Cognitive functioning and well-being in euthyroid patients on thyroxine replacement therapy for primary hypothyroidism
|
|
|
- Iris Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Endocrinology (2005) ISSN CLINICAL STUDY Cognitive functioning and well-being in euthyroid patients on thyroxine replacement therapy for primary hypothyroidism Ellie M Wekking, Bente C Appelhof 1, Eric Fliers 1, Aart H Schene, Jochanan Huyser, Jan G P Tijssen 2 and Wilmar M Wiersinga 1 Department of Psychiatry, 1 Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, and 2 Department of Cardiology, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (Correspondence should be addressed to E M Wekking; ewekking@fsw.leidenuniv.nl) E M Wekking is now at Leiden University, Departments of Psychology, Neurology and Neuropsychology, PO Box 9555, 2300 RB Leiden, The Netherlands Abstract Objective: Hypothyroidism is associated with neurocog.nitive impairment. Sparse data suggest that treatment of hypothyroidism, resulting in a return to euthyroidism, may be associated with only partial recovery of overall neurocognitive functioning. The aim of this study was to assess neurocognitive functioning and well-being in euthyroid patients with primary hypothyroidism on adequate thyroxine (T4) treatment. We also investigated whether serum TSH and thyroid antibodies are determinants of neurocognitive functioning and well-being. Design: We assessed neurocognitive functioning and well-being in 141 patients with primary hypothyroidism. Methods: Neurocognitive test results and scores on questionnaires measuring well-being of 141 patients were compared with the reference values for these tests as published and used in Dutch clinical neuropsychological practice. Assessment of neurocognitive functioning included tests for cognitive or psychomotor speed, attention, working memory as well as learning and memory. Well-being was measured with the Symptom Check List-90 total score and the Rand 36-item Health Survey subscales for mental health and vitality. Results: Patients showed poor performance on various domains of neurocognitive functioning compared with mean standard reference values, especially on a complex attention task and on verbal memory tests. Levels of well-being were significantly lower for patients compared with those of the general population. Neither serum TSH nor thyroid antibodies were determinants of neurocognitive functioning and well-being. Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that neurocognitive functioning as well as psychological well-being may not be completely restored in patients with hypothyroidism, despite T4 treatment. European Journal of Endocrinology Introduction Overt hypothyroidism is associated with deficits in general intelligence, memory, attention, psychomotor speed, visuoperceptual and constructional skills (1). Thyroxine (T4) replacement therapy is the standard treatment of hypothyroidism that appears effective in restoring biochemical euthyroidism as evidenced by serum thyrotropin (TSH), and free T4 and triiodothyronine (T3) concentrations within the normal range. Although hormonal substitution therapy has been very successful in reducing morbidity and mortality of primary hypothyroidism, it is well known in clinical practice that a minority of patients have persistent symptoms despite adequate T4 replacement therapy. These are often vague, aspecific complaints about fatigue, muscle aches, depressed mood or decreased memory function. A recent community study (2) provided the first evidence to indicate that patients on thyroxine replacement even those with a normal serum TSH display significant impairment in psychological well-being compared with controls of similar age and sex. These findings raise the question whether neurocognitive functioning in T4-treated hypothyroid patients might also be impaired. A review of neurocognitive aspects of hypothyroidism suggested that successful treatment of hypothyroidism might be associated with only partial and typically inconsistent patterns of recovery of overall neurocognitive functioning (1). However, this conclusion was reached from only a few studies on neurocognitive functioning carried out q 2005 Society of the European Journal of Endocrinology DOI: /eje Online version via
2 748 E M Wekking and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) 153 shortly after re-establishing euthyroidism with thyroid replacement therapy in hypothyroid patients. In 1969, Whybrow et al. reported on four such patients, and concluded that when the hypothyroidism had been long-standing, brain impairment persisted after thyroid replacement therapy (3). Osterweil et al. reported on neurocognitive functioning of 54 patients with overt or minimal hypothyroidism (4). A subset of 11 to 34 patients was available for neurocognitive retesting. It was concluded that the deleterious effect of hypothyroidism is at least partly reversible, but possibly not completely, as some test results remained significantly impaired compared with euthyroid controls without hypothyroidism (4). A single case report by Mennemeier et al. reported similar conclusions (5). As almost no data are available concerning neurocognitive functioning of patients with T4-treated hypothyroidism, we investigated the level of cognitive functioning in a large group of Dutch patients, all adequately treated for primary autoimmune hypothyroidism, and compared the results with the normal reference values for these tests. This is the first study to evaluate neurocognitive functioning after long-standing T4 therapy (median duration of substitution therapy 5.5 years). Secondly, we investigated whether psychological well-being in this patient group differs from healthy subjects. Finally, we examined whether serum TSH or thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO-ab) are determinants of neurocognitive performance and well-being. Subjects and methods Subjects Patients were recruited from 13 general practices in the cities of Amsterdam and Almere. At these practices, prescribing records were checked to identify all patients receiving levothyroxine (T4) treatment. After checking for exclusion criteria, patients eligible for participation were invited by letter to participate in the study. All patients were between 18 and 70 years of age and had been on T4 replacement therapy for primary autoimmune hypothyroidism for at least 6 months. At inclusion, all patients were on an adequate dose of T4 as evidenced by a serum TSH concentration between 0.11 and 4.0 mu/l, as measured in the morning before levothyroxine intake. The lower end of this TSH interval was chosen because TSH levels of 0.10 mu/l or lower are associated with a higher risk of atrial fibrillation and bone loss, suggesting a too high T4 replacement dose. One hundred and fortyone patients participated in the study. This study was carried out between October 2001 and December 2003 at the Academic Medical Center of the University of Amsterdam. The protocol was approved by the institutional ethics review committee and all patients provided written informed consent. For more details see Appelhof et al. (6). Study design Patients arrived in the morning in a fasting state. After blood sampling, patients took their usual dose of levothyroxine and had breakfast at the Academic Medical Center. About one hour later they proceeded with the neurocognitive testing session that lasted for approximately 1.5 h, and handed over the baseline set of questionnaires that they had filled out on the day prior to the visit. Neurocognitive tests Assessment of neurocognitive functioning included neuropsychological domains that are believed to be affected in hypothyroid patients (7) and consisted of tests for cognitive or psychomotor speed, attention, working memory as well as learning and memory. Cognitive or psychomotor speed was measured by the following tests. (1) The Dutch adaptation of the Digit Symbol subtest (8, 9) in which patients are presented with a key that pairs digits to geometrical symbols. Subsequently, patients are presented with a string of symbols and are required to pair each symbol with the correct digit, using the key, during 90 s. The raw score consists of the total number of correctly completed entries. The score is transformed into a standard value based on a normative population (n ¼ 745) with a score range from 1 to 19, with a mean of 10 and a standard deviation (S.D.) of 3. (2) The Memory Comparison Task, paper and pencil version (MCT) (10). During this task patients have to memorize visually presented target letters. Subsequently, they have to detect these on a paper amongst other non-target letters and strike out the target letter(s). The test consists of an example-task (%) and 4 subtasks with increasing memory load (1, 2, 3 or 4 letters to memorize). The time in seconds needed to complete the respective subtasks is measured. Attention was measured by the Dutch adaptation of the Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task (PASAT) (11, 12). In this task, tape-recorded one digit numbers are presented in different blocks of 60 items at different rates. The test consists of 5 blocks with decreasing interstimulus intervals. Patients are required to add every pair of successive numbers and immediately give the addition sum. The total number of correct answers, calculated over all 5 blocks, is scored (13). Working memory was measured by the Digit Span subtest (WAIS-III) (8, 9) in which the patient is required to repeat spoken digit series in the same order (forward recall) or in reverse order (backward recall). With each series, the number of digits increases. The total score consists of the total number of correctly repeated digits of both the forward and backward tests. The total score is converted into a standard score in the same manner as for the Digit Symbol test (8).
