Detailed Descriptors, Testing Methods and Evidence Drinks: Levels 0-4
|
|
|
- Norma Hampton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Detailed Descriptors, Testing Methods and Evidence Drinks: Levels 0-4 The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 1
2 INTRODUCTION The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) was founded in 2013 with the goal of developing new global standardised terminology and definitions to describe texture modified foods and thickened liquids used for individuals with dysphagia of all ages, in all care settings, and all cultures. Three years of ongoing work by the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Committee has culminated in a final dysphagia diet framework consisting of a continuum of 8 levels (0-7). Levels are identified by numbers, text labels and colour codes. This document provides detailed descriptors for the 5 levels of drinks in the IDDSI Framework (Levels 0-4). Descriptors are supported by simple measurement methods that can be used by people with dysphagia or by caregivers, clinicians, food service professionals or industry to confirm the level of a drink. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution Sharealike 4.0 Licence Attribution is requested as follows: The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative Attribution is NOT PERMITTED for derivative works incorporating any alterations to the IDDSI Framework that extend beyond language translation. Supplementary Notice: Modification of the diagrams or descriptors within the IDDSI Framework is DISCOURAGED and NOT RECOMMENDED. Alterations to elements of the IDDSI framework may lead to confusion and errors in diet texture or drink selection for patients with dysphagia. Such errors have previously been associated with adverse events including choking and death. The IDDSI Committee would like to acknowledge the interest and participation of the global community including patients, caregivers, health professionals, industry, professional associations and researchers. Co-Chairs: Peter Lam (CAN) & Julie Cichero (AUS); The IDDSI Committee: Committee Members: Jianshe Chen (CHN), Roberto Dantas (BRA), Janice Duivestein (CAN), Ben Hanson (UK), Jun Kayashita (JPN), Caroline Lecko (UK), Joe Murray (USA), Mershen Pillay (ZAF), Soenke Stanschus (GER), Catriona Steele (CAN). The International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative Inc. (IDDSI) is an independent, not-for-profit entity. IDDSI is grateful to a large number of agencies, organizations and industry partners for financial and other support. Sponsors have not been involved with the design or development of the IDDSI framework. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 2
3 Evidence and Measurement Evidence A systematic review of the literature was conducted to examine the impact of drink thickness and food texture on swallowing behavior across the age spectrum (Steele et al., 2015 Dysphagia, 30(1): 2-26). With regards to liquids, the results of the systematic review determined: Thicker liquids reduce the risk of penetration aspiration, but also increase the risk of post-swallow residue in the pharynx The literature was insufficient to support the delineation of specific viscosity boundaries or other quantifiable material properties related to these clinical outcomes Of the 36 studies that met the eligibility criteria for the systematic review, 26 related to function in healthy populations whilst only 10 were related to individuals with dysphagia. Of these 10 studies, one related to infants and the remainder investigated swallowing function in adults with neurological or neurogenic conditions, or dysphagia associated with treatment for oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal cancer. The results of IDDSI s international stakeholder surveys demonstrated common use of thin drinks plus three levels of increasing drink thickness for the management of swallowing problems across the age spectrum. The systematic review also found research investigating the impact of thickened drinks according to this general framework (i.e., thin drinks plus three levels of increasing thickness) and described using labels previously found in previous national terminologies such as Nectar/Syrup/Level 150/Mildly thick; Honey/Custard/Level 400/Moderately thick and Pudding/Spoon thick/ Level 900/Extremely thick (Steele et al., 2015, Dysphagia, 30(1): 2-26). In addition, paediatric stakeholders reported common use of a drink thicker than water but thinner than the commencement point of thickened liquids commonly used for adults. This level has been incorporated into the IDDSI Framework as Level 1 Slightly Thick. Level 1 Slightly thick drinks has also been verified as distinct from other thickness levels in the literature, however, as with all other thickened liquids, this level lacks data to determine the exact thickness required for therapeutic benefit. Given the paucity of research regarding therapeutic thickness levels for thickened drinks, the IDDSI framework is based on an understanding that increasing thickness has a demonstrated therapeutic benefit for reducing the risk of penetration/aspiration. The number of levels of drink thickness included in the framework and recommended for best practice is based on clinical experience, stakeholder consensus and expert opinion. The systematic review points to an urgent need to conduct quality research to determine thickness levels that provide therapeutic benefit by reducing risk for penetration/aspiration and/or improving swallowing function. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 3
4 Measurement Accurate measurement of fluid flow properties is a complex task. To date, both research and existing national terminologies, have studied or recommended the classification of drinks based on viscosity. However, viscosity measurement is not accessible to most clinicians or caregivers. Furthermore, viscosity is not the only relevant parameter: the flow of a drink as it is consumed is influenced by multiple other variables including density, yield stress, temperature, propulsion pressure and fat content (O Leary et al., 2010; Sopade et al., 2007, Sopade et al., 2008a,b; Hadde et al.2015a,b). The systematic review demonstrated wide variability in testing techniques used and found that other key parameters such as shear rates, sample temperature, density and yield stress were rarely reported (Steele et al., 2015; Cichero et al., 2013). Drinks thickened with different thickening agents may have the same measurement of apparent viscosity at one particular shear rate, and yet have very different flow characteristics in practice (Steele et al. 2015; O Leary et al.,2010; Funami et al., 2012; Ashida et al., 2007; Garcia et al., 2005). In addition to variations in flow associated with drink characteristics, flow rates during swallowing are expected to differ depending on a person s age and level of impairment of swallowing function (O Leary et al., 2010). For these reasons, a measurement of viscosity has not been included in the IDDSI descriptors. Instead, a gravity flow test using a 10ml slip tip syringe has been chosen by IDDSI as a practical objective measure to classify drinks based on their rate of flow. The controlled conditions are broadly representative of drinking through a straw or beaker. Although the equipment is simple, it is already internationally standardised and the IDDSI Flow Test has been found to categorise a wide range of liquids reliably, in agreement with currently existing laboratory tests and expert judgement. It has been found to be sensitive enough to demonstrate small changes in thickness associated with change in serving temperature. For extremely-thick drinks, which do not flow through a syringe in 10 seconds and are best consumed with a spoon, a Fork Test is recommended as a method for determining consistency. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 4
5 Evidence relating to levels of thickness and an accompanying grading of evidence (NHMRC, 2000) is shown in the table below. Note: despite best efforts, this list is not exhaustive. We intend to continue to update this descriptors document over time as further research is conducted and reported. Variable Reference Grade of Evidence Investigations of Levels 0 Thin in the research literature As noted in Steele et al. (2015): Barata et al., 2013 Binjie et al., 2010 Bisch et al., 1994 Butler et al., 2004 Chen et al., 1992 Chi-Fishman & Sonies, 2002 dos Santos et al., 2011 Goldfield et al., 2013 Igarashi et al., 2010 Ishida et al., 2002 Lee et al., 2012 Lee et al., 2010 Lin et al., 2011 Linden et al., 1989 Oommen et al., 2011 Reimers-Neils et al., 1994 Ruark et al., 2002 Saitoh et al., 2007 Steele & Van Lieshout, 2004 Steele & Van Lieshout, 2005 Taniwaki et al., 2013 Troche et al., 2008 Youmans et al., 2009 I Evidence for existence of Level 1 Slightly Thick in the research literature Investigations of Level 2 Mildly Thick in the research literature Stuart & Motz, 2009 de Almeida et al., 2011 Cichero et al., 2011 September et al., 2014 As noted in Steele et al. (2015): Barata et al., 2013 Chen et al., 1992 Chi-Fishman & Sonies, 2002 Goldfield et al Igarashi et al., 2010 Inagaki et al., 2008 Inagaki et al., 2009a Inagaki et al., 2009b Lee et al., 2010 Oommen et al., 2011 Reimers-Neils et al., 1994 Ruark et al., 2002 Steele & Van Lieshout, 2004 Steele & Van Lieshout, 2005 Youmans et al., 2009 In vitro bench test In vitro bench test In vitro bench test In vitro bench test I The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 5
