Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs)
|
|
|
- Darren Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 5: Electromyograms (EMGs) Overview A motorneuron and all the muscle fibers that it innervates is known as a motor unit. Under normal circumstances, a neuronal action potential activates all of the muscle fibers in the motor unit. This activation process involves a muscular action potential and a contraction of the muscle fibers. During a contraction, there is synchronous activity in a number of fibers in the same muscle. The electrical signal recorded from a contracting muscle is called an electromyogram or EMG. As in the electrocardiogram (ECG), this activity can be detected by electrodes placed on the skin. A muscle contraction is produced by multiple action potentials in multiple fibers. Therefore, the EMG is not a series of predictable waves like those of the ECG, but a burst of spike-like signals. Integrating this complex signal will give an indication of the intensity of muscle activity during a contraction. Clinically, recording of EMGs is very important to detect the cause of motor unit diseases. The motor unit has four functional components: the motoneuron, the axon of the motoneuron, the neuromuscular junction and the muscle cells innervated by the motoneuron. Recording of the EMG may help determine whether a motor unit disease is due to injury of the nerve or the muscle. Thus, motoneuron injuries are characterized by spontaneous activity at rest (also known as fibrillations or spontaneous activity in single muscle fibers), and reduced spike amplitude during maximal contraction. These features are absent following muscle injuries (like muscular dystrophies and myotonia). Nerve injuries resulting from demyelination generate a significant slow down in the conduction velocity of electrical signals in a nerve and can be detected by EMG. In this lab you will record EMGs from arm muscles and examine recruitment, tetanus and temporal motor activity of antagonistic muscle groups. Equipment Required PC computer iworx/214 and USB cable AAMI cable and five EMG leads Alcohol swabs Notice: During the following experiments the person being tested can not look at the computer screen! Equipment Setup 1 Connect the iworx/214 unit to the computer. 2 The volunteer should remove all jewelry from their wrists and ankles. 3 Use an alcohol swab to clean and scrub three regions on the left forearm for electrode attachment (Figure 3-15). One area is near the wrist, the second is in the middle of the forearm, and the third area is about 2 inches from the elbow. Let the areas dry.
2 4 Remove the plastic disk from a disposable electrode and apply it to one of the scrubbed areas. Repeat for the other two areas. 5 Attach the AAMI connector on one end of the cable to the isolated Channel 1 and 2 inputs on the iworx/214 unit. 6 Attach three color-coded electrode cables to the ground and Channel 1 inputs on the lead pedestal and snap the other ends onto the disposable electrodes, so that: the red +1 lead is attached to the electrode near the elbow the black -1 lead is attached to the electrode in the middle of the forearm. the green C lead (the ground) is attached to the electrode on the wrist. 7 The volunteer should hold a small object (like the bulb of the hand dynamometer) in their right hand. Figure 3-15: The equipment used to monitor EMGs from a volunteer. Start the Software 1 Click the Windows Start menu, move the cursor to Programs and then to the iworx folder and select LabScribe; or click on the LabScribe icon on the Desktop 2 When the program opens, select Load Group from the Settings menu. 3 When the dialog box appears, select ahk214.iws and then click Load. 4 Click on the Settings menu again and select the EMG-214 settings file. 5 After a short time, LabScribe will appear on the computer screen as configured by the EMG-214 settings. Exercise 1: Recruitment and the EMG Aim: To examine the EMG when more fibers are recruited into a single twitch. Procedure 1 Click Start. The subject should hold a ball in their hand. Squeeze the ball using a
3 single, brief twitch of your fingers. Click Stop. 2 Click the AutoScale buttons for the EMG (CH 1) and EMG Integral (CH 2) channels. Examine the recording; it should be similar to Figure Figure 3-16: The EMG (upper trace) and the integral (lower trace) recorded during three increasing finger movements. The data are displayed in the Analysis window and the two cursors are positioned to measure the amplitude of the second integrated response. 3 Click Start, Type EMG and Increasing Twitches in the comment line to the right of the Marks button. Press the Enter key on the keyboard. 4 Record EMGs from a series of single twitches that begin with a gentle contraction and gradually increase in intensity until a maximum response is attained. Press the Enter key on the keyboard, when each contraction occurs. Click Stop to halt recording. 5 Select Save As in the File menu, type a name for the file. Choose a desti-nation on the computer in which to save the file(e.g. the iworx or class folder). Click the Save button to save the file (as an *.iwd file). Data Analysis 1 Scroll the data on the Main window until the first twitch of the series is positioned in the center of the screen. 2 Click the 2-Cursor icon (Figure 3-17), so that two blue vertical lines appear over the recording window. 3 Drag the lines to the left and right so that the twitch is between the two blue lines. 4 Click the Analysis icon (Figure 3-17) to open the Analysis window. 5 Display only the EMG Integral (CH 2) by clicking and deselecting Channel 1 (EMG) in Display Channel list, on the left side of the Analysis window.
