INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES
|
|
|
- Mitchell Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FACTORIAL ANOVA
2 INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES Revise factorial ANOVA (from our last lecture) Discuss degrees of freedom in factorial ANOVA Recognise main effects and interactions Discuss simple effects
3 QUICK REMINDER FROM LAST LECTURE ON FACTORIAL ANOVA And brief revision of a one-way ANOVA
4 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TYPES OF ANOVA Last semester we studied a one-way ANOVA How many IVs did a one-way ANOVA have? The clue is in the name (it had one!) Depending on the study, a one-way ANOVA could have many levels of the IV A one-way ANOVA tests for a difference between 3 or more levels of one IV on one DV
5 So the basic formula is pretty simple...we are aiming to solve the overall division/ratio: F Ratio Recap ANOVA model F MSbetweengroups MS withingroups and both the MS parts can be broken down into individual variance equations MSbetweengroups SSbetweengroups df betweengroups MSwithingroups SSwithingroups df withingroups
6 But the reason ANOVA maths gets difficult is because we don t have all the numbers up front. first, we are able to get an overall SS SS total When comparing two or more samples the mean of all the scores together is known as the grand mean x Any score can be expressed as a deviation from the grand mean ie so SS total x x x x ONCE WE HAVE THE SS TOTAL WE KNOW WE CAN BREAK IT DOWN BY PARTITIONING TO GET THE TWO THINGS WE ACTUALLY WANT (SS within and SS between)
7 Partitioning of Sums of Squares for Oneway ANOVA SS total SS between SS within So remember ANOVA was always checking whether the between groups variance was bigger than that within the within groups variance (which is just general individual differences and nothing to do with the psychological variable of interest).
8 FACTORIAL ANOVA The main difference here is that since you have the addition of at least one other IV, you now have to do a little more work to calculate the ANOVA
9 I want to research the effect of therapy on locus of control in people with schizophrenia & people with depression Locus of control is a characteristic of self esteem which we all have and it is markedly low in psychological illness I want to know if therapies will help this one single aspect of psychological illness 3 different levels of therapy (CBT, psychoanalytic, family therapy) & levels of illness types (SZ and depression) My dependent measure is the IMPROVEMENT scores on a test for locus of control by how many they increased from baseline after the therapy (not the raw scores)
10 EXAMPLE DATA- THE EFFECT OF THERAPY ON LOCUS OF CONTROL FOR DIFFERENT PATIENT GROUPS Factor 1: Therapy Therapy A Therapy B Therapy C x Factor : diagnosis Schizophrenia Depression x 3 x 6 x x 1 x x x x
11 Partitioning of Sums of Squares for Twoway Factorial ANOVA So the between section is now divided into our two factors (IVs) plus the interaction of the two factors. So it s the SS between that is affected and makes it more complicated. The SS within doesn t change here. SS total SS between SS within (error) SS F1 SS F SS F1xF
12 SUMS OF SQUARES disorder SZ DP Therapy A B C x 3 x 6 x x 1 x x 3 x 4 3 x 3 x 4 a) SStotal ( x x) ( 3) (4 3) (5 3) etc 36
13 b) Sum of squares for therapy SS factor 1 nf 1( x f 1 x) A B C 5 x 3 7 x 6 4 x x 1 1 x 3 x 3 x 4 3 x 3 x 4 4( 3) 4(4 3) 4(3 3) 8
14 c) sum of squares for diagnosis SS factor nf ( x f x) A B C 5 x 3 7 x 6 4 x x 1 1 x 3 x 3 x 4 3 x 3 x 4 6(4 3) 6( 3) 1
15 SS d) sum of squares for therapy x diagnosis cells n (3 cells ( x 3) cells x) (6 3) (3 5 x 3 7 x 6 4 x x 1 1 x 3 x 3 x 4 3 x 3 3) x 4 (1 3) ( 3) (3 3) 8 SS f SS 8 (8 1) 8 ( SSfactor1 SS ) 1xf cells factor
16 e) error sum of squares SS error SS total SS cells or SS total ( SS SS SS factor1 factor f 1xf ) 36 (8 1 8) 8
17 SS total SS between SS within SS F1 SS F SS F1xF So for all the SS we need, we have done 1) Each individual score minus the overall mean (SS total) ) Each row mean minus the overall mean (SSfactor 1) 3) Each column mean minus the overall mean (SSfactor ) 4) Each individual cell mean minus the overall mean (SS cells/interaction) 5) The total minus the cells/interaction (SSwithin/error)
18 DEGREES OF FREEDOM... NO MAJOR CALCULATIONS HERE! dftotal total number of scores dffactor1 number of levels of factor dffactor number of levels of factor
19 Interaction degrees of freedom is a simple calculation Multiply the two degrees of freedom for the two factors (IVs) df f1xf df f1 x df f x 1
20 Error (within) degrees of freedom is another simple calculation df error df total - (df f1 df f df f1xf ) 11- ( 1 ) 6
21 OVERALL MEAN SQUARES mean square for therapy mean square for diagnosis MS MS factor1 factor SS df 8 factor1 factor SS df factor factor 1
22 mean square for interaction therapy x diagnosis MS f 1xf SS df 8 f 1xf f 1xf 4 mean square for error/within MS error SS df error error
23 FINAL F RATIOS therapy F factor1 MS MS factor1 error diagnosis F factor MS MS factor error interaction Ff 1 therapy x diagnosis xf MS MS f 1xf error
24 Let s go back to our Interaction Graph Therapy A and C are not different from each other in the schizophrenia group! Schizophrenia Mean improvement score Depression Therapy A Therapy B Therapy C Type of treatment No difference between conditions for Therapy C!
25 SIMPLE EFFECTS How you can learn to love simple effects
26 A -WAY ANOVA -way ANOVA independent variables (IVs) can have: Main Effect The effects of one independent variable (factor) summed (averaged) over all levels of the other independent variable. Interaction When the effect of one factor is not constant across all levels of the other factors. Significant interactions have implications for main effects!!
