Shoulder abduction fatiguability
|
|
|
- Easter Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
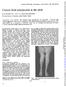
1 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1987;5: J NICKLIN, Y KARNI, C M WILES From the Departments of Clinical Neurophysiology and Physiotherapy, The National Hospitalfor Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London, UK SUMMARY Shoulder abduction fatiguability has been measured using a hand held myometer in normal subjects and patients with peripheral neuromuscular diseases. An index of fatiguability was based on the decline in force over a series of ten maximum voluntary contractions performed in under a minute. The technique was repeatable and well tolerated. Patients with myasthenia, mitochondrial myopathy and motor neuron disease tended to show excess fatiguability independent of muscle strength. Serial measurements demonstrated alterations in fatiguability but not necessarily strength, associated with changes in symptoms. Fatiguability is a common symptom in peripheral neuromuscular disease. Commonly the clinician assesses this subjectively by repetitive manual "breaking" of shoulder abduction or some other muscle group. However, this is difficult to quantify and compare from examination to examination. More elaborate techniques utilising electrically stimulated muscle contractions' or isokinetic dynamometry2 have been used, particularly for assessing knee extension, but generally require complex apparatus and are impractical for routine use. In this study we define fatiguability as the reduction in muscle contraction force with repeated maximum efforts. We have developed a simple technique to quantify fatiguability, which can be employed in the clinic; the percentage decline in shoulder abduction force over ten successive maximum voluntary contractions (MVC), is measured using a hand held dynamometer. A preliminary report of this work was made at the Association of British Neurologists' Meeting, Belfast, April Methods (A) Technique The subject is seated, the back unsupported, with the nondominant arm to be assessed abducted to 9, the elbow flexed to 9 and the forearm pronated (fig. 1). In the small number of patients where shoulder abduction strength was less than MRC3 grade 3, the fatiguability test was conducted Address for reprint requests: Dr CM Wiles, The National Hospital for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London WCIN 3BG, UK. Received 3 May Accepted 8 August 1986 )*da," t VI.""i 11i Z.:..IA... Fig Positioning of operator and subject for the fatiguability test. with the patient in supine position. The method and necessity to maintain the arm position throughout the test is explained carefully to the subject. A hand held dynamometer (Penny and Giles Ltd., Airfield Road, Christchurch, Dorset), is positioned by the examiner just proximal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus,4 and sufficient 423 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 14 September 218 by guest.
2 424 Table Weakness andfatiguability in peripheral neuromuscular diseases Weak Fatiguable Both Diagnosis Total No. (%) No. (%) No. (%) Myasthenia gravis 16 1 (62 4) 14 (87 5) 1 (62-5) Congenital myasthenia 9 8 (88 8) 9 (1) 8 (88-8) Lambert Eaton Syndrome 11 5(45.4) 7(63 5) 3(27-3) Mitochondrial myopathy 1 6 (6) 4 (4) 3 (3) Other myopathies (5) 4 (14 2) 3 (1-7) Muscular dystrophy 8 8 (1) 1 (12 5) 1 (12 5) Neuropathy (68 4) 4 (21 1)* 3 (15.8)* Motor neuron disease 9 5 (56) 4 (45) 3 (33) Unknown 5 3(62 8) () () Total (62 6) 47 (4 8) 34 (29 5) *Guillain-Barre syndrome. counterforce applied to just overcome the subject's maximum effort: the peak force is registered by the dynamometer. The subject is then required to make a series of ten maximum contractions over a total of 5-55 seconds, with approximately two seconds rest between each contraction. A Fatigue Index (FI) is calculated as the difference between the mean of the first two and last two contractions, expressed as a percentage of the mean of the first two; that is Fl,2 - F9, 1 x loo% Fl1,2 ' x1 The possibility that failure to maintain the starting position would influence MVC and hence Fl was investigated in a sample of 21 normal subjects (11 females, 1 males). Each was asked to produce three MVCs first at 9 and then at 6 of shoulder abduction. This sequence was then reversed in a second series to eliminate the effects of order. The same technique was applied to compare 9 and 6 of flexion in abduction. Inter-observer variability was also examined in a sample of 11 patients with diverse neuromuscular diseases. The FI was measured twice within four hours on the same patient, by two examiners independently. (B) Subjects and patients Normal values were obtained in 5 control subjects, 25 females (aged 2-65, median 3 years), and 25 males (aged 2-6, median 34 years). The test was incorporated at the end of our routine assessment of patients with peripheral neuromuscular disorders which includes myometry,4 performance test,5 and a visual analogue score of symptomatic state. Results from 115 consecutive patients with a variety of neuromuscular diseases are reported in this paper (see table). Only patients with a definite diagnosis were included, apart from a small group whose main clinical features were nonspecific "weakness and fatigue". The results included are the first Fl measurement made in each patient regardless of treatment status. For each patient the values of the 1 force measurements were plotted onto a standard graph of the normal values for sex and were classified as "weak" and/or "fatiguable" by an observer who was unaware of the diagnosis. In a number of patients we have also made serial measurements of Fl during the course of their treatment. 21 I 15 J --u Female +2Sd M o-o *--- -2Sd Nicklin, Karni, Wiles ioo-l. * * * ---* * 357 Force (N) Male 3 3- Force (N) P- o f- v.i*, * v * _, Contraction No Fig 2 (a) Normal range ofmean shoulder abduction strength in 25females ( + / - 2SD). Force increasedfrom the first to the second contraction and then declined. (b) Normal range ofmean shoulder abduction strength in 25 males (+ /-2SD). Force declinedftom thefirst to the fifth contraction then remained constant. Results (a) Normal subjects (fig 2A, B) Mean shoulder abduction strength (mean of the first two measurements) in females was 1 5ON (range 97-23N, + / - 2SD) and in males it was 227N (range N, +/- 2SD). Strength declined slightly with age in men (r = -47, p = < -2), but not in women (r = -29, p = < 1). In both sexes the fatiguability index (FI) had a normal distribution of values. The mean in females was 6-1 % (range to %, +/- 2SD) and in males 6-1% (range- 7.3 to %, + 2SD): the mean values for males and females were not significantly different (p > 1) and the combined values for both sexes was to + 19-% (mean 6 1%). Thus a few subjects showed a slight increase in force (negative values) over 1 contractions. No correlation was found between Fl and strength (p = >- 1). As mentioned in Methods, the effect of deviations from the starting position was examined. There was found to be no significant difference (p =.4) J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 14 September 218 by guest.
