A study of Adenoid Facies: Clinicoradiological correlation and its sequalae
|
|
|
- Shannon Oswin Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Research Article A study of Adenoid Facies: Clinicoradiological correlation and its sequalae Rahul 1, Shubhankur Gupta 2*, Anil Pandey 2, Khushboo Jain 3 1 Senior Resident, Department of ENT, Vivekanand Hospital, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India 2 Senior Resident, Department of ENT, AIIMS Rishikesh, India 3 NSCB Medical College, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India * Corresponding author shubhankur1407@gmail.com International Archives of Integrated Medicine, Vol. 3, Issue 10, October, Copy right 2016, IAIM, All Rights Reserved. Available online at ISSN: (P) ISSN: (O) Received on: Accepted on: Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None declared. How to cite this article: Rahul, Gupta S, Pandey A, Jain K. A study of Adenoid Facies: Clinicoradiological correlation and its sequalae. IAIM, Abstract Introduction: This study aimed to clinically correlate adenoid facies with various clinical features related to ear, nose and throat and to broadly study the various sequelae of adenoid hypertrophy on the physical, mental as well as the social conditioning of children. Materials and methods: After taking approval of the institutional ethics committee the study was carried out in the department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College and Hospital, Jabalpur from January 2012 till December Patients who presented to the outpatient clinic or were admitted in the indoor ward with adenoid facies were included in the study. After detailed history taking and clinical examination, data was analysed with appropriate statistical methods. Results: 30 patients with adenoid facies of varying degrees were included in the study. Nasal block was the most commonly presenting symptom. Pain in throat was complained of by 66.66% of cases. In 50% of cases the parents complained of irregular dentition. Decreased airflow upon functional examination of the nose was seen to be bilateral in majority of cases. A hitched upper lip was found in 100% of cases. High arched palate was seen in all cases, grade III tonsil enlargement was seen in 63.33% cases while grade II tonsil enlargement was seen in 30%. It was seen that mastoid pneumatization was affected by adenoids, being partial cellular in 48.33% of the cases and sclerosed in 18.33% ears. Conclusions: This study concluded that adenoids affect each part of ear nose and throat system, thus its effect can actually be quite devastating in growing children. Key words Adenoids, Outcomes, Nasal obstruction, Nasopharyngeal. Page 87
2 Introduction Adenoid is a collection of lymphoid tissue in the mucous membrane overlying the basisphenoid area. It has an oblong shape, similar to that of a truncated pyramid. It in fact virtually hangs from the roof of the nasopharynx. The anterior edge of this tissue is vertical and lies in the same plane as the post-nasal aperture. Its posterior edge gradually merges into the posterior pharyngeal wall and its lateral edges incline towards midline. It is lined by ciliated columnar epithelium. The surface of adenoid has deep clefts, but no crypts or capsule like palatine tonsil. The adenoid normally enlarges during childhood between 3-4 years. This is a period during which the child is most prone to respiratory infections [1]. As the child grows older the adenoid regresses in size, may even disappear during puberty. The initial reduction in the size of adenoid has been attributed to the rapid enlargement of the nasopharynx when compared to the size of the adenoid [2]. This study aimed to assess the relevance of adenoid facies as a diagnostic benchmark for morbidity in otorhinolaryngology, to clinically correlate adenoid facies with various clinical features related to ENT. We also aimed to correlate radiologically the presence of adenoid facies with mastoid pneumatisation and nasopharyngeal thickness impact and to broadly study the various sequelae of adenoid hypertrophy on the physical, mental as well as the social conditioning of children. Materials and methods Study design and patient population The present study was carried out in the department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College and Hospital, Jabalpur from January 2012 till December The patients with features of adenoid facies with relevant clinical features pertaining to ear, nose and throat or overall physical, mental and social development of a child were included. Data collection and analysis After taking approval of the institutional ethics committee, the patients were consented and enrolled for the study. A thorough history was taken for each patient in the greatest detail so as to cover symptoms pertaining to ear, nose and oral cavity as well as mental, physical and social development of the patient. A detailed general, rhinological, otological and oral examination of the patient was done, along with adenoid examination by way of palpation and posterior rhinoscopic examination will be done. Depending on the history and clinical examination a provisional diagnosis was reached. Equipment used in the study were Bull s eye lamp, head mirror, tongue depressor, nasal speculum, indirect laryngoscopy mirror, posterior rhinoscopy mirror, ear speculum, Siegles speculum, tuning forks, Jobson horn probe, Otoscope, Eustachian tube catheter, pure tone audiometer and endoscopes were used when required. Data obtained from hospitals was codified and entered into Microsoft excel sheets. Data were then analyzed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 21. Results The present study was conducted in total 30 patients with adenoid facies of varying degrees. It was observed that nasal block was a presenting symptom in most of the cases (83.33%) followed by nasal discharge. Nasal bleed and frequent headaches accounted for 10% and 13.33% of cases respectively. Most cases were found to be bilateral (96% of symptomatic patients) while 4% of patients showed laterality to left side. None of the cases under study showed laterality to right side. Most of the cases were seen in children between 5-9 years of age (56.66%) while 43.33% cases were seen in children of age >10 years. No cases were seen in <5 years of age. It was observed that patient presented with pain in ear, decreased hearing and blocked ear in maximum number of patients i.e. 40%, 36.66% and 33.33% of patients respectively while discharging ears were seen in 26.66% of cases. Pain in throat on and off was complained of by Page 88
