A descriptive study of aetiopathological evaluation of hoarseness: our experience
|
|
|
- Edmund Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Sindhu BS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg Mar;4(2): pissn eissn Original Research Article DOI: A descriptive study of aetiopathological evaluation of hoarseness: our experience Sindhu B. S. 1, Jayaprabha S. 2 * 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Government of T D Medical College, Alappuzha, Kerala, India 2 Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, India Received: 09 November 2017 Revised: 18 January 2018 Accepted: 19 January 2018 *Correspondence: Dr. Jayaprabha S., jpsvinayak@gmail.com Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: Hoarseness is a quality of voice that is rough, grating, harsh, more or less discordant and lower than normal in pitch for the individual. Besides affecting useful communication leading to tremendous alterations in daily living, voice problem may also signify the presence of more serious medical illnesses; such as malignancy or airway compromise. Hence this study is undertaken to determine the relative incidence of cases presented at a tertiary hospital, to analyse the hoarseness population based on age, sex, occupation etc, to find out the pathogenesis of hoarseness in the cases and to postulate the risk factors implicated in each. Methods: Descriptive cross sectional study was conducted on patients with hoarseness reported at Government Medical College, Trivandrum for a period of twelve months. Detailed history regarding duration, onset, nature of hoarseness, aggravating and relieving factors, voice fatiguability, diurnal variation, associated symptoms and history of upper respiratory infection were taken. Results: Being the tertiary hospital, the incidence was noted to be 0.7%. Majority of patients are in 4 th to 7 th decades and the most commonly affected age group was years. Male preponderance with 4:1 ratio was observed in which manual labourers constitute the single largest group. Smoking, alcohol intake and vocal abuse are found to be the major etiological factors. Majority of lesions were malignant in nature, commonest being Carcinoma Glottis. In benign lesions, majority was vocal cord polyp. Conclusions: Early detection of pathology and awareness is very important in the management of hoarseness. Keywords: Hoarseness, Descriptive, Aetiopathological, Tertiary, Population INTRODUCTION An individual is suffering from hoarseness when he/she could produce voice only with a pitch lower than his/her normal. Voice is said to have become hoarse when it is deep, rough and harsh and the clarity of syllables are lost. 1 Hoarseness as a symptom can occur in conditions as diverse as simple inflammation like laryngitis to the rare malignancies of the larynx. 2 Hoarseness is more prevalent in certain professionals such as singers and teachers but all age groups and both genders can be affected. In majority of cases it is due to benign conditions but still a thorough and proper evaluation is required. In the absence of an upper respiratory tract infection, any patient with hoarseness persisting for more than two weeks requires a complete evaluation. Aetiological factors implicated have a far and wide bearing on the pathogenesis of hoarseness; and in turn can serve as a pointer towards prevention and management of the same. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 356
2 When the patient gives a history of smoking, alcohol and tobacco use, cancer of head and neck must be considered and ruled out. Vocal abuse is one of the most common causes of hoarseness and can lead to other vocal pathologies such as vocal nodule. Good vocal hygiene can prevent and treat some pathologies and voice therapy is a cornerstone of treatment in some cases of hoarseness. In this context, the study is undertaken to analyse the aetiopathogenesis of hoarseness. METHODS This is a descriptive study and was approved by Human Ethical Committee, Government Medical College Trivandrum. The study was conducted in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Government Medical College, Trivandrum between July 2006 and June Patients reported to the Outpatient Department of Otorhinolaryngology with hoarseness were taken for the study. Children below the age of 9 years and those patients who could not undergo laryngoscopy were excluded. Detailed history regarding occupation, habits, onset of hoarseness, duration, nature of hoarseness, aggravating and relieving factors, voice fatiguability, diurnal variation, associated symptoms and history of upper respiratory tract infection were taken. All patients in the study group underwent general examination, systemic examination and local examination including indirect laryngoscopy and flexible laryngoscopy. Apart from routine blood and urine tests, blood sugar, RFT, sputum for acid fast bacilli, PA view X- ray chest PA view and soft tissue neck lateral view were taken. Other relevant investigations like FNAC, TFT, Barium Swallow, Thyroid Scan and CT scan base of skull, neck & chest were taken in indicated cases. Patients had detailed evaluation by microlaryngoscopic evaluation and necessary surgical procedures were done. Diagnosis was confirmed by histopathological examination. The statistical data was analysed using SPSS Statistics software (IBM). RESULTS A total cases attended the Outpatient wing of Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Government Medical College, Trivandrum during study period. Out of these, 184 patients presented with hoarseness, thus the incidence was noted to be 0.7%. The age of patients ranged from 9 years to 85 years (Table 1) with 149 (81%) were males and 35 (19%) were females. Male preponderance was observed with M:F ratio 149:35= 4:1. Majority of the patients were in the age group of years (20.7%) and years (19.6%) followed by years (16.8%) and years (16.3%) with mean and median of age of and 56.5 years respectively. Equally higher percentage of 22.2% of male patients was presented in age group of years and years while female patients showed in years of age group with higher percentage of 28.5%. Table 1: Distribution according to age group and sex. Age group (Yrs) Male Female Total % Total Manual labourers constituted the single largest group of patients (50%) (Table 2) followed by housewives (15.2%), unemployed (13.6%), salesmen (5.4%), teachers (4.3%), students (3.8%), and politician and vendor 2.2% each. Vocal abuse was noted in 12.5% cases. 68.5% of patients were smokers and 24.5% were alcoholics. 3.3% were passive smokers. 93.5% and 38% of manual labourers were smokers and alcoholic respectively. Hoarseness was due to malignant lesions in 56% and benign lesions in 44%. Among the malignant lesions, most common was carcinoma glottis (31%) followed by carcinoma supraglottis (10.3%), carcinoma hypopharynx (8.7%), carcinoma esophagus (2.2%), transglottic carcinoma (1.6%), carcinoma bronchus (1.6%) and carcinoma thyroid (0.5%) (Table 3). Among the premalignant lesions of larynx producing hoarseness, most common was solitary squamous papilloma (1.6%), followed by dysplasia and keratosis. Of the benign lesions, majority were due to vocal cord polyp (14.1%), followed by vocal cord nodule (6%). 20 cases in the study had laryngitis (10.8%) (Table 4): maximum patients had chronic laryngitis (4.9%) and 4.3% had acute laryngitis. 1.6% patients had TB laryngitis. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 357
3 Table 2: Incidence according to occupation. Occupation No % Manual labourer House wife Unemployed Teacher Salesman Politician Student Vendor Tailor Cashew worker Farmer Barber Clerk Total % of cases of hoarseness were due to vocal cord palsy (Table 5). Incidence of vocal cord palsy was more in males with M:F ratio 3:1; the commonest etiology being carcinoma esophagus (2.2%) (Table 5) followed by carcinoma bronchus (1.63%) and idiopathic (1.1%). Other causes for Vocal cord palsy included carcinoma thyroid, post thyroidectomy, viral neuronitis and cricoarytenoid joint fixation. Neck nodes noted in 17.4% patients, tracheostomy was done in 4.9% cases and thyroid swelling noted for 0.5%. FNAC for neck nodes came as metastasis from Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) in 12.5% cases, moderately differentiated SCC in 4.9%, well differentiated SCC in 1.1%, 1.6% was inconclusive and reactive change seen in 1.6% cases. Sputum AFB was positive in 1.1% cases. Table 3: Incidence and sex distribution of patients as per different conditions causing hoarseness. Aetiology Male Female Incidence % Carcinoma glottis Carcinoma supraglottis Carcinoma hypopharynx Transglottic carcinoma Vocal cord polyp Vocal cord nodule Reinke s edema Sulcus vocalis TB larynx Squamous papilloma Vocal cord palsy Acute laryngitis Ca-in-situ glottis Keratosis Dysphonia plica ventricularis Total Table 4: Incidence of laryngitis. Laryngitis No % Acute laryngitis Chronic laryngitis TB larynx Total Table 5: Aetiology of vocal cord palsy according to gender. Aetiology Male Female Total % Ca. bronchus Ca. esophagus Idiopathic Cricoarytenoid joint fixation Ca. thyroid Post thyroidectomy Viral neuronitis Total International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 358
