Effects of Condensate in the Exhalation Limb of Neonatal Circuits on Airway Pressure During Bubble CPAP
|
|
|
- Loreen Casey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effects of Condensate in the Exhalation Limb of Neonatal Circuits on Airway Pressure During Bubble CPAP Tiffany M Youngquist, C Peter Richardson PhD, and Robert M DiBlasi RRT NPS FAARC BACKGROUND: Bubble CPAP is frequently used in spontaneously breathing infants with lung disease. Often bubble CPAP systems lack pressure alarms and pressure-release valves. We observed a large volume of condensate in the exhalation limb of a patient circuit and conducted a series of experiments to test the hypothesis that accumulated condensate could affect delivered pressures. METHODS: An anatomically accurate nasal airway model of a preterm infant was attached to a spontaneously breathing lung model. A bubble CPAP system was attached to the nasal airway with bi-nasal short prongs, and the rate of fluid condensation was measured. Next, tracheal pressures were monitored digitally to detect changes in airway pressure related to condensate accumulation. Measurements were obtained with volumes of 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 ml of water in the exhalation limb, at flows of 4, 6, 8, and 10 L/min. Measurements with 20 ml in the exhalation limb were recorded with and without a pressure-relief valve in the circuit. RESULTS: The rate of condensate accumulation was 3.8 ml/h. At volumes of > 10 ml, noticeable alterations in the airway pressure waveforms and significant increases in mean tracheal pressure were observed. The pressure-relief valve effectively attenuated peak tracheal pressure, but only decreased mean pressure by cm H 2 O. CONCLUSIONS: Condensate in the exhalation limb of the patient circuit during bubble CPAP can significantly increase pressure delivered to the patient. The back and forth movement of this fluid causes oscillations in airway pressure that are much greater than the oscillations created by gas bubbling out the exhalation tube into the water bath. We recommend continuously monitoring pressure at the nasal airway interface, placing an adjustable pressurerelief valve in the circuit, set to 5 cm H 2 O above the desired mean pressure, and emptying fluid from the exhalation limb every 2 3 hours. Key words: bubble CPAP; condensate; resistance; patient safety; airway pressure; neonatal intensive care; maintenance; lung protection; noninvasive ventilation. [Respir Care 2013;58(11): Daedalus Enterprises] Introduction Nasal bubble CPAP is a form of noninvasive respiratory support used in spontaneously breathing infants with lung The authors are affiliated with the Center for Developmental Therapeutics, Seattle Children s Research Institute, Seattle, Washington. Dr Richardson is also affiliated with the Pulmonary Division, Department of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, Washington. Mr DiBlasi is also affiliated with the Respiratory Therapy Department, Seattle Children s Hospital, Seattle, Washington. The authors have disclosed no conflicts of interest. Ms Youngquist presented a version of this paper at the OPEN FORUM at the AARC Congress 2012, held November 10 13, 2012, in New Orleans, Louisiana. disease. Its popularity in the neonatal ICU has been on the rise since a multicenter randomized controlled trial 1 showed no difference in the rate of complications between infants supported by bubble CPAP or ventilator-derived CPAP, as well as a lower incidence of reintubation in the bubble CPAP group. Clinicians prescribe the level of airway pressure desired for the infant and frequently use the depth of the expiratory tube in water (the water pressure seal) as an estimate of the pressure delivered to the patient. Correspondence: Tiffany M Youngquist. tiffymy1@u.washington. edu. DOI: /respcare RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO 11
2 When applying bubble CPAP to infants, many institutions construct their own homemade systems. Unlike ventilator-derived CPAP, the homemade systems described in the literature frequently lack safety alarms and high-pressure pressure-relief valves. 2-7 SEE THE RELATED EDITORIAL ON PAGE 1990 Kahn et al 8,9 have shown that the bias flow coursing through the circuit can lead to an underestimation of the delivered pressure. The present investigation pursues an additional clinical event that may also contribute to the disparity between tube depth setting and the actual pressure delivered to the patient. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that increases in the condensate level within the expiratory tubing would result in a greater pressure than a dry circuit. Lung Model Methods We modeled lung mechanics using a neonatal test lung (ASL 5000, Ingmar Medical, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania), configured to represent the pulmonary mechanics of an extremely-low-birth-weight infant with respiratory distress syndrome: lung compliance 0.5 ml/cm H 2 O, resistance 100 cm H 2 O/L/s. The lung model was made to breathe spontaneously by setting a simulated pleural pressure profile: 10 cm H 2 O (yielding tidal volume of 5 ml), and breathing frequency 50 breaths/min. 10 Nasal Airway Model A head computed tomography scan from a 26-week gestational age infant was loaded into cranial imaging software (V-Works 4.0, CyberMed, Centreville, Virginia), upper airway anatomy was cropped out of each image, and relevant files were exported in a stereolithography format. Files were then loaded into a rapid prototyping system and a 3-dimensional model of the upper airway was printed with a 3-dimensional printer (V-Flash, 3D Systems, Rock Hill, South Carolina). The model was then glued to a 15 mm adapter to attach to the lung model. Bubble CPAP System All testing was conducted using a commercially available bubble CPAP system (Fisher & Paykel, Auckland, New Zealand). A standard oxygen flow rotameter provided fresh gas to the dry side of the humidifier via the pressure manifold. QUICK LOOK Current knowledge Nasal bubble CPAP is a form of noninvasive respiratory support used in spontaneously breathing infants with lung disease, and is often delivered with homemade devices that have not been safety tested and have few if any alarms. What this paper contributes to our knowledge During bubble CPAP, condensate in the expiratory limb of the ventilatory circuit significantly increased the delivered airway pressure and the magnitude of the pressure oscillations. Proximal airway pressure monitoring, a pressure-relief valve, and frequent removal of condensate from the circuit may improve safety