6/27/2018. Approach to Elevated Liver Tests. At the conclusion the audience should have a better understanding of
|
|
|
- Colleen Cummings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Approach to Elevated Liver Tests Eric R Kallwitz, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Loyola University Medical Center Section of Hepatology At the conclusion the audience should have a better understanding of What constitutes an abnormal aminotransferase How to make an initial evaluation of an abnormal test Understand disease specific serologic tests Understand laboratories which are prognostic in chronic liver disease You follow a 65 year old male at VA clinic His ALT is 58 IU/ml (within normal limits) On a rotation through cardiology, you see him at LUMC He is to be started on a statin, his ALT at LUMC is 55 IU/ml (H) He asks you what this means? The left depicts 177 overweight patients undergoing routine surgery The right depicts 629 patients undergoing evaluation for HCV For obese persons undergoing bariatric surgery 2 SD above the mean was an ALT of 60 IU/mL The right is the ability of ALT to discriminate the presence of fatty liver disease in patients undergoing bariatric surgery (AUC = 0.653) Population of persons donating blood Selected those at lowest risk for liver disease (normal BMI, normal lipids and glucose, no medications) Median ALT was 11 U/L Value at the 95 th percentile for Women was 19 U/L Men was 30 U/L Applied this to a population with HCV RNA Reference of lab abnormal was 55% sensitive and 97% specific The above criteria was 76% sensitive and 89% specific Prati Ann Intern Med 2002;137:1-9 1
2 Data from Italy-patients at risk for NAFLD 63/458 patients had a liver biopsy with an ALT < 40 U/L (long standing steatosis) Mean ALT was 28 ± 7 U/L Fibrosis 2 (moderate) was seen in 22% with normal ALT and 34% with increased ALT (p=ns) 5/63 (8%) persons had cirrhosis Of 37% of persons with NASH and a normal ALT, 27% met more stringent criteria for normal Fracanzani Hepatology 2008 ;48: Most laboratories use > 2 SD to define abnormal The differences in clinical laboratories abnormal is based on the health of the reference population There is difficulty defining normal so your clinical suspicion for disease should must supersede labs A normal ALT does not exclude liver disease or histologic damage No recommendation to routinely test healthy, asymptomatic persons Screened disease Medically important Yes Relatively high prevalence Yes Natural history of disease should be known Limited data (Lack of population based data) Effective intervention should exist Limited interventions for some diseases (NAFLD) NHANES III data Used ALT > 40 for men and > 31 for women as abnormal Prevalence of abnormal aminotransferases was 7.9% Men 9.3%, women 6.6% Hispanic 14.9%, African American 8.1% and non- Hispanic white 7.1% Only 31% of cases had an etiology for abnormal aminotransferases (viral hepatitis, alcohol, iron overload) If more stringent criteria for abnormal ALT used 26% had an elevated ALT, of which 21.2% had no explanation Clark Am J Gastroenterol yo male TB 1.8 AP 180 AST 2789 ALT 6239 Alb 3.0 PT yo female TB 22.0 AP 99 AST 560 ALT 901 Alb 2.1 PT 66 True liver function tests What does the liver do? Hepatocellular damage Cholestasis Listing for fulminant hepatic failure requires onset of encephalopathy within 8 weeks of onset of liver disease symptoms and one of the following: 1) ventilator dependence, 2) requiring renal replacement therapy or 3) INR > 2.0 Are the abnormalities noted acute or chronic? 2
3 Albumin Low albumin: edema, anasarca Nephrotic syndrome, malnutrition, protein losing enteropathy Prothrombin time High PT/INR: increased risk of bleeding Vitamin K deficiency, consumptive coagulopathy Bilirubin Jaundice (total bilirubin > 2-3 mg/dl) Cholesterol Machines are calibrated to activated thromboplastins for patients on warfarin There is significant variation in INR from lab to lab in cirrhotic patients Common clinical dilemma- vitamin K deficiency, consumptive coagulopathy or cirrhosis Factor Cirrhosis Vit K def Consumption Abnormal V Yes No Yes Abnormal VII Yes Yes Yes Abnormal VIII No No Yes ALT (alanine aminotransferase--sgpt) Cytosol of hepatocytes More hepatocyte specific AST (aspartate aminotransferase--sgot) Cytosol and mitochondria Muscle, intestine, brain, kidney, pancreas, red blood cells Mitochondrial induction/damage by alcohol explains higher AST levels in persons consuming excessive ETOH, vitamin deficiency leads to lower ALT Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) Can be markedly elevated in shock liver Drug/toxin induced injury Acetaminophen NOT alcohol alone Acute viral hepatitis Shock liver Autoimmune hepatitis Common bile duct stone In most liver diseases ALT > AST Exceptions: Alcoholic liver disease >2:1 ratio Wilson s disease Accompanying hemolytic anemia Advanced fibrosis AST/ALT ratio >1 had a sensitivity of 41%, a specificity of 78% to identify advanced fibrosis Unpublished data 3