3 66.66% of cases. In 50% of cases the parents complained of irregular dentition. A pinched in nostril was found in 73.33% of children with a normal of 26.66%. Septal deviation was maximally seen as being to the left side (70%), while in 30% of cases it was seen to the right. Decreased airflow upon functional examination of the nose was seen to be bilateral in majority of cases (73.33%), in 20% of cases airflow was found to be normal while airflow decreased only on the left side was found in 6.66% of cases. In majority of the cases, adenoid hypertrophy was found directly visualized in posterior rhinoscopy examination, in one single case it was seen that a nasal polyp was visualized. It was seen that most children with adenoid facies presented with open mouth for breathing (70%). A hitched upper lip was found in 100% of cases. Merely enlarged central upper incisors were seen in 80% of cases, while 40% of cases showed crowded central upper incisors, sometimes with enlargement or sometimes without. High arched palate was seen in all cases (100%), grade III tonsil enlargement was seen in 63.33% cases while grade II tonsil enlargement was seen in 30% cases. 3.33% cases showed an extreme of Grade I or Grade IV tonsil enlargement. Most of cases (71.66 %) had clear ear canals, 16.66% and 13.33% of cases had ear discharge and ear wax respectively. An equal number of cases (33.33%) had an intact or retracted tympanic membrane while 15% cases presented glue ear and 13.33% cases had a central perforation. Cholesteatoma was seen in 5% of cases. When hearing loss was assessed, 65% of ears were found to be having conductive hearing loss, while a further 33.33% had normal hearing, while only 1 ear was found to have sensorineural hearing loss. It was seen that mastoid pneumatization was affected by adenoids, being partial cellular in majority of the cases (48.33%) and sclerosed in 18.33% ears. A normal cellularity was seen in 33.33% of the ears (Table 1, 2, 3). Table 1: Characteristics of patients involved in the study. Total patients enrolled in the study 30 Males 24 Age distribution Less than 5 years of age years of age 17 More than 10 years of age 13 Nasal symptoms Nasal blockage 25 Nasal discharge 19 Nasal bleed 3 Frequent headache 4 Laterality of disease Right side 0 Left side 1 Bilateral 24 Ear symptoms Blocked ear 20 Decreased hearing 22 Pain in ear 24 Ear discharge 16 Oral symptoms Frequent sore throat 21 Pain in throat 20 Mouth breathing 27 Irregular teeth 15 Other symptoms General ill health 19 Poor nutrition 13 Dullness 7 Lack of attention 7 Lacking in studies 7 Discussion The present study is an attempt to analyse patients with the atypical appearance of the face, often referred to as adenoid facies and the actual disease prevalence in such children, the disease morbidity in them as a sequelae of possessing such facial features, due to affection by upper respiratory obstruction symptoms caused by adenoid hypertrophy, be it clinically or radiologically. The present study was conducted at NSCB Medical College and Hospital, Jabalpur Page 89
4 (M.P) in total 30 number of patients with adenoid facies of varying degrees, where some of the patients were seen in our outpatient department while some of them were admitted in ENT ward of the same hospital for surgical interventions. While most cases presented with the expected complaints of nasal obstruction or nasal discharge due to rhinosinusitis, or even those related to tonsils like frequent sore throat or pain in throat, some cases presented with primary complaints related only to ear which later turned out to be recurrent acute otitis media, chronic suppurative otitis media, serous otitis media etc. Though our study shows a male preponderance of 80% compared to females 20%, in the form of more boys presenting with disease rather than girls, this may be ascribed to more environmental exposure in males leading to more upper respiratory tract infections as well as better medical exposure of the male child, which may actually be telling on the discrimination towards the female child rather than significant as a statistical finding. When age groups were reviewed, most of the cases were seen in children between 5-9 years of age. No cases were seen in < 5 years of age, which may be due to a chance factor though cases have been described of adenoid hypertrophy even in infants as well [3]. It was observed that nasal block was a dominant presenting symptom in most of the cases (83.33%). It also leads to mouth breathing, obstructive sleep apnea and snoring. Nasal obstruction also interferes with feeding or suckling of a child. As respiration and feeding cannot take place simultaneously, a child with adenoid enlargement fails to thrive. Nasal bleed i.e. epistaxis is seen when adenoids are acutely inflamed; in some cases epistaxis may occur even with nose blowing. In one recent study, 6 out of 50 patients above age 15 were found to be suffering from enlarged congested adenoids [4]. This study showed most cases to be bilateral in terms of nasal symptoms (96% of symptomatic patients) while 4% of patients showed laterality to left side. None of the cases under study showed laterality to right side. Most cases are expected to be bilateral as adenoids are classically situated at the junction of roof and posterior wall of nasopharynx, and nasopharynx being the common pathway for both nostrils. Later septal deviation was maximally seen as being to the left side (70%) which could be a contributory factor in a number of cases, but one that is difficult to separate from the original factor under study. We saw that mouth breathing at presentation was not a commonly observed feature by parents, but when probed in detail and the parents were asked to observe the child while sleeping, in 90% of cases it was reported positively. Behlfelt showed that 62.58% of the children with adenoid hypertrophy had mouth breathing during the day and 84.78% during nights, which is only slightly less than the figures observed here, hence one would like to point out the need to deeply probe this aspect, asking the right questions and asking the parents to be vigilant as well as the value to the clinician of following up the patient [5]. Upon nasal examination, more attention was paid to the outward appearance of the nasal dorsum as an important part of adenoid facies. An elongated nasal dorsum was found in around 90% of children that suggests craniofacial dysmorphologic trait in the child. Pinched in nostrils were found in about 73.33% of cases which can again be considered a facial landmark for such children. This finding while expected to be bilateral due to the anatomical positioning of the adenoids, though in 20% of cases airflow was found to be normal, perhaps emphasizing the importance of infectious status of adenoids, as well as confounding factors like use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops at the time of examination etc. and one has not even mentioned the wide availability of various antibiotics at every step. High-arched palate is associated with difficulties, including disrupted sleep caused by obstruction of the nasal passages, besides the sleep apnea discussed above, speech problems, and with dental problems, such as crowding of the molars, as discussed above. It also poses challenges for feeding and speech, hence Page 90
