HIGH SCHOOL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE. Customized for Prevention.org
|
|
|
- Lilian Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIGH SCHL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE Customized for Prevention.org
2 LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Science, Anatomy and Physiology, Biology, Health and PE, Sports, Exercise, and Health Science Activity Duration 1 class session (45 minutes) Grade Level Grades 9 12 Essential Questions What are opioids, and how do they impact the human body? What are neurons and neurotransmitters, and what part do they play when opioids enter the body? What are the effects of opioid use on the brain? In this lesson, students will examine misconceptions and facts about opioids. Through a series of investigations, they then will learn the science behind prescription opioid misuse and heroin use, overdose, and withdrawal. Students will discover that opioid use may start off as a choice, but it can become a chemical dependency. The accompanying presentation was created with PowerPoint so that it can be used in a variety of classrooms. If you are using a laptop with an LCD projector, simply progress through the PowerPoint by clicking to advance. All of the interactive aspects of the presentation are set to occur on click. This includes images, animations, videos, answer keys, and text boxes. The corresponding videos are embedded in the slide. Hover over the video window to reveal the play arrow at the bottom. If you are using an interactive whiteboard, tap on each slide with your finger or stylus to activate the interactive aspects of the presentation. It does not matter where you tap, but you can make it appear as if you are making certain things happen by tapping them. In the notes for each slide, there will be instruction on how to proceed and information to support facilitating graphics and statistics. Materials Chart paper and markers Access to the Internet Student Activity Sheet: Types of Opioids (one per student) Student Activity Sheet: Parts of a Neuron (one per student) Student Activity Sheet: Brain Basics (one per student) Objectives Analyze the misuse of opioids and suggest factors responsible for the progression from misuse to physical dependency. Explain how opioid misuse affects the brain and other body systems. Explain information processing by following sensory information through neural transmission. page 2
3 BACKGROUND INFO commonly prescribed in forms of medications that relieve pain and reduce the intensity of pain signals reaching the brain. Prescription opioid misuse is the use of a medication without a prescription. This may mean taking more than prescribed or for the feeling of being high. Prescription medications that are examples of opioids include hydrocodone (e.g., Vicodin ), oxycodone (e.g., OxyContin, Percocet ), morphine (e.g., Kadian, Avinza ), and codeine. Opioids act by attaching to specific opioid receptors. Endorphins are naturally produced in our bodies to help manage pain. When opioid drugs attach to these receptors, they also reduce the awareness of pain. The misuse of opioids such as heroin, morphine, and prescription medications is a serious national problem that affects the health, social, and economic welfare of communities. There are approximately 144 drug overdose deaths per day in the United States with 63% of those deaths related to pharmaceutical opioids or heroin. About 15 million people indicated misusing or abusing prescription painkillers in 2014 while nearly one in five teens say they have used prescription medicine at least once in their lifetimes to get high. To address this complex problem, federal agencies are working to inform patients, parents, teens, pharmacists, and educators about the dangers of opioid misuse. This guide was created to give educators ideas and strategies for presenting the content in the digital lesson. It provides slide-by-slide details for educators to be prepared to engage, explain, discuss, and effectively facilitate the content in the presentation. The presentation is designed to cover one 45-minute class session, but it is flexible, depending on the student's needs and time available. During the lesson, students will learn that opioids are drugs that are derived from the opium poppy plant or are synthetic equivalents, such as methadone and fentanyl. Heroin is an illegal opioid, but many opioids are legal. Opioids are After considering several facts vs. misconceptions, students will examine the adverse effects of opioids on the nervous system. They will learn that opioids act upon the opioid receptors in our nervous system, and many parts of our nervous system are affected by opioid misuse. Different messages are communicated through our bodies using neurotransmitters. A person's experiences when misusing a drug match to a specific neurotransmitter whose activity it disrupts. Simply put, when opioids enter the body, they make us feel extremely happy. That positive feeling may make someone want to take the substance again. What is not obvious, is how opioids are hijacking the pleasure center of the brain. This region is normally activated by healthy activities, like eating and sleeping, but it is also activated during the misuse of opioids. Opioids target this part of the brain by flooding it with dopamine, a type of chemical signal that makes people feel good. Long-term misuse can lead the body to produce less dopamine over time, causing cravings. Students will begin to uncover that, with all these changes in the human nervous system, drug misuse is no longer a choice. When opioids are misused for pleasure they can lead to physical and chemical changes in our bodies. These changes can prevent us from controlling the impulse to continue misusing opioids. The initial decision is typically voluntary but can lead to tolerance and dependence. page 3
4 BACKGROUND INFO Embedded within this lesson is a clip from the video "Chasing the Dragon: The Life of an Opiate Addict," a documentary aimed at educating students and young adults about the dangers of addiction. This video was released by the FBI and DEA in an effort to combat the growing epidemic of prescription drug misuse and heroin use. There are graphic descriptions of the impact opioid misuse can have on the body including bodily fluid (vomiting, blood, open wounds) and violence, as well as strong language. Instructors should watch this clip prior to sharing with students to determine if it is appropriate for the audience. At different points in the lesson, students may be tempted to share personal information about opioid misuse by themselves or others. As always, be sure to follow school or district policies about the sharing of personal information about minors. page 4