6 Investigations of Level 3 Moderately thick/liquidised in the research literature Investigations of Level 4 Extremely thick / Pureed in the research literature Drinks that are too thick increase the risk of post swallow residue in the pharynx As noted in Steele et al. (2015): Butler et al., 2004 Chi-Fishman & Sonies, 2002 Igarashi et al., 2010 Inagaki et al., 2008 Inagaki et al., 2009a Inagaki et al., 2009b Steel & Van Lieshout, 2004 Steele & Van Lieshout, 2005 Youmans et al., 2009 As noted in Steele et al. (2015): Barata et al., 2013 Bingjie et al., 2010 Bisch et al., 1994 Butler et al., 2004 Chen et al., 1992 Chi-Fishman & Sonies, 2002 Dos Santos et al., 2011 Gisel, 1991 Inagaki et al., 2008 Inagaki et al., 2009a Inagaki et al., 2009b Ishida et al., 2002 Kim & Han, 2005 Lin et al., 2011 Reimers-Neils et al., 1994 Taniwaki et al., 2013 Troche et al., 2008 Youmans et al., 2009 Hind et al., (2012) Robbins et al., (2008) I I II Grading of evidence National Health and Medical Research Council (2000) I II III-1 III-3 Evidence from systematic review of all relevant randomised controlled trials Evidence from at least one properly designed randomised controlled trial, retrospective studies Evidence from well-designed pseudo-randomised controlled trials (e.g., alternate allocation or some other method) Evidence from comparative studies with concurrent controls and allocation not randomised (cohort studies), case-control studies, or interrupted time-series with a control group (i.e., non-consecutive cohort study) Evidence from comparative studies with historical control, two or more single-arm studies, or interrupted time series without a parallel control group Evidence from case series, either post-test or pre-test and post-test, or superseded reference standards The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 6
7 Description/ Characteristics Physiological rationale for this level of thickness Testing method IDDSI Flow Test* Flows like water Fast flow Can drink through any type of teat/nipple, cup or straw as appropriate for age and skills Functional ability to safely manage liquids of all types Test liquid flows through a 10 ml slip tip syringe completely within 10 seconds, leaving no residue (see IDDSI Flow Test instructions*) The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 7
8 Description/ Characteristics Physiological rationale for this level of thickness Thicker than water Requires a little more effort to drink than thin liquids Flows through a straw, syringe, teat/nipple Similar to the thickness of commercially available Anti-regurgitation (AR) infant formula Predominantly used in the paediatric population as a thickened drink that reduces speed of flow yet is still able to flow through an infant teat/nipple. Consideration to flow through a teat/nipple should be determined on a case-by-case basis. Testing method IDDSI Flow Test* Test liquid flows through a 10 ml slip tip syringe leaving 1-4 ml in the syringe after 10 seconds (see IDDSI Flow Test instructions*) The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 8
9 Description/ Characteristics Physiological rationale for this level of thickness Testing method IDDSI Flow Test* Flows off a spoon Sippable, pours quickly from a spoon, but slower than thin drinks Effort is required to drink this thickness through standard bore straw (standard bore straw = inch or 5.3 mm diameter) If thin drinks flow too fast to be controlled safely, these Mildly Thick liquids will flow at a slightly slower rate May be suitable if tongue control is slightly reduced. Test liquid flows through a 10 ml slip tip syringe leaving 4 to 8 ml in the syringe after 10 seconds (see IDDSI Flow Test instructions*) The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 9
10 Description/ Characteristics Physiological rationale for this level of thickness Testing method IDDSI Flow Test* Fork Test Will not hold its shape on a spoon Sippable, pours slowly off a spoon Difficult to suck through a standard bore or wide bore straw (wide bore straw = inch or 6.9mm) Cannot be piped, layered or moulded Cannot be eaten with a fork because it drops through the prongs If tongue control is insufficient to manage Mildly Thick drinks (Level 2), this Moderately Thick/Liquidised level may be suitable Flows slowly from a spoon or cup: easier to control Allows more time for oral control Needs some tongue propulsion effort Test liquid flows slowly through a 10 ml slip tip syringe leaving more than 8 ml in the syringe after 10 seconds (see IDDSI Flow Test instructions*) Prongs of a fork do not make a clear pattern on the surface Spreads out if spilled The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 10
11 Description/ Characteristics Physiological rationale for this level of thickness Holds shape on spoon Flows very slowly under gravity Does not require chewing Could be piped, layered or moulded No lumps Falls off spoon in a single spoonful when tilted and continues to hold a shape on a plate Cannot be sucked through a straw Not sticky Liquid does not separate from solid If tongue control is significantly reduced, this category may be easiest to manage. Requires less propulsion than Minced & Moist (Level 5), Soft (Level 6) and Regular (Level 7) but more than Moderately Thick/Liquidised (Level 3) No biting or chewing required Increased residue is a risk Testing method IDDSI Flow Test* Fork Test Indicators that a sample is too thick Caution No flow or drip through a slip tip syringe after 10 sec (see IDDSI Flow Test instructions*) A full spoonful must plop off the spoon if the spoon is tilted or turned sideways; a very gentle flick may be necessary to dislodge the sample from the spoon, but the sample should slide off easily with very little food left on the spoon; i.e. the sample should not be firm and sticky The prongs of a fork can make a clear pattern on the surface, and/or the sample retains the indentation from the fork Spreads or slumps very slowly if spilled Does not fall off the spoon when tilted Sticks to spoon Samples that are too thick increase the risk of post-swallow residue in the pharynx (Hind et al., (2012), J Rehab Res Dev, 49: ; Robbins et al., (2008), Annals of Internal Medicine, 148: ). The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 11
12 The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 12
13 The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 13
14 FAQs: Drinks Q: My facility only uses two levels of drink thickness; do we have to use all of the IDDSI drink thickness levels? A: No, although the IDDSI framework includes five different levels of increasing drink thickness, there is no expectation that every facility will use all five levels. For example, some aged care facilities may only use Level 0 -Thin, Level 3- Moderately Thick/Liquidised and Level 4 Extremely Thick/Pureed. By labeling the drinks in this way, when a patient/client moves from a facility with fewer drink levels to a hospital with more drink levels, it will be faster, safer and more accurate for health professionals and care staff to provide the appropriate drink thickness level. Q: I ve not heard of Level 1 Slightly Thick before, what is this level? A: Level 1 Slightly Thick is predominantly used by paediatric clinicians and refers to the thickness level similar to commercially prepared anti-regurgitation infant formula. It is noticeably thicker than regular Level 0 thin drinks, but thinner than Level 2 Mildly Thick drinks. It is thick enough to slow the flow rate through a teat/nipple, whereas Level 2 Mildly thick fluids are too thick to flow through a teat/ nipple. Clinicians working with adult caseloads may find that some products that they have previously described as naturally thick fall in this Level 1 Slightly Thick category. Q: My facility has used the terms nectar and honey for decades; why weren t these terms used in the IDDSI framework? A: Two international stakeholder surveys were conducted encompassing more than 5000 responses. Although the terms nectar and honey were widely understood in some parts of the world, they had no meaning in other parts of the world, particularly Asia. Other considerations included the natural variability of honey in its crystalline and liquid states, and that that the food honey is a botulism risk for infants under the age of 12 months. As an international framework suitable for use across the age spectrum, it was decided that terms that described variations of drink thickness would be most appropriate. Q: Why are Liquidised foods and Moderately thick drinks on the same level and why are Extremely thick drinks and Pureed foods on the same level? A: When viewed from a drink thickness perspective, regardless of whether an item is a food (e.g. liquidised soup), or a drink (e.g. moderately thick liquid), the texture and flow characteristics are very similar. The IDDSI framework demonstrates this equivalence in texture, regardless of whether these items would conventionally be referred to as food or drinks. Q: Won t fruit smoothies and liquidised soups clog up the syringe? A: The official IDDSI recommendation is that products in Levels 0-4 should be smooth and homogenous, without particles or lumps. If you are blending a smoothie, then you must take care to ensure there are no lumps or seeds. If particles clog the syringe, then additional blending or passing through a sieve is recommended. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 14
15 Q: What does a 10 ml Slip Tip syringe look like and can I be sure it is the same around the world? A: A 10 ml slip tip syringe is shown in the photo below. It is sold as a plastic sterile hypodermic syringe for single use. It is also known as a Luer slip tip syringe. The tip of the syringe is smooth and without a locking system. It does not matter if the tip is situated to be central or eccentric (positioned off to one side). The slip tip hypodermic syringe is manufactured to international standards (ISO ) to ensure that it is the same around the world. The syringes come in different capacities (e.g. 1 ml, 5 ml, 10 ml, 20 ml etc.). We have chosen the 10 ml syringe to be used for the IDDSI Flow test. Before use, check the nozzle is clear and free from any plastic residue or manufacturing defects that very occasionally occur. A very quick way to check is to ensure that 10ml of water flows completely through the syringe within 10 seconds using the IDDSI Flow test instructions. The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 15
