Autoimmune Hepatitis Chronic hepatitis with
|
|
|
- Byron Hodges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Autoimmune Hepatitis -Chronic hepatitis with immunologic abnormalities -Histologic features are similar to chronic viral hepatitis -Indolent or severe course -Dramatic response to immunosuppressive therapy
2 Features: 1-Female predominance (70%) 2-Negative serelogy for viral Ags. 3- serum Ig (>2.5 g/dl) 4-High titers of autoantibodies (80% of cases) 5-The presence of other autoimmune diseases as RA, thyroiditis, sjogern syndrome, UC in 60% of the cases -
3 The type of autoantibodies 1-Antismooth myuscle abs anti actin anti troponin anti tropomyosin 2-liver/kidney microsomal Abs anti cytochrome P-450 components anti UDP-glucuronosyl transferases 3-Anti soluble liver / pancreas antigen
4 Outcome Mild to severe chronic hepatitis Full remission is unusual Risk of cirrhosis is 5% which is the main cause of death
5 Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Types: 1.Steatosis ( Fatty liver) 2.Steatohepatitis hepatocyte destruction parenchymal inflammation progressive pericellular fibrosis
6 Predisposing factors : 1-Type 2 DM 2-Obesity : body mass index > 30 kg /m2 in caucasians > 25 kg /m2 in Asians 3-Dyslipidemia ( TG, LDL, HDL)
7 . TNF, IL6, chemokine liver inflammation & damage Pathogenesis.Metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance. Obesity. Dyslipidemia.Mechanism of fatty accumulation 1.Impaired oxidation of fatty acids 2.Increased synthesis & uptake of FFA 3.Decreased hepatic sec. of VLDL
8 Clinically -NAFLD is the most common cause of incidental in transaminases -Most pts. are asymptomatic -Non-specific symptoms Fatigue, malaise, RUQ discomfort -Severe symptoms -Liver Bx is required for dx. -NAFLD m.b a significant contributer to cryptogenic cirrhosis
9 Hemochsomatosis -Excessive accumalation of body iron (liver & pancreas) -1ry or 2ry (genetic or acquired )
10 j Causes of acquired hemosidrosis : 1-multiple transfusions 2-ineffective erythropoiesis ( thalassemia ) 3-increased iron intake (Bantu sidrosis ) 4-chronic liver disease
11 -Features: 1-Micronodular cirrhosis (all patients) 2-D.M ( 75 80%) 3-skin prigmentation 75-80%) 4-cardiomegaly, joints disease, testicular atrophy
12 Symptoms appear 5 th 6 th decades not before age 40 -M:F ratio 5-7: 1 -Genetic hemochromatosis ( 4 variants) -The most common form is aut. recessive disease of adult onset caused by mutation in the HFE gene on chr.6
13 Pathogenesis -1ry defect in intestinal absorption of dietary iron. -Total body iron 2-6gm in adults 0.5gm in liver mostly in hepatocytes -In disease >50gm Fe accumulated 1/3 in liver
14 -In herediatary hemochromatosis there is a defect in regulation of intestinal absorption of dietary iron leading to net iron accumulation of gm/yr -The gene responsible is HFE gene located on chr.6 close to HLA gene complex -HFE gene regulates the level of hepcidin hormone synthesized in liver -Hepcidin (-) Fe. absorption from intestine -HFE gene deletion causes iron overload
15 -Two mutation can occur in HFE gene: 1-Mutation at 845 nucleotide tyrosine substitution for cystine at AA 282 ( C282 Y ) 2-aspartate substitution for histidine at AA 63 ( H63D) 10% of pts. have other gene mutations
16 -Carrier rate for C282Y is 1/70 -Homozygosity is 1/200-80% of pts. are homozygous for (C282Y) mutation & have the highest incidence of iron accumulation -10% of pts. are either homozygous for H63D mutation or compound heterozygous for C282Y/H63D mutation
17 Excessive Fe deposition toxicity of the tissues : 1. Lipid peroxidation 2. Stimulation of collagen formation 3. DNA damage
18 Morphological changes: 1-Deposition of hemosiderin in diffferent orgens Liver Pancreas Myocardium Pituitary Adrenal Thyroid & parathyroid Joints Skin 2-Cirrhosis 3-Pancreatic fibrosis
19 -No inflammation -Fibrosis -Cirrhosis -Synovitis -Polyarthritis(pseudogout) -Pigmentation of liver -fibrosis of pancreas & myocardium -Atrophy of testes
20 Clinical presentation M:F 5 7 :1 5 6 the decades Hepatomegaly Abdominal pain Skin pigmentation D.M Cardiac dysfunction Atypical arthritis Hypogonadism serum Fe ferritin HCC 200x in the risk
21 Wilson Disease -aut. Recessive disorder of Cu metabolism -mutation in ATP7B gene on chr. 13 which encodes an ATPase metal ion transporter in Golgi region -> 80 mutations -Gene freq. 1:200 -Incidence is 1:30000
22 Pathogenesis Main source of Cu is from diet Absorption of ingested Cu ( 2-5 mg/d) Complex with albumin Hepatocellular uptake Incorporation with α-2-globulin to form Ceruloplasmin
23 Sec. into plasma (90 95% of plasma Cu) Hepatic uptake of ceruloplasmin Lysosomal degradation Secretion of free Cu into bile
24 - In Wilson disease absorbed Cu. Fails to enter the circulation in the form of ceruloplamin & the biliary excertion of Cu. is - Defective function of ATP-7B failure of Cu. excretion into bile & inhibits sec. of ceruloplasmin into the plasma Cu. accumulation in liver
25 - Cu. Accumulation in the liver reults in:- 1-Production of free radicals 2-binding to sulfhydryl groups of cellular proteins 3-displacement of other metals in hepatic metalloenzymes
26 -By the age of 5yrs. Cu. Spills over to circulation causing hemolysis & involvement of other organs as brain & cornea also kidneys, bones joints & parathyroid glands -Urinary exc. Of cu.