during bubble CPAP. Instrumentation Micro-machined piezoresistive silicon pressure transducers (G4-V, All Sensors, Morgan Hill, California, range cm H 2 O), for measuring airway pressure, were calibrated using 2-point calibrations with a pre-calibrated manometer (PM-23, Digitron, Devon, United Kingdom). Analog signals from the pressure transducer were sampled at 1,024 khz with a 16-bit analog-to-digital converter (DT BNC Box USB 9804, Data Translation, Waltham, Massachusetts) and recorded on a laptop computer. Pressure signals were recorded digitally and calculations of mean airway pressure, amplitude of oscillations in airway pressure, and peak frequency of oscillations were made using custom software (Visual Basic, Microsoft, Redmond, Washington). Rate of Condensate Accumulation The average rate of condensate accumulation in the exhalation limb during bubble CPAP was determined so that approximate volumes could be used in a controlled fashion for the second phase of testing. The nasal airway model was attached to the spontaneously breathing lung model. The expiratory circuit was removed from the bubble CPAP system and the mass of the dry circuit was measured on a scale (n 3) and reattached to the bubble CPAP system. The expiratory hose was placed into a 27 cm fixed Ushaped configuration, 11 and the position was secured by taping the hose to the table (Fig. 1). The CPAP level was setat5cmh 2 O, with a flow of 6 L/min. The nasal prongs were attached to the nasal airway openings and secured by a bonnet fixation. Continuous bubbling during the entire RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO
3 Fig. 1. Experimental setup. respiratory cycle indicated a good seal at the prongs. The humidifier was set at 37 C in the Invasive Mode, and the internal components of the lung model were held at 37 C using an integrated warmer. Ambient temperature was controlled in the room ( 21 C) with a pre-set thermostat, and an oscillating fan set on medium was placed 2.4 m away from the bubble CPAP system, to simulate drafts from ceiling vents or excessive movement around the circuit, which are encountered in the clinical setting. The study began following a 20-min temperature stabilization period with the system running. Every 2 hours the volume of accumulated fluid in the expiratory hose was assessed by removing and weighing the tubing and comparing the measurement to the mass of the dry circuit. Tubing was reattached to the bubble CPAP system after each measurement, without removing fluid. The lung model breathed for a total of 8 hours during bubble CPAP, and the experiment was conducted 3 times with a new dry circuit. Effect of Condensate on Delivered Pressure Nasal prongs were inserted into a nasal airway model and a tight seal (no leak) was made by forming medicalgrade putty around the interface. The nasal airway model was connected to the test lung, and tracheal pressure (P tracheal ) was monitored between the nasal airway model and test lung in a simulated trachea consisting of small plastic 15-mm outer diameter adapters (see Fig. 1). The initial measurements were recorded using a dry circuit, with no pressure manifold in the system, and P tracheal was collected for 8 seconds, at flows of 4, 6, 8, and 10 L/ min. The expiratory hose was disconnected and water was added in 5 ml increments to the U in the exhalation circuit, though a feeding catheter attached to a glass syringe. P tracheal measurements were obtained for 8 seconds at each flow setting, with volumes of 5, 10, 15, and 20 ml of water in the circuit. Three separate pressure measurements were recorded for each set of conditions. Effectiveness of the Pressure-Relief Valve Following the final measurement (20 ml water), the bubble CPAP pressure manifold (pressure-relief valve) was introduced into the circuit. P tracheal measurements were obtained for 8 seconds at each flow (4, 6, 8, and 10 L/min) with CPAP set to 5 cm H 2 O RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO 11
4 Fig. 2. Mean tracheal pressure with varying volumes of condensate in the exhalation limb. Groups not sharing similar symbols are significantly different (P.05). Fig. 3. Amplitude of oscillations in tracheal pressure with varying volumes of condensate in the exhalation limb. Groups not sharing similar symbols are different (P.05). Data Analysis Data from the study that assessed the rate of condensate accumulation were saved in a spreadsheet (Excel, Microsoft, Redmond, Washington), and the rate was calculated from a linear regression using the least-squares method. Mean P tracheal was calculated for each 8-second run (n 3). The mean SD of the amplitudes of the P tracheal oscillations ( P tracheal ) was then calculated from the P tracheal signals using an algorithm (described elsewhere 12 ) that determines the amplitude of individual oscillations. The peak frequency was calculated using spectral power analysis to define frequencies, with the maximum power observed in each testing condition. For data collected without the pressure-relief valve in the system, a one-way analysis of variance was used, with a Tukey test for post hoc analysis, to compare the mean P tracheal and P tracheal at each volume of condensate at similar flows. Data collected with 20 ml of condensate in the circuit while the pressure-relief valve was in place were compared to data collected with the same volume of condensate in a circuit without a pressure-relief valve using a paired t test. Statistical significance was set a priori at P.05. Results The rate of fluid accumulation in the exhalation limb of the bubble CPAP system remained constant (R ) at 3.8 ml/h over the 8-hour period. The condensate formed a pool in the low point of the expiratory circuit, which became intermittent at large volumes (15 and 20 ml) as the air pushed past the occlusion. RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO
5 Fig. 5. Mean tracheal pressure with and without a pressure-relief valve in the circuit, with 20 ml of condensate in the circuit, and a CPAP depth setting of 5 cm H 2 O. * P.05. Fig. 4. Tracheal pressure waveforms with condensate volumes of 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 ml at a CPAP depth setting of 5 cm H 2 O and a flow of 8 L/min. The tracheal pressure signals were sampled at 1,024 khz for 8 s. There were no differences in the mean P tracheal (Fig. 2) or P tracheal (Fig. 3) between 0 and 5 ml at similar flows during bubble CPAP. However, the addition of larger volumes of fluid ( 5 ml) to the exhalation limb increased both sets of pressure measurements at each flow (P.05). Figure 4 shows examples of P tracheal waveforms. There were noticeable changes in pressure waveform characteristics at volumes 5 ml. The mean P tracheal was cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, and cm H 2 O with volumes of 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 ml, respectively. The P tracheal was cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, cm H 2 O, and cm H 2 O with volumes of 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 ml, respectively. The peak frequencies were Hz, Hz, Hz, Hz, and Hz with volumes of 0, 5, 10, 15, 20 ml, respectively. The pressure-relief valve significantly decreased the mean P tracheal and P tracheal (Figs. 5 and 6, respectively, P.05), with each flow, with the exception of mean P tracheal at 8 L/min. This component had a greater influence on P tracheal than on mean P tracheal. Figure 7 compares 2 pressure waveforms with and without the pressurerelief valve. The frequency of P tracheal was higher without the pressure-relief valve, and peak P tracheal was well above Fig. 6. Amplitude of tracheal pressure oscillations with and without a pressure-relief valve, with 20 ml of condensate in the circuit, and a CPAP depth setting of 5 cm H 2 O. * P cm H 2 O. However, with the pressure-relief valve the peak P tracheal was blunted to cm H 2 O, and the consequent lower frequency resulted in a longer duration at the peak P tracheal, which in turn resulted in only minor decreases in the mean P tracheal. Discussion The major finding of this study was that condensate in the exhalation limb of the patient circuit during bubble CPAP can result in mean P tracheal significantly higher than the CPAP depth setting. Additionally, the flow-induced movement of accumulated condensate and the patient s spontaneous respiratory efforts cause P tracheal oscillations that are greater than the oscillations created solely by gas bubbling out of the expiratory tubing. The combination of increases in both mean P tracheal and P tracheal results in airway pressures that may surpass safe levels. To discuss this point in detail, at volumes of 10 ml, mean P tracheal is noticeably increased from dry circuit measurements but might still appear to be relatively benign. However, when combined with the increased pressure os RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO 11
6 Fig. 7. Pressure waveforms with and without a pressure-relief valve in the circuit. The pressure signals were sampled at 1,024 khz for 8 s, the CPAP depth was 5 cm H 2 O, the flow was 10 L/min, and the condensate volume was 20 ml. cillations, it is evident that the peak pressures reaching the infant are cause for concern. For example, at a flow of 6 L/min a dry circuit delivers a peak pressure of 7.5 cm H 2 O (mean P tracheal 4.9 cm H 2 O, P tracheal 2.6 cm H 2 O) while a wet circuit containing 10 ml of condensate delivers a peak pressure of 10.4 cm H 2 O (mean P tracheal 5.8 cm H 2 O, P tracheal 4.6 cm H 2 O), which is twice the set CPAP level. Taking into account our measured rate of fluid accumulation of 3.8 ml/h, and using 10 ml as an arbitrary marker for the onset of unwarranted pressure spikes, an unattended bubble CPAP system in conditions similar to our experimental setup can reach potentially unsafe pressures ( 12 cm H 2 O) in 3 hours. Allowing delivered pressures to reach pressures significantly higher than those intended can result in serious physical consequences such as air leaks, overdistention, and gastric distention. 13 Physiological consequences may include increased P aco2, reduction in venous return, and compromised cardiac output. 14,15 The additional resistive loading of the infant respiratory system from excessive fluid accumulation in the bubble CPAP circuit could potentially add to respiratory failure, by superimposing large airway pressure oscillations that are out of phase with the patient s intrinsic respiratory efforts. Imposed resistance through any or all of the airways during exhalation can produce alveolar hyperinflation, uneven regional ventilation, and excessive respiratory muscle loading, leading to increased work of breathing, impaired gas exchange, 16 and failure to wean As expected, the pressure-relief valve had an appreciable effect on the magnitude and frequency of the P tracheal (see Figs. 6 and 7) but did little to decrease mean P tracheal (see Fig. 5) to a level considered safe for some preterm neonates. Thus, an adjustable pressure-relief valve may provide better control over excessive pressure from condensate. Further, high-pressure audio alarms may be useful in warning clinicians of rising pressure. Our suggestion that circuits be emptied every 2 3 hours, to avoid potentially unsafe pressure, is based on our accumulation rate and pressure data, which have inherent limitations. We conducted the accumulation rate study at a single flow (6 L/min); it may be reasonable to suspect that higher flows will result in greater fluid accumulation rates, due to the increased volume of humidified air flowing through the circuit. The test lung, though heated to 37 C and programmed to simulate breaths, cannot predict how the physiology of an infant s lung contributes to condensate formation in the expiratory circuit. However, since the exhaled gas is at body temperature and is saturated, it is likely that the infant will add moisture to the air, in which case our results may somewhat underestimate the actual rate of condensate formation. By having a completely airtight system, our measurements may overestimate the pressure that an infant actually receives. Small leaks around the prongs or at the mouth are commonplace in the neonatal ICU, especially if chin straps or pacifiers are not being used. Additionally, if a chinstrap is not in place, the mouth may serve as a natural pressure-relief valve should an obstruction in the circuit cause pressure to drastically increase. Substitutions for or alterations in the proprietary nonheated exhalation circuit used with the Fisher & Paykel bubble CPAP system may decrease the rate of condensate accumulation. An exhalation circuit with a heated wire may allow water to remain in vapor form; the extent to which a heated expiratory circuit affects condensate formation is an area for further study. Fisher & Paykel s novel Evaqua 2 circuit allows water vapor to diffuse out of the tubing wall, which drastically decreases the amount of fluid condensate and circuit maintenance required. However, the added expense of the Evaqua 2 may make it inaccessible to many clinicians, particularly those in resource limited settings. Water traps have also been integrated into exhalation circuits to catch condensate and keep the circuit clear, but they are not well suited for use with bubble CPAP because the volume they add to the circuit may increase overall compliance and dampen the pressure oscillations that are both characteristic of, and desirable in, bubble CPAP. Conclusions Accumulated condensate in the expiratory limb of a bubble CPAP circuit increases the delivered pressure. We recommend that the operators of basic (ie, commercial RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO
7 systems without specialized circuits) or home-made bubble CPAP systems monitor pressure at the nasal airway interface to ensure that the pressure delivered to the infant matches the intended pressure. We encourage frequent emptying of condensate from the circuit, verification of proper heated humidifier settings, and the use of a pressure-relief valve set to 5 cm H 2 O above the desired mean pressure. REFERENCES 1. Gupta S, Sinha SK, Tin W, Donn SM. A randomized controlled trial of post-extubation bubble continuous positive airway pressure versus Infant Flow Driver continuous positive airway pressure in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr 2009;154(5): Narendran V, Donovan EF, Hoath SB, Akinbi HT, Steichen JJ, Jobe AH. Early bubble CPAP and outcomes in ELBW preterm infants. J Perinatol 2003;23(3): Aly H, Milner JD, Patel K, El-Mohandes AA. Does the experience with the use of nasal continuous positive airway pressure improve over time in extremely low birth weight infants? Pediatrics 2004; 114(3): Lee KS, Dunn MS, Fenwick M, Shennan AT. A comparison of underwater bubble continuous positive airway pressure with ventilator-derived continuous positive airway pressure in premature neonates ready for extubation. Biol Neonate 1998;73(2): Nekvasil R, Kratky J, Penková Z, Stejskal J. [High frequency bubble oscillation ventilation in the neonatal period.]. Cesk Pediatr 1992;47(8): Article in Czech. 6. Kaur C, Sema A, Beri RS, Puliyel JM. A simple circuit to deliver bubbling CPAP. Indian Pediatr 2008;45(4): Liptsen E, Aghai ZH, Pyon KH, Saslow JG, Nakhla T, Long J, et al. Work of breathing during nasal continuous positive airway pressure in preterm infants: a comparison of bubble vs variable-flow devices. J Perinatol 2005;25(7): Kahn DJ, Courtney SE, Steele AM, Habib RH. Unpredictability of delivered bubble nasal continuous positive airway pressure: role of bias flow magnitude and nares-prong air leaks. Pediatr Res 2007; 62(3): Kahn DJ, Habib RH, Courtney SE. Effects of flow amplitudes on intraprong pressures during bubble versus ventilator-generated nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants. Pediatrics 2008;122(5): DiBlasi RM, Salyer JW, Zignego JC, Redding GJ, Richardson CP. The impact of imposed expiratory resistance in neonatal mechanical ventilation: a laboratory evaluation. Respir Care 2008;53(11): Chan KM, Chan HB. The use of bubble CPAP in premature infants: local experience. HK J Paediatr (new series) 2007;12(2): DiBlasi RM, Zignego JC, Tang DM, Hildebrandt J, Smith CV, Hansen TN, et al. Noninvasive respiratory support of juvenile rabbits by high-amplitude bubble continuous positive airway pressure. Pediatr Res 2010;67(6): DiBlasi RM. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for the respiratory care of the newborn infant. Respir Care 2009;54(9): Shaffer TH, Koen PA, Moskowitz GD, Ferguson JD, Delivoria- Papadopoulos M. Positive end expiratory pressure: effects on lung mechanics of premature lambs. Biol Neonate 1978;34(1-2): Hobelmann CF Jr, Smith DE, Virgilio RW, Peters RM. Mechanics of ventilation with positive end-expiratory pressure. Ann Thorac Surg 1977;24(1): Yoder BA, Martin H, McCurnin DC. Lung function measurements in a preterm animal model of respiratory failure: comparison of two different neonatal ventilators. Pediatr Pulmonol 2006;41(11): Banner MJ, Downs JB, Kirby RR, Smith RA, Boysen PG, Lampotang S. Effects of expiratory flow resistance on inspiratory work of breathing. Chest 1988;93(4): Isono S, Nishino T, Sugimori K, Mizuguchi T. Respiratory effects of expiratory flow-resistive loading in conscious and anesthetized humans. Anesth Analg 1990;70(6): Kirton OC, DeHaven CB, Morgan JP, Windsor J, Civetta JM. Elevated imposed work of breathing masquerading as ventilator weaning intolerance. Chest 1995;108(4): Kirton OC, Banner MJ, Axelrad A, Drugas G. Detection of unsuspected imposed work of breathing: case reports. Crit Care Med 1993; 21(5): Morganroth ML, Morganroth JL, Nett LM, Petty TL. Criteria for weaning from prolonged mechanical ventilation. Arch Intern Med 1984;144(5): Dubois AB. Resistance to breathing. In: Fenn WO, Rahn H, editors. Handbook of physiology and respiration, volume 1. Washington, DC: American Physiology Society; 1964: This article is approved for Continuing Respiratory Care Education credit. For information and to obtain your CRCE (free to AARC members) visit RESPIRATORY CARE NOVEMBER 2013 VOL 58 NO 11
Effects of Condensate in the Exhalation Limb of Neonatal Circuits on. Airway Pressure During Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
 1 Effects of Condensate in the Exhalation Limb of Neonatal Circuits on Airway Pressure During Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Tiffany M Youngquist BS C Peter Richardson PhD * Robert M DiBlasi
1 Effects of Condensate in the Exhalation Limb of Neonatal Circuits on Airway Pressure During Bubble Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Tiffany M Youngquist BS C Peter Richardson PhD * Robert M DiBlasi
Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model
 Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model Stephanie A Bailes RRT-NPS NREMT-B, Kimberly S Firestone MSc RRT, Diane K Dunn RRT-NPS, Neil
Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model Stephanie A Bailes RRT-NPS NREMT-B, Kimberly S Firestone MSc RRT, Diane K Dunn RRT-NPS, Neil
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY
 ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Evaluation of a Nasal Cannula in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator
 Evaluation of a Nasal in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator Narayan P Iyer MD and Robert Chatburn MHHS RRT-NPS FAARC BACKGROUND: Nasal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a common form of noninvasive
Evaluation of a Nasal in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator Narayan P Iyer MD and Robert Chatburn MHHS RRT-NPS FAARC BACKGROUND: Nasal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a common form of noninvasive
In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System