4 Figure 3-17: The LabScribe toolbar. 6 Use the mouse to click and drag one cursor to the baseline, prior to the first response, and the second cursor to the peak of the integrated response (Figure 3-18). 7 Select Title and V2-V1 from the Table Functions list on the left side of the Analysis window. This data can be entered into the Journal by either typing the titles and values directly or by using the right-click menu. Place the cursors to take measurements; then, select Add Title to Journal or Add Data to Journal from the right click menu to add the measurements to the Journal.Repeat for all responses. 8 Measure the amplitudes of the other twitch integrals in the series and record their values in the Journal. Questions 1 Is there a correlation between the amplitude of the integrated EMG signal and the amount of contraction? 2 Look at your data. Is the duration (length) of each integrated signal about the same for each contraction? If not, this would indicate that some fibers are contracting more than once because they were stimulated by more than a single action potential in the motorneurons. 3 How do you explain the increase in the amplitude of the integrated EMG signal with an increase in contraction? Hint: If a contraction involves a single twitch of the contracting muscle fibers, how can the contraction amplitude be increased without making the muscle fibers twitch more than once? Exercise 2: Maximum Finger Contraction Aim: To measure the EMG when the fingers are squeezed hard. Procedure 1 Click Start. Type Hard Squeeze. in the comment line to the right of the Marks button. 2 Ask the subject to squeeze the ball in their hand as hard as they can. Press the Enter key on the keyboard. Have the subject relax their hand. 3 Click Stop to halt recording.
5 4 Select Save in the File menu. Figure 3-18: An EMG (upper trace) and the integral (lower trace) recorded during a maximum contraction. The data are displayed in the Analysis window and the two cursors are positioned to measure the amplitude of the integrated response. Data Analysis Your EMG data should like Figure Click the 2-Cursor icon (Figure 3-17), so that two blue vertical lines appear over the recording window. 2 Drag the lines to the left and right so that the whole contraction is between the two blue lines. 3 Click the Analysis icon (Figure 3-17) to open the Analysis window. 4 Select EMG integral from the Value from Ch menu. Select Title, V2-V1, and T2-T1 from the Table Functions list. 5 Use the mouse to click and drag: one cursor to the baseline, prior to the contraction, and the second cursor on the peak of the integral on Channel 2 (EMG Integral) to measure the amplitude of the contraction (V2-V1). one cursor to the beginning and the other to the end of the EMG trace recorded on Channel 1 (EMG) to measure the contraction time (T2-T1). 6 This data can be entered into the Journal by either typing the titles and values directly or by using the right-click menu. Place the cursors to take measurements; then, select Add Title to Journal or Add Data to Journal from the right click menu to add the measurements to the Journal. 7 Also, measure V2-V1 and T2-T1for the largest single twitch recorded in the previous exercise.