16 References Ashida I, Iwamori H, Kawakami SY, Miyaoka Y, Murayama A. Analysis of physiological parameters of masseter muscle activity during chewing of agars in healthy young males. J Texture Stud. 2007;38: Barata LF, De Carvalho GB, Carrara-De Angelis E, De Faria JCM, Kowalski LP. Swallowing, speech and quality of life in patients undergoing resection of soft palate. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013;270: Bingjie L, Tong Z, Xinting S, Jianmin X, Guijun J. Quantitative videofluoroscopic analysis of penetration aspiration in poststroke patients. Neurol India. 2010;58:42 7. Bisch EM, Logemann JA, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ, Lazarus CL. Pharyngeal effects of bolus volume, viscosity, and temperature in patients with dysphagia resulting from neurologic impairment and in normal subjects. J Speech HearRes. 1994;37: Butler SG, Postma GN, Fischer E. Effects of viscosity, taste, and bolus volume on swallowing apnea duration of normal adults. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;131: Chen MYM, Peele VN, Donati D, Ott DJ, Donofrio PD, Gelfand DW. Clinical and videofluoroscopic evaluation of swallowing in 41 patients with neurologic disease. Gastrointest Radiol. 1992;17:95 8. Chi-Fishman G, Sonies BC. Effects of systematic bolus viscosity and volume changes on hyoid movement kinematics. Dysphagia. 2002;17: Cichero JAY, Nicholson T, Dodrill PM. Barium liquid is not representative of infant formula: characterisation of rheological and material properties. Dysphagia. 2011;26(3): Cichero JAY, Steele CM, Duivestein J, Clave P, Chen J, Kayashita J, Dantas R, Lecko C, Speyer R, Lam P. The need for international terminology and definitions for texture modified foods and thickened liquids used in dysphagia management: foundations of a global initiative. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. 2013;1: de Almeida MB, de Almeida JAG, Moreira MEL, Novak FR. Adequacy of human milk viscosity to respond to infants with dysphagia: experimental study. J Appl Oral Sci. 2011;19(6): Dos Santos CM, Cassiani RA, Dantas RO. Videofluoroscopic evaluation of swallowing in Chagas disease. Dysphagia. 2011;26: Funami T, Ishihara S, Nakauma M, Kohyama K, Nishinari K. Texture design for products using food hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocolloids. 2012;26: Garcia JM, Chambers ET, Matta Z, Clark M. Viscosity measurementsof nectar- and honey-thick liquids: product, liquid, and time comparisons. Dysphagia. 2005;20: Gisel EG. Effect of food texture on the development of chewing of children between six months and two years of age. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991;33: Goldfield EC, Smith V, Buonomo C, Perez J, Larson K. Preterm infant swallowing of thin and nectar-thick liquids: changes in lingual-palatal coordination and relation to bolus transit. Dysphagia. 2013;28: Hadde EK, Nicholson TM, Cichero JAY. Rheological characterisation of thickened fluids under different temperature, ph and fat contents. Nutrition & Food Science, 2015a; 45 (2): The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 16
17 Hadde Ek, Nicholson TM, Cichero JAY. Rheological characterization of thickened milk components (protein, lactose and minerals). J of Food Eng. 2015b; 166: Hind J, Divyak E, Zielinski J, Taylor A, Hartman M, Gangnon R, Robbins J. Comparison of standardized bariums with varying rheological parameters on swallowing kinematics in males. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2012;49: Igarashi A, Kawasaki M, Nomura S, Sakai Y, Ueno M, Ashida I, Miyaoka Y. Sensory and motor responses of normal young adults during swallowing of foods with different properties and volumes. Dysphagia. 2010;25: Inagaki D, Miyaoka Y, Ashida I, Yamada Y. Influence of food properties and body posture on durations of swallowing-related muscle activities. J Oral Rehabil. 2008;35: Inagaki D, Miyaoka Y, Ashida I, Yamada Y. Activity pattern of swallowing-related muscles, food properties and body position in normal humans. J Oral Rehabil. 2009;36: Inagaki D, Miyaoka Y, Ashida I, Yamada Y. Influence of food properties and body position on swallowing-related muscle activity amplitude. J Oral Rehabil. 2009;36: Ishida R, Palmer JB, Hiiemae KM. Hyoid motion during swallowing: factors affecting forward and upward displacement. Dysphagia. 2002;17: ISO : 1993 (E) Sterile hypodermic syringes for single use: Part 1: syringes for manual use. International Standards Organisation Kim IS, Han TR. Influence of mastication and salivation on swallowing in stroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86: Lee J, Sejdic E, Steele CM, Chau T. Effects of liquid stimuli on dual-axis swallowing accelerometry signals in a healthy population. Biomed Eng Online. 2010;9:7. Lee KL, Kim WH, Kim EJ, Lee JK. Is swallowing of all mixed consistencies dangerous for penetration aspiration? Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;91: Lin P, Hsiao T, Chang Y, Ting L, Chen W, Chen S, Wang T. Effects of functional electrical stimulation on dysphagia caused by radiation therapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Support Care Cancer. 2011;19:91 9. Linden P, Tippett D, Johnston J, Siebens A, French J. Bolus position at swallow onset in normal adults: preliminary observations. Dysphagia. 1989;4: National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. How to use the evidence: assessment and application of scientific evidence. Canberra: Biotext; 2000 O Leary M, Hanson B, Smith C. Viscosity and non-newtonian features of thickened fluids used for dysphagia therapy. J of Food Sci, 2010: 75(6): E330-E338. Oommen ER, Kim Y, McCullough G. Stage transition and laryngeal closure in poststroke patients with dysphagia. Dysphagia. 2011;26: Reimers-Neils L, Logemann J, Larson C. Viscosity effects on EMG activity in normal swallow. Dysphagia. 1994;9: The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 17
18 Robbins J, Gensler G, Hind J, Logemann J, Lindblad AS, Brandt D. & Miller-Gardner PJ. Comparison of two interventions for liquid aspiration on pneumonia incidence: a randomized trial. Annals of Internal Medicine, 2008; 148; Ruark JL, McCullough GH, Peters RL, Moore CA. Bolus consistency and swallowing in children and adults. Dysphagia. 2002; 17: Saitoh E, Shibata S, Matsuo K, Baba M, Fujii W, Palmer JB. Chewing and food consistency: effects on bolus transport and swallow initiation. Dysphagia. 2007;22: September C, Nicholson, T, Cichero J. Implications of changing the amount of thickener in thickened infant formula for infants with dysphagia. Dysphagia, 2014; 29: Sopade PA, Halley PJ, Cichero JAY, Ward LC Rheological characterization of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. I: water and cordial. J Food Eng 79: Sopade PA, Halley PJ, Cichero JAY, Ward LC, Liu J, Teo KH. 2008a. Rheological characterization of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. II. Milk as a dispersing medium. J Food Eng 84(4): Sopade PA, Halley PJ, Cichero JAY, Ward LC, Liu J, Varliveli S. 2008b. Rheological characterization of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. III. Fruit juice as a dispersing medium. J Food Eng 86(4): Steele, C, Alsanei, Ayanikalath et al.the influence of food texture and liquid consistency modification on swallowing physiology and function: A systematic review. Dysphagia, 2015; 30(1): Steele CM, Van Lieshout PH. Influence of bolus consistency on lingual behaviors in sequential swallowing. Dysphagia. 2004;19: Steele CM, van Lieshout PH. Does barium influence tongue behaviors during swallowing? Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2005;14: Stuart S, Motz JM. Viscosity in infant dysphagia management: comparison of viscosity of thickened liquids used in assessment and thickened liquids used in treatment. Dysphagia. 2009;24(4): Taniwaki M, Gao Z, Nishinari K, Kohyama K. Acoustic analysis of the swallowing sounds of food with different physical properties using the cervical auscultation method. J Texture Stud. 2013; 44: Troche MS, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC. Effects of bolus consistency on timing and safety of swallow in patients with Parkinson s disease. Dysphagia. 2008;23: Youmans SR, Youmans GL, Stierwalt JA. Differences in tongue strength across age and gender: is there a diminished strength reserve? Dysphagia. 2009;24: The IDDSI Framework and Descriptors are licensed under the CreativeCommons Attribution 18
%&&'%$()*+#,-).$$ J930#/2#$'5*5#+#/5$
 %&&'%$()*+#,-).$$ J930#/2#$'5*5#+#/5$!!"#$%&&'%$()*+#,-).$*/0$)345-)1$*)#$632#/1#0$7/0#)$5"#$$ 8)#*539#8-++-/1$:55)3;753-/
%&&'%$()*+#,-).$$ J930#/2#$'5*5#+#/5$!!"#$%&&'%$()*+#,-).$*/0$)345-)1$*)#$632#/1#0$7/0#)$5"#$$ 8)#*539#8-++-/1$:55)3;753-/
Dysphagia goes International
 Sponsor Disclosure: Support for this presentation was provided by the Foodservice Express division of Med-Diet, Inc. The material herein is for educational purposes only. Reproduction or distribution of
Sponsor Disclosure: Support for this presentation was provided by the Foodservice Express division of Med-Diet, Inc. The material herein is for educational purposes only. Reproduction or distribution of
Dysphagia goes International
 Sponsor Disclosure: Support for this presentation was provided by the Foodservice Express division of Med-Diet, Inc. The material herein is for educational purposes only. Reproduction or distribution of
Sponsor Disclosure: Support for this presentation was provided by the Foodservice Express division of Med-Diet, Inc. The material herein is for educational purposes only. Reproduction or distribution of
Developments on the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative, IDDSI
 Developments on the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative, IDDSI Dr Ben Hanson, University College London UCL 1. Where we are now timeline and what s happening 2. IDDSI: What? and Why?