3 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) 153 Learning and memory were tested by the following tests. (1) The Dutch adaptation of the California Verbal Learning Test (CVLT) (14). A shopping list is presented orally 5 successive times. The outcome measures include (a) the total number of items correctly recalled after 5 successive trials (immediate recall), (b) the number of items recalled after a 20-min delay (delayed recall) and finally (c) the number of items correctly identified amongst distracting items (recognition). These three scores are transformed into a standard value with a mean of zero and a S.D. of 2 based on the Dutch CLVTreference group (14). (2) The Dutch version of the Rivermead Behavioral Memory Test, Story Recall (Rivermead, stories) (15, 16). Patients have to repeat two short stories immediately after oral presentation and after a 20-min delay. The sum of the correctly recalled elements of the two stories is calculated, both for the immediate recall as well as for the delayed recall. In addition, the ratio of the delayed recall relative to the immediate recall is calculated (relative delayed recall). The raw scores are converted into standard scores (T-scores, mean ¼ 50, S.D. ¼ 10) (17). All tests are widely used and internationally accepted (18), or have previously been used in earlier research on neurocognitive functioning in hypothyroid patients before and after combined therapy with T4 and T3 (MCT, paper and pencil version, also known as visual scanning test) (19). The tests were administered by a trained psychometrician, under the supervision of a clinical neuropsychologist (E W). All investigations were carried out once in each patient. Raw test scores, except for the PASAT, are corrected for education, age and gender if these variables in the reference groups proved to be relevant, and converted into standard scores. The PASAT score is corrected only for education. Finally, all test scores of the T4-treated hypothyroid patients were compared with the scores in the reference groups, thus following the standard procedure in Dutch clinical neuropsychological practice. Questionnaires Well-being was measured by means of self-report questionnaires, filled out on the day prior to the study visit and included the (Dutch version of) the Symptom Checklist (SCL-90) (20) and the mental health and vitality subscales of the Rand 36-item Health Survey (Rand-36) (21). The SCL-90 is a 90 item self report scale containing 8 subscales, measuring multidimensional psychopathology. In this study, the total score (the sum-score of all 90 items) is reported. This score can be considered as a measure of psychoneuroticism or general level of psychological and somatic wellbeing. The higher the total score, the higher the level of psychoneuroticism and the lower the level of wellbeing. The SCL-90 is a widely used international instrument in studies on psychological consequences of somatic diseases (22). The scores are compared with the reference values for the Dutch general population, based on a sample of 2368 individuals with a mean age of 41 years (20). The Rand-36 is the Dutch version of the MOS Short-Form General Health Survey (23) and measures health-related quality of life. It is known for its high standards of reliability and validity (24, 25). In this study, only the subscales mental health and vitality were used, measuring feelings of depression and nervousness, and feelings of energy and fatigue respectively. Scores are compared with reference values of a representative sample of the Dutch population (n ¼ 1063) with a mean age of 44 years. Biochemical measurements All blood samples were collected in the morning before T4 medication was ingested. Serum TSH and free T4 were measured by time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay (htsh Ultra and Delfia FT4 respectively; Wallac Oy, Turku, Finland), with a detection limit of 0.01 mu/l and 2 pmol/l respectively; serum T3 was measured by an in-house RIA method (26), and anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO-ab) by chemiluminescence immunoassay LUMI-test anti-tpo (Brahms, Berlin, Germany) with a detection limit of 30 ku/l. The cut-off value for a positive anti-tpo titer was 60 ku/l. Statistical methods All data were analyzed with SPSS version 11.5 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA). The mean scores of the neurocognitive tests were compared with the mean scores of the reference population by means of a one-sample t-test. Pearson correlation coefficients were used in order to study the relationship between neurocognitive functioning, well-being and serum TSH values. Serum TSH was log-transformed to normalize distribution before statistical analysis. Statistical significance was defined as a 2- tailed P, Test results were considered impaired if below the 5th percentile of the reference groups. Results Cognitive functioning in hypothyroidism 749 In total, 141 patients were tested. The patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Patients were predominantly middle-aged females, with a mid-level educational standard. Table 2 shows the mean scores of the neurocognitive tests and well-being questionnaires of the patients and the reference populations. Neurocognitive tests Cognitive speed/psychomotor speed Digit symbol scores of the patients were not significantly different from those of the reference population. However, patients performed significantly slower on the easier
4 750 E M Wekking and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) 153 Table 1 Patient characteristics (n ¼ 141). Female (n, %) 121 (85.8%) Age (mean^s.d.) 47.8^9.8 Duration of substitution therapy (yr; 5.5 ( ) median, range) Serum TSH at inclusion (mu/l median, 1.4 ( ) range) Serum free T4 (pmol/l; mean^s.d.) 14.8^2.9 Serum T3 (nmol/l; means^s.d.) 1.7^0.33 Educational level (n, %) 1 Primary education 15 (10.6%) Education lower than mid-level 20 (14.2%) Mid-level education 61 (43.3%) College level 45 (31.5%) 1 The level of education is not based on years of education but on level of education attained. parts of the MCT paper and pencil tasks (% and 1 letter) compared with the reference population. In fact, for these tests 26.4% and 16.4% of the patients respectively had impaired scores, i.e. scores below the 5th percentile of the reference values. By contrast, patients performed significantly better on the most complex task (4 letters) compared with the reference group. Attention PASAT scores of the patients were significantly lower compared with the reference