27 Morphology Liver 1-Fatty change 2-Acute hepatitis 3-chronic hepatitis 4-cirrhosis 5-massive hepatic necrosis ( rhodanine stain or orcein stain )
28 Brain: Toxic injury to basal ganglia esp. the putamen causing atrophy & cavitation
29 Eye: kayser- fleischer rings green brown depositis of Cu. in descemet membrane in the limbus of the cornea (hepatolenticular degenceration)
30 Clinically -Presentation > 6 yrs of age -Most common presentation is acute on chronic hepatitis -Neuropsychiatric presentation can occur behavioral changes Frank psychosis Parkinson disease- like syndrome
31 DX 1- in serum ceruloplasmin level 2- in urinary exc. Of Cu. 3- hepatic content of copper > 250 mg/gm dry wt.
32 α-1-antitrypsin Defeciency -- Aut. Recessive disorder - freq. 1:7000 in N. american white population - α-1-antiryrpsin is a protease inhibtor as elastase, cathepsing, proteinase 3 which are released from neutrophils at the site of inflammation -The gene pi. Is located on chr. 14 -At least 75 forms of gene mutation are present -The most common genotype is pi.mm present in 90% of individuals -PiZZ genotype level of α-1-antitrypsin in blood (only 10% of normal) are at high risk of developing clinical disease
33 Pathogenesis -The mutant polypeptide (PiZ) is abnormally folded & polymerizes causing its retention in the ER of hepatocytes -Athoyugh all individual with PiZZ genotype accumulate α-1-at-z protein only 10% of them develop clinical liver disease.
34 -The accumulated α-1-at-z is not toxic but the autophagocytic response stimulated within the hepatocytes appear to be the cause of liver injury by autophagocytosis of the mitochondria -8-10% of patients develop significant liver damage
35 Morphology -Intracytoplasmic globular inclusions in hepatocytes which are acidophilic in H&E. sections -The inclusions are PAS-+ve & diastase resistant -Neonatal hepatitis cholestasis & fibrosis Chronic hepatitis Cirrhosis Fatty change Mallory bodies Clinical features -neonatal hepatitis with cholestatic jaundice appears in 10 20% of newborns with the disease -Attacks of hepatitis in adolescance -chronic hepatitis & cirrhosis -HCC in 2-3 % of Pizz adults + cirrhosis
36 Reye s Syndrome -Fatty change in liver & encephalopathy -< 4 yr d after viral illness - liver & abn. LFT Vomiting lethargy. 25% may go into coma
37 Pathogenesis -Derangement of mitochondrial function along or in combination with viral infection & salicylate -Microvesicular steatosis -Brain edema -Absent inflammation -Sk. Muscles, heart, kidneys fatty change
38 Budd Chiari Syndrome -Thrombotic occlusion of the hepatic vein -Hepatomegaly -Wt.gain -Ascitis -Abd. Pain
39 Causes: 1-PCV 2-Pregnancy 3-Postpartum 4-Oral contraceptive 5-PNH 7-Mechanical obstruction 8-Tumors as HCC 9-Idiopathic in 30% of the cases -
40 Morphology -Swollen liver, red with tense capsule -centrilobular congestion & necrosis -Fibrosis -Thrombi Clinically Mortality rate is high if not treated
41 Primary sclerosing cholangitis -Inflammation, obliterative firosis, & segmental dilation of the obstructed intra hepatic & extra hepatic bile ducts -In PSC, UC coexists in 70% of patients -in patients of UC, 4% develop PSC -3-5 the decades M: F 2:1 *
42 -asymptomatic pts. - -persistent serum alkaline phosphatase fatigue, pruritis, jaundice, wt loss, ascitis, bleeding, encephalopathy - - -antimitochondrial Abs < 10% of cases - -Antinuclear cytoplasmic Abs in 80% of cases
43 Morphology -Concentric periductal onion-skin fibrosis & lymphocytic infilrate -Atrophy & obliteration of bile ducts -Dilation of bile ducts inbetween areas of stricture -Cholestasis & fibrosis -Cirrhosis, cholangiocarcinoma ( 10 15%) *
44 Pathogenesis -Exposure to gut derived toxins -Immune attack -Ischemia of biliary tree
45 Secondary biliary cirrhosis -Prolonged obst. To extrahepatic biliary tree -Causes: 1-cholelithiasis 2-biliary atresia 3-malignancies 4-stricutres
46 Primary biliary Cirrhosis -chronic, progressive & often fatal cholestatic liver disease -Non-suppurative granulomatous destruction of medium-sized intrahepatic bile ducts, portal inflammation & scarring
47 -Age 20-80yrs ( peak 40-50yrs) -F>M -Insidious onset -Pruritis, jaundice -Cirrhosis over 2 or more decdes
48 - Alkaline phosphatase & cholesterol -Hyperbilirubinemia = hepatic decompansation -Antimitochondrial Abs > 90% Antimitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase -Associated conditions: sjogern synd. Scleroderma thyroiditis, RA, Raynauds phenomenon. MGN, celiac disease.