Developments on the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative, IDDSI Dr Ben Hanson, University College London UCL 1. Where we are now timeline and what s happening 2. IDDSI: What? and Why?
WILTSHIRE FARM FOODS
 WILTSHIRE FARM FOODS WILTSHIRE FARM FOODS NACC South West Specialised Nutrition Presentation December 2018 What is IDDSI? Why IDDSI? What does it mean? Nutrition Labels Timescales WILTSHIRE Agenda FARM
WILTSHIRE FARM FOODS WILTSHIRE FARM FOODS NACC South West Specialised Nutrition Presentation December 2018 What is IDDSI? Why IDDSI? What does it mean? Nutrition Labels Timescales WILTSHIRE Agenda FARM
Filling the Nutritional Gap in Dysphagia
 Filling the Nutritional Gap in Dysphagia Krystel Ouaijan, RDN, MSc Nutrition Support Dietitian in Saint George Hospital UMC PhD in University of Geneva Krystel Ouaijan - Dubai -2018 1 Patient Profiles
Filling the Nutritional Gap in Dysphagia Krystel Ouaijan, RDN, MSc Nutrition Support Dietitian in Saint George Hospital UMC PhD in University of Geneva Krystel Ouaijan - Dubai -2018 1 Patient Profiles
Examination of Swallowing Varies Depending on Food Types
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2010, 220, 41-46 The Risk of Penetration or Aspiration during VF 41 The Risk of Penetration or Aspiration during Videofluoroscopic Examination of Swallowing Varies Depending on Food
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2010, 220, 41-46 The Risk of Penetration or Aspiration during VF 41 The Risk of Penetration or Aspiration during Videofluoroscopic Examination of Swallowing Varies Depending on Food
Stage Transition And Laryngeal Closure In Poststroke Patients With Dysphagia
 Archived version from NCDOCKS Institutional Repository http://libres.uncg.edu/ir/asu/ Stage Transition And Laryngeal Closure In Poststroke Patients With Dysphagia By: Elizabeth Rachel Oommen Youngsun Kim
Archived version from NCDOCKS Institutional Repository http://libres.uncg.edu/ir/asu/ Stage Transition And Laryngeal Closure In Poststroke Patients With Dysphagia By: Elizabeth Rachel Oommen Youngsun Kim
SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD
 Nutrition, eating and swallowing needs, challenges and solutions Workshop SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD Angela Nuzzi Speech and Language Pathologist (SLP) EHDN Language Coordinator - Italy The role of
Nutrition, eating and swallowing needs, challenges and solutions Workshop SWALLOWING DIFFICULTIES IN HD Angela Nuzzi Speech and Language Pathologist (SLP) EHDN Language Coordinator - Italy The role of
Quick Death, Slow Death, Hopefully No Death
 Quick Death, Slow Death, Hopefully No Death Collaborative presentation on learning from choking and nutrition incidents in RWT. Introduction of IDDSI for food and fluids Why there is an NPSA Alert Safe
Quick Death, Slow Death, Hopefully No Death Collaborative presentation on learning from choking and nutrition incidents in RWT. Introduction of IDDSI for food and fluids Why there is an NPSA Alert Safe
Dysphagia Identification and Management
 Dysphagia Identification and Management Presented By Speech-Language Pathologist Developmental Disabilities Administration DC Department on Disability Services Training Objectives After this training session
Dysphagia Identification and Management Presented By Speech-Language Pathologist Developmental Disabilities Administration DC Department on Disability Services Training Objectives After this training session
Department of Dentistry, School of Medicine, Fujita Health University, Toyoake, Aichi, Japan 2
 72 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Efficacy of a novel training food based on the process model of feeding for mastication and swallowing A preliminary
72 Japanese Journal of Comprehensive Rehabilitation Science (2014) Original Article Efficacy of a novel training food based on the process model of feeding for mastication and swallowing A preliminary
Specialist Diets. To arrange a free tasting experience or to find out more, just get in touch. Call
 apetito Ltd. Canal Road, Trowbridge, Wiltshire, BA14 8RJ T. 01225 753 636 F. 01225 777084 www.apetito.co.uk To arrange a free tasting experience or to find out more, just get in touch. Call 01225 569335
apetito Ltd. Canal Road, Trowbridge, Wiltshire, BA14 8RJ T. 01225 753 636 F. 01225 777084 www.apetito.co.uk To arrange a free tasting experience or to find out more, just get in touch. Call 01225 569335
SILENT ASPIRATION AND SWALLOWING PHYSIOLOGY AFTER RADIOTHERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH NASOPHARYNGEAL CARCINOMA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SILENT ASPIRATION AND SWALLOWING PHYSIOLOGY AFTER RADIOTHERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH NASOPHARYNGEAL CARCINOMA Louisa K. Y. Ng, MSc, 1 Kathy Y. S. Lee, PhD, 1 Sung Nok Chiu, Dr.rer.nat., 2 Peter
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SILENT ASPIRATION AND SWALLOWING PHYSIOLOGY AFTER RADIOTHERAPY IN PATIENTS WITH NASOPHARYNGEAL CARCINOMA Louisa K. Y. Ng, MSc, 1 Kathy Y. S. Lee, PhD, 1 Sung Nok Chiu, Dr.rer.nat., 2 Peter
Standardisation of Videofluoroscopy: Where is it taking us?
 Standardisation of Videofluoroscopy: Where is it taking us? Jodi Allen, Senior Speech and Language Therapist, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery If somebody asked you. What do you start
Standardisation of Videofluoroscopy: Where is it taking us? Jodi Allen, Senior Speech and Language Therapist, The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery If somebody asked you. What do you start
EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE
 EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE DISCLOSURES I have no personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
EATING SAFELY AND TALKING ABOUT IT KIERA N BERGGREN, MA/CCC-SLP, MS 2018 FSHD CONNECT CONFERENCE DISCLOSURES I have no personal financial relationships with commercial interests relevant to this presentation
Clinical Swallowing Exam
 Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล
 Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Dysphagia in Stroke The incidence of dysphagia after stroke ranging from 23-50% 1 Location
Swallowing Screen Why? How? and So What? พญ.พวงแก ว ธ ต สก ลช ย ภาคว ชาเวชศาสตร ฟ นฟ คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Dysphagia in Stroke The incidence of dysphagia after stroke ranging from 23-50% 1 Location
Critical Review: Is a chin-down posture more effective than thickened liquids in eliminating aspiration for patients with Parkinson s disease?
 Critical Review: Is a chin-down posture more effective than thickened liquids in eliminating aspiration for patients with Parkinson s disease? Nadia Torrieri, M.Cl.Sc. (SLP) Candidate The Unversity of
Critical Review: Is a chin-down posture more effective than thickened liquids in eliminating aspiration for patients with Parkinson s disease? Nadia Torrieri, M.Cl.Sc. (SLP) Candidate The Unversity of
For all the places our children have meal times.
 Donna Edwards, MA CCC SLP, BCS S Board Certified Specialist in Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders ASHA Fellow Dayton Children s Hospital Dayton, OH For Children! For Parents! For Professionals! For the
Donna Edwards, MA CCC SLP, BCS S Board Certified Specialist in Swallowing and Swallowing Disorders ASHA Fellow Dayton Children s Hospital Dayton, OH For Children! For Parents! For Professionals! For the
Management of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 Management of oropharyngeal dysphagia Course Objectives Know the normal anatomy of swallowing Know the normal physiology of swallowing Enumerate different etiologies of oropharyngeal dysphagia Be able
Management of oropharyngeal dysphagia Course Objectives Know the normal anatomy of swallowing Know the normal physiology of swallowing Enumerate different etiologies of oropharyngeal dysphagia Be able
Puree Diet. Patient Information Leaflet.