5 ENGAGE ENGAGE SLIDES 1-5 Overview: Students will identify and justify their beliefs about a series of facts and misconceptions related to opioid misuse. Students will be introduced to what an opioid is, the different types of drugs that are classified as opioids, and common reasons why they are taken. SLIDE 1 Arrange students in small groups, and hang a blank sheet of chart paper for each group in different areas of the room. Ask: What do you know about opioids? and instruct student groups to list everything they know or think they know about opioids, using the chart paper to capture their ideas. At set intervals, ask students to rotate and annotate the other groups chart paper to identify which statements they agree or disagree with. Introduce the concept of a misconception. A misconception is an idea or opinion that is incorrect because it is based on a mistaken thought or understanding. Invite students to revisit their chart papers and identify what they think the biggest misconceptions are about opioids. Click on the slide to reveal statistics about America s opioid epidemic. Explain to students that opioids are drugs that influence the nervous system to reduce feelings of pain. Heroin is an illegal opioid, but many opioids are legal. Opioids are commonly prescribed in forms of medications. Students might have heard of heard of Vicodin, OxyContin, Percocet, morphine, and codeine. These are all types of prescription opioids. page 5
6 ENGAGE SLIDES 2-3 Combine the small groups to form two large groups of students. Explain that there are many misconceptions about opioid misuse. It is important to be able to separate truth from misconception. Distribute two index cards to each group: one with Fact written and one with Misconception. Read aloud the first statement on slide 2 and invite students to discuss their response as a group. Invite each group to hold up the card they think is correct. Reveal the correct answer and explain using slide notes. Repeat these directions for all statements. After all of the statements have been reviewed, lead a discussion around the following guiding questions: Which fact or misconception statement is most surprising? What misconception do you think is most common with teens your age, and why? Which misconception do you think is most important for teens your age to understand, and why? SLIDE 4 Invite students to use the information from their chart papers, and information they obtained from reviewing the statements on slides 2-3, to develop a definition of what an opioid is. Students can capture this information on an index card or on the same chart paper. Next, showcase some of these ideas on chart paper. Invite students to vote and pick the three answers that best describe what opioids are and where they came from. Then, click to display the definition of opioids. Compare the definition on the slide to student answers. Ask about potential discrepancies between their definitions and the one provided. Could any of these stem from misconceptions? Have students discuss in what cases someone their age might be prescribed an opioid. page 6
7 ENGAGE SLIDE 5 It s important for students to know that synthetic and natural opioids work in our bodies the same way. The table shows the different types of opioids, how they are derived, and examples. But some of the information is missing. Ask students to fill in the chart on the slide using the word bank provided. Students can use the slide or the Types of Opioids student activity sheet to complete the chart. Then, reveal the correct answers by clicking on the slide. Discuss why opioids that are synthetic can be a problem they are made much stronger than natural opioids, and street manufacturers can put dangerous ingredients into them. page 7
8 EXPLORE EXPLORE SLIDES 6-10 Overview: Students will compare and contrast models of a healthy nervous system with the natural release of endorphins to prescription opioid misuse and heroin use. Students will be able to explain the chemical imbalances in each to describe why opioids are prescribed. The neuroscience concepts in this section will be discussed specifically in terms of the effects of opioids on the brain and body. SLIDE 6 Ask students: Do you know which system of the body helps you learn? Or which system your dreams come from? It is anticipated students will be able to identify the nervous system or the brain. Invite students to make observations of the two brain scans on the slide. At least one of which has been influenced by drugs. Instruct students to note the differences between the brains in the image. Then, challenge them to answer the three questions that appear on the slide: What do you notice about the two brains? How are they different? How do you think these differences might be impacting the human body? Invite students to share their observations, and discuss as a class. Next, play the video The Reward Circuit: How the Brain Responds : Ask students: What role did the nervous system likely play in drug addiction in this video? It is anticipated students will identify the brain as part of the nervous system. Clarify with students that when opioids enter the body, they make us feel extremely happy. That positive feeling may make someone want to take the substance again. page 8
9 EXPLORE SLIDE 7 This slide introduces the biological messages, sent through the nervous system, that can cause a person to misuse prescription drugs. Begin by asking students: How do you think disruptions or changes in the nervous system might impact our behavior? Students may want to revisit slide 7. Discuss their responses as a class. Click the embedded link in the slide to watch part of the Chasing the Dragon documentary, from 29:00 to 31:53. The video discusses how many individuals begin with prescription drugs prescribed by doctors, only to find they cannot stop using the drugs. This begins the discussion on the biological processes that cause opioid misuse. NOTE: There are graphic descriptions of the impact opioid misuse can have on the body including bodily fluid and violence. Instructors should watch this clip prior to sharing with students to determine if it is appropriate for the audience. When students finish watching, ask: How do you think what we learned about the nervous system can help explain the challenges faced by the people in this video? When opioids enter the body, they hijack the pleasure center of the brain. This region is normally activated by healthy activities, like eating and sleeping, but it is also activated during the misuse of opioids. page 9
10 EXPLORE SLIDE 8 Invite students to take a look deeper inside the nervous system to learn how pain and pleasure messages travel to and from the brain. Remind students that the brain is impacted by opioid misuse and that our brain is part of a larger system in our bodies: the nervous system. We also know the nervous system helps us communicate information throughout our bodies. Ask students: How are messages sent throughout our bodies? and invite students to share out their ideas. The slide shows a diagram of two neurons. Remind students there are millions of neurons in our bodies communicating information through a vast network. Distribute the Parts of a Neuron student activity sheet. Explain that each term in the word bank completes one of the blanks in the diagram. Challenge students to identify where in the diagram to place the corresponding labels. Answers will be revealed with click of slide. Point out that the two neurons are not touching each other in the image. But, messages (like pain or pleasure messages) still have to get from one neuron to another to be able to travel to and from the brain. Ask: How do you think that happens? The answer? The synaptic gap (synapse). This is the small space between neurons, which the message must cross as it makes its way to and from the brain. The synaptic gap is where our body has receptors to transfer the messages of pain and pleasure throughout our bodies. SLIDE 9 Ask students to compare and contrast the diagram of the people talking with how neurons are communicating. Point out that neurotransmitters are like the words we use to talk to another person and give them instructions. The neurotransmitter that moves from one neuron to the next is specific to certain messages, the strength of these messages, and how long these messages continue to be conveyed. Ask: Based on what you have learned; how do you think drugs affect this process of messaging in the brain? The messages that are sent from one neuron to the next are altered by the actions of the drugs on the neurotransmitters. The drugs act on the messengers to change the message. Students learned earlier that opioids could attach to the same receptors as endorphins. page 10
