Behavioral Study of Obedience. Stanley Milgram 1963
|
|
|
- Charleen Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Behavioral Study of Obedience Stanley Milgram 1963
2 Bell Ringer C.P. Snow (1961) noted that when you think of the long and gloomy history of man, you will find more hideous crimes have been committed in the name of obedience than have ever been committed in the name of rebellion. Give an example of a time in your life that you obeyed a rule that you didn t agree with.
3 Bell Ringer Define obedience, conformity, compliance, and acceptance, using examples, and indicate how these labels reflect Western culture. Conformity
4 Background Many historians in attempting to explain these horrors have argued that the destruction of Jews, gypsies, homosexuals and many others was made possible because of some sort of character defect which makes Germans more obedient. Milgram s study is an attempt to test the Germans are different hypothesis.
5 Background The Germans are different hypothesis states that German s have a basic character deficit which means they have a readiness to obey people in authority regardless of the act they are being asked to carryout. This is an example of a dispositional attribution- arguing that the cause of behavior is believed to result from the persons own personality or characteristics.
6 Background Milgram set out to question this dispositional attribution of the Germans. He believed that the situation had led to the inhumane behavior of the Nazis and therefore that anybody in the same situation as those committing such atrocities would have done the same in the same circumstances. Milgram argued that people would commit atrocities if required to do so by an authority figure. = situational attribution. The Obedience Study
7 AIM The aim of the experiment was to investigate what level of obedience would be shown when participants were told by an authority figure to administer electric shocks to another person.
8 Method/Procedure This study is often described as an experiment. However as there is no control condition (i.e. all of the participants took place in the same experimental procedure) it is not strictly speaking an experiment. The IV could be considered to be the prods provided by the experimenter for the participant to carry on, and the DV could be considered to be the degree of obedience. = how far up the shock scale the participant went.
9 Method/Procedure More accurate -the method used a type of controlled observation. The study collected both quantitative data in the way that it measured the amount of volts given and qualitative data in the way that Milgram observed the participants emotional responses and interviewed the participants after the study.
10 Method/Procedure 40 males aged between 20-50, were recruited from the New Haven area. They were obtained by responding to a newspaper and direct mail advertisement which asked for volunteers to participate in a study of memory and learning at Yale University. The participants represented a wide range of occupations, including postal clerks, high-school teachers, salesmen, engineers and laborers. They were paid $4.50 for their participation in the experiment but importantly they were told that the payment was simply for coming to the laboratory, regardless of what happened after they arrived.
11 Method/Procedure Milgram created a phoney shock generator which in the 1960s looked very impressive and realistic. The phony shock generator had 30 switches marked clearly in 15 volt increments from 15 to 450 volts.
12 Bell Ringer Another updated version 1. Why do you think so many people obey when they feel coerced? 2. Why do you think closeness of the authority figure makes a difference in obedience?
13 Method/Procedure To improve the authenticity of the phoney shock generator written labels were also clearly indicated for groups of four switches: slight shock, moderate shock, strong shock, very strong shock, intense shock, extreme intensity shock, danger: severe shock. Two switches after this were marked XXX).
14 Method/Procedure The phony generator also had buzzers, flashing lights and moving dials. The generator could give a 45-volt shock, which again was designed to make it appear genuine. The experiment took place in a smart psychology laboratory in Yale University. The role of experimenter was played by a 31-yearold biology teacher, who introduced himself as Jack Williams. He wore a grey technician s coat and appeared stern and emotionless throughout the experiment.
15 Method/Procedure The victim was played by Mr Wallace, a 47- year-old accountant, trained for the role, whom most observers found mild-mannered and likeable. One participant and one victim (a confederate) were used in each trial. In order to justify the administration of the electric shocks by the participant a cover story was used. After a general introduction about the relation between punishment and learning the participants were told:
16 Method/Procedure But actually we know very little about the effect of punishment on learning, because almost no truly scientific studies have been made of it in human beings. For instance, we don't know how much punishment is best for learning, and we don't know how much difference it makes as to who is giving the punishment, whether an adult learns best from a younger or an older person than himself, or many things of that sort. So in this study we are bringing together a number of adults of different occupations and ages. And we re asking some of them to be teachers and some of them to be learners. We want to find out just what effect different people have on each other as teachers and learners, and also what effect punishment will have on learning in this situation. Therefore, I m going to ask one of you to be the teacher here tonight and the other one to be the learner. Does either of you have a preference?
17 Method/Procedure Participant drew a slip of paper from a hat to determine which role he would play. The draw was rigged so the participant was always the teacher and Mr. Wallace (the confederate) was always the learner. The teacher (participant) and learner were taken to an adjacent room and in full view of the teacher (participant) the learner was strapped into the electric chair. The experimenter explained to the teacher (participant) that the straps were to prevent excessive movement while the learner was being shocked =make it impossible for him to escape the situation. An electrode was attached to the learner s wrist and electrode paste (cream) was applied to avoid blisters and burns. The participant (teacher) then heard the experimenter tell the learner although the shocks can be extremely painful, they cause no permanent tissue damage.
18 Method/Procedure To further enhance the authenticity of the generator the participant (teacher) was given a sample shock of 45 volts, applied by pressing the third switch.
19 Method/Procedure The participant was then seated in an adjacent room in front of the shock generator and asked to read a series of word pairs to the learner. The learner was asked to learn (memorize) these pairs. The participant then tests the learner by giving him one of the words in a pair along with 4 other words. The learner has to indicate which of the 4 words had originally been paired with the first word. The learner s answer was communicated by pressing 1 of 4 switches which illuminated a light on top of the shock generator. If the answer was correct the participant had to move onto the next word on the list, if the answer was wrong the participant had to tell the learner the correct answer and then the level of punishment that they were going to give them. For every subsequent incorrect answer the participant was required to move one switch up the scale of shocks.