 Information Prescriptions Information Prescriptions are a quick and easy way to provide information about your condition and local services. www.nhs.uk/ips How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections?
Information Prescriptions Information Prescriptions are a quick and easy way to provide information about your condition and local services. www.nhs.uk/ips How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections?
Swallow-respiratory coordination. Liza Bergström, Leg. logoped.
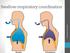 Swallow-respiratory coordination Liza Bergström, Leg. logoped. Biological timeshare When we breathe, we don t swallow When we swallow, we don t breathe Body will always choose to breathe over anything
Swallow-respiratory coordination Liza Bergström, Leg. logoped. Biological timeshare When we breathe, we don t swallow When we swallow, we don t breathe Body will always choose to breathe over anything
Critical Review: The effect of time and temperature on the viscosity of thickened liquids
 Critical Review: The effect of time and temperature on the viscosity of thickened liquids Buckland, S.A. M.Cl.Sc (S-LP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
Critical Review: The effect of time and temperature on the viscosity of thickened liquids Buckland, S.A. M.Cl.Sc (S-LP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
National Descriptors for Texture Modification in Adults
 National Descriptors for Texture Modification in Adults Published: April 2009, Review date: April 2011 Code of Professional Conduct 1 Contents Section 1... 2 1.1 Background... 2 1.2 Who is the guidance
National Descriptors for Texture Modification in Adults Published: April 2009, Review date: April 2011 Code of Professional Conduct 1 Contents Section 1... 2 1.1 Background... 2 1.2 Who is the guidance
Roger Newman 1,5 Natàlia Vilardell
 Dysphagia (2016) 31:232 249 DOI 10.1007/s00455-016-9696-8 EDITORIAL Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal
Dysphagia (2016) 31:232 249 DOI 10.1007/s00455-016-9696-8 EDITORIAL Effect of Bolus Viscosity on the Safety and Efficacy of Swallowing and the Kinematics of the Swallow Response in Patients with Oropharyngeal
Exercise- Based Approaches to Dysphagia Rehabilitation
 Interventions Cichero J, Clavé P (eds): Stepping Stones to Living Well with Dysphagia. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 72, pp 109 117, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG., Basel, 2012 Exercise- Based Approaches
Interventions Cichero J, Clavé P (eds): Stepping Stones to Living Well with Dysphagia. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 72, pp 109 117, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG., Basel, 2012 Exercise- Based Approaches
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOWING EXAM
 VIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOWING EXAM INDENTIFYING INFORMATION May include the following: Name, ID/medical record number, date of birth, date of exam, referred by, reason for referral HISTORY/SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION
VIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOWING EXAM INDENTIFYING INFORMATION May include the following: Name, ID/medical record number, date of birth, date of exam, referred by, reason for referral HISTORY/SUBJECTIVE INFORMATION
What is Dysphagia? An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION What is Dysphagia? An information guide What is Dysphagia? If someone has dysphagia, this means they have difficulty in swallowing. Dysphagia
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION What is Dysphagia? An information guide What is Dysphagia? If someone has dysphagia, this means they have difficulty in swallowing. Dysphagia
Understanding the World of Viscosity: A Tutorial on Rheology
 Understanding the World of Viscosity: A Tutorial on Rheology Catriona M. Steele, Ph.D., CCC Jane Mertz Garcia, Ph.D., CCC Russell H. Mills, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BRS Ph.D., CCC-SLP, S-LP(C) S Ph.D., CCC-SLP
Understanding the World of Viscosity: A Tutorial on Rheology Catriona M. Steele, Ph.D., CCC Jane Mertz Garcia, Ph.D., CCC Russell H. Mills, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BRS Ph.D., CCC-SLP, S-LP(C) S Ph.D., CCC-SLP
Nutricia. Nutrition and Dysphagia
 Nutricia Nutrition and Dysphagia 1 Introduction What is Dysphagia? The inability to swallow normally or freely. Disorder in the swallowing process that does not allow safe passing of food from the mouth
Nutricia Nutrition and Dysphagia 1 Introduction What is Dysphagia? The inability to swallow normally or freely. Disorder in the swallowing process that does not allow safe passing of food from the mouth
Pediatric Modified Barium Swallow Studies. Presented by Jody Bousquet, MA, CCC- SLP Susan Shonbrun, MS, CCC- SLP November 7, 2015
 Pediatric Modified Barium Swallow Studies Presented by Jody Bousquet, MA, CCC- SLP Susan Shonbrun, MS, CCC- SLP November 7, 2015 Definition * Modified Barium Swallow Study * Assesses swallow functions
Pediatric Modified Barium Swallow Studies Presented by Jody Bousquet, MA, CCC- SLP Susan Shonbrun, MS, CCC- SLP November 7, 2015 Definition * Modified Barium Swallow Study * Assesses swallow functions
Dysphagia Management in TCP. Susan Smith and Vanessa Barkla Speech Pathologists, Ballarat Health Services May 2012
 Dysphagia Management in TCP Susan Smith and Vanessa Barkla Speech Pathologists, Ballarat Health Services May 2012 The role of the Speech Pathologist To assess swallowing status To provide management and
Dysphagia Management in TCP Susan Smith and Vanessa Barkla Speech Pathologists, Ballarat Health Services May 2012 The role of the Speech Pathologist To assess swallowing status To provide management and
Swallowing & Communication in Advancing Vascular Dementia Topics of Interest. Dr Jackie Kindell
 Swallowing & Communication in Advancing Vascular Dementia Topics of Interest Dr Jackie Kindell Eating and Swallowing Difficulty Can occur at any stage of vascular dementia More common in the later stages
Swallowing & Communication in Advancing Vascular Dementia Topics of Interest Dr Jackie Kindell Eating and Swallowing Difficulty Can occur at any stage of vascular dementia More common in the later stages
Chef Rick Schmitt, CDM, CFPP Assistant Dining Director/Executive Chef Westminster Towers Rock Hill, SC
 Chef Rick Schmitt, CDM, CFPP Assistant Dining Director/Executive Chef Westminster Towers Rock Hill, SC Water/Hydration Food/Nutrition Shelter/Security Love/Acceptance/Belonging Definition A chronic or
Chef Rick Schmitt, CDM, CFPP Assistant Dining Director/Executive Chef Westminster Towers Rock Hill, SC Water/Hydration Food/Nutrition Shelter/Security Love/Acceptance/Belonging Definition A chronic or
Appendix 3B: Thick Fluids poster fluids, follow instructions for thickener use, as well as
 Audience: Production and Food Service Staff Length: 20 minutes (10 minute presentation with 10 minute practice preparation) Outcomes Materials needed/introduction By the end of this presentation participants
Audience: Production and Food Service Staff Length: 20 minutes (10 minute presentation with 10 minute practice preparation) Outcomes Materials needed/introduction By the end of this presentation participants
Respiratory Swallow Coordination in Healthy Individuals
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Speech and Hearing Research 2012, Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 1-9, Article ID Med-03 Research Article Open Access Respiratory Swallow Coordination in Healthy
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Speech and Hearing Research 2012, Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 1-9, Article ID Med-03 Research Article Open Access Respiratory Swallow Coordination in Healthy
Kinematic and Temporal Factors Associated with Penetration Aspiration in Swallowing Liquids
 Dysphagia (2014) 29:269 276 DOI 10.1007/s00455-013-9506-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinematic and Temporal Factors Associated with Penetration Aspiration in Swallowing Liquids Sonja M. Molfenter Catriona M. Steele
Dysphagia (2014) 29:269 276 DOI 10.1007/s00455-013-9506-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinematic and Temporal Factors Associated with Penetration Aspiration in Swallowing Liquids Sonja M. Molfenter Catriona M. Steele
Swallowing problems. Patient information. Name: Date: Speech and Language Therapist: Reviewed: May 2016 Next review: June 2017 Version 1
 Patient information Swallowing problems Name: Date: Speech and Language Therapist: Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk Reviewed:
Patient information Swallowing problems Name: Date: Speech and Language Therapist: Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk Reviewed:
Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 National Multiple Sclerosis Society 733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
National Multiple Sclerosis Society 733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Reluctance or refusal to feed or eat. Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies. Presentation Outline. Learning Objectives
 Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies Amy Houtrow, MD, MPH Pediatric Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation UCSF Department of Pediatrics June 2, 2007 Learning Objectives Learners will be
Understanding Feeding Aversion in a City Full of Foodies Amy Houtrow, MD, MPH Pediatric Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation UCSF Department of Pediatrics June 2, 2007 Learning Objectives Learners will be
Main Aspects of the Management of Neurogenic Dysphagia
 Main Aspects of the Management of Neurogenic Dysphagia Mario Prosiegel/München German Society of Neurology (DGN) prosiegel@t-online.de DYSPHAGIA October 8-10, 2015 Pavia, Italy Overview Diagnosis Causal
Main Aspects of the Management of Neurogenic Dysphagia Mario Prosiegel/München German Society of Neurology (DGN) prosiegel@t-online.de DYSPHAGIA October 8-10, 2015 Pavia, Italy Overview Diagnosis Causal
Normal and Abnormal Oral and Pharyngeal Swallow. Complications.