11 EXPLORE SLIDE 10 The messages that travel across a synaptic gap are called neurotransmitters. Different neurotransmitters are specific to different types of messages. Explain to students that opioids mimic neurotransmitters and either excite or inhibit a response like euphoria or moodiness in the body. This slide displays a chart that identifies and describes the neurotransmitters most often affected by prescription opioids, which functions they normally affect, and how they are affected by opioids. Invite students to consider how each of the neurotransmitters, affected by opioids, could impact the human body by reviewing the chart and answering the following guiding questions: Answers are in red: Which neurotransmitter could cause dry mouth or an irritable mood? endogenous opioids Which neurotransmitter is responsible for overstimulating the nervous system creating a euphoric effect? dopamine O O Which neurotransmitter could cause sleepiness? gamma-aminobutyric acid page 11
12 EXPLAIN EXPLAIN SLIDES Overview: Students will analyze images produced by brain mapping to explain how opioid misuse can cause changes in areas of the brain related to judgment, decision making, learning and memory, and behavior control. Students will construct an explanation of how this is evidence of a brain disease. Students will learn and be able to explain how brain development during adolescence leads to additional risks on their bodies. SLIDE 11 Ask students to consider how addiction is a disease by comparing the brain and heart images. As students view the images on the slide, ask: How are the diseased heart and the diseased brain similar? (In each case, disease reduces the ability of the organ to use energy, making it less effective in the body.) SLIDE 12 Distribute the Brain Basics student activity sheet to provide students with information about the different parts of the brain. Invite students to use this information to review the diagram in the slide and identify which parts of the brain are responsible for the highlighted processes. (For example, the highlighted parts labeled judgment and sensations are both controlled by the frontal lobe.) page 12
13 EXPLAIN SLIDE 13 Divide the class into pairs of students. Invite students to use their completed Brain Basics student activity sheet as a reference and have each pair look at the information on the slide. Guide students to come up with as many factors that might influence risk based on adolescent brain development. Anticipated responses include difficulty controlling emotions, poor planning and judgment, and risky, impulsive behavior. Ask students to share their lists with the whole class. Capture student ideas using chart paper or the provided space on the slide. Have students rank them in order from most influential to least influential, giving reasons for their rankings. SLIDE 14 Share with students that we have learned opioids can have many different impacts to our bodies. When opioids are misused they can lead to physical and chemical changes in our bodies. These changes can lead to a lack of impulse control resulting in the continued misuse of opioids. The initial decision is typically voluntary but can lead to tolerance and dependence. Invite students to use the text and image on the slide to identify similarities and differences in a person that has developed a tolerance to one that is dependent on the misuse of opioids. It is anticipated students will identify that when the body adapts to the drug, and requires more of it to achieve a certain feeling, an individual has developed a tolerance. A person that is dependent on a drug will experience withdrawal symptoms when use of the drug is suddenly reduced or stopped. Revisit the people that shared their stories in Chasing the Dragon. Ask students: How could you now explain their challenges with withdrawal? Remind students that opioids flood the brain with dopamine, a type of signal that makes people feel good. Long-term misuse can lead the body to produce less dopamine over time, causing cravings that can lead to tolerance or physical dependency. page 13
14 STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET TYPES OF OPIOIDS Directions: The table below shows the different types of opioids, how they are derived, and examples. But some of the information is missing. Using the word bank, complete the chart with the correct answers. Word bank: poppy Morphine opioids heroin fully synthetic opioids man-made fentanyl Type of opioid Where they come from Examples Natural opioids (made from the plant) Alkaloids, that occur in plants such as the opium codeine Semi-synthetic, man-made Created in labs from natural opioids Hydrocodone, oxycodone, man-made Completely methadone, tramadol page 14
15 STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET PARTS OF A NEURON Directions: Each term in the word bank completes one of the blanks in the diagram on the slide. Using the following definitions, identify where in the diagram to place the corresponding labels. Word bank: Axon Branches of axon Cell body Dendrites Nucleus Terminal bulbs Synaptic gap Definitions: The cell body contains the nucleus, which determines whether the message will continue down the axon to be sent to another neuron. Dendrites receive the impulse, or message, from another neuron and send it to the cell body. The axon is the long part of the neuron that takes the message from the cell body to the terminal bulbs. O O The terminal bulbs are at the sending end of the neuron. They release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap. page 15
16 STUDENT ACTIVITY SHEET BRAIN BASICS Directions: Listed below are descriptions of different parts of the brain. Using this information and the image on the slide, identify which parts of the brain are impacted by opioid misuse. Description Does this system appear to be impacted by opioid misuse? Why or why not? Use evidence from the brain scan in your response. The brainstem controls basic functions that humans need to survive. These include breathing, sleeping, and maintaining a heart rate. These functions are involuntary, which means they happen without our thinking about them. The cerebral cortex is divided into several areas. Different areas control different functions. For example: Thinking happens in the front part of the cortex (also called the prefrontal cortex, or forebrain). Processes in the frontal cortex allow us to plan, make decisions, and solve problems. Other areas in the cerebral cortex process sensory information. These processes allow us to see, feel, hear, taste, and touch. The limbic system consists of many different brain structures. Together, they control and regulate how we experience pleasure. When a behavior causes us to feel pleasure, we are likely to repeat that behavior. This reward circuit in the brain reinforces behaviors that are necessary to our survival. Processes in the limbic system also shape how we experience positive and negative emotions. Eating, socializing, and other healthy behaviors activate the limbic system and give us pleasure. However, misusing and abusing drugs also activate the limbic system. Using drugs can also affect our moods by changing processes in the limbic system that shape emotions. page 16
