VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND
|
|
|
- Priscilla Cannon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VALIDATION OF THE SHORT MICHIGAN ALCOHOLISM SCREENING TEST THAI VERSION IN NORTHEASTERN THAILAND Somsong Nanakorn 1, Katsuhiro Fukuda 2, Itsuro Ogimoto 2, Tawee Tangseree 3 and Suchart Treethiptikhun 4 1 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen, Thailand; 2 Department of Public Health, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume city, Japan; 3 Khon Kaen Psychiatric Hospital; 4 Northeastern Drug Dependence Treatment Center, Khon Kaen, Thailand Abstract. This study aimed to validate the Short Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test-Thai version-12 items (SMAST-T) compared to the psychiatrist s diagnosis based on DSM-III-R criteria, as a gold standard, among psychiatric patients residing in the northeast of Thailand. Sixty-one pairs of male cases with alcohol use disorders (AUD) and controls were collected through routine examination of psychiatric outpatients, years old, who visited the Khon Kaen Psychiatric Hospital or the Northeast Drug Dependence Treatment Center, located in Khon Kaen Province, northeast Thailand, between November, 1996 and February, Controls were matched for each case in terms of age (±5 years), province and urbanization of residence. They were interviewed using the SMAST-T and a structured questionnaire. Receiver operating characteristic analysis revealed that the optimum cutoff point of 4 or over on the SMAST-T yielded the best sensitivity and specificity (96.7% and 95.1%, respectively), along with the area under the curve of 0.994, indicating that it was sensitive and specific in discriminating AUD from the non-aud patients. Validation of the SMAST-T suggests its applicability as a screening interview questionnaire to detect AUD among northeast Thai males, with a specific cutoff point. INTRODUCTION The field of mental health research, and in particular, alcohol use disorders, has frequently relied on the use of screening instruments to assess individuals symptomatology (Jacobson, 1983). Such screens are typically easy to administer, interpret, score and are relatively short. A number of such screens have been developed to identify problem drinkers. These include the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST, Selzer, 1971) and its derivatives: brief MAST (Pokorny et al, 1972), short MAST (SMAST, Selzer et al, 1975), the Cutdown-Annoyed-Guilt-Eye-opener (CAGE, Mayfield et al, 1974), the Munich Alcoholism Test (MALT, Bech et al, 1993), and the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT, Babor et al, 1989). The SMAST, developed and shorten modified by Selzer and colleagues (1975), is a questionnaire consisting of 13 yes-no questions of items 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 14, 16, 20, 21, 24 and 25 of the original full-length MAST (25-item; Table 1) with unweighted scoring. The SMAST has been proven Correspondence: Somsong Nanakorn, Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen 40002, Thailand. somnan@kku.ac.th reliable and valid for screening alcohol problems in medical populations (Woodall, 1988; Al-Ansari and Negrete, 1990; Hays and Revetto, 1992; Nilssen and Cone, 1994), and general populations (Lowe et al, 1997) in many countries including Thailand. In Thailand, it is the consensus of authorities that alcohol use, and hence alcohol misuse, is on the increase (McGovern, 1982). Several studies using some of these screening instruments have shown a prevalence of alcohol problems varying from 15 to 32% among various groups of the Thai population, for example, 15% among male medical outpatients in the southern region of Thailand by the SMAST-Thai version (SMAST-T; consisting of 12 items from the SMAST except item 9; Table 1, Assanangkornchai, 1993), 25% among the same subjects by the MAST-Thai version (MAST-T; 23- item, Tanchaiswad, 1988) and 32% among bus drivers in Bangkok by the MAST-T (Otrakul et al, 1988). The relatively large variation of these prevalences may be partly due to the extent of instrument validity. Empirical studies have shown that a screening instrument is valid if a special cutoff point is used on a special population (Storgaard et al, 1994; Cherpitel, 1995). It is therefore important to validate an alcohol screening instrument for future studies among the northeast Thai population, 780
2 SHORT MAST VALIDITY AMONG NORTHEASTERN THAIS as there has been no validation study of such an instrument before. The present study reports the validity of the SMAST-T with possible cutoff points to differentiate the alcohol use disorders (AUD) patients from the other psychiatric patients residing in northeast Thailand, using the DSM-III-R diagnostic criteria as a gold standard. This study was approved by the Ethical Review of Research Committee, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. MATERIAL AND METHODS Questionnaires Two sets of questionnaires were used for the present study. The SMAST-T questionnaire consisted of 12 items, as shown in Table 1. The second questionnaire contained socio-demographic characteristics, past, present and family histories of illnesses, including smoking and drinking habits. Method of data collection has been described elsewhere (Nanakorn et al, 1998). In brief, eligible subjects were males years of age living in the northeast of Thailand, and being outpatients of the Khon Kaen Psychiatric Hospital or the Northeastern Drug Dependence Treatment Center which are located in Khon Kaen Province, between November, 1996 and February, The eligible AUD cases were identified among the eligible subjects through a routine outpatient examination by Board certified psychiatrists (TT and ST) based on the DSM-III-R diagnostic criteria (American Psychiatric Association, 1987) as alcohol abuse (305.00), alcohol dependence (303.90), uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal (291.80), alcohol withdrawal delirium (291.00), alcohol hallucinosis (291.30), alcohol amnestic disorder (291.10), or dementia associated with alcoholism (291.20) within one month after the first visit. The potential controls were selected from those eligible subjects who were diagnosed by the same psychiatrists as having other psychiatric disorders without AUD, past history of AUD, and/or alcoholic liver diseases. The eligible control was obtained for each case by matching in terms of age (±5 years), province, and rural/ urban classification of residence. Sixty-one pairs of case-control were recruited for analyses. Data analysis Chi-square testing for 2 x n tables was used to compare statistical differences between cases and controls. The Fisher s exact test and rankorder Tau-b correlation were used as appropriate. The related two sample t tests based on equal and unequal variances were used for means comparison (Armitage and Berry, 1994; SAS Institute Inc, 1990). All statistically significant differences were detected at the 5% level. The score of one for each item of the SMAST-T was used according to the original SMAST (Selzer et al, 1975). A reliability of the SMAST-T was assessed in terms of an internal consistency using the Cronbach alpha coefficient (α). Correlation between the SMAST- T scores of the present study and the MAST-T scores of the previous study (Nanakorn et al, 1998) obtained from the same subjects was performed as well by using the Pearson Product Moment Correlation coefficient (r p ). Validity of the SMAST-T was evaluated by Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis (Murphy et al, 1987). The ROC was obtained by plotting sensitivities against one minus specificities for all possible cutoff points. The ROC curve and the area under the curve (AUC) were constructed using the proc logistic and proc gplot procedure in the SAS/STAT software release 6.12 (SAS Institute Inc, 1997). Finally, an optimum cutoff point that provides the best sensitivity and specificity was selected by acquiring two conditions. Firstly, the value of the sensitivity should be larger than specificity for the purpose of screening (Griner et al, 1981). Secondly, the sum of the sensitivity and specificity should be the maximum, as compared to other possible sets. RESULTS Sociodemographic, clinical diagnoses, family histories, smoking and drinking habits Subjects characteristics have been detailed elsewhere (Nanakorn et al, 1998). Briefly, the majority of cases and controls live in rural areas. The average ages (mean±sd) were 38.4±9.7 and 38.7±9.6 years for the cases and controls, respectively. Significant differences were observed between the cases and controls in terms of occupations but not for the marital status and educational background. Based on the DSM-III-R diagnostic criteria, the cases included 37.7% with alcohol dependence, 24.6% with alcohol hallucinosis, 21.3% with alcohol abuse, and 16.4% with alcohol withdrawal delirium, while most of the controls were diagnosed with anxiety disorders. 781
