Dr. A I Ladu, Consultant Haematologist / Lecturer, College of Medical Science University of Maiduguri, Nigeria
|
|
|
- Jean Barber
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH 2017, Science Huβ, ISSN: X, doi: /ajsir Review of thepotential role of three serum biomarkers: Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase1 (TIMP1), aminoterminal peptide of type 111 procollagen (P111NP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) in the evaluation of patients with liver fibrosis. Dr. A I Ladu, Consultant Haematologist / Lecturer, College of Medical Science University of Maiduguri, Nigeria ABSTRACT Liver fibrosis is a major complication of alcoholic liver disease (ALD). It is also a side effect of long time therapy with methotrexate (MTX), a hepatotoxic agent used in individuals with psoriasis. It is important to have accurate information about the degree of fibrosis, considering that the condition has no specific symptoms and signs, and can ultimately progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.existing guidelines and recommendation indicates that staging of liver fibrosis is the most important factor in defining prognosis and subsequent management. Liver biopsy has historically been considered the gold standard for assessing the stage of liver fibrosis. However, liver biopsy is not suitable as a screening test, given that of the millions of people affected worldwide by chronic liver disease, only 2040% will go on to develop liver fibrosis in their life time. In addition, it is an invasive procedure, associated with complication such as pain and haemorrhage. Given the drawbacks of liver biopsy, serum markers of liver fibrosis are been investigated, to determine if they can be used as potential biomarkers of fibrosis. The advantages of serum markers include, less invasiveness, more cost effective and can be used for ongoing monitoring of fibrosis. This review examined the potential role of three biomarkers, namely tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase1 (TIMP1), aminoterminal peptide of type 111 procollagen (P111NP) and hyaluronic acid (HA), singly and in combination (as panels) in the diagnosis and management of patients with liver fibrosis resulting from ALD and chronic treatment with MTX. Overall the performance of the panel markers in detecting cirrhosis and differentiating between early and advanced stages of liver fibrosis was significant compared with the single markers. However this conclusion need to be considered with caution given the multiple confounding factors that may have affected the outcomes of these studies. This include, limited studies evaluating the performance of these markers in ALD, and less so in MTX induced liver fibrosis, few participants, varying inclusion criteria and cutoff points. INTRODUCTION Liver fibrosis can be defined as the common response of the liver to injury whether the injury is caused by viruses, alcohol or fat deposition (1). The importance of early identification of liver fibrosis cannot be overemphasized given that the disease can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinomas (1,2).The pathogenic mechanism involved in liver fibrosis can be divided into two stages; In the acute stage, there is recruitment of variety of cells at the sites of injury, such as immune cells, inflammatory cells and secretion of extra cellular matrix proteins; In the chronic stage, there is accumulation of excess fibrous tissue with distortion of the normal liver parenchyma and impaired function. Ultimately, septae and nodules are formed giving rise to a cirrhotic architecture (3). Liver fibrosis is a major complication of alcoholic liver disease (ALD). It is also a side effect of long time therapy with methotrexate (MTX), a hepatotoxic agent used in individuals with psoriasis. It is important to have accurate information about the degree of fibrosis, considering that, the condition have no specific symptoms and signs; this will assist the Clinician in the assessment of severity and prognosis of the disease. It will also help in the management and monitoring of response to treatment (4).
2 Am. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2017, 8(2):1621 Existing guidelines and recommendation indicates that staging of liver fibrosis is the most important factor in defining prognosis and subsequent management. There are several methods for staging liver fibrosis, amongst them, the METAVIR score is a widely used scoring method, and classified fibrosis into five stages as, no fibrosis (F0); portal fibrosis without septa (F1); portal fibrosis with few septa (F2); septal fibrosis without cirrhosis (F3) and cirrhosis (F4) (5). In this regard, liver biopsy has historically been considered the gold standard for assessing the stage of liver fibrosis. However, liver biopsy is not suitable as a screening test, given that of the millions of people affected worldwide by chronic liver disease, only 2040% will go on to develop liver fibrosis in their life time (5). In addition, it is an invasive procedure, associated with complication such as pain and haemorrhage. Other limiting factors to its diagnostic abilities include sampling errors, length of biopsy, observer variability (5). Given the drawbacks of liver biopsy, serum markers of liver fibrosis are being investigated, to determine if they can be used as potential biomarkers of fibrosis. The diagnostic performance of a serum marker is evaluated by using the receiveroperatingcharacteristic (ROC) curves and calculating the area under the ROC curve (AUROC), this combines the sensitivity and specificity of a particular serum marker to determine the diagnosis of a specific stage of fibrosis. For a particular test, sensitivity and specificity are usually calculated by computing the correct diagnosis of advanced fibrosis versus minimal fibrosis (3). The advantages of serum markers include, less invasiveness, more cost effective, can be used for on going calibration and monitoring of fibrosis (4). In the light of these advantages of serum markers, this review sought to determine the potential role of three biomarkers, namely tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase1 (TIMP1), aminoterminal peptide of type 111 procollagen (P111NP) and hyaluronic acid (HA), singly and in combination, in the diagnosis and management of patients with liver fibrosis resulting from ALD and chronic treatment with MTX. SINGLE MARKERS Hyaluronic acid (HA): Hyaluronic acid is an extracellular matrix protein found in several tissues. In various inflammatory conditions of the liver, its synthesis increases in parallel with increasing collagen synthesis, thereby resulting in raised serum levels (6). It is the most frequently measured amongst the single markers. Several studies have evaluated its performance in patients with ALD and liver fibrosis (4). The diagnostic performance of HA in detecting cirrhosis using the AUROC determined by three studies showed discrepancies; Stickel, et al reported AUROC of 0.78 (7), Nguyenkhac 0.80 (8) and Naveau, et al., 0.93 (9). In their study, Plevris, et al., reported a sensitivity and specificity of 87% and 89% respectively and also noted that the serum HA increases in proportion to the severity of cirrhosis (10). This varied results