 ESPEN Congress Gothenburg 2011 Assessment and treatment of dysphagia What is the evidence? Normal and Abnormal Oral and Pharyngeal Swallow. Complications. Pere Clavé Educational Session. Assessment and
ESPEN Congress Gothenburg 2011 Assessment and treatment of dysphagia What is the evidence? Normal and Abnormal Oral and Pharyngeal Swallow. Complications. Pere Clavé Educational Session. Assessment and
Management of dysphagia in MS
 Management of dysphagia in MS Marta Renom Speech and Language Therapist CEM-CAT (UNeR) Barcelona INTRODUCTION Normal swallowing Dual function: transporting / protecting airway oral phase pharyngeal phase
Management of dysphagia in MS Marta Renom Speech and Language Therapist CEM-CAT (UNeR) Barcelona INTRODUCTION Normal swallowing Dual function: transporting / protecting airway oral phase pharyngeal phase
5 Things I Want You to Know About Dysphagia. Prof Maggie-Lee Huckabee The University of Canterbury Rose Centre for Stroke Recovery and Research
 5 Things I Want You to Know About Dysphagia Prof Maggie-Lee Huckabee The University of Canterbury Rose Centre for Stroke Recovery and Research 5 things 1) Why we can t diagnose dysphagia at bedside. 2)
5 Things I Want You to Know About Dysphagia Prof Maggie-Lee Huckabee The University of Canterbury Rose Centre for Stroke Recovery and Research 5 things 1) Why we can t diagnose dysphagia at bedside. 2)
Factors Associated With Compliance With Viscosity-Modified Diet Among Dysphagic Patients Jae Seong Shim, MD, Byung-Mo Oh, MD, Tai Ryoon Han, MD
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(5):628-632 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.5.628 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Factors Associated With Compliance With
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37(5):628-632 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.5.628 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Factors Associated With Compliance With
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA
 TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
Safe swallowing strategies
 Learning Guide Safe swallowing strategies 27468 Apply safe swallowing strategies in a health or wellbeing setting Level 3 5 credits Name: Workplace: Issue 2.0 Copyright 2017 Careerforce All rights reserved.
Learning Guide Safe swallowing strategies 27468 Apply safe swallowing strategies in a health or wellbeing setting Level 3 5 credits Name: Workplace: Issue 2.0 Copyright 2017 Careerforce All rights reserved.
Dysphagia Diet Texture B Thin Puree
 The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Dysphagia Diet Texture B Thin Puree Rehabilitation & Support A guide for patients and carers Contents Swallowing...1 Swallowing problems...1 Who can
The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust Dysphagia Diet Texture B Thin Puree Rehabilitation & Support A guide for patients and carers Contents Swallowing...1 Swallowing problems...1 Who can
10/26/2017. Diagnostic Tests vs. Screening. Dysphagia Screening: What it is and what it is not
 Dysphagia Screening: What it is and what it is not Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director University of Kentucky Voice & Swallow Clinic Lexington, Kentucky ASHA's Preferred Practice Pattern on
Dysphagia Screening: What it is and what it is not Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director University of Kentucky Voice & Swallow Clinic Lexington, Kentucky ASHA's Preferred Practice Pattern on
Rationale for strength and skill goals in tongue resistance training: A review
 Rationale for strength and skill goals in tongue resistance training: A review Catriona M. Steele, Gemma L. Bailey, Sonja M. Molfenter & Erin M. Yeates Authors: Catriona M. Steele, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BRS-S
Rationale for strength and skill goals in tongue resistance training: A review Catriona M. Steele, Gemma L. Bailey, Sonja M. Molfenter & Erin M. Yeates Authors: Catriona M. Steele, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BRS-S
Gender Differences in Normal Swallow Ahlam A. Nabieh, Ahmed M. Emam, Eman M. Mostafa and Rasha M. Hashem
 EJNSO Gender Differences in Normal Swallow Ahlam A. Nabieh, Ahmed M. Emam, Eman M. Mostafa and Rasha M. Hashem Phoniatrics unit, ENT department, Sohag University Abstract Introduction: Swallowing is a
EJNSO Gender Differences in Normal Swallow Ahlam A. Nabieh, Ahmed M. Emam, Eman M. Mostafa and Rasha M. Hashem Phoniatrics unit, ENT department, Sohag University Abstract Introduction: Swallowing is a
Workbook. Apply safe swallowing strategies as a health assistant in an aged care, health or disability context. US Level 4 Credits 4. Name...
 Workbook Apply safe swallowing strategies as a health assistant in an aged care, health or disability context US 27468 Level 4 Credits 4 Name... US 27468 Level 4 Credits 4 All rights reserved. Careerforce
Workbook Apply safe swallowing strategies as a health assistant in an aged care, health or disability context US 27468 Level 4 Credits 4 Name... US 27468 Level 4 Credits 4 All rights reserved. Careerforce
A Comparative Study Between Modified Starch and Xanthan Gum Thickeners in Post-Stroke Oropharyngeal Dysphagia
 Dysphagia (2016) 31:169 179 DOI 10.1007/s00455-015-9672-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Study Between Modified Starch and Xanthan Gum Thickeners in Post-Stroke Oropharyngeal Dysphagia N. Vilardell 1 L.
Dysphagia (2016) 31:169 179 DOI 10.1007/s00455-015-9672-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Comparative Study Between Modified Starch and Xanthan Gum Thickeners in Post-Stroke Oropharyngeal Dysphagia N. Vilardell 1 L.
SWAL-QOL - Authors: McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE.