3 Table 1 Number of responses by SMAST-T items. SMAST-T items Cases Controls χ 2 1 Do you feel you are a normal drinker? (yes=0, no=1) a 3 Does your wife (or parents) ever worry or complain about your drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a 5 Do you ever feel bad about your drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a 6 Do friends or relatives think you are a normal drinker? (yes=0, no=1) a 8 Are you always able to stop drinking when you want to? (yes=0, no=1) a 11 Has drinking ever created problems with you and your wife? (yes=1, no=0) a 14 Have you ever gotten into trouble at work because of drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a 16 Have you ever neglected your obligations, your family, or your work for two or more days in a row because you were drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a 20 Have you ever gone to anyone for help about your drinking? (yes=1, no=o) a 21 Have you ever been in a hospital because of drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a 24 Have you ever been arrested, even for a few hours, because of drunk behavior? (yes=1, no=0) Have you ever been arrested for drunk driving or driving after drinking? (yes=1, no=0) a Item numbers correspond to those of the original full-length MAST (Selzer et al, 1971), scoring of one point (in the parenthesis) was assigned to each item for the SMAST (Selzer et al, 1975), and for the present study. a Statistically significant different at the 5% level. A smaller proportion of cases had a past history with stomach diseases compared with controls. Parents past histories were similar in cases and controls. The cases tended to currently smoke more than controls, and on average 14±7 cigarettes per day comparing to 11±7 for the controls. Statistically significant difference was observed for drinking habits. All the cases were current drinkers, while 55.8%, 31.1%, and 13.1% of the controls were current, ex-, and non-drinkers, respectively (χ 2 =34.7, df=2). The current drinkers drinking frequencies of <1-1/mo, 2-4/mo, 2-4/wk, and >4/wk were 23.1%, 13.7%, 11.6%, and 51.6%, respectively (Table 2). A statistically significant difference in the average amount of alcohol consumed on each occasion during the past year was observed (mean±sd; 120.6±70.9 g for the cases and 22.9±28.3 g for the controls; Student s t-test based on unequal variances = 9.89, df = 80.9). Reliability of the SMAST-T The Cronbach alpha coefficient was 0.89, indicating considerable intercorrelation between the SMAST-T items. A number of responses by each SMAST-T item are shown in Table 1. Eleven of the twelve items were shown as significantly different in the number of responses between the cases and the controls indicating that these items are able to differentiate the cases from the controls. Correlation between the SMAST-T scores and the MAST-T scores Pearson correlation between the SMAST-T scores and the MAST-T scores yielded r p = 0.98 (p = 0.001) suggesting that the SMAST-T is able to screen AUD as good as the MAST-T. Drinking frequency and the SMAST-T scores The proportion of drinking frequencies (<1-1/mo, 2-4/mo, 2-4/wk, and >4/wk) are associated with the SMAST-T scores (0, 1, 2, 3, and 4; χ 2 = 76.9, p = 0.000; Kendall s Tau-b = 0.67) as shown in Table 2, suggesting that, indeed, higher frequency drinkers tend to have higher scores on the SMAST-T. Sensitivity, specificity, cutoff point and ROC curve The SMAST-T scores for the cases and the controls ranged from 3 to 12 and 0 to 5 (mean±sd; 7.1±2.0, and 1.3±1.1, respectively). Table 3 shows 782
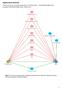
4 SHORT MAST VALIDITY AMONG NORTHEASTERN THAIS Table 2 Number and percentage of response to SMAST-T scores by drinking frequency levels of current drinkers. SMAST-T scores Drinking frequency levels of current drinkers Total <1-1/mo 2-4/mo 2-4/wk >4/wk (5) 0 (0) 18.2 (2) 0 (0) (7) (8) 23.1 (3) 9.1 (1) 0 (0) (12) (8) 7.7 (1)0 0 (0) 0 (0) (9) 3 0 (0) 15.4 (2) 9.1 (1) 4.1 (2) (5) (1) 53.8 (7) 63.6 (7) 95.9 (47) (62) Total 23.1 (22) 13.7 (13) 11.6 (11) 51.6 (49) (95) χ 2 = 76.9, df = 12; p = 0.000; Tau-b = distribution of the SMAST-T scores by cases and controls, and calculated sensitivity, specificity at various cutoff points. An optimal cutoff point of 4 was selected as it fulfilled the two conditions described above. It yielded 96.7% for the sensitivity and 95.1% for the specificity. Fig 1 displays the ROC curve constructed based on the SMAST-T scores yielding the AUC of Sensitivity Specificity Fig 1 The ROC curve for the Short Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test-Thai version (SMAST-T). The ROC curve and the Area Under the Curve (AUC) were constructed to evaluate the efficiency of the SMAST- T by using the proc logistic and proc gplot procedures provided in SAS/STAT 6.12 which calculated the AUC value of DISCUSSION The DSM-III-R diagnostic criteria was used as the gold standard in the present study instead of ICD-10. Although, there are differences among these two diagnostic systems, there is considerable similarity (Grant and Towle, 1990), or they do not produce dissimilar results from each other (Hasin et al, 1996a). Rounsaville et al (1993) and Cottler (1993) found a good agreement for dependence criteria across the DSM-III-R and the ICD-10, while there was a low level of concordance between the abuse and harmful use diagnoses. Moreover, it has been confirmed for the fair to good agreements on the alcohol abuse and the dependence diagnoses, respectively, between those two diagnostic systems supporting the hypothesis that they were measuring the same underlying construct (Hasin et al, 1996b). The highly significant correlation between the SMAST-T scores and the MAST-T scores (r p = 0.98) may indicate that the SMAST-T will perform as well as the MAST-T as a screening test for AUD. This result is consistent with the study by Selzer et al (1975) which yielded r p = 0.97 between the SMAST and the MAST. The SMAST had been shown to be as effective as the full-length MAST 783
5 Table 3 Sensitivity, and specificity of the SMAST-T at various cutoff point. SMAST-T score Cases Controls Sensitivity Specificity a Sensitivity: Proportion of AUD subjects having scores equal to or larger than the cutoff point on the SMAST-T. Specificity: Proportion of non-aud subjects with scores less than the cutoff point on the SMAST-T. a Selected cutoff point. as a screening test for AUD in American society (Selzer et al, 1975), in Arab Muslim society (Al- Ansari et al, 1990), and in Thai Buddhist society (Assanangkornchai, 1993). It has been used as a gold standard for criterion validation of biological alcohol markers in alcohol problems screening as well (Nilssen et al, 1996). The ability of the SMAST-T items to differentiate the cases from the controls was found in 11 of 12 items, except for the item Have you ever been arrested, even for a few hours because of drunk behavior? as shown in Table 1. One reason for that may be that police action was not active enough to do so in such a rural area. The SMAST-T scores were significantly moderately correlated with subjects drinking frequency levels (Tau-b = 0.67). It implies that the higher scores on the SMAST, the more severe the alcohol use disorders. This finding is consistent with the study by Harburg et al (1988) which found a significant correlation of total SMAST scores with subjects drinking levels among men (Tau-b = 0.21). The present study of the SMAST-T validity among psychiatric patients residing in northeastern Thailand showed high sensitivity and specificity (96.7% and 95.1%, respectively) at the cutoff point of 4. It is appreciable as it gave a high value of the AUC (0.994) indicating a high efficiency for discriminating an AUD from a non-aud. It is comparable to its validity performed among general patients residing in southern Thailand which provided a cutoff point of 3 with a sensitivity of 68.0%, and a specificity of 77.8% (Assanangkornchai, 1993). One possible reason for discrepancy of cutoff points is that the present study was undertaken in psychiatric or drug dependence care facilities where relatively severe AUD or drug addicts may visit, while the Assanangkornchai s study (1993) had been performed in general practice which contains a wide variety of drinkers from predependents to alcoholics. This phenomenon is consistent with the study by Robins (1985) which found that the Diagnostic Interview Schedule s sensitivity was higher in a patient sample than in a general population sample. There is ambiguous wording in some items of the SMAST-T that give different comprehension among respondents which arises during the interview, even though the MAST-T has been verified by a method of back translation (Tanchaiswad, 1988) and yields high sensitivity and specificity of validation among the southern Thai outpatients (Assanangkornchai, 1993). Such ambiguity, for example, is normal drinker, feel bad, or lost friends. Thus, to avoid an ambiguity of word-meaning in the SMAST-T items for a future study, an explanation should be paraphrased for those items to obtain a consistent comprehension and to enhance smooth interview. Therefore, a further validation 784