3 between MVCs at 9 and 6 of abduction, or MVCs at 9 and 6 of forward flexion in abduction. Therefore it seems unlikely that any failure to maintain the starting position would account for an increase in fatiguability index. Inter-observer variation was low; the correlation coefficient between Fl measured by two examiners in 11 patients was -96 (p <.1). (b) Patients (table) Patients classified as fatiguable all had a Fatigue Index (FI) > 2%; those whose initial strength (mean of first two contractions) was more than 2SD below the normal mean for sex were considered weak. In many of those with myasthenia, fatiguability was very abnormal; one third had an FT of more than 5%. Of the fatiguable myasthenic group, 7% were weak, but in 3% strength fell within the normal range. There was no statistically significant correlation between weakness and fatiguability in patients with myasthenia gravis or congenita. In the group with Lambert Eaton Syndrome there was a tendency for the Fl to increase (that is, more fatiguable) with increasing strength but this did not reach conventional statistical significance (r = -52, p = -8, n = 11). Within the mitochondrial myopathy group, 4% had a significant FT (ie > 2%); however, the mean for the whole group was 18 3%, considerably higher than the combined mean for normal males and females (mean = 6-1%). The four patients with neuropathy who showed excess fatiguability, all had Guillain-Barre syndrome, but none had a major degree of sensory loss. Four other patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome had normal FIs. Serial measurements in some patients yielded clinically useful data. Several cases have been looked at over a period of time, ranging from four weeks to four months: 2 Fatiguability index().-. Left shoulder abd o--o Right hip flex 1 O Time (days) Fig 3 Case 1. Female patient, aged 61 years with neurosarcoidosis. Serial measurements were made during treatment with prednisolone. 3 Fatiguability index (1.) 2 1 5i Subjective score (1. improvement) 25 v AI, ILI 9 Left shoulder abd. 2 Time walking (s) 12 Force (N) a O Prednisolone (mg/d) ] Plasma 2 3 exchange Time (days) Fig 4 Case 2. Female patient, aged 29 years with myasthenia gravis. Serial measurements of walking time over 3 metres, shoulder abduction strength (N), visual analogue scale ofsymptoms, and FI are shown. Case History 1. (fig 3) A female patient, aged 61 years with neurosarcoidosis and proximal weakness, was treated with prednisolone. Shoulder abduction strength, and that of other muscle groups recorded, only improved slightly. However, the FI declined markedly (that is, reduced fatiguability), in parallel with a striking improvement in her general symptoms. Case History 2. (fig 4) A 29 year old female patient with myasthenia gravis [ Left shoulder abd. Fatiguability index () o Right knee ext. I- force (N) I..% Time walking (s) I] 4 so Time (days) Fig 5 Case 3. Male, aged 25 years with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Both FI and timed walking could not be measured until 3 days post onset. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 14 September 218 by guest.
