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2001 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, so keep your eyes foveated on your own exam. I tend to think of a point as a minute, so be sure to spend the appropriate amount
Diamond Patterns: Cumulative Cornsweet Effects and Motion-Induced Brightening
 Short and Sweet Diamond Patterns: Cumulative Cornsweet Effects and Motion-Induced Brightening i-perception 2018 Vol. 9(4), 1 5! The Author(s) 2018 DOI: 10.1177/2041669518770690 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe
Short and Sweet Diamond Patterns: Cumulative Cornsweet Effects and Motion-Induced Brightening i-perception 2018 Vol. 9(4), 1 5! The Author(s) 2018 DOI: 10.1177/2041669518770690 journals.sagepub.com/home/ipe
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus
 THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
THE VISUAL WORLD! Visual (Electromagnetic) Stimulus Perceived color of light is determined by 3 characteristics (properties of electromagnetic energy): 1. Hue: the spectrum (wavelength) of light (color)
Vision Seeing is in the mind
 1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
1 Vision Seeing is in the mind Stimulus: Light 2 Light Characteristics 1. Wavelength (hue) 2. Intensity (brightness) 3. Saturation (purity) 3 4 Hue (color): dimension of color determined by wavelength
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8. Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017
 V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
V1 (Chap 3, part II) Lecture 8 Jonathan Pillow Sensation & Perception (PSY 345 / NEU 325) Princeton University, Fall 2017 Topography: mapping of objects in space onto the visual cortex contralateral representation
SENSES: VISION. Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014
 SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
SENSES: VISION Chapter 5: Sensation AP Psychology Fall 2014 Sensation versus Perception Top-Down Processing (Perception) Cerebral cortex/ Association Areas Expectations Experiences Memories Schemas Anticipation
A THEORY OF MCCOLLOUGH EFFECT AND. CHUN CHIANG Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica
 A THEORY OF MCCOLLOUGH EFFECT AND CONTINGENT AFTER-EFFECT CHUN CHIANG Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica A model is advanced to explain the McCollough effect and the contingent motion after-effect.
A THEORY OF MCCOLLOUGH EFFECT AND CONTINGENT AFTER-EFFECT CHUN CHIANG Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica A model is advanced to explain the McCollough effect and the contingent motion after-effect.
PSY 214 Lecture 5 (09/19/2010) (Vision) Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 5 Topic: Introduction to Vision Chapter 3, pages 55-71
 Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Corrections: No corrections needed Announcements: After the completion of chapter 4 a movie will be shown First test is October 3, 2011 Dr. Achtman is available during her office hours The test will include
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 05. Rods and cones
 Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
Neural circuits PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 05 Why do you need bright light to read? Rods and cones Photoreceptors are not evenly distributed across the retina 1 Rods and cones Cones are most dense in
lateral organization: maps
 lateral organization Lateral organization & computation cont d Why the organization? The level of abstraction? Keep similar features together for feedforward integration. Lateral computations to group
lateral organization Lateral organization & computation cont d Why the organization? The level of abstraction? Keep similar features together for feedforward integration. Lateral computations to group
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)
 Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN) What happens beyond the retina? What happens in Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)- 90% flow Visual cortex Information Flow Superior colliculus 10% flow Slide 2 Information
Structure of the eye and retina
 1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
1 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM Syllabus pdf file Course Schedule Structure of the eye and retina 2 of 10 3/6/2012 1:06 PM In-class demo: do Virtual Lab activity 3-6 (Visual Path in the Eyeball) Focusing, changes
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Multiple-choice questions are worth one point each, other questions
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2004 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect. Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Multiple-choice questions are worth one point each, other questions
Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 12. COC illusion
 Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 12 Is 100 billion neurons enough? COC illusion The COC illusion looks like real squares because the neural responses are similar True squares COC squares Ganglion
Neural codes PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 12 Is 100 billion neurons enough? COC illusion The COC illusion looks like real squares because the neural responses are similar True squares COC squares Ganglion
2/3/17. Visual System I. I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex
 1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
1 Visual System I I. Eye, color space, adaptation II. Receptive fields and lateral inhibition III. Thalamus and primary visual cortex 2 1 2/3/17 Window of the Soul 3 Information Flow: From Photoreceptors
M Cells. Why parallel pathways? P Cells. Where from the retina? Cortical visual processing. Announcements. Main visual pathway from retina to V1
 Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Announcements exam 1 this Thursday! review session: Wednesday, 5:00-6:30pm, Meliora 203 Bryce s office hours: Wednesday, 3:30-5:30pm, Gleason https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zdw7pvgz0um M Cells M cells
Brightness assimilation in bullseye displays
 Vision Research 44 (2004) 309 319 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Brightness assimilation in bullseye displays Daniel Bindman *, Charles Chubb Institute for Mathematical Behavioral Sciences, University
Vision Research 44 (2004) 309 319 www.elsevier.com/locate/visres Brightness assimilation in bullseye displays Daniel Bindman *, Charles Chubb Institute for Mathematical Behavioral Sciences, University
Contextual Influences in Visual Processing
 C Contextual Influences in Visual Processing TAI SING LEE Computer Science Department and Center for Neural Basis of Cognition, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA Synonyms Surround influence;
C Contextual Influences in Visual Processing TAI SING LEE Computer Science Department and Center for Neural Basis of Cognition, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA Synonyms Surround influence;
Context affects lightness at the level of surfaces
 Journal of Vision (2015) 15(1):15, 1 15 http://www.journalofvision.org/content/15/1/15 1 Context affects lightness at the level of surfaces Marianne Maertens Modelling of Cognitive Processes Group, Department
Journal of Vision (2015) 15(1):15, 1 15 http://www.journalofvision.org/content/15/1/15 1 Context affects lightness at the level of surfaces Marianne Maertens Modelling of Cognitive Processes Group, Department
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind
 Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Lesson 5 Sensation, Perception, Memory, and The Conscious Mind Introduction: Connecting Your Learning The beginning of Bloom's lecture concludes his discussion of language development in humans and non-humans
Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview
 Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview By Orazio Gallo, April 24th, 2008 The Visual System Our most advanced perception system: The optic nerve has 106 fibers, more than all the
Image Processing in the Human Visual System, a Quick Overview By Orazio Gallo, April 24th, 2008 The Visual System Our most advanced perception system: The optic nerve has 106 fibers, more than all the
Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2
 Name: ID # ID: A Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2 Multiple Choice (38 questions, 1 point each) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Name: ID # ID: A Psych 333, Winter 2008, Instructor Boynton, Exam 2 Multiple Choice (38 questions, 1 point each) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
IAT 355 Perception 1. Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get
 IAT 355 Perception 1 Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get Why we need to understand perception The ability of viewers to interpret visual (graphical) encodings of information and
IAT 355 Perception 1 Or What You See is Maybe Not What You Were Supposed to Get Why we need to understand perception The ability of viewers to interpret visual (graphical) encodings of information and
COMP 3020: Human-Computer Interaction I
 reddit.com 1 2 COMP 3020: Human-Computer Interaction I Fall 2017 Prototype Lifetime James Young, with acknowledgements to Anthony Tang, Andrea Bunt, Pourang Irani, Julie Kientz, Saul Greenberg, Ehud Sharlin,
reddit.com 1 2 COMP 3020: Human-Computer Interaction I Fall 2017 Prototype Lifetime James Young, with acknowledgements to Anthony Tang, Andrea Bunt, Pourang Irani, Julie Kientz, Saul Greenberg, Ehud Sharlin,
The Visual System. Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Chapter 3 The Visual System Figure 3.1: Left: The visual system seen from underneath the brain showing the nerve fibres from the retina cross over to the opposite sides of the brain. A small part of the
Senses are transducers. Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What?