6 SHORT MAST VALIDITY AMONG NORTHEASTERN THAIS of the SMAST-T with adoption of wording for some items in the general population, general practice clinic and other groups of the Thai population needs to be completed before use. However, the SMAST-T seems to be practically convenient use for alcohol screening purpose as its easiness in scoring, few items and equal validity comparing to the MAST-T. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors would like to thank Associate Professor Waran Tanchaiswad, Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University, Had Yai District Songkhla Province Thailand, for the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test-Thai version grant, and Professor Brian Sheehan, Rangsit University, Bangkok, Thailand, for editing this manuscript. This study was partly supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. REFERENCES Al-Ansari EA, Negrete JC. Screening for alcoholism among alcohol users in a traditional Arab Muslim society. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1990; 81: American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 3 rd ed. DSM-III-R. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, Armitage P, Berry G. Statistical methods in medical research, 3 rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications, Assanangkornchai S. Drinking problem: a hidden problem in general practice. J Med Assoc Thai 1993; 3: Babor TF, de la Fuente JR, Saunders J, et al. The alcohol use disorders identification test: guidelines for use in the primary health care. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1989; Bech P, Matt UF, Dencker SJ, et al. Scales for assessment of diagnosis and severity of mental disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1993; 87 (suppl): Cherpitel CJ. Analysis of cut points for screening instruments for alcohol problems in the emergency room. J Stud Alcohol 1995; 56: Cottler LR. Comparing DSM-III-R and ICD-10 substance use disorders. Addiction 1993; 88: Grant BF, Towle LH. Standardized diagnostic interviews for alcohol research. Epidemiol Bull 1990; 26: Griner PF, Mayewski RJ, Mushlin AI, et al. Selection and interpretation of diagnostic tests and procedures: principles and applications. Ann Intern Med 1981; 94: Harburg E, Gunn R, Glieberman L, et al. Using the short Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test to study social drinkers: Tecumseh, Michigan. J Stud Alcohol 1988; 49: Hasin D, McCloud S, Li Q, et al. Cross-system agreement among demographic subgroups: DSM-III, DSM-III- R, DSM-IV and ICD-10 diagnoses of alcohol use disorders. Drug Alcohol Depend 1996a; 41: Hasin D, McCloud S, Endicott J. Agreement between DSM- III, DSM-III-R, DSM-IV and ICD-10 alcohol diagnoses in US community-sample heavy drinkers. Addiction 1996b; 91: Hays RD, Revetto JP. Old and new MMPI-derived scales and the short-mast as screening tools for alcohol disorder. Alcohol Alcsm 1992; 27: Jacobson GR. Detection, assessment, and diagnosis of alcoholism: current techniques. Recent Dev Alcohol 1983; 1: Lowe LP, Long CA, Wallace RB, et al. Epidemiology of alcohol use in a group of older American Indians. Ann Epidemiol 1997; 7: Mayfield D, McLeod G, Hall P. The CAGE questionnaire: validation of a new alcoholism screening instrument. Am J Psychiatry 1974; 131: McGovern MP. Alcoholism in Southeast Asia: prevalence and treatment. Int J Soc Psychiatry 1982; 28: Murphy JM, Berwick DM, Weinstein MC, et al. Performance of screening and diagnostic tests: application of Receiver Operating Characteristic analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1987; 44: Nanakorn S, Fukuda K, Tangseree T, et al. Validation of the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test-Thai version in northeast Thailand. Kurume Med J 1998; 45: Nanakorn S, Fukuda K, Nishiyori A, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase genotypes and male alcohol use disorders: a case control study in Khon Kaen, northeast Thailand. Psychiatr Clin Neurosci 1999; 53: Nilssen O, Cone H. Screening patients for alcohol problems in primary health care setting. Alco Health Res World 1994; 2: Nilssen O, Ries R, Rivara FP, et al. The WAM score: sensitivity and specificity of a user friendly biological screening test for alcohol problems in trauma patients. Addiction 1996; 91: Otrakul A, Wong-arsa C, Boonshuya C, et al. Identification 785
7 of alcoholism among BMA bus drivers in Bangkok. J Psychiatr Assoc Thai 1988; 33: (in Thai). Pokorny AD, Miller BA, Kaplan HB. The Brief MAST: a shortened version of the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test. Am J Psychiatry 1972; 129: Robins LN. Epidemiology: reflections on testing the validity of psychiatric interviews. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1985; 42: Rounsaville BJ, Bryant K, Babor T, et al. Cross system agreement for substance use disorders: DSM-III-R, DSM-IV and ICD-10. Addiction 1993; 88: SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT User s guide. Version 6, 4 th ed. Vol 2, SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA, SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT software: changes and enhancements through release SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA, Selzer ML. The Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test: the quest for a new diagnostic instrument. Am J Psychiatry 1971; 127: Selzer ML, Vinokur A, van Rooijen L. A self-administered Short Michigan Alcoholism Screening (SMAST). J Stud Alcohol 1975; 36: Storgaard H, Nielsen SD, Gluud C. The validity of the Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST). Alcohol Alcsm 1994; 29: Tanchaiswad W. MAST: the instrument for screening alcoholism. J Psychiatr Assoc Thai 1988; 33: (in Thai). Woodal HE. Alcoholics remaining anonymous: resident diagnosis of alcoholism in a family practice center. J Fam Practice 1988; 26:
A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
 Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:11-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.1.11 A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
Korean J Fam Med. 2013;34:11-18 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2013.34.1.11 A Validation Study of the Brief Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test (AUDIT): A Brief Screening Tool Derived from the AUDIT
ALCOHOL DRUG EVALUATION PREPARATION
 Alcohol/Drug Evaluation The alcohol drug evaluation is critical to the success of your case. We want you to get the best evaluation possible with the least amount of treatment, or classes, necessary. In
Alcohol/Drug Evaluation The alcohol drug evaluation is critical to the success of your case. We want you to get the best evaluation possible with the least amount of treatment, or classes, necessary. In
KAP Keys. For Clinicians. Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care Clinicians. CSAT s Knowledge Application Program
 KAP KEYS Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care CSAT s Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care U.S.
KAP KEYS Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care CSAT s Knowledge Application Program KAP Keys For Based on TIP 24 A Guide to Substance Abuse Services for Primary Care U.S.
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students
 Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
Validity of the CAGE in Screening fbr Problem Drinking in College Students Edward J. Heck Department of Counseling Psychology, University of Kansas James W. Lichtenberg Department of Counseling Psychology,
Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and Alcohol Use Disorders
 Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:2-10 http://dx.doi.org/10.4082/kjfm.2014.35.1.2 Reliability and Validity of Alcohol Use Disorder Identification Test-Korean Revised Version for Screening At-risk Drinking and
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7. Screening and Assessment
 Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
Chapter 7 Screening and Assessment Screening And Assessment Starting the dialogue and begin relationship Each are sizing each other up Information gathering Listening to their story Asking the questions
THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 40, No. 6, pp. 578 583, 2005 Advance Access publication 22 August 2005 doi:10.1093/alcalc/agh198 THE USE OF AUDIT TO ASSESS LEVEL OF ALCOHOL PROBLEMS IN RURAL VIETNAM KIM BAO
Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care attenders?
 Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
Primary Care Mental Health 2005;3:00±00 # 2005 Radcliffe Publishing International research Which screening test for alcohol consumption is best associated with `at risk' drinking in older primary care
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency
 ScienceAsia 28 (2002) : 99-103 Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency Paiboon Mongconthawornchai a, *, Somsong
ScienceAsia 28 (2002) : 99-103 Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 Genotype Detection in Fingernails among Non-alcoholic Northeastern Thai Population and Derived Gene Frequency Paiboon Mongconthawornchai a, *, Somsong
BRIEF REPORT FACTORS ASSOCIATED WITH UNTREATED REMISSIONS FROM ALCOHOL ABUSE OR DEPENDENCE
 Pergamon Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 317 321, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0306-4603/00/$ see front matter PII S0306-4603(98)00130-0 BRIEF
Pergamon Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 25, No. 2, pp. 317 321, 2000 Copyright 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0306-4603/00/$ see front matter PII S0306-4603(98)00130-0 BRIEF
Factor analysis of alcohol abuse and dependence symptom items in the 1988 National Health Interview survey
 Addiction (1995) 90, 637± 645 RESEARCH REPORT Factor analysis of alcohol abuse and dependence symptom items in the 1988 National Health Interview survey BENGT O. MUTHEÂ N Graduate School of Education,
Addiction (1995) 90, 637± 645 RESEARCH REPORT Factor analysis of alcohol abuse and dependence symptom items in the 1988 National Health Interview survey BENGT O. MUTHEÂ N Graduate School of Education,
Diagnostic orphans for alcohol use disorders in a treatment-seeking psychiatric sample
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Drug and Alcohol Dependence 96 (2008) 187 191 Short communication Diagnostic orphans for alcohol use disorders in a treatment-seeking psychiatric sample Lara A.
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Drug and Alcohol Dependence 96 (2008) 187 191 Short communication Diagnostic orphans for alcohol use disorders in a treatment-seeking psychiatric sample Lara A.
ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE DISORDERS IN THE GENERAL POPULATION
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol 40, No 5, pp 441 446, 2005 Advance Access publication 11 July 2005 doi:101093/alcalc/agh183 ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol 40, No 5, pp 441 446, 2005 Advance Access publication 11 July 2005 doi:101093/alcalc/agh183 ALCOHOL ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE CRITERIA AS PREDICTORS OF A CHRONIC COURSE OF ALCOHOL USE
Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale
 The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
DESIGN TYPE AND LEVEL OF EVIDENCE: Randomized controlled trial, Level I
 CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Hasan, A. A., Callaghan, P., & Lymn, J. S. (2015). Evaluation of the impact of a psychoeducational intervention for people diagnosed with schizophrenia and their primary
CRITICALLY APPRAISED PAPER (CAP) Hasan, A. A., Callaghan, P., & Lymn, J. S. (2015). Evaluation of the impact of a psychoeducational intervention for people diagnosed with schizophrenia and their primary
Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online March 25, 2008 Screening for depressive symptoms: Validation of the CES-D scale in a multi-ethnic group of patients with diabetes in Singapore Stahl
Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders
 Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders Abstract Melissa A. Miller, M.S. and Mark T. Fillmore, Ph.D. Department of Psychology, University of Kentucky
Poor impulse control and heightened attraction to alcohol-related imagery in repeat DUI offenders Abstract Melissa A. Miller, M.S. and Mark T. Fillmore, Ph.D. Department of Psychology, University of Kentucky
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care
 Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
Screening for Alcohol Problems in Primary Care A Systematic Review ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION David A. Fiellin, MD; M. Carrington Reid, PhD, MD; Patrick G. O Connor, MD, MPH Background: Primary care physicians
Setting Non-profit psychiatric hospital. The economic analysis was carried out in the USA.
 Inpatient alcohol treatment in a private healthcare setting: which patients benefit and at what cost? Pettinati H M, Meyers K, Evans B D, Ruetsch C R, Kaplan F N, Jensen J M, Hadley T R Record Status This
Inpatient alcohol treatment in a private healthcare setting: which patients benefit and at what cost? Pettinati H M, Meyers K, Evans B D, Ruetsch C R, Kaplan F N, Jensen J M, Hadley T R Record Status This
EMERGENCY ROOM AND PRIMARY CARE SERVICES UTILIZATION AND ASSOCIATED ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE IN THE UNITED STATES GENERAL POPULATION
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 34, No. 4, pp. 581 589, 1999 EMERGENCY ROOM AND PRIMARY CARE SERVICES UTILIZATION AND ASSOCIATED ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE IN THE UNITED STATES GENERAL POPULATION CHERYL J. CHERPITEL
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 34, No. 4, pp. 581 589, 1999 EMERGENCY ROOM AND PRIMARY CARE SERVICES UTILIZATION AND ASSOCIATED ALCOHOL AND DRUG USE IN THE UNITED STATES GENERAL POPULATION CHERYL J. CHERPITEL
Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test
 JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
JGIM ORIGINAL ARTICLES Primary Care Validation of a Single-Question Alcohol Screening Test Peter C. Smith, MD, MSc 1,5, Susan M. Schmidt 1, Donald Allensworth-Davies, MSc 2, and Richard Saitz, MD, MPH
FINGERPRINT PATTERN SIMILARITY: A ZYGOSITY TEST CLASSIFIER IN A THAI TWIN STUDY
 Original Article 129 FINGERPRINT PATTERN SIMILARITY: A ZYGOSITY TEST CLASSIFIER IN A THAI TWIN STUDY Wibhu Kutanan, Somsong Nanakorn * Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon
Original Article 129 FINGERPRINT PATTERN SIMILARITY: A ZYGOSITY TEST CLASSIFIER IN A THAI TWIN STUDY Wibhu Kutanan, Somsong Nanakorn * Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Khon Kaen University, Khon
SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders
 SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-21-02 ABSTRACT The SAQ-Short Form (SAQ-SF) is an adult offender assessment test that accurately
SAQ-Short Form Reliability and Validity Study in a Large Sample of Offenders Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 10-21-02 ABSTRACT The SAQ-Short Form (SAQ-SF) is an adult offender assessment test that accurately
words excluding references
 Psychological problems in New Zealand primary health care: A report on the pilot phase of the Mental Health and General Practice Investigation (MaGPIe) NZ Med J 2001; 114, 11-13 The MaGPIe Research Group
Psychological problems in New Zealand primary health care: A report on the pilot phase of the Mental Health and General Practice Investigation (MaGPIe) NZ Med J 2001; 114, 11-13 The MaGPIe Research Group
Their Outcomes in Thailand. Social Administration Foundation
 Drinking Patterns and Their Outcomes in Thailand Tassanee Laknapichonchat Thammasat University & Social Administration Foundation Thailand Thai people: the characteristics of fun and easy life. In general,
Drinking Patterns and Their Outcomes in Thailand Tassanee Laknapichonchat Thammasat University & Social Administration Foundation Thailand Thai people: the characteristics of fun and easy life. In general,
MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE
 Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(2)131-137 MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE SURENDRA K.MATTOO, D.BASU, A.MALHOTRA & R.MALHOTRA ABSTRACT Motivation for
Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(2)131-137 MOTIVATION FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT-HINDI SCALE: DEVELOPMENT AND FACTOR STRUCTURE SURENDRA K.MATTOO, D.BASU, A.MALHOTRA & R.MALHOTRA ABSTRACT Motivation for
Estimates of the Reliability and Criterion Validity of the Adolescent SASSI-A2
 Estimates of the Reliability and Criterion Validity of the Adolescent SASSI-A 01 Camelot Lane Springville, IN 4746 800-76-056 www.sassi.com In 013, the SASSI Profile Sheets were updated to reflect changes