27 PROBLEM WITH THE FACTORIAL ANOVA? Going back to the example of a x ANOVA, you will be calculating 3 F values - One for IV1 (main effect) - One for IV (main effect) - One for the interaction between IV1 and IV When you find an interaction effect, you should be aware that all is not as it might seem, with your main effect So if this happens the test is fine, you haven t done anything bad at all just need to go back and do post hoc analysis to pick it all apart
28 WHAT ARE SIMPLE EFFECTS? In order to interpret any potential main effects, an analysis of Simple Effects should be conducted (i.e., You should conduct an analysis of simple effects to disentangle the interaction) A simple effects is the effect of ONE independent variable (factor) at each individual level of the other IV (factor) In order for a main effect to be interpretable, the simple effects for that variable must be the same for all levels of the other independent variable.
29 SIMPLE EFFECTS TESTING FOR TYPE OF THERAPY In this example, there are two simple effects for type of therapy: 1. The effect of treatment for schizophrenia, i.e., the difference between therapies for people with schizophrenia. The effect of treatment for depression, i.e., the difference between therapies for people with depression Analysis = Conduct TWO separate one-way independent groups ANOVA. Using the MSerror from the original two-way ANOVA and appropriate degrees of freedom, to assess if there is any difference between the scores of the three therapies
30 If the effect of drug is the same for schizophrenics and depressives then there is an interpretable main effect for drug. The question we are addressing here is: - Is the effect for drug consistent (the same) for people with schizophrenia and depression? All we are doing is going back and looking at each group of patients individually, instead of all at once.
31 SIMPLE EFFECTS TESTING FOR TYPE OF DIAGNOSIS There are three simple effects for type of diagnosis: 1. the differences between patient groups for Therapy A. the differences between patient groups for Therapy B 3. the differences between patient groups for Therapy C Analysis = Conduct one-way independent groups ANOVA (or in this case could do post hoc t-tests as only two groups) using the MSerror from the original two-way ANOVA and appropriate degrees of freedom, to assess if there is any difference between the scores of the participants for each therapy alone
32 If differences between schizophrenics and depressives are in the same direction for all three types of drug then there is an interpretable main effect for type of problem. The question we are addressing here is: - Is the effect for type of diagnosis consistent (the same) for all three types of drug?
33 Interaction Graph Schizophrenia Mean improvement score Depression therapy A therapy B therapy C Type of treatment
34 BONFERRONI If you use the Bonferroni correction when doing simple effects, just like in the one-way ANOVA, the alpha level (.05) is divided by the number of tests you are doing So if you are doing simple effects and your IV has 3 levels, alpha would become.016 If your IV has levels, the alpha would become.05 Remember, we re just dividing.05 by the number of levels of the IV
35 IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS Factors: independent variables each with a number of levels Factorial Design: an experimental design which uses all combinations of levels of factors. These are called crossed factors. Treatment: A particular combination of levels of the factors. Also known as a cell (in an independent groups design also a group). Main Effect: The effects of one independent variable (factor) summed (averaged) over all levels of the other independent variable Interaction: When the effect of one factor is not constant across all levels of the other factors.
36 SUMMARY Introduced factorial ANOVA Calculated factorial ANOVA! Discussed main effects and interactions
37 Next class: Power
Week 8 Factorial ANOVA (Independent groups) Simple (main) effects and interactions, theoretical stuff
 PSY2004 Week 8 Factorial ANOVA (Independent groups) Simple (main) effects and interactions, theoretical stuff Aims To introduce research questions involving factorial ANOVA To go through theoretical examples
PSY2004 Week 8 Factorial ANOVA (Independent groups) Simple (main) effects and interactions, theoretical stuff Aims To introduce research questions involving factorial ANOVA To go through theoretical examples
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
 Research Methods and Ethics in Psychology Week 4 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) One Way Independent Groups ANOVA Brief revision of some important concepts To introduce the concept of familywise error rate.
Research Methods and Ethics in Psychology Week 4 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) One Way Independent Groups ANOVA Brief revision of some important concepts To introduce the concept of familywise error rate.
ANOVA. Thomas Elliott. January 29, 2013
 ANOVA Thomas Elliott January 29, 2013 ANOVA stands for analysis of variance and is one of the basic statistical tests we can use to find relationships between two or more variables. ANOVA compares the
ANOVA Thomas Elliott January 29, 2013 ANOVA stands for analysis of variance and is one of the basic statistical tests we can use to find relationships between two or more variables. ANOVA compares the
Analysis of Variance: repeated measures
 Analysis of Variance: repeated measures Tests for comparing three or more groups or conditions: (a) Nonparametric tests: Independent measures: Kruskal-Wallis. Repeated measures: Friedman s. (b) Parametric
Analysis of Variance: repeated measures Tests for comparing three or more groups or conditions: (a) Nonparametric tests: Independent measures: Kruskal-Wallis. Repeated measures: Friedman s. (b) Parametric
Between Groups & Within-Groups ANOVA
 Between Groups & Within-Groups ANOVA BG & WG ANOVA Partitioning Variation making F making effect sizes Things that influence F Confounding Inflated within-condition variability Integrating stats & methods
Between Groups & Within-Groups ANOVA BG & WG ANOVA Partitioning Variation making F making effect sizes Things that influence F Confounding Inflated within-condition variability Integrating stats & methods
One-Way ANOVAs t-test two statistically significant Type I error alpha null hypothesis dependant variable Independent variable three levels;
 1 One-Way ANOVAs We have already discussed the t-test. The t-test is used for comparing the means of two groups to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between them. The t-test
1 One-Way ANOVAs We have already discussed the t-test. The t-test is used for comparing the means of two groups to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between them. The t-test
Comparing 3 Means- ANOVA
 Comparing 3 Means- ANOVA Evaluation Methods & Statistics- Lecture 7 Dr Benjamin Cowan Research Example- Theory of Planned Behaviour Ajzen & Fishbein (1981) One of the most prominent models of behaviour
Comparing 3 Means- ANOVA Evaluation Methods & Statistics- Lecture 7 Dr Benjamin Cowan Research Example- Theory of Planned Behaviour Ajzen & Fishbein (1981) One of the most prominent models of behaviour
Advanced ANOVA Procedures
 Advanced ANOVA Procedures Session Lecture Outline:. An example. An example. Two-way ANOVA. An example. Two-way Repeated Measures ANOVA. MANOVA. ANalysis of Co-Variance (): an ANOVA procedure whereby the
Advanced ANOVA Procedures Session Lecture Outline:. An example. An example. Two-way ANOVA. An example. Two-way Repeated Measures ANOVA. MANOVA. ANalysis of Co-Variance (): an ANOVA procedure whereby the
One-Way Independent ANOVA
 One-Way Independent ANOVA Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a common and robust statistical test that you can use to compare the mean scores collected from different conditions or groups in an experiment.