group, indicating impaired performance on this complex attention task. Impaired scores (below the 5th percentile of the reference values) were observed in 14.9% of the patients. PASAT scores were corrected for educational level but not for age. However, correlation analyses revealed no significant relationship between age and the education-corrected PASAT score (r ¼ 20.12, P # 0.24). Working memory, and learning and memory For Digit Span there were no significant differences between patients and the reference population. Patients had significantly lower CLVT scores for immediate recall, and 10.6% of the patients scored more than 2 standard deviations below the mean of the reference population (normally about 2.5%). For the Rivermead stories patients had significantly lower scores on all indices, indicating worse performance on this memory test as compared with the reference population. Both immediate and delayed recall scores were impaired in 25% of the patients for the relative delayed recall this was 18.7%. Questionnaires Figure 1 shows the scores on the SCL-90 and Rand-36 questionnaires. T4-treated patients had significantly higher SCL-90 total scores compared with the Dutch general reference population. Using SCL-90, the mean total score of the patients would be classified as high Table 2 Scores on neurocognitive tests and well-being questionnaires. Higher scores indicate better performance/higher level of wellbeing except for MCT and SCL-90. n Patients n Reference population P value Cognitive psychomotor speed Digit symbol Total score 9.9^3.8 10^ MCT (paper & pencil version) % symbol (s) 21.6^ ^ letler (s) 26.2^ ^ letlers (s) 36.6^ ^ letlers (s) 45.0^ ^ letlers (s) 57.0^ ^ Attention PASAT Total score 146.5^ ^ Working memory Digit span Total score 10^3 10^ Learning and memory CVLT Immediate recall 21.1^2.2 0^ Delayed recall 0.19^2.6 0^ Recognition 20.11^ ^ Rivermead (stories) Immediate recall 42.5^11 50^ Absolute delayed recall 41.7^ ^ Relative delayed recall 44.5^ ^ Well-being SCL-90 total score ^ ^ RAND-36 Mental health ^ ^ RAND-36 Vitality ^ ^
5 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) 153 Figure 1 Questionnaire scores for patients (shaded bars) and the reference group (open bars). Lower levels of well-being are indicated by higher SCL-90 scores and lower RAND-36 scores. (a score between the 80th and 95th percentile of the reference values for the general population), indicating a lower mean level of general psychological and somatic well-being. Likewise, scores on the RAND-36 mental health and vitality subscales were significantly lower as compared with healthy controls of roughly the same age, indicating a lower level of health-related quality of life. The RAND-36 score for mental health lies within 1 standard deviation below the mean of the reference population, whereas the score for vitality was between 1 and 2 standard deviations below the mean. For the RAND-36, these figures indicate that the score for vitality (in particular), which measures feelings of energy and fatigue, is impaired in hypothyroid patients. Serum TSH, TPO-ab and their relationship with neurocognitive functioning and well-being The patient group was divided into patients with a mean TSH lower than 2 mu/l (n ¼ 101) and patients with a mean TSH higher than 2 mu/l (n ¼ 40). There appeared to be no significant differences between these groups on either the neurocognitive tests or the SCL-90 and RAND-36 scores. Furthermore, scores on neurocognitive tests and well-being questionnaires were not significantly different for patients with a positive (. 60 ku/l) TPO-ab titer (n ¼ 29) compared with patients with a negative (, 60 ku/l) TPO-ab titer (n ¼ 112). Discussion In this study, we investigated several domains of neurocognitive functioning in a large group of patients with treated hypothyroidism. The results were compared with standard reference values as applied in Dutch clinical neuropsychological practice. In addition, we Cognitive functioning in hypothyroidism 751 evaluated whether psychological well-being in this patient group differed from healthy subjects and whether serum TSH was a determinant of neurocognitive performance and well-being. Patients had poor performance on various domains of neurocognitive functioning compared with the mean standard reference values, especially on a complex attention task and on verbal memory tests. No less than a quarter of the patients had impaired scores (below the 5th percentile) on the memory test story recall, both for immediate reproduction and for delayed recall. These findings support the sparse findings from earlier studies reporting a significant decrease in memory function in hypothyroid patients after adequate thyroid replacement treatment as compared with normal controls (4). Similarly, Burmeister et al. reported on the neurocognitive functioning of 13 athyrotic patients while on T4 therapy and again after discontinuing thyroid hormone treatment (7). It was reported that discontinuing T4 therapy led to a decrement in delayed recall of verbal information, but not in other objective measures of cognition. Performance on tests for cognitive speed seemed contradictory: patients had significantly slower performance at the beginning of the tests (MCT paper and pencil), but could compare favourably with the reference group, or perform even better, when the task progressed and increased in difficulty. These findings could indicate some starting slowness. This could also explain why Rivermead delayed recall but not CLVT delayed recall was impaired. In the former test, the stories to be memorized are presented only once, whereas in the latter, a shopping list is repeated 5 times, giving patients the opportunity to compensate for starting slowness. This starting slowness could also account for part of the attention impairment. Levels of well-being, as measured with the SCL-90 total score and Rand-36 subscales for mental health and for vitality, were significantly lower for patients compared with those of the general population. This corroborates the findings of the community-based study of Saravanan et al. (2), who found that patients on thyroxine replacement display significant impairment in psychological well-being as compared with controls of similar age and sex. One could hypothesize that a decreased level of well-being is the cause of decreased neurocognitive performance in this population. Indeed, correlation analyses revealed that the SCL-90 total score was weakly, but significantly, correlated with about half, but not all of the neurocognitive test results (correlation coefficients between and ). Serum TSH concentrations were not related to outcome on neurocognitive function tests nor with scores on questionnaires concerning well-being. Apparently, neurocognitive functioning and well-being in patients with serum TSH values above 2 mu/l (but below 4.0 mu/l) is not different from patients with TSH values below 2 mu/l, but this might well be