could be attributed to the differences in the number of subjects used in these studies (Tables A). In terms of detecting fibrosis at each of the various stages, the performance of HA was not significant; in three studies, the AUROCs determined for stages F012 versus F34 was 0.76 (7), 0.83 (8) and 0.69 (11). These findings suggest that HA is poor in differentiating early fibrosis from advanced stages, and therefore not a good marker for screening in early disease. Comparison of diagnostic performance of HA in nonalcoholic related liver fibrosis revealed HA to be the best class 1 biomarker and was associated with AUROCs of 0.92 (6), 0.98 (12) and 0.97 (13) in three studies. This raises the question of whether aetiological factor influences the performance of a particular biomarker. Experiment in animal models has suggested that alcohol influences communication between liver cells thereby altering the clearance of HA; furthermore, alcohol causes dysfunction of the hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells (4). Amino terminal peptide of type 111 procollagen (P111NP): This is an important component of the connective tissue. During hepatogenesis, the basement membrane concentration increases, and this is closely followed by an increase in its serum level (3). There are few studies on its use as a single marker in subjects with ALD. In two small studies, the performance of P111NP in differentiating between fibrosis(f14) and nonfibrosis cases(f0) was high; Gabrielli, et al., (14) reported a sensitivity and specificity of 90% and 59% respectively while Li, et al., (15) reported an AUROC of In contrast, the performance of P111NP in differentiating early fibrosis(f12) from advanced stages(f34) was not significant; Gabrielli, et al., (14) reported a sensitivity and specificity of 71% and 56%, while Lieber, et al., (11) reported an AUROC of 0.67(Table A). Review of the literature indicated that P111NP was the single most evaluated markers in liver fibrosis 17
3 Am. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2017, 8(2):1621 following treatment with methotrexate (MTX). Risteli, et al., (16) evaluated 24 patients on methotrexate using liver biopsies and serum assay of P111NP, and found that 90% of patients with serum level above normal had liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Similarly, Oogarah, et al., (17) reported highest level of serum P111NP in patients with hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis, further screening of patients with high P111NP and normal liver histology using electron microscope revealed presence of fibrosis in the space of Disse, they concluded that MTX causes subtle liver damage in a majority of treated patients. Mitchell, et al., (18) corroborated this finding in their study (Table B). In a clinical audit, Khan, Subedi, and Chowdhury., (19), assessed guidelines produced by Manchester on P111NP monitoring in patients receiving MTX, in order to determine if the agreed level correlates with histological severity; they concluded that a higher cumulative dose of MTX correlates significantly with maximum levels of P111NP. Currently, the British, EU and German guidelines recommends P111NP as a baseline test in psoriasis patients receiving treatment with MTX (20). Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 (TIMP1):Tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase 1 are secreted proteins that interacts with matrix metalloprotein (MMP) thereby regulating their activities and function. Levels of this protein have been shown to be raised in chronic liver disease (3). In two studies that evaluated its performance in ALD, Li, et al., (15) reported a high AUROC of 0.98 in the detection of any fibrosis; However, this result needs careful interpretation giving the small number of subjects (Table A); Lieber, et al., (11) in their evaluation of 247 subjects reported the AUROC to be 0.68 in discriminating between stages F012 vs 34. Panelmarkers: There was paucity of studies that evaluated the test performance of the three markers as a panel in alcoholic liver disease and none in MTX induced liver fibrosis; One of such combination of the three markers is the Enhanced liver fibrosis test (ELF), first developed by a group of European researchers in 1997, their work led to the identification of a combination of direct markers (HA, PIIINP & TIMP1) that have been validated. Rosenberg, et al., (21) in a large international multicentre cohort study, to assess the performance of serum markers in detecting significant histologic fibrosis, evaluated a subset of 64 with alcoholic liver disease using the ELF test. The AUROC obtained was 0.94 (p<0.0001; 95% CI ) in differentiating F012 vs F34. In detection of fibrosis stages 3 or 4 using a threshold of 0.87, the sensitivity and NPV were both 100% (specificity 17%, PPV 75%), at a lower cutoff value of 0.43 for the prediction of fibrosis, the sensitivity and specificity was 93% and 100% respectively, PPV was 100%, and NPV 86% (Table C). In the only study that compared the performance of the markers singly and as a panel in ALD, Lieber, et al.,( 11 ) reported a lower AUROC for the individual markers (HA 0.69, TIMP1 0.68, P111NP 0.67) while the overall performance of the panel in predicting different stages of fibrosis showed a sensitivity of 76%, specificity of 68% (PPV 53%, NPV 86%). Overall the performance of the panel markers in detecting cirrhosis and differentiating between early and advanced stages of liver fibrosis was significant compared with the single markers. However this conclusion need to be considered with caution given the multiple confounding factors that may have affected the outcomes of these studies. This include, limited studies evaluating the performance of these markers in ALD, and less so in MTX induced liver fibrosis, few participants, varying inclusion criteria and cutoff points.the importance of early detection of fibrosis is that it provides the opportunity in planning of effective management and monitoring of these groups of patients; therefore the combined markers undoubtedly will be a useful test for both the patients and Clinicians. 18
4 Am. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2017, 8(2):1621 Table A: Diagnostic performance of single markers (Table partly reproduced from: Parkes et al.,2012. Comparative Hepatology) Degree of fibrosis tested Study Subjects AUROC SEN (%) SPE (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) HYALURONIC ACID Cirrhosis Plevris(2000) Stickel(2003) Naveau(2005) Nguyen Khac(2008) F012 vs 34 Stickel(2003) Nguyen Khac(2008) Lieber(2008) F01vs234 Naveau(2005) Nguyen Khac(2008) P111NP F01vs34 Gabrielli (1989) Lieber(2005) F0vsF16 Gabrielli(1989) Li(1994) TIMP1 F012vs34 Lieber(2008) Any fibrosis Li(1994) 0.96 AUROC= Area under the receiver operating curve. SEN Sensitivity SPE Specificity PPV Positive predictive value NPVnegative predictive value no record 19