 1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
1 Vision 2 TRANSDUCTION Senses are transducers Change one form of energy into another Light, sound, pressure, etc. into What? Action potentials! Sensory codes Frequency code encodes information about intensity
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II
 Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
Mr. Silimperi Council Rock High School South AP Psychology Name: Date: Chapter 5 Sensation Sensation II Psychophysics study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological
psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015
 psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 Lesson #2: Sept. 29 th 2014 Lecture plan: SENSORY AND PERCEPTUAL PROCESSES Basic concepts; Sensation;
psychology of visual perception C O M M U N I C A T I O N D E S I G N, A N I M A T E D I M A G E 2014/2015 Lesson #2: Sept. 29 th 2014 Lecture plan: SENSORY AND PERCEPTUAL PROCESSES Basic concepts; Sensation;
PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II
 PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II Session 4 Background of Object Recognition Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept., of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education
PSYC 441 Cognitive Psychology II Session 4 Background of Object Recognition Lecturer: Dr. Benjamin Amponsah, Dept., of Psychology, UG, Legon Contact Information: bamponsah@ug.edu.gh College of Education
Theoretical Neuroscience: The Binding Problem Jan Scholz, , University of Osnabrück
 The Binding Problem This lecture is based on following articles: Adina L. Roskies: The Binding Problem; Neuron 1999 24: 7 Charles M. Gray: The Temporal Correlation Hypothesis of Visual Feature Integration:
The Binding Problem This lecture is based on following articles: Adina L. Roskies: The Binding Problem; Neuron 1999 24: 7 Charles M. Gray: The Temporal Correlation Hypothesis of Visual Feature Integration:
Sensation & Perception PSYC420 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D.
 Sensation & Perception PSYC420 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D. Objects & Forms When we look out into the world we are able to see things as trees, cars, people, books, etc. A wide variety of objects and
Sensation & Perception PSYC420 Thomas E. Van Cantfort, Ph.D. Objects & Forms When we look out into the world we are able to see things as trees, cars, people, books, etc. A wide variety of objects and
The Luminance Misattribution in Lightness Perception
 UDC 159.937.514.072 PSIHOLOGIJA, 2010, Vol. 43 (1), 159.937.3 2010 by the Serbian Psychological Association DOI: 10.2298/PSI1001033S The Luminance Misattribution in Lightness Perception Alessandro Soranzo
UDC 159.937.514.072 PSIHOLOGIJA, 2010, Vol. 43 (1), 159.937.3 2010 by the Serbian Psychological Association DOI: 10.2298/PSI1001033S The Luminance Misattribution in Lightness Perception Alessandro Soranzo
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception
 COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 7: Color (Chapter 6) Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
COGS 101A: Sensation and Perception 1 Virginia R. de Sa Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Lecture 7: Color (Chapter 6) Course Information 2 Class web page: http://cogsci.ucsd.edu/ desa/101a/index.html
Prof. Greg Francis 7/31/15
 s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
s PSY 200 Greg Francis Lecture 06 How do you recognize your grandmother? Action potential With enough excitatory input, a cell produces an action potential that sends a signal down its axon to other cells
Laboratory for Shape and Depth/Distance Perception
 Name Laboratory for Shape and Depth/Distance Perception 1. Pictorial Depth Cues [Monocular Cues] a. Depth Cue Where it appears in the painting What time of day might be depicted in the painting and what
Name Laboratory for Shape and Depth/Distance Perception 1. Pictorial Depth Cues [Monocular Cues] a. Depth Cue Where it appears in the painting What time of day might be depicted in the painting and what
Main Study: Summer Methods. Design