6 752 E M Wekking and others EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) 153 different for patients with abnormal serum TSH concentrations. However, Osterweil et al. found no correlation between serum TSH levels and neurocognitive functioning in patients during hypothyroidism (mean serum TSH: 66 mu/l) either (4). They suggested that the duration of untreated hypothyroidism might be a more significant determinant. Furthermore, dividing the group into patients with positive TPO antibodies (. 60) versus patients with negative TPO antibodies (# 60) did not result in significant differences in the results of tests and questionnaires, possibly indicating that a high level of thyroid antibodies is not related to neurocognitive dysfunctions and a lower level of well-being. A major limitation of this study is the lack of a proper control group, with controls individually matched for age, sex and educational level. Results of neurocognitive tests and questionnaires were compared with their reference values for the general population. Therefore, we cannot exclude the possibility that these results are due to differences in patient characteristics. On the other hand, the reference values of the neurocognitive tests have already been corrected for factors relevant to the specific test, such as age and education, and are commonly used to evaluate individual scores in Dutch clinical neuropsychological practice. In summary, despite its limitations, this study is the first to provide some evidence for cognitive impairment in a large group of adequately treated patients with hypothyroidism, especially concerning the domains of attention and memory. Results of tests for cognitive speed revealed some starting slowness, but otherwise normal performance. Levels of well-being, as measured with the SCL-90 total score and Rand-36 subscales for mental health and for vitality, were significantly lower for patients compared with those of the general population. Our findings corroborate earlier sparse reports, as well as the widespread clinical notion that neurocognitive function and psychological well-being may not be completely restored in patients with hypothyroidism, despite adequate T4 treatment. Whether these impairments in neurocognitive functioning and well-being could be due to imperfections of the substitution therapy, because cognitive and affective functioning is not fully restored, or to the autoimmune process that caused the hypothyroidism, or reflect having a chronic disease in general, remains to be clarified. Future studies might first attempt to confirm the presence of neurocognitive impairment in T4-treated patients in a controlled study, comparing patients with healthy individuals, closely matched for sex, age and educational level. In order to investigate whether symptoms may be due to chronic disease in general, it would be interesting to compare levels of well-being and neurocognitive function of T4-treated patients with hypothyroidism, with those of a group of patients who suffer from an equally chronic disease that can be treated with a single portion of medication a day, for example patients with essential hypertension. Acknowledgements This study was supported by a grant from the Academic Medical Center Anton Meelmeijer Fund (fund number: SAG 05002). We would like to thank Leonie van der Heuvel, Diane Jungerman, Tea Elezovic, Tanja de Krijger, Famke Stegenga and Aram Tefsen for the assessment of the neuropsychological tests. References 1 Dugbartey AT. Neurocognitive aspects of hypothyroidism. Archives of Internal Medicine Saravanan P, Chau WF, Roberts N, Vedhara K, Greenwood R & Dayan CM. Psychological well-being in patients on adequate doses of l-thyroxine: results of a large, controlled communitybased questionnaire study. Clinical Endocrinology Whybrow PC, Prange AJ Jr & Treadway CR. Mental changes accompanying thyroid gland dysfunction. A reappraisal using objective psychological measurement. Archives of General Psychiatry Osterweil D, Syndulko K, Cohen SN, Pettler-Jennings PD, Hershman JM, Cummings JL, Tourtellotte WW & Solomon DH. Cognitive function in non-demented older adults with hypothyroidism. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society Mennemeier M, Garner RD & Heilman KM. Memory, mood and measurement in hypothyroidism. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Appelhof BC, Fliers E, Wekking EM, Schene AH, Huyser J, Tijssen JG, Endert E, Van Weert HCPM & Wiersinga WM. Combined therapy with levothyroxine and liothyronine in two ratios compared with levothyroxine monotherapy in primary hypothyroidism; a double blind, randomized controlled clinical trial. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism Burmeister LA, Ganguli M, Dodge HH, Toczek T, DeKosky ST & Nebes RD. Hypothyroidism and cognition: preliminary evidence for a specific defect in memory. Thyroid Uterwijk J. WAIS-III. Nederlandstalige Bewerking. Technische Handleiding. Lisse: Swets & Zeitlinger, Wechsler D. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale III: Technical Manual. San Antonio, TX: The Psychological Corporation, Brand AN & Jolles J. Information processing in depression and anxiety. Psychological Medicine Gronwall DMA & Sampson H. The Psychological Effects of Concussion. Auckland, New Zealand: Auckland University Press, Spikman JM, van Zomeren AH & Deelman BG. Deficits of attention after closed-head injury: slowness only? Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology Aarnoudse CC, van den Burg W & Saan R. De Paced Auditory Serial Addition Task (PASAT) in Een Steekproef van Gezonde Personen. Betrouwbaarheden en Normeringen. Internal report, Department of Neuropsychology, Academic Hospital, University of Groningen, The Netherlands. Ref Type: Report, Mulder JL, Dekker R & Dekker PH. Verbale Leer en Geheugen Test: Handleiding. Lisse: Swets & Zeitlinger, Wilson B, Cockburn J & Baddeley AD. The Rivermead Behavioural Memory Test. Bury St Edmunds, UK: Thames Valley Test Company, 1985.