17 NATIONAL STANDARDS This lesson plan has been developed based on the following national standards: Next Generation Science Standards LS1.A: Structure and Function Feedback mechanisms maintain a living system s internal conditions within certain limits and mediate behaviors, allowing it to remain alive and functional even as external conditions change within some range. Feedback mechanisms can encourage (through positive feedback) or discourage (negative feedback) what is going on inside the living system. (HS-LS1-3) PS1.B: Chemical Reactions Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy. (HS-PS1-4),(HS-PS1-5) LS1.D: Information Processing, Grade Band Endpoints By the end of grade 12: In complex animals, the brain is divided into several distinct regions and circuits, each of which primarily serves dedicated functions, such as visual perception, auditory perception, interpretation of perceptual information, guidance of motor movement, and decision making about actions to take in the event of certain inputs. In addition, some circuits give rise to emotions and memories that motivate organisms to seek rewards, avoid punishments, develop fears, or form attachments to members of their own species and, in some cases, to individuals of other species (e.g., mixed herds of mammals, mixed flocks of birds). The integrated functioning of all parts of the brain is important for successful interpretation of inputs and generation of behaviors in response to them. National Health Education Standards Addressed Analyze the potential severity of injury or illness if engaging in unhealthy behaviors. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST Integrate and evaluate multiple sources of information presented in diverse formats and media (e.g., quantitative data, video, multimedia) in order to address a question or solve a problem. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RST Synthesize information from a range of sources (e.g., texts, experiments, simulations) into a coherent understanding of a process, phenomenon, or concept, resolving conflicting information when possible. page 17
HIGH SCHOOL DIGITAL LESSON
 HIGH SCHL DIGITAL LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Science, Anatomy and Physiology, Biology, Health and PE, Sports, Exercise, and Health Science Activity Duration 3-4 class sessions
HIGH SCHL DIGITAL LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Science, Anatomy and Physiology, Biology, Health and PE, Sports, Exercise, and Health Science Activity Duration 3-4 class sessions
MIDDLE SCHOOL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE. Customized for Prevention.org
 MIDDLE SCHL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE Customized for Prevention.org LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences, Health, and Physical Education Activity Duration 1 class session (45 minutes)
MIDDLE SCHL DIGITAL 1-DAY LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE Customized for Prevention.org LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences, Health, and Physical Education Activity Duration 1 class session (45 minutes)
Opioids: Real People. Real Stories. Real Science.
 Opioids: Real People. Real Stories. Real Science. Virtual Field Trip Companion Activity The use and misuse of opioids in the United States is a problem that is not going away. Although we continue to learn
Opioids: Real People. Real Stories. Real Science. Virtual Field Trip Companion Activity The use and misuse of opioids in the United States is a problem that is not going away. Although we continue to learn
ELEMENTARY SCHOOL DIGITAL LESSON
 ELEMENTARY SCHL DIGITAL LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences and Health Education Activity Duration 3 class sessions (45 minutes each) Grade Level Grades 3-5 Essential Questions
ELEMENTARY SCHL DIGITAL LESSON EDUCATOR GUIDE LESSON OVERVIEW Content Areas Life Sciences and Health Education Activity Duration 3 class sessions (45 minutes each) Grade Level Grades 3-5 Essential Questions
THE SCIENCE OF ADDICTION: THE STORIES OF TEENS EDUCATOR GUIDE
 THE SCIENCE OF ADDICTION: THE STORIES OF TEENS EDUCATOR GUIDE EDUCATOR GUIDE THE SCIENCE OF ADDICTION: THE STORIES OF TEENS Millions of people misuse opioids every year, millions more become dependent,
THE SCIENCE OF ADDICTION: THE STORIES OF TEENS EDUCATOR GUIDE EDUCATOR GUIDE THE SCIENCE OF ADDICTION: THE STORIES OF TEENS Millions of people misuse opioids every year, millions more become dependent,
Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse
 SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
SOME BASIC NEUROSCIENCE Neurons have specialised extensions 1: Label the parts of a neuron by selecting the correct term from the box below. Cell body, axon, dendrite, synapse 1 dendrite synapse cell body
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Drugs and the Teen Brain
 HEADS UP REAL NEWS ABOUT DRUGS AND YOUR BODY A Message from Scholastic and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Drugs and the Teen Brain Adolescence is a critical time in brain development. That
HEADS UP REAL NEWS ABOUT DRUGS AND YOUR BODY A Message from Scholastic and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) Drugs and the Teen Brain Adolescence is a critical time in brain development. That
The Opioid Epidemic and Youth Prescription Drug Abuse. Sandy Chung, MD Chair, Board of Trustees Virginia Foundation for Healthy Youth
 The Opioid Epidemic and Youth Prescription Drug Abuse Sandy Chung, MD Chair, Board of Trustees Virginia Foundation for Healthy Youth Disclosures: I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s)
The Opioid Epidemic and Youth Prescription Drug Abuse Sandy Chung, MD Chair, Board of Trustees Virginia Foundation for Healthy Youth Disclosures: I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s)
Prescription Opioids
 What are prescription opioids? Prescription Opioids Opioids are a class of drugs naturally found in the opium poppy plant. Some prescription opioids are made from the plant directly, and others are made
What are prescription opioids? Prescription Opioids Opioids are a class of drugs naturally found in the opium poppy plant. Some prescription opioids are made from the plant directly, and others are made
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs
 Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
Activity 2 The Brain and Drugs Core Concept: Addictive drugs affect signaling at the synapses in the reward pathway of the brain. Class time required: Approximately 40-60 minutes Teacher Provides: For
General Functions (3) 1.Sensory gathers information 2.Integrative information is brought together 3.Motor responds to signals, homeostasis
 Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