4 Table 6: Incidence of different laryngeal diseases causing hoarseness in different studies. Diseases Ghosh et al (%) Baitha et al (%) Our study (%) Laryngitis Vocal cord polyp Vocal cord nodule Reinke s edema Vocal cord palsy Neoplastic DISCUSSION In this descriptive study of hoarseness, incidence of hoarseness among the total OPD patients was 0.7%. The youngest patient reported was 9 year old and the oldest was 85 year old. Majority of patients were in years age group (57.1%). According to Baitha et al, 4 th decade was the most commonly affected age group. 3 Ghosh et al reported maximum number of patients in years age group. 4 In our study, since mean and median of age are and 56.5 years respectively, predominant group is years (20.7%). Deshmukh and Mehta reported incidence in age group of years to be 63.1% and 67.2% respectively. 5,6 Male preponderance was noted in all of the major studies in the literature. According to Ghosh et al the sex incidence was more in male (56%) than in females (44%). Baitha et al observed M:F ratio of 2:1. In our study also M:F ratio was 4:1. Other studies by Deshmukh, Vrat et al and Mehta also showed male preponderance. 5,7 As far as occupation was concerned, manual labourers constituted the single largest group of patients (50%) and followed by housewives (15.2%). According to Baitha et al, incidence is commonest in manual labourers (36.36%) followed by housewives (21.81%). In the view of Ghosh et al, maximum incidence was among housewives. According to Chopra et al only 5.97% patients were farmers. 8 Our finding was in confirmation with that of Baitha et al. and Ghosh et al who observed vocal abuse in 72% of cases. In our study, vocal abuse only 12.5%. There is almost invariably an associated social relationship between tobacco and alcohol and thus a distinction between 2 factors is difficult to make. Cohort studies in France are seen to postulate a reduction of laryngeal cancer as a result of deprivation of both alcohol and tobacco (Robin et al). 9 The incidence of smokers in our study of hoarseness population was 68.5%, passive smokers 3.3% and alcoholics 24.5%. In a series of patients with chronic laryngitis, percentage of smokers is high as reported by Putney and O Keefe (1953) 89.8% and Norris and Peale 94%. 10,11 Alcohol is also often mentioned as a causative factor (Hinds et al). 12 Baitha et al opines chronic laryngitis as the commonest cause (49%) of hoarseness followed by acute laryngitis (26.3%). In our study also chronic laryngitis was slightly higher (4.9%) than acute laryngitis (4.3%). According to Bailey, for malignancy larynx M:F ratio has changed from 12:1 to 6:1 due to changing patterns of smoking and alcohol intake in Western countries. 13 But in our study, out of 72 cases of malignancy larynx, only 4 females were detected to have malignancy. Incidence of malignant lesions in our study was 56% i.e. percentage of malignant lesions was consistently higher than that of benign lesions. A discrepancy in the relative proportion of benign and malignant lesions was noted with respect to previous reported studies. After a careful revision of data and other factors we have come to a conclusion that the altered proportion could be attributed to the fact that cases were selected from a tertiary care hospital. Most of the benign lesions might have tackled in primary or secondary care hospitals and hence didn t come to the tertiary care level. Chopra, Kapoor reported that the incidence of benign glottic lesions to be 73.14% whereas our study revealed incidence to be 44%. Incidences of hoarseness vary in children. Silverman and Zimmer reported 23.4%, while Yairi et al reported 13%. 14,15 In our study, incidence of hoarseness in children below 9 year was 0.5% and between 10 to 19 year 1.1%. The low incidence can be attributed to screening of cases in primary or secondary care hospitals. According to Singh, vocal cord polyp was the commonest non-neoplastic condition as also reported by Kleinsasser (1982). 16,17 Singh found a male preponderance (66.6%) similar to Kleinsasser s (76%) study. Klenisasser opines that polyps of vocal cords are the most common benign lesions of larynx. Incidence noted as 70% for male and 24% for female. Of these 80-90% were smokers. Many of them reported that they had abused their voice. In our study, incidence is 14.1% with M:F ratio of 16:10. Sinha et al observed 53% incidence for vocal nodules. 18 According to Ghosh et al vocal nodule was the commonest disease of larynx (30%). A comparison of incidence of different laryngeal diseases causing hoarseness in our study with that of Ghosh et al and Baitha et al are given in Table 6, Lundy and Silva found most common incidence as vocal nodules. 19 Chopra and Kapoor observed an incidence of 33.33% for vocal nodules, 16% for vocal polyps and 17.3% for vocal cord cysts. NJ Kay opines that one of the most widely quoted factors associated with vocal nodule in children is vocal International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 359
5 abuse. 20 He found the incidence to be 33%. In our study incidence of vocal abuse is 12.5%. According to Singh et al, laryngeal papilloma constituted 90% of all benign tumours. This is in accordance with the figures (84%) reported by Jones et al. 21 We observed a very low incidence of 2.2%. Reinke s edema was observed to be 9% of cases (Ghosh et al). Singh et al found only 1% of incidence, which is very near to our observation of 1.75%. According to Robin and Olofsson, Reinke s edema comprises about 10% of benign laryngeal lesions. According to James and Blalock, majority of the patients who had functional voice disorders fitted into the category of vocal abuse syndrome. 22 They included patients with vocal nodules, polypoid degeneration, contact ulcers and granulomas in their study. Six separate functional voice disorders were identified. Over all treatment revealed a successful outcome in 69% of cases. We observed an incidence of 6.5% for functional voice disorders. According to Donna, the two most common causes of hoarseness found in 393 patients older than 65 years were vocal cord bowing and unilateral vocal cord palsy followed by benign vocal cord lesions, voice tremors and spasmodic dysphonia. According to British literature, incidence of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy range from 1.5 to 14%. Thyroid surgery was the cause in 16.3% cases. In our study, vocal cord palsy has a M:F distribution of 3:1. Carcinoma esophagus noted as the commonest cause, then carcinoma bronchus. Carcinoma thyroid, post thyroidectomy, cricoarytenoid joint fixation, viral infections were the other major causes. Two cases were found to be idiopathic. Aurebach et al found laryngeal involvement in 37.5% of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. 23 Age of patients were between 20 and 40 years. In our study, laryngeal tuberculous is 1.6%. Ghosh et al noted incidence to be 1% and Baitha found much higher incidence of 5.45%. 