4 426 was admitted for a course of plasma exchange. In the following three weeks, muscle strength changed minimally but her fatiguability index improved as did her timed walking and symptomatic state. Case History 3. (fig 5) A male, age 25 years with Guillain-Barre syndrome, was followed up over four months. In contrast to the other two cases, muscle strength improved greatly but the FI still remained high. Late improvement in fatiguability may account for the prolonged period required to return to premorbid fitness. Discussion The term "muscle fatigue" has been used to refer to a variety of phenomena associated with prolonged or repeated contractions. These include a decline in force,6 selective force loss at high7 or low frequencies8 of electrical stimulation, slowing of contractile properties9 and changes in the EMG power spectrum' and muscle fibre conduction velocity." By using the term fatiguability, we refer to the clinically apparent reduction in maximum voluntary strength with repeated contractions. The technique described has allowed us to express such fatiguability in a reproducible, quantifiable manner, helpful in monitoring patients. There are some difficulties inherent in the test. We noted that some subjects did not sustain concentration throughout the test and it is therefore important to achieve cooperation between operator and patient and maintain effective verbal encouragement at all times to produce their best efforts especially in the latter half of the test. Afferent influences, notably pain but also input from the joint capsule, may inhibit production of an MVC.'2 In some patients with mitochondrial myopathy we had the impression that the initial contraction was somewhat tentative: a failure to make a full initial effort would tend to lead to an apparently low fatiguability index. Significant fatiguability could be demonstrated in 83% of the myasthenic patients even though these patients were all on treatment though not in full clinical remission. In line with clinical impressions 4% of the patients with mitochondrial myopathy were fatiguable. Other groups rarely showed fatigue (as defined by our test), except for two groups: these were patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome and motor neuron disease. Our sample size for these groups is small, but their fatiguability is an area we would like to investigate further. Within the motor neuron disease group, it has been our impression that there are two sub-groups: those who fatigue severely, that is, four Nicklin, Karni, Wiles patients with a mean FI of 47% (range 21[7 to 66&3%) and those who do not fatigue, five patients with a mean FT of 8-2% (range - 16 to 17-5%). Three of the fatiguable patients were also weak as were two of the non-fatiguable patients. None of the undiagnosed group with non-specific "weakness and fatigue" were shown to have significant fatiguability (mean FI 7-6%, range 1 to 14 4%, n = 5) despite 6% being weak. Although it might be expected that pathophysiological processes leading to fatiguability and weakness would be similar, we find that in our population of patients there is no simple correlation. This is confirmed in the limited serial data on treated patients which demonstrates that strength and fatiguability in individual muscle groups may vary independently. We are now collecting more serial data on patients with a view to investigating this more closely. Few tests of fatiguability applicable to patients have been described in the literature. Test of timed performance'3 in which the time that the head or leg can be held in a standard position have been used, but seem to be more dependent on the patient's motivation and, in our hands produce rather variable results. In one study14 these tests were found to discriminate between diseased and normal muscle, but were an insensitive means of monitoring progress. Many authors have previously emphasised the value of serial strength measurements in monitoring patients with peripheral neuromuscular diseases;4 nevertheless, we are aware that a few patients complain more of fatiguability than weakness. The fatiguability index can be used to document excessive fatiguability in shoulder abduction but it should not be assumed that FT will be similar in other muscle groups. Serial measurements may indicate changes in clinical state which are not obvious from examination in simple strength measurements, but which the patient finds significant. The test appears robust, easy to perform and reliable, but as with all such tests, should be interpreted in conjunction with changes in symptoms, clinical performance and strength. We are grateful to Professor J Newsom-Davis and Dr JA Morgan-Hughes and other physicians at the National Hospital for allowing us to study patients under their care. The equipment used was funded by a grant from Action Research for the Crippled Child. References 1 Wiles CM, Jones DA, Edwards RHT. Fatigue in human metabolic myopathy. In: Human Muscle Fatigue: Physiological Mechanisms. Pitman Medical, London (Ciba Foundation Symposium No. 82) 1981: Barnes WS. Isokinetic fatigue curves at different contractile velocities. Arch Phys Med Rehab 198 1;62:66-9. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 14 September 218 by guest.
5 3 Medical Research Council. Aids to Examination of the Peripheral Nervous System. Memorandum No. 45. London: HMSO, Wiles CM, Karni Y. The measurement of muscle strength in patients with peripheral neuromuscular disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1983;46: Karni Y, Archdeacon L, Mills KR, Wiles CM. Clinical assessment and physiotherapy in Guillain-Barre syndrome. Physiother 1984;7: Edwards RHT. Physiological analysis of muscle weakness and fatigue. Clin Sci Mol Med 1978;54: Jones DA, Bigland-Ritchie B, Edwards RHT. Excitation frequency and muscle fatigue: mechanical responses during voluntary and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 1979;64: Edwards RHT, Hill DK, Jones DA, Merton PA. Fatigue of long duration in human skeletal muscle after exercise. J Physiol (Lond) 1977;272: Wiles CM, Edwards RHT. The effect of temperature, ischaemia and contractile activity on the relaxation 427 rate of human muscle. Clin Physiol 1982;2: Lindstrom L, Magnusson R, Petersen I. Muscular fatigue and action potential conduction velocity changes studied with frequency analysis of EMG signals. Electromyography 197;4: Arendt-Nielsen L, Mills KR. The relationship between mean power frequency of the EMG signal and muscle fibre conduction velocity. Electroencephalogr Clinical Neurophysiol 1984;6: Stokes M, Young A. The contribution of reflex inhibition to arthogenous muscle weakness. Clin Sci 1984;67: Fessel WJ, Taylor JA, Johnson ES. Evaluating the complaint of muscle weakness. Simple quantative clinical tests. In: Walton JN, Canal N, Scarlatto G, eds. Muscle Diseases. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica, 197: Hosking GP, Bhat US, Dubowitz V, Edwards RHT. Measurements of muscle strength in children with normal and diseased muscle. Arch Dis Child 1976;51: J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry: first published as /jnnp on 1 April Downloaded from on 14 September 218 by guest.