7 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (2005) Wimmers WFHG & van Balen HGG. Rivermead Behavioural Memory Test, Nederlandstalige Bewerking. Lisse: Swets & Zeitlinger, Schmand B, Houx P & de Koning I. Normen voor Stroop Kleurwoord Tests, Trail Making Test en Story Recall van de Rivermead Behavioral Memory Test. Sectie Neuropsychologie, Nederlands Centrum voor Psychologen, Amsterdam, Ref Type: Report, Lezak MD, Howieson DB & Loring DW. Neuropsychological Assessment, 4th ed., Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, Bunevicius R, Kazanavicius G, Zalinkevicius R & Prange AJ Jr. Effects of thyroxine as compared with thyroxine plus triiodothyronine in patients with hypothyroidism. New England Journal of Medicine Ettema JHM & Arrindell WA. Symptom Checklist-90. In Handleiding Bij een Multi-dimensionele Psychopathologie-indicator. Amsterdam: Harcourt Test Publisher, Aaronson NK, Muller M, Cohen PD, Essink-Bot ML, Fekkes M, Sanderman R, Sprangers MA, te Velde A & Verrips E. Translation, validation, and norming of the Dutch language version of the SF- 36 Health Survey in community and chronic disease populations. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology Derogatis LR & Savitz KL. The SCL-90, brief symptom inventory, and matching clinical rating scales. In The use of Psychological Testing for Treatment Planning and Outcome Assessment. pp Ed. ME Maruish. New Jersey: Erlbaum, Ware JE Jr & Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36) I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care van der Zee KI, Sanderman R. Het Meten van de Algemene Gezondheidstoe-stand Met de RAND-36. Een Handleiding. Groningen: Rijksuniversiteit, van der Zee KI & Sanderman R, Heyink J & de Haes H. The psychometric qualities of the RAND 36-item Health Survey 1.0: a multidimensional measure of general health status. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine Wiersinga WM & Chopra IJ. Radioimmunoassay of thyroxine (T4), 3,5,3 0 -triiodothyronine (T3), 3,3 0,5 0 -triiodothyronine (reverse T3, rt3), and 3,3 0 -diiodothyronine (T2). Methods in Enzymology Received 27 April 2005 Accepted 1 September 2005 Cognitive functioning in hypothyroidism 753
Vaitsa Giannouli Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, Bulgaria Nikolaos Syrmos Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece
 15 A 2-YEAR PRELIMINARY LONGITUDINAL STUDY OF NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL FUNCTIONING IN HASHIMOTO S THYROIDITIS UNDER LEVOTHYROXINE TREATMENT: ONLY TRAIL MAKING TEST IS MAKING A DIFFERENCE Vaitsa Giannouli Bulgarian
15 A 2-YEAR PRELIMINARY LONGITUDINAL STUDY OF NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL FUNCTIONING IN HASHIMOTO S THYROIDITIS UNDER LEVOTHYROXINE TREATMENT: ONLY TRAIL MAKING TEST IS MAKING A DIFFERENCE Vaitsa Giannouli Bulgarian
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL DOMAIN-SPECIFIC COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN PATIENTS WITH COPD AND CONTROL SUBJECTS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL DOMAIN-SPECIFIC COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN PATIENTS WITH COPD AND CONTROL SUBJECTS Fiona A.H.M. Cleutjens, Frits M.E. Franssen, Martijn A. Spruit, Lowie E.G.W. Vanfleteren, Candy Gijsen,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL DOMAIN-SPECIFIC COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT IN PATIENTS WITH COPD AND CONTROL SUBJECTS Fiona A.H.M. Cleutjens, Frits M.E. Franssen, Martijn A. Spruit, Lowie E.G.W. Vanfleteren, Candy Gijsen,
New Medicine Recommendation
 May 2016 New Medicine Recommendation Liothyronine 20microgram Tablets Liothyronine as an add-on treatment for refractory hypothyroidism despite adequate monotherapy with levothyroxine Prescribing within
May 2016 New Medicine Recommendation Liothyronine 20microgram Tablets Liothyronine as an add-on treatment for refractory hypothyroidism despite adequate monotherapy with levothyroxine Prescribing within
Do we need still more trials on T 4 and T 3 combination therapy in hypothyroidism?
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2009) 161 955 959 ISSN 0804-4643 COMMENTARY Do we need still more trials on T 4 and T 3 combination therapy in hypothyroidism? Wilmar M Wiersinga Department of Endocrinology
European Journal of Endocrinology (2009) 161 955 959 ISSN 0804-4643 COMMENTARY Do we need still more trials on T 4 and T 3 combination therapy in hypothyroidism? Wilmar M Wiersinga Department of Endocrinology
J Clin Endocrin Metab. First published ahead of print March 12, 2010 as doi: /jc
 J Clin Endocrin Metab. First published ahead of print March 12, 2010 as doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Prevalence of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Hashimoto s Thyroiditis
J Clin Endocrin Metab. First published ahead of print March 12, 2010 as doi:10.1210/jc.2009-2016 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Prevalence of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Hashimoto s Thyroiditis
APPENDIX A TASK DEVELOPMENT AND NORMATIVE DATA
 APPENDIX A TASK DEVELOPMENT AND NORMATIVE DATA The normative sample included 641 HIV-1 seronegative gay men drawn from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). Subjects received a test battery consisting
APPENDIX A TASK DEVELOPMENT AND NORMATIVE DATA The normative sample included 641 HIV-1 seronegative gay men drawn from the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study (MACS). Subjects received a test battery consisting
THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS
 THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS John P. Kress, MD, Brian Gehlbach, MD, Maureen Lacy, PhD, Neil Pliskin, PhD, Anne S. Pohlman, RN, MSN, and
THE LONG TERM PSYCHOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF DAILY SEDATIVE INTERRUPTION IN CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS John P. Kress, MD, Brian Gehlbach, MD, Maureen Lacy, PhD, Neil Pliskin, PhD, Anne S. Pohlman, RN, MSN, and
THE USE OF L-T4 + L-T3 IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPOTHYROIDISM. AN ETA GUIDELINE 2012
 THE USE OF L-T4 + L-T3 IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPOTHYROIDISM. AN ETA GUIDELINE 2012 Birte Nygaard, Department of Endocrinology, Herlev Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. International guidelines
THE USE OF L-T4 + L-T3 IN THE TREATMENT OF HYPOTHYROIDISM. AN ETA GUIDELINE 2012 Birte Nygaard, Department of Endocrinology, Herlev Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Denmark. International guidelines
THE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY OF POST-POLIO FATIGUE. Richard L. Bruno, Thomas Galski, John DeLuca.