What Is Heroin? Examples of Opioids. What Science Says about Opioid Use Disorder and Its Treatment 6/27/2016
 What Science Says about Opioid Use Disorder and Its Treatment Perilou Goddard, Ph.D. Department of Psychological Science Northern Kentucky University Examples of Opioids Agonists (activate opioid receptors)
What Science Says about Opioid Use Disorder and Its Treatment Perilou Goddard, Ph.D. Department of Psychological Science Northern Kentucky University Examples of Opioids Agonists (activate opioid receptors)
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs. CHM 108 Lab. Spring Dr. Angela King
 Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
Modeling Neurotransmission and Drugs CHM 18 Lab Spring 28 Dr. Angela King Part A: How does the brain communicate? The human brain is the most complex organ in the body. This three-pound mass of gray and
The Nervous System IN DEPTH
 The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
The Nervous System IN DEPTH The right half of the brain controls the left half of the body. This means that only left handed people are in their right mind. Note taking tips Make sure that you have written
Heroin. Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor
 Heroin Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor Heroin H, Smack, Dope, Junk Can be purchased as a white powder White China or a dark resin Black Tar Opiates Derived from the opium poppy Morphine:
Heroin Brain Research Institute, UCLA Alison Taylor Heroin H, Smack, Dope, Junk Can be purchased as a white powder White China or a dark resin Black Tar Opiates Derived from the opium poppy Morphine:
The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction
 National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Last Updated January 2007 https://www.drugabuse.gov 1 Table of Contents The Neurobiology of Drug Addiction Section I: Introduction
Opioid Epidemic Update
 Opioid Epidemic Update - 2018 Talal Khan MD Addiction Psychiatrist Pine Rest What are Opioids? Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium Poppy plant. Papaver somniferum The psychoactive
Opioid Epidemic Update - 2018 Talal Khan MD Addiction Psychiatrist Pine Rest What are Opioids? Opiates are alkaloid compounds naturally found in the opium Poppy plant. Papaver somniferum The psychoactive
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells
 Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
Biological Psychology Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. What are the two basic types of cells in the nervous system? Neurons and Glial Cells a. Cells that process incoming signals and respond by sending out
AVAILABLE ONLINE: Mapping the Brain Page 2. Stressed Out? Page 4. Opioids and the Overdose Epidemic Page 6. Compilation TEACHER EDITION
 Compilation 2016 17 TEACHER EDITION Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body Brought to you by Scholastic and the scientists at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health,
Compilation 2016 17 TEACHER EDITION Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body Brought to you by Scholastic and the scientists at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health,
Health Smart Virginia - Sample Lesson Plan
 Health Smart Virginia - Sample Lesson Plan Grade 5 Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drug Use Prevention Unit 9_ SOLs: 5.3h Identify how culture, family, friends, and the media influence health practices about
Health Smart Virginia - Sample Lesson Plan Grade 5 Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drug Use Prevention Unit 9_ SOLs: 5.3h Identify how culture, family, friends, and the media influence health practices about
Brain & Behavior Syllabus V Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006
 Brain & Behavior Syllabus V55.0306 Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006 Week 1 INTRODUCTION 1/17 Lecture 1 Introduction and History of Neuroscience early influences Reading: Chapter 1, pp 2 23 1/19 Lecture
Brain & Behavior Syllabus V55.0306 Instructor Mike Hawken Spring 2006 Week 1 INTRODUCTION 1/17 Lecture 1 Introduction and History of Neuroscience early influences Reading: Chapter 1, pp 2 23 1/19 Lecture
Dr. Solomon Derese. Department of Chemistry University of Nairobi
 Dr. Solomon Derese Department of Chemistry University of Nairobi sderese@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Alcohol and Drug Addiction 3 The word addiction is derived from a Latin term for enslaved by or bound to 4 Addiction
Dr. Solomon Derese Department of Chemistry University of Nairobi sderese@uonbi.ac.ke 1 Alcohol and Drug Addiction 3 The word addiction is derived from a Latin term for enslaved by or bound to 4 Addiction
The human brain is a very complicated organ.
 DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Hi there! Mind Matters is a series that explores the ways that different drugs affect your brain, body, and life. In this issue, we are going to talk about how drugs affect your brain.
DRUGS AND THE BRAIN Hi there! Mind Matters is a series that explores the ways that different drugs affect your brain, body, and life. In this issue, we are going to talk about how drugs affect your brain.
Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Presented by: Dr. Rochelle D. Schwartz-Bloom March 24, 2011 Understanding the Brain: What Drugs Can Tell Us Rochelle
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
ADDITIONAL TOOLS: Pushing Pause From Heads Up. Suggested Answers for Lesson Discussion Questions headsup.scholastic.com/pushingpause/lesson
 ADDITIONAL TOOLS: Pushing Pause From Heads Up Dear Teacher, The following tools are designed to help support and enrich the Heads Up lesson plan and student article Pushing Pause : 1A) Suggested Answers
ADDITIONAL TOOLS: Pushing Pause From Heads Up Dear Teacher, The following tools are designed to help support and enrich the Heads Up lesson plan and student article Pushing Pause : 1A) Suggested Answers
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
YOUTH OPIOID ABUSE PREVENTION TOOLKIT
 YOUTH OPIOID ABUSE PREVENTION TOOLKIT President Trump, the First Lady and the entire Trump Administration is committed to combatting the opioid crisis. The youth opioid abuse prevention campaign will be
YOUTH OPIOID ABUSE PREVENTION TOOLKIT President Trump, the First Lady and the entire Trump Administration is committed to combatting the opioid crisis. The youth opioid abuse prevention campaign will be
Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at:
 NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
NAME Explore the Neuroscience for Kids Web Site (QUESTIONS) Start at: http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/neurok.html On the left side, click on Explore, then click on The Neuron, then click on Millions
The Contribution of Neuroscience to Understanding Human Behaviour
 The Contribution of Neuroscience to Understanding Human Behaviour Gail Tripp Human Developmental Neurobiology Unit Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Promotion Corporation Okinawa Japan Today
The Contribution of Neuroscience to Understanding Human Behaviour Gail Tripp Human Developmental Neurobiology Unit Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Promotion Corporation Okinawa Japan Today
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
H NDS-ONHealth. Prescription Drug Abuse. Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been higher.