 Main Study: Summer 2000 Methods Design The experimental design is within-subject each participant experiences five different trials for each of the ten levels of Display Condition and for each of the three
Main Study: Summer 2000 Methods Design The experimental design is within-subject each participant experiences five different trials for each of the ten levels of Display Condition and for each of the three
Early Stages of Vision Might Explain Data to Information Transformation
 Early Stages of Vision Might Explain Data to Information Transformation Baran Çürüklü Department of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University Västerås S-721 23, Sweden Abstract. In this paper
Early Stages of Vision Might Explain Data to Information Transformation Baran Çürüklü Department of Computer Science and Engineering Mälardalen University Västerås S-721 23, Sweden Abstract. In this paper
Opponent theory PSY 310 Greg Francis. Lecture 18. Trichromatic theory
 PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 18 Reach that last 1%. Trichromatic theory Different colors are represented as a pattern across the three basic colors Nicely predicted the existence of the three cone types
PSY 310 Greg Francis Lecture 18 Reach that last 1%. Trichromatic theory Different colors are represented as a pattern across the three basic colors Nicely predicted the existence of the three cone types
Vision. The Eye External View. The Eye in Cross-Section
 Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Vision The Eye External View cornea pupil iris The Eye in Cross-Section Light enters via cornea, Is focused by cornea and lens, Forming image on retina, Which contains photoreceptors. 1 The Retina Photoreceptors
Sensation vs. Perception
 PERCEPTION Sensation vs. Perception What s the difference? Sensation what the senses do Perception process of recognizing, organizing and dinterpreting ti information. What is Sensation? The process whereby
PERCEPTION Sensation vs. Perception What s the difference? Sensation what the senses do Perception process of recognizing, organizing and dinterpreting ti information. What is Sensation? The process whereby
A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception E. Overload
 Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Unit 4 Review #1 The longer an individual is exposed to a strong odor, the less aware of the odor the individual becomes. This phenomenon is known as sensory A. Acuity B. Adaptation C. Awareness D. Reception
Introduction to Cognitive Psychology: PSY 200
 1 Introduction to Cognitive Psychology: PSY 200 Greg Francis, PhD, gfrancis@purdue.edu Department of Psychological Sciences Psychological Sciences Building, Room 3186, (765) 494-6934 http://www.psych.purdue.edu/
1 Introduction to Cognitive Psychology: PSY 200 Greg Francis, PhD, gfrancis@purdue.edu Department of Psychological Sciences Psychological Sciences Building, Room 3186, (765) 494-6934 http://www.psych.purdue.edu/
B.A. II Psychology - Paper A. Form Perception. Dr. Neelam Rathee. Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh
 B.A. II Psychology - Paper A Form Perception Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh Form Perception What it is? How do we recognize an object? (form perception) 2 Perception of
B.A. II Psychology - Paper A Form Perception Dr. Neelam Rathee Department of Psychology G.C.G.-11, Chandigarh Form Perception What it is? How do we recognize an object? (form perception) 2 Perception of
PERCEPTION. Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs
 PERCEPTION Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs Perception Definition The method by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion
PERCEPTION Our Brain s Interpretation of Sensory Inputs Perception Definition The method by which the sensations experienced at any given moment are interpreted and organized in some meaningful fashion
Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy. (the part that s visible to us!)
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Vision ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ /~ksweeney/psy260.html Lighta part of the spectrum of Electromagnetic Energy (the part that s visible to us!)