49 Morphology -interlobular bile ducts are absent or severely destructed (florid duct lesion) -intra epithelial inflammation -Granulomatous inflammation Bile ductular proliferation Cholestesis Necrosis of parenchyma Cirrhosis
50 Sinusoidal Obstruction Syndrome ( Veno-occlusive disease) -Originally described in Jamaican drinkers of bush-tea containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids -This occurs in the first days after bone marrow transplantation. Which is caused by: 1-Drugs as cyclophosphamide 2-Total body radiation
51 .Incidence -20% in recepients of allogeneic marrow transplant -Clinical presentation Mild severe Death if does not resolve in 3 months -
52 Mechanism Toxic injury to sinusoidal endothelium emboli blockage of bl. Flow Passage of blood into space of Disse stellate cells fibrosis
53 Peliosis Hepatis -sinusoidal dilatation -Causes: 1-anabolic steroids 2-oral contraceptive 3-danazol -Pathogenesis Unknown
54 -Asymptomatic -Intra abdominal hemorrhage -Liver failure -reversible
55 Liver tumors Benign Most common is cavernous hemagioma Usually <2cm Subcapsular Liver cell adenoma Young female Hx of oral contraceptive intake May rupture esp. during pregnancy causing severe intraperitoneal hemorrhage Rarely may contain HCC Misdx. Of HCC
56 Liver Nodules Focal noudular hyperplasia Well demarcated hyperplastic hepatocytes with central scar. Non-cirrhotic liver Not neoplasm but nodular regeneration Local vascular injury Females of reproductive age No risk of malignancy 20% of cases have cavernous hemagnioma
57 Macroregenerative Nodules Cirrhotic liver Larger than cirrhotic nodules No atypical features, Reticulin is intact No malignant potential
58 Dysplastic nodules Larger than 1 mm Cirrhotic liver Atypical features, pleomorphism and crowding High proliferative activity High or low dysplasia Precancerous (monoclonal, +ve gene mutations Types: 1. Small cell dysplastic nodules 2. Large cell dysplastic nodules
59 Hepatocellular carcinoma 5.4% of all cancers Incidence: <5/ population in N&S America N& central Europe Australia 15/ population in Mediterranean 36/ population in Korea, Taiwan mozambique, china
60 Blacks > white M:F ratio 3:1 in low incidence areas. >60yr 8:1 in high incidence areas yr
61 Predisposing Factors 1. Hepatitis carrier state vertical transmission increases the risk 200X cirrhosis mau be absent young age group (20-40yr) 2. >85% of cases of HCC occur in countries with high rates of chronic HBV infection
62 3-Cirrhosis In western countries cirrhosis is present in 85-90% of cases >60yr HCV & alcoholism 4. Aflatoxins 5. Hereditary tyrosinemia (in 40% of cases) 6. Hereditary hemochromatosis
63 Pathogenesis 1. Repeated cycles of cell death & regeneration HBC, HCV, gene mutations, Genomic instability 2. Viral integration HBV DNA intergration which leads to clonal expansion 3. HBV DNA intergration which leads to genomic instability not limited to integration site.