 FROM The Post-Polio Institute and The International Centre for Post-Polio Education and Research postpolioinfo@aol.com Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 1993; 74: 1061-1065. THE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY
FROM The Post-Polio Institute and The International Centre for Post-Polio Education and Research postpolioinfo@aol.com Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 1993; 74: 1061-1065. THE NEUROPSYCHOLOGY
Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
T he estimated annual incidence of bacterial meningitis is 4
 1092 PAPER Cognitive outcome in adults after bacterial meningitis Martine Hoogman, Diederik van de Beek, Martijn Weisfelt, Jan de Gans, Ben Schmand... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
1092 PAPER Cognitive outcome in adults after bacterial meningitis Martine Hoogman, Diederik van de Beek, Martijn Weisfelt, Jan de Gans, Ben Schmand... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Frontotemporal dementia and neuropsychology: the value of missing values
 726 Department of Neurology H2 222, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, PO Box 22700, NL-1100 DD Amsterdam, The Netherlands H M M Smeding Department of Neurology H660, University Hospital
726 Department of Neurology H2 222, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, PO Box 22700, NL-1100 DD Amsterdam, The Netherlands H M M Smeding Department of Neurology H660, University Hospital
THE OCCURRENCE OF various abnormalities in brain
 0021-972X/06/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 91(9):3389 3393 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0414 Psychological Well-Being Correlates
0021-972X/06/$15.00/0 The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 91(9):3389 3393 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2006 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0414 Psychological Well-Being Correlates
European Journal of Endocrinology (2009) ISSN
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2009) 161 895 902 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Effect of combination therapy with thyroxine (T 4 ) and 3,5,3 0 -triiodothyronine versus T 4 monotherapy in patients with
European Journal of Endocrinology (2009) 161 895 902 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Effect of combination therapy with thyroxine (T 4 ) and 3,5,3 0 -triiodothyronine versus T 4 monotherapy in patients with
Rapidly-administered short forms of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 3rd edition
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 22 (2007) 917 924 Abstract Rapidly-administered short forms of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 3rd edition Alison J. Donnell a, Neil Pliskin a, James Holdnack
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 22 (2007) 917 924 Abstract Rapidly-administered short forms of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale 3rd edition Alison J. Donnell a, Neil Pliskin a, James Holdnack
Using contextual analysis to investigate the nature of spatial memory
 Psychon Bull Rev (2014) 21:721 727 DOI 10.3758/s13423-013-0523-z BRIEF REPORT Using contextual analysis to investigate the nature of spatial memory Karen L. Siedlecki & Timothy A. Salthouse Published online:
Psychon Bull Rev (2014) 21:721 727 DOI 10.3758/s13423-013-0523-z BRIEF REPORT Using contextual analysis to investigate the nature of spatial memory Karen L. Siedlecki & Timothy A. Salthouse Published online:
Interpreting change on the WAIS-III/WMS-III in clinical samples
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 16 (2001) 183±191 Interpreting change on the WAIS-III/WMS-III in clinical samples Grant L. Iverson* Department of Psychiatry, University of British Columbia, 2255 Wesbrook
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 16 (2001) 183±191 Interpreting change on the WAIS-III/WMS-III in clinical samples Grant L. Iverson* Department of Psychiatry, University of British Columbia, 2255 Wesbrook
Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study Grigoris Effraimidis,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endocrine Care Brief Report Discontinuation of Smoking Increases the Risk for Developing Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies and/or Thyroglobulin Antibodies: A Prospective Study Grigoris Effraimidis,
HYPOTHYROIDISM IS ONE OF
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Combined Levothyroxine Plus Liothyronine Compared With Levothyroxine Alone in Primary Hypothyroidism A Randomized Controlled Trial Patrick W. Clyde, MD Amir E. Harari, MD Eric J.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Combined Levothyroxine Plus Liothyronine Compared With Levothyroxine Alone in Primary Hypothyroidism A Randomized Controlled Trial Patrick W. Clyde, MD Amir E. Harari, MD Eric J.
Detecting neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected youth: Are we focusing on the wrong factors?
 Detecting neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected youth: Are we focusing on the wrong factors? Jennifer Lewis, PsyD; Mathew Hirsch, PsyD & Susan Abramowitz, PhD NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY Friday,
Detecting neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected youth: Are we focusing on the wrong factors? Jennifer Lewis, PsyD; Mathew Hirsch, PsyD & Susan Abramowitz, PhD NYU School of Medicine, New York, NY Friday,
Improving the Methodology for Assessing Mild Cognitive Impairment Across the Lifespan
 Improving the Methodology for Assessing Mild Cognitive Impairment Across the Lifespan Grant L. Iverson, Ph.D, Professor Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Harvard Medical School & Red Sox
Improving the Methodology for Assessing Mild Cognitive Impairment Across the Lifespan Grant L. Iverson, Ph.D, Professor Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Harvard Medical School & Red Sox
Serial 7s and Alphabet Backwards as Brief Measures of Information Processing Speed
 Pergamon Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, Vol. 11, No. 8, pp. 651-659, 1996 Copyright 9 1996 National Academy of Neuropsychology Printed in the USA. All fights reserved 0887-6177/96 $15.00 +.00 PH
Pergamon Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, Vol. 11, No. 8, pp. 651-659, 1996 Copyright 9 1996 National Academy of Neuropsychology Printed in the USA. All fights reserved 0887-6177/96 $15.00 +.00 PH
Process of a neuropsychological assessment
 Test selection Process of a neuropsychological assessment Gather information Review of information provided by referrer and if possible review of medical records Interview with client and his/her relative
Test selection Process of a neuropsychological assessment Gather information Review of information provided by referrer and if possible review of medical records Interview with client and his/her relative
M P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist
 M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
M------- P---- Ph.D. Clinical Psychologist / Neuropsychologist NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EVALUATION Name: Date of Birth: Date of Evaluation: 05-28-2015 Tests Administered: Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale Fourth
Subjective sleep problems in later life as predictors of cognitive decline. Report from the Maastricht Ageing Study MAAS)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2002; 17: 73±77. DOI: 10.1002/gps.529 Subjective sleep problems in later life as predictors of cognitive decline. Report from the
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRY Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2002; 17: 73±77. DOI: 10.1002/gps.529 Subjective sleep problems in later life as predictors of cognitive decline. Report from the
Method. NeuRA Schizophrenia and bipolar disorder April 2016
 Introduction Schizophrenia is characterised by positive, negative and disorganised symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to experiences additional to what would be considered normal experience, such as hallucinations
Introduction Schizophrenia is characterised by positive, negative and disorganised symptoms. Positive symptoms refer to experiences additional to what would be considered normal experience, such as hallucinations
PRELIMINARY NORMS FOR YEAR OLDS ON THE MEMORY TEST FOR OLDER ADULTS (MTOA:S) ABSTRACT
 The University of British Columbia PRELIMINARY NORMS FOR 85-99 YEAR OLDS ON THE MEMORY TEST FOR OLDER ADULTS (MTOA:S) Anita M. Hubley University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada Poster presented
The University of British Columbia PRELIMINARY NORMS FOR 85-99 YEAR OLDS ON THE MEMORY TEST FOR OLDER ADULTS (MTOA:S) Anita M. Hubley University of British Columbia Vancouver, BC, Canada Poster presented
Dexamethasone and Long-Term Outcome in Adults with Bacterial Meningitis
 Dexamethasone and Long-Term Outcome in Adults with Bacterial Meningitis Martijn Weisfelt, MD, 1 Martine Hoogman, MSc, 1 Diederik van de Beek, PhD, 1 Jan de Gans, PhD, 1 Wouter A. Dreschler, PhD, 2 and
Dexamethasone and Long-Term Outcome in Adults with Bacterial Meningitis Martijn Weisfelt, MD, 1 Martine Hoogman, MSc, 1 Diederik van de Beek, PhD, 1 Jan de Gans, PhD, 1 Wouter A. Dreschler, PhD, 2 and
Elderly Norms for the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised*
 The Clinical Neuropsychologist -//-$., Vol., No., pp. - Swets & Zeitlinger Elderly Norms for the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised* Rodney D. Vanderploeg, John A. Schinka, Tatyana Jones, Brent J. Small,
The Clinical Neuropsychologist -//-$., Vol., No., pp. - Swets & Zeitlinger Elderly Norms for the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised* Rodney D. Vanderploeg, John A. Schinka, Tatyana Jones, Brent J. Small,
Cognitive Impairment in Adults with Good Recovery after Bacterial Meningitis
 1047 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Cognitive Impairment in Adults with Good Recovery after Bacterial Meningitis Diederik van de Beek, 1,2 Ben Schmand, 1 Jan de Gans, 1 Martijn Weisfelt, 1 Heleen Vaessen, 1 Jacob
1047 CONCISE COMMUNICATION Cognitive Impairment in Adults with Good Recovery after Bacterial Meningitis Diederik van de Beek, 1,2 Ben Schmand, 1 Jan de Gans, 1 Martijn Weisfelt, 1 Heleen Vaessen, 1 Jacob
An Initial Validation of Virtual Human Administered Neuropsychological Assessments
 Annual Review of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2017 123 An Initial Validation of Virtual Human Administered Neuropsychological Assessments Thomas D. PARSONS a,*, Paul SCHERMERHORN b, Timothy MCMAHAN a,
Annual Review of Cybertherapy and Telemedicine 2017 123 An Initial Validation of Virtual Human Administered Neuropsychological Assessments Thomas D. PARSONS a,*, Paul SCHERMERHORN b, Timothy MCMAHAN a,
Table 1: Summary of measures of cognitive fatigability operationalised in existing research.