EDGE DETECTION. Edge Detectors. ICS 280: Visual Perception
 EDGE DETECTION Edge Detectors Slide 2 Convolution & Feature Detection Slide 3 Finds the slope First derivative Direction dependent Need many edge detectors for all orientation Second order derivatives
EDGE DETECTION Edge Detectors Slide 2 Convolution & Feature Detection Slide 3 Finds the slope First derivative Direction dependent Need many edge detectors for all orientation Second order derivatives
The effects of global grouping laws on surface lightness perception
 Perception & Psychophysics 2004, 66 (5), 792-799 The effects of global grouping laws on surface lightness perception SONGJOO OH and JUNG-OH KIM Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea Previous studies
Perception & Psychophysics 2004, 66 (5), 792-799 The effects of global grouping laws on surface lightness perception SONGJOO OH and JUNG-OH KIM Seoul National University, Seoul, South Korea Previous studies
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing
 Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
Neuroscience - Problem Drill 13: The Eye and Visual Processing Question No. 1 of 10 needed, (3) Pick the answer, and (4) Review the core concept tutorial as needed. 1. Which of the following statements
A scaling analysis of the snake lightness illusion
 Perception & Psychophysics 2008, 70 (5), 828-840 doi: 10.3758/PP.70.5.828 A scaling analysis of the snake lightness illusion Alexander D. Logvinenko Glasgow Caledonian University, Glasgow, Scotland Karin
Perception & Psychophysics 2008, 70 (5), 828-840 doi: 10.3758/PP.70.5.828 A scaling analysis of the snake lightness illusion Alexander D. Logvinenko Glasgow Caledonian University, Glasgow, Scotland Karin
Lecture 2.1 What is Perception?
 Lecture 2.1 What is Perception? A Central Ideas in Perception: Perception is more than the sum of sensory inputs. It involves active bottom-up and topdown processing. Perception is not a veridical representation
Lecture 2.1 What is Perception? A Central Ideas in Perception: Perception is more than the sum of sensory inputs. It involves active bottom-up and topdown processing. Perception is not a veridical representation
9.35 Sensation And Perception
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.35 Sensation And Perception Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.35 Recitation 1 Eye
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.35 Sensation And Perception Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 9.35 Recitation 1 Eye
The effect of contrast intensity and polarity in the achromatic watercolor effect
 Journal of Vision (2011) 11(3):18, 1 8 http://www.journalofvision.org/content/11/3/18 1 The effect of contrast intensity and polarity in the achromatic watercolor effect Bo Cao Arash Yazdanbakhsh Ennio
Journal of Vision (2011) 11(3):18, 1 8 http://www.journalofvision.org/content/11/3/18 1 The effect of contrast intensity and polarity in the achromatic watercolor effect Bo Cao Arash Yazdanbakhsh Ennio
Sensation and Perception. A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations
 I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
I. Overview Sensation and Perception A. Sensation: awareness of simple characteristics B. Perception: making complex interpretations C. Top-Down vs Bottom-up Processing D. Psychophysics -- thresholds 1.
On the Perception of Brightness and Contrast of Variegated Backgrounds
 Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Presentations and other scholarship 2000 On the Perception of Brightness and Contrast of Variegated Backgrounds Mark Fairchild Rochester Institute of
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Presentations and other scholarship 2000 On the Perception of Brightness and Contrast of Variegated Backgrounds Mark Fairchild Rochester Institute of
Why we see things the way we do: evidence for a wholly empirical strategy of vision
 doi 10.1098/rstb.2000.0772 Why we see things the way we do: evidence for a wholly empirical strategy of vision Dale Purves *, R. Beau Lotto, S. Mark Williams, Surajit Nundy and Zhiyong Yang Box 3209, Duke
doi 10.1098/rstb.2000.0772 Why we see things the way we do: evidence for a wholly empirical strategy of vision Dale Purves *, R. Beau Lotto, S. Mark Williams, Surajit Nundy and Zhiyong Yang Box 3209, Duke
Supplemental Information
 Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Neural Correlates of Crowding-Induced Changes in Appearance Elaine J. Anderson, Steven C. Dakin, D. Samuel Schwarzkopf, Geraint Rees, and John Greenwood
Current Biology, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Neural Correlates of Crowding-Induced Changes in Appearance Elaine J. Anderson, Steven C. Dakin, D. Samuel Schwarzkopf, Geraint Rees, and John Greenwood
What is mid level vision? Mid Level Vision. What is mid level vision? Lightness perception as revealed by lightness illusions
 What is mid level vision? Mid Level Vision March 18, 2004 Josh McDermott Perception involves inferring the structure of the world from measurements of energy generated by the world (in vision, this is
What is mid level vision? Mid Level Vision March 18, 2004 Josh McDermott Perception involves inferring the structure of the world from measurements of energy generated by the world (in vision, this is
(SAT). d) inhibiting automatized responses.