6 Questions 1 Using the EMG Integral data, compare the amplitude of the maximum (hard) squeeze with the maximum single twitch. Which is larger? 2 If all fibers were contracting in both instances (maximum squeeze and maximum single twitch) explain why the maximum squeeze produced a larger contraction. 3 Compare the duration of this maximum squeeze with the maximum single twitch. Which is longer? 4 How does the amplitude of the EMG Integral correlate to the duration of the contraction? Hint: During the second exercise do you think each motor axon fired only once to produce the maximum squeeze? Does the level of intracellular calcium return to normal immediately after a contraction? Exercise 3: Tetanus and Movement Aim: To examine the relationship between tetanus and movement. Procedure 1 Place recording electrodeson the left biceps as shown in Figure the red +1 lead is attached to the electrode just below the shoulder. the black -1 lead is attached to the electrode in the middle of the biceps. the green C lead is attached to the electrode just above the elbow. 2 Ask the subject to sit on a chair and support their left elbow with their right hand. Place your left hand over the bench top with the palm facing up. Place a heavy book on top of the hand. 3 Click Start. Type Tetanus in the comment line to the right of the Marks button. 4 Ask the subject to flex their left arm against the weight of the book. 5 Press the Enter key on the keyboard. Figure 3-19: The equipment used to monitor EMGs from the biceps muscle of a volunteer.
7 6 After 15 seconds of hard flexing ask the volunteer to stop, extend their arm and relax (the right hand should still support the left elbow). 7 Click Stop to halt recording. 8 Select Save in the File menu. Questions 1 When the lower arm was bent toward the shoulder, was the biceps muscle contracting or relaxing? 2 Does myogram activity in the biceps muscle occur during flexion or extension? 3 How does the lower arm move in the absence of significant EMG activity in the biceps? Exercise 4: Integration of motor activity Aim: To study activity in antagonistic muscles during normal movement. Procedure 1 Place another pair of recording electrodes on the left triceps, so that : the white +2 lead is placed on the upper portion of the triceps. the brown -2 lead is placed in the middle of the triceps. 2 Go to the Settings menu and select. EMG-OpposingMuscles-214. LabScribe will be configured to record EMGs from the biceps and the triceps on Channels 1 and 2, respectively, and their respective EMG Integrals on Channels 3 and 4. 3 Ask the volunteer to stand up. 4 Click Start. Type No Weight in the comment line to the right of the Mark button, and press the Enter key on the keyboard. 5 Ask the volunteer to bend and extend their arm slowly. Type Bend and press the Enter key every time they bend their arm. 6 Click Stop to halt recording 7 Repeat the experiment, while the volunteer try to move the arms against the weight of another person. For this purpose ask the volunteer to try to flex the arm against another person holding his wrist. 8 Click Start. Type Weight on the comment line to the right of the Mark button, and press the Enter key to annotate the record. 9 Ask the volunteer to try to contract the arm against the person holding his wrist.
8 10 Click Stop to halt recording. 11 Select Save in the File menu. 12 Repeat while the volunteer try to push down the arm against the person holding his wrist. Questions: Look at your data: 1 Where do you see myogram activity when the arm is extended away from the shoulder? When the arm is flexed? 2 Does EMG activity increase or decrease when more weight is moved? What is the relationship between motorneuron activity, EMGs, muscle performance, and work? 3 If the weight is held at arm s length, does EMG activity increase, decrease, or remain constant for the duration of the experiment? 4 Why would muscle activity increase if the load being moved is constant?
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Background The arterial system functions as a pressure reservoir. Blood enters via the heart and exits through the capillaries.
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling
 Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
Experiment HM-11: Electromyograms (EMG) for Paired Arm Wrestling Background The movement of parts of the body is accomplished through a system of levers composed of skeletal muscles and bones. In a lever,
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation
 Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
Experiment HH-3: Exercise, the Electrocardiogram, and Peripheral Circulation Exercise 1: The ECG and the Pulse in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure and correlate the ECG and the pulse in a resting individual.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity
 Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HC-3: Pulse Wave Velocity Exercise 1: The Pulse Wave Velocity at Rest Aim: To measure the pulse wave velocity in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion
 Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
Experiment HM-7: Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Antagonistic Muscles and Range of Motion Exercise 1: Antagonistic Muscles in Forearm Aim: To study the EMG activity in muscles that work in opposition
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds
 Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
Experiment HH-2: The Electrocardiogram and Heart Sounds Exercise 1: The ECG in a Resting Subject Aim: To measure the ECG in a resting individual. Procedure 1. Click on the Record button, located on the
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Experiment HP-7: Hypothesis-driven Biofeedback Lab/Research Study What is Biofeedback? Biofeedback is a technique that people can use to learn to control their body's physiological functions. The definition
Warning: Avoid putting the tip of the syringe needle too deeply into the hole to avoid damage to the heart tissue.