4 Alkaline phosphatase Localized in microvilli of bile canaliculus Hepatic synthesis in cholestasis Fractionation can help Bone, intestine, placenta Gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) Induced by alcohol, medications 5 -Nucleotidase Specific to liver Bilirubin Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia Gilbert s syndrome Crigler-Najjer syndrome Hemolysis Hematoma resorption Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia Bile duct obstruction Severe hepatitis Cirrhosis Medication/Toxin PBC PSC Sepsis TPN Benign recurrent cholestasis Vanishing bile duct syndrome Dubin-Johnson syndrome Rotor syndrome Elevated Alkaline phosphatase Hepatobiliary Bile duct obstruction PBC PSC Medications Hepatic metastasis Severe hepatitis Cirrhosis Vanishing bile duct syndrome Benign recurrent cholestasis Infiltrating diseases Sarcoid TB Fungal Amyloidosis Heme malignancy Bilirubin is a normal heme degredation product Predominant excretion is in bile Unconjugated (indirect) is taken up by hepatocytes Conjugated (direct) by the endoplasmic reticulum using enzyme bilirubin UDP-glucuronyltransferase Water soluble bilirubin glucuronides secreted across canicular membrane into bile Clinical correlate: Gilbert s syndrome Diminshed expression of bilirubin UDPglucuronyltransferase Up to 5% of population Benign, unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia Can be worsened by stress, fasting Repeat abnormal tests(?????) Many will normalize without intervention, ONLY consider if no risk factors are present Discontinue alcohol, potential hepatotoxins Would not wait however if there are signs of synthetic dysfunction Elevated bilirubin, PT prolongation Continued Elevation Work up is based on pattern of abnormalities Hepatocellular injury versus cholestatic Acute versus Chronic A 55 year old man is admitted overnight, he is new to LUMC and presents with melena On US he has a nodular appearing liver with possible fatty infiltration Relevant labs ALT 55, AST 77, TB 0.9, AP 88, PLT 55, HGB 8.9 He undergoes endoscopy finding recently bleeding varices which were banded Which of the following labs sent over night are unnecessary? Acute hepatitis panel (hep A IgM, HB S AG, Anti-HBV core AB total, Anti-HCV) ANA, ASMA, AMA Ceruloplasmin Alpha-1 antitrypsin Ferritin, iron, TIBC Tylenol level Serum alcohol 4
5 Liver consult HAV IgM HBV s Ag, core IgM Anti-HCV AMA ANA, ASMA Ceruloplasmin Alpha-1 antitrypsin Iron, TIBC, ferritin Tox screen RUQ US Consider Biopsy Chronic hepatitis? Is there cholestasis? Patient age? Persistently elevated Symptomatic Impaired synthetic function Elevated ALT/AST Duration < 3 months Elevation < 3 fold Asymptomatic Preserved synthetic function Acute hepatitis Chronic hepatitis Repeat tests in 3 months US, IgM anti-hav, HBsAg, IgM anti-hbc, HCV RNA, ANA, ASMA Ceruloplasmin if < 40 yo, consider biopsy US, HBVsAg, ANA, ASMA, anti-hcv, iron studies, A1AT phenotype, ceruloplasmin if < 40 yo, consider biopsy Dilated ducts MRCP/ERCP Cholestasis (Alk Phos ± bilirubin) Liver fraction and/or GGT abnormal US Liver mass CT, tumor markers, biopsy Liver fraction and GGT normal Pursue non-hepatic causes Normal Pursue intrahepatic causes Drug history AMA Biopsy, MRCP/ERCP? Sex: Female (AIH, PBC) Male (PSC) Age: Neonatal (A1AT) < 40 (Wilson s, AIH) > 40 (viral, HFE) Medications: Antiepileptics HAART INH Risk factors (HCV): IVDA (viral, EtOH) Blood transfusions Tattoos Comorbidities: DM/obesity: NASH CHF: HFE Family Hx A1AT deficiency Hemachromatosis Country of Birth HBV History Component Remote history of jaundice Medical history of autoimmune diseases Hypothyroidism History of liver disease as a newborn Family history of liver disease History of alcohol abuse, DUI History of IVDA, blood transfusion prior to 1990 Diabetes Components of Metabolic Syndrome Disease Correlation Viral hepatitis AIH AIH, PBC Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency HBV, hemochromatosis Alcohol HCV Hemochromatosis, NAFLD NAFLD Physical Exam Findings Spider angiomas Palmar erythema Splenomegaly Jaundice Hyperpigmentation Kayser-Fleisher rings Emphysema/Lung disease Ascites Disease Correlates Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Portal hypertension Cirrhosis, Biliary obstruction, hemolysis, Gilbert s Hemochromatosis Wilsons disease Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Portal hypertenson, cirrhosis Medications, CAM therapy Drug induced liver injury Asterixis Portal hypertension Pruritis PBC Xanthalasma PBC Ulcerative Colitis PSC Arthritis Hemochromatosis, HCV 5