 Which of the following findings does NOT support the existence of task-specific mental resources? 1. a) It is more difficult to combine two verbal tasks than one verbal task and one spatial task. 2. b)
Which of the following findings does NOT support the existence of task-specific mental resources? 1. a) It is more difficult to combine two verbal tasks than one verbal task and one spatial task. 2. b)
Sensation and Perception
 1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
1 Sensation and Perception DR. ARNEL BANAGA SALGADO, Doctor of Psychology (USA) FPM (Ph.D.) Psychology (India) Doctor of Education (Phl) Master of Arts in Nursing (Phl) Master of Arts in Teaching Psychology
Perception Outline Chapter 6, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition
 Perception Outline Chapter 6, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition By transforming sensation into perception we create meaning - Selective Attention - Perception comes to us moment by moment 1. Selective
Perception Outline Chapter 6, Psychology, David G Meyers, 7 th Edition By transforming sensation into perception we create meaning - Selective Attention - Perception comes to us moment by moment 1. Selective
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS
 SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
SENSATION AND PERCEPTION KEY TERMS BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING BOTTOM-UP PROCESSING refers to processing sensory information as it is coming in. In other words, if I flash a random picture on the screen, your
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development
 Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Plasticity of Cerebral Cortex in Development Jessica R. Newton and Mriganka Sur Department of Brain & Cognitive Sciences Picower Center for Learning & Memory Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge,
Presence and Perception: theoretical links & empirical evidence. Edwin Blake
 Presence and Perception: theoretical links & empirical evidence Edwin Blake edwin@cs.uct.ac.za This Talk 2 Perception Bottom-up Top-down Integration Presence Bottom-up Top-down BIPs Presence arises from
Presence and Perception: theoretical links & empirical evidence Edwin Blake edwin@cs.uct.ac.za This Talk 2 Perception Bottom-up Top-down Integration Presence Bottom-up Top-down BIPs Presence arises from
Sensation & Perception The Visual System. Subjectivity of Perception. Sensation vs. Perception 1/9/11
 Sensation & Perception The Visual System Subjectivity of Perception We do not perceive the world directly Perception depends on brain stimulation Distinction between sensation and perception Sensation
Sensation & Perception The Visual System Subjectivity of Perception We do not perceive the world directly Perception depends on brain stimulation Distinction between sensation and perception Sensation
Gestalt Principles of Grouping
 Gestalt Principles of Grouping Ch 4C depth and gestalt 1 There appears to be some inherent cognitive process to organize information in a simple manner (nativist perspective). Without some sort of mental
Gestalt Principles of Grouping Ch 4C depth and gestalt 1 There appears to be some inherent cognitive process to organize information in a simple manner (nativist perspective). Without some sort of mental
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
Sensation and Perception 1 Chapters 4 of the required textbook Introduction to Psychology International Edition bv James Kalat (2010) 9 th Edition EXPECTED LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this chapter,
Perception. Chapter 8, Section 3
 Perception Chapter 8, Section 3 Principles of Perceptual Organization The perception process helps us to comprehend the confusion of the stimuli bombarding our senses Our brain takes the bits and pieces
Perception Chapter 8, Section 3 Principles of Perceptual Organization The perception process helps us to comprehend the confusion of the stimuli bombarding our senses Our brain takes the bits and pieces
Sensory Memory, Short-Term Memory & Working Memory
 Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Sensory, Short-Term & Working Psychology 355: Cognitive Psychology Instructor: John Miyamoto 04/17/2018: Lecture 04-2 Note: This Powerpoint presentation may contain macros that I wrote to help me create
Center of Dilation. Vertical Distance: 6. Horizontal Distance: 4
 .1 Constructing Dilations It is useful to be able to perform transformations using the coordinate plane. This allows us to specify the exact coordinates of the pre-image, image, and other important reference
.1 Constructing Dilations It is useful to be able to perform transformations using the coordinate plane. This allows us to specify the exact coordinates of the pre-image, image, and other important reference
Distortions in the perceived lightness of faces: The role of race categories. Daniel T. Levin. Vanderbilt University. Mahzarin R.