20 Method/Procedure In all conditions the learner gives a predetermined set of responses to the word pair test, based on approximately 3 wrong answers to 1 correct answer. In this very first experiment, the procedure continued as the remote victim experiment-no vocal response or other sign of protest was heard from the learner until the shock level of 300 volts was reached. At this point the learner pounded on the wall of the room and could be heard by the participant. From this point on, the learner s answers no longer appeared on the panel, and many participants usually began to turn to the experimenter for guidance. The participant was instructed to treat the absence of a response as a wrong answer and to shock the learner according to the usual schedule, allowing 5 to 10 seconds before considering no response as a wrong answer. The pounding on the wall was repeated after the 315 volt shock but subsequently the learner was not heard from, and his answers did not reappear on the panel.
21 Method/Procedure If the participant asked advice from the experimenter, whether it be; should I continue administering shocks, or some other indication that he did not wish to go on, he would be given encouragement to continue with a sequence of standardised prods : Prod 1: Please continue or Please go on ; Prod 2: The experiment requires that you continue ; Prod 3: It is absolutely essential that you continue ; Prod 4: You have no other choice, you must go on.
22 Method/Procedure The prods were always made in sequence. Only if Prod 1 was unsuccessful could Prod 2 be used, etc. If the participant continued to disobey after Prod 4, the experiment was terminated. The experimenter s tone of voice was always firm, but not impolite.
23 Bell Ringer Hofling Hospital Experiment Would you let someone wanting to repeat Hofling's 1966 experiment today carry out the same procedure? Consider in what ways Hofling's experiment was considered ethical or unethical. Hofling Animated
24 Method/Procedure If the participant asked if the learner could suffer permanent physical injury, a special prod was used; although the shocks may be painful, there is no permanent tissue damage, so please go on, followed by Prods 2, 3 and 4 if necessary. If the participant said that the learner did not want to go on, another special prod was used; whether the learner likes it or not, you must go on until he has learned all the word pairs correctly, so please go on, followed by Prods 2, 3 and 4 if necessary. The experiment would end either when the 450 volt shock had been administered, or when the participant walked out.
25 Method/Procedure A participant who breaks off at any point prior to the highest shock level (450 volts) is called a defiant participant, while one who obeys up to the 450 volts is called an obedient participant. The sessions were also filmed and notes were taken by observers looking through an observation mirror. The latency and duration of shocks were timed.
26 Method/Procedure After the experiment, the participants were thoroughly debriefed using open-ended questions and to test that the participants were not harmed a number of psychometric measures (projective tests and attitude scales) were used. The participant was also reunited with the victim to show them that the victim was not harmed and it was explained to them that there behaviour was normal. These measures were taken to ensure that the participants left that laboratory in a state of well being
27 Results/Findings All 40 of the participants obeyed up to 300 volts at which point 5 refused to continue. 4 more gave one further shock before refusing; two broke off at the 330 volts level and one each at 345, 360 and 375 volts. Therefore, a total of 14 participants defied the experimenter, and 26 obeyed. Overall, 65% of the participants gave shocks up to 450 volts (obeyed) and 35% stopped sometime before 450 volts;
28 Results/Findings After the maximum shock had been administered, the participant was asked to continue at this level until the experimenter eventually called a halt to the proceedings, at which point many of the obedient participants heaved sighs of relief or shook their heads in apparent regret.
29 Results/Findings During the study many participants showed signs of nervousness and tension. Participants sweated, trembled, stuttered, bit their lips, groaned, dug fingernails into their flesh, and these were typical not exceptional responses. Quite a common sign of tension was nervous laughing fits (14 out of 40 participants), which seemed entirely out of place, even bizarre. Full-blown uncontrollable seizures were observed for 3 participants. On one occasion, a participant had such a violently convulsive seizure that the experiment had to be halted; the 46-year-old encyclopedia salesman was extremely embarrassed. Participants took pains to point out that they were not sadistic types, and that the laughter did not mean they enjoyed shocking the learner.
30 Results/Findings With few exceptions, participants were convinced of the reality of the situation In the post-experimental interview, participants were asked: How painful to the learner were the last few shocks you administered to him? On a printed 14- point scale ranging from 1 ( not at all painful ) to 14 ( extremely painful ), the mean was
31 Explanation Milgram put forward a number of features of the experiment which may explain why such high levels of obedience occurred even when such extreme tension was created by the procedure: The fact that the experiment took place at the prestigious Yale University lent the study and procedure credibility and respect. The participant believed that the experiment was for a worthy purpose - to advance knowledge and understanding of learning processes. The participant believed the victim had volunteered to be in the study and therefore has an obligation to take part even if the procedures become unpleasant.
32 Explanation The participant felt himself to be similarly obligated to take part in the procedures as planned. Being paid increased the sense of obligation. As far as the participant was concerned, the roles of learner and teacher had been allocated fairly, by drawing lots. Thus the learner could not feel aggrieved that he had been unfairly assigned his role. As most participants had never been a participant in a psychology experiment before, they had little idea about the rights and expectations of experimenter and participant. The situation was novel and there were no norms operating and nobody with whom to discuss ambiguities and doubts. The participants had been assured that the shocks were painful but not dangerous. This short-term pain was balanced with the possibility of long-term scientific gain. The victim responded to all of the questions until the 300 volt level was reached. They had thus indicated their willingness to take part.
33 Explanation To test some of these explanations Milgram carried out many more variations of his experiment. For example in one variation to his experiment Milgram altered the location to a run-down office building in downtown Bridgeport, Connecticut. In this setting the obedience rate was 47.5%, suggesting that the original location had played some part, but it was not a crucial factor
34 Explanation Milgram was therefore arguing that an important factor influencing behavior is the situation a person is in. He believes that we often make dispositional attributions about behavior, which are incorrect.