3,4 CONCLUSION In our study, incidence of hoarseness during the study period was observed to be 0.7% of all cases attending outpatient wing of Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Government Medical College, Trivandrum which is a tertiary care hospital. Majority of patients were in the group of 30 to 79 years and most commonly affected age group was 50 to 59 years. Hoarseness has a male preponderance of 4:1. Smoking, alcohol intake and vocal abuse are found to be the major etiological factors for hoarseness. Passive smoking is also found to be an etiological factor especially in women and children. Manual labourers constituted the single largest group of patients with hoarseness which may be due to the habit of smoking and alcohol intake. Majority of lesions are malignant in nature. Commonest cause were carcinoma glottis, commonest benign lesion was vocal cord polyp. Vocal cord paralysis was a minor group in the present study. Majority of vocal cord palsy was due to carcinoma esophagus. Commonest premalignant condition for Carcinoma larynx is found to be dysplasia. Early detection of pathology is very important in the management of hoarseness. Microlaryngoscopy is the investigation of choice in the early detection and management of hoarseness. The results of present study very well matches with outcome of the published data for the tertiary care hospitals. Suggested remedial measures include avoidance of risk factors like smoking, alcohol and voice abuse and creation of awareness among public about the ill effects of smoking and alcohol. Screening to be conducted among vulnerable population. Teaching professional voice users about vocal hygiene- avoiding vocal activities such as loud talking, yelling, screaming and habitual throat clearing. Early referral of hoarse patients to otolaryngologist is needed for indirect laryngoscopic examination. Use of specialised diagnostic methods like microlaryngoscopy, stroboscopy, computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are suggested for accurate diagnosis. Increased co-operation between patient, otolaryngologist, speech pathologist, neurologist and gastroenterologist is essential. Prompt and regular follow up of diagnosed cases are essential. To summarise, hoarseness as a symptom should never be meddled with and requires prompt medical attention, failing which may lead to serious consequences. Funding: No funding sources Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram REFERENCES 1. Kataria G, Saxena A, Singh B, Bhagat S, Singh R. Hoarseness of voice: Etiological spectrum Online J Otolaryngol. 2015;5(1): Gaelyn GC, Ossoff RH. Hoarseness. Med. Clin. North Am. 1999;83(1): Baitha S, Raizada RM, Singh AKK, Puttewar MP, Chaturvedi VN. Clinical profile of hoarseness of voice. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;54(1): Ghosh SK, Chattopadhyay S, Bora H, Mukherjee PB. Microlaryngoscopic study of 100 cases of hoarseness of voice. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2001;53(4): Deshmukh. Clinical Study of hoarseness of voice. A thesis submitted for MS (Otorhinolaryngology) Gujarat University; Mehta. An Aetiological study of hoarseness of voice. A thesis submitted for MS (Otorhinolaryngology) Gujarat University Vrat V, Abrol BM, Fande JN. Evaluation of some of the vocal dynamic function tests in laryngeal disease and voice disorders. Indian J of Otolaryngology. 1981;33(1):15-7. International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 360
6 8. Chopra H, Kapoor M. Study of Benign glottic lesions undergoing Microlaryngeal Surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.1997; Robin PE, Jan Olofsson. Tumours of larynx. In- Alan G. Kerr, John Groves, John N. G. Evans John N. G. eds. Scott- Brown s Otolaryngology. 6th ed. 1991;5: Putney, O Keefe. The clinical significance of Keratosis of larynx as a premalignant lesion. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1953;62(2): Norris CM, Peale AR. Keratosis of the Larynx. J. Laryng.1963;77: Hinds MW, Thomas DB, OReilly HP. Asbestos, dental x-rays, tobacco and alcohol in the epidemiology of laryngeal cancer. Cancer. 1979;44: Bailey BJ. In: Johnson JT, Newlands SD, Bailey BJ, eds. Head and Neck Surgery Otolaryngology. 4th ed. Philadelphia; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Silverman EM, Zimmer CH. Incidence of chronic hoarseness among school-age children. J Speech Hear Dis. 1975;40: Yairi E, Duff M, Proctor A. Prevalence of voice disorders in African American and European American preschoolers. J Voice. 2004;18(3): Singh M, Bandyopadhyay S, Gupta SC, Rai A. Benign Laryngeal Lesions - A Clinicopathological study of Eleven Years and a Case Report of Pleomorphic Lipoma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2002;54(3): Kleinsasser O. Pathogenesis of vocal cord polyps. Ann Otol Rhinol.1982;91: Sinha A, Kacker SK, Pramanik KN. Pathology and etiology of vocal nodules. Indian J Otol. 1966;18: Lundy DS, Silva C. Cause of hoarseness in elderly patients. Otolaryngol, Head Neck Surg. 1998;118(4): Kay NJ. Vocal nodules in children aetiology and management J Laryngol Otol. 1992;96: Jones SR, Benign EM. Neoplasms of larynx. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 1984;17: James A, Koufman P. David Blalock. Functional Voice Disorders. OCNA. 1991;24: Auerbach O, Hammond EC, Garfinkel L. Histologic changes in the larynx in relation to smoking habits. Cancer. 1970; 25: Cite this article as: Sindhu BS, Jayaprabha S. A descriptive study of aetiopathological evaluation of hoarseness: our experience. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2018;4: International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery March-April 2018 Vol 4 Issue 2 Page 361
ISSN International Journal of Advanced Research (2016), Volume 4, Issue 2, RESEARCH ARTICLE
 ISSN 2320-5407 International Journal of Advanced Research (206), Volume 4, Issue 2, 227-234 Journal homepage: http://www.journalijar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Hoarseness
ISSN 2320-5407 International Journal of Advanced Research (206), Volume 4, Issue 2, 227-234 Journal homepage: http://www.journalijar.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH RESEARCH ARTICLE Hoarseness
Clinico-etiopathological and management profile of laryngeal tumours in a tertiary care centre
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Pal P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Oct;3(4):913-917 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Pal P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Oct;3(4):913-917 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Journal of Medical Science & Technology
 Page130 Journal of Medical Science & Technology Original Article Open Access Benign Lesions of the Vocal Cords in different ages: prospective Study of 60 Cases Dr. Suliman Saudi 1 1. Senior Specialist
Page130 Journal of Medical Science & Technology Original Article Open Access Benign Lesions of the Vocal Cords in different ages: prospective Study of 60 Cases Dr. Suliman Saudi 1 1. Senior Specialist
Benign Lesions of Larynx A Clinicopathological Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. I (September. 2016), PP 09-17 www.iosrjournals.org Benign Lesions of Larynx A Clinicopathological
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 9 Ver. I (September. 2016), PP 09-17 www.iosrjournals.org Benign Lesions of Larynx A Clinicopathological
Tumours and tumour like lesions of larynx: a clinicopathological study
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kavitha Y et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 May;4(3):794-799 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Kavitha Y et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 May;4(3):794-799 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Stroboscopy: an evolving tool for voice analysis in vocal cord pathologies
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajput SD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Oct;3(4):927-931 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajput SD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Oct;3(4):927-931 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
The Paediatric Voice Clinic
 The Paediatric Voice Clinic Smillie I 1, McManus K 1, Cohen W 2, Wynne D1. Department of Paediatric Otolaryngology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Glasgow. 2 School of Psychological Sciences and Health,
The Paediatric Voice Clinic Smillie I 1, McManus K 1, Cohen W 2, Wynne D1. Department of Paediatric Otolaryngology, Royal Hospital for Sick Children, Glasgow. 2 School of Psychological Sciences and Health,
International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn eissn
 Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 INCIDENCE AND ETIO-PATHOGENESIS OF VOCAL CORD PARALYSIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Natwar
Original research article International Journal of Medical Science and Education pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208 INCIDENCE AND ETIO-PATHOGENESIS OF VOCAL CORD PARALYSIS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL Natwar
Contents. Part A Clinical Evaluation of Laryngeal Disorders. 3 Videostroboscopy and Dynamic Voice Evaluation with Flexible Laryngoscopy...