64 4. HBV X-protein which leads to transactivation of viral & cellular promoters, Activation of oncogenes, Inhibition of apoptosis 5. Aflatoxins ( fungus Aspirgillus flavus) mutation of p53 6. Cirrhosis HCV Alcohol Hemochromatosis Tyrosinemia (40% of pts. Develop HCC despite adequate dietary control
65 Morphology 1. HCC 2. CC 3. Mixed Unifocal Multfiocal Diffusely infiltrative
66 Vascular invasion is common in all types. Well ---- Anaplastic Fibrolamellar carcinoma yr. M=F No relation to HBV or cirrhosis better prognosis single hard scirrhous tumor Cholangiocarcinoma are desmoplastic
67 metastasis Vascular lungs, bones, adrenals, brain, in 50% of cholagiocarcinoma
68 C/P abd. Pain, malaise, wt. loss increase α-feto protein in 60 75% of pts.
69 α-feto protein increases also with: 1-yolk sac tumor 2- cirrhosis, 3-massive liver necrosis, 4-chronic hepatitis, 5-normal pregnancy, 6-fetal distress or death 7- fetal neural tube defect.
70 Prognosis Death within 7-10 months Causes: 1-Cachexia 2-GI bleeding 3-Liver failure 4-Tumor rupture and hemorrhage
71 THE END
Causes of acquired hemosidrosis : 1-multiple transfusions 2-ineffective erythropoiesis (β-thalassemia ) 3-increased iron intake (Bantu sidrosis )
 Hemochromatosis Excessive accumalation of body iron (liver & pancreas) 1ry or 2ry (genetic or acquired ) Genetic hemochromatosis ( 4 variants) The most common form is aut.recessive disease of adult onset
Hemochromatosis Excessive accumalation of body iron (liver & pancreas) 1ry or 2ry (genetic or acquired ) Genetic hemochromatosis ( 4 variants) The most common form is aut.recessive disease of adult onset
Omar Sami. Maha Shomaf. 1 P a g e
 aa 4 Omar Sami - Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e In the last lecture we have talked about inherited metabolic liver diseases, and we started with Hemochromatosis, throughout this sheet we will talk about Wilson
aa 4 Omar Sami - Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e In the last lecture we have talked about inherited metabolic liver diseases, and we started with Hemochromatosis, throughout this sheet we will talk about Wilson
-sheet 3. -Waseem Alhaj. Maha Shomaf
 -sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
-sheet 3 -Basheer egbaria -Waseem Alhaj Maha Shomaf 1 P a g e Viral hepatitis have many types each type is associated with different outcomes complication, some can result in acute one,others result in
Hepatitis. Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic
 Liver diseases II Hepatitis Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic infectious Hepatitis Several clinical
Liver diseases II Hepatitis Causes: - infectious Hepatitis: viral, Bacterial, Parasitic, and Helminthic - Autoimmune Hepatitis - Drug- and Toxin (Alcohol) - Metabolic infectious Hepatitis Several clinical
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP
 Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Autoimmune Hepatobiliary Diseases PROF. DR. SABEHA ALBAYATI CABM,FRCP Autoimmune hepatobiliary diseases The liver is an important target for immunemediated injury. Three disease phenotypes are recognized:
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk Fatty liver disease Is there fatty
Metabolic Liver Diseases
 Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Metabolic Liver Diseases Howard J. Worman, M. D. Department of Medicine Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons Three Classical Inherited Disorders of Metabolism Affecting the Liver Hereditary
Hemosiderin. Livia Vida 2018
 Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Hemosiderin Livia Vida 2018 Questions Histochemical caracteristics of the different pigments. Exogenous pigments. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Causes and forms of jaundice. Hemoglobinogenic pigments. Pathological
Metabolic Liver Disease
 Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Metabolic Liver Disease Peter Eichenseer, MD No relationships to disclose. Outline Overview Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Wilson s disease Hereditary hemochromatosis Pathophysiology Clinical features
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT
 Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
Dhanpat Jain Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, CT Case history 15 years old female presented with fatigue. Found to have features suggestive of cirrhosis with esophageal varices, splenomegaly
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Steatosis/Steatohepatitis
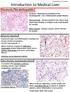 Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Prepared by Kurt Schaberg Introduction to Medical Liver Steatosis/Steatohepatitis Alcoholic Hepatitis Hepatocyte injury and inflammation resulting from chronic alcohol consumption AST/ALT ratio typically
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction. Ductal Diseases: Stones Tumors. Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis Toxin (APAP/Etoh) Reye s Shock.
 Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
Extrahepatic Biliary Obstruction Stones Tumors Ductal Diseases: Ductal Diseases: Primary Biliary Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Sclerosing Cholangitis Sclerosing Cholangitis Acute Injury: Viral Hepatitis
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017
 CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
CURRENT ISSUES IN ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY 2017 I HAVE NOTHING TO DISCLOSE Linda Ferrell PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF MEDICAL LIVER DISEASE WITH TWO CONCURRENT ETIOLOGIES Linda Ferrell, MD, UCSF THE PROBLEM
Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology
 Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology SCBM342 Systemic Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D. (Pathobiology) Email: witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives 1. Understand etiology and pathogenesis of common
Liver, Pancreas and Gall Bladder Pathology SCBM342 Systemic Pathology Witchuda Payuhakrit, Ph.D. (Pathobiology) Email: witchuda.pay@mahidol.ac.th Objectives 1. Understand etiology and pathogenesis of common
Histology. The pathology of the. bile ducts. pancreas. liver. The lecture in summary. Vt-2006
 Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Vt-2006 The pathology of the liver, bile ducts and pancreas Richard Palmqvist Docent, ST-läkare, Klin Pat Lab, Labcentrum The lecture in summary Introduction, histology & physiology in brief General phenomenon
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Liver Tumors. Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy
 Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Liver Tumors Prof. Dr. Ahmed El - Samongy Objective 1. Identify the most important features of common benign liver tumors 2. Know the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
What Is Cirrhosis? CIRRHOSIS. Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is. by chronic conditions and diseases. permanently scarred or injured
 What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
What Is Cirrhosis? Cirrhosis occurs when the liver is permanently scarred or injured by chronic conditions and diseases. Common causes of cirrhosis include: Long-term alcohol abuse. Chronic viral hepatitis
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy?
 Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Metabolic Liver Disease: What s New in Diagnosis and Therapy? Bruce R. Bacon, M.D. James F. King M.D. Endowed Chair in Gastroenterology Professor of Internal Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA
 LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
LIVER SPECIALTY CONFERENCE USCAP 2016 Maha Guindi, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pathology Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nothing to disclose Case History 47-year-old male, long standing ileal
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need?
 Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Basic patterns of liver damage what information can a liver biopsy provide and what clinical information does the pathologist need? Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk @robdgol FATTY LIVER DISEASE Brunt
Metabolic liver disease
 Metabolic liver disease Metabolic liver disease Group of diseases due to disorders of metabolism Acquired Inherited A- Acquired Non alcoholic fatty liver disease B- Inherited Hemochromatosis Wilson disease
Metabolic liver disease Metabolic liver disease Group of diseases due to disorders of metabolism Acquired Inherited A- Acquired Non alcoholic fatty liver disease B- Inherited Hemochromatosis Wilson disease
Cross section of normal liver
 THE LIVER 1 Functions 1-processing of dietary amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and vitamins. 2-synthesis of serum proteins. 3-detoxification and excretion into bile of endogenous waste products and
THE LIVER 1 Functions 1-processing of dietary amino acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and vitamins. 2-synthesis of serum proteins. 3-detoxification and excretion into bile of endogenous waste products and
I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation LIVER TESTS: WHAT IS INCLUDED? LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM OBJECTIVES
 LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
LIVER TESTS: HOW TO UTILIZE THEM I have no disclosures relevant to this presentation José Franco, MD Professor of Medicine, Surgery and Pediatrics Medical College of Wisconsin OBJECTIVES Differentiate
Slide 7 demonstrates acute pericholangitisis with neutrophils around proliferating bile ducts.
 Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Many of the histologic images and the tables are from MacSween s Pathology of the Liver (5 th Edition). Other images were used from an online source called PathPedia.com. A few images from other sources
Chapter 18 LIVER BILIARY TRACT
 Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Chapter 18 LIVER & BILIARY TRACT DUCT SYSTEM N O FIBROUS TISSUE PORTAL TRIAD CENTRAL VEIN PATTERNS OF HEPATIC INJURY Degeneration: Balooning, feathery degeneration, fat, pigment Inflammation:
Special stains in liver pathology
 Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Liver Diseases. Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD
 Liver Diseases Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD ILOs Recognize different causes of Live failure Recall and understand clinical picture and complication of Liver failure Discuss causes and clinical picture of hepatic
Liver Diseases Yasmine Lashine MD, PhD ILOs Recognize different causes of Live failure Recall and understand clinical picture and complication of Liver failure Discuss causes and clinical picture of hepatic
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas
 Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Disorders of the Liver and Pancreas Liver Lobule Hexagonal plates Sinusoids Triads Bile duct branch Arteriole Venuole Blood flows from periphery to Central vein Space of Dissé Lobular Microanatomy Hepatocytes
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids. Cholestasis
 Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
Noncalculous Biliary Disease Dean Abramson, M.D. Gastroenterologists, P.C. Cedar Rapids Cholestasis Biochemical hallmark Impaired bile flow from liver to small intestine Alkaline phosphatase is primary
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS MIA MANABAT DO PGY6 MOA 119 TH ANNUAL SPRING SCIENTIFIC CONVENTION MAY 19, 2018 EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Review of liver enzymes vs liver function tests Clinical
Liver Failure. The most severe clinical consequence of liver disease is liver failure:
 Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Liver diseases I The major primary diseases of the liver are: - Viral hepatitis, - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), - Alcoholic liver disease, - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) Hepatic damage also
Hepatocytes produce. Proteins Clotting factors Hormones. Bile Flow
 R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