35 Evaluation of Procedure The most common criticism of Milgram s work is concerned with its ethics: Participants were deceived as to the exact nature of the study for which they had volunteered, and by making them believe they were administering real electric shocks to a real participant. However Milgram could not have found results that truly reflected the way people behave in real situations if he had not deceived his participants, all of whom were thoroughly debriefed afterwards. It can also be argued that Milgram did not take adequate measures to protect his participants from the stress and emotional conflict they experienced. Milgram s defence was that he, and the students and psychiatrists - who had been asked to predict the results of the first experiment - did not expect the results he obtained, and went on to ask whether such criticisms are based as much on the unexpected results as on the procedure itself.
36 Evaluation of Procedure It is possible that being involved in the experiment may have had a long-term effect on the participants. Before the experiment they might have considered themselves incapable of inflicting harm on another person unless the circumstances were extreme. Afterwards, this view of themselves was shattered. Milgram argued that such self-knowledge was valuable. A year after the experiments an independent psychiatrist interviewed 40 of the participants (many of whom had experienced extreme stress), and found no evidence of psychological harm or evidence of traumatic reactions.
37 Evaluation of Procedure In terms of the right to withdraw, it was good that Milgram stated at the start that the money paid to the participants was theirs regardless of whether they continued with the experiment. However, during the experiment the prods used suggested that withdrawal was not possible. This is ethically incorrect. Even so, we should consider whether the experiment would have been valid if the experimenter kept reminding the participant about his right to withdraw.
38 Evaluation of Procedure A major criticism of Milgram s study was his unrepresentative sample. Only American men (thus he was deliberately ethnocentric), but from a variety of backgrounds and different ages. It could be argued that by using men this produced a sample that was biased, or did not reflect the general population. The study was also limited to those people who read the advertisement and were prepared to participate in a laboratory experiment. These men who replied may have been somehow different from the general population.
39 Evaluation of Procedure Because of such an unrepresentative sample the results cannot be generalized to all people. Despite this, Milgram concluded that obedience to authority is not a feature of German culture but a seemingly universal feature of human behaviour. A number of crosscultural replications of Milgram s experiment have been done (e.g. Italy and Australia) gaining similar results.
40 Evaluation of Procedure Another main criticism of Milgram s experiment was that it was not ecologically valid. It can be argued that it was carried out in an artificial setting and has little relevance to the real world. However, less artificial studies have been carried out gaining similar results. For example in Hoffling s study (1966), nurses were asked to give potentially lethal injections to patients, and 21 out of 22 appeared prepared to do it. A further study was carried out by Sheridan and King (1972), where people were asked to give real electric shocks to a puppy. The participants obeyed even though they could see the distress of the animal.
41 Evaluation of Procedure A main strength of Milgram s experiment was the amount of control he was able to administer. For example, participants believed they were being randomly assigned to either the teacher or learner, they believed they were actually administering electric shocks, they all used the same apparatus, had the same prods from the same person and so on. A further strength of this study is that it collected both quantitative and qualitative data which it can be argued increases the validity of the study. Quantitative data included the level of shocks administered and qualitative data was provided through interviews and observation.
42 Evaluation of Explanation Milgram believes that it is the situation that people find themselves in rather than their dispositions that best explain their actions. This argument gains support from many studies in social psychology. However this argument can be seen as too deterministic. For example in Milgram s study not all of the participants were willing to go all the way to 450 volts. Perhaps the reason why some of the participants were less willing was something to do with their personalities. It can also be argued that we are socialized to be obedient and that it is therefore easier to obey than disobey.
Milgram (obedience) Milgram. S (1963) Behavioural Study of Obedience. Background
 Milgram (obedience) Milgram. S (1963) Behavioural Study of Obedience. Background C.P. Snow (1961) noted that when you think of the long and gloomy history of man, you will find more hideous crimes have
Milgram (obedience) Milgram. S (1963) Behavioural Study of Obedience. Background C.P. Snow (1961) noted that when you think of the long and gloomy history of man, you will find more hideous crimes have
MILGRAM EXPERIMENT. Research on people s obedience. Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School
 MILGRAM EXPERIMENT Research on people s obedience Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School October 14 th, 2014 ABSTRACT This paper is written in order to research and understand about the famous
MILGRAM EXPERIMENT Research on people s obedience Mugi Kito Grade 11B Wells International School October 14 th, 2014 ABSTRACT This paper is written in order to research and understand about the famous
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being
 Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
Asch (1951) found that participants would even give answers which they knew to be untrue, rather than ones which deviated from the views being expressed by others. The task in Asch s studies involved judging
The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008
 Name: Class: The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 In 1963, Stanley Milgram conducted a study on obedience. Using a series of social psychology experiments, Milgram measured participants willingness
Name: Class: The Milgram Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 In 1963, Stanley Milgram conducted a study on obedience. Using a series of social psychology experiments, Milgram measured participants willingness
Conformity & Obedience
 Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
Higher Psychology Conformity & Obedience Exam Revision 1 This is the mandatory topic in the Social Behaviour unit. This means it will probably come up in the exam. What to revise: - Types of conformity
CIE Psychology A-level Social Psychology
 CIE Psychology A-level Social Psychology Notes Part 1: Milgram s Research into Variables Affecting Obedience Participants Aim Procedure Findings Factors affecting obedien ce Randomly selected participants
CIE Psychology A-level Social Psychology Notes Part 1: Milgram s Research into Variables Affecting Obedience Participants Aim Procedure Findings Factors affecting obedien ce Randomly selected participants
(Refer Slide Time: 1:30)
 Great Experiments in Psychology Professor Rajlakshmi Guha Centre for Educational Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Module 2 Lecture No 10 Milgram s Study on Obedience Hello everybody
Great Experiments in Psychology Professor Rajlakshmi Guha Centre for Educational Technology Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Module 2 Lecture No 10 Milgram s Study on Obedience Hello everybody
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Explanations of Obedience.
 www.tutor2u.net/psychology Social Psychology Explanations of Obedience tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission
www.tutor2u.net/psychology Social Psychology Explanations of Obedience tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission
Obedience to Authority
 Obedience to Authority Jan. 9, 2005 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.34 2005 David Schweingruber Milgram s experiment Experiment: research method designed to elicit some sort of behavior, typically conducted
Obedience to Authority Jan. 9, 2005 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.34 2005 David Schweingruber Milgram s experiment Experiment: research method designed to elicit some sort of behavior, typically conducted
OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67,
 1 OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67, 371-378. If someone in a position of authority ordered you to deliver an electrical
1 OBEY AT ANY COST? Milgram, S. (1963). Behavioral study of obedience. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 67, 371-378. If someone in a position of authority ordered you to deliver an electrical
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Authoritarian Personality.
 Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Social Psychology Authoritarian Personality tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
BEHAVIORAL STUDY OFOBEDIENCE 1
 Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 1963, Vol. 67, No. 4, 371-378 BEHAVIORAL STUDY OFOBEDIENCE 1 STANLEY MILGRAM 2 Yale University This article describes a procedure for the study of destructive
Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology 1963, Vol. 67, No. 4, 371-378 BEHAVIORAL STUDY OFOBEDIENCE 1 STANLEY MILGRAM 2 Yale University This article describes a procedure for the study of destructive
In Defense of the Milgram Experiments
 In Defense of the Milgram Experiments Abstract (the experimenter) who instructed them to administer electrical shocks to a confederate Although the electrical shocks were fake, these famous obedience experiments
In Defense of the Milgram Experiments Abstract (the experimenter) who instructed them to administer electrical shocks to a confederate Although the electrical shocks were fake, these famous obedience experiments
Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change.
 1 Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change. Extra space (Total 6 marks) Page 1 of 15 2 Explain what is meant by locus of control. Extra space (Total
1 Describe how social influence research has contributed to our understanding of social change. Extra space (Total 6 marks) Page 1 of 15 2 Explain what is meant by locus of control. Extra space (Total
Ones Way of Thinking. Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will
 Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
Guerrero 1 Ypani Guerrero Prof Serpas Exp 389 11/28/12 Ones Way of Thinking Every day, people make decisions that determine where the next step we take in life will be. We often don t know whether those
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE. Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL
 AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Questions + Answers SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE
Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures?
 WELCOME to the NBAA HPN Regional June 2018 Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures? Bob Gould Bravo Golf Aviation Question? How many of you have NOT followed a prescribed procedure in an operations or maintenance
WELCOME to the NBAA HPN Regional June 2018 Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures? Bob Gould Bravo Golf Aviation Question? How many of you have NOT followed a prescribed procedure in an operations or maintenance
Topics for today Ethics Bias
 HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
HCI and Design Topics for today Ethics Bias What are ethics? The study of moral standards and how they affect conduct Moral standards are A system of principles governing the appropriate conduct of an
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Factors Affecting Obedience.
 Social Psychology Factors Affecting Obedience tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Social Psychology Factors Affecting Obedience tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint This tutor2u Full Lesson PowerPoint is copyrighted and may not be reproduced or shared without permission from the author. All
Nature or Nurture? Reading Practice
 Reading Practice A Nature or Nurture? A few years ago, in one of the most fascinating and disturbing experiments in behavioural psychology, Stanley Milgram of Yale University tested 40 subjects from all
Reading Practice A Nature or Nurture? A few years ago, in one of the most fascinating and disturbing experiments in behavioural psychology, Stanley Milgram of Yale University tested 40 subjects from all
Asch Model Answers. Aims and Context
 Asch Model Answers Aims and Context Conformity is yielding to group pressure to fit in with others or come to a decision on what to do if unsure based on other people s actions. One of the earliest studies
Asch Model Answers Aims and Context Conformity is yielding to group pressure to fit in with others or come to a decision on what to do if unsure based on other people s actions. One of the earliest studies
A B C. Copyright Allyn and Bacon 2005
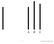 A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
A B C 1 A B C 2 A B C 3 A B C 4 Asch, 1951 How many of you own something from one of these companies? 5 Fads 6 Lecture 10 Social Influence 7 Social Influence Have you ever: Asked a friend what was appropriate
Factors that affect interpersonal attraction:
 Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
Introduction: You are a member of a social world on a planet containing about 7 billion people. Our behaviors differ in different settings (like if we are in the college, market, or at home). Human behavior
SAMPLE. 1. Would you describe in your own words your experiences during this experiment?
 RM Application Worksheet: Social Key Study: Asch (1956) Asch (1956) conducted research to examine the extent to which social pressure from a majority, affects conformity. Using a line judgement task, he
RM Application Worksheet: Social Key Study: Asch (1956) Asch (1956) conducted research to examine the extent to which social pressure from a majority, affects conformity. Using a line judgement task, he
Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION
 Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION 1 The biggest change from the old Higher course (up to 2014) is the possibility of an analysis and evaluation question (8-10) marks asking you to comment on aspects
Higher Psychology RESEARCH REVISION 1 The biggest change from the old Higher course (up to 2014) is the possibility of an analysis and evaluation question (8-10) marks asking you to comment on aspects
What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority.
 What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority. Resisting order or commands from people in authority. What is the core theory called? What does
What does defiance mean? What does obedience mean? Following orders or commands from people in authority. Resisting order or commands from people in authority. What is the core theory called? What does
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level PSYCHOLOGY 9698/22 Paper 2 Core Studies 2 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level PSYCHOLOGY 9698/22 Paper 2 Core Studies 2 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published
Ethics of Experimentation
 Ethics of Experimentation Scientists in most fields have rules or guidelines that limit the research they can peform. These principles may be enforced by: professional societies and journals; government
Ethics of Experimentation Scientists in most fields have rules or guidelines that limit the research they can peform. These principles may be enforced by: professional societies and journals; government
What is Social Psychology
 The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
The Social World What is Social Psychology An attempt to understand and explain how the thoughts, feelings, and behavior of individuals are influenced by the actual, imagined, or implied presence of others
The Darker Side of Persuasion:
 PROPOSAL Management The Darker Side of Persuasion The Darker Side of Persuasion: STANLEY MILGRAM S EXPERIMENTS ON OBEDIENCE TO AUTHORITY By Dr. Jayme A. Sokolow In the 1960s, psychologist Stanley Milgram
PROPOSAL Management The Darker Side of Persuasion The Darker Side of Persuasion: STANLEY MILGRAM S EXPERIMENTS ON OBEDIENCE TO AUTHORITY By Dr. Jayme A. Sokolow In the 1960s, psychologist Stanley Milgram
8 Diffusion of Responsibility
 Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
Ruggerio Chapter : The Basic Problem: Mine is Better Aronson & Tavris Book- Chapter 1 & Self- Justification Norms Rules that regulate human life, including social conventions, explicit laws, and implicit
COURSE COMPANION. J Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance.