 Table 1: Summary of measures of cognitive fatigability operationalised in existing research. Candidate Mmeasures Studies Procedure Self-reported fatigue measure Key Findings The auditory As and auditory
Table 1: Summary of measures of cognitive fatigability operationalised in existing research. Candidate Mmeasures Studies Procedure Self-reported fatigue measure Key Findings The auditory As and auditory
Effects of Comorbid Disease on Pre-treatment Neurobehavioral Functioning. Sunita K. Patel, PhD Assistant Professor. City of Hope Medical Center
 Effects of Comorbid Disease on Pre-treatment Neurobehavioral Functioning. Sunita K. Patel, PhD Assistant Professor City of Hope Medical Center Duarte, California. Pre-Chemotherapy e e apycognitive Functioning
Effects of Comorbid Disease on Pre-treatment Neurobehavioral Functioning. Sunita K. Patel, PhD Assistant Professor City of Hope Medical Center Duarte, California. Pre-Chemotherapy e e apycognitive Functioning
NEUROBEHAVIORAL EVALUATION OF HOUSEHOLD EXPOSURE TO DURSBAN 1
 RAYMOND SINGER, PH.D. A Professional Association 444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444 36 Alondra Road / Santa Fe, New Mexico / 87508 Alternate office: 180 E. 79th Street / Suite 1-C / New
RAYMOND SINGER, PH.D. A Professional Association 444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444444 36 Alondra Road / Santa Fe, New Mexico / 87508 Alternate office: 180 E. 79th Street / Suite 1-C / New
Using Neuropsychological Experts. Elizabeth L. Leonard, PhD
 Using Neuropsychological Experts Elizabeth L. Leonard, PhD Prepared for Advocate. Arizona Association for Justice/Arizona Trial Lawyers Association. September, 2011 Neurocognitive Associates 9813 North
Using Neuropsychological Experts Elizabeth L. Leonard, PhD Prepared for Advocate. Arizona Association for Justice/Arizona Trial Lawyers Association. September, 2011 Neurocognitive Associates 9813 North
The Thr92Ala polymorphism in the type 2 deiodinase is not associated with thyroxin dose in athyroid patients or patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis
 12 The Thr92Ala polymorphism in the type 2 deiodinase is not associated with thyroxin dose in athyroid patients or patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis K.A. Heemstra, H.C. Hoftijzer, W.M. van der Deure,
12 The Thr92Ala polymorphism in the type 2 deiodinase is not associated with thyroxin dose in athyroid patients or patients with Hashimoto thyroiditis K.A. Heemstra, H.C. Hoftijzer, W.M. van der Deure,
Personality and Individual Differences
 Personality and Individual Differences 98 (2016) 85 90 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Personality and Individual Differences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/paid Relations of naturally
Personality and Individual Differences 98 (2016) 85 90 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Personality and Individual Differences journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/paid Relations of naturally
The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Effort Scale
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 27 (2012) 190 195 The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Effort Scale Julia Novitski 1,2, Shelly Steele 2, Stella Karantzoulis 3, Christopher
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 27 (2012) 190 195 The Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status Effort Scale Julia Novitski 1,2, Shelly Steele 2, Stella Karantzoulis 3, Christopher
Glucose on the Ageing Mind
 Glucose on the Ageing Mind Healthy Brain Ageing Symposium Erin Walsh Centre for Research on Ageing, Health and Wellbeing Research School of Population Health, ANU 2 Brain Ageing Normal brain ageing can
Glucose on the Ageing Mind Healthy Brain Ageing Symposium Erin Walsh Centre for Research on Ageing, Health and Wellbeing Research School of Population Health, ANU 2 Brain Ageing Normal brain ageing can
Test Assessment Description Ref. Global Deterioration Rating Scale Dementia severity Rating scale of dementia stages (2) (4) delayed recognition
 Table S. Cognitive tests used in the Georgia Centenarian Study. Test Assessment Description Ref. Mini-Mental State Examination Global cognitive performance A brief screening of orientation, memory, executive
Table S. Cognitive tests used in the Georgia Centenarian Study. Test Assessment Description Ref. Mini-Mental State Examination Global cognitive performance A brief screening of orientation, memory, executive
Brief Report. Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived?
 Brief Report Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived? Delia C. Randall, BSc,*y Aparna Viswanath,* Punam Bharania,* Sarah M. Elsabagh, BSc,* David E.
Brief Report Does Modafinil Enhance Cognitive Performance in Young Volunteers Who Are Not Sleep-Deprived? Delia C. Randall, BSc,*y Aparna Viswanath,* Punam Bharania,* Sarah M. Elsabagh, BSc,* David E.
Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale
 The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
The University of British Columbia Hubley Depression Scale for Older Adults (HDS-OA): Reliability, Validity, and a Comparison to the Geriatric Depression Scale Sherrie L. Myers & Anita M. Hubley University
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cognitive functioning in patients with suspected chronic toxic encephalopathy: evidence for neuropsychological disturbances after controlling for insufficient effort
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Cognitive functioning in patients with suspected chronic toxic encephalopathy: evidence for neuropsychological disturbances after controlling for insufficient effort
Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Early stages of thyroid autoimmunity: follow-up studies in the Amsterdam AITD cohort Effraimidis, G. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Effraimidis,
21/05/2018. Today s webinar will answer. Presented by: Valorie O Keefe Consultant Psychologist
 Today s webinar will answer. 1. What is the RBANS, and how is the updated version different than the original version? 2. What are the neurocognitive areas assessed by the RBANS and what scores are available?