 H NDS-ONHealth Health Wave Newsletter, October 2013 Visit us on our website at www.healthwaveinc.com Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been
H NDS-ONHealth Health Wave Newsletter, October 2013 Visit us on our website at www.healthwaveinc.com Drug overdose death rates in the United States have more than tripled since 1990 and have never been
BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES
 Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
Name: Pages: 326-327, 341-343 Date: BIOLOGY 12 TRANSMISSION OF IMPULSES ACROSS SYNAPSES How does a nerve impulse make a connection from an axon to the next nerve cell? The impulse must travel from the
The Nervous System. Nerves, nerves everywhere!
 The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
The Nervous System Nerves, nerves everywhere! Purpose of the Nervous System The information intake and response system of the body. Coordinates all body functions, voluntary and involuntary! Responds to
Physical and Physiological Aspects of Drug Use and Abuse
 Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Question 1: What are neurons and neurotransmitters? Answer 1: A neuron is a nerve cell. It is estimated that there are 100 billion neurons in the average human brain (Levinthal, 2008). Neurons receive
Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain
 Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, 2017 The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain David Reyher, MSW, CAADC Behavioral Health Program Director Alvernia University Defining Addiction
Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, 2017 The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain David Reyher, MSW, CAADC Behavioral Health Program Director Alvernia University Defining Addiction
Heroin What You Need to Know
 Heroin What You Need to Know More People Died from Drug Overdoses than Car Crashes and Gun Deaths in 2015 52,404 people died from drug overdoses (33,091 involved an opioid including heroin) 37,757 people
Heroin What You Need to Know More People Died from Drug Overdoses than Car Crashes and Gun Deaths in 2015 52,404 people died from drug overdoses (33,091 involved an opioid including heroin) 37,757 people
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Nerve Cell Communication
 Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Nerve Cell Communication Core Concept: Nerve cells communicate using electrical and chemical signals. Class time required: Approximately 40 minutes if Part 4 is completed for homework. Teacher Provides:
Top 10 narcotic pain pills
 Top 10 narcotic pain pills Click to go to the item or just scroll down the page. Doctors Respond to FDA Panel Recommendations FDA Considers Banning Popular Prescription Pain Medications and. Top 10 Natural
Top 10 narcotic pain pills Click to go to the item or just scroll down the page. Doctors Respond to FDA Panel Recommendations FDA Considers Banning Popular Prescription Pain Medications and. Top 10 Natural
Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass
 Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass Overview Summary Marijuana is the most commonly abused illegal drug in the United States. Nearly half of all high school students have used marijuana. Many children and adolescents,
Module 4 Weeding Out the Grass Overview Summary Marijuana is the most commonly abused illegal drug in the United States. Nearly half of all high school students have used marijuana. Many children and adolescents,
INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE
 INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE TRUE OR FALSE? We only use 10% of our brain. Ages zero-three years are more important than any other for learning. There are critical periods for learning important
INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE TRUE OR FALSE? We only use 10% of our brain. Ages zero-three years are more important than any other for learning. There are critical periods for learning important
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research. Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc.
 Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc. The Neurobiology of Addiction About the speaker Gary M. Henschen, M.D. is
Addiction in the Brain - Latest Research Gary M. Henschen, MD, LFAPA Chief Behavioral Health Officer Magellan Healthcare, Inc. The Neurobiology of Addiction About the speaker Gary M. Henschen, M.D. is
Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County. Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018
 Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018 OPIOIDS 101 What are Opioids? Opioids 101 Opium Poppy Plant Opiates: A type of pain medication that is naturally
Opioids and Heroin in Snohomish County Marijuana and Opioid Prevention Training May 2018 OPIOIDS 101 What are Opioids? Opioids 101 Opium Poppy Plant Opiates: A type of pain medication that is naturally
2Lesson. Outline 1.5. Lesson Plan. The OVERVIEW. Lesson 1.5: How do the parts of my brain work together? LESSON. Unit1.2
 Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to emphasize the need of the structures of the brain to work together to create and control behaviors, like the creation and comprehension
Outline 2Lesson Unit1.2 OVERVIEW Rationale: This lesson is intended to emphasize the need of the structures of the brain to work together to create and control behaviors, like the creation and comprehension
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
FACING ADDICTION OVER DINNER
 FACING ADDICTION OVER DINNER The NATIONAL NIGHT of CONVERSATION November 17, 2016 The dinner table is one of the most important places in the house for improving the health of your family, but not only
FACING ADDICTION OVER DINNER The NATIONAL NIGHT of CONVERSATION November 17, 2016 The dinner table is one of the most important places in the house for improving the health of your family, but not only
Addressing Alaska s Opioid Epidemic From Understanding to Action
 Addressing Alaska s Opioid Epidemic From Understanding to Action The opioid epidemic is devastating American families and communities. To curb these trends and save lives, we must help prevent addiction
Addressing Alaska s Opioid Epidemic From Understanding to Action The opioid epidemic is devastating American families and communities. To curb these trends and save lives, we must help prevent addiction
<ctrl> <click> Here to the start the sound.