5 resulting in poor feeding and undernutritioned child. Table 2: Examination findings in the included patients. Nasal examination Nasal dorsum Elongated 27 Normal 3 Nostril Pinched in 22 Normal 8 Functional airflow Decreased in right only 0 Decreased in left only 2 Decreased in both sides 22 Normal 6 Post rhinoscopy examination Adenoid hypertrophy 29 Other 1 Oral cavity examination Outer appearance Open mouth at presentation 21 Normal 9 Upper lip Hitched up 30 Teeth (upper incisor) Enlarged 24 Crowded 12 Hard palate High arched 30 Tonsil enlargement Grade I 1 Grade II 9 Grade III 19 Grade IV 1 Ear Examination Ear canal Discharge 10 Wax 8 Clear 43 Tympanic membrane Intact 20 Retracted 20 Effusion 9 Perforation 8 Cholesteatoma 3 Hearing loss Conductive 39 Sensory 1 Normal 20 Face Examination Elongated 30 Frontal bossing 26 Dull expression 9 Table 3: Radiological examination of the patients. Radiological examination (Schuller s view) Cellular 20 Partial cellular 29 Sclerosed 11 X-ray Nasopharynx soft tissue lateral view Adenoid grade I 3 Adenoid grade II 7 Adenoid grade III 17 Adenoid grade IV 3 The adenoids are in the midline of the nasopharynx, situated at the junction of roof and posterior wall of nasopharynx and the Eustachian tubes open to the right and left of them. Very large adenoids will physically block the Eustachian tubes opening which can lead to otitis media. The benefit of adenoidectomy in the management of otitis media with effusion (OME) has traditionally been ascribed to the relief of anatomical obstruction of the Eustachian tube [6]. While this may be a contributory factor, it is clear that adenoid size and physical obstruction alone cannot account for the benefit following adenoidectomy where the adenoid is small. It is likely that recurrent acute or chronic inflammation of the adenoid also play a role. These changes increase bacterial adherence. This is likely to contribute to the development of a biofilm infection resulting in middle ear Page 91
6 effusion [7]. There is now good evidence to support consideration of adjuvant adenoidectomy in children over the age of three who are undergoing insertion of tympanostomy tube. Low dose prophylactic antibiotic treatment is preferred to adenoidectomy in this group as a means of preventing recurrent otitis media and the sequelae of infection until maturation of the immune system occurs naturally [8]. An elongated face was one defining characteristic of this study like hitched up upper lip seen earlier being seen in 100% of cases, it can be explained in the same way as high arched palate, due to unopposed medial forces of the buccinators and masseter muscles leading to the face being rather long drawn. An Elongated nasal dorsum is an accompanying part of an elongated face, as seen earlier, during nasal examination. Forehead bossing was seen in 86.66% cases, being a rather prominent feature, though it is not described at all places as being a part of adenoid facies. Vacant dull expression has been described being due to the open mouth and hearing loss combining to give the child a dull idiotic look, which need not be elaborated further will be seen only in cases, with larger grades of adenoid hypertrophy, though 65% of ears were found to be having a conductive type of hearing loss, but it was mild in most cases, in this study was noted in 9 cases (30%) out of which all cases of grade 4 adenoids in this study were present and none of the remaining cases had adenoid enlargement less than grade 3. The role of Eustachian tube in the pneumatisation of the mastoid air cells is an important one. In a child with Eustachian tube compression/ edema due to adenoid infection or hypertrophy, it is the mastoid that is likely to suffer after the affection of the middle ear, though their relation to some extent is still under research, but one must remember the theories of Wittmaack regarding the development of cholesteatoma in order to gain more insight into this relationship who gave a normal middle ear to be a prerequisite for a normal mastoid development [9]. This was later supported by the studies of Tumarkin who further emphasised that middle ear diseases are the cause of reduced mastoid pneumatisation [10]. The degree to which mastoid pneumatization affected by adenoids was the aim here, with mastoid antrum being partial cellular in majority of the cases (48.33%) and sclerosed in 18.33% ears. A normal cellularity was seen in 33.33% ears. Hence we conclude that majority of the antrums were affected to some extent thus concluding with earlier studies and making a point to go in for X-ray mastoid in all patients of adenoids, especially to look for the life threatening CSOM unsafe type in such patients. Conclusion This study was conducted in total 30 patients with adenoid facies of varying degrees. The most common age group affected were children between the age group of 5-9 years, thus signifying the early effect of adenoid hypertrophy in this age. Dullness, lack of attention, lacking behind in studies was seen very commonly. These are indicative of the need for vigilance in children at school level, with school teachers playing an important role as well as the need for regular ENT checkup in all school going children. Thus in summary this study concludes that adenoids affect each part of ear nose and throat system, thus its effect can actually be quite devastating in growing children, hence the need to be on the look out for its facial features in all pediatric ENT patients, which makes for a very quick and easy diagnosis, and a major clinical strong point for all ENT practitioners. References 1. Khalid A, Al-Mazrou, Abdulaziz S, Al- Khattaf. Adherant Biofilms in adenotonsillar diseases in children. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg., 2008; 134: Suzuki M., Watanabe T., Mogi G. Clinical, bacteriological, and histological study of adenoids in children. Am. J. Otolaryngol., 1999; 20: Page 92
7 3. Morse JL. Diseases of the nasopharynx in infancy. The Journal of Laryngology, Rhinology, and Otology, 1907; 22(8): Vinay Kumar MV, Raghavendra Prasad KU, Belure Gowda PR, Manohar SR, Chennaveerappa PK. Rigid nasal endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of epistaxis. Journal of clinical and diagnostic research: JCDR, 2013; 7(5): Behlfelt K. Enlarged tonsils and the effect of tonsillectomy. Characteristics of the dentition and facial skeleton. Posture of the head, hyoid bone and tongue. Mode of breathing. Swed Dent J., 1990; 72: Nguyen LHP, Manoukain JJ, Yoskvitch A, AI Sebeih KH. Adenoidectomy selection criteria for surgical cases of otitis media. Laryngoscope, 2004; 114: Fergie N, Bayton R, Pearson JP, Birchall JP. Is otitis media with effusion in biofilm infection? Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences, 2004; 29: Rovers MM, Schilder AG, Zielhuis GA, Rosenfeld RM. Otitis media. The Lancet, 2004; 363(9407): Wittmaack K. Über die normale und die pathologische Pneumatisation des Schläfenbeines: einschliesslich ihrer Beziehungen zu den Mittelohrerkrankungen. Fischer; Tumarkin A. On the nature and vicissitudes of the accessory air spaces of the middle ear. J Laryngol Otol., 1957; 71: Page 93
A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty
 Original Research Article A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty Khushboo Jain 1, Anil Pandey 2, Shubhankur Gupta 2*, Rahul 3 1 Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur,
Original Research Article A Clinical Study of Hearing Outcome after Type I Tympanoplasty Khushboo Jain 1, Anil Pandey 2, Shubhankur Gupta 2*, Rahul 3 1 Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur,
The Ear, Nose and Throat in MPS