 COURSE COMPANION Social influenece J Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. J Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence, and
COURSE COMPANION Social influenece J Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. J Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence, and
Situationism. Consider a few of the famous experiments that kicked things off:
 Situationism 1. Situationism: Let s return to the issue of moral luck, with which we started. Situationism is a thesis of psychology that deals with something like what we called circumstantial luck (this
Situationism 1. Situationism: Let s return to the issue of moral luck, with which we started. Situationism is a thesis of psychology that deals with something like what we called circumstantial luck (this
Obedience to Authority/ Social Order in Emergency Situations
 Obedience to Authority/ Social Order in Emergency Situations Aug. 30, 2006 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.134 2006 David Schweingruber Professor of Old Testament (150 volts) E: It s absolutely essential to
Obedience to Authority/ Social Order in Emergency Situations Aug. 30, 2006 http://www.iastate.edu/~soc.134 2006 David Schweingruber Professor of Old Testament (150 volts) E: It s absolutely essential to
Conformity Asch study (1951) Which of the lines below is the same as the line to the right?
 a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
a change in a belief or behavior with the intent to follow a perceived social norm May lead to positive or negative behaviors E.g., conforming to a norm of volunteering versus conforming to a norm of cheating
Page 1 of 10 Saylor URL:
 This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Page
This text was adapted by The Saylor Foundation under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work s original creator or licensee. Page
Conformity ASCH S STUDY 12/8/2010 ASCH S STUDY. Social Psychology (581, ) Others Focus on Social Influences on Our Behavior
 Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Social Psychology (581, 592-598) Study of how people behave, think, and feel in social situations Relatively recent addition to psychology Research influenced by current social problems Researchers in
Obediance and conformity
 Obediance and conformity PSY 268 Contemporary Issues in Psychology Fall 2012 Mgr. Zuzana Petrovicova QUIZ Briefly summarize main findings of Milgram s experiment ( do not describe the experiment itself)
Obediance and conformity PSY 268 Contemporary Issues in Psychology Fall 2012 Mgr. Zuzana Petrovicova QUIZ Briefly summarize main findings of Milgram s experiment ( do not describe the experiment itself)
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level PSYCHOLOGY 9698/21 Paper 2 Core Studies 2 May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published This mark
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level PSYCHOLOGY 9698/21 Paper 2 Core Studies 2 May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 70 Published This mark
Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being?
 Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Social Behavior ~ Social Psychology Altruism; Conformity; Obedience; Compliance Are they formed through education or is it just part of being a human being? YouTube: Referee Helps Girl Finish Anthem YouTube:
Cognitive Dissonance. by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated
 Cognitive Dissonance by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated Cognitive dissonance refers to a situation involving conflicting attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. This produces a feeling of discomfort leading
Cognitive Dissonance by Saul McLeod published 2008, updated Cognitive dissonance refers to a situation involving conflicting attitudes, beliefs or behaviors. This produces a feeling of discomfort leading
Chapter 13. Social Psychology
 Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
Social Psychology Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Social Psychology Interpreting the Behavior of Others Behaving in the Presence of Others Establishing Relations With Others Social
PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies
 PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies show? MYTH #1 NOTES GUIDE 1. Do you think there s truth to the statement, Psychology
PSYCHWRITE #3: Why do you believe people are so inclined to believe what they read and hear, especially if it says, studies show? MYTH #1 NOTES GUIDE 1. Do you think there s truth to the statement, Psychology
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AE. What is Psychology?
 Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AE What is Psychology? Let's say a psychologist wanted to test whether people who are thirsty do more poorly on math tests than people who are well-hydrated.
Marshall High School Psychology Mr. Cline Unit One AE What is Psychology? Let's say a psychologist wanted to test whether people who are thirsty do more poorly on math tests than people who are well-hydrated.
PRACTICE EXAM PAPER. AQA Psychology Advanced Subsidiary Mark Scheme. Mark Scheme Paper 1 Introductory Topics in Psychology (Set A) SAMPLE ONLY
 PRACTICE EXAM PAPER AQA Psychology Advanced Subsidiary Mark Scheme Mark Scheme Paper 1 Introductory Topics in Psychology (Set A) Section A Social Influence 01 Which two of the following statements about
PRACTICE EXAM PAPER AQA Psychology Advanced Subsidiary Mark Scheme Mark Scheme Paper 1 Introductory Topics in Psychology (Set A) Section A Social Influence 01 Which two of the following statements about
SAMPLE. Social Psychology. Minority Influence & Social Change.
 Social Psychology Minority Influence & Social Change Social Psychology Lesson Objectives: To outline and evaluate three aspects of minority influence, including: Consistency Commitment Flexibility Five,
Social Psychology Minority Influence & Social Change Social Psychology Lesson Objectives: To outline and evaluate three aspects of minority influence, including: Consistency Commitment Flexibility Five,
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience
 Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Chapter 8- Conformity, Compliance and Obedience Objectives 1) knowledge about various forms of social influence, such as social facilitation, social loafing, conformity, compliance, and obedience. 2) An
Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures?