 Experiment AM-12: Crayfish Electrocardiogram (ECG) Exercise 1: The Crayfish ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record the electrical trace (ECG) produced by the contraction of a resting heart, and to determine
Experiment AM-12: Crayfish Electrocardiogram (ECG) Exercise 1: The Crayfish ECG and Heart Rate Aim: To record the electrical trace (ECG) produced by the contraction of a resting heart, and to determine
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography
 Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
Exercise 5: Muscle Physiology I - Electromyography Readings: Silverthorn, 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 Your brain communicates with your muscles through action potentials on the motor neurons, which are then transmitted
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors
 Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Experiment AN-5: Cockroach Leg Mechanoreceptors Exercise 1: Chordotonal Organs Aim: To explore the basic characteristics of the chordotonal organs, their response to direction and intensity of leg movement,
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm
 Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Experiment HP-13: The Gaze Cue Paradigm Background During almost all social interactions, people s eyes convey information about their direction of attention as well as their emotional and mental status.
Exercise 2: Effects of Cold Temperature Aim: To record changes in heart rate after the heart is bathed in cold Ringer s solution.
 Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
Experiment AM-3: Heart Muscle Warning: The heart preparation used in this experiment is functional for a limited period of time. If the muscle is bathed periodically in Ringer s solution, it will work
Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography
 7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Exercise 1: Six Lead ECG from Resting Subject Aim: To record a Six Lead ECG from a resting subject and determine the QRS axis of the subject s heart. Procedure
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position
 Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Experiment HC-1: Blood Pressure, Peripheral Circulation, and Body Position Exercise 1: Blood Pressures from the Left Arm Aim: To determine the systolic and diastolic blood pressures in a reclining subject,
Figure HN-5-L1: The Sequence menu containing the preprogramming light sequences used in this experiment.
 HN-5: Visual Reflexes and Color Stimulation Exercise 1: Reaction Time and Single Color Visual Cues Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject to:
HN-5: Visual Reflexes and Color Stimulation Exercise 1: Reaction Time and Single Color Visual Cues Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject to:
Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study
 Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study Equipment Required PC or Mac Computer IXTA, USB cable and power supply iwire-b3g cable and EEG leads Reusable Gold-Cup EEG Electrodes
Experiment HP-28: Control of EEG and Biofeedback Lab/Research Study Equipment Required PC or Mac Computer IXTA, USB cable and power supply iwire-b3g cable and EEG leads Reusable Gold-Cup EEG Electrodes
Electromyography (EMG)
 Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
Introduction In this laboratory, you will explore the electrical activity of skeletal muscle by recording an electromyogram (EMG) from a volunteer. You will examine the EMG of both voluntary and evoked
Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand.
 Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
Experiment HN-4: Hand vs. Foot Reactions Exercise 1: Eye-Hand Reaction Times Aim: To measure the reaction time of a subject to a visual cue when responding with the hand. Procedure 1. Instruct the subject
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Red Light - Green Light
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HN-9 Red Light - Green Light Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HN-9 Red Light - Green Light Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease
 Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
ECE ECE PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
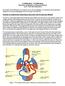 ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
ECE0909.404.01 ECE 0909.504.03 PRINCIPLES OF BIOMEDICAL SYSTEMS & DEVICES LAB 1 - ELECTROCARDIOGRAM The purpose of this laboratory is to introduce you to electrocardiogram, its acquisition and interpretation.