 The Ear, Nose and Throat in MPS Annerose Keilmann Voice Care Center Bad Rappenau, Germany Preciptorship program on MPS Wiesbaden, November 2 nd 2015 Alterations of the outer and middle ear in MPS I narrowing
The Ear, Nose and Throat in MPS Annerose Keilmann Voice Care Center Bad Rappenau, Germany Preciptorship program on MPS Wiesbaden, November 2 nd 2015 Alterations of the outer and middle ear in MPS I narrowing
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology
 Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
Subspecialty Rotation: Otolaryngology Faculty: Evelyn Kluka, M.D. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's and other specialists' roles
ACUTE ADENOIDITIS -An infection & enlargement of the adenoid A disease causing nasal obstruction CHRONIC ADENOIDITIS when adenoid hypertrophied it
 ACUTE ADENOIDITIS -An infection & enlargement of the adenoid A disease causing nasal obstruction CHRONIC ADENOIDITIS when adenoid hypertrophied it obstruct posterior nose or Eustachian tube extension of
ACUTE ADENOIDITIS -An infection & enlargement of the adenoid A disease causing nasal obstruction CHRONIC ADENOIDITIS when adenoid hypertrophied it obstruct posterior nose or Eustachian tube extension of
Relationship between Adenotonsillar Hypertrophy and Otitis Media with Effusion
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Relationship between Adenotonsillar Hypertrophy and Otitis Media with Effusion Anupama Vijayan 1, V.R. Ramakrishnan 2, Thampi John Manjuran 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Otitis
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Relationship between Adenotonsillar Hypertrophy and Otitis Media with Effusion Anupama Vijayan 1, V.R. Ramakrishnan 2, Thampi John Manjuran 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Otitis
Adenoid facies and chronic refractory rhinosinusitis managed by endoscopic-assisted
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 4 2015 Adenoid facies and chronic refractory rhinosinusitis managed by endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy A Study Sudhir M Naik 1, Ravishankara S 2, Mohan Appaji 2, Goutham
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 4 2015 Adenoid facies and chronic refractory rhinosinusitis managed by endoscopic-assisted adenoidectomy A Study Sudhir M Naik 1, Ravishankara S 2, Mohan Appaji 2, Goutham
Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children, Baugh et al Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, 2011 J and: 144 (1 supplement) S1 30.
 Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Pediatric ENT Guidelines Jane Cooper, FNP, CORLN References: Clinical Practice Guideline: Tympanostomy tubes in children, Rosenfeld et al., American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery Foundation
Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No.1, March 2013 Effectiveness of Grommet Insertion in Resistant Otitis Media with Effusion Ali Maeed S Al-Shehri, MD, Fach Arzt* Ahmad Neklawi, MD** Ayed A Shati, MD,
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Otolaryngology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Otolaryngology 1. GOAL: Hearing Loss. Understand the morbidity of hearing loss, intervention strategies, and the pediatrician's
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G)
 CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology. ENT Specialty Programs
 Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 01 Page January 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Efficacy of Intranasal Steroid Spray in the Treatment of Post Adenoidectomy Recurrence Authors Dr. B.V. Chandre Gowda 1, Dr. Smitha.S.G
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Efficacy of Intranasal Steroid Spray in the Treatment of Post Adenoidectomy Recurrence Authors Dr. B.V. Chandre Gowda 1, Dr. Smitha.S.G
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request
 Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 21 August 2015 Version: 1516.1.01 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire
Commissioning Policy Individual Funding Request Criteria Based Access Policy Date Adopted: 21 August 2015 Version: 1516.1.01 Individual Funding Request Team Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire
Recognize the broad impact of hearing impairment on child and family, including social, psychological, educational and financial consequences.
 Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Otolaryngology Note: The goals and objectives described in detail below are not meant to be completed in a single one month block rotation but are meant to be cumulative, culminating in a thorough and
Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2
 Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2 CAUSES OF SNORING AND SLEEP APNEA We inhale air through our nose and mouth. From the nostrils, air flows
Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Patient s Guide to Minimally Invasive Treatments Chapter 2 CAUSES OF SNORING AND SLEEP APNEA We inhale air through our nose and mouth. From the nostrils, air flows
THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHOID HYPERPLASIA OF NASOPHARYNX BY RADIUM
 THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHOID HYPERPLASIA OF NASOPHARYNX BY RADIUM H. E. HARRIS, M.D., and E. L. MONTGOMERY, M.D. Department of Otolaryngology Many patients have developed excessive hyperplasia of lymphoid
THE TREATMENT OF LYMPHOID HYPERPLASIA OF NASOPHARYNX BY RADIUM H. E. HARRIS, M.D., and E. L. MONTGOMERY, M.D. Department of Otolaryngology Many patients have developed excessive hyperplasia of lymphoid
Comparison of Outcome of Myringotomy with and without ventilation tube in glue ear
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Outcome of Myringotomy with and without ventilation tube in glue ear JAWAD AHMAD, BILAL HUSSAIN, MAZHAR IFTIKHAR ABSTRACT Aim: To compare the outcome of myringotomy with/
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Outcome of Myringotomy with and without ventilation tube in glue ear JAWAD AHMAD, BILAL HUSSAIN, MAZHAR IFTIKHAR ABSTRACT Aim: To compare the outcome of myringotomy with/
Primary Care ENT. Dr Layth Delaimy
 Primary Care ENT Dr Layth Delaimy EAR NOSE THROAT Examinations Inspecting the external ear Swab any discharge, and remove any wax. Look for obvious signs of abnormality: Size and shape of pinna Extra cartilage
Primary Care ENT Dr Layth Delaimy EAR NOSE THROAT Examinations Inspecting the external ear Swab any discharge, and remove any wax. Look for obvious signs of abnormality: Size and shape of pinna Extra cartilage
EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE. Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are:
 EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are: I) Allergic vasomotor rhinitis II) Cholesteatoma III) Deafness
EDITORIAL FOR THE MONTH OF MARCH 2010 COMMON E.N.T. PROBLEMS IN MY PRACTICE Most common problems that I have encountered in my practice are: I) Allergic vasomotor rhinitis II) Cholesteatoma III) Deafness
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS 1 INTRODUCTION Most common problem in children below 5 years. In this age group they get about 6 8 episodes per year. It includes infections of nasal cavity, throat,