 Contents Part A Clinical Evaluation of Laryngeal Disorders 1 Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx....... 3 1.1 Anatomy.................................. 3 1.1.1 Laryngeal Cartilages........................
Contents Part A Clinical Evaluation of Laryngeal Disorders 1 Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx....... 3 1.1 Anatomy.................................. 3 1.1.1 Laryngeal Cartilages........................
Management of Hoarseness in Primary Care
 Management of Hoarseness in Primary Care Dr Jeeve Kanagalingam MA (Cantab), BM BCh (Oxon), DLO, DOHNS, FRCS Eng (ORL-HNS), FAMS (ORL) Consultant Department of Otorhinolaryngology TTSH Apr 1, 2010 Straits
Management of Hoarseness in Primary Care Dr Jeeve Kanagalingam MA (Cantab), BM BCh (Oxon), DLO, DOHNS, FRCS Eng (ORL-HNS), FAMS (ORL) Consultant Department of Otorhinolaryngology TTSH Apr 1, 2010 Straits
Correlations between Videostroboscopy and Constant Light Examination with Intraoperative Findings and Histopathology Our Experience
 International Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 2016, 5, 215-227 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijohns ISSN Online: 2168-5460 ISSN Print: 2168-5452 Correlations between Videostroboscopy
International Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, 2016, 5, 215-227 http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijohns ISSN Online: 2168-5460 ISSN Print: 2168-5452 Correlations between Videostroboscopy
Shifts in Relative Prevalence of Laryngeal Pathology in a Treatment-Seeking Population
 Journal of Voice Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 424-440 2001 The Voice Foundation Shifts in Relative Prevalence of Laryngeal Pathology in a Treatment-Seeking Population *Suzanne M. Coyle, Barbara D. Weinrich, and
Journal of Voice Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 424-440 2001 The Voice Foundation Shifts in Relative Prevalence of Laryngeal Pathology in a Treatment-Seeking Population *Suzanne M. Coyle, Barbara D. Weinrich, and
Histopathological study of neoplastic lesions of oral cavity and oropharynx
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta M et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 May;4(5):1506-1510 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161219
(2014) 99 (10) ISSN
 Smillie, Ian and McManus, Kirsy and Cohen, Wendy and Lawson, Elizabeth and Wynne, David MacGregor (2014) The paediatric voice clinic. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 99 (10). pp. 912-915. ISSN 0003-9888,
Smillie, Ian and McManus, Kirsy and Cohen, Wendy and Lawson, Elizabeth and Wynne, David MacGregor (2014) The paediatric voice clinic. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 99 (10). pp. 912-915. ISSN 0003-9888,
LARYNGEAL CANCER AT THE KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL ACCRA GHANA
 LARYNGEAL CANCER AT THE KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL ACCRA GHANA * E.D. KITCHER, J. YARNEY 1, R.K. GYASI 2 AND C. CHEYUO Departments of Surgery and 2 Pathology, University of Ghana Medical School, P O Box
LARYNGEAL CANCER AT THE KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL ACCRA GHANA * E.D. KITCHER, J. YARNEY 1, R.K. GYASI 2 AND C. CHEYUO Departments of Surgery and 2 Pathology, University of Ghana Medical School, P O Box
A clinicopathological study of masses of nasal cavity paranasal sinuses and nasopharynx
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Sharma R et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):253-258 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Sharma R et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):253-258 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Normal Voice. Evaluation of a Patient with Hoarseness. No disclosures. Hoarseness. Assessment. Assessment
 Evaluation of a Patient with Hoarseness No disclosures Mari Hagiwara, MD NYU Langone Medical Center ASHNR 2017 Hoarseness Symptom: any deviation from normal voice quality as perceived by self or others;
Evaluation of a Patient with Hoarseness No disclosures Mari Hagiwara, MD NYU Langone Medical Center ASHNR 2017 Hoarseness Symptom: any deviation from normal voice quality as perceived by self or others;
Hoarseness. Evidence-based Key points for Approach
 Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
Hoarseness Evidence-based Key points for Approach Sasan Dabiri, Assistant Professor Department of otorhinolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Amir A lam hospital Tehran University of Medial Sciences Definition:
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 01 Page January 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.43 Clinicopathological Study of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i1.43 Clinicopathological Study of
Hearing loss following temporal bone fractures- a study on classification of fractures and the prognosis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Maradi N et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):390-394 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Maradi N et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Apr;3(2):390-394 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
ANALYSIS OF SECONDARY NECK NODES IN MALIGNANCIES OF UPPER AERODIGESTIVE TRACT
 CIBTech Journal of Surgery ISSN: 39-3875 (Online) 03 Vol. () May-August, pp.-6/renukananda et al. ANALYSIS OF SECONDARY NECK NODES IN MALIGNANCIES OF UPPER AERODIGESTIVE TRACT Renukananda G.S., Santosh
CIBTech Journal of Surgery ISSN: 39-3875 (Online) 03 Vol. () May-August, pp.-6/renukananda et al. ANALYSIS OF SECONDARY NECK NODES IN MALIGNANCIES OF UPPER AERODIGESTIVE TRACT Renukananda G.S., Santosh
Diagnosis and Management of Hoarseness in Developing Country
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnosis and Management of Hoarseness in Developing Country Waheed Atilade Adegbiji 1, Shuaib Kayode Aremu 2 *, Clement Nwawolo 3, Oyebanji Anthony Olajuyin 1, Fatai Olatoke 4 1 Ekiti
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnosis and Management of Hoarseness in Developing Country Waheed Atilade Adegbiji 1, Shuaib Kayode Aremu 2 *, Clement Nwawolo 3, Oyebanji Anthony Olajuyin 1, Fatai Olatoke 4 1 Ekiti
Hoarseness. Common referral Hoarseness reflects any abnormality of normal phonation
 Hoarseness Kevin Katzenmeyer, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 24, 2001 Hoarseness Common referral
Hoarseness Kevin Katzenmeyer, MD Faculty Advisor: Byron J Bailey, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation October 24, 2001 Hoarseness Common referral
Speech and Language Therapy. Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist
 Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Speech and Language Therapy Kerrie McCarthy Senior Speech and Language Therapist Contents 1. Voice disorders 2. Swallow disorders 3. Videofluroscopy 4. Adult Acquired Communication Disorders 5. How to
Original article Bronchoscopic profile of various diseases in a rural care hospital
 J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer
 Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer Wojciech Golusiński Department of Head and Neck Surgery The Great Poland Cancer Centre, Poznan, Poland Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland Silver
Organ preservation in laryngeal cancer Wojciech Golusiński Department of Head and Neck Surgery The Great Poland Cancer Centre, Poznan, Poland Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland Silver
Case Presentation. Faysal Ghazzay Ahmed
 Faysal Ghazzay Ahmed Case Presentation He is 49 years old male living in Al-Qaem Town (Al-Anbar Gov.), Muslim, and was previously serving in the army, but now he is idle. He was admitted to Al-Jumhoory
Faysal Ghazzay Ahmed Case Presentation He is 49 years old male living in Al-Qaem Town (Al-Anbar Gov.), Muslim, and was previously serving in the army, but now he is idle. He was admitted to Al-Jumhoory
Clinical Policy: Voice Therapy Reference Number: CP.MP.HN 134
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.HN 134 Effective Date: 4/10 Last Review Date: 09/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.HN 134 Effective Date: 4/10 Last Review Date: 09/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
A clinical study of head and neck malignancy in a tertiary hospital
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shetty H et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Oct;1(2):69-74 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Research
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shetty H et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015 Oct;1(2):69-74 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Research
Laryngeal schwannoma - A rarely occurring benign tumor.