 WELCOME TO NBAA BACE Las Vegas 2017 Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures? Bob Gould Bravo Golf Aviation Question for You How many of you have NOT followed a prescribed procedure in a maintenance manual
WELCOME TO NBAA BACE Las Vegas 2017 Why Do We Fail to Follow Procedures? Bob Gould Bravo Golf Aviation Question for You How many of you have NOT followed a prescribed procedure in a maintenance manual
Why do Psychologists Perform Research?
 PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
PSY 102 1 PSY 102 Understanding and Thinking Critically About Psychological Research Thinking critically about research means knowing the right questions to ask to assess the validity or accuracy of a
18. Scientific Ethics
 18. Scientific Ethics Answer Questions Ethics of Experimentation Government Rules 1 18.1 Ethics of Experimentation Scientists in almost every field have codified rules or guidelines that determine the
18. Scientific Ethics Answer Questions Ethics of Experimentation Government Rules 1 18.1 Ethics of Experimentation Scientists in almost every field have codified rules or guidelines that determine the
Social Psychology. What We Will Cover in This Section. Roles. PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
Social Psychology Dr. Dennis C. Sweeney What We Will Cover in This Section Conformity Attitudes Group Behavior Prejudice Roles Socially defined expectations that we expect individuals to fulfill in a given
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE. Syllabus Notes SAMPLE MATERIAL
 AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Syllabus Notes SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE CONFORMITY
AQA A-level Psychology Unit 1 (7182/1) SOCIAL INFLUENCE Syllabus Notes SAMPLE MATERIAL Copyright 2017, StudyLogic. All rights reserved. UNIQUE PRODUCT IDENTIFIER: DOCUMENT #4534478 SOCIAL INFLUENCE CONFORMITY
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY. 9698/22 Paper 22 (Core Studies 2), maximum raw mark 50
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY 9698/22
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY 9698/22
Asking and answering research questions. What s it about?
 2 Asking and answering research questions What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 24 54) Social psychologists strive to reach general conclusions by developing scientific theories about why people behave
2 Asking and answering research questions What s it about? (Social Psychology pp. 24 54) Social psychologists strive to reach general conclusions by developing scientific theories about why people behave
OUTPATIENT SERVICES PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES CONTRACT
 OUTPATIENT SERVICES PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES CONTRACT (This is a detailed document. Please feel free to read at your leisure and discuss with Dr. Gard in subsequent sessions. It is a document to review over
OUTPATIENT SERVICES PSYCHOLOGICAL SERVICES CONTRACT (This is a detailed document. Please feel free to read at your leisure and discuss with Dr. Gard in subsequent sessions. It is a document to review over
The Stanford Prison Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008
 Name: Class: The Stanford Prison Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 The Stanford Prison Experiment was conducted by Phillip Zimbardo in 1973. By organizing an exercise that simulated prison life, Zimbardo
Name: Class: The Stanford Prison Experiment By Saul McLeod 2008 The Stanford Prison Experiment was conducted by Phillip Zimbardo in 1973. By organizing an exercise that simulated prison life, Zimbardo
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II
 THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II THEORIES OF PERSONALITY II Learning Theory SESSION 8 2014 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the contents of the document.
Cognitive, Social, and Physiological Determinants of Emotional State. Schachter, S. & Singer, J.E. (1962).
 Cognitive, Social, and Physiological Determinants of Emotional State. Schachter, S. & Singer, J.E. (1962). Bell Ringer How do we recognize the emotions we feel? If we see a bull running towards us, do
Cognitive, Social, and Physiological Determinants of Emotional State. Schachter, S. & Singer, J.E. (1962). Bell Ringer How do we recognize the emotions we feel? If we see a bull running towards us, do
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM
 ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
ORIENTATION SAN FRANCISCO STOP SMOKING PROGRAM PURPOSE To introduce the program, tell the participants what to expect, and set an overall positive tone for the series. AGENDA Item Time 0.1 Acknowledgement
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS
 Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
Chapter 15 Learning Objectives with SubQuestions PERSON PERCEPTION: FORMING IMPRESSIONS OF OTHERS #1) Explain how schemas, stereotypes, and other factors contribute to subjectivity in person perception
This paper contains analysis of the results of these processes and sets out the programme of future development.
 Fitness to Practise Committee, 14 February 2013 HCPC witness support programme Executive summary and recommendations Introduction This paper outlines the approach taken by HCPC in relation to witness management
Fitness to Practise Committee, 14 February 2013 HCPC witness support programme Executive summary and recommendations Introduction This paper outlines the approach taken by HCPC in relation to witness management
The Power of Positive Thinking
 The Power of Positive Thinking Youhaveprobablyhadsomeonetellyouto'thinkpositive'whenyouwereinatrying situation. That is because the power of positive thinking is something that is a widely heldbelief-andnotwithoutgoodreason.
The Power of Positive Thinking Youhaveprobablyhadsomeonetellyouto'thinkpositive'whenyouwereinatrying situation. That is because the power of positive thinking is something that is a widely heldbelief-andnotwithoutgoodreason.