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002
 1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
1724 Lab: Frog Skeletal Muscle Physiology (Marieb Exercise 16A) Marieb/iWorx / Ziser, 2002 I. Introduction. Read the introductory material in your lab manual Marieb Ex 16A: Skeletal Muscle Physiology Frog
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output
 Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Experiment HC-5: Body Position, Exercise, and Cardiac Output Exercise 1: Cardiac Output While Reclining Aim: To determine the cardiac output of a subject through the measurement of blood pressures and
Posner s Attention Test
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-18 Posner s Attention Test Background Setup Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User
The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HP-17 The Gaze Cueing Paradigm with Eye Tracking Background Set-up Lab Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Manual Revision PL3.7.0 080706 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Evaluation copy. EMG and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
BP-600 Noninvasive Blood Pressure Sensor
 Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Technical Note BP-600 Overview A person's cardiac output, peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure, and other cardiovascular parameters change in response to the activities and events taking place
Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue
 Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Physiology Lessons for use with the PC running Windows 98SE, Me, 2000 Pro, XP Pro/Home/Media Lesson 2 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY II Motor unit recruitment Fatigue Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 080706 Richard Pflanzer,
Lab #9: Muscle Physiology
 Background Overview of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Sarcomere Thick Filaments Skeletal muscle fibers are very large, elongated cells (Fig 9.1). Roughly 80% of the content of each muscle fiber consists of
Background Overview of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Sarcomere Thick Filaments Skeletal muscle fibers are very large, elongated cells (Fig 9.1). Roughly 80% of the content of each muscle fiber consists of
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor
 Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
Experiment HP-6: Cynicism/Hostility and the Hot Reactor Exercise 1: Baseline Heart Rate and Blood Pressure Aim: To determine the resting heart rate and blood pressure of the subject. Procedure 1. Select
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 2 EMG 2 Electromyography: Mechanical Work PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 5.23.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42
Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles
 Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Lab written in conjunction with: Kelly Helm PhD, Director Exercise Science, Department of Kinesiology; Amanda Ulin & Kelsey
Experiment HM-5: Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Lab written in conjunction with: Kelly Helm PhD, Director Exercise Science, Department of Kinesiology; Amanda Ulin & Kelsey
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab. Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 1 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY I Standard and Integrated EMG Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School of Medicine
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
Experiment HE-12: Targeted Exercise with Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Get Your Cardio On Preparations for this experiment need to be reviewed with the students in advance. There will be exercise routines
Electromyography II Laboratory (Hand Dynamometer Transducer)
 (Hand Dynamometer Transducer) Introduction As described in the Electromyography I laboratory session, electromyography (EMG) is an electrical signal that can be recorded with electrodes placed on the surface
(Hand Dynamometer Transducer) Introduction As described in the Electromyography I laboratory session, electromyography (EMG) is an electrical signal that can be recorded with electrodes placed on the surface
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 5 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) I Procedure Rev. 07112013 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University School
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
FT-302 Force Transducer
 Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Technical Note FT-302 LabScribe is a trademark of 2015 Overview The FT-302 is a high-sensitivity dual-range research grade force transducer designed to measure forces in the 0.005 to 10 gram and 0 to 100
Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HM-9 Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HM-9 Kinesiology and Electromyogram (EMG) Activity in Targeted Muscles Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials
 Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials Exercise 1: Impaling Muscle Fibers Aim: To measure the membrane potentials in different muscle fibers. Procedure 1. Look through the microscope; you should see the
Experiment AN-1: Membrane Potentials Exercise 1: Impaling Muscle Fibers Aim: To measure the membrane potentials in different muscle fibers. Procedure 1. Look through the microscope; you should see the
Muscle Function Analysis
 Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Overview Active Learning
 : EMG Active Learning Updated 01-06-11 This lesson is based on a presentation given by Dr. Jennifer Lundmark and Ms. Andrea Salmi at the HAPS Conference, Maui, HI, June 2-7, 2001 Overview Active Learning