One-Way Independent ANOVA Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) is a common and robust statistical test that you can use to compare the mean scores collected from different conditions or groups in an experiment.
EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TWO-WAY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY)
 EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TO-AY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY) A researcher conducts a study to evaluate the effects of the length of an exercise program on the flexibility of female and male
EPS 625 INTERMEDIATE STATISTICS TO-AY ANOVA IN-CLASS EXAMPLE (FLEXIBILITY) A researcher conducts a study to evaluate the effects of the length of an exercise program on the flexibility of female and male
Research paper. One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Research paper. SPSS output. Learning objectives. Alcohol and driving ability
 Research paper Alcohol and driving ability One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Thirty-six people took part in an experiment to discover the effects of alcohol on drinking ability. They were randomly assigned
Research paper Alcohol and driving ability One-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Thirty-six people took part in an experiment to discover the effects of alcohol on drinking ability. They were randomly assigned
15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA
 15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA Statistics does all kinds of stuff to describe data Talk about baseball, other useful stuff We can calculate the probability.
15.301/310, Managerial Psychology Prof. Dan Ariely Recitation 8: T test and ANOVA Statistics does all kinds of stuff to describe data Talk about baseball, other useful stuff We can calculate the probability.
PSY 216: Elementary Statistics Exam 4
 Name: PSY 16: Elementary Statistics Exam 4 This exam consists of multiple-choice questions and essay / problem questions. For each multiple-choice question, circle the one letter that corresponds to the
Name: PSY 16: Elementary Statistics Exam 4 This exam consists of multiple-choice questions and essay / problem questions. For each multiple-choice question, circle the one letter that corresponds to the
Two-Way Independent ANOVA
 Two-Way Independent ANOVA Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) a common and robust statistical test that you can use to compare the mean scores collected from different conditions or groups in an experiment. There
Two-Way Independent ANOVA Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) a common and robust statistical test that you can use to compare the mean scores collected from different conditions or groups in an experiment. There
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript
 Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript DR. JENNIFER ANN MORROW: Welcome to Analysis of Variance. My name is Dr. Jennifer Ann Morrow. In today's demonstration, I'll review with you the definition
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Program Transcript DR. JENNIFER ANN MORROW: Welcome to Analysis of Variance. My name is Dr. Jennifer Ann Morrow. In today's demonstration, I'll review with you the definition
Study Guide for the Final Exam
 Study Guide for the Final Exam When studying, remember that the computational portion of the exam will only involve new material (covered after the second midterm), that material from Exam 1 will make
Study Guide for the Final Exam When studying, remember that the computational portion of the exam will only involve new material (covered after the second midterm), that material from Exam 1 will make
Repeated Measures ANOVA and Mixed Model ANOVA. Comparing more than two measurements of the same or matched participants
 Repeated Measures ANOVA and Mixed Model ANOVA Comparing more than two measurements of the same or matched participants Data files Fatigue.sav MentalRotation.sav AttachAndSleep.sav Attitude.sav Homework:
Repeated Measures ANOVA and Mixed Model ANOVA Comparing more than two measurements of the same or matched participants Data files Fatigue.sav MentalRotation.sav AttachAndSleep.sav Attitude.sav Homework:
Sources of Variance & ANOVA
 ANOVA ANalysis Of VAriance Sources of Variance & ANOVA BG ANOVA Partitioning Variation making F making effect sizes Things that influence F Confounding Inflated within-condition variability Integrating
ANOVA ANalysis Of VAriance Sources of Variance & ANOVA BG ANOVA Partitioning Variation making F making effect sizes Things that influence F Confounding Inflated within-condition variability Integrating
FORM C Dr. Sanocki, PSY 3204 EXAM 1 NAME
 PSYCH STATS OLD EXAMS, provided for self-learning. LEARN HOW TO ANSWER the QUESTIONS; memorization of answers won t help. All answers are in the textbook or lecture. Instructors can provide some clarification
PSYCH STATS OLD EXAMS, provided for self-learning. LEARN HOW TO ANSWER the QUESTIONS; memorization of answers won t help. All answers are in the textbook or lecture. Instructors can provide some clarification
8/28/2017. If the experiment is successful, then the model will explain more variance than it can t SS M will be greater than SS R
 PSY 5101: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 1 If the ANOVA is significant, then it means that there is some difference, somewhere but it does not tell you which means are different
PSY 5101: Advanced Statistics for Psychological and Behavioral Research 1 If the ANOVA is significant, then it means that there is some difference, somewhere but it does not tell you which means are different
CHAPTER ONE CORRELATION
 CHAPTER ONE CORRELATION 1.0 Introduction The first chapter focuses on the nature of statistical data of correlation. The aim of the series of exercises is to ensure the students are able to use SPSS to
CHAPTER ONE CORRELATION 1.0 Introduction The first chapter focuses on the nature of statistical data of correlation. The aim of the series of exercises is to ensure the students are able to use SPSS to
Exercise Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment.