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
 TYPES OF CONFORMITY Specification: Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence, and variables
TYPES OF CONFORMITY Specification: Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence, and variables
Deception in Human Subjects Research. J. Bruce Smith, MD, CIP IRB Members C E
 Deception in Human Subjects Research J. Bruce Smith, MD, CIP IRB Members C E Milgram Study research on obedience 1963 at Yale University Subjects recruited to participate in a teacher-learner experiment
Deception in Human Subjects Research J. Bruce Smith, MD, CIP IRB Members C E Milgram Study research on obedience 1963 at Yale University Subjects recruited to participate in a teacher-learner experiment
Scarcity & Behavior. Eldar Shafir Princeton University. Toronto, Nov. 2, 2015
 Scarcity & Behavior Eldar Shafir Princeton University Toronto, Nov. 2, 2015 The plan: - The behavioral view of human nature - The psychology of scarcity - Some policy implications - Discussion Much of
Scarcity & Behavior Eldar Shafir Princeton University Toronto, Nov. 2, 2015 The plan: - The behavioral view of human nature - The psychology of scarcity - Some policy implications - Discussion Much of
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
 Title: Types of Conformity Specification: Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence,
Title: Types of Conformity Specification: Types of conformity: internalisation, identification and compliance. Explanations for conformity: informational social influence and normative social influence,
QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY
 Module 16 QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY BERNIE SIEGEL, MD 2 Q How do our thoughts and beliefs affect the health of our bodies? A You can t separate thoughts and beliefs from your body. What you think and what
Module 16 QUESTIONS ANSWERED BY BERNIE SIEGEL, MD 2 Q How do our thoughts and beliefs affect the health of our bodies? A You can t separate thoughts and beliefs from your body. What you think and what
Social Biases and Pressures. Critical Thinking
 Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Social Biases and Pressures Critical Thinking Humans are Social Animals We are very sensitive to what others do and think. Most of our deep-rooted beliefs and values come from family and society we grow
Step Five. Admitted to ourselves and another human being the exact nature of our wrongs.
 Step Five Admitted to ourselves and another human being the exact nature of our wrongs. Our Basic Text tells us that Step Five is not simply a reading of Step Four. Yet we know that reading our Fourth
Step Five Admitted to ourselves and another human being the exact nature of our wrongs. Our Basic Text tells us that Step Five is not simply a reading of Step Four. Yet we know that reading our Fourth
Study #36 A PRISON BY ANY OTHER NAME
 Study #36 A PRISON BY ANY OTHER NAME 1. In Zimbardo s prison study, he set out to prove his theory that : Regardless of an individual s situation, no matter how desperate or horrific, their genetic predispositions
Study #36 A PRISON BY ANY OTHER NAME 1. In Zimbardo s prison study, he set out to prove his theory that : Regardless of an individual s situation, no matter how desperate or horrific, their genetic predispositions
Dissociation Explanation
 Dissociation Explanation Introduction: What is Dissociation? Dissociation is the term used to describe a coping mechanism that is used by people to disconnect from some aspect of experience in life. Often
Dissociation Explanation Introduction: What is Dissociation? Dissociation is the term used to describe a coping mechanism that is used by people to disconnect from some aspect of experience in life. Often
AP Psychology. Unit 14: Social Psychology. Social Influences
 AP Psychology Unit 14: Social Psychology Mod.75: Conformity & Obedience: Social Influences I. Conformity: Complying With Social Pressures: A. Automatic Mimicry: 1. Behavior is contagious! fish, birds,
AP Psychology Unit 14: Social Psychology Mod.75: Conformity & Obedience: Social Influences I. Conformity: Complying With Social Pressures: A. Automatic Mimicry: 1. Behavior is contagious! fish, birds,
How to Work with the Patterns That Sustain Depression
 How to Work with the Patterns That Sustain Depression Module 5.2 - Transcript - pg. 1 How to Work with the Patterns That Sustain Depression How the Grieving Mind Fights Depression with Marsha Linehan,
How to Work with the Patterns That Sustain Depression Module 5.2 - Transcript - pg. 1 How to Work with the Patterns That Sustain Depression How the Grieving Mind Fights Depression with Marsha Linehan,
Chapter 2: Psychological Research Methods & Statistics Notes
 Chapter 2: Psychological Research Methods & Statistics Notes Ethics In order for psychology to be taken seriously as a behavior science, research & experiments are an essential part of the field. Before
Chapter 2: Psychological Research Methods & Statistics Notes Ethics In order for psychology to be taken seriously as a behavior science, research & experiments are an essential part of the field. Before
Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error.
 Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error. 3 Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy of their beliefs. 4 Case studies are particularly useful because of the similarities we
Human intuition is remarkably accurate and free from error. 3 Most people seem to lack confidence in the accuracy of their beliefs. 4 Case studies are particularly useful because of the similarities we
Lawrence Kohlberg (1958) agreed with Piaget's (1932) theory of moral development in principle but wanted to develop his ideas further.
 Kohlberg www.simplypsychology.org /kohlberg.html Saul McLeod Lawrence Kohlberg (1958) agreed with Piaget's (1932) theory of moral development in principle but wanted to develop his ideas further. He used
Kohlberg www.simplypsychology.org /kohlberg.html Saul McLeod Lawrence Kohlberg (1958) agreed with Piaget's (1932) theory of moral development in principle but wanted to develop his ideas further. He used
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY
 SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY IB SYLLABUS SAYS: Evaluate research on conformity to group norms. Discuss factors influencing conformity. Textbook pages: 119-123 WHAT IS CONFORMITY? One of the key ways that
SOCIAL INFLUENCE: CONFORMITY IB SYLLABUS SAYS: Evaluate research on conformity to group norms. Discuss factors influencing conformity. Textbook pages: 119-123 WHAT IS CONFORMITY? One of the key ways that
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology
 AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
AP Psychology -- Chapter 02 Review Research Methods in Psychology 1. In the opening vignette, to what was Alicia's condition linked? The death of her parents and only brother 2. What did Pennebaker s study
Self-directed support
 Self-directed support Mental health and self-directed support Self- directed support is for everyone who is eligible for social care funding. This answers some of the most commonly heard questions about