R.J.Bailey MD Hepatocytes produce Proteins Clotting factors Hormones Bile Flow Trouble.. for the liver! Trouble for the Liver Liver Gall Bladder Common Alcohol Hep C Fatty Liver Cancer Drugs Viruses Uncommon
Workup of a Solid Liver Lesion
 Workup of a Solid Liver Lesion Joseph B. Cofer MD FACS Chief Quality Officer Erlanger Health System Affiliate Professor of Surgery UTHSC-Chattanooga I have no financial or other relationships with any
Workup of a Solid Liver Lesion Joseph B. Cofer MD FACS Chief Quality Officer Erlanger Health System Affiliate Professor of Surgery UTHSC-Chattanooga I have no financial or other relationships with any
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY
 2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
2014 CURRENT ISSUES IN PATHOLOGY SPECIAL STAINS IN LIVER BIOPSY PATHOLOGY Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Trichrome stain : (1) Assess degree of fibrosis. H&E stain is not reliable
Interpreting Liver Function Tests
 PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
PSH Clinical Guidelines Statement 2017 Interpreting Liver Function Tests Dr. Asad A Chaudhry Consultant Hepatologist, Chaudhry Hospital, Gujranwala, Pakistan. Liver function tests (LFTs) generally refer
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon
 What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
What to do with abnormal LFTs? Andrew M Smith Hepatobiliary Surgeon "it looks like there's something wrong.with your television set. Matt Groenig, creator of The Simpsons Probability of an abnormal screening
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology
 Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Linda Ferrell, MD Distinguished Professor Vice Chair Director of Surgical Pathology Dept of Pathology Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and Fatty Liver Disease Liver manifestations of the obesity epidemic Changes
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Interesting Cases from Liver Tumor Board Jeffrey C. Weinreb, M.D.,FACR Yale University School of Medicine jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Common Liver Diseases Hemangioma Cyst FNH Focal Fat/Sparing THID Non-Cirrhotic
Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology. Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D.
 Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D. GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Gallbladder Pancreas GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Hepa**s Alcoholic
Gastrointes*nal and Liver Pathology Kris*ne Kra5s, M.D. GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Gallbladder Pancreas GI Pathology Outline Esophagus Stomach Intes*ne Liver Hepa**s Alcoholic
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
Hereditary Haemochromatosis For GPs What is Hereditary Haemochromatosis? Hereditary Haemochromatosis () is a common autosomal recessive disease resulting in excessive absorption of dietary iron from the
How to Approach a Medical Liver Biopsy. 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology. Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015
 1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
1 A Brief Introduction to the Liver Sessions 9 th Bryan Warren School of Pathology Pancreatic and Liver Pathology Sarajevo, 6 th -7 th November 2015 Stefan Hübscher, Institute of Immunology & Immunotherapy,
CHAPTER 1. Alcoholic Liver Disease
 CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
CHAPTER 1 Alcoholic Liver Disease Major Lesions of Alcoholic Liver Disease Alcoholic fatty liver - >90% of binge and chronic drinkers Alcoholic hepatitis precursor of cirrhosis Alcoholic cirrhosis end
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries Paul Y. Kwo, MD, FACG, FAASLD 1, Stanley M. Cohen, MD, FACG, FAASLD 2, and Joseph K. Lim, MD, FACG, FAASLD 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology,
Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
 The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases 27 th Annual Scientific Meeting and International Symposium on Hepatology 16 November 2014 Genetic Diagnosis of Liver Diseases Dr Chloe Mak MD,
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function tests / tests of
)Liver diseases I and II)
 )Liver diseases I and II) The liver is vulnerable to a wide variety of metabolic, toxic, microbial, circulatory, and neoplastic insults. The major primary diseases of the liver are viral hepatitis, nonalcoholic
)Liver diseases I and II) The liver is vulnerable to a wide variety of metabolic, toxic, microbial, circulatory, and neoplastic insults. The major primary diseases of the liver are viral hepatitis, nonalcoholic
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Key Points: Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective. Jenny Heathcote, MD. University of Toronto
 Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Autoimmune Liver Disease: Update for Pathologists from the Hepatologist s Perspective Jenny Heathcote, MD University of Toronto Key Points: AILD comprise autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis
Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis. By Dr. Seham Seif
 Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis By Dr. Seham Seif Definition NAFL describe a common clinicopathological conditions characterized by significant lipid deposition in the hepatocytes
Non alcoholic fatty liver and Non alcoholic Steatohepatitis By Dr. Seham Seif Definition NAFL describe a common clinicopathological conditions characterized by significant lipid deposition in the hepatocytes
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions. American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course
 Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Evaluation of Liver Mass Lesions American College of Gastroenterology 2013 Regional Postgraduate Course Lewis R. Roberts, MB ChB, PhD Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Mayo Clinic College of
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee
 Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
Hereditary Haemochromatosis (A pint too many: discussing haemochromatosis) John Lee Hereditary Haemochromatosis A disorder of iron metabolism Inherited disorder Iron Essential micro-nutrient Toxicity when
Natural history of α-1-atd in children
 Natural history of α-1-atd in children Agnieszka Bakuła Dpt of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Nutrition Disorders and Paediatrics The Children s Memorial Health Institute Warsaw, Poland Topics to be discussed
Natural history of α-1-atd in children Agnieszka Bakuła Dpt of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Nutrition Disorders and Paediatrics The Children s Memorial Health Institute Warsaw, Poland Topics to be discussed
Morning Report Presentation. Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005
 Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
Morning Report Presentation Sarah Hughes, MD January 11, 2005 Primary Biliary Cirrhosis! PBC is a chronic, progressive, cholestatic liver disease of unknown cause that usually affects middle-aged women
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Hepatology referral pathways for GP 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for hepatology referral 3. Raised
Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for liver cancer.