6 A clinician is better able to understand the evaluation of liver disease with a basic understanding of each individual disease The next section will focus on serology of chronic liver diseases Disorder Acute Chronic Hepatitis A + Hepatitis B + + Hepatitis C + + Hepatitis E + (rare) Autoimmune hepatitis + + Wilson Disease + + Hemochromatosis + Alpha-1 AT deficiency (neonatal) + NAFLD + Alcohol + + Medication/Toxin + + Vertical Immune Tolerance Immune Tolerance: Normal ALT DNA > 20,000,000 IU/ml Low grade on biopsy Horizontal HBeAg+ Chronic HBV Seroconversion Chronic HBV: Elevated ALT E Antigen Positive DNA > 20,000 IU/ml E Antigen Negative DNA > 2,000 IU/ml Resolved HBV (seroclearance) Inactive carrier HBeAg- Chronic HBV Inactive Carrier: HbeAg-/Anti-HBe+ Normal ALT HBV DNA < 2,000 HBsAg HBc HBe HBsAb HBV DNA Acute HBsAg HBcIgM + Chronic (immune tolerant or active) Inactive Carrier HBsAg HBcIgG HBeAg+ or eag- > HBsAg HBcIgG eab+ <10 4 Immune HBcIgG HBsAb Vaccinated HBsAb HCV test Anti-HCV HCV RIBA HCV RNA HCV genotype Comment Seropositive in past and current infection Seldom used Can distinguish false positive AB from past infection Viremia indicates current infection Viral load does not correlate with severity of liver disease Measure if considering interferon based therapy Genotype 1 predominates in US LABS: iron/tibc, ferritin, genotype Clinical suspicion Fatigue, arthralgia, diabetes mellitus, hyperpigmentation, impotence Transferrin saturation and ferritin TS > 45% Sensitivity >97% Specificity 45% Ferritin > 1000 mg/ml marker of significant disease Genotype C282Y (prevalence 5/1000 if Northern European descent) Accounts for 80-85% of typical hemochromatosis Only 10% of C282Y homozygotes will have end organ damage Other mutations: ie H63D, S65C controversial 6
7 LABS: ANA, ASMA, anti-lkm (kids), immunoglobulins Type 1 AIH Women (4:1), peak 20 s to 40 s All ages and ethnic groups susceptible ANA (67%), SMA (87%) ANA found in PBC, PSC, viral hepatitis, drug related hepatitis, NASH, ETOH panca common Hyperglobulinemia (high IgG) Type 2 AIH (young women) Anti-LKM1 Less hyperglobulinemia Tends to be more severe at onset and more likely to progress to cirrhosis LABS: ceruloplasmin, 24 urine copper, serum copper, genetic testing Test WD Comments Ceruloplasmin <20 mg/dl 95% homozygotes 20% heterozygotes Slit-lamp KF rings Absent early F(+) cholestatic disease 24 hour urine >100 ug F(-) early F(+) cholestatic disease Hepatic copper >250 ug/g F(+) cholestatic disease F (-) sampling error Genetic testing by whole-gene sequencing exists, but can be difficult as most persons with WD are compound heterozygotes and there are roughly 300 mutations LABS: alpha1-antitrypsin level, phenotype Serine protease inhibitor for which liver disease results from failure to export History 10% develop neonatal hepatitis or obstructive jaundice Serum levels Low Phenotyping PiZZ Liver histology A1AT globules in ER of periportal hepatocytes PAS positive, diastase-resistant NAFLD 20-30% in US NASH 3% of general population 20% of obese individuals Disease associations Metabolic syndrome Visceral obesity, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia (HDL, TG), elevated blood pressure Asymptomatic transaminase elevation ALT > AST GGT may be increased Alk phos usually < 2x ULN Elevated ferritin 60% (marker for IR) Diagnosis-History Ask about DUI AST>>ALT (both typically < 300 U/L) Elevated bilirubin and prolonged PT Alkaline phosphatase often normal Calculate discriminant function Serum bilirubin + 4.6*(patient PT- control PT) DF > 32 is important Designates poor prognosis, high mortality Marker for therapy consideration Prednisolone, pentoxifylline Commonly prescribed Medication Augmentin Anti-Epileptics Azole (antifungal) Isoniazid Anesthetics Halothane Nicotinic acid Nitrofurantion Propylthiouricil Oral hypoglycemics Glyburide TZDs HMG CoA reductase inhibitors Protease inhibitors OTC, CAM, illicit Acetaminophen NSAIDs Ephedra Kava Chaparral Black Cohosh Ecstasy Hydrofluorocarbons Chloroform Toluene 7
8 Chronic aminotransferase elevation and histological injury has never been convincingly proven Significant hepatotoxicity attributable to statins is very rare Use of lower doses and highly lipophilic (cerivastatin, lovastatin, simvastatin) may reduce hepatotoxicity Agent RR CI Highly Lipophilic , 3.05 Mildly Lipophilic , 5.58 Argo et al Hepatology 2008;48:662 Disorder Acute Chronic PBC + PSC + Obstructive Jaundice +(pain) + Medications/Toxins + + LABS: AMA, immunosglobulins Serologic Anti-mitochondrial antibody (AMA) 95% positive in PBC 1% general population 5% PBC patients AMA negative Targets mitochondrial specific complexes High levels of IgM Alkaline phosphatase elevation > aminotransferases Increased bilirubin associated with worsened disease severity High cholesterol (especially HDL) More common in men UC coexists in 90% panca common Check IgG4-exclude autoimmune pancreatitis If dominant stricture check Ca 19-9 Anabolic steroids Allopurinol Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid Atazanavir Diltiazem Erythromycin Estrogens Indinavir Nevirapine Methyltestosterone Quinidine Total parenteral nutrition Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 8