Self-directed support Mental health and self-directed support Self- directed support is for everyone who is eligible for social care funding. This answers some of the most commonly heard questions about
COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES
 Dr. Moshe ben Asher SOC 356, Introduction to Social Welfare CSUN, Sociology Department COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES WHAT DISTINGUISHES A PROFESSIONAL FROM OTHER KINDS OF WORKERS? Education and training
Dr. Moshe ben Asher SOC 356, Introduction to Social Welfare CSUN, Sociology Department COUNSELING INTERVIEW GUIDELINES WHAT DISTINGUISHES A PROFESSIONAL FROM OTHER KINDS OF WORKERS? Education and training
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY 9698/23
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2012 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9698 PSYCHOLOGY 9698/23
THE FORMATION OF FALSE MEMORIES LOFTUS AND PECKRILL (1995)
 THE FORMATION OF FALSE MEMORIES LOFTUS AND PECKRILL (1995) Bell Ringer Eyewitness Testimony Prior to viewing this clip, what is your opinion on eyewitness accounts? Why? MEMORY Your memory is your mind
THE FORMATION OF FALSE MEMORIES LOFTUS AND PECKRILL (1995) Bell Ringer Eyewitness Testimony Prior to viewing this clip, what is your opinion on eyewitness accounts? Why? MEMORY Your memory is your mind
Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research
 Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research Ten Points of the Nuremberg Code (1947) 1. The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential. This means that the person involved
Ethical Issues in the Conduct of Psychological Research Ten Points of the Nuremberg Code (1947) 1. The voluntary consent of the human subject is absolutely essential. This means that the person involved
12/15/2011. PSY 450 Dr. Schuetze
 PSY 450 Dr. Schuetze Ethics: rules for distinguishing between right and wrong. Norms for conduct that distinguish between acceptable and unacceptable behavior. Psychologists must ask and answer questions
PSY 450 Dr. Schuetze Ethics: rules for distinguishing between right and wrong. Norms for conduct that distinguish between acceptable and unacceptable behavior. Psychologists must ask and answer questions
 www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for
www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for
LEAVING EVERYONE WITH THE IMPRESSION OF INCREASE The Number One Key to Success
 LESSON ELEVEN LEAVING EVERYONE WITH THE IMPRESSION OF INCREASE The Number One Key to Success 167 Lesson Eleven AREA 1 NAME AREA 2 NAME AREA 3 NAME KEY POINTS Riches, in the context of this program, refers
LESSON ELEVEN LEAVING EVERYONE WITH THE IMPRESSION OF INCREASE The Number One Key to Success 167 Lesson Eleven AREA 1 NAME AREA 2 NAME AREA 3 NAME KEY POINTS Riches, in the context of this program, refers
Subliminal Messages: How Do They Work?
 Subliminal Messages: How Do They Work? You ve probably heard of subliminal messages. There are lots of urban myths about how companies and advertisers use these kinds of messages to persuade customers
Subliminal Messages: How Do They Work? You ve probably heard of subliminal messages. There are lots of urban myths about how companies and advertisers use these kinds of messages to persuade customers
Do I Have a Drinking Problem?
 People drink for all sorts of reason. Some reasons are to socialize, celebrate and relax. Other times people use alcohol as a form of self-medication to help them manage stress, anxiety or to use it to
People drink for all sorts of reason. Some reasons are to socialize, celebrate and relax. Other times people use alcohol as a form of self-medication to help them manage stress, anxiety or to use it to
Introduction to Research Methods
 Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Introduction to Research Methods Updated August 08, 2016 1 The Three Types of Psychology Research Psychology research can usually be classified as one of three major types: 1. Causal Research When most
Social Psychology. Social Psychology. Friends agree that person is: Friends agree that person is:
 Social Psychology Social Psychology Chapter 13 Impression formation and Attribution theory Study of the ways in which thoughts, feelings, perceptions, motives, and behavior are influenced by interactions
Social Psychology Social Psychology Chapter 13 Impression formation and Attribution theory Study of the ways in which thoughts, feelings, perceptions, motives, and behavior are influenced by interactions
klm Mark Scheme Psychology 1181 Specification A General Certificate of Education Social Psychology and Individual Differences
 Version 1.0: 0109 klm General Certificate of Education Psychology 1181 Specification A Unit 2 (PSYA2) Biological Psychology, Social Psychology and Individual Differences Mark Scheme January examination
Version 1.0: 0109 klm General Certificate of Education Psychology 1181 Specification A Unit 2 (PSYA2) Biological Psychology, Social Psychology and Individual Differences Mark Scheme January examination
Reliability, validity, and all that jazz
 Reliability, validity, and all that jazz Dylan Wiliam King s College London Published in Education 3-13, 29 (3) pp. 17-21 (2001) Introduction No measuring instrument is perfect. If we use a thermometer
Reliability, validity, and all that jazz Dylan Wiliam King s College London Published in Education 3-13, 29 (3) pp. 17-21 (2001) Introduction No measuring instrument is perfect. If we use a thermometer
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles
 Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
Chapter 1. Dysfunctional Behavioral Cycles For most people, the things they do their behavior are predictable. We can pretty much guess what someone is going to do in a similar situation in the future
Research Methods. Page 1 of 23
 Research Methods Page 1 of 23 Research Methods Revision Guide The Various Experimental and Non-Experimental Research Methods 1 2 Experimental Research Methods, including: Laboratory Experiment features,
Research Methods Page 1 of 23 Research Methods Revision Guide The Various Experimental and Non-Experimental Research Methods 1 2 Experimental Research Methods, including: Laboratory Experiment features,
London. London. Last year, as Speaking Up and Advocacy Partners, we:
 Easy Read Last year, as Speaking Up and Advocacy Partners, we: worked with 10,139 people had 113 services, in 36 areas gave out 453 of our easyread SEN resources had 534 paid staff and volunteers working
Easy Read Last year, as Speaking Up and Advocacy Partners, we: worked with 10,139 people had 113 services, in 36 areas gave out 453 of our easyread SEN resources had 534 paid staff and volunteers working
Examiners Report June GCE Psychology 6PS01 01
 Examiners Report June 2014 GCE Psychology 6PS01 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range of qualifications
Examiners Report June 2014 GCE Psychology 6PS01 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the UK s largest awarding body. We provide a wide range of qualifications
Chapter 14. Social Psychology. How Does the Social Situation Affect our Behavior? Social Psychology
 Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
Chapter 14 Social Psychology This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: Any public performance or display, including transmission of