 SWAL-QOL - Authors: McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE. Exit this survey 1. In the last month, how true have the following statements been for you? Very much
SWAL-QOL - Authors: McHorney CA, Robbins J, Lomax K, Rosenbek JC, Chignell K, Kramer AE, Bricker DE. Exit this survey 1. In the last month, how true have the following statements been for you? Very much
New Evidence-Based Support of a 3 Ounce Water Swallow Challenge Protocol
 New Evidence-Based Support of a 3 Ounce Water Swallow Challenge Protocol Steven B. Leder, Ph.D. Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, Connecticut Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D. VA Medical Center-Memphis
New Evidence-Based Support of a 3 Ounce Water Swallow Challenge Protocol Steven B. Leder, Ph.D. Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, Connecticut Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D. VA Medical Center-Memphis
Review of dysphagia in poststroke
 Review of dysphagia in poststroke patients Danielle Thompson, Speech and Language Therapist Northwick Park Hospital With acknowledgement to Mary McFarlane, Principal Speech and Language Therapist, Acute
Review of dysphagia in poststroke patients Danielle Thompson, Speech and Language Therapist Northwick Park Hospital With acknowledgement to Mary McFarlane, Principal Speech and Language Therapist, Acute
Commercial Bulleting Aloe Flakes
 Commercial Bulleting Aloe Flakes Be a Pioneer using Aloe Vera Flakes in food and beverage industry AMB s exclusive Aloe Flakes demonstrates superior solubility retaining the highest percentage of the benefical
Commercial Bulleting Aloe Flakes Be a Pioneer using Aloe Vera Flakes in food and beverage industry AMB s exclusive Aloe Flakes demonstrates superior solubility retaining the highest percentage of the benefical
Dysphagia. What is Dysphagia? Diagnosis and Treatment
 Dysphagia C A R E & M A N AG E M E N T S O L U T I O N S What is Dysphagia? Diagnosis and Treatment 1 Diagnosis contents and Treatment 2What is Dysphagia? 3 What is Dysphagia? KAPITEX are specialists in
Dysphagia C A R E & M A N AG E M E N T S O L U T I O N S What is Dysphagia? Diagnosis and Treatment 1 Diagnosis contents and Treatment 2What is Dysphagia? 3 What is Dysphagia? KAPITEX are specialists in
No large-scale randomized, multi-institutional clinical trials have
 A Randomized Study of Three Interventions for Aspiration of Thin Liquids in Patients With Dementia or Parkinson s Disease Jeri A. Logemann Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Gary Gensler The EMMES Corporation,
A Randomized Study of Three Interventions for Aspiration of Thin Liquids in Patients With Dementia or Parkinson s Disease Jeri A. Logemann Northwestern University, Evanston, IL Gary Gensler The EMMES Corporation,
Daniels SK & Huckabee ML (2008). Dysphagia Following Stroke. Muscles of Deglutition. Lateral & Mesial Premotor Area 6. Primary Sensory
 An Overview of Dysphagia in the Stroke Population Stephanie K. Daniels, PhD Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center PM & R, Baylor College of Medicine Communication Sciences and Disorders, University of Houston
An Overview of Dysphagia in the Stroke Population Stephanie K. Daniels, PhD Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center PM & R, Baylor College of Medicine Communication Sciences and Disorders, University of Houston
FLOOVIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOW STUDIES: LOOKING BEYOND ASPIRATION. Brenda Sitzmann, MA, CCC-SLP (816)
 FLOOVIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOW STUDIES: LOOKING BEYOND ASPIRATION Brenda Sitzmann, MA, CCC-SLP bksitzmann@cmh.edu (816) 302-8037 DISCLOSURES Ms. Sitzmann is speech-language pathologist at Children s Mercy
FLOOVIDEOFLUOROSCOPIC SWALLOW STUDIES: LOOKING BEYOND ASPIRATION Brenda Sitzmann, MA, CCC-SLP bksitzmann@cmh.edu (816) 302-8037 DISCLOSURES Ms. Sitzmann is speech-language pathologist at Children s Mercy
Guideline of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS) in Speech Therapy
 Page 1 of 9 Guideline of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS) in Speech Therapy Version 1.0 Effective Date Document Number HKIST-C-VFG-v1 Author HKAST AR Sub-committee Custodian Chairperson of HKIST
Page 1 of 9 Guideline of Videofluoroscopic Swallowing Study (VFSS) in Speech Therapy Version 1.0 Effective Date Document Number HKIST-C-VFG-v1 Author HKAST AR Sub-committee Custodian Chairperson of HKIST
Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy
 Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy Diane Longnecker, M.S.,CCC-SLP, BCS-S Baylor Institute for Rehabilitation at Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Disclosure Statement No relevant financial
Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy Diane Longnecker, M.S.,CCC-SLP, BCS-S Baylor Institute for Rehabilitation at Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Disclosure Statement No relevant financial
Patient and Family Resource Guide to ALS. Section 6. Nutritional Support
 Patient and Family Resource Guide to ALS Section 6 Nutritional Support 6 5550 W. Touhy Avenue, Skokie IL, 60077 847 679 3311 lesturnerals.org info@lesturnerals.org Nutritional Support Many factors can
Patient and Family Resource Guide to ALS Section 6 Nutritional Support 6 5550 W. Touhy Avenue, Skokie IL, 60077 847 679 3311 lesturnerals.org info@lesturnerals.org Nutritional Support Many factors can
SUPER-SUPRAGLOTTIC SWALLOW IN IRRADIATED HEAD AND NECK CANCER PATIENTS
 SUPER-SUPRAGLOTTIC SWALLOW IN IRRADIATED HEAD AND NECK CANCER PATIENTS Jeri A. Logemann, PhD, 1 Barbara Roa Pauloski, PhD, 1 Alfred W. Rademaker, PhD, 2 Laura A. Colangelo, MS 2 1 Department of Communication
SUPER-SUPRAGLOTTIC SWALLOW IN IRRADIATED HEAD AND NECK CANCER PATIENTS Jeri A. Logemann, PhD, 1 Barbara Roa Pauloski, PhD, 1 Alfred W. Rademaker, PhD, 2 Laura A. Colangelo, MS 2 1 Department of Communication
HOMES AND SENIORS SERVICES. APPROVAL DATE: August 1985 REVISION DATE: January 2015 REVIEW DATE: May 2018
 POLICY: Page 1 of 10 Residents who experience signs and symptoms associated with dysphagia will have their nutrition and hydration needs met in a safe, coordinated manner as managed by the interdisciplinary
POLICY: Page 1 of 10 Residents who experience signs and symptoms associated with dysphagia will have their nutrition and hydration needs met in a safe, coordinated manner as managed by the interdisciplinary
Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study in Elderly Patients Admitted to a Geriatric Hospital and a Long-Term Care Facility
 Original Article DOI:10.4235/jkgs.2009.13.4.195 Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study in Elderly Patients Admitted to a Geriatric Hospital and a Long-Term Care Facility Sang Jun Kim, MD, Tai Ryoon Han, MD Department
Original Article DOI:10.4235/jkgs.2009.13.4.195 Fluoroscopic Swallowing Study in Elderly Patients Admitted to a Geriatric Hospital and a Long-Term Care Facility Sang Jun Kim, MD, Tai Ryoon Han, MD Department
2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference
 Providing Quality Affordable Continuing Education and Treatment Materials for over 30 years. 2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference Session 9 Bedside Assessment: What Does It Tell You? 10:00 11:30 am Saturday,
Providing Quality Affordable Continuing Education and Treatment Materials for over 30 years. 2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference Session 9 Bedside Assessment: What Does It Tell You? 10:00 11:30 am Saturday,
Swallowing Course (RHS )
 Swallowing Course (RHS ) Dr/Mohamed Farahat Ibrahim, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Consultant Phoniatrician (Communication and Swallowing Disorders) Chairman, Communication and Swallowing Disorders Unit (CSDU)
Swallowing Course (RHS ) Dr/Mohamed Farahat Ibrahim, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Consultant Phoniatrician (Communication and Swallowing Disorders) Chairman, Communication and Swallowing Disorders Unit (CSDU)
Bolus effects on patient awareness of swallowing difficulty and swallow physiology after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bolus effects on patient awareness of swallowing difficulty and swallow physiology after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer Nicole M. Rogus-Pulia, PhD, CCC-SLP, 1* Margaret Pierce,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bolus effects on patient awareness of swallowing difficulty and swallow physiology after chemoradiation for head and neck cancer Nicole M. Rogus-Pulia, PhD, CCC-SLP, 1* Margaret Pierce,
Understanding your child s videofluoroscopic swallow study report
 Understanding your child s videofluoroscopic swallow study report This leaflet is given to you during your child s appointment in order to explain some of the words used by the speech and language therapist
Understanding your child s videofluoroscopic swallow study report This leaflet is given to you during your child s appointment in order to explain some of the words used by the speech and language therapist
Effects of a Sour Bolus on Oropharyngeal Swallowing Measures in Patients With Neurogenic Dysphagia
 Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, Volume 38, 556-563, June 1995 Effects of a Sour Bolus on Oropharyngeal Swallowing Measures in Patients With Neurogenic Dysphagia Jeri A. Logemann Barbara Roa Pauloski
Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, Volume 38, 556-563, June 1995 Effects of a Sour Bolus on Oropharyngeal Swallowing Measures in Patients With Neurogenic Dysphagia Jeri A. Logemann Barbara Roa Pauloski
Dysphagia Treatment: What are We Doing, and Why?