Clinical study of otological manifestations among children with cleft palate from a tertiary care teaching hospital
 Original Research Article Clinical study of otological manifestations among children with cleft palate from a tertiary care teaching hospital Ziauddin Ahmad 1, Abhishek Singh 2*, Shewtank Goel 3, Aakansha
Original Research Article Clinical study of otological manifestations among children with cleft palate from a tertiary care teaching hospital Ziauddin Ahmad 1, Abhishek Singh 2*, Shewtank Goel 3, Aakansha
A study on the effect of adenoidectomy with tonsillectomy in otitis media with effusion in children
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajayan PV et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 May;5(5):1796-1801 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20171521
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajayan PV et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 May;5(5):1796-1801 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20171521
4 ENT. 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids. 4.2 Cochlear implants. (
 4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
4 ENT 4.1 Bone anchored hearing aids This commissioning responsibility has transferred to NHS England (http://www.england.nhs.uk/). Queries around treatment availability and eligibility, as well as referrals
Upper Airway Obstruction
 Upper Airway Obstruction Adriaan Pentz Division of Otorhinolaryngology University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Hospital Stridor/Stertor Auditory manifestations of disordered respiratory function ie noisy
Upper Airway Obstruction Adriaan Pentz Division of Otorhinolaryngology University of Stellenbosch and Tygerberg Hospital Stridor/Stertor Auditory manifestations of disordered respiratory function ie noisy
Original article Paediatrics Today 2014;10(1):1-7 DOI /p
 Original article Paediatrics Today 2014;10(1):1-7 DOI 10.5457/p2005-114.82 ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA IN CHILDREN: CORRELATION WITH PALATINE TONSIL SIZE, ADENOIDECTOMY AND ADENOTONSILLECTOMY Dalibor VRANJEŠ¹,
Original article Paediatrics Today 2014;10(1):1-7 DOI 10.5457/p2005-114.82 ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA IN CHILDREN: CORRELATION WITH PALATINE TONSIL SIZE, ADENOIDECTOMY AND ADENOTONSILLECTOMY Dalibor VRANJEŠ¹,
(1) TONSILS & ADENOIDS
 (1) TONSILS & ADENOIDS (2) Your child has been referred to have his tonsils and adenoids removed. This operation is commonly called an adenotonsillectomy and is one of the most common major operations
(1) TONSILS & ADENOIDS (2) Your child has been referred to have his tonsils and adenoids removed. This operation is commonly called an adenotonsillectomy and is one of the most common major operations
Ear Nose and Throat ENT 316. Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery; MB, BCh. Fourth. (department council approval)
 1* Ear Nose and Throat ENT 316 Basic Information Program Title Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery; MB, BCh Department Offering the Course Ear Nose and Throat Academic Year / Level Fourth Date of Specification
1* Ear Nose and Throat ENT 316 Basic Information Program Title Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery; MB, BCh Department Offering the Course Ear Nose and Throat Academic Year / Level Fourth Date of Specification
ADULT ONSET ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA - A PRELIMINARY REPORT Mukta Pagrani 1, Abhinav Srivastava 2, Chander Mohan 3
 ADULT ONSET ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA - A PRELIMINARY REPORT Mukta Pagrani 1, Abhinav Srivastava 2, Chander Mohan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mukta Pagrani, Abhinav Srivastava, Chander Mohan. Adult Onset Acute
ADULT ONSET ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA - A PRELIMINARY REPORT Mukta Pagrani 1, Abhinav Srivastava 2, Chander Mohan 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Mukta Pagrani, Abhinav Srivastava, Chander Mohan. Adult Onset Acute
Assessment of otological and audiological status in patients of allergic rhinitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kumar S et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):956-960 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kumar S et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):956-960 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
 02 RJR 02 2011.qxd:Interior 4/26/11 11:57 AM Page 80 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 1, No. 2, April - June 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
02 RJR 02 2011.qxd:Interior 4/26/11 11:57 AM Page 80 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 1, No. 2, April - June 2011 ORIGINAL PAPERS Is adenoidectomy an effective therapy for otitis media with effusion?
Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010
 Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010 System/ Body Area Constitutional Measurement of any three of the following seven vital signs: 1) sitting or standing blood pressure,
Compliance Department ELEMENTS OF EAR, NOSE AND THROAT EXAMINATION 11/2010 System/ Body Area Constitutional Measurement of any three of the following seven vital signs: 1) sitting or standing blood pressure,
Effects of adenoidectomy and adenotonsillectomy on the components of Waldeyer ring
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Bhat VK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):290-297 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Bhat VK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):290-297 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX. By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
THE INTERIOR OF THE PHARYNX By Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi The Cavity The cavity of the pharynx is divided into: 1. The Nasal part (called Nasopharynx) 2. The Oral part (called the Oropharynx), 3. And the
Comparative Study in Management of Serous Otitis Media Edical Management Versus Grommet Insertion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. IV (October. 2016), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Study in Management of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. IV (October. 2016), PP 24-28 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Study in Management of
Original Article Correlation of Enlarged Adenoids with conductive hearing impairment in children under twelve
 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 62-68 Original Article Correlation of Enlarged Adenoids with conductive hearing impairment in children under twelve S M Sarwar 1, Masroor Rahman 2, Mohammad Idrish
Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2015; 21(2): 62-68 Original Article Correlation of Enlarged Adenoids with conductive hearing impairment in children under twelve S M Sarwar 1, Masroor Rahman 2, Mohammad Idrish
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal Adults And Those With Middle Ear Disease
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. V (May. 2017), PP 76-80 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. V (May. 2017), PP 76-80 www.iosrjournals.org Study of Eustachian Tube Function in Normal