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 1.5 2015 Laryngeal schwannoma - A rarely occurring benign tumor. *Nikhil Arora *Kirti Jain *Ramanuj Bansal *Passey JC *Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi Abstract: Neurogenic
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 5 Issue 1.5 2015 Laryngeal schwannoma - A rarely occurring benign tumor. *Nikhil Arora *Kirti Jain *Ramanuj Bansal *Passey JC *Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi Abstract: Neurogenic
Dr Sabah Mohammed Hassan. Consultant Phoniatrician
 Consultant Phoniatrician King Abul Aziz University Hospital King Saud University Non-organic (Functional)Voice Disorders Introduction Etiological Classification Of Voice Disorders: 1-Organic. 2- Non-Organic
Consultant Phoniatrician King Abul Aziz University Hospital King Saud University Non-organic (Functional)Voice Disorders Introduction Etiological Classification Of Voice Disorders: 1-Organic. 2- Non-Organic
Pleomorphic adenoma of submandibular gland: not so common occurrence
 International Surgery Journal Gajbhiye AS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Feb;5(2):657-661 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20180371
International Surgery Journal Gajbhiye AS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Feb;5(2):657-661 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20180371
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Diagnostic Contributions of Videolaryngostroboscopy in the Pediatric Population
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic Contributions of Videolaryngostroboscopy in the Pediatric Population Melissa Mortensen, MD; Madeline Schaberg, MD; Peak Woo, MD Objective: Videolaryngostroboscopy (VLS) is a
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic Contributions of Videolaryngostroboscopy in the Pediatric Population Melissa Mortensen, MD; Madeline Schaberg, MD; Peak Woo, MD Objective: Videolaryngostroboscopy (VLS) is a
Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses
 Original article Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses 1Dr. Seema Bijjaragi, 2 Dr Vardendra G. Kulkarni, 3 Dr. Japji Singh 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of
Original article Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses 1Dr. Seema Bijjaragi, 2 Dr Vardendra G. Kulkarni, 3 Dr. Japji Singh 1,2 Assistant Professor, Department of
Prevalence of Head and Neck Cancer in the State of Meghalaya: Hospital-based Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1127 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence of Head and Neck Cancer in the State of Meghalaya: Hospital-based Study Neizekhotuo Brian Shunyu, Judita Syiemlieh ABSTRACT In India, 20 to 40%
10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1127 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence of Head and Neck Cancer in the State of Meghalaya: Hospital-based Study Neizekhotuo Brian Shunyu, Judita Syiemlieh ABSTRACT In India, 20 to 40%
Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses
 Original article Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses 1Dr. Seema Bijjaragi, 2 Dr Vardendra G. Kulkarni, 3 Dr. Japji Singh 1Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor,
Original article Histomorphological study of polypoidal lesions of nose and paranasal sinuses 1Dr. Seema Bijjaragi, 2 Dr Vardendra G. Kulkarni, 3 Dr. Japji Singh 1Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor,
Histological correlation of nasal mass: a five year retrospective and prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Panchonia A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2014 Aug;2(3):842-846 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140805
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Panchonia A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2014 Aug;2(3):842-846 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140805
Benign Lesions of the Vocal Folds
 Benign Lesions of the Vocal Folds Noah Meltzer, M.D. Zandy Hillel, M.D. December 14, 2007 Learning Objectives 1) Review the presentation, pathophysiology, and stroboscopic exams of benign vocal fold lesions.
Benign Lesions of the Vocal Folds Noah Meltzer, M.D. Zandy Hillel, M.D. December 14, 2007 Learning Objectives 1) Review the presentation, pathophysiology, and stroboscopic exams of benign vocal fold lesions.
General Concepts - Why
 Surgery for Benign Laryngeal Disease: When and How General Concepts - When Surgery should never be the initial treatment option Only when there is persistent troublesome dysphonia after completing work
Surgery for Benign Laryngeal Disease: When and How General Concepts - When Surgery should never be the initial treatment option Only when there is persistent troublesome dysphonia after completing work
Sunshine Act Disclosure
 A Laryngologist s Approach to Voice Presentation at the Nebraska Speech- Language-Hearing Association Fall Convention Thursday, September 27, 2018 15:45-16:45 Christopher M. Bingcang, MD Assistant Professor
A Laryngologist s Approach to Voice Presentation at the Nebraska Speech- Language-Hearing Association Fall Convention Thursday, September 27, 2018 15:45-16:45 Christopher M. Bingcang, MD Assistant Professor
Chorus Study Guide Unit 1: Know Thy Voice
 Chorus Study Guide Unit 1: Know Thy Voice INSTRUCTOR: Mrs. DJ Ross Djuana.Ross@charlottelearningacademy.org Please study notes below in preparation for the unit test. www.nidcd.nih.gov Structures involved
Chorus Study Guide Unit 1: Know Thy Voice INSTRUCTOR: Mrs. DJ Ross Djuana.Ross@charlottelearningacademy.org Please study notes below in preparation for the unit test. www.nidcd.nih.gov Structures involved
T1/T2 LARYNX CANCER. Click to edit Master Presentation Date. Thomas J Gernon, MD Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery
 ADVANCES IN TREATMENT OF T1/T2 LARYNX CANCER Click to edit Master Presentation Date Thomas J Gernon, MD Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery I have nothing to disclose CHANGING TRENDS IN HNSCC GLOTTIC
ADVANCES IN TREATMENT OF T1/T2 LARYNX CANCER Click to edit Master Presentation Date Thomas J Gernon, MD Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery I have nothing to disclose CHANGING TRENDS IN HNSCC GLOTTIC
Pattern of oral lesions Cytohistopathological study in tertiary care centre.