9 AASLD recommends US (and AFP*) every 6-12 months for surveillence Hepatitis B carriers Asian males 40 Asian females 50 Cirrhosis at any age Positive family history Africans 20 For those not listed above HCC risk varies; consider HBV viral load and grade of inflammation Bruix Hepatology 2010 (AASLD position paper) *AFP was dropped from 2010 guidelines Non-hepatitis B Cirrhosis Hepatitis C Alcohol Hemochromatosis PBC Alpha-1 antitrypsin NASH Autoimmune hepatitis AFP is a marker of liver rejeneration It is often elevated in viral hepatitis AFP can be used for surveillance and diagnosis AFP > 20 ug/dl Sensitivity 41-65% Specificity 80-94% Positive LR Negative LR Gupta Ann Intern Med 2003 AFP > 20 Positive LR 5 Post-test probability = ~10% HCV with Cirrhosis 2% HCC AFP < 20 Negative LR 0.5 Post-test Probability = 1% A 45 year old woman sees you in follow up. She has HCV and alcohol cirrhosis, but stopped drinking 2 years ago Her labs include CR 0.8, TB 0.9 and INR 1.1, AST 66, ALT 48 She recently saw hepatology and was told she did not need transplant As her primary care doctor she asks if you agree Child-Turcotte-Pugh System (CTP) Not formally validated as prognostic tool Useful means to rapidly assess prognosis Also useful for pre-operative risk assessment Semi-Subjective Model for End stage Liver Disease (MELD) Currently used for transplant listing Based on creatinine, INR, total bilirubin (Cr and INR more heavily weighted) Objective values comprise score Validated to predict survival 3 month survival for a MELD of 6 >90% 40 7% Malinchoc Hepatology point 2 points 3 points Grade None encephalopathy Ascites Absent Slight Moderate or more Bilirubin >3 Bilirubin (for PBC >10 patients) Albumin > <2.8 INR < >2.3 Merion Am J Transplant 2005 Score 6 Class A, 7-9 Class B, 10 Class C 9
10 Emphysema and Liver disease Cirrhosis, DM, arthritis, AFIB IBD and elevated alkaline phosphatase Viral hepatitis associated with liver failure in pregnancy Liver disease, with anemia and psychosis ALT greater than 5000 in someone with alcoholism Elevated alkaline phosphatase with itching and fatigue seen in a 50 year old woman A 25 year old presents 3 days after a significant acetaminophen ingestion There is AMS and they are intubated early in the course- NAC is started Lab Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 TB AST ALT INR By Day 3 is the course better, worse or stable? A person is referred for initial elevation in ALT (52)- synthetic function is normal and there are no prior available liver tests Ultrasound one year prior suggested a fatty liver Clinical history includes a blood transfusion in 1988 for a trauma, DM, BMI 29 and a family history of cancer in the liver but might have been metastatic Medications include metformin, losartan and atorvastatin When evaluating suspected liver disease Realize that aminotransferases are imperfect markers of disease state Following synthetic function is of vital importance Remember medications and complementary medicines Approach patients based on risk factors and pattern of liver injury (hepatocellular or cholestatic) Use models to assess severity of liver injury 10
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Interpreting Liver Function Tests
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
4/27/2018. Disclosures LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
Abnormal Liver Chemistries. Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University
 Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
Abnormal Liver Chemistries Lauren Myers, MMsc. PA-C Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure 1. The speaker/planner Lauren Myers, MMSc, PA-C have no relevant financial relationships to disclose
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS
 CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
9/28/2016. Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach. Objectives. Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
 Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Scott W. Biggins, MD, MAS Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology UCSF Scott.Biggins@ucsf.edu (Thanks to Hal Yee, MD) This Morning s Presentation Clinical vignettes
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease. Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya
 Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
What are LFTs? What are LFTs? 3/20/2017. Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests. Transaminases. Alkaline phosphatase.
 Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests James Panetta, DO What are LFTs? Transaminases Alkaline phosphatase Bilirubin Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase What are LFTs? 5 nucleosidase Lactate Dehydrogenase
Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistry Tests James Panetta, DO What are LFTs? Transaminases Alkaline phosphatase Bilirubin Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase What are LFTs? 5 nucleosidase Lactate Dehydrogenase
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD
 Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
Interpreting Liver Tests What Do They Mean? Roman E. Perri, MD The assessment of patients with abnormal liver tests is common in both primary care and gastroenterology clinics. However, among patients
IN THE NAME OF GOD. D r. MANIJE DEZFULI AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST
 IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
IN THE NAME OF GOD AZAD UNIVERCITY OF TEHRAN BOOALI HOSPITAL D r. MANIJE DEZFULI INFECTIOUS DISEASES SPECIALIST Acute Viral Hepatitis The Anatomy of the Liver Hepatic Physiology Liver: Largest solid organ
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Acute Hepatitis: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes. Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC
 : An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
: An Approach to Infectious and Other Causes Mary Anne Cooper MSc, MD, MEd, FRCPC Faculty: Dr. Mary Anne Cooper Relationships with commercial interests: Consulting Fees: Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Canada Objectives
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES
 GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES American Academy of Insurance Medicine Triennial Course in Insurance Medicine 2012 Clifton Titcomb Jr., MD (Hannover Re) James Topic, MD (Protective Life) 1 CASE #1 Application
GI DISEASE WORKSHOP CASE STUDIES American Academy of Insurance Medicine Triennial Course in Insurance Medicine 2012 Clifton Titcomb Jr., MD (Hannover Re) James Topic, MD (Protective Life) 1 CASE #1 Application
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
LFTs: an update A MacGilchrist PLIG meeting 31st January 2019
 LFTs: an update A MacGilchrist PLIG meeting 31 st January 2019 LFTs: what are we trying to achieve? (1) The case against investigation abnormal LFTs in up to 21% of the population only 1-2% develop significant
LFTs: an update A MacGilchrist PLIG meeting 31 st January 2019 LFTs: what are we trying to achieve? (1) The case against investigation abnormal LFTs in up to 21% of the population only 1-2% develop significant
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Disclosure. Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes
 Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Evaluation of Abnormal Hepatic Enzymes Bruce D. Askey, MS, ANP-BC Associate Lecturer North Andover, MA Adult Nurse Practitioner Dept. of Hepatology/Gastroenterology Guthrie Clinic Sayre, Pa Disclosure
Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives
 Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives 1. Define 3 key components of the patient history that should be further evaluated when liver function testing reveals elevated aminotransferases. 2. Identify
Session 11: The ABCs of LFTs Learning Objectives 1. Define 3 key components of the patient history that should be further evaluated when liver function testing reveals elevated aminotransferases. 2. Identify
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests
 A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
A Rational Evidence-based Approach to Abnormal Liver Tests Jane D. Ricaforte-Campos, MD FPCP, FPSG, FPSDE 2013 HSP Post-graduate Course Radisson Blu Hotel, Cebu City misnomer Liver Function Tests Does
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist
 Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Hepatology for the Nonhepatologist Kenneth E. Sherman, MD, PhD Gould Professor of Medicine Director, Division of Digestive Diseases University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio Learning
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes
 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Enzymes Donald Gardenier, DNP, FNP-BC Assistant Professor and Clinical Program Director Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, NY Conflict of Interest
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant. Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP-BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC
 End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
End Stage Liver Disease & Disease Specific Indications for Liver Transplant Susan Kang, RN, MSN, ANP BC Introduction (https://www.srtr.org) 1 What does the liver do? STORAGE METABOLIC DETOXIFICATION SYNTHETIC
Interpreting Your Tests
 Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
Interpreting Your Tests Lisa M. Forman, MD, MSCE Associate Professor of Medicine Section Hepatology and Liver Transplantation University of Colorado Denver Outline Bile Duct Anatomy Lab Tests LFTs Tumor
-Liver function tests -
 -Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
-Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
HEPATOLOGY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 PART 1 HEPATOLOGY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER 1 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Tests Charissa Y. Chang Division of Liver Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY,
PART 1 HEPATOLOGY COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER 1 Approach to the Patient with Abnormal Liver Tests Charissa Y. Chang Division of Liver Diseases, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY,
GI Workshop Case Studies
 GI Workshop Case Studies Cliff Titcomb MD Hannover Re AAIM Annual Meeting San Diego, October, 2012 5 Tests Commonly Known as Liver Function Tests Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) Aspartate Aminotransferase
GI Workshop Case Studies Cliff Titcomb MD Hannover Re AAIM Annual Meeting San Diego, October, 2012 5 Tests Commonly Known as Liver Function Tests Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) Aspartate Aminotransferase