 Exercise 2.2.1 Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment y ijk y = ( y i y ) + ( y j y ) + [( y ij y ) ( y i y ) ( y j y
Exercise 2.2.1 Verify that the term on the left of the equation showing the decomposition of "total" deviation in a two-factor experiment y ijk y = ( y i y ) + ( y j y ) + [( y ij y ) ( y i y ) ( y j y
Steps in Inferential Analyses. Inferential Statistics. t-test
 Steps in Inferential Analyses Inferential Statistics Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos VassarStats: http://faculty.vassar.edu/lowry/vassarstats.html In any inferential statistic, the first step is always
Steps in Inferential Analyses Inferential Statistics Dr. K. A. Korb University of Jos VassarStats: http://faculty.vassar.edu/lowry/vassarstats.html In any inferential statistic, the first step is always
25. Two-way ANOVA. 25. Two-way ANOVA 371
 25. Two-way ANOVA The Analysis of Variance seeks to identify sources of variability in data with when the data is partitioned into differentiated groups. In the prior section, we considered two sources
25. Two-way ANOVA The Analysis of Variance seeks to identify sources of variability in data with when the data is partitioned into differentiated groups. In the prior section, we considered two sources
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical)
 ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
ANOVA in SPSS (Practical) Analysis of Variance practical In this practical we will investigate how we model the influence of a categorical predictor on a continuous response. Centre for Multilevel Modelling
Final Exam PS 217, Spring 2004
 Final Exam PS 217, Spring 24 1. What is the relationship between power and effect size? That is, when you are considering a research design in which there is a large effect size, what are the implications
Final Exam PS 217, Spring 24 1. What is the relationship between power and effect size? That is, when you are considering a research design in which there is a large effect size, what are the implications
Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance
 Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance of Variance Chapter 12 presents the general logic and basic formulas for the hypothesis testing procedure known as analysis of variance (ANOVA). The purpose
Chapter 12: Introduction to Analysis of Variance of Variance Chapter 12 presents the general logic and basic formulas for the hypothesis testing procedure known as analysis of variance (ANOVA). The purpose
Factorial Analysis of Variance
 Factorial Analysis of Variance Overview of the Factorial ANOVA In the context of ANOVA, an independent variable (or a quasiindependent variable) is called a factor, and research studies with multiple factors,
Factorial Analysis of Variance Overview of the Factorial ANOVA In the context of ANOVA, an independent variable (or a quasiindependent variable) is called a factor, and research studies with multiple factors,
USING STATCRUNCH TO CONSTRUCT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS and CALCULATE SAMPLE SIZE
 USING STATCRUNCH TO CONSTRUCT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS and CALCULATE SAMPLE SIZE Using StatCrunch for confidence intervals (CI s) is super easy. As you can see in the assignments, I cover 9.2 before 9.1 because
USING STATCRUNCH TO CONSTRUCT CONFIDENCE INTERVALS and CALCULATE SAMPLE SIZE Using StatCrunch for confidence intervals (CI s) is super easy. As you can see in the assignments, I cover 9.2 before 9.1 because
Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide
 Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide Notes This handout provides perfect answers to the sample exam paper. I would not expect you to be able to produce such perfect answers in an exam. So, use this document
Sample Exam Paper Answer Guide Notes This handout provides perfect answers to the sample exam paper. I would not expect you to be able to produce such perfect answers in an exam. So, use this document
Business Statistics Probability
 Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Analysis of Variance ANOVA, Part 2. What We Will Cover in This Section. Factorial ANOVA, Two-way Design
 Analysis of Variance ANOVA, Part //007 P33 Analysis of Variance What We Will Cover in This Section Introduction. Overview. Factorial ANOVA Repeated Measures ANOVA. //007 P33 Analysis of Variance Factorial
Analysis of Variance ANOVA, Part //007 P33 Analysis of Variance What We Will Cover in This Section Introduction. Overview. Factorial ANOVA Repeated Measures ANOVA. //007 P33 Analysis of Variance Factorial
Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education
 Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education What is Multiple Regression? When using Multiple Regression in education, researchers use the term independent variables to identify those variables that
Study Guide #2: MULTIPLE REGRESSION in education What is Multiple Regression? When using Multiple Regression in education, researchers use the term independent variables to identify those variables that
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS
 ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS REVIEW Testing hypothesis using the difference between two means: One-sample t-test Independent-samples t-test Dependent/Paired-samples
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE (ANOVA): TESTING DIFFERENCES INVOLVING THREE OR MORE MEANS REVIEW Testing hypothesis using the difference between two means: One-sample t-test Independent-samples t-test Dependent/Paired-samples
APPENDIX N. Summary Statistics: The "Big 5" Statistical Tools for School Counselors
 APPENDIX N Summary Statistics: The "Big 5" Statistical Tools for School Counselors This appendix describes five basic statistical tools school counselors may use in conducting results based evaluation.
APPENDIX N Summary Statistics: The "Big 5" Statistical Tools for School Counselors This appendix describes five basic statistical tools school counselors may use in conducting results based evaluation.
Chapter 12: Analysis of covariance, ANCOVA
 Chapter 12: Analysis of covariance, ANCOVA Smart Alex s Solutions Task 1 A few years back I was stalked. You d think they could have found someone a bit more interesting to stalk, but apparently times
Chapter 12: Analysis of covariance, ANCOVA Smart Alex s Solutions Task 1 A few years back I was stalked. You d think they could have found someone a bit more interesting to stalk, but apparently times
1-way ANOVA indepenpendent groups Page 1 of 60. One-way ANOVA. Copyright 1998, 2000 Tom Malloy
 1-way ANOVA indepenpendent groups Page 1 of 60 One-way ANOVA Copyright 1998, 2000 Tom Malloy This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You
1-way ANOVA indepenpendent groups Page 1 of 60 One-way ANOVA Copyright 1998, 2000 Tom Malloy This is the text of the in-class lecture which accompanied the Authorware visual graphics on this topic. You
Interactions between predictors and two-factor ANOVA
 Interactions between predictors and two-factor ANOVA March 6, 2017 psych10.stanford.edu Announcements / Action Items Quiz 4 is on Wednesday 3/7 Option to earn extra credit (added to Quiz 3) New topics
Interactions between predictors and two-factor ANOVA March 6, 2017 psych10.stanford.edu Announcements / Action Items Quiz 4 is on Wednesday 3/7 Option to earn extra credit (added to Quiz 3) New topics
Testing Means. Related-Samples t Test With Confidence Intervals. 6. Compute a related-samples t test and interpret the results.