 Senior Scholars at Queens Audio Wrapper version 1.6 Here to the start the sound. Press enter or use arrow keys to go the next slide. paul - brent - foushee [ Document subtitle ] Societal
Senior Scholars at Queens Audio Wrapper version 1.6 Here to the start the sound. Press enter or use arrow keys to go the next slide. paul - brent - foushee [ Document subtitle ] Societal
At a Glance. Background Information. Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate
 Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
Lesson 3 Drugs Change the Way Neurons Communicate Overview Students build upon their understanding of neurotransmission by learning how different drugs of abuse disrupt communication between neurons. Students
HEADS UP REAL NEWS ABOUT DRUGS AND YOUR BODY
 HEADS UP REAL NEWS ABOUT DRUGS AND YOUR BODY A Message from Scholastic and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) You probably know that drugs that don t come from a pharmacy or other legal distributor
HEADS UP REAL NEWS ABOUT DRUGS AND YOUR BODY A Message from Scholastic and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) You probably know that drugs that don t come from a pharmacy or other legal distributor
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
 Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Name: Block: Chapter 7: The Nervous System Lesson 1: How the Nervous System Works What is the Role of the Nervous System? Your nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
3 Basic Nerve Cells. Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON
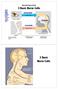 Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
Senses TASTE SMELL VISION HEARING TOUCH Pressure Temp. Stretch Pain Neurobiology in Brief 3 Basic Nerve Cells SENSORY NEURON INTERNEURON MOTOR NEURON Muscles and Glands typically react to motor output
590,000 deaths can be attributed to an addictive substance in some way
 Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
Mortality and morbidity attributable to use of addictive substances in the United States. The Association of American Physicians from 1999 60 million tobacco smokers in the U.S. 14 million dependent on
National Council on Patient Information and Education
 National Council on Patient Information and Education You are not alone The type of pain that caused your doctor to prescribe a pain medicine for you can make you feel that you are different from everyone
National Council on Patient Information and Education You are not alone The type of pain that caused your doctor to prescribe a pain medicine for you can make you feel that you are different from everyone
Nervous System Communication. Nervous System Communication. The First Nerve Cells 1/2/11
 Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Nervous System Communication Nervous System Communication Process information Transfer information to other neurons Generate behavior and experience The First Nerve Cells Developed in primitive animals
Do your Part Be the Solution
 Do your Part Be the Solution Objectives: 1) What is opioid addiction? 2) How bad is it? 3) What can be done? a) Prevention i. Primary prevention (reduce new cases) ii.. Secondary prevention (manage the
Do your Part Be the Solution Objectives: 1) What is opioid addiction? 2) How bad is it? 3) What can be done? a) Prevention i. Primary prevention (reduce new cases) ii.. Secondary prevention (manage the
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
18. Mind and Addiction
 18. Mind and Addiction What is Mind? Chemistry of the Brain: drugs and love 2% body weight Human Brain 20% energy expenditure 100 billion neurons 25,000 connections per neuron 100 trillion connections
18. Mind and Addiction What is Mind? Chemistry of the Brain: drugs and love 2% body weight Human Brain 20% energy expenditure 100 billion neurons 25,000 connections per neuron 100 trillion connections
35-2 The Nervous System
 1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
1 of 38 Do Now Finish the matching quiz. You may use your brain hat to help you. 2 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System What are the functions of the nervous system? 3 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous
Body control systems. Let s start at the top: the human brain. The Cerebrum. The human brain. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
What parts of your brain are you using right now? Body control systems Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Movement and conscious thought; Frontal speech
Heroin and Opioid Awareness Pilot Program
 Heroin and Opioid Awareness Pilot Program Presented to Norwin Board of Education December 5, 2016 Dr. William Kerr, Superintendent of Schools, Norwin School District Mr. Tim Kotch, Assistant Superintendent
Heroin and Opioid Awareness Pilot Program Presented to Norwin Board of Education December 5, 2016 Dr. William Kerr, Superintendent of Schools, Norwin School District Mr. Tim Kotch, Assistant Superintendent
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Peripheral Nervous System
 Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Your Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2. Integration
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Mapping the Brain Page 2. Stressed Out? Page 4. Opioids and the Overdose Epidemic Page 6 STUDENT ARTICLES INSIDE: AVAILABLE ONLINE:
 Compilation 2016 17 STUDENT EDITION Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body Brought to you by Scholastic and the scientists at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health,
Compilation 2016 17 STUDENT EDITION Heads Up: Real News About Drugs and Your Body Brought to you by Scholastic and the scientists at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health,
Medicated Assisted Treatment
 Medicated Assisted Treatment Enhancing the Potential for Recovery Part I Diana Padilla Program Manager NeC-ATTC 2 Diana Padilla, RCR, CASAC-T padilla@ndri.org Diana Padilla is a program manager at NDRI-USA,
Medicated Assisted Treatment Enhancing the Potential for Recovery Part I Diana Padilla Program Manager NeC-ATTC 2 Diana Padilla, RCR, CASAC-T padilla@ndri.org Diana Padilla is a program manager at NDRI-USA,
Modeling Effects of Drugs on Neuron Communication
 Modeling Effects of Drugs on Neuron Communication How do neurons communicate? Your nervous system is made of nerve cells called neurons. Neurons do not touch each other. They are separated by a small gap
Modeling Effects of Drugs on Neuron Communication How do neurons communicate? Your nervous system is made of nerve cells called neurons. Neurons do not touch each other. They are separated by a small gap
Effects of Drugs on the Brain and Behavior in Adolescents
 Effects of Drugs on the Brain and Behavior in Adolescents Lucas Moore, LCSW, SAC-IT Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment Coordinator July 20, 2015 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Today What would
Effects of Drugs on the Brain and Behavior in Adolescents Lucas Moore, LCSW, SAC-IT Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment Coordinator July 20, 2015 Wisconsin Department of Health Services Today What would
TEEN EDUCATION. Medication Safety for Teens.