Estimates of the Reliability and Criterion Validity of the Adolescent SASSI-A 01 Camelot Lane Springville, IN 4746 800-76-056 www.sassi.com In 013, the SASSI Profile Sheets were updated to reflect changes
OUTCOMES OF DICHOTOMIZING A CONTINUOUS VARIABLE IN THE PSYCHIATRIC EARLY READMISSION PREDICTION MODEL. Ng CG
 ORIGINAL PAPER OUTCOMES OF DICHOTOMIZING A CONTINUOUS VARIABLE IN THE PSYCHIATRIC EARLY READMISSION PREDICTION MODEL Ng CG Department of Psychological Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University Malaya,
ORIGINAL PAPER OUTCOMES OF DICHOTOMIZING A CONTINUOUS VARIABLE IN THE PSYCHIATRIC EARLY READMISSION PREDICTION MODEL Ng CG Department of Psychological Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University Malaya,
Mental health of adolescent school children in Sri Lanka a national survey
 Mental health of adolescent school children in Sri Lanka a national survey H Perera 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2004; 33: 78-81 (Key words: Adolescence, epidemiology, mental health) Abstract Objectives
Mental health of adolescent school children in Sri Lanka a national survey H Perera 1 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2004; 33: 78-81 (Key words: Adolescence, epidemiology, mental health) Abstract Objectives
Association between Alcoholism Family History and Alcohol Screening Scores among Alcohol-dependent Patients
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/0.9758/cpn.203..2.89 pissn 738-088 / eissn 2093-4327 Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 203;(2):89-95 Copyrightc 203, Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/0.9758/cpn.203..2.89 pissn 738-088 / eissn 2093-4327 Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 203;(2):89-95 Copyrightc 203, Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Gambl Stud. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 December 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Gambl Stud. 2010 December ; 26(4): 639 644. doi:10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x. Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Gambl Stud. 2010 December ; 26(4): 639 644. doi:10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x. Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview
THE HAMILTON Depression Rating Scale
 Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale A. Akdemir, M.H. Türkçapar, S.D. Örsel, N. Demirergi, I. Dag, and M.H. Özbay The aim of the study was to examine
Reliability and Validity of the Turkish Version of the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale A. Akdemir, M.H. Türkçapar, S.D. Örsel, N. Demirergi, I. Dag, and M.H. Özbay The aim of the study was to examine
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 November 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003 October ; 57(5): 542 544. An Open Pilot Study of Gabapentin vs. Trazodone to Treat Insomnia in Alcoholic
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2003 October ; 57(5): 542 544. An Open Pilot Study of Gabapentin vs. Trazodone to Treat Insomnia in Alcoholic
How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress?
 J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
J Occup Health 2017; 59: 356-360 Brief Report How accurately does the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire identify workers with or without potential psychological distress? Akizumi Tsutsumi 1, Akiomi Inoue
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED YEARS
 CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
Najat M. Al-Saffar, Dara A. Saeed Dept. of Medicine- Psychiatry unit, College of Medicine, Mosul University
 Generalized anxiety disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus In Suleimaniya city Najat M. Al-Saffar, Dara A. Saeed Dept. of Medicine- Psychiatry unit, College of Medicine, Mosul University Abstract To determine
Generalized anxiety disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus In Suleimaniya city Najat M. Al-Saffar, Dara A. Saeed Dept. of Medicine- Psychiatry unit, College of Medicine, Mosul University Abstract To determine
The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale
 IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 4, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2015), PP 12-16 www.iosrjournals.org The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh
IOSR Journal of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-issn: 2320 1959.p- ISSN: 2320 1940 Volume 4, Issue 2 Ver. I (Mar.-Apr. 2015), PP 12-16 www.iosrjournals.org The Bengali Adaptation of Edinburgh
CLINICAL COURSE OF ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE
 Indian J. Psychiat, 199, 39(4), 294299 CLINICAL COURSE OF ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE S.K. MATTOO & D. BASU ABSTRACT In 4 subjects having alcohol dependence syndrome, the progression of alcohol related milestones
Indian J. Psychiat, 199, 39(4), 294299 CLINICAL COURSE OF ALCOHOL DEPENDENCE S.K. MATTOO & D. BASU ABSTRACT In 4 subjects having alcohol dependence syndrome, the progression of alcohol related milestones
Measurement of Psychopathology in Populations. William W. Eaton, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
PREDICTORS FOR HIDDEN PROBLEM DRINKERS IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 287296, 1996 PREDICTORS FOR HIDDEN PROBLEM DRINKERS IN GENERAL PRACTICE MICHIEL CORNEL*, RONALD A. KNIBBE 1, J. ANDRE KNOTTNERUS, ALEX VOLOVICS 2 and MARIA J. DROP
Alcohol & Alcoholism Vol. 3, No. 3, pp. 287296, 1996 PREDICTORS FOR HIDDEN PROBLEM DRINKERS IN GENERAL PRACTICE MICHIEL CORNEL*, RONALD A. KNIBBE 1, J. ANDRE KNOTTNERUS, ALEX VOLOVICS 2 and MARIA J. DROP
Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar
 Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar Saw Morgan Soe Win 1, Chitlada Areesantichai 2. 1 College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University,
Patterns of binge drinking among adults in urban and rural areas of Pha-An township, Myanmar Saw Morgan Soe Win 1, Chitlada Areesantichai 2. 1 College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University,
Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 14:1609-1613, 2008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detecting Lifetime Alcohol Problems in Individuals Referred for Liver Transplantation for Nonalcoholic Liver Failure Ed Day, 1 David Best, 1 Ruth
CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS. This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to
 CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to make decisions or inferences about population. Populations are group of interest
CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to make decisions or inferences about population. Populations are group of interest
Identifying Adult Mental Disorders with Existing Data Sources
 Identifying Adult Mental Disorders with Existing Data Sources Mark Olfson, M.D., M.P.H. New York State Psychiatric Institute Columbia University New York, New York Everything that can be counted does not
Identifying Adult Mental Disorders with Existing Data Sources Mark Olfson, M.D., M.P.H. New York State Psychiatric Institute Columbia University New York, New York Everything that can be counted does not
CONSUMERS PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF HEALTH PERSONNEL IN SUB-DISTRICT HEALTH PROMOTING HOSPITALS
 2014 Bali, Indonesia Global Illuminators, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. CONSUMERS PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF HEALTH PERSONNEL IN SUB-DISTRICT HEALTH PROMOTING HOSPITALS, KHON KAEN PROVINCE. 1 SumaleeLarangsitand
2014 Bali, Indonesia Global Illuminators, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. CONSUMERS PROTECTION PERFORMANCE OF HEALTH PERSONNEL IN SUB-DISTRICT HEALTH PROMOTING HOSPITALS, KHON KAEN PROVINCE. 1 SumaleeLarangsitand
Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013
 Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013 The Company You Keep 1 Antitrust 2 New York Life adheres to the letter and spirit of the antitrust laws.
Underwriting the Habits Risk of Alcohol Use Gregory Ferrara New York Life Underwriting January, 2013 The Company You Keep 1 Antitrust 2 New York Life adheres to the letter and spirit of the antitrust laws.
SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires
 SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires 1. Brief Screens: NIAAA quantity and frequency Single alcohol screening question) Single drug screening question Conjoint screening questions 2. Full
SBIRT Screening and Brief Assessment Questionnaires 1. Brief Screens: NIAAA quantity and frequency Single alcohol screening question) Single drug screening question Conjoint screening questions 2. Full
Implementation of primary care alcohol screening, brief interventions and referral as routine practice in PHC in South Africa
 Implementation of primary care alcohol screening, brief interventions and referral as routine practice in PHC in South Africa Karl Peltzer, Gladys Matseke Matevha Aswihangwisi, Tom Babor Presentation First
Implementation of primary care alcohol screening, brief interventions and referral as routine practice in PHC in South Africa Karl Peltzer, Gladys Matseke Matevha Aswihangwisi, Tom Babor Presentation First
THE CONSISTENCY OF RECALLED AGE AT FIRST SEXUAL INTERCOURSE
 Revise 1st proof 6.11.96 J. biosoc. Sci. (1997) 29,1 7 1997 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom THE CONSISTENCY OF RECALLED AGE AT FIRST SEXUAL INTERCOURSE MICHAEL P. DUNNE*, NICHOLAS
Revise 1st proof 6.11.96 J. biosoc. Sci. (1997) 29,1 7 1997 Cambridge University Press Printed in the United Kingdom THE CONSISTENCY OF RECALLED AGE AT FIRST SEXUAL INTERCOURSE MICHAEL P. DUNNE*, NICHOLAS
ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS
 R2 (REVISED MANUSCRIPT BLUE 200208-877OC) ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS Mario Castro, M.D., M.P.H. Nina A. Zimmermann R.N. Sue
R2 (REVISED MANUSCRIPT BLUE 200208-877OC) ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT - ASTHMA INTERVENTION PROGRAM PREVENTS READMISSIONS IN HIGH HEALTHCARE UTILIZERS Mario Castro, M.D., M.P.H. Nina A. Zimmermann R.N. Sue
Supplementary Materials:
 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Results from the South Dakota Health Survey. Presented by: John McConnell, Bill Wright, Donald Warne, Melinda Davis & Norwood Knight Richardson
 Results from the South Dakota Health Survey Presented by: John McConnell, Bill Wright, Donald Warne, Melinda Davis & Norwood Knight Richardson May 2015 Overview Why the interest in South Dakota? Survey
Results from the South Dakota Health Survey Presented by: John McConnell, Bill Wright, Donald Warne, Melinda Davis & Norwood Knight Richardson May 2015 Overview Why the interest in South Dakota? Survey
Coping Styles and Levels of Depression, Anxiety and Stress among Siblings of Alcohol and Other Drug Users
 Edith Cowan University Research Online School of Psychology and Social Science Presentations 2012 Coping Styles and Levels of Depression, Anxiety and Stress among Siblings of Alcohol and Other Drug Users
Edith Cowan University Research Online School of Psychology and Social Science Presentations 2012 Coping Styles and Levels of Depression, Anxiety and Stress among Siblings of Alcohol and Other Drug Users
LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015
 LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015 LBPN Care Path Aim: To develop and implement standard protocols, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical
LifeBridge Physician Network Care Path Depression, Substance Abuse June 26, 2015 LBPN Care Path Aim: To develop and implement standard protocols, based on the best evidence, that provide a consistent clinical
Module Three Screening and Assessment V
 Module Three Screening and Assessment V1.7.13.141031 Introduction to Modules Three and Four Modules Three and Four cover the key components of SBIRT screening, assessment and brief intervention. The screening,
Module Three Screening and Assessment V1.7.13.141031 Introduction to Modules Three and Four Modules Three and Four cover the key components of SBIRT screening, assessment and brief intervention. The screening,
Depression and anxiety are reported to have a
 Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
Validation of Mood Measures for People with Multiple Sclerosis Tessa M. Watson, DClinPsy; Emma Ford, BSc; Esme Worthington, PhD; Nadina B. Lincoln, PhD Background: Valid assessments are needed in order
One important measure of the clinical relevance of a
 Article Five-Year Clinical Course Associated With DSM-IV Alcohol Abuse or Dependence in a Large Group of Men and Women Marc A. Schuckit, M.D. Tom L. Smith, Ph.D. George P. Danko, Ph.D. Kathleen K. Bucholz,
Article Five-Year Clinical Course Associated With DSM-IV Alcohol Abuse or Dependence in a Large Group of Men and Women Marc A. Schuckit, M.D. Tom L. Smith, Ph.D. George P. Danko, Ph.D. Kathleen K. Bucholz,
Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires
 Q J Med 2002; 95:591 595 Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires M.T. MCCUSKER 1, J. BASQUILLE 1,M.KHWAJA 1, I.M. MURRAY-LYON 2 and J. CATALAN 3 From
Q J Med 2002; 95:591 595 Hazardous and harmful drinking: a comparison of the AUDIT and CAGE screening questionnaires M.T. MCCUSKER 1, J. BASQUILLE 1,M.KHWAJA 1, I.M. MURRAY-LYON 2 and J. CATALAN 3 From
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems Per E. Danielsson, MD; Frederick P. Rivara, MD, MPH; Larry M. Gentilello, MD; Ronald V. Maier, MD Background: Alcohol screening
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reasons Why Trauma Surgeons Fail to Screen for Alcohol Problems Per E. Danielsson, MD; Frederick P. Rivara, MD, MPH; Larry M. Gentilello, MD; Ronald V. Maier, MD Background: Alcohol screening
The Relation of Internet Addiction, Insomnia and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Korean College Students
 , pp.91-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.1.10 The Relation of Internet Addiction, Insomnia and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Korean College Students Shin Mee-Kyung Korea Nazarene University,
, pp.91-98 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.1.10 The Relation of Internet Addiction, Insomnia and Excessive Daytime Sleepiness in Korean College Students Shin Mee-Kyung Korea Nazarene University,
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey
 Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
Prevalence and Characteristics of Hazardous Drinkers: Results of the Greater Milwaukee Survey Lisa K. Berger, PhD; Michael Fendrich, PhD; Adam Lippert, MA ABSTRACT Context: At-risk drinking is of particular
Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores
 Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 31 (2006) 17 24 Regular article Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores Samuel H. Rikoon, (B.A.) a, John S. Cacciola,
Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 31 (2006) 17 24 Regular article Predicting DSM-IV dependence diagnoses from Addiction Severity Index composite scores Samuel H. Rikoon, (B.A.) a, John S. Cacciola,
2016 Indiana College Substance Use. Survey SAMPLE UNIVERSITY
 2016 Indiana College Substance Use Survey SAMPLE UNIVERSITY Results of the Indiana College Substance Use Survey 2016 Sample University Indiana Prevention Resource Center 501 N. Morton St., Suite 110 Bloomington,
2016 Indiana College Substance Use Survey SAMPLE UNIVERSITY Results of the Indiana College Substance Use Survey 2016 Sample University Indiana Prevention Resource Center 501 N. Morton St., Suite 110 Bloomington,
MEASURING INTERVIEWER EFFECTS ON SELF-REPORTS FROM HOMELESS PERSONS
 MEASURING INTERVIEWER EFFECTS ON SELF-REPORTS FROM HOMELESS PERSONS Timothy P. Johnson, Jennifer A. Parsons, Survey Research Laboratory, University of Illinois Timothy Johnson, 910 West VanBuren, Suite
MEASURING INTERVIEWER EFFECTS ON SELF-REPORTS FROM HOMELESS PERSONS Timothy P. Johnson, Jennifer A. Parsons, Survey Research Laboratory, University of Illinois Timothy Johnson, 910 West VanBuren, Suite
PREVALENCE OF POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER AMONG BASRAH MEDICAL STUDENTS
 THE MEDICAL JOURNAL OF BASRAH UNIVERSITY PREVALENCE OF POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER AMONG BASRAH MEDICAL STUDENTS Asaad Q. Al-Yassen, Aqeel Ibrahim Salih ABSTRACT Background Post traumatic stress disorder
THE MEDICAL JOURNAL OF BASRAH UNIVERSITY PREVALENCE OF POST TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER AMONG BASRAH MEDICAL STUDENTS Asaad Q. Al-Yassen, Aqeel Ibrahim Salih ABSTRACT Background Post traumatic stress disorder
The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study.