5 Am. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2017, 8(2):1621 Table B : Summaries of studies evaluating serum PIIINP in Psoriasis patients on long term methotrexate treatment. Author/date of studies No of patients Recruitment details % abnormal liver histology Comments Ristelli (1989) 24 Consecutive,Prospective 33(cirrhosis + fibrosis) Oogarah (1995) 22 Consecutive,Prospective 82 (Electron microscope) P111NP can be used as a valuable marker of fibrosis in patients MTX causes subtle liver damage in the majority of treated patients Mitchell (1990) 51 Consecutive,Prospective Highest P111NP value found in groups with cirrhosis and fibrosis Khan ( ) 65 Retrospective High cumulative dose of MTX corr.significantly with high mean P111NP MTX methotrexate no record Table C: Diagnostic performance of panel markers (Table partly reproduced from:parkes et al.,2012. Comparative Hepatology) Study Fibrosis grade No of AUROC cutoff %SEN. %SPE. PPV NPV Subjects Rosenberg F012vs (2004) Lieber F012 vs (2008) Mild Fibrosis AUROC= Area under the receiver operating curve. SEN Sensitivity SPE Specificity PPV Positive predictive value NPVnegative predictive value 20
6 Am. J. Sci. Ind. Res., 2017, 8(2):1621 REFERENCES 1. Parkes J, Guha IN, Roderick S, Harris S, Cross R and Manos MM, Irving W., Enhance Liver Fibrosis (ELF) test accurately identifies liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Journal of viral hepatitis, 18,pp Wahl K, Rosenberg W, Vaske B, Manns MP and SchulzeOsthoff K., Biopsy Controlled Liver Fibrosis staging using the Enhanced Liver fibrosis (ELF) score compared to transient elastography.plos ONE 7(12):e51906.doi: /journal.pone Baranova A, Lal P, Birerdinc A and Younossi ZM.,2011. NonInvasive markers for hepatic fibrosis. BMC Gastroenterology, 11: Parkes J, Guha IN, Harris S, Rosenberg WMC and Roderick PJ Systematic review of the diagnostic performance of serum markers of liver fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease. Comparative Hepatology, 11:5 5. Sebastiani G, Gkouvatsos K and Plebani M., Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis: it is time for laboratory medicine. Clinical Chemistry laboratory Medicine, 49(1),pp Suzuki A, Angulo P, Lymp J, Li D and Satomura S., Hyaluronic acid, an accurate serum marker for severe hepatic fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver International, 25, pp Stickel F, Poeschl G, Schuppan D, Conradt C and StrengeHese A, et al., Serum hyaluronate correlates with histological progression in alcoholic liver disease. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 15(9), pp NguyenKhacE,Chaldelain D, Tramier B, Decrombecque C and Robert B, et al., Assessment of asymptomatic liver fibrosis in alcoholic patients using fibro scan: prospective comparison with seven noninvasive laboratory tests. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 28: doi: /j x 9. Naveau S, RaynardB,RatziuV,Abella A, Imbert BismutF,Messous D, et al.,2005. Biomarkers for the prediction of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic alcoholic liver disease. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 3(2),pp Plevris JN, Haydom GH, Simpson KJ, Dawkes R and Ludlum CA Serum hyaluronan, a noninvasive test for diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. European Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 12(10), pp Lieber CS, Weiss DG and Paronetto F., 2008.Value of fibrosis markers for staging liver fibrosis in patients with precirrhotic alcoholic liver disease. Alcoholism, Clinical and experimental research, 32(6), pp Parsian H, Rahimipour A, Nouri M,Somi MH and Qujeq D, et al., Serum Hyaluronic acid and Laminin as Biomarkers in Liver fibrosis. Journal of Gastrointestinal Liver disease, 19(2), pp Kaneda H,HashimotoE,Yatsuji S, TokushigeK,Shiratori K.,2006. Hyaluronic acid levels cam predict severe fibrosis and platelet counts can predict cirrhosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 21, pp Gabrielli GB, Faccioli G, Casaril M, Capra F, Bonazi L, Falezza G et al Procollagen 111 peptide and fibronectin in alcohol related liver disease: correlations with morphological features and biochemical tests. International journal of clinical chemistry, 179(3), pp Li J, Rosman AS, Leo MA, Nagai Y, and Lieber CS., 1994.Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase is increased in the serum of precirrhotic and cirrhotic alcoholic patients and can serve as a marker of fibrosis. Hepatology, 19(6), pp Risteli J, Sogaard H, OikarinenA,Risteli L and Karvonen, et al.,1988.aminoterminal propeptide of type 111 procollagen in methotrexateinduced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. The British journal of Dermatology, 119(3), pp Oogarah PK, Rowland PL, Mitchell DM, Smith A and Chalmers RJ et al., Abnormalities of Serum type 111 procollagen amino terminal peptide in methotrexatetreated psoriatic patients with normal liver histology do not correlate with hepatic ultrastructural changes. The British journal of Dermatology, 133(4), pp Mitchell D, Smith A,Rowan B, Warnes TW and Haboubi NY et al., Serum type 111 procollagen peptide, dynamic liver function tests and hepatic fibrosis in psoriatic patients receiving methotrexate. The British journal of Dermatology, 122(1), pp Khan S, Subedi D, Chowdary MM., Use of amino terminal type 111 procollagen peptide assay in methotrexate therapy for psoriasis. Postgraduate Medical journal, 82(967), pp Barker J, Horn EJ, Lebwohl M, Warren RB, Nast A, Rosenberg WM et al., Assessment and management of methotrexate hepatotoxicity in psoriasis patients: reports from a consensus conference to evaluate current practise and identify key questions towards optimizing methotrexate use in the clinic. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 25, pp Rosenberg WM, Voelker M, Thiel R, Becka M, Burt A, Schuppan D et al Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology; 127(6):
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis. June 2008
 Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis June 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Test (ELF) for evaluating liver fibrosis June 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Study population The study population comprised patients with psoriasis who were receiving long-term methotrexate.
 Replacement of routine liver biopsy by procollagen III aminopeptide for monitoring patients with psoriasis receiving long-term methotrexate: a multicentre audit and health economic analysis Chalmers R
Replacement of routine liver biopsy by procollagen III aminopeptide for monitoring patients with psoriasis receiving long-term methotrexate: a multicentre audit and health economic analysis Chalmers R
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
 The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
The role of non-invasivemethods in evaluating liver fibrosis of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Objectives: Liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing the extent of fibrosis in NAFLD/NASH;
Journal of Asian Scientific Research
 Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 COULD SERUM LAMININ REPLACE LIVER BIOPSY AS GOLD STANDARD FOR PREDICTING SIGNIFICANT FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS
Journal of Asian Scientific Research journal homepage: http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5003 COULD SERUM LAMININ REPLACE LIVER BIOPSY AS GOLD STANDARD FOR PREDICTING SIGNIFICANT FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS
NHSScotland is required to consider the Scottish Health Technologies Group (SHTG) advice.