Tympanoplasty with and without cortical mastoidectomy in CSOM: A comparative study
 Original article: Tympanoplasty with and without cortical in CSOM: A comparative study 1 Dr. Parag V. Doifode, 2 Dr. Sandeep Dabhekar, 3 Dr. S. H. Gawarle 1Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Original article: Tympanoplasty with and without cortical in CSOM: A comparative study 1 Dr. Parag V. Doifode, 2 Dr. Sandeep Dabhekar, 3 Dr. S. H. Gawarle 1Assistant Professor, Department of ENT, Government
Royal Victoria Hospital Montreal General Hospital Jewish General Hospital. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery
 Royal Victoria Hospital Montreal General Hospital Jewish General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery A. GENERAL COMPETENCIES ( )denotes optional competencies At the completion of
Royal Victoria Hospital Montreal General Hospital Jewish General Hospital Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery A. GENERAL COMPETENCIES ( )denotes optional competencies At the completion of
Paediatric Otolaryngology
 Paediatric Otolaryngology Antony A Narula MA FRCS FRCS Ed Consultant St Mary s & Ealing Hospitals Hon. Professor, Middlesex University 17 th July 2004 Otology Acute Otitis Media Otitis Media with Effusion
Paediatric Otolaryngology Antony A Narula MA FRCS FRCS Ed Consultant St Mary s & Ealing Hospitals Hon. Professor, Middlesex University 17 th July 2004 Otology Acute Otitis Media Otitis Media with Effusion
Tonsillectomy/Adenoidectomy
 Last Review Date: January 12, 2018 Number: MG.MM.SU.58C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: January 12, 2018 Number: MG.MM.SU.58C2 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Assisting in Otolaryngology
 Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Assisting in Otolaryngology Learning Objectives Identify the structures and explain the functions of the external, middle, and internal ear. Describe the conditions that can lead to hearing loss, including
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Tympanometric changes following adenoidectomy in children with adenoid hypertrophy
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajashekhar RP et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):391-396 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajashekhar RP et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):391-396 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide
 Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
Vinod K. Anand, MD, FACS Nose and Sinus Clinic Middle Ear Fluid in Young Children: Parent Guide Purpose of This Booklet This booklet is about middle ear fluid in children ages 1 through 3 who have no other
Test Results: Audiometry test shows conductive hearing loss at 30 decibels and flat tympanogram.
 Note for Jane Doe on 2/10/2005- Chart 2646 Consultation was requested by Dr. Welby. Chief Complaint (1/1): This 3 year-old female presents today for evaluation of chronic ear infections bilateral. Associated
Note for Jane Doe on 2/10/2005- Chart 2646 Consultation was requested by Dr. Welby. Chief Complaint (1/1): This 3 year-old female presents today for evaluation of chronic ear infections bilateral. Associated
Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (7) 264:1387 1391 DOI 1.17/s5-7-374-1 OTOLOGY Objective assessment of autophony in patients with patulous Eustachian tube Yoko Hori Tetsuaki Kawase Takeshi Oshima Shuichi Sakamoto
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
BIOS222 TUTORIAL ACTIVITY SESSION 1
 BIOS222 TUTORIAL ACTIVITY SESSION 1 Instructions: The Tutorial activities are designed to help you practice the concepts learned in the lecture. Read the following case studies and answer the questions
BIOS222 TUTORIAL ACTIVITY SESSION 1 Instructions: The Tutorial activities are designed to help you practice the concepts learned in the lecture. Read the following case studies and answer the questions
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Otitis Media
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Otitis Media Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in
Assessment of Hearing Level after Resolution of Acute Otitis Media. Ali Maeed Al-shehri*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 4, December 2010 Assessment of Hearing Level after Resolution of Acute Otitis Media Ali Maeed Al-shehri* Background: Acute otitis media is a very common global bacterial
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 4, December 2010 Assessment of Hearing Level after Resolution of Acute Otitis Media Ali Maeed Al-shehri* Background: Acute otitis media is a very common global bacterial
Prophylactic Tobramycin Drops After Tympanostomy Tube Placement
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2018; 4(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijo doi: 10.11648/j.ijo.20180401.12 ISSN: 2472-2405 (Print); ISSN: 2472-2413 (Online) Prophylactic
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology 2018; 4(1): 6-10 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijo doi: 10.11648/j.ijo.20180401.12 ISSN: 2472-2405 (Print); ISSN: 2472-2413 (Online) Prophylactic
Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship EAR INFECTIONS - OBJECTIVES examine the outer ear, ear canal and tympanic membrane and describe normal versus abnormal findings differentiate
Learning Objectives for Rotation in Otolaryngology Year 3 Clerkship EAR INFECTIONS - OBJECTIVES examine the outer ear, ear canal and tympanic membrane and describe normal versus abnormal findings differentiate
Neoplasms that present as a swelling in the neck may be either
 Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
The Throat. Image source:
 The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
The Throat Anatomy Image source: http://anatomyforlayla.blogspot.co.za/2007/04/blog-post.html The Throat consists of three parts: 1. The Nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat and it is situated behind
Otitis Media. Anatomy & Hearing Our ears are very specialized organs that allow us to hear and keep our balance.
 Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
Otitis Media Introduction Otitis media is a middle ear infection. 75% of all children experience at least one episode of otitis media before they turn 3 years old. If otitis media is left untreated, it
TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH
 Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Dr.Yahya A. Ali 3/10/2012 F.I.C.M.S TRAUMA TO THE FACE AND MOUTH Bailey & Love s 25 th edition Injuries to the orofacial region are common, but the majority are relatively minor in nature. A few are major
Effect of Topical Intranasal Steroid in Management of Otitis Media with Effusion
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 761-765, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effect of Topical Intranasal Steroid in Management of Otitis Media with Effusion MEDHAT M. SHARSHAR, M.D.
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 761-765, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Effect of Topical Intranasal Steroid in Management of Otitis Media with Effusion MEDHAT M. SHARSHAR, M.D.