 In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System Kimberly D Farney RRT, Brandon T Kuehne RRT MBA, Laurie A Gibson RT (N), Leif D Nelin MD, and Edward G Shepherd
In Vitro Evaluation of Radio-Labeled Aerosol Delivery Via a Variable-Flow Infant CPAP System Kimberly D Farney RRT, Brandon T Kuehne RRT MBA, Laurie A Gibson RT (N), Leif D Nelin MD, and Edward G Shepherd
Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants: work of breathing and gas exchange
 (011) 1, 44 50 r 011 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. 04-846/11 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants:
(011) 1, 44 50 r 011 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. 04-846/11 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants:
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study
 D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Resistance of Colorimetric Carbon Dioxide Detectors Commonly Utilized in Neonates
 Resistance of Colorimetric Carbon Dioxide Detectors Commonly Utilized in Neonates Melissa K Brown RRT-NPS, Danielle V Lazarus RRT, Sarah R Gonzales RRT, Wade D Rich RRT-NPS CCRC, Madeline J Wozniak, Debra
Resistance of Colorimetric Carbon Dioxide Detectors Commonly Utilized in Neonates Melissa K Brown RRT-NPS, Danielle V Lazarus RRT, Sarah R Gonzales RRT, Wade D Rich RRT-NPS CCRC, Madeline J Wozniak, Debra
Ventilator Waveforms: Interpretation
 Ventilator Waveforms: Interpretation Albert L. Rafanan, MD, FPCCP Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Chong Hua Hospital, Cebu City Types of Waveforms Scalars are waveform representations of pressure,
Ventilator Waveforms: Interpretation Albert L. Rafanan, MD, FPCCP Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine Chong Hua Hospital, Cebu City Types of Waveforms Scalars are waveform representations of pressure,
Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP. By Joanne Cookson March 2008
 Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP By Joanne Cookson March 2008 Aim To introduce clinical practioners to the new SiPAP machine Objectives To define what is SiPAP To look at different modes able to be
Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP By Joanne Cookson March 2008 Aim To introduce clinical practioners to the new SiPAP machine Objectives To define what is SiPAP To look at different modes able to be
5/3/2012. Goals and Objectives HFNC. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad?
 High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry
 GE Healthcare Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry Test results are based on the Master s thesis, Comparison between patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry by Saana Jenu, 2011
GE Healthcare Comparison of patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry Test results are based on the Master s thesis, Comparison between patient spirometry and ventilator spirometry by Saana Jenu, 2011
600 RESPIRATORY CARE MAY 2016 VOL 61 NO 5
 Quantifying Aerosol Delivery in Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Patients With Tracheostomy Using Different Humidification Systems With or Without Exhaled Humidity Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Robert
Quantifying Aerosol Delivery in Simulated Spontaneously Breathing Patients With Tracheostomy Using Different Humidification Systems With or Without Exhaled Humidity Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Robert
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
Recognizing and Correcting Patient-Ventilator Dysynchrony
 2019 KRCS Annual State Education Seminar Recognizing and Correcting Patient-Ventilator Dysynchrony Eric Kriner BS,RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist MedStar Washington Hospital Center Washington,
2019 KRCS Annual State Education Seminar Recognizing and Correcting Patient-Ventilator Dysynchrony Eric Kriner BS,RRT Pulmonary Critical Care Clinical Specialist MedStar Washington Hospital Center Washington,
TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT:
 fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
Comparison between Bubble CPAP and Ventilator-derived CPAP in Rabbits
 Pediatr Neonatol 2008;49(6):223 229 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between Bubble CPAP and Ventilator-derived CPAP in Rabbits Wen-Chin Huang 1, Yi-Ming Hua 1 *, Chuen-Ming Lee 1, Chun-Cheng Chang 2, Yeong-Seng
Pediatr Neonatol 2008;49(6):223 229 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between Bubble CPAP and Ventilator-derived CPAP in Rabbits Wen-Chin Huang 1, Yi-Ming Hua 1 *, Chuen-Ming Lee 1, Chun-Cheng Chang 2, Yeong-Seng
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
9/15/2017. Disclosures. Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Objectives. Aerogen Pharma
 Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Development and Testing of a Bubble Bi-Level Positive Airway Pressure System
 Development and Testing of a Bubble Bi-Level Positive Airway Pressure System Stephen C John, Joseph D Barnett, Nickolas D Habben, Hoa T Le, Eric Cheng RRT, Sunil P John MD, and Peter A Gustafson PhD BACKGROUND:
Development and Testing of a Bubble Bi-Level Positive Airway Pressure System Stephen C John, Joseph D Barnett, Nickolas D Habben, Hoa T Le, Eric Cheng RRT, Sunil P John MD, and Peter A Gustafson PhD BACKGROUND:
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Goldman Sachs JBWere Australasian Investment Forum New York - 7 March 2006
 Goldman Sachs JBWere Australasian Investment Forum New York - 7 March 2006 Investment Highlights Leading player in heated humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing
Goldman Sachs JBWere Australasian Investment Forum New York - 7 March 2006 Investment Highlights Leading player in heated humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing
BiLevel Pressure Device
 PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 7 Purpose Scope Classes/ Goals Define indications and care settings for acute and chronic initiation of Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation. Identify the role of Respiratory
PROCEDURE - Page 1 of 7 Purpose Scope Classes/ Goals Define indications and care settings for acute and chronic initiation of Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation. Identify the role of Respiratory
NI 60. Non-invasive ventilation without compromise. Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia. Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support
 NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants
 (), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
(), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D.
 Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
STATE OF OKLAHOMA 2014 EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES PROTOCOLS
 3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
3K NON-INVASIVE POSITIVE PRESSURE VENTILATION (NIPPV) ADULT EMT EMT-INTERMEDIATE 85 ADVANCED EMT PARAMEDIC Indications: 1. Dyspnea Uncertain Etiology Adult. 2. Dyspnea Asthma Adult. 3. Dyspnea Chronic
Investment Highlights
 FY08 Full Year Update and Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in respiratory humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2.5+ billion and growing market opportunity High level
FY08 Full Year Update and Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in respiratory humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2.5+ billion and growing market opportunity High level
The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv
 The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv J Mechanics on the Adequacy of Controlled Ventilation Peter Hutchin, M.D., and Richard M. Peters, M.D. W ' hereas during spontaneous respiration the individual determines
The Influence of Altered Pulmonarv J Mechanics on the Adequacy of Controlled Ventilation Peter Hutchin, M.D., and Richard M. Peters, M.D. W ' hereas during spontaneous respiration the individual determines
Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing
 Original articles Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing C. J. FRENCH*, R. BELLOMO, J. BUCKMASTER *Department of Intensive Care, Western Hospital, Footscray, VICTORIA Department of
Original articles Effect of Ventilation Equipment on Imposed Work of Breathing C. J. FRENCH*, R. BELLOMO, J. BUCKMASTER *Department of Intensive Care, Western Hospital, Footscray, VICTORIA Department of
This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review.
 This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review. The version of record [Journal of Neonatal Nursing (February 2013)
This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review. The version of record [Journal of Neonatal Nursing (February 2013)
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด
 Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model
 Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Khalid S Alwadeai MSc RRT-NPS, and
Effects of Heat and Moisture Exchangers and Exhaled Humidity on Aerosol Deposition in a Simulated Ventilator-Dependent Adult Lung Model Arzu Ari PhD RRT PT CPFT FAARC, Khalid S Alwadeai MSc RRT-NPS, and
Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) NICU POCKET GUIDE
 Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Disclosures. Why not invasive ventilation? Objectives. Currently available modes
 CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants within the neonatal service.
 UHL Neonatal Guideline: CPAP Nursing Care University Hospitals of Leicester NHS NHS Trust Nov 2018 Nov 2021 Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants
UHL Neonatal Guideline: CPAP Nursing Care University Hospitals of Leicester NHS NHS Trust Nov 2018 Nov 2021 Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP
 I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
I. Subject: Pressure Support Ventilation (PSV) with BiPAP Device/Nasal CPAP II. Policy: PSV with BiPAP device/nasal CPAP will be initiated upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel trained
Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution
 Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Charisma High-flow CPAP solution Homecare PNEUMOLOGY Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support charisma High-flow CPAP solution Evidence CPAP therapy
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan Prepared by MEKICS. OmniOx-HFT500 Jan ver1.1 1
 OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan. 2013. Prepared by MEKICS OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013 ver1.1 1 0. Index 1. Introduce of OmniOx (HTF500) 2. Specification (HFT, CPAP+) 3. The World Best Features 2 OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013
OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan. 2013. Prepared by MEKICS OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013 ver1.1 1 0. Index 1. Introduce of OmniOx (HTF500) 2. Specification (HFT, CPAP+) 3. The World Best Features 2 OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013
INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2
 2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call
 AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
Learning Objectives. 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence
 Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
FY06 Full Year Update & Overview
 FY06 Full Year Update & Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in heated humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing market opportunity High level of innovation
FY06 Full Year Update & Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in heated humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing market opportunity High level of innovation
FY07 Full Year Update & Overview
 FY07 Full Year Update & Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in respiratory humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing market opportunity High level
FY07 Full Year Update & Overview Investment Highlights Leading player in respiratory humidification systems Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$2+ billion and growing market opportunity High level
PORTO 2 VENT CPAP OS. Operator s Manual. PORTO 2VENT CPAP OS System Operator s Manual Part Number Rev I
 PORTO 2 VENT CPAP OS Operator s Manual 1 2 TABLE of CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3. Operating Instructions 1a. Definitions 3a. Setting the CPAP Level 1b. General Description 3b. Applying the Breathing Circuit
PORTO 2 VENT CPAP OS Operator s Manual 1 2 TABLE of CONTENTS 1. Introduction 3. Operating Instructions 1a. Definitions 3a. Setting the CPAP Level 1b. General Description 3b. Applying the Breathing Circuit
Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants <34 weeks gestation.
 Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Capnography Connections Guide
 Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
Capnography Connections Guide Patient Monitoring Contents I Section 1: Capnography Introduction...1 I Section 2: Capnography & PCA...3 I Section 3: Capnography & Critical Care...7 I Section 4: Capnography
A Comparison of Leak Compensation in Acute Care Ventilators During Noninvasive and Invasive Ventilation: A Lung Model Study
 A Comparison of Leak Compensation in Acute Care Ventilators During Noninvasive and Invasive Ventilation: A Lung Model Study Jun Oto MD PhD, Christopher T Chenelle, Andrew D Marchese, and Robert M Kacmarek
A Comparison of Leak Compensation in Acute Care Ventilators During Noninvasive and Invasive Ventilation: A Lung Model Study Jun Oto MD PhD, Christopher T Chenelle, Andrew D Marchese, and Robert M Kacmarek
How to write bipap settings
 How to write bipap settings 6-6-2013 Living On O2 for Life If you use a bipap machine, like I do, this post is for you. I've been using a bipap machine since 1993 which is a pretty long time. BiPAP 's
How to write bipap settings 6-6-2013 Living On O2 for Life If you use a bipap machine, like I do, this post is for you. I've been using a bipap machine since 1993 which is a pretty long time. BiPAP 's
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities
 Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Vancouver Coastal Health Guidelines for the use of Respiratory Equipment for Patients on Airborne Precautions in Acute Care Facilities Goals 1. To meet respiratory care needs in patients who are on airborne
Lung Wit and Wisdom. Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate. Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital
 Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Advantages and disadvantages of different nasal CPAP systems in newborns
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
Biphasic Capnogram in a Single Lung Transplant Recipient A Case Report
 TITLE PAGE Biphasic Capnogram in a Single Lung Transplant Recipient A Case Report Authors: Hardeep S. Rai, MD, Cleveland Clinic, Respiratory Institute, Cleveland, OH 44195 Justin Boehm, RRT, Cleveland
TITLE PAGE Biphasic Capnogram in a Single Lung Transplant Recipient A Case Report Authors: Hardeep S. Rai, MD, Cleveland Clinic, Respiratory Institute, Cleveland, OH 44195 Justin Boehm, RRT, Cleveland
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery
 Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
A multipurpose ventilator. Flow-SNIPPV - a new challenge in neonatal respiratory care
 Neonatal Ventilator A multipurpose ventilator Giulia Ventilator is a next-generation ventilator designed to give the best respiratory support at every step of the clinical treatment of the respiratory
Neonatal Ventilator A multipurpose ventilator Giulia Ventilator is a next-generation ventilator designed to give the best respiratory support at every step of the clinical treatment of the respiratory
Guidelines and Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide
 Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
2014 Full Year Results Presentation. Year ended 31 March 2014
 2014 Full Year Results Presentation Year ended 31 March 2014 26-30 May 2014 1 Full year result highlights 12 months to 31 March 2014 NZ$M PCP CC 1 Record net profit after tax 97.1 +26% +46% Record operating
2014 Full Year Results Presentation Year ended 31 March 2014 26-30 May 2014 1 Full year result highlights 12 months to 31 March 2014 NZ$M PCP CC 1 Record net profit after tax 97.1 +26% +46% Record operating
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
Faculty Disclosure. Off-Label Product Use
 Faculty Disclosure X No, nothing to disclose Yes, please specify: Company Name Honoraria/ Expenses Consulting/ Advisory Board Funded Research Royalties/ Patent Stock Options Equity Position Ownership/
Faculty Disclosure X No, nothing to disclose Yes, please specify: Company Name Honoraria/ Expenses Consulting/ Advisory Board Funded Research Royalties/ Patent Stock Options Equity Position Ownership/
Research in high flow therapy: Mechanisms of action. Kevin Dysart, Thomas L. Miller, Marla R. Wolfson, Thomas H. Shaffer
 Research in high flow therapy: Mechanisms of action Kevin Dysart, Thomas L. Miller, Marla R. Wolfson, Thomas H. Shaffer 64666_03_Mech0fAction.indd 1 Respiratory Medicine (2009) xx, 1e6 ARTICLE IN PRESS
Research in high flow therapy: Mechanisms of action Kevin Dysart, Thomas L. Miller, Marla R. Wolfson, Thomas H. Shaffer 64666_03_Mech0fAction.indd 1 Respiratory Medicine (2009) xx, 1e6 ARTICLE IN PRESS
C l i n i c a lcpap. Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care
 C l i n i c a lcpap Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care This is tex which explains in moderate clinicsal detail, the background and structure of the patient indication for CPAP. This is tex which
C l i n i c a lcpap Advanced Solutions in Acute Respiratory Care This is tex which explains in moderate clinicsal detail, the background and structure of the patient indication for CPAP. This is tex which
Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector
 Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector Presentation redeveloped for this program by Rosemarie Boland from an original presentation by Johnston, Adams & Stewart, (2006) Background Clinical methods of endotracheal tube
Pedi-Cap CO 2 detector Presentation redeveloped for this program by Rosemarie Boland from an original presentation by Johnston, Adams & Stewart, (2006) Background Clinical methods of endotracheal tube
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Neonatal and Pediatric Securement From Salter
 Neonatal and Pediatric Securement From Salter The touch that says so much Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION Now with options for ncpap,, and low flow therapy. Collaborative Innovation Today, Salter
Neonatal and Pediatric Securement From Salter The touch that says so much Striving to be #1 IN PATIENT SATISFACTION Now with options for ncpap,, and low flow therapy. Collaborative Innovation Today, Salter
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better
 Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Analysis of Three Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices During Simulated Breathing
 Analysis of Three Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices During Simulated Breathing Doug Pursley, MEd, RRT-ACCS, FAARC Introduction Previous studies reporting performance characteristics of Oscillating
Analysis of Three Oscillating Positive Expiratory Pressure Devices During Simulated Breathing Doug Pursley, MEd, RRT-ACCS, FAARC Introduction Previous studies reporting performance characteristics of Oscillating
APRV Ventilation Mode
 APRV Ventilation Mode Airway Pressure Release Ventilation A Type of CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) with an intermittent release phase. Patient cycles between two levels of CPAP higher
APRV Ventilation Mode Airway Pressure Release Ventilation A Type of CPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) with an intermittent release phase. Patient cycles between two levels of CPAP higher
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials
 Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
Neonatal Life Support Provider (NLSP) Certification Preparatory Materials NEONATAL LIFE SUPPORT PROVIDER (NRP) CERTIFICATION TABLE OF CONTENTS NEONATAL FLOW ALGORITHM.2 INTRODUCTION 3 ANTICIPATION OF RESUSCITATION
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
 The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
Cough assist T70 for the Tracheostomy Child
 Patient and Family Education Cough assist 70 for the racheostomy Child with or without a ventilator What is a Cough assist device? he Cough assist 70 device removes mucus (secretions) from your child s
Patient and Family Education Cough assist 70 for the racheostomy Child with or without a ventilator What is a Cough assist device? he Cough assist 70 device removes mucus (secretions) from your child s
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During. Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Handling Common Problems & Pitfalls During ACUTE SEVERE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Pravit Jetanachai, MD QSNICH Oxygen desaturation in patients receiving mechanical ventilation Causes of oxygen desaturation 1.