Liver Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for liver cancer.
HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM
 EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
EVALUATION OF LIVER FUNCTION R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEPETIC SYSTEMS BIOCHEMICAL HEPATOCYTIC SYSTEM HEPATOBILIARY SYSTEM RETICULOENDOTHELIAL SYSTEM METABOLIC FUNCTION
: Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract. : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015. : Dr. Samir Bashir. 1 P a g e
 21 : Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015 : Dr. Samir Bashir 1 P a g e *Check last page please before you start. Cholelithiasis: -Small, round stones in the gallbladder.
21 : Disease of extrahepatic biliary tract : Jumana Abu Hamour : 6/12/2015 : Dr. Samir Bashir 1 P a g e *Check last page please before you start. Cholelithiasis: -Small, round stones in the gallbladder.
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders
 Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
Gastrointestinal System: Accessory Organ Disorders Mary DeLetter, PhD, RN Associate Professor Dept. of Baccalaureate and Graduate Nursing Eastern Kentucky University Disorders of Accessory Organs Portal
9/28/2016. Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach. Objectives. Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
 Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Elevated Liver Function Tests: A Case Based Approach Terrance M. James, NP C The Oregon Clinic Hepatology 503 963 2707 tejames@orclinic.com Objectives Identify patterns of abnormal liver function tests
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis
 Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Overview of PSC Making the Diagnosis Tamar Taddei, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Yale University School of Medicine Overview Definition Epidemiology Diagnosis Modes of presentation Associated diseases
Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis
 Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis Basic Overview Clinical Aspects Management What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Autosomal recessive disease W-1:3000, H-1:10,000, AA-1:15,000 Mutations of CFTR defective Cl - transport
Liver Disease in Cystic Fibrosis Basic Overview Clinical Aspects Management What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Autosomal recessive disease W-1:3000, H-1:10,000, AA-1:15,000 Mutations of CFTR defective Cl - transport
Liver Cancer And Tumours
 Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
Liver Cancer And Tumours What causes liver cancer? Many factors may play a role in the development of cancer. Because the liver filters blood from all parts of the body, cancer cells from elsewhere can
LIVER DISEASES. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
LIVER DISEASES Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn Viral Hepatitis Cirrhosis of liver Liver cancer Viral Hepatitis DEFINITION Primary hepatic infections
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis
 Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
Patterns of abnormal LFTs and their differential diagnosis Professor Matthew Cramp South West Liver Unit and Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, Plymouth Outline liver function / liver function
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Biliary tract diseases of the liver
 Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
Biliary tract diseases of the liver Digestive Diseases Course Bucharest 2016 Rob Goldin r.goldin@imperial.ac.uk How important are biliary tract diseases? Hepatology 2011 53(5):1608-17 Approximately 16%
LIVER DISEASES. Anatomy
 LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
LIVER DISEASES Anatomy PHYSIOLOGY Bilirubin metabolism: 250-300 mg/d SER Bile UDPG-A B. diglucuronide Unc. B B. monoglucuronide Albumin Glucuronyltransferase 100-200 mg/d Bacteria 4mg In urine urobilinogen
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS
 CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
CITY AND HACKNEY CCG ABNORMAL LIVER FUNCTION TESTS (LFTs) in ADULTS Interpreting abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) and trying to diagnose any underlying liver disease is a common scenario in Primary
Biliary Atresia. Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s
 Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Biliary Atresia Karen F. Murray, MD Professor of Pediatrics Director, Hepatobiliary Program Seattle Children s Biliary Atresia Incidence: 1/8,000-15,000 live births Girls > boys 1.5:1 The most common cause
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy
 Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
Fat, ballooning, plasma cells and a +ANA. Yikes! USCAP 2016 Evening Specialty Conference Cynthia Guy Goals Share an interesting case Important because it highlights a common problem that we re likely to
2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen
 1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
1 Scope For use within hepatology Contents 2. Liver blood tests and what they mean p2 Acute and chronic liver screen p2 Common reasons for referral 3. Raised ALT +/- GGT p3 4. Non alcoholic fatty liver
Special stains in liver pathology
 Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
Current Issues in Surgical Pathology 2014 Special stains in liver pathology Which, why, how Really? Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco Outline Which stains Why the stain is done How
-Liver function tests -
 -Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
-Liver function tests - Biochimestry teamwork Osamah Al-Jarallah Abdulaziz Al-Shamlan Abdullah Al-Mazyad Turki Al-Otaibi Khalid Al-Khamis Saud Al-awad KhaledAlmohaimede Meshal Al-Otaibi Al-Anood Asiri
Serologic Markers CONVENTIONAL ANTIBODIES ANTIBODIES UNCONVENTIONAL. AIH Type I
 Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Autoimmune Hepatitis By Thomas Frazier Objective What we need to know about AIH Diagnosis Treatment Difficulties in both Liver transplantation concerns AASLD Guidelines: Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):2193-213.