 Advice Statement 010-18 July 2018 Advice Statement What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic acid, P3NP, Fibroscan or ARFI elastography) for detecting and staging liver
Advice Statement 010-18 July 2018 Advice Statement What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic acid, P3NP, Fibroscan or ARFI elastography) for detecting and staging liver
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis. Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology
 Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis Patricia Slev, PhD University of Utah Department of Pathology Disclosure Patricia Slev has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. 2 Chronic Liver Disease
Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis
 NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
NORTHWEST AIDS EDUCATION AND TRAINING CENTER Non-Invasive Testing for Liver Fibrosis John Scott, MD, MSc Associate Professor, University of Washington Associate Clinic Director, Hep/Liver Clinic, Harborview
The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) Panel: Analyte Stability Under Common Sample Storage Conditions Used in Clinical Practice
 The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) Panel: Analyte Stability Under Common Sample Storage Conditions Used in Clinical Practice Oliver J. Kennedy, 1 Julie Parkes, 1,2 Sudeep Tanwar, 2 Paul Trembling, 2 and
The Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) Panel: Analyte Stability Under Common Sample Storage Conditions Used in Clinical Practice Oliver J. Kennedy, 1 Julie Parkes, 1,2 Sudeep Tanwar, 2 Paul Trembling, 2 and
In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network
 Evidence Note Number 82 July 2018 In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic
Evidence Note Number 82 July 2018 In response to an enquiry from the Scottish Clinical Biochemistry Managed Diagnostic Network What is the most accurate and cost-effective direct test (ELF test, hyaluronic
Procollagen-III-peptide, Brochure
 Procollagen-III-peptide, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T BE +32 (0)2 502 12 53 Begonialaan
Procollagen-III-peptide, Brochure Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect Diagnostics. Bio-Connect Diagnostics B.V. T NL +31 (0)26 326 44 60 T BE +32 (0)2 502 12 53 Begonialaan
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes deaths
 Original Article / Liver Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International Diagnostic accuracy of enhanced liver test to assess liver in patients with chronic hepatitis C Roberto Catanzaro, Michele Milazzo,
Original Article / Liver Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International Diagnostic accuracy of enhanced liver test to assess liver in patients with chronic hepatitis C Roberto Catanzaro, Michele Milazzo,
Making the best use of liver biopsy: clinical perspective. Steve Ryder Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham
 Making the best use of liver biopsy: clinical perspective Steve Ryder Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham Trepanning most efficacious for the relief of maladies so diverse and troublesome
Making the best use of liver biopsy: clinical perspective Steve Ryder Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham Trepanning most efficacious for the relief of maladies so diverse and troublesome
HEPATIC FIBROSIS AND CIRrhosis
 STUDY Reliability of the Roenigk Classification of Liver Damage After Methotrexate Treatment for Psoriasis A Clinicopathologic Study of 160 Liver Biopsy Specimens Maartje A. M. Berends, MD; Martijn G.
STUDY Reliability of the Roenigk Classification of Liver Damage After Methotrexate Treatment for Psoriasis A Clinicopathologic Study of 160 Liver Biopsy Specimens Maartje A. M. Berends, MD; Martijn G.
Liver 102: Injury and Healing
 Liver 102: Injury and Healing Dawn Pease, MSN, RN, ANP-BC Brackenridge Specialty Clinics University Medical Center Brackenridge Austin, TX Seton Healthcare Family Liver 102 Outline Biochemical patterns
Liver 102: Injury and Healing Dawn Pease, MSN, RN, ANP-BC Brackenridge Specialty Clinics University Medical Center Brackenridge Austin, TX Seton Healthcare Family Liver 102 Outline Biochemical patterns
Break the Liver Biopsy Habit
 Break the Liver Biopsy Habit Dirk Elston MD Professor and Chairman Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery Medical University of South Carolina No conflict of interest Father of one of my nurses:
Break the Liver Biopsy Habit Dirk Elston MD Professor and Chairman Department of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery Medical University of South Carolina No conflict of interest Father of one of my nurses:
Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, Vol.46, No.1, April 2016 J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. (JESP), 46(1), 2016:
 Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, Vol.46, No.1, April 2016 J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. (JESP), 46(1), 2016: 125-130 SERUM MARKERS FOR ASSESSING LIVER FIBROSIS IN EGYPTIAN PA- TIENTS WITH CHRONIC
Journal of the Egyptian Society of Parasitology, Vol.46, No.1, April 2016 J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. (JESP), 46(1), 2016: 125-130 SERUM MARKERS FOR ASSESSING LIVER FIBROSIS IN EGYPTIAN PA- TIENTS WITH CHRONIC
Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 492-497 Original Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index in children with cholestatic liver diseases to assess liver fibrosis Aysel Ünlüsoy-Aksu 1,
INHSU th International Symposium on Hepatitis Care In Substance Users
 INHSU 2015 4 th International Symposium on Hepatitis Care In Substance Users Sydney, 7 October 2015 Non-invasive liver fibrosis assessment: Opportunities for enhanced liver disease assessment and treatment
INHSU 2015 4 th International Symposium on Hepatitis Care In Substance Users Sydney, 7 October 2015 Non-invasive liver fibrosis assessment: Opportunities for enhanced liver disease assessment and treatment
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic
 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseasean underestimated epidemic Amir Shlomai MD,PhD Head, Department of Medicine D The Liver Institute Rabin Medical Center, Beilinson Hospital The IASLD semi-annual meeting-
Quantitative Assessment of the Liver: Breath Tests. M. Shadab Siddiqui, M.D. Virginia Commonwealth University
 Quantitative Assessment of the Liver: Breath Tests M. Shadab Siddiqui, M.D. Virginia Commonwealth University Objectives Principles of breath tests Breath tests in NAFLD Potential applications of breath