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal resuscitation guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005
 Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Table 1: The major changes in AHA / AAP neonatal guidelines2010 compared to previous recommendations in 2005 Resuscitation step Recommendations (2005) Recommendations (2010) Comments/LOE 1) Assessment
Anesthesia Monitoring. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Anesthesia Monitoring D. J. McMahon 150114 rev cewood 2018-01-19 Key Points Anesthesia Monitoring: - Understand the difference between guidelines & standards - ASA monitoring Standard I states that an
Anesthesia Monitoring D. J. McMahon 150114 rev cewood 2018-01-19 Key Points Anesthesia Monitoring: - Understand the difference between guidelines & standards - ASA monitoring Standard I states that an
Abstract. , FiO2, volume flow, and airway pressure.
 Abstract A Bench Study to Compare Portable Therapies for Respiratory Insufficiency: Continuous Flow Oxygen (CF), Intermittent Flow Oxygen (IF), and Non-Invasive Open Ventilation (NIOV) Background Respiratory
Abstract A Bench Study to Compare Portable Therapies for Respiratory Insufficiency: Continuous Flow Oxygen (CF), Intermittent Flow Oxygen (IF), and Non-Invasive Open Ventilation (NIOV) Background Respiratory
Fisher & Paykel Healthcare
 Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Deutsche Bank / Craigs New Zealand Corporate Day 1 Sydney March 2014 Investment Highlights A leader in respiratory and OSA treatment devices Consistent growth strategy Estimated
Fisher & Paykel Healthcare Deutsche Bank / Craigs New Zealand Corporate Day 1 Sydney March 2014 Investment Highlights A leader in respiratory and OSA treatment devices Consistent growth strategy Estimated
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING
 PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
Preventing Respiratory Complications of Muscular Dystrophy
 Preventing Respiratory Complications of Muscular Dystrophy Jonathan D. Finder, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Introduction Respiratory
Preventing Respiratory Complications of Muscular Dystrophy Jonathan D. Finder, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Introduction Respiratory
Audu LI Otuneye AT Mairami AB Mukhtar MY ORIGINAL. Niger J Paed 2015; 42 (1): 12 16
 Niger J Paed 2015; 42 (1): 12 16 Audu LI Otuneye AT Mairami AB Mukhtar MY ORIGINAL Improvised bubble continuous positive airway pressure (BCPAP) device at the National Hospital Abuja gives immediate improvement
Niger J Paed 2015; 42 (1): 12 16 Audu LI Otuneye AT Mairami AB Mukhtar MY ORIGINAL Improvised bubble continuous positive airway pressure (BCPAP) device at the National Hospital Abuja gives immediate improvement
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants. Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid
 Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
VENTILATOR GRAPHICS ver.2.0. Charles S. Williams RRT, AE-C
 VENTILATOR GRAPHICS ver.2.0 Charles S. Williams RRT, AE-C Purpose Graphics are waveforms that reflect the patientventilator system and their interaction. Purposes of monitoring graphics: Allow users to
VENTILATOR GRAPHICS ver.2.0 Charles S. Williams RRT, AE-C Purpose Graphics are waveforms that reflect the patientventilator system and their interaction. Purposes of monitoring graphics: Allow users to
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim
 Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Evaluation of Endotracheal Tube Scraping on Airway Resistance
 Evaluation of Endotracheal Tube Scraping on Airway Resistance J Brady Scott MSc RRT-ACCS AE-C FAARC, Meagan N Dubosky MSc RRT-ACCS RRT-NPS AE-C, David L Vines, MHS RRT FAARC, Adewunmi S Sulaiman MSc RRT,
Evaluation of Endotracheal Tube Scraping on Airway Resistance J Brady Scott MSc RRT-ACCS AE-C FAARC, Meagan N Dubosky MSc RRT-ACCS RRT-NPS AE-C, David L Vines, MHS RRT FAARC, Adewunmi S Sulaiman MSc RRT,
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
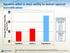 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Pediatrics in mechanical ventilation
 Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
Pediatrics Optimization Intitulé du cours of aerosol therapy in mechanical ventilation Thèmes donnés Ermindo Di Paolo, PhD Departments of Pharmacy and Pediatrics Lausanne University Hospital Switzerland
October Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE
 October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
October 2017 Paediatric Respiratory Workbook APCP RESPIRATORY COMMITTEE This workbook is designed to introduce to you the difference between paediatric and adult anatomy and physiology. It will also give
Half Year Update FY2012 November 2011
 Half Year Update FY2012 November 2011 1 Investment Highlights A leader in respiratory and OSA treatment devices Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$3.0+ billion and growing market opportunity High
Half Year Update FY2012 November 2011 1 Investment Highlights A leader in respiratory and OSA treatment devices Consistent growth strategy Estimated US$3.0+ billion and growing market opportunity High