 Distortions in lightness 1 Distortions in the perceived lightness of faces: The role of race categories Daniel T. Levin Vanderbilt University Mahzarin R. Banaji Harvard University Address Correspondence
Distortions in lightness 1 Distortions in the perceived lightness of faces: The role of race categories Daniel T. Levin Vanderbilt University Mahzarin R. Banaji Harvard University Address Correspondence
Pathway from the eye to the cortex
 Vision: CNS 2017 Pathway from the eye to the cortex Themes of this lecture Visual information is analyzed in more complicated ways than in the retina. One major pathway from the eye leads to the striate
Vision: CNS 2017 Pathway from the eye to the cortex Themes of this lecture Visual information is analyzed in more complicated ways than in the retina. One major pathway from the eye leads to the striate
Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation. Date Period. 1) sensation. 2) perception. 3) bottom-up processing. 4) top-down processing
 Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Name Ms. Gabriel/Mr. McManus Date Period AP Psychology Review Sheet: Sensation and Perception (6-8%) Sensation 1) sensation 2) perception 3) bottom-up processing 4) top-down processing Thresholds 5) psychophysics
Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina
 The visual system Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina 0.5 mm thick The retina 0.5 mm thick The photosensors
The visual system Light passes through the lens, through the inner layer of ganglion cells and bipolar cells to reach the rods and cones. The retina 0.5 mm thick The retina 0.5 mm thick The photosensors
ASSUMPTION OF COGNITIVE UNIFORMITY
 The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
The Human Brain cerebral hemispheres: two most important divisions of the brain, separated by the longitudinal fissure corpus callosum: a large bundle of axons that constitutes the major connection between
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2003 Read each question carefully and answer it completely. Pay careful attention to the point value of questions so that you allocate your time appropriately (1 point = 1 minute).
Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world
 Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Name: 1 Shaw - PSYC& 100 Lilienfeld et al (2014) - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How we sense and conceptualize the world 1 Distinguish between sensation and perception. Include as part of your answer
Attention and Scene Perception
 Theories of attention Techniques for studying scene perception Physiological basis of attention Attention and single cells Disorders of attention Scene recognition attention any of a large set of selection
Theories of attention Techniques for studying scene perception Physiological basis of attention Attention and single cells Disorders of attention Scene recognition attention any of a large set of selection
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007
 ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
ID# Exam 1 PS 325, Fall 2007 As always, the Skidmore Honor Code is in effect, which you ll acknowledge when you turn in your exam. Each multiple-choice question is worth 1 point and the value of the other
Definition Slides. Sensation. Perception. Bottom-up processing. Selective attention. Top-down processing 11/3/2013
 Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception = the process of organizing and interpreting
= add definition here. Definition Slide
 = add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
= add definition here Definition Slide Definition Slides Sensation = the process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus energies from our environment. Perception
Psychology Perception
 Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
Psychology 343 - Perception James R. Sawusch, 360 Park Hall jsawusch@buffalo.edu 645-0238 TA is Timothy Pruitt, 312 Park tapruitt@buffalo.edu Text is Sensation & Perception by Goldstein (8th edition) PSY
1. The responses of on-center and off-center retinal ganglion cells
 1. The responses of on-center and off-center retinal ganglion cells 2. Responses of an on-center ganglion cell to different light conditions 3. Responses of an on-center ganglion cells to different light
1. The responses of on-center and off-center retinal ganglion cells 2. Responses of an on-center ganglion cell to different light conditions 3. Responses of an on-center ganglion cells to different light
Required Slide. Session Objectives
 Vision: CNS 2018 Required Slide Session Objectives Visual system: CNS At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Understand how axons from the eyes travel through the optic nerves and tracts
Vision: CNS 2018 Required Slide Session Objectives Visual system: CNS At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1. Understand how axons from the eyes travel through the optic nerves and tracts
Is the straddle effect in contrast perception limited to secondorder spatial vision?