 10 Learning Objectives Testing Means After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Related-Samples t Test With Confidence Intervals 1. Describe two types of research designs used when we select related
10 Learning Objectives Testing Means After reading this chapter, you should be able to: Related-Samples t Test With Confidence Intervals 1. Describe two types of research designs used when we select related
Inferential Statistics
 Inferential Statistics and t - tests ScWk 242 Session 9 Slides Inferential Statistics Ø Inferential statistics are used to test hypotheses about the relationship between the independent and the dependent
Inferential Statistics and t - tests ScWk 242 Session 9 Slides Inferential Statistics Ø Inferential statistics are used to test hypotheses about the relationship between the independent and the dependent
Exam 3 PS 217, Spring 2011
 Exam 3 PS 217, Spring 2011 1. First, some random questions about topics we covered this semester. [10 pts] a. In a repeated measures design, what is the effect of counterbalancing on order or carry-over
Exam 3 PS 217, Spring 2011 1. First, some random questions about topics we covered this semester. [10 pts] a. In a repeated measures design, what is the effect of counterbalancing on order or carry-over
Lecture 20: Chi Square
 Statistics 20_chi.pdf Michael Hallstone, Ph.D. hallston@hawaii.edu Lecture 20: Chi Square Introduction Up until now, we done statistical test using means, but the assumptions for means have eliminated
Statistics 20_chi.pdf Michael Hallstone, Ph.D. hallston@hawaii.edu Lecture 20: Chi Square Introduction Up until now, we done statistical test using means, but the assumptions for means have eliminated
appstats26.notebook April 17, 2015
 Chapter 26 Comparing Counts Objective: Students will interpret chi square as a test of goodness of fit, homogeneity, and independence. Goodness of Fit A test of whether the distribution of counts in one
Chapter 26 Comparing Counts Objective: Students will interpret chi square as a test of goodness of fit, homogeneity, and independence. Goodness of Fit A test of whether the distribution of counts in one
HPS301 Exam Notes- Contents
 HPS301 Exam Notes- Contents Week 1 Research Design: What characterises different approaches 1 Experimental Design 1 Key Features 1 Criteria for establishing causality 2 Validity Internal Validity 2 Threats
HPS301 Exam Notes- Contents Week 1 Research Design: What characterises different approaches 1 Experimental Design 1 Key Features 1 Criteria for establishing causality 2 Validity Internal Validity 2 Threats
PSYCHOLOGY 300B (A01)
 PSYCHOLOGY 00B (A01) Assignment February, 019 t = n M i M j + n SS R = nc (M R GM ) SS C = nr (M C GM ) SS error = (X M) = s (n 1) SS RC = n (M GM ) SS R SS C SS total = (X GM ) df total = rcn 1 df R =
PSYCHOLOGY 00B (A01) Assignment February, 019 t = n M i M j + n SS R = nc (M R GM ) SS C = nr (M C GM ) SS error = (X M) = s (n 1) SS RC = n (M GM ) SS R SS C SS total = (X GM ) df total = rcn 1 df R =
Lesson 9: Two Factor ANOVAS
 Published on Agron 513 (https://courses.agron.iastate.edu/agron513) Home > Lesson 9 Lesson 9: Two Factor ANOVAS Developed by: Ron Mowers, Marin Harbur, and Ken Moore Completion Time: 1 week Introduction
Published on Agron 513 (https://courses.agron.iastate.edu/agron513) Home > Lesson 9 Lesson 9: Two Factor ANOVAS Developed by: Ron Mowers, Marin Harbur, and Ken Moore Completion Time: 1 week Introduction
Psy201 Module 3 Study and Assignment Guide. Using Excel to Calculate Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
 Psy201 Module 3 Study and Assignment Guide Using Excel to Calculate Descriptive and Inferential Statistics What is Excel? Excel is a spreadsheet program that allows one to enter numerical values or data
Psy201 Module 3 Study and Assignment Guide Using Excel to Calculate Descriptive and Inferential Statistics What is Excel? Excel is a spreadsheet program that allows one to enter numerical values or data
Math Section MW 1-2:30pm SR 117. Bekki George 206 PGH
 Math 3339 Section 21155 MW 1-2:30pm SR 117 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu 206 PGH Office Hours: M 11-12:30pm & T,TH 10:00 11:00 am and by appointment More than Two Independent Samples: Single Factor Analysis
Math 3339 Section 21155 MW 1-2:30pm SR 117 Bekki George bekki@math.uh.edu 206 PGH Office Hours: M 11-12:30pm & T,TH 10:00 11:00 am and by appointment More than Two Independent Samples: Single Factor Analysis
The t-test test and ANOVA
 The t-test test and ANOVA David L. Streiner, Ph.D. Director, Kunin-Lunenfeld Applied Research Unit Assistant V.P., Research Baycrest Centre for Geriatric Care Professor, Department of Psychiatry University
The t-test test and ANOVA David L. Streiner, Ph.D. Director, Kunin-Lunenfeld Applied Research Unit Assistant V.P., Research Baycrest Centre for Geriatric Care Professor, Department of Psychiatry University
kxk BG Factorial Designs kxk BG Factorial Designs Basic and Expanded Factorial Designs
 kxk BG Factorial Designs expanding the 2x2 design F & LSD for orthogonal factorial designs using the right tests for the right effects F & follow-up analyses for non-orthogonal designs Effect sizes for
kxk BG Factorial Designs expanding the 2x2 design F & LSD for orthogonal factorial designs using the right tests for the right effects F & follow-up analyses for non-orthogonal designs Effect sizes for
Analysis of single gene effects 1. Quantitative analysis of single gene effects. Gregory Carey, Barbara J. Bowers, Jeanne M.