 The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study. C.A.D. Kamp 1,2, L. de Vroege 1,2, J. F. van Eck van der Sluijs 1,2, W.J. Kop 3, & C.M. van der Feltz-
The Somatic Symptom Disorder B Criteria Scale (SSD-12) in a Dutch Clinical Sample. A validation study. C.A.D. Kamp 1,2, L. de Vroege 1,2, J. F. van Eck van der Sluijs 1,2, W.J. Kop 3, & C.M. van der Feltz-
Consumers Protection Performance of Health Personnel in Sub-district Health Promoting Hospitals, Khon Kaen Province
 Available online at www.globalilluminators.org GlobalIlluminators FULL PAPER PROCEEDING Multidisciplinary Studies Full Paper Proceeding GTAR-2014, Vol. 1, 536-547 ISBN: 978-969-9948-30-5 GTAR-14 Consumers
Available online at www.globalilluminators.org GlobalIlluminators FULL PAPER PROCEEDING Multidisciplinary Studies Full Paper Proceeding GTAR-2014, Vol. 1, 536-547 ISBN: 978-969-9948-30-5 GTAR-14 Consumers
Gambling Decision making Assessment Validity
 J Gambl Stud (2010) 26:639 644 DOI 10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x ORIGINAL PAPER Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview for Gambling Severity (DIGS) with the South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS)
J Gambl Stud (2010) 26:639 644 DOI 10.1007/s10899-010-9189-x ORIGINAL PAPER Comparing the Utility of a Modified Diagnostic Interview for Gambling Severity (DIGS) with the South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS)
STA 3024 Spring 2013 EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID #
 STA 3024 Spring 2013 Name EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID # Instructions: This exam contains 34 Multiple Choice questions. Each question is worth 3 points, for a total of 102 points (there are TWO bonus
STA 3024 Spring 2013 Name EXAM 3 Test Form Code A UF ID # Instructions: This exam contains 34 Multiple Choice questions. Each question is worth 3 points, for a total of 102 points (there are TWO bonus
A Comprehensive Model of Stepped Care for Substance Misuse Prevention on a College Campus
 A Comprehensive Model of Stepped Care for Substance Misuse Prevention on a College Campus Steven W. Clarke, PhD Director of Health Promotion & Prevention Services Binghamton University Jennifer F. Wagstaff,
A Comprehensive Model of Stepped Care for Substance Misuse Prevention on a College Campus Steven W. Clarke, PhD Director of Health Promotion & Prevention Services Binghamton University Jennifer F. Wagstaff,
Accepted Manuscript. The moderating effect of social cognitive factors on self-management activities and HbA1c in Thai adults with type-2 diabetes
 Accepted Manuscript The moderating effect of social cognitive factors on self-management activities and HbA1c in Thai adults with type-2 diabetes Somsak Thojampa, Barbara Mawn PII: S2352-0132(16)30143-0
Accepted Manuscript The moderating effect of social cognitive factors on self-management activities and HbA1c in Thai adults with type-2 diabetes Somsak Thojampa, Barbara Mawn PII: S2352-0132(16)30143-0
Charis Theou I,Asha K Nayak & Tessy Treesa Jose 1 2 3
 Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.1, March 015, ISSN 49-7110 A STUDY TO DETERMINE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF AN AWARENESS PROGRAMME ON KNOWLEDGE ON SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES AMONG THE STUDENTS OF
Original Article NUJHS Vol. 5, No.1, March 015, ISSN 49-7110 A STUDY TO DETERMINE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF AN AWARENESS PROGRAMME ON KNOWLEDGE ON SUBSTANCE ABUSE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES AMONG THE STUDENTS OF
Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA
 Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA 2 Evidence-Based Screening and Brief Interventions for Alcohol and Psychoactive Medication Misuse in Older Adults 3 Speakers Frederic C. Blow, Ph.D. Professor
Funded by SAMHSA in collaboration with AoA 2 Evidence-Based Screening and Brief Interventions for Alcohol and Psychoactive Medication Misuse in Older Adults 3 Speakers Frederic C. Blow, Ph.D. Professor
Impact of Comorbidities on Self-Esteem of Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.1, DIP: 18.01.011/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03416-9 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Impact
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 3, No.1, DIP: 18.01.011/20160303 ISBN: 978-1-365-03416-9 http://www.ijip.in April - June, 2016 Impact
Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings
 DOI 10.7603/s40790-014-0001-8 Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings H. Edward Fouty, Hanny C. Sanchez, Daniel S. Weitzner,
DOI 10.7603/s40790-014-0001-8 Convergent Validity of a Single Question with Multiple Classification Options for Depression Screening in Medical Settings H. Edward Fouty, Hanny C. Sanchez, Daniel S. Weitzner,
Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States.
 Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States. Mariana Cremonte UMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Rubén Ledesma UNMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Cheryl Cherpitel
Psychometric properties of the RAPS4 in Argentina, Mexico and United States. Mariana Cremonte UMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Rubén Ledesma UNMDP CONICET Mar del Plata, Argentina Cheryl Cherpitel
The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, Alcohol dependence technical overview
 The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2016 Alcohol dependence technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
The Scottish Burden of Disease Study, 2016 Alcohol dependence technical overview This resource may also be made available on request in the following formats: 0131 314 5300 nhs.healthscotland-alternativeformats@nhs.net
SUBSTANCE ABUSE DISORDERS continue to be a major. The Magnitude and Correlates of Alcohol and Drug Use Before Traumatic Brain Injury
 1765 The Magnitude and Correlates of Alcohol and Drug Use Before Traumatic Brain Injury Charles H. Bombardier, PhD, Carl T. Rimmele, PhD, Heather Zintel, BA ABSTRACT. Bombardier CH, Rimmele CT, Zintel
1765 The Magnitude and Correlates of Alcohol and Drug Use Before Traumatic Brain Injury Charles H. Bombardier, PhD, Carl T. Rimmele, PhD, Heather Zintel, BA ABSTRACT. Bombardier CH, Rimmele CT, Zintel
Alcohol dependence what actually works
 what actually works Alcohol dependence is the most common addiction that a generalist will encounter. D Wilson, FCPsych (SA) Psychiatrist and Head of Addictions Division, University of Cape Town/Groote
what actually works Alcohol dependence is the most common addiction that a generalist will encounter. D Wilson, FCPsych (SA) Psychiatrist and Head of Addictions Division, University of Cape Town/Groote
Prevalence and Correlates of Withdrawal-Related Insomnia among Adults with Alcohol Dependence: Results from a National Survey
 The American Journal on Addictions, 19: 238 244, 2010 Copyright C American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry ISSN: 1055-0496 print / 1521-0391 online DOI: 10.1111/j.1521-0391.2010.00035.x Prevalence and
The American Journal on Addictions, 19: 238 244, 2010 Copyright C American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry ISSN: 1055-0496 print / 1521-0391 online DOI: 10.1111/j.1521-0391.2010.00035.x Prevalence and
Early Psychosis Services: Philadelphia PEACE Program
 Early Psychosis Services: Philadelphia PEACE Program Irene Hurford, M.D. Clinical Director, PEACE Program, Horizon House Assistant Professor, Department of Psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania 1 John
Early Psychosis Services: Philadelphia PEACE Program Irene Hurford, M.D. Clinical Director, PEACE Program, Horizon House Assistant Professor, Department of Psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania 1 John
Latent Trait Standardization of the Benzodiazepine Dependence. Self-Report Questionnaire using the Rasch Scaling Model