Central and peripheral fatigue in sustained maximum voluntary contractions of human quadriceps muscle
 Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine (1978) 54,609-614 Central and peripheral fatigue in sustained maximum voluntary contractions of human quadriceps muscle B. BIGLAND-RITCHIE*, D. A. JONES, G. P. HOSKING
Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine (1978) 54,609-614 Central and peripheral fatigue in sustained maximum voluntary contractions of human quadriceps muscle B. BIGLAND-RITCHIE*, D. A. JONES, G. P. HOSKING
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM. Andrzej Sladkowski
 Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Critical Illness Polyneuropathy CIP and Critical Illness Myopathy CIM Andrzej Sladkowski Potential causes of weakness in the ICU-1 Muscle disease Critical illness myopathy Inflammatory myopathy Hypokalemic
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory myositis
 Rheumatology 26;45:874 879 Advance Access publication 31 January 26 Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory
Rheumatology 26;45:874 879 Advance Access publication 31 January 26 Two simple, reliable and valid tests of proximal muscle function, and their application to the management of idiopathic inflammatory
Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function. Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth
 Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth http://www.visualphotos.com/image/2x2696104/test_tube_over_a_bunsen_burner http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_95/journal/vol4/ykl/report.html
Effects of Temperature on Neuromuscular Function Jon Marsden School of Health Professions University of Plymouth http://www.visualphotos.com/image/2x2696104/test_tube_over_a_bunsen_burner http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/~nd/surprise_95/journal/vol4/ykl/report.html
SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE
 of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
of 4 SITES OF FAILURE IN MUSCLE FATIGUE Li-Qun Zhang -4 and William Z. Rymer,2,4 Sensory Motor Performance Program, Rehabilitation Institute of Chicago Departments of 2 Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation,
Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy'
 Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
Jourtial of Neurology, Neurosurgery, anid Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 647-652 Sensory conduction of the sural nerve in polyneuropathy' DAVID BURKE, NEVELL F. SKUSE, AND A. KEITH LETHLEAN From the Unit of Clinical
ASSESSMENT OF MUSCLE strength is an integral part of
 653 Muscle Force Measured Using Break Testing With a Hand-Held Myometer in Normal Subjects Aged to 69 Years Beverley A. Phillips, Ph, Sing K. Lo, Ph, Frank L. Mastaglia, M ABSTRACT. Phillips BA, Lo SK,
653 Muscle Force Measured Using Break Testing With a Hand-Held Myometer in Normal Subjects Aged to 69 Years Beverley A. Phillips, Ph, Sing K. Lo, Ph, Frank L. Mastaglia, M ABSTRACT. Phillips BA, Lo SK,
New method for the estimation of the number of
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1974, 37, 1195-121 New method for the estimation of the number of motor units in a muscle 2 Duchenne, limb-girdle and facioscapulohumeral, and myotonic
skeletal muscle is essentially caused by failure of membrane excitation or by decrease (Received 16 September 1982)
 J. Physiol. (1983), 339, pp. 33-40 33 With 6 text-figures Printed in Great Britain ELECTROMYOGRAM, FORCE AND RELAXATION TIME DURING AND AFTER CONTINUOUS ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF HUMAN SKELETAL MUSCLE
J. Physiol. (1983), 339, pp. 33-40 33 With 6 text-figures Printed in Great Britain ELECTROMYOGRAM, FORCE AND RELAXATION TIME DURING AND AFTER CONTINUOUS ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF HUMAN SKELETAL MUSCLE
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 653-658 Distal chronic spinal muscular atrophy involving the hands D. J. O'SULLIVAN AND J. G. McLEOD From St Vincent's Hospital, and Department
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Examination of the Motor System Reviewed & ratified by: o o o o Dr D Smith Consultant Neurologist Dr R Davies Consultant Neurologist Dr B Michael Neurology Clinical
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1 Pause and Practice: Facilitating Trunk and Shoulder Control with the Therapy Ball
 1 Pause and Practice: Facilitating Trunk and Shoulder Control with the Therapy Ball This is an example of Facilitating Combinations of Movements and Active Assist. Starting Position Have your patient sit
1 Pause and Practice: Facilitating Trunk and Shoulder Control with the Therapy Ball This is an example of Facilitating Combinations of Movements and Active Assist. Starting Position Have your patient sit
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine
 Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning It can help to shape a basic fitness training programme
 Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques. Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright
 Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
Joint Range of Motion Assessment Techniques Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.Ed Copyright 2001-2006 Objectives Understand how joint range of motion & goniometric assessment is an important component
Evaluation copy. EMG and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
MOTOR FUNCTION MEASURE for neuromuscular diseases M F M
 MOTOR FUNCTION MEASURE for neuromuscular diseases M F M SCORING SHEET 1 Patient birth s name, surname: Married name: Date of birth: / / Patient age: / year month day years months Assessment date: / / year
MOTOR FUNCTION MEASURE for neuromuscular diseases M F M SCORING SHEET 1 Patient birth s name, surname: Married name: Date of birth: / / Patient age: / year month day years months Assessment date: / / year
Electromyography (EMG)
 Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
Exercise performance and fatiguability in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome
 J'ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1993;56:993-998 Muscle Research Centre, Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool, PO Box 147, Liverpool L69 3BX, UK H Gibson N Carroll J E Clague
J'ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1993;56:993-998 Muscle Research Centre, Department of Medicine, University of Liverpool, PO Box 147, Liverpool L69 3BX, UK H Gibson N Carroll J E Clague