 Analysis of single gene effects 1 Quantitative analysis of single gene effects Gregory Carey, Barbara J. Bowers, Jeanne M. Wehner From the Department of Psychology (GC, JMW) and Institute for Behavioral
Analysis of single gene effects 1 Quantitative analysis of single gene effects Gregory Carey, Barbara J. Bowers, Jeanne M. Wehner From the Department of Psychology (GC, JMW) and Institute for Behavioral
Still important ideas
 Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous Chapters 17 & 18 - Chapter 17: Social Influences - Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions Still important ideas Contrast the measurement
Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous Chapters 17 & 18 - Chapter 17: Social Influences - Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions Still important ideas Contrast the measurement
3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS
 3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS In this chapter, we examine the conceptual foundations of statistics. The goal is to give you an appreciation and conceptual understanding of some basic statistical
3 CONCEPTUAL FOUNDATIONS OF STATISTICS In this chapter, we examine the conceptual foundations of statistics. The goal is to give you an appreciation and conceptual understanding of some basic statistical
PSYCHOLOGY 320L Problem Set #4: Estimating Sample Size, Post Hoc Tests, and Two-Factor ANOVA
 PSYCHOLOGY 320L Problem Set #4: Estimating Sample Size, Post Hoc Tests, and Two-Factor ANOVA Name: Score: 1. Suppose you are planning an experiment for a class project with a group of students and you
PSYCHOLOGY 320L Problem Set #4: Estimating Sample Size, Post Hoc Tests, and Two-Factor ANOVA Name: Score: 1. Suppose you are planning an experiment for a class project with a group of students and you
Research Analysis MICHAEL BERNSTEIN CS 376
 Research Analysis MICHAEL BERNSTEIN CS 376 Last time What is a statistical test? Chi-square t-test Paired t-test 2 Today ANOVA Posthoc tests Two-way ANOVA Repeated measures ANOVA 3 Recall: hypothesis testing
Research Analysis MICHAEL BERNSTEIN CS 376 Last time What is a statistical test? Chi-square t-test Paired t-test 2 Today ANOVA Posthoc tests Two-way ANOVA Repeated measures ANOVA 3 Recall: hypothesis testing
Chapter 18 Repeated-Measures Analysis of Variance Cont.
 Chapter 18 Repeated-Measures PSY 95 Oswald Outline What are repeated-measures? An example Assumptions Advantages and disadvantages Effect sizes Review questions Effects of Counseling For Post-Traumatic
Chapter 18 Repeated-Measures PSY 95 Oswald Outline What are repeated-measures? An example Assumptions Advantages and disadvantages Effect sizes Review questions Effects of Counseling For Post-Traumatic
Statistics for Psychology
 Statistics for Psychology SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 12 Prediction Prediction a major practical application of statistical methods: making predictions make informed (and precise) guesses about such things as
Statistics for Psychology SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 12 Prediction Prediction a major practical application of statistical methods: making predictions make informed (and precise) guesses about such things as
Describe what is meant by a placebo Contrast the double-blind procedure with the single-blind procedure Review the structure for organizing a memo
 Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Business Statistics The following was provided by Dr. Suzanne Delaney, and is a comprehensive review of Business Statistics. The workshop instructor will provide relevant examples during the Skills Assessment
Estimation. Preliminary: the Normal distribution
 Estimation Preliminary: the Normal distribution Many statistical methods are only valid if we can assume that our data follow a distribution of a particular type, called the Normal distribution. Many naturally
Estimation Preliminary: the Normal distribution Many statistical methods are only valid if we can assume that our data follow a distribution of a particular type, called the Normal distribution. Many naturally
Before we get started:
 Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
Before we get started: http://arievaluation.org/projects-3/ AEA 2018 R-Commander 1 Antonio Olmos Kai Schramm Priyalathta Govindasamy Antonio.Olmos@du.edu AntonioOlmos@aumhc.org AEA 2018 R-Commander 2 Plan
HS Exam 1 -- March 9, 2006
 Please write your name on the back. Don t forget! Part A: Short answer, multiple choice, and true or false questions. No use of calculators, notes, lab workbooks, cell phones, neighbors, brain implants,
Please write your name on the back. Don t forget! Part A: Short answer, multiple choice, and true or false questions. No use of calculators, notes, lab workbooks, cell phones, neighbors, brain implants,
1. You want to find out what factors predict achievement in English. Develop a model that
 Questions and answers for Chapter 10 1. You want to find out what factors predict achievement in English. Develop a model that you think can explain this. As usual many alternative predictors are possible
Questions and answers for Chapter 10 1. You want to find out what factors predict achievement in English. Develop a model that you think can explain this. As usual many alternative predictors are possible
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Behavioral Research Chapter 10. Simple designs. Factorial design. Complex Experimental Designs
 Slide 1 Behavioral Research Chapter 10 Complex Experimental Designs Slide 2 Simple designs Composed of one indep var that is manipulated with two levels and one dep var which is measured. Example: IV:
Slide 1 Behavioral Research Chapter 10 Complex Experimental Designs Slide 2 Simple designs Composed of one indep var that is manipulated with two levels and one dep var which is measured. Example: IV:
Homework Exercises for PSYC 3330: Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
 Homework Exercises for PSYC 3330: Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences compiled and edited by Thomas J. Faulkenberry, Ph.D. Department of Psychological Sciences Tarleton State University Version: July
Homework Exercises for PSYC 3330: Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences compiled and edited by Thomas J. Faulkenberry, Ph.D. Department of Psychological Sciences Tarleton State University Version: July
Stat Wk 9: Hypothesis Tests and Analysis
 Stat 342 - Wk 9: Hypothesis Tests and Analysis Crash course on ANOVA, proc glm Stat 342 Notes. Week 9 Page 1 / 57 Crash Course: ANOVA AnOVa stands for Analysis Of Variance. Sometimes it s called ANOVA,
Stat 342 - Wk 9: Hypothesis Tests and Analysis Crash course on ANOVA, proc glm Stat 342 Notes. Week 9 Page 1 / 57 Crash Course: ANOVA AnOVa stands for Analysis Of Variance. Sometimes it s called ANOVA,
Standard Deviation and Standard Error Tutorial. This is significantly important. Get your AP Equations and Formulas sheet
 Standard Deviation and Standard Error Tutorial This is significantly important. Get your AP Equations and Formulas sheet The Basics Let s start with a review of the basics of statistics. Mean: What most
Standard Deviation and Standard Error Tutorial This is significantly important. Get your AP Equations and Formulas sheet The Basics Let s start with a review of the basics of statistics. Mean: What most
Designing Psychology Experiments: Data Analysis and Presentation
 Data Analysis and Presentation Review of Chapter 4: Designing Experiments Develop Hypothesis (or Hypotheses) from Theory Independent Variable(s) and Dependent Variable(s) Operational Definitions of each
Data Analysis and Presentation Review of Chapter 4: Designing Experiments Develop Hypothesis (or Hypotheses) from Theory Independent Variable(s) and Dependent Variable(s) Operational Definitions of each
MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil. 1. Is there a difference in depression as a function of group and drug?
 MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil Table of Contents Research Scenario and General Assumptions Questions for Dataset (Questions are hyperlinked to detailed answers) 1. Is there a difference
MMI 409 Spring 2009 Final Examination Gordon Bleil Table of Contents Research Scenario and General Assumptions Questions for Dataset (Questions are hyperlinked to detailed answers) 1. Is there a difference
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research Steps in Nonexperimental Research
 Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
Chapter 11 Nonexperimental Quantitative Research (Reminder: Don t forget to utilize the concept maps and study questions as you study this and the other chapters.) Nonexperimental research is needed because
The Association Design and a Continuous Phenotype
 PSYC 5102: Association Design & Continuous Phenotypes (4/4/07) 1 The Association Design and a Continuous Phenotype The purpose of this note is to demonstrate how to perform a population-based association
PSYC 5102: Association Design & Continuous Phenotypes (4/4/07) 1 The Association Design and a Continuous Phenotype The purpose of this note is to demonstrate how to perform a population-based association
Still important ideas
 Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 + 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 2, 3, and 4 Chapter 2: Cognitive Dissonance, Chapter 3: Memory and Hindsight Bias, Chapter 4: Context Dependence Still
Readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 11 + 13 & Appendix D & E (online) Plous - Chapters 2, 3, and 4 Chapter 2: Cognitive Dissonance, Chapter 3: Memory and Hindsight Bias, Chapter 4: Context Dependence Still
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression
 Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Section 3.2 Least-Squares Regression Linear relationships between two quantitative variables are pretty common and easy to understand. Correlation measures the direction and strength of these relationships.
Research Methods 1 Handouts, Graham Hole,COGS - version 1.0, September 2000: Page 1:
 Research Methods 1 Handouts, Graham Hole,COGS - version 10, September 000: Page 1: T-TESTS: When to use a t-test: The simplest experimental design is to have two conditions: an "experimental" condition
Research Methods 1 Handouts, Graham Hole,COGS - version 10, September 000: Page 1: T-TESTS: When to use a t-test: The simplest experimental design is to have two conditions: an "experimental" condition
Simple Linear Regression the model, estimation and testing
 Simple Linear Regression the model, estimation and testing Lecture No. 05 Example 1 A production manager has compared the dexterity test scores of five assembly-line employees with their hourly productivity.
Simple Linear Regression the model, estimation and testing Lecture No. 05 Example 1 A production manager has compared the dexterity test scores of five assembly-line employees with their hourly productivity.
Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation. I. Scales of Measurement A Review
 Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation The description and presentation of results involves a number of topics. These include scales of measurement, descriptive statistics used to summarize
Results & Statistics: Description and Correlation The description and presentation of results involves a number of topics. These include scales of measurement, descriptive statistics used to summarize
Psychology Research Process
 Psychology Research Process Logical Processes Induction Observation/Association/Using Correlation Trying to assess, through observation of a large group/sample, what is associated with what? Examples:
Psychology Research Process Logical Processes Induction Observation/Association/Using Correlation Trying to assess, through observation of a large group/sample, what is associated with what? Examples:
To open a CMA file > Download and Save file Start CMA Open file from within CMA
 Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Symptom relief Mean difference (Hours to relief) Basic Basic Reference Cochrane Figure 4 Synopsis We have a series of studies that evaluated the effect
Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Symptom relief Mean difference (Hours to relief) Basic Basic Reference Cochrane Figure 4 Synopsis We have a series of studies that evaluated the effect
CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION
 CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION 2.0 Introduction The second chapter, Regression analysis is an extension of correlation. The aim of the discussion of exercises is to enhance students capability to assess the effect
CHAPTER TWO REGRESSION 2.0 Introduction The second chapter, Regression analysis is an extension of correlation. The aim of the discussion of exercises is to enhance students capability to assess the effect
Chapter 13: Introduction to Analysis of Variance
 Chapter 13: Introduction to Analysis of Variance Although the t-test is a useful statistic, it is limited to testing hypotheses about two conditions or levels. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was developed
Chapter 13: Introduction to Analysis of Variance Although the t-test is a useful statistic, it is limited to testing hypotheses about two conditions or levels. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) was developed
Testing the effect of two factors at different levels (two treatments). Examples: Yield of a crop varying with fertilizer type and seedling used.
 ANOVA TWO-WAY Testing the effect of two factors at different levels (two treatments). Examples: Yield of a crop varying with fertilizer type and seedling used. Gas mileage depends on gas additive and tires
ANOVA TWO-WAY Testing the effect of two factors at different levels (two treatments). Examples: Yield of a crop varying with fertilizer type and seedling used. Gas mileage depends on gas additive and tires
Module 28 - Estimating a Population Mean (1 of 3)
 Module 28 - Estimating a Population Mean (1 of 3) In "Estimating a Population Mean," we focus on how to use a sample mean to estimate a population mean. This is the type of thinking we did in Modules 7
Module 28 - Estimating a Population Mean (1 of 3) In "Estimating a Population Mean," we focus on how to use a sample mean to estimate a population mean. This is the type of thinking we did in Modules 7
Chapter 9. Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors 10/22/ Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors
 Chapter 9 Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors 10/22/2001 1 Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors Recall that in one-way ANOVA we study the relation between one criterion variable and
Chapter 9 Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors 10/22/2001 1 Factorial ANOVA with Two Between-Group Factors Recall that in one-way ANOVA we study the relation between one criterion variable and
Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4
 Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4 Finding clarity using data Today 1. Hypothesis Testing with Z Scores (continued) 2. Chapters 6 and 7 in Book 2 Review! = $ & '! = $ & ' * ) 1. Which formula
Applied Statistical Analysis EDUC 6050 Week 4 Finding clarity using data Today 1. Hypothesis Testing with Z Scores (continued) 2. Chapters 6 and 7 in Book 2 Review! = $ & '! = $ & ' * ) 1. Which formula
Utilizing t-test and One-Way Analysis of Variance to Examine Group Differences August 31, 2016
 Good afternoon, everyone. My name is Stan Orchowsky and I'm the research director for the Justice Research and Statistics Association. It's 2:00PM here in Washington DC, and it's my pleasure to welcome
Good afternoon, everyone. My name is Stan Orchowsky and I'm the research director for the Justice Research and Statistics Association. It's 2:00PM here in Washington DC, and it's my pleasure to welcome