Submucosal Diathermy for Nasal Obstruction: A Case Study of 30 Cases
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/216 Submucosal Diathermy for Nasal Obstruction: A Case Study of 30 Cases M S Vishnu 1, A B Harikrishnan 1, K B Rajamma 2 1 Resident, Department of ENT, Sree Gokulam
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/216 Submucosal Diathermy for Nasal Obstruction: A Case Study of 30 Cases M S Vishnu 1, A B Harikrishnan 1, K B Rajamma 2 1 Resident, Department of ENT, Sree Gokulam
ADENOIDECTOMY SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY 1516.v1b
 ADENOIDECTOMY SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Ratified by: Somerset CCG COG Date Ratified: March 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: IFR Manager SCCG
ADENOIDECTOMY SECONDARY CARE PRIOR APPROVAL POLICY Version: Ratified by: Somerset CCG COG Date Ratified: March 2016 Name of Originator/Author: Name of Responsible Committee/Individual: IFR Manager SCCG
Treatment of Snoring. Useful Telephone Numbers. Information for Patients on. North Hampshire ENT Partnership Hampshire Clinic
 Useful Telephone Numbers North Hampshire ENT Partnership Hampshire Clinic - 01256 377733 The Hampshire Clinic Switchboard - 01256 357111 Lyde Ward - 01256 377773 Enbourne Ward - 01256 377772 Frimley Park
Useful Telephone Numbers North Hampshire ENT Partnership Hampshire Clinic - 01256 377733 The Hampshire Clinic Switchboard - 01256 357111 Lyde Ward - 01256 377773 Enbourne Ward - 01256 377772 Frimley Park
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ACTINOMYCOSIS OF TONSILS INCIDENTAL OR PATHOLOGICAL? A CASE REPORT ABSTRACT
 Case Report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ACTINOMYCOSIS OF TONSILS INCIDENTAL OR PATHOLOGICAL? A CASE REPORT Dr.S.ANU PRIYADHARSHINI* 1, Dr.A.R.SUBHASHREE 2
Case Report Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ACTINOMYCOSIS OF TONSILS INCIDENTAL OR PATHOLOGICAL? A CASE REPORT Dr.S.ANU PRIYADHARSHINI* 1, Dr.A.R.SUBHASHREE 2
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis
 Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Acute Otitis Media, Acute Bacterial Sinusitis, and Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis This guideline, developed by Larry Simmons, MD, in collaboration with the ANGELS team, on October 3, 2013, is a significantly
Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM
 Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2015: Vol.-5, Issue- 1, P. 766-770 766-771 Original article: Study of etiological factors and sensitivity pattern in CSOM Paresh Chavan, G
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS
 Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy
 Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.2, Vol.24, Serial No.67, Spring-2012 Original Article Abstract Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy 1* Fatholah Behnoud
Iranian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology No.2, Vol.24, Serial No.67, Spring-2012 Original Article Abstract Evaluation of Children with Chronic Rhinosinusitis after Adenotonsillectomy 1* Fatholah Behnoud
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009
 Common ENT Problems: How to evaluate and when to refer Maria C. Veling M.D. Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009 1 Objectives Identify symptoms and findings of clinically significant
Common ENT Problems: How to evaluate and when to refer Maria C. Veling M.D. Pediatric Otolaryngology University of Kentucky April 2009 1 Objectives Identify symptoms and findings of clinically significant
Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka
 Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka Rubasinghe M.S., De Silva M.D.K., Wanasinghe W.M.S.C.L., De Livera R.J.K., Wimalaratna
Patient profile, indications, complications and Evaluation of Septoplasty outcome in a Base Hospital in Sri Lanka Rubasinghe M.S., De Silva M.D.K., Wanasinghe W.M.S.C.L., De Livera R.J.K., Wimalaratna
1. GOAL 2. OBJECTIVES a) KNOWLEDGE b) SKILLS c) INTEGRATION
 1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
EFFICACY OF INTRANASAL MOMETASONE FUROATE AS AN ADD ON THERAPY IN THE TREATMENT OF ADENOIDAL HYPERTROPHY IN ADOLESCENTS
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 101-106 www.iosrjournals.org EFFICACY OF INTRANASAL MOMETASONE
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 101-106 www.iosrjournals.org EFFICACY OF INTRANASAL MOMETASONE
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Dynamic Slow Motion Video Endoscopy as an Adjunct to Impedance Audiometry in the Assessment of Eustachian Tube Function
 THIEME Original Research 141 Dynamic Slow Motion Video Endoscopy as an Adjunct to Impedance Audiometry in the Assessment of Eustachian Tube Function Sanoop E. Sanu 1 Shilpa Divakaran 2 Sabarinath Vijayakumar
THIEME Original Research 141 Dynamic Slow Motion Video Endoscopy as an Adjunct to Impedance Audiometry in the Assessment of Eustachian Tube Function Sanoop E. Sanu 1 Shilpa Divakaran 2 Sabarinath Vijayakumar
The Effect of Beclomethasone Nasal Spray on the Size of Adenoid and its Related Obstructive Symptoms in Children with Adenoid Hypertrophy.
 In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2009 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol10/jan2009/86051.htm The Effect of Beclomethasone Nasal Spray on the Size of Adenoid and its Related Obstructive
In the name of God Shiraz E-Medical Journal Vol. 10, No. 1, January 2009 http://semj.sums.ac.ir/vol10/jan2009/86051.htm The Effect of Beclomethasone Nasal Spray on the Size of Adenoid and its Related Obstructive
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Alexandria Workshop on
 Alexandria Workshop on 1 Snoring & OSA Surgery Course Director: Yassin Bahgat MD Claudio Vicini MD Course Board: Filippo Montevecchi MD Pietro Canzi MD Snoring & Obstructive ti Sleep Apnea The basic information
Alexandria Workshop on 1 Snoring & OSA Surgery Course Director: Yassin Bahgat MD Claudio Vicini MD Course Board: Filippo Montevecchi MD Pietro Canzi MD Snoring & Obstructive ti Sleep Apnea The basic information
Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma
 Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
Medicine Otorhinolaryngology fields Okayama University Year 2003 Surgical intervention in middle-ear cholesterol granuloma Manabu Maeta Ryusuke Saito Fumio Nakagawa Takakazu Miyahara Okayama University
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 8.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 12 15, 21, 24, 31-34, 39, 40, 54 8.2 Describe the anatomy and physiology of the upper and lower
A study of causes of nasal obstruction in Garhwal region of Uttarakhand
 Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations
 White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
White Paper: Balloon Sinuplasty for Chronic Sinusitis, The Latest Recommendations For Health Plans, Medical Management Organizations and TPAs Executive Summary Despite recent advances in instrumentation
9/18/2018. Disclosures. Objectives
 Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
Is It Really Acute Bacterial Rhinosinusitis? Assessment, Differential Diagnosis and Management of Common Sinonasal Symptoms Kristina Haralambides, MS, RN, FNP-C Disclosures The content of this presentation
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma. Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal
 Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Int. Adv. Otol. 2012; 8:(1) 63-68 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A New Staging System for Tympano-mastoid Cholesteatoma Aziz Belal, Mahmoud Reda, Ahmed Mehana, Yousef Belal Alexandria Ear Hospital Alexandria Egypt (AB,
Postnatal Growth. The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health and nutrition assessment
 Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Growth of The Soft Tissues Postnatal Growth Postnatal growth is defined as the first 20 years of growth after birth krogman 1972 The study of growth in growing children is for two reasons : -For health
Role of adenoid hypertrophy in causation of chronic middle ear effusion
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Timna CJ et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):203-209 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Timna CJ et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):203-209 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Importance of nasal endoscopy for the evaluation of epistaxis
 Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 18(1): 11-15 Original Article Importance of nasal endoscopy for the evaluation of epistaxis Ritam Ray 1, Manoj Mukherjee 2, Manotosh Dutta 3, Mousumi Neogi 4, Ganesh
Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 2012; 18(1): 11-15 Original Article Importance of nasal endoscopy for the evaluation of epistaxis Ritam Ray 1, Manoj Mukherjee 2, Manotosh Dutta 3, Mousumi Neogi 4, Ganesh
ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS.
 ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS. Outline: Extent of the problem. Defining the problem. Tips to improving diagnostic accuracy. Review of current
ENT approach to middle ear disease in children: the evidence. Dr Trish MacFarlane MBBS, FRACS. Outline: Extent of the problem. Defining the problem. Tips to improving diagnostic accuracy. Review of current
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
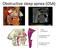 Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) In a healthy sleeping child, the mouth is typically closed, the oral cavity is collapsed, and the nasopharynx and hypopharynx are patent with minimal wall motion Obstructive
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) In a healthy sleeping child, the mouth is typically closed, the oral cavity is collapsed, and the nasopharynx and hypopharynx are patent with minimal wall motion Obstructive
Spectrum of ear, nose and throat disorders among children reporting to the out-patient department of a tertiary care center, Nepal
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chaudhari BK et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Sep;4(5):1125-1129 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Commen Nose Diseases
 Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Commen Nose Diseases Symptoms List: Nasal obstruction. Nasal discharge: Anterior (Rhinorrhea). Posterior (Postnasal discharge). Epistaxis. Hyposmia and Anosmia. Headache. Snoring. Nasal Obstruction Definition:
Home Video to Assess the Snoring Child
 Home Video to Assess the Snoring Child Federico Murillo-González Consider the following case: a 5 year-old child who snores and constantly wakesup every night, breathes through the mouth during the day,
Home Video to Assess the Snoring Child Federico Murillo-González Consider the following case: a 5 year-old child who snores and constantly wakesup every night, breathes through the mouth during the day,
College & Hospital, DPU Vidyapeeth Pimpri, Pune, India. *Corresponding Author:
 Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2278-3784.2017.0001 Evaluation of changes in maxillary arch dimensions, Posterior Transverse Inter Arch Discrepancy (PTID), upper and lower incisor inclination in
Original Research Article DOI: 10.18231/2278-3784.2017.0001 Evaluation of changes in maxillary arch dimensions, Posterior Transverse Inter Arch Discrepancy (PTID), upper and lower incisor inclination in
Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery R L A Raja Ahmad, MS (ORL)*, B S Gendeh, MS (ORL)** Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Kulliyyah
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery R L A Raja Ahmad, MS (ORL)*, B S Gendeh, MS (ORL)** Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Kulliyyah
1/13/2009. Classification:
 SUPPURATIONS OF SPACES RELATED TO THE PHARYNX Assistant Professor, Department of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University Classification: I. Intratonsillar abscess.
SUPPURATIONS OF SPACES RELATED TO THE PHARYNX Assistant Professor, Department of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University Classification: I. Intratonsillar abscess.
Snoring. Forty-five percent of normal adults snore at least occasionally and 25
 Snoring Insight into sleeping disorders and sleep apnea Forty-five percent of normal adults snore at least occasionally and 25 percent are habitual snorers. Problem snoring is more frequent in males and
Snoring Insight into sleeping disorders and sleep apnea Forty-five percent of normal adults snore at least occasionally and 25 percent are habitual snorers. Problem snoring is more frequent in males and
EAR, NOSE AND THROAT (ENT) ASSESSMENT
 This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT
This decision support tool is effective as of October 2016. For more information or to provide feedback on this or any other decision support tool, email certifiedpractice@crnbc.ca EAR, NOSE AND THROAT
Updating Intracapsular Technique for Tonsillectomy
 Updating Intracapsular Technique for Tonsillectomy James S. Reilly and Richard J. Schmidt We will review some of the newer techniques for tonsillectomy surgery. The indications for tonsil surgery can be
Updating Intracapsular Technique for Tonsillectomy James S. Reilly and Richard J. Schmidt We will review some of the newer techniques for tonsillectomy surgery. The indications for tonsil surgery can be
Mammals. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National Zoological Park. Dr. Peter Emily - Father of Veterinarian Dentistry.
 Mammals There are 4640 species of mammals. Most are ideal. Humans are but one species. Mammals are unique in that they have an epiglottis. All species breastfeed their young. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National
Mammals There are 4640 species of mammals. Most are ideal. Humans are but one species. Mammals are unique in that they have an epiglottis. All species breastfeed their young. Dr. Olaf Oftedal - National
The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment Line in Revision Myringoplasty
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 77, No. 2, September: 53-57, 2009 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com The Value of Computed Tomography Scanning in Assessment of Aditus ad Antrum Patency and Choice of Treatment
Preface... Contributors... 1 Embryology... 3
 Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
Contents Preface... Contributors... vii xvii I. Pediatrics 1 Embryology... 3 Pearls... 3 Branchial Arch Derivatives... 3 Branchial Arch Anomalies: Cysts, Sinus, Fistulae... 4 Otologic Development... 4