Steatotic liver disease
 Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
Steatotic liver disease Fatty liver disease Prof. Dr. ANNE HOORENS Non-Neoplastic Liver Pathology December 8th 2018 Working Group of Digestive Pathology Belgian Society of Pathology OUTLINE NAFLD = Non-Alcoholic
National Liver EQA Scheme. Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004
 National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
National Liver EQA Scheme Open meeting, Glasgow March 24th 2004 Participants meeting SOP8 Case discussion Are we quorate All please sign attendance sheet There were 20 EQA participants and 7 non-members
What is Liver Cancer? About the Liver
 Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
Your liver is important and it has many functions. The top three are that it cleans your blood of toxins, gives you energy and produces bile for digestion. What is Liver Cancer? Cancer starts when cells
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014
 Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Sarah Landes October 23, 2014 A T-cell mediated inflammatory destruction of intralobular bile ducts progressively leading to cholestasis and cirrhosis 9:1 F to M ratio Mostly diagnosed between 30-60 years
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male
 Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Idiopathic adulthood ductopenia manifesting as jaundice in a young male Deepak Jain*,1, H. K. Aggarwal 1, Avinash Rao 1, Shaveta Dahiya 1, Promil Jain 2 1 Department of Medicine, Pt. B.D. Sharma University
Role of Liver Biopsy. Role of Liver Biopsy 9/3/2009. Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging
 Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Liver Biopsies in Viral Hepatitis: Beyond Grading and Staging for further reference: Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach Neil Theise, MD. Depts of Pathology
Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases
 Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
Kris V. Kowdley, MD, FAASLD Director, Liver Care Network and Organ Care Research Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, WA Postgraduate Course: Adults with Inherited Liver Diseases Challenges in Management of
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE
 GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
WEEK. MPharm Programme. Liver Biochemistry. Slide 1 of 49 MPHM14 Liver Biochemistry
 MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
MPharm Programme Liver Biochemistry Slide 1 of 49 MPHM Liver Biochemistry Learning Outcomes Assess and evaluate the signs and symptoms of illness Assess and critically appraise a patients medication regimen,
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis. Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K.
 Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension and Incomplete Septal Cirrhosis Stefan Hübscher, University of Birmingham, Birmingham B15 2TT, U.K. Non-Cirrhotic Portal Hypertension Problems with Liver Biopsy Diagnosis
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases
 Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Patologia sistematica V Gastroenterologia Prof. Stefano Fiorucci Autoimmune liver diseases Harrison s Principles of Internal Medicine 18-19 Ed. 2012 e seguenti Chronic hepatitis classification by cause
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and
 Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland
 Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures in Liver Disease: Adventures in Liverland Sanjiv Chopra, MD, MACP Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Editor In Chief Hepatology Section Up To Date Serum
Drug therapy in patient with hepatic impairment
 Drug therapy in patient with hepatic impairment Arzneimitteltherapie bei Leberinsuffizienz Dominik Wilke 03/04 Mai 2018 43. ADKA-Kongress, Stuttgart Functions of the Liver I Metabolism (Carbohydrates,
Drug therapy in patient with hepatic impairment Arzneimitteltherapie bei Leberinsuffizienz Dominik Wilke 03/04 Mai 2018 43. ADKA-Kongress, Stuttgart Functions of the Liver I Metabolism (Carbohydrates,
ACP-BSG meeting The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders. Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust
 ACP-BSG meeting 10.12.09 The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust Wide range of diseases General inflammatory disorders Connective tissue
ACP-BSG meeting 10.12.09 The liver in systemic inflammatory disorders Dr Adrian C Bateman Southampton University Hospitals NHS Trust Wide range of diseases General inflammatory disorders Connective tissue
Transplant Hepatology
 Transplant Hepatology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified
Transplant Hepatology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease. Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya
 Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Biochemical Investigations in Liver Disease Dr Roshitha de Silva Department of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Kelaniya Biochemical markers Albumin ALP ALT, AST Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
4/27/2018. Disclosures LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS LIVER FUNCTION TESTS APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS
 APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
APPROACH TO THE PATIENT WITH ABNORMAL TESTS Kimberly A. Brown, M.D, FAST, FAASLD, AGAF Chief, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Henry Ford Hospital Henry Ford Health System Detroit, Michigan