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 P-ISJN: A4372-3064, E -ISJN: A4372-3061 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume 3, Issue 10-2017 Pattern of oral lesions
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
A Study of Thyroid Swellings and Correlation between FNAC and Histopathology Results
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 265-269 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.030
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 4 (2017) pp. 265-269 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.604.030
Laryngeal cancer: a clinicopathological study of 65 cases
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chauhan JPS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):163-168 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chauhan JPS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jan;4(1):163-168 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
A descriptive study on solitary nodular goitre
 Original Research Article A descriptive study on solitary nodular goitre T. Chitra 1*, Dorai D. 1, Aarthy G. 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Post Graduate Department of General Surgery, Govt. Stanley Medical
Original Research Article A descriptive study on solitary nodular goitre T. Chitra 1*, Dorai D. 1, Aarthy G. 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Post Graduate Department of General Surgery, Govt. Stanley Medical
HPV-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cancers
 2015 Wisconsin Comprehensive Cancer Control Summit Aligning Partners, Priorities, and the Plan HPV-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cancers MCW Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences MCW
2015 Wisconsin Comprehensive Cancer Control Summit Aligning Partners, Priorities, and the Plan HPV-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cancers MCW Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences MCW
CASE STUDIES CONTENTS PART REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7. fiabit COUGH, 15 MUSCLE TENSION DYSPHONIA, 18 PUBERPHONIA, 33
 CONTENTS PART I CASE STUDIES REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 CASE STUDY 1-1: Postoperative Reinke's Edema, 4 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7 CASE STUDY 2-1: Vocal Cord Dysfunction, 8 CASE STUDY 2-2: Vocal Cord Dysfunction,
CONTENTS PART I CASE STUDIES REINKE' S EDEMA, 3 CASE STUDY 1-1: Postoperative Reinke's Edema, 4 VOCAL CORD DYSFUNCTION, 7 CASE STUDY 2-1: Vocal Cord Dysfunction, 8 CASE STUDY 2-2: Vocal Cord Dysfunction,
Case Presentation JC: 65 y/o retired plumber CC: Hoarseness HPI: Admitted to a local hospital on May 30 for severe pneumonia. Intubated in ICU for 10
 GBMC Stroboscopy Rounds October 12, 2007 Case Presentation JC: 65 y/o retired plumber CC: Hoarseness HPI: Admitted to a local hospital on May 30 for severe pneumonia. Intubated in ICU for 10 days, total
GBMC Stroboscopy Rounds October 12, 2007 Case Presentation JC: 65 y/o retired plumber CC: Hoarseness HPI: Admitted to a local hospital on May 30 for severe pneumonia. Intubated in ICU for 10 days, total
Patterns in the Evaluation of Hoarseness: Time to Presentation, Laryngeal Visualization, and Diagnostic Accuracy
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Patterns in the Evaluation of Hoarseness: Time to Presentation, Laryngeal Visualization, and Diagnostic Accuracy
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Patterns in the Evaluation of Hoarseness: Time to Presentation, Laryngeal Visualization, and Diagnostic Accuracy
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue Among Young Indian Adults
 BRIEF ARTICLE, pp. 273 277 www.nature.com/neo Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue Among Young Indian Adults 273 Elizabeth Mathew Iype*, Manoj Pandey*, Aleyamma Mathew y, Gigi Thomas z, Paul Sebastian*
BRIEF ARTICLE, pp. 273 277 www.nature.com/neo Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Tongue Among Young Indian Adults 273 Elizabeth Mathew Iype*, Manoj Pandey*, Aleyamma Mathew y, Gigi Thomas z, Paul Sebastian*
A CLINICAL CORRELATION OF OCULAR ADNEXAL TUMOURS IN RELATION TO FNAC AND HISTOPATHOLOGY
 A CLINICAL CORRELATION OF OCULAR ADNEXAL TUMOURS IN RELATION TO FNAC AND HISTOPATHOLOGY Gautam Paul 1, Pranab Chakraborty 2, Abhisek Mondal 3, Mamata Naiding 4 1Senior Assistant Professor, Department of
A CLINICAL CORRELATION OF OCULAR ADNEXAL TUMOURS IN RELATION TO FNAC AND HISTOPATHOLOGY Gautam Paul 1, Pranab Chakraborty 2, Abhisek Mondal 3, Mamata Naiding 4 1Senior Assistant Professor, Department of
Chronic Cough. Dr Peter George Consultant Respiratory Physician Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals
 Chronic Cough Dr Peter George Consultant Respiratory Physician Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals Overview Common causes of chronic cough Important diagnoses not to miss How to investigate a cough
Chronic Cough Dr Peter George Consultant Respiratory Physician Royal Brompton and Harefield Hospitals Overview Common causes of chronic cough Important diagnoses not to miss How to investigate a cough
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Salvage Surgery After Failure of Nonsurgical Therapy for Carcinoma of the Larynx and Hypopharynx
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Salvage Surgery After Failure of Nonsurgical Therapy for Carcinoma of the Larynx and Hypopharynx Sandro J. Stoeckli, MD; Andreas B. Pawlik, MD; Margareta Lipp, MD; Alexander Huber, MD;
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Salvage Surgery After Failure of Nonsurgical Therapy for Carcinoma of the Larynx and Hypopharynx Sandro J. Stoeckli, MD; Andreas B. Pawlik, MD; Margareta Lipp, MD; Alexander Huber, MD;
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Allergic rhinitis in India: an overview
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chandrika D. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 217 Jan;3(1):1-6 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 244-929 eissn 244-937 Review Article
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Chandrika D. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 217 Jan;3(1):1-6 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 244-929 eissn 244-937 Review Article
Flexible Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy: diagnostic yield
 Original Article ABSTRACT Flexible Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy: diagnostic yield Zafar Iqbal, Mohammad Zafar Rabbani, Muhammad Jawad Zafar Objective To examine the diagnostic effectiveness of the Flexible
Original Article ABSTRACT Flexible Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy: diagnostic yield Zafar Iqbal, Mohammad Zafar Rabbani, Muhammad Jawad Zafar Objective To examine the diagnostic effectiveness of the Flexible
USE OF POWERED INSTRUMENTATION IN MICROLARYNGEAL SURGERY: A CLINICAL STUDY T. Shankar 1, Benjamin Rajendra Kumar 2
 USE OF POWERED INSTRUMENTATION IN MICROLARYNGEAL SURGERY: A CLINICAL STUDY T. Shankar 1, Benjamin Rajendra Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: T. Shankar, Benjamin Rajendra Kumar. Use of Powered Instrumentation
USE OF POWERED INSTRUMENTATION IN MICROLARYNGEAL SURGERY: A CLINICAL STUDY T. Shankar 1, Benjamin Rajendra Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: T. Shankar, Benjamin Rajendra Kumar. Use of Powered Instrumentation
After reviewing this module, the student will have the ability to: - Create a broad differential diagnosis for the hoarse patient
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reviewing this module, the student will have the ability to: - Create a broad differential diagnosis for the hoarse patient - Describe the most common causes and the most concerning
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After reviewing this module, the student will have the ability to: - Create a broad differential diagnosis for the hoarse patient - Describe the most common causes and the most concerning
Carcinoma of the Larynx in Malaysia
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 47 NoA December 1992 Carcinoma of the Larynx in Malaysia A. Sani, MS(Orl) H. Said, FRCS S. Lokman, FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 47 NoA December 1992 Carcinoma of the Larynx in Malaysia A. Sani, MS(Orl) H. Said, FRCS S. Lokman, FRCS Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan
Mohamed Farahat Ibrahim, MD, PhD
 Mohamed Farahat Ibrahim, MD, PhD Consultant, Assistant Professor Phoniatrics (Communication and Swallowing Disorders) Deputy chairman, Communication and Swallowing Disorders Unit (CSDU) King Abdulaziz
Mohamed Farahat Ibrahim, MD, PhD Consultant, Assistant Professor Phoniatrics (Communication and Swallowing Disorders) Deputy chairman, Communication and Swallowing Disorders Unit (CSDU) King Abdulaziz
Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute of health sciences, Dharan, Nepal: A five-year study
 ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 2(12) pp. 122-127 January 2013 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2013 Basic Research Journal Full Length Research Paper Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute
ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 2(12) pp. 122-127 January 2013 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2013 Basic Research Journal Full Length Research Paper Cancer profile in B.P. Koirala institute
Learning objectives Describe anatomically and clinically the di ifference between laryngeal cancer and hypopharyngeal cancer Be able to describe clini
 Laryngeal cancer Hanwei PENG, MD, PhD Thyroid Surgery Research Center, SU UMC Head and Neck Department, Cancer Hospital, SUMC Learning objectives Describe anatomically and clinically the di ifference between
Laryngeal cancer Hanwei PENG, MD, PhD Thyroid Surgery Research Center, SU UMC Head and Neck Department, Cancer Hospital, SUMC Learning objectives Describe anatomically and clinically the di ifference between
A Reflection on Voice Care for Teachers
 MENU PRINT VERSION HELP & FAQS A Reflection on Voice Care for Teachers Fiona Eastley Doshisha University A teacher s voice is probably their most valued possession, but most teachers are unaware of the
MENU PRINT VERSION HELP & FAQS A Reflection on Voice Care for Teachers Fiona Eastley Doshisha University A teacher s voice is probably their most valued possession, but most teachers are unaware of the
Causes of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis
 Auris Nasus Larynx 29 (2002) 41 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/anl Causes of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis Eiji Yumoto a, *, Ryosei Minoda a, Masamitsu Hyodo b, Takahiko Yamagata b a Department of Otolaryngology-Head
Auris Nasus Larynx 29 (2002) 41 45 www.elsevier.com/locate/anl Causes of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis Eiji Yumoto a, *, Ryosei Minoda a, Masamitsu Hyodo b, Takahiko Yamagata b a Department of Otolaryngology-Head
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 2, March 2014
 INCIDENCE OF PRIMARY HEAD AND NECK CANCERS AT B K L W HOSPITAL & RURAL MEDICAL COLLEGE, A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE IN KONKAN, MAHARASHTRA RAJASHREE A KULKARNI* MAHESH S PATIL** *Assistant Professor, Dept.
INCIDENCE OF PRIMARY HEAD AND NECK CANCERS AT B K L W HOSPITAL & RURAL MEDICAL COLLEGE, A TERTIARY CARE CENTRE IN KONKAN, MAHARASHTRA RAJASHREE A KULKARNI* MAHESH S PATIL** *Assistant Professor, Dept.
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G)
 CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
CURRICULLUM OF ENT (U.G) OBJECTIVES: 1. To enable the student to familiarize himself with the common problems related to the subject of ENT. 2. To enable the student to be competent to evaluate the symptoms,
A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy
 Original Research Article A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy R. Maheshwari 1*, Rakesh Fernando 2 1 Professor, 2 Assistant Professor Department of General Surgery, Tirunelveli Medical
Original Research Article A Clinicopathological study on Cervical Lymphadenopathy R. Maheshwari 1*, Rakesh Fernando 2 1 Professor, 2 Assistant Professor Department of General Surgery, Tirunelveli Medical
Comparison between Voice Handicap Index and Voice Symptom Scale by Subjective Analysis of Voice Disorders
 Comparison between Voice Handicap Index and Voice Symptom Scale by 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1153 Subjective Analysis of Voice Disorders ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between Voice Handicap Index and Voice
Comparison between Voice Handicap Index and Voice Symptom Scale by 10.5005/jp-journals-10023-1153 Subjective Analysis of Voice Disorders ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between Voice Handicap Index and Voice
Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases
 FIBEROPTIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY MEDICAL JOURNAL Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases Ragheed Turky Miteab ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: In
FIBEROPTIC THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY MEDICAL JOURNAL Accuracy of Fiberoptic Nasopharyngoscopy in the Diagnosis of Pharyngolaryngeal Diseases Ragheed Turky Miteab ABSTRACT: BACKGROUND: In
Permanent tracheostomy: Its social impacts and their management in Ondo State, Southwest, Nigeria
 Original Article Permanent tracheostomy: Its social impacts and their management in Ondo State, Southwest, Nigeria MI Akenroye, AT Osukoya Departments of Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgery, State
Original Article Permanent tracheostomy: Its social impacts and their management in Ondo State, Southwest, Nigeria MI Akenroye, AT Osukoya Departments of Ear, Nose and Throat Head and Neck Surgery, State
Clinical Discussion. Dr Pankaj Chaturvedi. Professor and Surgeon Tata Memorial Hospital
 Clinical Discussion Dr Pankaj Chaturvedi Professor and Surgeon Tata Memorial Hospital chaturvedi.pankaj@gmail.com 47/M/smoker Hopkins : Transglottic lesion No cartilage infiltration but sclerosis Left
Clinical Discussion Dr Pankaj Chaturvedi Professor and Surgeon Tata Memorial Hospital chaturvedi.pankaj@gmail.com 47/M/smoker Hopkins : Transglottic lesion No cartilage infiltration but sclerosis Left
ISPUB.COM. A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar INTRODUCTION MATERIAL AND METHOD
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Spectrum Of Cytological Findings In Patients With Lymphadenopathy In Rural Population Of Southern A Kochhar, G Duggal, K Singh, S Kochhar
What is head and neck cancer? How is head and neck cancer diagnosed and evaluated? How is head and neck cancer treated?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that start in the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, salivary glands, nasal cavity or paranasal sinuses. They usually begin
Ramesh P. M.*, Saravanan M.
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Ramesh PM et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Jun;5(3):561-565 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20181663
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Ramesh PM et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Jun;5(3):561-565 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20181663
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
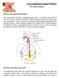 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Voice. What is voice? Why is voice important?
 Voice What is voice? Voice is the sound that we hear when someone talks. It is produced by air coming from the diaphragm and lungs passing through the voice box (vocal folds) causing them to vibrate and
Voice What is voice? Voice is the sound that we hear when someone talks. It is produced by air coming from the diaphragm and lungs passing through the voice box (vocal folds) causing them to vibrate and
Why Can t I breathe? Asthma vs. Vocal Cord Dysfunction (VCD) Lindsey Frohn, M.S., CCC-SLP Madonna Rehabilitation Hospital (Lincoln, NE)
 Why Can t I breathe? Asthma vs. Vocal Cord Dysfunction (VCD) Lindsey Frohn, M.S., CCC-SLP Madonna Rehabilitation Hospital (Lincoln, NE) Objectives Examine Vocal Cord Dysfunction Examine Exercise Induced
Why Can t I breathe? Asthma vs. Vocal Cord Dysfunction (VCD) Lindsey Frohn, M.S., CCC-SLP Madonna Rehabilitation Hospital (Lincoln, NE) Objectives Examine Vocal Cord Dysfunction Examine Exercise Induced
Head and Neck Cancer. What is head and neck cancer?
 Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Scan for mobile link. Head and Neck Cancer Head and neck cancer is a group of cancers that usually originate in the squamous cells that line the mouth, nose and throat. Typical symptoms include a persistent
Clinicopathological study of cervical lymphadenopathy at rural tertiary health care centre
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Paikrao YM et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Feb;5(1):154-158 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20180076
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Paikrao YM et al. Int J Adv Med. 2018 Feb;5(1):154-158 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20180076
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
Poor Outcomes in Head and Neck Non-Melanoma Cutaneous Carcinomas
 10 The Open Otorhinolaryngology Journal, 2011, 5, 10-14 Open Access Poor Outcomes in Head and Neck Non-Melanoma Cutaneous Carcinomas Kevin C. Huoh and Steven J. Wang * Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology,
10 The Open Otorhinolaryngology Journal, 2011, 5, 10-14 Open Access Poor Outcomes in Head and Neck Non-Melanoma Cutaneous Carcinomas Kevin C. Huoh and Steven J. Wang * Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology,
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology. ENT Specialty Programs
 Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
Department of Pediatric Otolarygnology ENT Specialty Programs Staffed by fellowship-trained otolaryngologists, assisted by pediatric nurse practitioners, ENT (Otolaryngology) at Nationwide Children s Hospital
HOARSENESS. Prevention and types of treatment
 HOARSENESS Prevention and types of treatment What is hoarseness? What are the causes of hoarseness? How is hoarseness evaluated? When do I need to seek specialized medical evaluation? What are the treatments
HOARSENESS Prevention and types of treatment What is hoarseness? What are the causes of hoarseness? How is hoarseness evaluated? When do I need to seek specialized medical evaluation? What are the treatments
Fig year-old man with bilateral glottic cancer with subglottic extensions.
 245 A B Fig. 1. 64-year-old man with bilateral glottic cancer with subglottic extensions. Axial scans at the level of the glottis (A) shows bilateral soft tissue masses protruding into the lumen. Bilateral
245 A B Fig. 1. 64-year-old man with bilateral glottic cancer with subglottic extensions. Axial scans at the level of the glottis (A) shows bilateral soft tissue masses protruding into the lumen. Bilateral
Laryngoscopy Examinations
 Laryngoscopy Examinations Laryngoscopy is a visual examination of the back of the throat where the voice box (larynx) and vocal cords are located. The procedure is done by using hand mirrors and a light
Laryngoscopy Examinations Laryngoscopy is a visual examination of the back of the throat where the voice box (larynx) and vocal cords are located. The procedure is done by using hand mirrors and a light
Wojciech K. Mydlarz, M.D. Pharyngocutaneous Fistulas after Salvage Laryngectomy: Need for Vascularized Tissue
 Wojciech K. Mydlarz, M.D. Pharyngocutaneous Fistulas after Salvage Laryngectomy: Need for Vascularized Tissue Disclosures No Relevant Financial Relationships or Commercial Interests Educational Objectives
Wojciech K. Mydlarz, M.D. Pharyngocutaneous Fistulas after Salvage Laryngectomy: Need for Vascularized Tissue Disclosures No Relevant Financial Relationships or Commercial Interests Educational Objectives
NECK MASS. Clinical history and examination: Document detail history of mass. Imaging: US or CT of neck
 ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
ENT ENT Referral Referral Guidelines Guidelines Austin Health ENT Clinic holds fortnightly multidisciplinary meetings with Plastics/ Maxillary Facial and Oncology units to discuss and plan the treatment
BILATERAL ABDUCTOR VOCAL CORD PALSY. Dr NITYA G Final year PG KIMS
 BILATERAL ABDUCTOR VOCAL CORD PALSY Dr NITYA G Final year PG KIMS INTRODUCTION Vocal cord paralysis is a sign of a disease It results from dysfunction of Recurrent laryngeal nerves on both sides Paralysis
BILATERAL ABDUCTOR VOCAL CORD PALSY Dr NITYA G Final year PG KIMS INTRODUCTION Vocal cord paralysis is a sign of a disease It results from dysfunction of Recurrent laryngeal nerves on both sides Paralysis
Original Research Article LARYNGEAL POLYPOSIS; A NEWLY INTRODUCED ENTITY: UPDATE
 Original Research Article LARYNGEAL POLYPOSIS; A NEWLY INTRODUCED ENTITY: UPDATE Introduction Abstract Vocal fold polyps are caused by inflammation caused by stress or irritation. Laryngeal polyp may be
Original Research Article LARYNGEAL POLYPOSIS; A NEWLY INTRODUCED ENTITY: UPDATE Introduction Abstract Vocal fold polyps are caused by inflammation caused by stress or irritation. Laryngeal polyp may be
Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults
 Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Annual Refresher Course for
Evaluation of Head and Neck Masses in Adults Kristi Chang, MD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Annual Refresher Course for
Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology Grading
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Laryngoscopic Characteristics in Vocal Leukoplakia: Inter-rater Reliability and Correlation With Histology
Microlaryngoscopy: A Guide to the Management of Laryngeal Pathologies
 IJCMR 844 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Microlaryngoscopy: A Guide to the Management of Laryngeal Pathologies Pradip Kumar Tiwari 1, Debajit Das 2 ABSTRACT Intoduction: Dysphonia is the main symptom of lesions that
IJCMR 844 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Microlaryngoscopy: A Guide to the Management of Laryngeal Pathologies Pradip Kumar Tiwari 1, Debajit Das 2 ABSTRACT Intoduction: Dysphonia is the main symptom of lesions that
International Journal of Infectious Diseases
 International Journal of Infectious Diseases 14 (2010) e230 e235 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Infectious Diseases journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ijid Changing
International Journal of Infectious Diseases 14 (2010) e230 e235 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Infectious Diseases journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ijid Changing
Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide. Effective January 1, 2009
 Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide Transnasal Esophagoscopy Laryngeal Sensory Testing FEES FEEST Transnasal Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy Stroboscopy Disposable Sheaths Effective January
Medtronic ENT Transnasal Endoscopic Procedures Coding Guide Transnasal Esophagoscopy Laryngeal Sensory Testing FEES FEEST Transnasal Fiberoptic Laryngoscopy Stroboscopy Disposable Sheaths Effective January
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3
 PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
PROFILE OF PAEDIATRIC PATIENTS WITH CERVICAL LYMPHADENOPATHY: A STUDY FROM CENTRAL INDIA Jharna Mishra 1, M. Maheshwari 2, Roshan Chanchlani 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Jharna Mishra, M. Maheshwari, Roshan
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary
 Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
Management of Neck Metastasis from Unknown Primary.. Definition Histologic evidence of malignancy in the cervical lymph node (s) with no apparent primary site of original tumour Diagnosis after a thorough
University of Groningen. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus
 University of Groningen Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis Tjon-Pian-Gi, Robin Edward Adrianus IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL
 STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL S. Venkataramana Rao 1, V. S. Sharma 2, M. V. Subba Rao 3, B. J. Prasad 4, Kalyan 5, Pravin Tez 6, Vijay Kumar 7, G. S. Keerthi 8 1Professor,
STUDY OF VARIOUS CAUSES OF FACIAL PALSY AND ITS MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL S. Venkataramana Rao 1, V. S. Sharma 2, M. V. Subba Rao 3, B. J. Prasad 4, Kalyan 5, Pravin Tez 6, Vijay Kumar 7, G. S. Keerthi 8 1Professor,