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Liver Biochemistry. Slide 1 of 49 MPHM14 Liver Biochemistry
 MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy. Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH
 Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Initial Evaluation for HCV Therapy Hope McGratty PA-C, MPH Conflict of Interest Disclosure Statement None Who are we talking about today? Treatment naïve Chronic infection This patient seems complicated
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests
 Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Investigating and Referring Incidental Findings of Abnormal Liver Tests Note on Referral Guidelines: these revised guidelines are presented as a tool to aid appropriate referral and management of common
Pittsburgh CME Conference November 7-9, 2014
 Disclosures: Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation Pittsburgh CME Conference November 7-9, 2014 Abnormal LFT s Now What? (Patient Safety) Bruce Gebhardt, MD St. Vincent Health System, Erie,
Disclosures: Pennsylvania Academy of Family Physicians Foundation Pittsburgh CME Conference November 7-9, 2014 Abnormal LFT s Now What? (Patient Safety) Bruce Gebhardt, MD St. Vincent Health System, Erie,
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Overview. The Liver and Biliary System 10 cases to guide you. Liver Function. Background/Patterns. Case #1
 Overview The Liver and Biliary System 10 cases to guide you Chapy Venkatesan, MD Department of Medicine VCU School of Medicine Inova Campus 1 To be familiar with the approach to differential diagnosis
Overview The Liver and Biliary System 10 cases to guide you Chapy Venkatesan, MD Department of Medicine VCU School of Medicine Inova Campus 1 To be familiar with the approach to differential diagnosis
ABIM Review Hepatobiliary
 ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Danielle Brandman, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco ABIM Certification Exam ABIM Certification Exam Hepatobiliary Review Diagnostic
ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Danielle Brandman, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco ABIM Certification Exam ABIM Certification Exam Hepatobiliary Review Diagnostic
The widespread availability and frequent use of serum
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2002;123:1367 1384 AGA Technical Review on the Evaluation of Liver Chemistry Tests This literature review and the recommendations therein were prepared for the American Gastroenterological
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2002;123:1367 1384 AGA Technical Review on the Evaluation of Liver Chemistry Tests This literature review and the recommendations therein were prepared for the American Gastroenterological
Learning Objectives. Case 1. Case Presentations. Interpretation of Liver Tests. Interpretation of Liver Tests. Presenter Disclosure Information
 Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Interpretation of Liver Tests SPEAKER Steven-Huy Han, MD, AGAF, FAASLD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Steven-Huy Han, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 11:05 11:45am Interpretation of Liver Tests SPEAKER Steven-Huy Han, MD, AGAF, FAASLD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Steven-Huy Han, MD,
Drug-induced liver injury
 Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
Drug-induced liver injury Vincent Wong MBChB(Hons), MD, FRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Professor, Department of Medicine and Therapeutics Director, Cheng Suen Man Shook Foundation Centre for Hepatitis Studies Deputy
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease
 AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
AAIM: GI Workshop Follow Up to Case Studies Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ulcerative Colitis Crohn s Disease Daniel Zimmerman, MD VP and Medical Director, RGA Global October 2015 Non-alcoholic Fatty
Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 25 Number 1 Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane. V Sampathi,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 25 Number 1 Suspected Isoflurane Induced Hepatitis from Cross Sensitivity in a Post Transplant for Fulminant Hepatitis from Halothane. V Sampathi,
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice
 CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
CrackCast Episode 28 Jaundice Episode overview: 1) Describe heme metabolism 2) List common pre-hepatic/hepatic/post-hepatic causes of jaundice Wisecracks: 1) What are clinical signs of liver disease? 2)
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Hepatitis. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 5/2/2019. Mob:
 Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
Hepatitis Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 5/2/2019 Hepatitis Hepatitis means the inflammation of the liver. May cause by viruses or bacteria, parasites, radiation, drugs, chemical and toxins (alcohol).
LIVER DISEASES. Anatomy
 LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
ACCME/Disclosures. The Overlap Syndromes: Do They Exist? Key Points and Questions 4/6/2016. Hans Popper Hepatopathology Society
 ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS which they or their spouse/partner
Viral hepatitis. Supervised by: Dr.Gaith. presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a
 Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Viral hepatitis Supervised by: Dr.Gaith presented by: Shaima a & Anas & Ala a Etiology Common: Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Less common: Cytomegalovirus EBV Rare: Herpes
Biochemistry Liver Function Tests (LFTs)
 HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
HbA NH 2 H 2 O 2 KClO3 Cl 2 O 7 PO 4 CH2O NAOH KMnO 4 M E D I C I N E KING SAUD UNIVERSITY Co 2 COOH MgCl 2 H 2 O Important Extra Information Doctors slides Doctors notes SO 2 HCN CCl 4 CuCl 2 SiCl 4 Biochemistry
Abnormal LFTs GP CME 2014 Workshop Fri 55 mins. Dr Alasdair Patrick Macmurray Center GP CME 2014
 Abnormal LFTs GP CME 2014 Workshop Fri 55 mins Dr Alasdair Patrick Macmurray Center GP CME 2014 Dr Alasdair Patrick Gastroenterologist Overview Liver Function Tests Cholestasis Hepatocellular / Hepatitic