 Journal of Vision (2018) 18(5):15, 1 43 1 Is the straddle effect in contrast perception limited to secondorder spatial vision? Norma V. Graham Department of Psychology, Columbia University, New York, NY,
Journal of Vision (2018) 18(5):15, 1 43 1 Is the straddle effect in contrast perception limited to secondorder spatial vision? Norma V. Graham Department of Psychology, Columbia University, New York, NY,
Psychology and You. Dear Students,
 Psychology and You Dear Students, December, 2009 2 nd Edition Welcome to the second edition of Psychology and You, a newsletter covering basic psychology principles and scientific research, presented in
Psychology and You Dear Students, December, 2009 2 nd Edition Welcome to the second edition of Psychology and You, a newsletter covering basic psychology principles and scientific research, presented in
Consciousness and Blindsight
 Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Consciousness and Blindsight Blindsight: The ability to respond appropriately to visual inputs while lacking the feeling of having seen them These patients are unable to see, but are able to reach for
Goals. Visual behavior jobs of vision. The visual system: overview of a large-scale neural architecture. kersten.org
 The visual system: overview of a large-scale neural architecture Daniel Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota Goals Provide an overview of a major brain subsystem to help
The visual system: overview of a large-scale neural architecture Daniel Kersten Computational Vision Lab Psychology Department, U. Minnesota Goals Provide an overview of a major brain subsystem to help
Perceptual Disorders. Agnosias
 Perceptual Disorders Agnosias Disorders of Object Recognition AGNOSIA : a general term for a loss of ability to recognize objects, people, sounds, shapes, or smells. Agnosias result from damage to cortical
Perceptual Disorders Agnosias Disorders of Object Recognition AGNOSIA : a general term for a loss of ability to recognize objects, people, sounds, shapes, or smells. Agnosias result from damage to cortical
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception
 Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
Test Bank Chapter 2: The Beginnings of Perception MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Our perception of the environment depends on a. the properties of the objects in the environment. b. the properties of the electrical
Sperling conducted experiments on An experiment was conducted by Sperling in the field of visual sensory memory.
 Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
Levels of category Basic Level Category: Subordinate Category: Superordinate Category: Stages of development of Piaget 1. Sensorimotor stage 0-2 2. Preoperational stage 2-7 3. Concrete operational stage
PSYC& Lilienfeld et al. - Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception: How We Sense and Conceptualize the World Study Guide
 Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
Many first time college students struggle adjusting to expectations of college-level courses. One reason for this is that college-level courses require students to learn new content and apply that content
PSY 214 Lecture # 3 (09/07/2011) - Physiology of Perception Dr. Achtman PSY 214. Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31
 PSY 214 Corrections: Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31 None needed Lecture Notes: I. Review The Perceptual Process Dillon Foley, Dfoley7@mail.naz.edu Page 1 of 8 A: Psychophysics-
PSY 214 Corrections: Lecture 3 Topic: Physiology of Perception Chapter 2, pages 23-31 None needed Lecture Notes: I. Review The Perceptual Process Dillon Foley, Dfoley7@mail.naz.edu Page 1 of 8 A: Psychophysics-
The whole is other than the sum of the parts. Kurt Koffka
 The Gestalt Principles of Design are design principles devised from the psychology of how humans visually perceive things. Therefore, designers can use them in their work to create a more unified and effective
The Gestalt Principles of Design are design principles devised from the psychology of how humans visually perceive things. Therefore, designers can use them in their work to create a more unified and effective