: EMG Active Learning Updated 01-06-11 This lesson is based on a presentation given by Dr. Jennifer Lundmark and Ms. Andrea Salmi at the HAPS Conference, Maui, HI, June 2-7, 2001 Overview Active Learning
Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation
 Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
Exercise 6: Muscle Physiology II Twitch & Summation Text Reading: Silverthorn, 5 th ed. 412 419, 425 427; 6 th ed. pg. 410 420 In this exercise, we will investigate the physiology of contraction in the
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Humans make voluntary decisions to talk, walk, stand up, or sit down. The
 2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define motor unit, twitch, latent period, contraction phase, relaxation phase, threshold, summation, tetanus, fatigue, isometric contraction,
2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define motor unit, twitch, latent period, contraction phase, relaxation phase, threshold, summation, tetanus, fatigue, isometric contraction,
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Lab 8b: Electrical activity of muscular contractions
 Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
EQA DISCUSSION QUESTIONS: INFLUENCE OF MUSCLE FIBER TYPE ON MUSCLE CONTRACTION. Influence of Muscle Fiber Type on Muscle Contraction
 0907T_c13_205-218.qxd 1/25/05 11:05 Page 209 EXERCISE 13 CONTRACTION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE 209 Aerobic cellular respiration produces ATP slowly, but can produce large amounts of ATP over time if there is
0907T_c13_205-218.qxd 1/25/05 11:05 Page 209 EXERCISE 13 CONTRACTION OF SKELETAL MUSCLE 209 Aerobic cellular respiration produces ATP slowly, but can produce large amounts of ATP over time if there is
BC1002 Module 1. Biol BC1002, Spring semester 2005, Module 1, Lab 1-1
 BC1002 Module 1 Biol BC1002, Spring semester 2005, Module 1, Lab 1-1 MODULE 1: LAB 1 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Spring semester 2005, Week of January 24-28. Learning objectives to learn the microscopic structure
BC1002 Module 1 Biol BC1002, Spring semester 2005, Module 1, Lab 1-1 MODULE 1: LAB 1 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Spring semester 2005, Week of January 24-28. Learning objectives to learn the microscopic structure
BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject
 Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Updated 12-22-03 BSL PRO Lesson H03: Nerve Conduction Velocity: Along the Ulnar Nerve of a Human Subject This PRO lesson describes hardware and software setup of the BSL PRO System to record and measure
Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. J.C. Uyehara, Ph.D. William McMullen David Pittman, Ph.D. Manual Revision PL3.7.0 M3.0.6 Modified by David Pittman
 ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
ELECTROMYOGRAPHY (EMG) Laboratory Motor unit recruitment & Fatigue Comparison of dominant versus non-dominant arm using a within subject repeated measures statistical analysis Written by: Richard Pflanzer,
Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol
 Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
Skeletal muscles are composed of hundreds to thousands of individual cells,
 2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define these terms used in describing muscle physiology: multiple motor unit summation, maximal stimulus, treppe, wave summation,
2 E X E R C I S E Skeletal Muscle Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define these terms used in describing muscle physiology: multiple motor unit summation, maximal stimulus, treppe, wave summation,
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure
 Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Zool 430L Protocols Page 8 of 12 Protocol 4: Measuring Blood Pressure 4.1 Via Auscultation (listening through stethoscope) The estimate of blood pressure is obtained by cutting off blood flow with a known
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) II Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
OpenSim Tutorial #2 Simulation and Analysis of a Tendon Transfer Surgery
 OpenSim Tutorial #2 Simulation and Analysis of a Tendon Transfer Surgery Laboratory Developers: Scott Delp, Wendy Murray, Samuel Hamner Neuromuscular Biomechanics Laboratory Stanford University I. OBJECTIVES
OpenSim Tutorial #2 Simulation and Analysis of a Tendon Transfer Surgery Laboratory Developers: Scott Delp, Wendy Murray, Samuel Hamner Neuromuscular Biomechanics Laboratory Stanford University I. OBJECTIVES
Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise
 iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HE-1 Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User Area
iworx Physiology Lab Experiment Experiment HE-1 Metabolic and Thermal Response to Exercise Note: The lab presented here is intended for evaluation purposes only. iworx users should refer to the User Area
Biology 325 Fall 2003 Human anatomy and physiology
 SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
SKELETAL MUSCLE PROPERTIES Background : In this experiment, you will investigate the physiological properties of skeletal muscle from the isolated amphibian gastrocnemius. You will examine skeletal muscle
iworx Sample Lab Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor
 Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor Background Animals use their senses to gather information about their environment. Most senses use specialized sensory organs (eyes, ears, nares) to receive
Experiment AN-10: Crustacean Stretch Receptor Background Animals use their senses to gather information about their environment. Most senses use specialized sensory organs (eyes, ears, nares) to receive
Each student should record the ECG of one of the members of the lab group and have their own ECG recorded.
 EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
When Technology Strikes Back!
 When Technology Strikes Back! Suffering from thumb or wrist pain from chronic texting? Many tech-savvy individuals have felt the side-effects of texting, typing, or web browsing. This is the pain you get
When Technology Strikes Back! Suffering from thumb or wrist pain from chronic texting? Many tech-savvy individuals have felt the side-effects of texting, typing, or web browsing. This is the pain you get
Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure. Rev
 42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117 www.biopac.com Biopac Student Lab Lesson 20 SPINAL CORD REFLEXES Analysis Procedure Rev. 12292017 Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D. Associate Professor Emeritus Indiana University
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Resistance Training Program
 Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Name: Resistance Training Program How to do Resistance Training: Warm up for 5 minutes before resistance training e.g., walk or cycle slowly o Avoid stretching before resistance training Do all exercises
Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 10 Aerobic Exercise Physiology PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 12.19.2005 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19
 Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting. Individual
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue JB19 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting. Individual
Bod-eComm A/WL Owners Manual
 Appearance and Part Names Bod-eComm A/WL Owners Manual Interface Box Light Wand AC Adapter Optical Standard Light Shield RS-232 Cable RS-232 Cable Biceps Locator Fitness Wheel The Bod-eComm A/WL should
Appearance and Part Names Bod-eComm A/WL Owners Manual Interface Box Light Wand AC Adapter Optical Standard Light Shield RS-232 Cable RS-232 Cable Biceps Locator Fitness Wheel The Bod-eComm A/WL should
Monster Walk Stand with your feet slightly closer than shoulder-width apart in an athletic stance. Loop an elastic band around your ankles.
 Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
Starting a Strength Training Program
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Starting a Strength Training Program About This Kit The key to improving strength is applying resistance to the muscle
1. Abs Triangle of Control Muscle: Upper abdominals Resistance: Body weight Body Connection: Legs
 Program C1 Chest and Shoulders 1. Abs Muscle: Upper abdominals Resistance: Body weight Lie flat with legs hooked through upper bench, adjusted so that the knees and hips are at 90 degrees. Extend arms
Program C1 Chest and Shoulders 1. Abs Muscle: Upper abdominals Resistance: Body weight Lie flat with legs hooked through upper bench, adjusted so that the knees and hips are at 90 degrees. Extend arms
The Muscular System. Muscles are. There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood
 The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating
 Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating This iworx lab experiment was graciously provided by Dr. Paul Wagner and Dr. Tracy Wagner, Asst. Professors, Washburn University,
Experiment HP-4: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Investigation into Cheating This iworx lab experiment was graciously provided by Dr. Paul Wagner and Dr. Tracy Wagner, Asst. Professors, Washburn University,
Muscle Size & Strength
 Muscle Size & Strength 1 Name Muscle Size & Strength PURPOSE: To compare muscle size and strength MATERIALS: Tape measure Bathroom scale PROCEDURE: Part 1 Measuring the size of your muscles: 1. Work with
Muscle Size & Strength 1 Name Muscle Size & Strength PURPOSE: To compare muscle size and strength MATERIALS: Tape measure Bathroom scale PROCEDURE: Part 1 Measuring the size of your muscles: 1. Work with
Dumbbell Bent Over Lateral Rear Delt Raises / Flyes. These are harder than they look! Start with 5lbs (it will feel easy) up to 10lbs week 2.