Quantitative Assessment of the Liver: Breath Tests M. Shadab Siddiqui, M.D. Virginia Commonwealth University Objectives Principles of breath tests Breath tests in NAFLD Potential applications of breath
New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV
 New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV Jidong Jia, MD, PhD Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University 2016-3-14 Disclosure Consultation for Abbvie
New Tools for Assessing Disease Sererity, progression and regression in HBV and HCV Jidong Jia, MD, PhD Beijing Friendship Hospital, Capital Medical University 2016-3-14 Disclosure Consultation for Abbvie
Pretreatment Evaluation
 Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
Pretreatment Evaluation Disclosures Research supported by Gilead Sciences Inc.: Site investigator for HIV/HCV SWITCH Registry Study Key personnel for FOCUS HCV Screening Program through Vanderbilt University
The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
RESEARCH ARTICLE The role of ARFI and APRI in diagnosis of liver fibrosis on patients with common chronic liver diseases Objective: This study aimed to investigate the value of liver fibrosis assessment
Fatty Liver Disease. Mark Thursz. Imperial College
 Fatty Liver Disease Mark Thursz Imperial College Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease UK adult obesity (BMI>30) 1980: 6% [M], 8% [F]. 1997: 17% [M], 20% [F]. By 2004, 23.6% of men and 23.8% of women were
Fatty Liver Disease Mark Thursz Imperial College Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease UK adult obesity (BMI>30) 1980: 6% [M], 8% [F]. 1997: 17% [M], 20% [F]. By 2004, 23.6% of men and 23.8% of women were
What to do about the high ALT picked up at the annual review. Dr Michael Yee Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology
 What to do about the high ALT picked up at the annual review Dr Michael Yee Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Mrs DC HPC PMH Type 2 Diabetes (decades) Regular retinal screening No foot complications/neuropathy
What to do about the high ALT picked up at the annual review Dr Michael Yee Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Mrs DC HPC PMH Type 2 Diabetes (decades) Regular retinal screening No foot complications/neuropathy
Abstract INTRODUCTION RAPID COMMUNICATION
 Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 2008 December 14; 14(46): 7117-7121 wjg@wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 doi:10.3748/wjg.14.7117 2008 The WJG Press.
Online Submissions: wjg.wjgnet.com World J Gastroenterol 2008 December 14; 14(46): 7117-7121 wjg@wjgnet.com World Journal of Gastroenterology ISSN 1007-9327 doi:10.3748/wjg.14.7117 2008 The WJG Press.
European. Young Hepatologists Workshop. Organized by : Quantification of fibrosis and cirrhosis outcomes
 supported by from Gilea Quantification of fibrosis and cirrhosis outcomes th 5 European 5 European Young Hepatologists Workshop Young Hepatologists Workshop August, 27-29. 2015, Moulin de Vernègues Vincenza
supported by from Gilea Quantification of fibrosis and cirrhosis outcomes th 5 European 5 European Young Hepatologists Workshop Young Hepatologists Workshop August, 27-29. 2015, Moulin de Vernègues Vincenza
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Review Article Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: An Overview
 Advances in Hepatology, Article ID 357287, 15 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/357287 Review Article Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: An Overview Hind I. Fallatah Fellowship of American College
Advances in Hepatology, Article ID 357287, 15 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/357287 Review Article Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: An Overview Hind I. Fallatah Fellowship of American College
International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN
 Report International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN 973-8363 to diagnose fibrosis in patients with chronic active Hepatitis C Mosa T E 1, Abd El-Maksoud M D 1,*,
Report International Journal of Integrative Biology A journal for biology beyond borders ISSN 973-8363 to diagnose fibrosis in patients with chronic active Hepatitis C Mosa T E 1, Abd El-Maksoud M D 1,*,
Invasive. Sampling error. Interobserver variability. Nondynamic evaluation of
 How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
How to assess liver fibrosis Serum markers or FibroScan vs. liver biopsy? Laurent CASTERA & Pierre BEDOSSA Hôpital Beaujon, AP-HP, Clichy Université Paris-VII France 4 th Paris Hepatitis Conference, Paris,
Bio Predictive. FibroTest/FibroSure Scientific Publications. Houot 2015 FibroTest, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis
 AASLD 2015 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Section 1 - compared to APRI, FIB-4 and transient elastography Houot 2015, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis is superior to TE by Fibroscan, APRI and Fib-4 using
AASLD 2015 /FibroSure Scientific Publications Section 1 - compared to APRI, FIB-4 and transient elastography Houot 2015, TE, FIB-4, APRI Meta-analysis is superior to TE by Fibroscan, APRI and Fib-4 using
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2018 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2019 Policy Blue Cross and
The ability of Hepascore to predict liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease: A metaanalysis
 The University of Notre Dame Australia ResearchOnline@ND Health Sciences Papers and Journal Articles School of Health Sciences 2016 The ability of Hepascore to predict liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease:
The University of Notre Dame Australia ResearchOnline@ND Health Sciences Papers and Journal Articles School of Health Sciences 2016 The ability of Hepascore to predict liver fibrosis in chronic liver disease:
Pretreatment assessment of Chronic Hepatitis C and Compensated Cirrhosis and Indications for Therapy
 Pretreatment assessment of Chronic Hepatitis C and Compensated Cirrhosis and Indications for Therapy Teerha Piratvisuth MD. Prince of Songkla University Treatment of chronic hepatitis C and response rates
Pretreatment assessment of Chronic Hepatitis C and Compensated Cirrhosis and Indications for Therapy Teerha Piratvisuth MD. Prince of Songkla University Treatment of chronic hepatitis C and response rates
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing?
 Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Why to biopsy? Indications for liver biopsy in common medical liver diseases- how are they changing? Stephen D Ryder Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust and Biomedical research Unit What are we currently
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease Policy Number: 2.04.41 Last Review: 2/2019 Origination: 2/2017 Next Review: 2/2020 Policy Blue Cross and
Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 1 Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK 2 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne,
1 Liver Unit, Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Trust, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK 2 Institute of Cellular Medicine, Faculty of Medical Sciences, Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne,
Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: Clinical Applications and Future Directions
 Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:245 256 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0061-z MATRIX PATHOBIOLOGY (YOUHUA LIU, SECTION EDITOR) Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: Clinical Applications and Future Directions
Curr Pathobiol Rep (2014) 2:245 256 DOI 10.1007/s40139-014-0061-z MATRIX PATHOBIOLOGY (YOUHUA LIU, SECTION EDITOR) Noninvasive Biomarkers of Liver Fibrosis: Clinical Applications and Future Directions
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes. Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD
 Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
Fibrosis & Structural Decline of Liver Allografts: what and how to measure & potential underlying causes Carla Venturi Monteagudo MD, PhD THE NORMAL LIVER ARCHITECTURE Parenchymal Cells -Hepatocytes -Cholangiocytes
Laura Smart 9/22/2011
 Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Laura Smart 9/22/2011 Fibrosis is a wound healing response in which damaged regions are encapsulated by an extracellular matrix or scar. Fibrosis develops in almost all patients with chronic liver injury
Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: June Policy No: 47 Effective Date: August 1, 2013
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Evaluation of Fibrosis Progression by Noninvasive Biochemical Markers in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B
 EJOHG 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1016 Evaluation of Fibrosis Progression by Noninvasive Biochemical Markers in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fibrosis Progression
EJOHG 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1016 Evaluation of Fibrosis Progression by Noninvasive Biochemical Markers in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fibrosis Progression
In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
REVIEW In Search of New Biomarkers for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Ting-Ting Chan, M.R.C.P., and Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, M.D. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) affects 15% to 40% of the general
CLINICAL LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:160 167 CLINICAL LIVER, BILIARY TRACT Performance of ELF Serum Markers in Predicting Fibrosis Stage in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease VALERIO NOBILI,* JULIE PARKES,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:160 167 CLINICAL LIVER, BILIARY TRACT Performance of ELF Serum Markers in Predicting Fibrosis Stage in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease VALERIO NOBILI,* JULIE PARKES,
CLINICAL STUDIES. Liver International ISSN
 Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 CLINICAL STUDIES Biochemical and biophysical assessment of MTX-induced liver brosis in psoriasis patients: predicts the presence and Fibroscan s predicts the absence
Liver International ISSN 1478-3223 CLINICAL STUDIES Biochemical and biophysical assessment of MTX-induced liver brosis in psoriasis patients: predicts the presence and Fibroscan s predicts the absence
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association
 CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lynch M, Higgins E, McCormick PA, et al. The use of transient elastography and FibroTest for monitoring hepatotoxicity in patients receiving methotrexate for psoriasis. JAMA
Supplementary Online Content Lynch M, Higgins E, McCormick PA, et al. The use of transient elastography and FibroTest for monitoring hepatotoxicity in patients receiving methotrexate for psoriasis. JAMA
Xiao-Ling Chi, Mei-Jie Shi, Huan-Ming Xiao, Yu-Bao Xie, and Gao-Shu Cai. Correspondence should be addressed to Xiao-Ling Chi;
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers
 Non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers Liver Forum, November 12 th, 2015 Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc Professor of Medicine (with tenure) Director, NAFLD Research Center, Division of Gastroenterology, Department
Non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers Liver Forum, November 12 th, 2015 Rohit Loomba, MD, MHSc Professor of Medicine (with tenure) Director, NAFLD Research Center, Division of Gastroenterology, Department
I N Guha, J Parkes, P R Roderick, S Harris, W M Rosenberg
 1650 Recent advances in clinical practice NON-INVASIVE MARKERS ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER FIBROSIS IN NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr I N
1650 Recent advances in clinical practice NON-INVASIVE MARKERS ASSOCIATED WITH LIVER FIBROSIS IN NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE See end of article for authors affiliations Correspondence to: Dr I N
Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio Index for Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Prediction in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients
 BJID 2008; 12 (February) 15 Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio Index for Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Prediction in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Roberto Gomes da Silva Junior 1, Ricardo Fakhouri 2,
BJID 2008; 12 (February) 15 Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Platelet Ratio Index for Fibrosis and Cirrhosis Prediction in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Roberto Gomes da Silva Junior 1, Ricardo Fakhouri 2,
Multianalyte assays with algorithmic analyses are considered investigational for the diagnosis or monitoring of patients with chronic liver disease.
 2.04.41 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.04 Pathology/Laboratory Effective Date September
2.04.41 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection 2.04 Pathology/Laboratory Effective Date September
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS. Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust
 ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS Dr Uthayanan Chelvaratnam Hepatology Consultant North Bristol NHS Trust INTRODUCTION Liver function tests Cases Non invasive fibrosis measurement Questions UK MORTALITY RATE
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii
 HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
HEP DART 2017, Kona, Hawaii Rong Yu 1, Ke Xu 1, Jing Li 1, Tong Sun 1, Shengjiang Zhang 2, Jinhua Shao 2, Jin Sun 2, Qiong He 3, Jianwen Luo 3, Cheng Wang 4, Yudong Wang 4, Jing Chen 4, Vanessa Wu 4, George
M30 Apoptosense ELISA. A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH
 M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
M30 Apoptosense ELISA A biomarker assay for detection and screening of NASH NASH A Global Disease In the Western countries, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease, strongly
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
 NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
NON-ALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND NON-ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES Preface Zobair M. Younossi xiii Epidemiology and Natural History of NAFLD and NASH 1 Janus P. Ong and Zobair M. Younossi Understanding
Page: 1 of 19. Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Page: 1 of 19 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Description Options for noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis
and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Page: 1 of 19 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Description Options for noninvasive monitoring of liver fibrosis
Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis by Serum Enhanced Liver Fibrosis Assay
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Public Health Resources Public Health Resources 2008 Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis by Serum
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Public Health Resources Public Health Resources 2008 Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis by Serum
Assessment of liver fibrosis before and after antiviral therapy by different serum marker panels in patients with chronic hepatitis C
 Assessment of liver fibrosis before and after antiviral therapy by different serum marker panels in patients with chronic hepatitis C Stella M Martinez, Guillermo Fernández-Varo, Patricia González, Ellen
Assessment of liver fibrosis before and after antiviral therapy by different serum marker panels in patients with chronic hepatitis C Stella M Martinez, Guillermo Fernández-Varo, Patricia González, Ellen
NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION IN CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES
 Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
Best of EASL -, Ethiopia 29 Sep to 01 Oct, 2016 Inaugural meeting of the Sub Saharan GI-Hepatology Working Group Incorporating Best of AGA and Best of EASL NON INVASIVE EVALUATION OF DISEASE PROGRESSION
Simple Tests to Predict Hepatic Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Chronic Liver Diseases
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2007, pp. 145-150 original article Simple Tests to Predict Hepatic Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Chronic Liver Diseases Woon Geon Shin*, Sang Hoon Park*, Sun-Young Jun,
Gut and Liver, Vol. 1, No. 2, December 2007, pp. 145-150 original article Simple Tests to Predict Hepatic Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Chronic Liver Diseases Woon Geon Shin*, Sang Hoon Park*, Sun-Young Jun,
/ FIB4 Index , simple steatosis. FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index FIB4 Index. Sterling FIB4 Index. FIB4 Index AST AST ALT
 原 著 29 34-41, 2014 FIB4 Index 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 FIB4 Index FIB4 Index cut off 2.67 2.67 12,059 FIB4 IndexFIB4 Index 2.67 / FIB4 Index AST ALT FIB4 Index 2.67 161 1.3% FIB4 Index 5 FIB4 Index 1.1 5 1.6 FIB4
原 著 29 34-41, 2014 FIB4 Index 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 FIB4 Index FIB4 Index cut off 2.67 2.67 12,059 FIB4 IndexFIB4 Index 2.67 / FIB4 Index AST ALT FIB4 Index 2.67 161 1.3% FIB4 Index 5 FIB4 Index 1.1 5 1.6 FIB4
Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
 Medical Policy Manual Laboratory, Policy No. 47 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Next Review: May 2018 Last Review:
Medical Policy Manual Laboratory, Policy No. 47 Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Next Review: May 2018 Last Review:
Case #1. Digital Slides 11/6/ year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests. Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis
 45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
45 year old woman presented with abnormal liver function tests Liver Biopsy to r/o autoimmune hepatitis Further down. ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 ANA 1: 160; ASMA 1:80 IgG = 14.5 g/l (upper normal range: 16)
Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis
 Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis Detlef Schuppan Institute of Translational Immunology and Research Center for Immune Therapy, University Medical Center
Study Design to Validate Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in NASH Due to Cirrhosis Detlef Schuppan Institute of Translational Immunology and Research Center for Immune Therapy, University Medical Center
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients
 Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
Evaluation of liver and spleen stiffness using a ultrasound guided method: Accuracy of ARFI(R) measurements in liver disease patients Poster No.: C-3242 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords:
doi: /jvh.12161
 Journal of Viral Hepatitis, 2014, 21, 430 438 doi:10.1111/jvh.12161 Performance of Enhanced Liver Fibrosis test and comparison with transient elastography in the identification of liver fibrosis in patients
Journal of Viral Hepatitis, 2014, 21, 430 438 doi:10.1111/jvh.12161 Performance of Enhanced Liver Fibrosis test and comparison with transient elastography in the identification of liver fibrosis in patients
Hepatitis C Management and Treatment
 Hepatitis C Management and Treatment Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology 1 Discovery of Hepatitis C Key facts Hepatitis C: the virus can cause
Hepatitis C Management and Treatment Kaya Süer Near East University Faculty of Medicine Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology 1 Discovery of Hepatitis C Key facts Hepatitis C: the virus can cause
LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1028 1033 LIVER, PANCREAS, AND BILIARY TRACT Prevalence and Indicators of Portal Hypertension in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease FLAVIA D.
Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease
 HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
HKASLD 30 th ASM and International Symposium on Hepatology 2017 Screening cardiac patients for advanced liver disease 5 Nov 2017 Dr. Lau Yue Leung Joulen Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital NAFLD
MP Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients With Chronic Liver Disease
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.41 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 9.01.502 Experimental / Investigational Services DISCLAIMER Our medical policies
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Page 1 of 34 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Professional
Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed Date: May Policy No: 47 Effective Date: August 1, 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Multianalyte Assays with Algorithmic Analysis for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Date of Origin: June 2013 Section: Laboratory Last Reviewed
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): What the Gastroenterologist Should Know
 Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): What the Gastroenterologist Should Know Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of GI and Hepatology
Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): What the Gastroenterologist Should Know Naga P. Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of GI and Hepatology
Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient Elastography in Diabetics with Fatty Liver A Single Center Cross Sectional observational Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. IV (June. 2017), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Liver Stiffness by Transient
The diagnostic value of a globulin/platelet model for evaluating liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients
 1130-0108/2015/107/12/740-744 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2015 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid) Vol. 107, N.º 12, pp. 740-744, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPERS The diagnostic
1130-0108/2015/107/12/740-744 Revista Española de Enfermedades Digestivas Copyright 2015 Arán Ediciones, S. L. Rev Esp Enferm Dig (Madrid) Vol. 107, N.º 12, pp. 740-744, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPERS The diagnostic
Screening for Portal Hypertension in Cirrhosis
 Screening for Portal Hypertension in Cirrhosis MASSIMO PINZANI, MD, PhD, FRCP Sheila Sherlock Chair of Hepatology UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health Royal Free Hospital, London, UK m.pinzani@ucl.ac.uk
Screening for Portal Hypertension in Cirrhosis MASSIMO PINZANI, MD, PhD, FRCP Sheila Sherlock Chair of Hepatology UCL Institute for Liver and Digestive Health Royal Free Hospital, London, UK m.pinzani@ucl.ac.uk
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO
 PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