Neuromuscular Mechanics
 Schematic Representation of Motor Units in Skeletal Muscle Neuromuscular Mechanics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 4) Whatever text you read do not focus on motorneuron structure and sensory receptors Muscle Fibres
Schematic Representation of Motor Units in Skeletal Muscle Neuromuscular Mechanics Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 4) Whatever text you read do not focus on motorneuron structure and sensory receptors Muscle Fibres
NEUROMUSCULAR ADAPTATIONS DURING LONG-TERM BED REST
 SUMMARY Summary 117 NEUROMUSCULAR ADAPTATIONS DURING LONG-TERM BED REST mechanical loading of the human body. The accompanying physical inactivity sets in motion a cascade of changes that affects practically
SUMMARY Summary 117 NEUROMUSCULAR ADAPTATIONS DURING LONG-TERM BED REST mechanical loading of the human body. The accompanying physical inactivity sets in motion a cascade of changes that affects practically
Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1983;46:305-309 Responses to electrical stimulation of denervated human muscle fibres recorded with single fibre EMG JOZE TRONTELJ, ERIK STALBERG From
Therapy Manual DO NOT PRINT
 Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
Therapy Manual Contents 1. Shoulder 2. Shoulder and elbow a. Protraction: 1 DoF 1 b. Flexion: 1 DoF 1-6 c. Extension: 1 DoF 1-2 d. Abduction: 1 DoF 1-4 e. External rotation: 1 DoF 1-14 a. Combined shoulder
EDX in Myopathies Limitations. EDX in Myopathies Utility Causes of Myopathy. Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers
 Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
Electrodiagnostic Assessment of Myopathy Myopathy: Issues for Electromyographers Often perceived as challenging Ian Grant Division of Neurology QEII Health Sciences Centre Halifax NS CNSF EMG Course June
How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic
 How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic Patrick Gordon Consultant Rheumatologist / Honorary Senior Lecturer King s Health Partners Email: patrick.gordon2@nhs.net Many
How to assess myositis disease activity in a busy general rheumatology clinic Patrick Gordon Consultant Rheumatologist / Honorary Senior Lecturer King s Health Partners Email: patrick.gordon2@nhs.net Many
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals
 FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
FES Standing: The Effect of Arm Support on Stability and Fatigue During Sit-to-Stand Manoeuvres in SCI Individuals Musfirah Abd Aziz and Nur Azah Hamzaid Abstract Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
in children with normal and diseased muscle
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1976, 51, 957. Measurements of muscle strength and performance in children with normal and diseased muscle G. P. HOSKING, U. S. BHAT, V. DUBOWITZ, and R. H. T. EDWARDS
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1976, 51, 957. Measurements of muscle strength and performance in children with normal and diseased muscle G. P. HOSKING, U. S. BHAT, V. DUBOWITZ, and R. H. T. EDWARDS
at least in part, by observing the effect of raising body temperature on the evoked potentials. upper limit of the normal value for latency of
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1979, 42, 250-255 Effect of raising body temperature on visual and somatosensory evoked potentials in patients with multiple sclerosis W. B. MATTHEWS,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1979, 42, 250-255 Effect of raising body temperature on visual and somatosensory evoked potentials in patients with multiple sclerosis W. B. MATTHEWS,
Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during treatment in hypothyroid myopathy
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1979, 32, 229-233 Central nuclear counts in muscle fibres before and during in hypothyroid myopathy R. 0. McKERAN",4, P. WARD2, G. SLAVIN2 3, AND E. A. PAUL5 From the Divisions
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles
 Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Relative Isometric Force of the Hip Abductor and Adductor Muscles WARREN W. MAY, Captain, AMSC A-LTHOUGH THE CONCEPT of the muscular force curve is not new, its clinical application has been generally
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation. The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer
 The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
The reliability of strength tests performed in elevated shoulder positions using a hand-held dynamometer Journal: Manuscript ID: JSR.2015-0034.R2 Manuscript Type: Technical Report Keywords: dynamometry,
CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich. St. Francis Xavier University. October 9, 2006
 CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich 200306793 St. Francis Xavier University October 9, 2006 1 Introduction The aim of the present study is to determine whether or not training
CAN TRAINING IMPROVE YOUR ABILITY TO CO-CONTRACT? Jordan Yurchevich 200306793 St. Francis Xavier University October 9, 2006 1 Introduction The aim of the present study is to determine whether or not training
Throwers Ten Exercise Program
 The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity
 THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
THE EXTREMITY SCREEN MANUAL: A Guide to the Subjective and Objective Outcomes Assessment of the Upper and Lower Extremity Steven G. Yeomans, DC, FACO INTRODUCTION: Objective screen for the extremities
ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS
 ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS CURE JM STANFORD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OCTOBER 3, 2014 Minal Jain, PT, DSc, PCS Research Coordinator, Physical Therapy Section Rehabilitation
ASSESSMENT OF STRENGTH IN CHILDREN WITH JUVENILE DERMATOMYOSITIS CURE JM STANFORD SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OCTOBER 3, 2014 Minal Jain, PT, DSc, PCS Research Coordinator, Physical Therapy Section Rehabilitation
WEEKEND 2 Elbow. Elbow Range of Motion Assessment
 Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
Virginia Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapy Institute - 2016 Technique Manual WEEKEND 2 Elbow Elbow Range of Motion Assessment - Patient Positioning: Sitting or supine towards the edge of the bed - Indications:
TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM
 TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM Patient Name: Date of Surgery: General Principles: The Throwing Athlete Exercise Program is designed to
TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM Patient Name: Date of Surgery: General Principles: The Throwing Athlete Exercise Program is designed to
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012
 Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Neonatal Hypotonia Guideline Prepared by Dan Birnbaum MD August 27, 2012 Hypotonia: reduced tension or resistance to range of motion Localization can be central (brain), peripheral (spinal cord, nerve,
Pediatric Aspects of EDX
 Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
Pediatric Aspects of EDX Albert C. Clairmont, MD Associate Professor-Clinical The Ohio State University February 25, 2013 Objectives Overview of Pediatric Electrodiagnosis (EDX) Understand the different
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE BEDSIDE QUANTIFICATION OF SPASTICITY: A PILOT STUDY
 AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE BEDSIDE QUANTIFICATION OF SPASTICITY: A PILOT STUDY T.A.T. Hughes 1, B.J. Western 2, M. Thomas 2, R.W.M. van Deursen 3, H. Griffiths 2 1 Department of Medicine (Neurology), University
AN INSTRUMENT FOR THE BEDSIDE QUANTIFICATION OF SPASTICITY: A PILOT STUDY T.A.T. Hughes 1, B.J. Western 2, M. Thomas 2, R.W.M. van Deursen 3, H. Griffiths 2 1 Department of Medicine (Neurology), University
Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work
 Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work RE: Baldwin ERL, Baldwin TD, Lancaster JS, et al. Neuromuscular electrical
Electrical stimulation for reducing trapezius muscle dysfunction in cancer patients: traditional treatment protocols also work RE: Baldwin ERL, Baldwin TD, Lancaster JS, et al. Neuromuscular electrical
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum
 American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
American Academy of Neurology Neuromuscular Section Resident Core Curriculum 10/03/01 1. Introduction: Neuromuscular disorders are a significant component of the diseases of the nervous system that neurologists
Biceps Activity EMG Pattern Recognition Using Neural Networks
 Biceps Activity EMG Pattern Recognition Using eural etworks K. Sundaraj University Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) School of Mechatronic Engineering 0600 Jejawi - Perlis MALAYSIA kenneth@unimap.edu.my Abstract:
Biceps Activity EMG Pattern Recognition Using eural etworks K. Sundaraj University Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) School of Mechatronic Engineering 0600 Jejawi - Perlis MALAYSIA kenneth@unimap.edu.my Abstract:
DEVELOPMENT OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM HDP1: Fall 2007 Joan Stiles Department of Cognitive Science University of California, San Diego Motor system development begins during the Prenatal period Thalamocortical
DEVELOPMENT OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM HDP1: Fall 2007 Joan Stiles Department of Cognitive Science University of California, San Diego Motor system development begins during the Prenatal period Thalamocortical
Muscle fatigue R. H. T. EDWARDS. B.Sc., Ph.D., M.B., M.R.C.P. the same observer or by different observers. A simple
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (March 1975) 51, 137-143. Muscle fatigue R. H. T. EDWARDS B.Sc., Ph.D., M.B., M.R.C.P. Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London Summary
Postgraduate Medical Journal (March 1975) 51, 137-143. Muscle fatigue R. H. T. EDWARDS B.Sc., Ph.D., M.B., M.R.C.P. Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London Summary
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs)
 Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the
Available online at Pelagia Research Library. European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):595-599 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Investigation of effects of imagery training on changes
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2014, 4(1):595-599 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Investigation of effects of imagery training on changes
Postgraduate Medical School, Du Cane Road, London W12 OHS, complete in a few minutes, but is not wholly so for many hours.
 J. Physiol. (1977), 272, pp. 769-778 769 With 7 text-fg'ure8 Printed in Great Britain FATIGUE OF LONG DURATION IN HUMAN SKELETAL MUSCLE AFTER EXERCISE BY R. H. T. EDWARDS,* D. K. HILL, D. A. JONES* AND
J. Physiol. (1977), 272, pp. 769-778 769 With 7 text-fg'ure8 Printed in Great Britain FATIGUE OF LONG DURATION IN HUMAN SKELETAL MUSCLE AFTER EXERCISE BY R. H. T. EDWARDS,* D. K. HILL, D. A. JONES* AND
Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper
 Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper Contract research for Actiweight AS by The Norwegian School of Sport Sciences 2016 Responsible: Tron Krosshaug,
Muscle Activation in strength training exercises with and without using the clip-on device Gripper Contract research for Actiweight AS by The Norwegian School of Sport Sciences 2016 Responsible: Tron Krosshaug,
Correlation of Electromyogram and Muscle Biopsy in Myopathy of Young Age
 780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
780 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Correlation of and Muscle Biopsy in of Young Age Jihoon Chang, MD, Yoon Ghil Park, MD, PhD, Young-chul Choi, MD, PhD, Jung Hwa Choi, MD, Jae Ho Moon, MD ABSTRACT. Chang JH, Park YG,
Parkinsonian rigidity
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Pyschiat., 1963, 26, 27 Studies on induced exacerbation of Parkinsonian rigidity The effect of contralateral voluntary activity KEIZO MATSUMOTO, FERDINAND ROSSMANN, TUNG HUI LIN,
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Pyschiat., 1963, 26, 27 Studies on induced exacerbation of Parkinsonian rigidity The effect of contralateral voluntary activity KEIZO MATSUMOTO, FERDINAND ROSSMANN, TUNG HUI LIN,
Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed. Elbow Room
 00 Elbow Room Free-motion elbow supports could be a key to reducing musculoskeletal disorders among dental hygienists. Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed and untreated injuries
00 Elbow Room Free-motion elbow supports could be a key to reducing musculoskeletal disorders among dental hygienists. Many dental hygiene professionals realize that undiagnosed and untreated injuries
Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Tuesday 5- Friday 8 May Clinical Neuroscience Lecture Theatre at 33 Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG PROGRAMME
 Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Tuesday 5- Friday 8 May 2015 Clinical Neuroscience Lecture Theatre at 33 Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG Day 1 Tuesday 5 May PROGRAMME 10:00 10:30 Registration* and coffee
Update in Neuromuscular Disorders Tuesday 5- Friday 8 May 2015 Clinical Neuroscience Lecture Theatre at 33 Queen Square, London WC1N 3BG Day 1 Tuesday 5 May PROGRAMME 10:00 10:30 Registration* and coffee
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
 ISO-INERTIAL MEASUREMENT OF MUSCULAR STRENGTH: AN ASSESSMENT ALTERNATIVE GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa INTRODUCTION Success in many
ISO-INERTIAL MEASUREMENT OF MUSCULAR STRENGTH: AN ASSESSMENT ALTERNATIVE GK Jane Division of Physical Education, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa INTRODUCTION Success in many
Original Article. MUNENORI KATOH, PT, PhD 1), YUKINOBU HIIRAGI, PT, PhD 2), MANABU UCHIDA, PT, PhD 3)
 Original Article Validity of Isometric Muscle Strength Measurements of the Lower Limbs Using a Handheld Dynamometer and Belt: a Comparison with an Isokinetic Dynamometer J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 23: 553 557,
Original Article Validity of Isometric Muscle Strength Measurements of the Lower Limbs Using a Handheld Dynamometer and Belt: a Comparison with an Isokinetic Dynamometer J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 23: 553 557,
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue
 Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Analysis of EMG and Biomechanical Features of Sports Aerobics Movements
 Analysis of EMG and Biomechanical Features of Sports Aerobics Movements Jingjing Wang* WuHan Sport University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430070, China *itrazyl@163.com Abstract To analyze electromyography (EMG) and
Analysis of EMG and Biomechanical Features of Sports Aerobics Movements Jingjing Wang* WuHan Sport University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430070, China *itrazyl@163.com Abstract To analyze electromyography (EMG) and
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular
 Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Is the Stimulation Frequency of the Repetitive Nerve Stimulation Test that You Choose Appropriate?
 186 Is the Stimulation Frequency of the Repetitive Nerve Stimulation Test that You Choose Appropriate? Yuan-Ting Sun and Thy-Sheng Lin Abstract- The repetitive nerve stimulation test (RNST) has been a
186 Is the Stimulation Frequency of the Repetitive Nerve Stimulation Test that You Choose Appropriate? Yuan-Ting Sun and Thy-Sheng Lin Abstract- The repetitive nerve stimulation test (RNST) has been a
Maturation of corticospinal tracts assessed by electromagnetic stimulation of the motor cortex
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 1347-1352 Maturation of corticospinal tracts assessed by electromagnetic stimulation of the motor cortex T H H G KOH AND J A EYRE Department of Child Health,
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 1347-1352 Maturation of corticospinal tracts assessed by electromagnetic stimulation of the motor cortex T H H G KOH AND J A EYRE Department of Child Health,
Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study
 Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Journal of Sport Rehabilitation, 1999, 8.50-59 O 1999 Human Kinetics Publishers, Inc. Can Muscle Power Be Estimated From Thigh Bulk Measurements? A Preliminary Study Eric Maylia, John A. Fairclough, Leonard
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19
 Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting. Individual
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting. Individual
Introduction to Electromyography (EMG) Hands-On Research School Shanghai Jiao Tong University Daniel Goldman, Sarah Sharpe, Nick Gravish
 Introduction to Electromyography (EMG) Hands-On Research School Shanghai Jiao Tong University Daniel Goldman, Sarah Sharpe, Nick Gravish Muscles: Motors of the human body Act to generate force and produce
Introduction to Electromyography (EMG) Hands-On Research School Shanghai Jiao Tong University Daniel Goldman, Sarah Sharpe, Nick Gravish Muscles: Motors of the human body Act to generate force and produce
Section: Critically Appraised Topic. Article Title: The Effect of Contralateral Exercise on Patient Pain and Range of Motion
 Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
Note: This article will be published in a forthcoming issue of the. The article appears here in its accepted, peer-reviewed form, as it was provided by the submitting author. It has not been copyedited,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) AND NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES (NCS)
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) AND NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES (NCS) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) AND NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES (NCS) Non-Discrimination Statement and Multi-Language Interpreter Services information are located at the end of this document. Coverage for services,
Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli
 Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli Julita Czarkowska-Bauch Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, 3 Pasteur St., 02-093 Warsaw, Poland Abstract. Influences
Variety of muscle responses to tactile stimuli Julita Czarkowska-Bauch Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, 3 Pasteur St., 02-093 Warsaw, Poland Abstract. Influences
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Skeletal Muscles and Functions
 Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Neurological Examination
 Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Neurological Examination Charles University in Prague 1st Medical Faculty and General University Hospital Neurological examination: Why important? clinical history taking and bedside examination: classical
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy
 Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
Test Bank for The Human Body in Health and Illness 4th Edition by Herlihy Chapter 9: Muscular System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following muscles is described as striated and involuntary?
UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM
 Hand Surgery, Vol. 13, No. 2 (2008) 79 83 World Scientific Publishing Company UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM Sebastián Axel Balan and Marc Garcia-Elias Institut
Hand Surgery, Vol. 13, No. 2 (2008) 79 83 World Scientific Publishing Company UTILITY OF THE POWERBALL IN THE INVIGORATION OF THE MUSCULATURE OF THE FOREARM Sebastián Axel Balan and Marc Garcia-Elias Institut
Impact of Demyelination Disease on Neuronal Networks
 Impact of Demyelination Disease on Neuronal Networks Sandeep Adem Chiyuan Chang Mark Fleming sadem@eng.ucsd.edu chc418@eng.ucsd.edu m3flemin@eng.ucsd.edu 1. Abstract Demyelination has a detrimental impact
Impact of Demyelination Disease on Neuronal Networks Sandeep Adem Chiyuan Chang Mark Fleming sadem@eng.ucsd.edu chc418@eng.ucsd.edu m3flemin@eng.ucsd.edu 1. Abstract Demyelination has a detrimental impact
REPRODUCIBILITY OF IEMG MEASUREMENTS ON THE M. TRICEPS BRACHII. Gernot Hering, Ewald Hennig and Hartmut J. Riehle
 Erschienen in: Biomechanics XI : XI. International Congress of Biomechanics / de Groot, Gert et al. (Hrsg.). - Amsterdam : Free Univ. Press, 1988. - S. 148-152. - ISBN 90-6256-679-0 REPRODUCIBILITY OF
Erschienen in: Biomechanics XI : XI. International Congress of Biomechanics / de Groot, Gert et al. (Hrsg.). - Amsterdam : Free Univ. Press, 1988. - S. 148-152. - ISBN 90-6256-679-0 REPRODUCIBILITY OF
PHYSICAL TRAINING INSTRUCTORS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5. Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1. Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3
 TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM
 Throwers Shoulder Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The throwers ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing.
Throwers Shoulder Home Exercise Program Clayton W. Nuelle, MD THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The throwers ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing.
Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1977, 40, 982-986 Median-ulnar nerve communications and carpal tunnel syndrome LUDWIG GUTMANN From the Department of Neurology, West Virginia University,
Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair
 Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Suturing of tears within the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle). Massive RCR usually involve more than the supraspinatus. b. May be done arthroscopically
Large/Massive Rotator Cuff Repair 1. Defined a. Suturing of tears within the rotator cuff (most commonly supraspinatus muscle). Massive RCR usually involve more than the supraspinatus. b. May be done arthroscopically
Toning Balls. Includes 15 Exercises:
 Toning Balls Includes 15 Exercises: p.2 Hundred p.2 Half Roll Back p.2 Ab Prep p.3 Single Leg Stretch p.3 Rolling Like a Ball p.3 Breast Stroke Prep p.4 Ab Prep with Biceps p.4 Obliques Roll Back p.4 Obliques
Toning Balls Includes 15 Exercises: p.2 Hundred p.2 Half Roll Back p.2 Ab Prep p.3 Single Leg Stretch p.3 Rolling Like a Ball p.3 Breast Stroke Prep p.4 Ab Prep with Biceps p.4 Obliques Roll Back p.4 Obliques
Social recovery during the year following severe head injury
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 798-802 Social recovery during the year following severe head injury MICHAEL ODDY AND MICHAEL HUMPHREY From St Francis Hospital, Haywards Heath,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1980, 43, 798-802 Social recovery during the year following severe head injury MICHAEL ODDY AND MICHAEL HUMPHREY From St Francis Hospital, Haywards Heath,
Assessment Form Post Polio Syndrome and Late Effects of Polio
 FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
FULL NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: PHONE NUMBER: CURRENT HOME ADDRESS: EMAIL ADDRESS: THERAPIST: REFERRAL SOURCE: CURRENT GP: NEXT OF KIN: ACC/NHI NUMBER: PATIENT GOALS OF TODAY S ASSESSMENT: MAIN PROBLEMS PATIENT
THROWER S TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM David Andrew Parker, MD
 THROWER S TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM David Andrew Parker, MD The thrower s ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing. The program s goal is to be an
THROWER S TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM David Andrew Parker, MD The thrower s ten exercise program has been designed to exercise the major muscles necessary to return to throwing. The program s goal is to be an
Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1981, 44, 419-425 Chronic focal polymyositis in the adult N E BHARUCHA AND J A MORGAN-HUGHES From the Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London S
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017
 Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases. Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2)
 Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2) ITIS d. o. o. Ljubljana, Center for Implantable Technology
Evaluation of the Torque Developed by the Elbow Flexors in Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases Janez Rozman, Matjaž Bunc (1) and Anton Zupan (2) ITIS d. o. o. Ljubljana, Center for Implantable Technology
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand)
 MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
Muscle Function Analysis
 Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation. Part I Curriculum & Weights
 American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
American Board of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Part I Curriculum & Weights Neurologic Disorders 30% Stroke Spinal Cord Injury Traumatic Brain Injury Neuropathies a) Mononeuropathies b) Polyneuropathies