Abnormal LFTs GP CME 2014 Workshop Fri 55 mins Dr Alasdair Patrick Macmurray Center GP CME 2014 Dr Alasdair Patrick Gastroenterologist Overview Liver Function Tests Cholestasis Hepatocellular / Hepatitic
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 18 PRACTICE GUIDELINES CME ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2 and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 Clinicians
18 PRACTICE GUIDELINES CME ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2 and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 Clinicians
Biochemistry Lecture #3
 1 P a g e Hello Awn.. This lecture includes the slides.. anything with (!) is important.. and Italic line Any sentence within Double Brackets {{ }} is just for understanding (Not from Slides) Let s start
1 P a g e Hello Awn.. This lecture includes the slides.. anything with (!) is important.. and Italic line Any sentence within Double Brackets {{ }} is just for understanding (Not from Slides) Let s start
AASLD Immune tolerant phase HBV NAFLD diagnostic HCC
 AASLD 2016 Immune tolerant phase HBV NAFLD diagnostic HCC Immune tolerant 3 Modified from Chan HLY and Wong VWS. Hepatitis B. In Zakim and Boyers s Hepatology 2012 2015 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE S1T6UDY
AASLD 2016 Immune tolerant phase HBV NAFLD diagnostic HCC Immune tolerant 3 Modified from Chan HLY and Wong VWS. Hepatitis B. In Zakim and Boyers s Hepatology 2012 2015 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE S1T6UDY
Management of Hepatitis C in Primary Care BABAFEMI ONABANJO, MD & BEN ALFRED, FNP UMASS FAMILY HEALTH CENTER WORCESTER
 Management of Hepatitis C in Primary Care BABAFEMI ONABANJO, MD & BEN ALFRED, FNP UMASS FAMILY HEALTH CENTER WORCESTER Objective Epidemiology Screening criteria Appropriate work up Treatment Guidelines
Management of Hepatitis C in Primary Care BABAFEMI ONABANJO, MD & BEN ALFRED, FNP UMASS FAMILY HEALTH CENTER WORCESTER Objective Epidemiology Screening criteria Appropriate work up Treatment Guidelines
ABIM Review Hepatobiliary
 Hepatobiliary Review ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Oren Fix, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Diagnostic algorithms for cholestatic versus hepatitic pattern of
Hepatobiliary Review ABIM Review Hepatobiliary Oren Fix, MD, MSc Assistant Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Diagnostic algorithms for cholestatic versus hepatitic pattern of
Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis
 Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis 1 Training Objectives At the end of the module, trainees will be able to ; Demonstrate improved knowledge of the global epidemiology of the viral hepatitis Understand
Module 1 Introduction of hepatitis 1 Training Objectives At the end of the module, trainees will be able to ; Demonstrate improved knowledge of the global epidemiology of the viral hepatitis Understand
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon
 What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
Viral Hepatitis. Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
Viral Hepatitis Dr. Abdulwahhab S. Abdullah CABM, FICMS-G&H PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Viral hepatitis Viral hepatitis must be considered in any patient presenting with hepatitis on LFTs (high
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
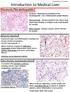 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
CHAPTER 1. Alcoholic Liver Disease
 CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
Chapter 18 LIVER BILIARY TRACT
 Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice
 1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis in Clinical Practice Atif Zaman, MD MPH Professor of Medicine Senior Associate Dean for Clinical and Faculty Affairs School of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Disclosure
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN
 Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Overview of PSC Jayant A. Talwalkar, MD, MPH Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN 2012 Annual Conference PSC Partners Seeking a Cure May 5, 2012 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis Multifocal
Mikhail Alper, PA-C California Gastroenterology Associates Fresno/Madera, CA. Dr. Robert Gish Dr. Sammy Saab Dr. Naeem Akhtar
 Mikhail Alper, PA-C California Gastroenterology Associates Fresno/Madera, CA Dr. Robert Gish Dr. Sammy Saab Dr. Naeem Akhtar 1 AST, ALT Alkaline Phosphatase GGT Bilirubin Albumin Protime/INR True liver
Mikhail Alper, PA-C California Gastroenterology Associates Fresno/Madera, CA Dr. Robert Gish Dr. Sammy Saab Dr. Naeem Akhtar 1 AST, ALT Alkaline Phosphatase GGT Bilirubin Albumin Protime/INR True liver
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Dr Mere Kende. MBBS,Mmed(Path), MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM Lecturer -SMHS
 Dr Mere Kende MBBS,Mmed(Path), MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM Lecturer -SMHS Reasons for LFT Classification of Liver Diseases Signs and Symptoms of Liver Disease Routine Liver Tests Jaundice Examples of Liver Diseases
Dr Mere Kende MBBS,Mmed(Path), MAACB, MACTM, MACRRM Lecturer -SMHS Reasons for LFT Classification of Liver Diseases Signs and Symptoms of Liver Disease Routine Liver Tests Jaundice Examples of Liver Diseases
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. G M Kellerman. Hunter Area Pathology Service
 LIVER FUNCTION TESTS G M Kellerman Hunter Area Pathology Service FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Carbohydrate metabolism storage (glycogen), release, synthesis (gluconeogenesis), interconversion (galactose, fructose),
LIVER FUNCTION TESTS G M Kellerman Hunter Area Pathology Service FUNCTIONS OF LIVER Carbohydrate metabolism storage (glycogen), release, synthesis (gluconeogenesis), interconversion (galactose, fructose),
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none none Risk Factors for Alcoholic Liver Disease Amount of alcohol consumed Duration of alcohol consumption Gender
Pediatric PSC A children s tale
 Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology. Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D.
 Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D. GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Gallbladder Pancreas GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Hepa**s Alcoholic
Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D. GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Gallbladder Pancreas GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Hepa**s Alcoholic
Hepatology Case reports
 Hepatology Case reports Prof.. MUDr. Libor VítekV tek,, PhD, MBA IV. Dept. Int Med and Institute of Clinical Biochemistry and laboratory diagnostics VFN and 1. LF UK in Praze Biochemical methods in hepatology
Hepatology Case reports Prof.. MUDr. Libor VítekV tek,, PhD, MBA IV. Dept. Int Med and Institute of Clinical Biochemistry and laboratory diagnostics VFN and 1. LF UK in Praze Biochemical methods in hepatology
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers
 Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Management of Hepatitis B - Information for primary care providers July 2018 Chronic hepatitis B (CHB) is often a lifelong condition. Not everyone infected needs anti-viral therapy. This document outlines
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease
 Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
Pathophysiology I Liver and Biliary Disease The Liver The liver is located in the right upper portion of the abdominal cavity just beneath the right side of the rib cage. The liver has many functions that
ABIM Review Hepatology
 ABIM Review Hepatology Norah Terrault, MD, MPH Associate Professor University of California San Francisco July 15, 2009 Liver Review Diagnostic algorithms for cholestatic versus hepatitic pattern of liver
ABIM Review Hepatology Norah Terrault, MD, MPH Associate Professor University of California San Francisco July 15, 2009 Liver Review Diagnostic algorithms for cholestatic versus hepatitic pattern of liver
Liver Network. Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities
 Liver Network Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities Dr Mark Hudson Dr Stuart McPherson On behalf of the North East & North Cumbria Hepatology Network 1
Liver Network Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities Dr Mark Hudson Dr Stuart McPherson On behalf of the North East & North Cumbria Hepatology Network 1
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases
 Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Not All Patients With Liver Disease Have HCV Diagnosis and Management of Some Common Non HCV Liver Diseases Prevalence of Chronic Liver Disorders in the United States Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disorder
Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD
 Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD Liver Unit, Internal Medicine Department Vall d Hebron Hospital 1 Clinical Case 70 year-old male Smoker, no alcohol intake No risk factors Diabetes Mellitus treated with
Clinical Case Maria Butí, MD, PhD Liver Unit, Internal Medicine Department Vall d Hebron Hospital 1 Clinical Case 70 year-old male Smoker, no alcohol intake No risk factors Diabetes Mellitus treated with
Harvard Medical School
 Harvard Medical School Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Tests in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Harvard Medical School Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Tests in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, MD, FACP Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Chronic Hepatitis. Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Chronic Hepatitis Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Autoimmune Hepatitis Annual incidence 1.9/100 000 in N Europe Prevalence 16.9/100 000 ~5% all liver transplants Female preponderance
Chronic Hepatitis Andrew Bathgate Chris Bellamy Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh Autoimmune Hepatitis Annual incidence 1.9/100 000 in N Europe Prevalence 16.9/100 000 ~5% all liver transplants Female preponderance
Management of acute alcoholic hepatitis
 Management of acute alcoholic hepatitis Yesim ALAHDAB Marmara University Hospital, Istanbul/TURKEY 5 th European Young Hepatologists Workshop August, 27-29, 2015 Moulin de Vernègues, France 1.4L ALCOHOL
Management of acute alcoholic hepatitis Yesim ALAHDAB Marmara University Hospital, Istanbul/TURKEY 5 th European Young Hepatologists Workshop August, 27-29, 2015 Moulin de Vernègues, France 1.4L ALCOHOL
Liver Function Testing. in primary care. Quiz Feedback
 Liver Function Testing in primary care Quiz Feedback Contents Expert Summary, Associate Professor Ed Gane 3 Liver Function Testing in Primary Care Quiz 4 Quiz Feedback: Responses from Colleagues, and Specialist
Liver Function Testing in primary care Quiz Feedback Contents Expert Summary, Associate Professor Ed Gane 3 Liver Function Testing in Primary Care Quiz 4 Quiz Feedback: Responses from Colleagues, and Specialist
Liver Network Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities
 Liver Network Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities Dr Mark Hudson Dr Stuart McPherson On behalf of the North East & North Cumbria Hepatology Network 1
Liver Network Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Asymptomatic Liver Function Abnormalities Dr Mark Hudson Dr Stuart McPherson On behalf of the North East & North Cumbria Hepatology Network 1
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management
 Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
Viral Hepatitis Diagnosis and Management CLINICAL BACKGROUND Viral hepatitis is a relatively common disease (25 per 100,000 individuals in the United States) caused by a diverse group of hepatotropic agents