 Arms(1) Arms, Chest, AP AT P. Begin with 15-20min cardio (any machine). Bosu Ball Chest Dumbbell Press Dumbbell Bent Over Lateral Rear Delt Raises / Flyes Dumbbell Overhead Shoulder Press 2 sets 15 reps
Arms(1) Arms, Chest, AP AT P. Begin with 15-20min cardio (any machine). Bosu Ball Chest Dumbbell Press Dumbbell Bent Over Lateral Rear Delt Raises / Flyes Dumbbell Overhead Shoulder Press 2 sets 15 reps
Osteoporosis Protocol
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Workout 1 Workout 2 Workout 1 Workout 2 Rest Workout 1 Rest
 60 Day Workout Plan 1 Workout Schedule Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Workout 1 Workout 2 Workout 1 Workout 2 Rest Workout 1 Rest Summary of workouts Workout 1 Workout 2 1. Cardiovascular-Walking/Jogging
60 Day Workout Plan 1 Workout Schedule Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7 Workout 1 Workout 2 Workout 1 Workout 2 Rest Workout 1 Rest Summary of workouts Workout 1 Workout 2 1. Cardiovascular-Walking/Jogging
Overview. Page 1 of 9. Impedance Cardiography
 Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Updated 05.14.10 BSL PRO Lesson H21: Impedance Cardiography Data collected from a subject using the referenced set-up procedure. Note that dz/dt maximum is determined on a cycle by cycle basis from the
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important?
 Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Operation Overhaul: January Challenge
 Name: Operation Overhaul: January Challenge STRENGTH TRAINING You will focus on challenging all muscle groups and increasing muscle mass, for upper or lower body strength. You may use weights or bands
Name: Operation Overhaul: January Challenge STRENGTH TRAINING You will focus on challenging all muscle groups and increasing muscle mass, for upper or lower body strength. You may use weights or bands
Evaluation copy. Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Computer 17 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting.
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Computer 17 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting.
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion
 Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion What is a GSR? The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) is one of several electrodermal responses (EDRs). EDRs are changes in the electrical properties
Experiment HP-1: The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) and Emotion What is a GSR? The Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) is one of several electrodermal responses (EDRs). EDRs are changes in the electrical properties
EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189
 imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Student Lab Lesson 6 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY II Bipolar Leads (Leads I, II, III) Einthoven s Law Mean Electrical Axis on the Frontal Plane Richard Pflanzer, Ph.D.
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
TPW 's Upper Back Menu
 TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab 11: Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab report due April 17 th
 BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
#4 Cardiovascular I The Heart & EKG
 #4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
#4 Cardiovascular I Objectives: Identify a list of human heart structures using a virtual human dissection Dissect a sheep heart to identify external and internal structures Identify a list of human heart
Strength and Balance Exercises
 Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
Strength and Balance Exercises LEG EXTENSIONS Purpose: Strengthen the thigh and leg muscles. Starting Position: Sit tall with your feet flat on floor, shoulderwidth apart. You may hold onto the sides of
3 DAY GYM TRAINING PROGRAM. Author: Holly Expert
 3 DAY GYM TRAINING PROGRAM Author: Holly Louise #thefitpharmacist @thefitpharmacist_ @bodyscience Expert 3 DAY GYM TRAINING PROGRAM Your program has been designed to be followed for 8-12 weeks. You will
3 DAY GYM TRAINING PROGRAM Author: Holly Louise #thefitpharmacist @thefitpharmacist_ @bodyscience Expert 3 DAY GYM TRAINING PROGRAM Your program has been designed to be followed for 8-12 weeks. You will
Home Therapy Program Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)
 Benjamin W. Sears, MD Home Therapy Program Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) PHASE 1 Goals: decrease inflammation and pain and promote tissue healing, the RICE principle: Rest - avoid further overuse,
Benjamin W. Sears, MD Home Therapy Program Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) PHASE 1 Goals: decrease inflammation and pain and promote tissue healing, the RICE principle: Rest - avoid further overuse,