 Slide 1 Welcome to today s program, My Generation Rx: Medication Safety for Teens. You may be asking yourself, What is My Generation Rx? My Generation Rx encourages teens to incorporate the Generation
Slide 1 Welcome to today s program, My Generation Rx: Medication Safety for Teens. You may be asking yourself, What is My Generation Rx? My Generation Rx encourages teens to incorporate the Generation
Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs
 Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Consciousness and the Two-Track Mind Chapter 3 Part 2: Tolerance, dependence, addiction, & types of drugs Unit 5 ~ AP Psychology ~ Ms. Justice 12: What are tolerance, dependence, and addiction, and what
Chapter 22. The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets. 561
 Chapter 22 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets (Opening image copyright by Sebastian Kaulitzki, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 22.1: The Nervous System Lesson 22.2: The
Chapter 22 The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Worksheets (Opening image copyright by Sebastian Kaulitzki, 2010. Used under license from Shutterstock.com.) Lesson 22.1: The Nervous System Lesson 22.2: The
Biological Bases of Behavior
 Biological Bases of Behavior What do neurons look like? I These are the basic parts Types of Neurons What do neurons (really) look like? What do neurons do? Collect inputs on their If sufficient input
Biological Bases of Behavior What do neurons look like? I These are the basic parts Types of Neurons What do neurons (really) look like? What do neurons do? Collect inputs on their If sufficient input
Required Text: Biological Psychology Breedlove et al. Sinauer, 2007, Fifth Edition
 Brain and Behavior, V55.0306 Mike Hawken Spring 2010 This is a MAP course which satisfies the Natural Science II requirement. The lectures are scheduled for 2:00-3:15, Tuesdays and Thursdays, Room 207
Brain and Behavior, V55.0306 Mike Hawken Spring 2010 This is a MAP course which satisfies the Natural Science II requirement. The lectures are scheduled for 2:00-3:15, Tuesdays and Thursdays, Room 207
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain
 Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Psychoactive Drugs & The Brain Psychoactive Substances & The Brain 1. Psychoactive substances enter the bloodstream via oral administration, inhalation, smoking, or injection 2. Psychoactive substances
Activity Overview. A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity 1A. The Brain: It s All In Your Mind
 A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
Substance Prevention
 First Name Last Name Period Substance Prevention POINTS ASSIGNMENT /65 pts Worksheet Total /10 pts Book Activity Page /10 pts Group Discussion on Substance Use in Teenagers /10 pts Teenage Drinking Brain
First Name Last Name Period Substance Prevention POINTS ASSIGNMENT /65 pts Worksheet Total /10 pts Book Activity Page /10 pts Group Discussion on Substance Use in Teenagers /10 pts Teenage Drinking Brain
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
Cell Communication. Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model STO-133
 STO-133 Cell Communication Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model In this activity you will use a model to explore how cells send, receive, and respond to signals. Then you will use this model to
STO-133 Cell Communication Part 1: Assemble a Cell Communication Model In this activity you will use a model to explore how cells send, receive, and respond to signals. Then you will use this model to
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
The Nervous System II Neurons
 The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
The Nervous System II Neurons Review Nervous System What is it? The system that receives, processes, stores and transmits information that comes from various parts of the body and the external world. Composed
How To Engage and Keep Youth and Families in Treatment: Focus on Opioid Use and Abuse
 How To Engage and Keep Youth and Families in Treatment: Focus on Opioid Use and Abuse What You Need to Know about Opioids MDFT Engagement Strategies That Everybody Can Use Gayle Dakof, Ph.D. MDFT International,
How To Engage and Keep Youth and Families in Treatment: Focus on Opioid Use and Abuse What You Need to Know about Opioids MDFT Engagement Strategies That Everybody Can Use Gayle Dakof, Ph.D. MDFT International,
Biological Psychology. Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!!
 Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
Biological Psychology Key Point for this Unit: Everything psychological is simultaneously biological!! NEURON Dendrites Dendrites receive messages from other cells and conduct impulses toward the cell
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM. Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder
 Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder Misuse of prescription pain relievers is, after marijuana use, the second most common form of
Prescription Drugs MODULE 5 ALLIED TRADES ASSISTANCE PROGRAM Preventative Education: Substance Use Disorder Misuse of prescription pain relievers is, after marijuana use, the second most common form of
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom //
 Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Let s Talk About. Marijuana. Grades 2 to 6 MM4326 TEACHER S GUIDE. Let s Talk About Marijuana Mazzarella Media, Inc. 1
 Let s Talk About Marijuana Grades 2 to 6 TEACHER S GUIDE MM4326 Let s Talk About Marijuana Mazzarella Media, Inc. 1 Table of Contents Why Young Learners Should View This Program 3 Learning Objectives..3
Let s Talk About Marijuana Grades 2 to 6 TEACHER S GUIDE MM4326 Let s Talk About Marijuana Mazzarella Media, Inc. 1 Table of Contents Why Young Learners Should View This Program 3 Learning Objectives..3
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System nervous system stimulus response Neuron structure and function neurons nerve impulses dendrite
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system is a network of communication used by body parts to maintain homeostasis and bodily functions. The nervous system gathers information
2018 Medical Marvels Research Competition A research competition for students in grades 9 and 10
 2018 Medical Marvels Research Competition A research competition for students in grades 9 and 10 Sponsored by the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research and the Center for Workforce Readiness The Northwell
2018 Medical Marvels Research Competition A research competition for students in grades 9 and 10 Sponsored by the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research and the Center for Workforce Readiness The Northwell