 Dysphagia Treatment: What are We Doing, and Why? ASHA Convention, 2014; Orlando James L. Coyle, Ph.D., CCC SLP, BCS S University of Pittsburgh jcoyle@pitt.edu 1 Treatment 2 Aims, targets and ingredients
Dysphagia Treatment: What are We Doing, and Why? ASHA Convention, 2014; Orlando James L. Coyle, Ph.D., CCC SLP, BCS S University of Pittsburgh jcoyle@pitt.edu 1 Treatment 2 Aims, targets and ingredients
Analyzing Swallow Studies in Pediatrics
 Analyzing Swallow Studies in Pediatrics About the Speaker Robert Beecher, M.S., CCC-SLP was formerly senior speech-language pahologist at the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin in Milwaukee. He is specialized
Analyzing Swallow Studies in Pediatrics About the Speaker Robert Beecher, M.S., CCC-SLP was formerly senior speech-language pahologist at the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin in Milwaukee. He is specialized
Which aspects of early dysphagia assessment and management reduce aspiration? Professor Sue Pownall
 Which aspects of early dysphagia assessment and management reduce aspiration? Professor Sue Pownall Sue.pownall@sth.nhs.uk Post Stroke Dysphagia Dysphagia incidence varies: Timing of assessment Tools used:
Which aspects of early dysphagia assessment and management reduce aspiration? Professor Sue Pownall Sue.pownall@sth.nhs.uk Post Stroke Dysphagia Dysphagia incidence varies: Timing of assessment Tools used:
Dysphagia as a Geriatric Syndrome Assessment and Treatment. Ashton Galyen M.A., CCC-SLP St. Vincent Indianapolis Acute Rehabilitation Unit
 Dysphagia as a Geriatric Syndrome Assessment and Treatment Ashton Galyen M.A., CCC-SLP St. Vincent Indianapolis Acute Rehabilitation Unit March 16, 2018 Ashton Galyen, M.A., CCC-SLP Master s degree in
Dysphagia as a Geriatric Syndrome Assessment and Treatment Ashton Galyen M.A., CCC-SLP St. Vincent Indianapolis Acute Rehabilitation Unit March 16, 2018 Ashton Galyen, M.A., CCC-SLP Master s degree in
Suitable food textures for videofluoroscopic studies of swallowing in esophageal cancer to
 1 Suitable food textures for videofluoroscopic studies of swallowing in esophageal cancer to prevent aspiration pneumonia Mika Sonoi, 1,4 Jun Kayashita, 2 Yoshie Yamagata, 2 Keiji Tanimoto, 3 Ken-ichi
1 Suitable food textures for videofluoroscopic studies of swallowing in esophageal cancer to prevent aspiration pneumonia Mika Sonoi, 1,4 Jun Kayashita, 2 Yoshie Yamagata, 2 Keiji Tanimoto, 3 Ken-ichi
Dysphagia. A Problem Swallowing Foods or Liquids
 Dysphagia A Problem Swallowing Foods or Liquids What Is Dysphagia? If you have a problem swallowing foods or liquids, you may have dysphagia. It has a number of causes. Your doctor can find out what is
Dysphagia A Problem Swallowing Foods or Liquids What Is Dysphagia? If you have a problem swallowing foods or liquids, you may have dysphagia. It has a number of causes. Your doctor can find out what is
Pharyngeal Effects of Bolus Volume, Viscosity, and Temperature in Patients With Dysphagia Resulting From Neurologic Impairment and in Normal Subjects
 Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, Volume 37, 1041-1049, October 1994 Pharyngeal Effects of Bolus Volume, Viscosity, and Temperature in Patients With Dysphagia Resulting From Neurologic Impairment
Journal of Speech and Hearing Research, Volume 37, 1041-1049, October 1994 Pharyngeal Effects of Bolus Volume, Viscosity, and Temperature in Patients With Dysphagia Resulting From Neurologic Impairment
Dysphagia (swallowing problems)
 Dysphagia (swallowing problems) Speech and Language Therapy Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have dysphagia. It gives information on what this condition
Dysphagia (swallowing problems) Speech and Language Therapy Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have dysphagia. It gives information on what this condition
Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury
 International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 2013; 15(5): 492 502 Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury CATRIONA M. STEELE 1,2,3,
International Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 2013; 15(5): 492 502 Outcomes of tongue-pressure strength and accuracy training for dysphagia following acquired brain injury CATRIONA M. STEELE 1,2,3,
Role of Dining Services and Dietary Needs of the Resident, 2014
 Role of Dining Services and Dietary Needs of the Resident, 2014 It is the dining services role to provide quality meals and service to all residents that is as home-like as possible. This will be done
Role of Dining Services and Dietary Needs of the Resident, 2014 It is the dining services role to provide quality meals and service to all residents that is as home-like as possible. This will be done
MULTIPLE reports have. Prediction of Aspiration in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Untreated Advanced Head and Neck Cancer ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction of Aspiration in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Untreated Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Arie Rosen, MD; Thomas H. Rhee, MD; Rene Kaufman, MS, CCC-SLP Objectives: To determine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction of Aspiration in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Untreated Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Arie Rosen, MD; Thomas H. Rhee, MD; Rene Kaufman, MS, CCC-SLP Objectives: To determine
YOUR COMPLETE GUIDE TO DYSPHAGIA
 YOUR COMPLETE GUIDE TO DYSPHAGIA Inspired by patients. Developed by experts. Delivered with care. Patient information for distribution by healthcare professionals only. PERSONAL INFORMATION Name: Date:
YOUR COMPLETE GUIDE TO DYSPHAGIA Inspired by patients. Developed by experts. Delivered with care. Patient information for distribution by healthcare professionals only. PERSONAL INFORMATION Name: Date:
Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE)
 Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Scan for mobile link. Video Fluoroscopic Swallowing Exam (VFSE) A video fluoroscopic swallowing exam (VFSE) uses a form of real-time x-ray called fluoroscopy to evaluate a patient s ability to swallow
Dysphagia and Swallowing. Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern
 Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN
 POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
IN SERVICE: FOOD CONSISTENCY FOR THE THERAPEUTIC DIET Mary White Lindsay Wexler
 IN SERVICE: FOOD CONSISTENCY FOR THE THERAPEUTIC DIET Mary White Lindsay Wexler Outline What is a therapeutic diet? What is food consistency? Types of food consistency Who needs it and why is it important?
IN SERVICE: FOOD CONSISTENCY FOR THE THERAPEUTIC DIET Mary White Lindsay Wexler Outline What is a therapeutic diet? What is food consistency? Types of food consistency Who needs it and why is it important?
SWALLOWING: HOW CAN WE HELP
 SWALLOWING: HOW CAN WE HELP Carol Romero-Clark, M.S., CCC-SLP University of New Mexico Hospital Speech Pathology Department November 10, 2017 What happens when you swallow? Mouth (Oral Phase) Your tongue
SWALLOWING: HOW CAN WE HELP Carol Romero-Clark, M.S., CCC-SLP University of New Mexico Hospital Speech Pathology Department November 10, 2017 What happens when you swallow? Mouth (Oral Phase) Your tongue
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32744 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Heemskerk, Anne-Wil Title: Dysphagia in Huntington s disease Issue Date: 2015-04-15
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/32744 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Heemskerk, Anne-Wil Title: Dysphagia in Huntington s disease Issue Date: 2015-04-15
Effect of posture on swallowing.
 Effect of posture on swallowing. Ahmad H. Alghadir, Hamayun Zafar, Einas S. Al-Eisa, Zaheen A. Iqbal Rehabilitation Research Chair, College of Applied Medical Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, KSA.
Effect of posture on swallowing. Ahmad H. Alghadir, Hamayun Zafar, Einas S. Al-Eisa, Zaheen A. Iqbal Rehabilitation Research Chair, College of Applied Medical Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, KSA.
28
 28 Contents Contents... 1 What is Dysphagia? How do I recognise dysphagia? Diagnosis and Treatment The Importance of Hydration Hydration and Dysphagia References... 2... 2... 4... 6... 7... 10 DRINK-RITE
28 Contents Contents... 1 What is Dysphagia? How do I recognise dysphagia? Diagnosis and Treatment The Importance of Hydration Hydration and Dysphagia References... 2... 2... 4... 6... 7... 10 DRINK-RITE
WHAT WORKS? A comprehensive guide to safer needle and syringe selection for injecting drug users. Second edition. Fully revised and updated
 WHAT WORKS? A comprehensive guide to safer needle and syringe selection for injecting drug users Second edition Fully revised and updated What works? 2011 Exchange Supplies Second edition, 2016 What works?
WHAT WORKS? A comprehensive guide to safer needle and syringe selection for injecting drug users Second edition Fully revised and updated What works? 2011 Exchange Supplies Second edition, 2016 What works?
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us. Introduction
 The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
The Volume- Viscosity Swallow Test for Clinical Screening of Dysphagia and Aspiration
 Detection Cichero J, Clavé P (eds): Stepping Stones to Living Well with Dysphagia. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 7, pp, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG., Basel, 0 The Volume- Viscosity Swallow Test
Detection Cichero J, Clavé P (eds): Stepping Stones to Living Well with Dysphagia. Nestlé Nutr Inst Workshop Ser, vol 7, pp, Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG., Basel, 0 The Volume- Viscosity Swallow Test
Speech and Language Therapy. Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist
 Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review
 Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review Lisa O Kane, B.A. Michael Groher, Ph.D. Boston University University of Redlands Boston, MA Redlands, CA ASHA Convention 2009 New Orleans
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review Lisa O Kane, B.A. Michael Groher, Ph.D. Boston University University of Redlands Boston, MA Redlands, CA ASHA Convention 2009 New Orleans
Assessing the Eating Needs of Personal Care Services (PCS) Beneficiaries Effective 12/1/2016
 Assessing the Eating Needs of Personal Care Services (PCS) Beneficiaries Effective 12/1/2016 The Freedom to Succeed November 22,2016 Content Introduction Signs and Symptoms Caring for Individuals with
Assessing the Eating Needs of Personal Care Services (PCS) Beneficiaries Effective 12/1/2016 The Freedom to Succeed November 22,2016 Content Introduction Signs and Symptoms Caring for Individuals with