 Chapter 7 Latent Trait Standardization of the Benzodiazepine Dependence Self-Report Questionnaire using the Rasch Scaling Model C.C. Kan 1, A.H.G.S. van der Ven 2, M.H.M. Breteler 3 and F.G. Zitman 1 1
Chapter 7 Latent Trait Standardization of the Benzodiazepine Dependence Self-Report Questionnaire using the Rasch Scaling Model C.C. Kan 1, A.H.G.S. van der Ven 2, M.H.M. Breteler 3 and F.G. Zitman 1 1
PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND
 JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
JOURNAL OF SCIENCE, Hue University, N 0 61, 2010 PREVALENCE OF HIV INFECTION AND RISK FACTORS OF TUBERCULIN INFECTION AMONG HOUSEHOLD CONTACTS IN AN HIV EPIDEMIC AREA: CHIANG RAI PROVINCE, THAILAND Pornnapa
Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain- Revised (SOAPP -R)
 Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain- Revised (SOAPP -R) The Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain- Revised (SOAPP -R) is a tool for clinicians to help determine how much
Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain- Revised (SOAPP -R) The Screener and Opioid Assessment for Patients with Pain- Revised (SOAPP -R) is a tool for clinicians to help determine how much
Chapter 3. Psychometric Properties
 Chapter 3 Psychometric Properties Reliability The reliability of an assessment tool like the DECA-C is defined as, the consistency of scores obtained by the same person when reexamined with the same test
Chapter 3 Psychometric Properties Reliability The reliability of an assessment tool like the DECA-C is defined as, the consistency of scores obtained by the same person when reexamined with the same test
COPING STRATEGIES OF THE RELATIVES OF SCHIZOPHRENIC PATIENTS
 Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(1 ),9-13 COPING STRATEGIES OF THE RELATIVES OF SCHIZOPHRENIC PATIENTS R.CHANDRASEKARAN, SIVAPRAKASH B.& S.R JAYESTRI ABSTRACT Families caring for a member with a chronic
Indian Journal of Psychiatry, 2002,44(1 ),9-13 COPING STRATEGIES OF THE RELATIVES OF SCHIZOPHRENIC PATIENTS R.CHANDRASEKARAN, SIVAPRAKASH B.& S.R JAYESTRI ABSTRACT Families caring for a member with a chronic
Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1990, 7, 155-162 Screening for psychiatric morbidity in an accident and emergency department GARY BELL, NICK HINDLEY, GITENDRA RAJIYAH & RACHEL ROSSER Department of Psychiatry,
Gambler Addiction Index: Gambler Assessment
 Gambler Addiction Index: Gambler Assessment Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 8-2-02 Abstract The Gambler Addiction Index (GAI) is an adult gambler assessment test that accurately measures gambler risk of gambling
Gambler Addiction Index: Gambler Assessment Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 8-2-02 Abstract The Gambler Addiction Index (GAI) is an adult gambler assessment test that accurately measures gambler risk of gambling
ALCOHOL/DRUG ASSESSMENT FORM
 ALCOHOL/DRUG ASSESSMENT FORM DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Date Client s Name Age Date of Birth Address How long have you lived at this address? Type of residence (Apt. Home, Duplex, Etc.) Rent? Own? With whom
ALCOHOL/DRUG ASSESSMENT FORM DEMOGRAPHIC INFORMATION Date Client s Name Age Date of Birth Address How long have you lived at this address? Type of residence (Apt. Home, Duplex, Etc.) Rent? Own? With whom
THE ADDICTIVE BRAIN SC 212 JANUARY 3, 2017 JOHN BUSH
 THE ADDICTIVE BRAIN SC 212 JANUARY 3, 2017 JOHN BUSH ADDICTS ADDICTIONS? WHAT CAUSES ADDICTIONS? Addiction is the result of substance abuse by people with moral failings or personality defects. Addiction
THE ADDICTIVE BRAIN SC 212 JANUARY 3, 2017 JOHN BUSH ADDICTS ADDICTIONS? WHAT CAUSES ADDICTIONS? Addiction is the result of substance abuse by people with moral failings or personality defects. Addiction
The Intention Model of Using Condom among the Youth in the Communities of Thailand
 DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2012. V58. 24 The Intention Model of Using Condom among the Youth in the Communities of Thailand Taweewun Chaleekrua 1+, Orathai Srithongtharm 2, and Buncha Promdit 3 1 Public Health
DOI: 10.7763/IPEDR. 2012. V58. 24 The Intention Model of Using Condom among the Youth in the Communities of Thailand Taweewun Chaleekrua 1+, Orathai Srithongtharm 2, and Buncha Promdit 3 1 Public Health
DUI Arrests, BAC at the Time of Arrest and Offender Assessment Test Results for Alcohol Problems
 DUI Arrests, BAC at the Time of Arrest and Offender Assessment Test Results for Alcohol Problems Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 8-14-01 Abstract Many DUI/DWI offenders have drinking problems. To further reduce
DUI Arrests, BAC at the Time of Arrest and Offender Assessment Test Results for Alcohol Problems Donald D Davignon, Ph.D. 8-14-01 Abstract Many DUI/DWI offenders have drinking problems. To further reduce
Chiang Mai University/Johns Hopkins University HIV/AIDS Research on VCT
 Chiang Mai University/Johns Hopkins University HIV/AIDS Research on VCT David Celentano, Professor of Epidemiology May 26, 2005 Scope of the CMU/JHU Collaborative HIV/AIDS Research Agenda HIV/AIDS research
Chiang Mai University/Johns Hopkins University HIV/AIDS Research on VCT David Celentano, Professor of Epidemiology May 26, 2005 Scope of the CMU/JHU Collaborative HIV/AIDS Research Agenda HIV/AIDS research
Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening
 Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening patients for substance use in a clinical setting. 1
Welcome to the second module of the Screening, Brief Intervention, and Referral to Treatment Core Curriculum. In this module, we ll address screening patients for substance use in a clinical setting. 1
J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2010; 6(3): Original Article
 49 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2010; 6(3):49-54 Original Article Clinical Features and Outcome of Conversion Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sujata Sethi, Raghu Gandhi*, Dharmendra**,
49 J. Indian Assoc. Child Adolesc. Ment. Health 2010; 6(3):49-54 Original Article Clinical Features and Outcome of Conversion Disorders in Children and Adolescents Sujata Sethi, Raghu Gandhi*, Dharmendra**,
DRINKING RISK LEVEL AND ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION SITUATION AMONG SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN A RURAL AREA OF THAILAND
 Original Article 187 DRINKING RISK LEVEL AND ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION SITUATION AMONG SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN A RURAL AREA OF THAILAND Donnapa Hongthong 1, 2, *, Chitlada Areesantichai 2, Wilas Kaunkaew
Original Article 187 DRINKING RISK LEVEL AND ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION SITUATION AMONG SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS IN A RURAL AREA OF THAILAND Donnapa Hongthong 1, 2, *, Chitlada Areesantichai 2, Wilas Kaunkaew
Defense mechanisms and symptom severity in panic disorder
 ACTA BIOMED 2010; 81: 30-34 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Defense mechanisms and symptom severity in panic disorder Marco Fario, Sonja Aprile, Chiara Cabrino, Carlo Maggini, Carlo Marchesi
ACTA BIOMED 2010; 81: 30-34 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Defense mechanisms and symptom severity in panic disorder Marco Fario, Sonja Aprile, Chiara Cabrino, Carlo Maggini, Carlo Marchesi
Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders
 Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders Kishore Desagani, MD General Adult and Forensic Psychiatrist Consultant Psychiatrist Medical Assessment and Policy Team
Mental Disorders with Associated Harmful Behavior and Substance-Related Disorders Kishore Desagani, MD General Adult and Forensic Psychiatrist Consultant Psychiatrist Medical Assessment and Policy Team