UNEQUAL CELL SIZES DO MATTER
 1 of 7 1/12/2010 11:26 AM UNEQUAL CELL SIZES DO MATTER David C. Howell Most textbooks dealing with factorial analysis of variance will tell you that unequal cell sizes alter the analysis in some way. I
1 of 7 1/12/2010 11:26 AM UNEQUAL CELL SIZES DO MATTER David C. Howell Most textbooks dealing with factorial analysis of variance will tell you that unequal cell sizes alter the analysis in some way. I
To open a CMA file > Download and Save file Start CMA Open file from within CMA
 Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Hospitalized Risk ratio Basic Basic Synopsis The US government has spent 1.4 billion dollars to stockpile Tamiflu, in anticipation of a possible flu
Example name Effect size Analysis type Level Tamiflu Hospitalized Risk ratio Basic Basic Synopsis The US government has spent 1.4 billion dollars to stockpile Tamiflu, in anticipation of a possible flu
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F
 Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 17 & 18 Chapter 17: Social Influences Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions
Readings: Textbook readings: OpenStax - Chapters 1 13 (emphasis on Chapter 12) Online readings: Appendix D, E & F Plous Chapters 17 & 18 Chapter 17: Social Influences Chapter 18: Group Judgments and Decisions
SPSS output for 420 midterm study
 Ψ Psy Midterm Part In lab (5 points total) Your professor decides that he wants to find out how much impact amount of study time has on the first midterm. He randomly assigns students to study for hours,
Ψ Psy Midterm Part In lab (5 points total) Your professor decides that he wants to find out how much impact amount of study time has on the first midterm. He randomly assigns students to study for hours,
A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics. Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs
 A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs What We ll Cover Fundamentals of measurement Parametric versus nonparametric tests Descriptive versus inferential
A Brief (very brief) Overview of Biostatistics Jody Kreiman, PhD Bureau of Glottal Affairs What We ll Cover Fundamentals of measurement Parametric versus nonparametric tests Descriptive versus inferential
Basic Statistics and Data Analysis in Work psychology: Statistical Examples
 Basic Statistics and Data Analysis in Work psychology: Statistical Examples WORK PSYCHOLOGY INTRODUCTION In this chapter we examine a topic which is given too little coverage in most texts of this kind,
Basic Statistics and Data Analysis in Work psychology: Statistical Examples WORK PSYCHOLOGY INTRODUCTION In this chapter we examine a topic which is given too little coverage in most texts of this kind,
Choosing a Significance Test. Student Resource Sheet
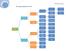 Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Choosing a Significance Test Student Resource Sheet Choosing Your Test Choosing an appropriate type of significance test is a very important consideration in analyzing data. If an inappropriate test is
Motor Programs Lab. 1. Record your reaction and movement time in ms for each trial on the individual data Table 1 below. Table I: Individual Data RT
 Motor Programs Lab Introduction. This lab will simulate an important experiment performed by Henry and Rogers (1960). The task involved the subject responding to an external signal then executing a simple,
Motor Programs Lab Introduction. This lab will simulate an important experiment performed by Henry and Rogers (1960). The task involved the subject responding to an external signal then executing a simple,
GENETIC DRIFT & EFFECTIVE POPULATION SIZE
 Instructor: Dr. Martha B. Reiskind AEC 450/550: Conservation Genetics Spring 2018 Lecture Notes for Lectures 3a & b: In the past students have expressed concern about the inbreeding coefficient, so please
Instructor: Dr. Martha B. Reiskind AEC 450/550: Conservation Genetics Spring 2018 Lecture Notes for Lectures 3a & b: In the past students have expressed concern about the inbreeding coefficient, so please
MBios 478: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks, 27 [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 27: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks
![MBios 478: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks, 27 [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 27: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks MBios 478: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks, 27 [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1. Lecture 27: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks](/thumbs/80/82116384.jpg) MBios 478: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks, 27 [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1 Lecture 27: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks Systems Biology and Regulatory Networks o Definitions o Network motifs o Examples
MBios 478: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks, 27 [Dr. Wyrick] Slide #1 Lecture 27: Systems Biology and Bayesian Networks Systems Biology and Regulatory Networks o Definitions o Network motifs o Examples
Chapter 9: Answers. Tests of Between-Subjects Effects. Dependent Variable: Time Spent Stalking After Therapy (hours per week)
 Task 1 Chapter 9: Answers Stalking is a very disruptive and upsetting (for the person being stalked) experience in which someone (the stalker) constantly harasses or obsesses about another person. It can
Task 1 Chapter 9: Answers Stalking is a very disruptive and upsetting (for the person being stalked) experience in which someone (the stalker) constantly harasses or obsesses about another person. It can
Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011
 Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011 What is Power? When conducting a research study using a statistical hypothesis test, power is the probability of getting statistical significance when
Sheila Barron Statistics Outreach Center 2/8/2011 What is Power? When conducting a research study using a statistical hypothesis test, power is the probability of getting statistical significance when
An Introduction to Research Statistics
 An Introduction to Research Statistics An Introduction to Research Statistics Cris Burgess Statistics are like a lamppost to a drunken man - more for leaning on than illumination David Brent (alias Ricky
An Introduction to Research Statistics An Introduction to Research Statistics Cris Burgess Statistics are like a lamppost to a drunken man - more for leaning on than illumination David Brent (alias Ricky
Chapter 23. Inference About Means. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
Chapter 23 Inference About Means Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Getting Started Now that we know how to create confidence intervals and test hypotheses about proportions, it d be nice to be able
Introduction to Multilevel Models for Longitudinal and Repeated Measures Data
 Introduction to Multilevel Models for Longitudinal and Repeated Measures Data Today s Class: Features of longitudinal data Features of longitudinal models What can MLM do for you? What to expect in this
Introduction to Multilevel Models for Longitudinal and Repeated Measures Data Today s Class: Features of longitudinal data Features of longitudinal models What can MLM do for you? What to expect in this
Regression Including the Interaction Between Quantitative Variables
 Regression Including the Interaction Between Quantitative Variables The purpose of the study was to examine the inter-relationships among social skills, the complexity of the social situation, and performance
Regression Including the Interaction Between Quantitative Variables The purpose of the study was to examine the inter-relationships among social skills, the complexity of the social situation, and performance