PROPOSTA DI UN NUOVO ALGORIMO PER LA DIAGNOSI ECOGRAFICA DELLE MALATTIE CRONICHE DEL FEGATO A. Giorgio Direttore del servizio di Ecografia Interventistica Istituto Clinico S.Rita -IRCCS -Atripalda (Avellino)
POWERED BY. Innovation in liver disease management
 POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
POWERED BY VCTE Innovation in liver disease management An intelligent solution to aid clinical diagnosis, FibroScan uses state of the art fibrosis and steatosis quantification with the most advanced non-invasive
NAFLD & NASH. Naga Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of GI and Hepatology
 NAFLD & NASH Naga Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of GI and Hepatology Indiana University School of Medicine ACG Midwest Regional Course,
NAFLD & NASH Naga Chalasani, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine and Cellular & Integrative Physiology Director, Division of GI and Hepatology Indiana University School of Medicine ACG Midwest Regional Course,
Clinical Trials & Endpoints in NASH Cirrhosis
 Clinical Trials & Endpoints in NASH Cirrhosis April 25, 2018 Peter G. Traber, MD CEO & CMO, Galectin Therapeutics 2018 Galectin Therapeutics NASDAQ: GALT For more information, see galectintherapeutics.com
Clinical Trials & Endpoints in NASH Cirrhosis April 25, 2018 Peter G. Traber, MD CEO & CMO, Galectin Therapeutics 2018 Galectin Therapeutics NASDAQ: GALT For more information, see galectintherapeutics.com
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation and Monitoring of Page 1 of 38 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Noninvasive Techniques for the Evaluation
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning
 Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
Improved Hepatic Fibrosis Grading Using Point Shear Wave Elastography and Machine Learning Presenter: Hersh Sagreiya 1, M.D. Authors: Alireza Akhbardeh 1, Ph.D., Isabelle Durot 1, M.D., Carlo Filice 2,
When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH
 When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Disclosures Received royalties from UpToDate, Inc. Staging refers to the assessment
When to Treat: Staging Liver Disease David L. Thomas, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Disclosures Received royalties from UpToDate, Inc. Staging refers to the assessment
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):5989-5998 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006112 Original Article Correlation of serum liver fibrosis markers with severity of liver dysfunction in liver cirrhosis: a retrospective
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):5989-5998 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006112 Original Article Correlation of serum liver fibrosis markers with severity of liver dysfunction in liver cirrhosis: a retrospective
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis
 REVIEW Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Erin Cleveland, M.D.,* Andrew Bandy, M.D., and Lisa B. VanWagner, M.D., M.Sc. *, Nonalcoholic fatty liver
REVIEW Diagnostic Challenges of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/ Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Erin Cleveland, M.D.,* Andrew Bandy, M.D., and Lisa B. VanWagner, M.D., M.Sc. *, Nonalcoholic fatty liver
Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies
 4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
4 Post Meeting A.I.S.F. Unmet Clinical Needs in Hepatology: New and upcoming diagnostic tools" Transient elastography in chronic liver diseases of other etiologies Dr. Vincenza Calvaruso Gastroenterologia
FibroScore for the Non-invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE FibroScore for the Non-invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis Shahzad Ashraf 1, Syed Azhar Ahmed 2, Jameel Ahmed 3 and Nadir Ali 4 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE FibroScore for the Non-invasive Assessment of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Viral Hepatitis Shahzad Ashraf 1, Syed Azhar Ahmed 2, Jameel Ahmed 3 and Nadir Ali 4 ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate
Non invasive assessment of liver fi brosis ONLY. liver diseases liver biopsy liver fibrosis biomarkers fibrotest fibroscan
 Ann Transplant, 2008; 13(2): 5-11 Received: 2008.04.15 Accepted: 2008.04.29 Published: 2008.06.17 Key words Full-text PDF: Word count: 1979 Tables: 1 Figures: 2 References: 50 Author s address: Non invasive
Ann Transplant, 2008; 13(2): 5-11 Received: 2008.04.15 Accepted: 2008.04.29 Published: 2008.06.17 Key words Full-text PDF: Word count: 1979 Tables: 1 Figures: 2 References: 50 Author s address: Non invasive
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target
 Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Interface hepatitis in PBC: Prognostic marker and therapeutic target Raoul Poupon Service d Hépatologie, Hôpital Saint-Antoine, Paris Faculté de Médecine Pierre & Marie Curie, Paris Key features of
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis. Pierre BEDOSSA
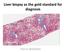 Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Liver biopsy as the gold standard for diagnosis Pierre BEDOSSA 1 PATHOLOGY OF NAFLD CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Grants and funding from Genfit, Intercept, Allergan, Inventiva, OWL, Echosens CEO and funding of
Xingshun Qi, Hongyu Li, Jiang Chen, Chunlian Xia, Ying Peng, Junna Dai, Yue Hou, Han Deng, Jing Li, and Xiaozhong Guo
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 15, Article ID 274534, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/15/274534 Research Article Serum Liver Fibrosis Markers for Predicting the Presence of Gastroesophageal
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 15, Article ID 274534, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/15/274534 Research Article Serum Liver Fibrosis Markers for Predicting the Presence of Gastroesophageal
Patients and Methods. study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
 SAFE Biopsy: A Validated Method for Large-Scale Staging of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Giada Sebastiani, 1 Philippe Halfon, 2 Laurent Castera, 3 Stanislas Pol, 4 David L. Thomas, 5 Alessandra
SAFE Biopsy: A Validated Method for Large-Scale Staging of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Giada Sebastiani, 1 Philippe Halfon, 2 Laurent Castera, 3 Stanislas Pol, 4 David L. Thomas, 5 Alessandra
A precision medicine approach to comprehensive NAFLD diagnosis via metabolomics-based liquid biopsy
 A precision medicine approach to comprehensive NAFLD diagnosis via metabolomics-based liquid biopsy International Workshop on NASH Biomarkers May 5-6 2017, Washington D.C. Pablo Ortiz, MD, PhD (OWL CEO)
A precision medicine approach to comprehensive NAFLD diagnosis via metabolomics-based liquid biopsy International Workshop on NASH Biomarkers May 5-6 2017, Washington D.C. Pablo Ortiz, MD, PhD (OWL CEO)
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI
 Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Update on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Timothy R. Morgan, MD Chief, Hepatology, VA Long Beach Professor of Medicine, UCI February 3, 2018 Disclosure Clinical trials: Genfit Speaker s Bureau: none
Evercore ISI Presentation- Madrigal
 Evercore ISI Presentation- Madrigal Forward-Looking Statements Any statements, other than statements of historical facts, made in this presentation regarding our clinical studies and our research and development
Evercore ISI Presentation- Madrigal Forward-Looking Statements Any statements, other than statements of historical facts, made in this presentation regarding our clinical studies and our research and development
Usefulness of Non-invasive Markers for Predicting Significant Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
 J Korean Med Sci 21; 25: 67-74 ISSN 111-8934 DOI: 1.3346/jkms.21.25.1.67 Usefulness of Non-invasive Markers for Predicting Significant Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease The purpose of this
J Korean Med Sci 21; 25: 67-74 ISSN 111-8934 DOI: 1.3346/jkms.21.25.1.67 Usefulness of Non-invasive Markers for Predicting Significant Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease The purpose of this