Today s webinar will answer. 1. What is the RBANS, and how is the updated version different than the original version? 2. What are the neurocognitive areas assessed by the RBANS and what scores are available?
Neuropsychological Evaluation of
 Neuropsychological Evaluation of Alzheimer s Disease Joanne M. Hamilton, Ph.D. Shiley-Marcos Alzheimer s Disease Research Center Department of Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Establish
Neuropsychological Evaluation of Alzheimer s Disease Joanne M. Hamilton, Ph.D. Shiley-Marcos Alzheimer s Disease Research Center Department of Neurosciences University of California, San Diego Establish
Cognitive outcome in adults with moderate disability after pneumococcal meningitis
 Journal of Infection (2006) 52, 433 439 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf Cognitive outcome in adults with moderate disability after pneumococcal meningitis Martijn Weisfelt a, *, Diederik van de Beek
Journal of Infection (2006) 52, 433 439 www.elsevierhealth.com/journals/jinf Cognitive outcome in adults with moderate disability after pneumococcal meningitis Martijn Weisfelt a, *, Diederik van de Beek
Score Report. Test Administered WMS IV (3/16/2009) Age at Testing 24 years 0 months Retest? No
 Score Report Examinee Name Date of Report 3/16/2009 Examinee ID 5823 Education 16 Date of Birth 3/16/1985 Home Language English Gender Male Handedness Left White not Hispanic Race/Ethnicity Origin Examiner
Score Report Examinee Name Date of Report 3/16/2009 Examinee ID 5823 Education 16 Date of Birth 3/16/1985 Home Language English Gender Male Handedness Left White not Hispanic Race/Ethnicity Origin Examiner
Are people with Intellectual disabilities getting more or less intelligent II: US data. Simon Whitaker
 Are people with Intellectual disabilities getting more or less intelligent II: US data By Simon Whitaker Consultant Clinical Psychologist/Senior Visiting Research Fellow The Learning Disability Research
Are people with Intellectual disabilities getting more or less intelligent II: US data By Simon Whitaker Consultant Clinical Psychologist/Senior Visiting Research Fellow The Learning Disability Research
Is the Combination of Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine Better than T4 alone for Hypothyroidism? ESEO Alexandria 2017
 Is the Combination of Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine Better than T4 alone for Hypothyroidism? ESEO Alexandria 2017 James V. Hennessey M. D. Associate Professor Harvard Medical School Case 53 year old woman
Is the Combination of Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine Better than T4 alone for Hypothyroidism? ESEO Alexandria 2017 James V. Hennessey M. D. Associate Professor Harvard Medical School Case 53 year old woman
Meta-analyses of cognitive functioning in euthymic bipolar patients and their first-degree relatives
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Meta-analyses of cognitive functioning in euthymic bipolar patients and their first-degree relatives B. Arts 1 *, N. Jabben 1, L. Krabbendam 1 and J. van Os 1,2 1 Department of Psychiatry
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Meta-analyses of cognitive functioning in euthymic bipolar patients and their first-degree relatives B. Arts 1 *, N. Jabben 1, L. Krabbendam 1 and J. van Os 1,2 1 Department of Psychiatry
Common Issues in Management of Hypothyroidism
 Common Issues in Management of Hypothyroidism Family Medicine Refresher Course April 5, 2018 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships
Common Issues in Management of Hypothyroidism Family Medicine Refresher Course April 5, 2018 Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. Disclosure of Financial Relationships Janet A. Schlechte, M.D. has no relationships
CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY PSYC32
 University of Toronto at Scarborough Department of Psychology CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY PSYC32 Ψ Course Instructor: Zakzanis Lab Instructor: Konstantine Eliyas Jeffay Course Code: PSYC32H3 Lecture: Tuesdays,
University of Toronto at Scarborough Department of Psychology CLINICAL NEUROPSYCHOLOGY PSYC32 Ψ Course Instructor: Zakzanis Lab Instructor: Konstantine Eliyas Jeffay Course Code: PSYC32H3 Lecture: Tuesdays,
Long-term effects of Graves ophthalmopathy on health-related quality of life
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 146 751 757 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Long-term effects of Graves ophthalmopathy on health-related quality of life Caroline Terwee 1,4, Iris Wakelkamp 2, Stevie
European Journal of Endocrinology (2002) 146 751 757 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Long-term effects of Graves ophthalmopathy on health-related quality of life Caroline Terwee 1,4, Iris Wakelkamp 2, Stevie
MOS SF-36 health survey (Ware &
 Biomedical and Physical Functioning General Health Height Weight Waist Circumfernece % Body Fat Tanita scale BMI Self-rated Health - overall clinical protocol Self-rated Health - rel. to age clinical protocol
Biomedical and Physical Functioning General Health Height Weight Waist Circumfernece % Body Fat Tanita scale BMI Self-rated Health - overall clinical protocol Self-rated Health - rel. to age clinical protocol
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Neuro Endocrinol Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 9.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011 ; 32(3): 279 285. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone and Cognition during Severe, Transient Hypothyroidism Frank
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011 ; 32(3): 279 285. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone and Cognition during Severe, Transient Hypothyroidism Frank
Base Rates of Impaired Neuropsychological Test Performance Among Healthy Older Adults
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, Vol. 13, No. 6, pp. 503 511, 1998 Copyright 1998 National Academy of Neuropsychology Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0887-6177/98 $19.00.00 PII S0887-6177(97)00037-1
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, Vol. 13, No. 6, pp. 503 511, 1998 Copyright 1998 National Academy of Neuropsychology Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0887-6177/98 $19.00.00 PII S0887-6177(97)00037-1
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Are patients with COPD psychologically distressed?
 Eur Respir J 2005; 26: 242 248 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.05.00010604 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2005 Are patients with COPD psychologically distressed? E.J. Wagena*, W.A. Arrindell #, E.F.M. Wouters " and
Eur Respir J 2005; 26: 242 248 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.05.00010604 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2005 Are patients with COPD psychologically distressed? E.J. Wagena*, W.A. Arrindell #, E.F.M. Wouters " and
Sprain of the neck: Quality of life and psychological functioning. A 4-year retrospective study
 Quality of Life Research 12: 335 343, 2003. Ó 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 335 Sprain of the neck: Quality of life and psychological functioning. A 4-year retrospective
Quality of Life Research 12: 335 343, 2003. Ó 2003 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands. 335 Sprain of the neck: Quality of life and psychological functioning. A 4-year retrospective
WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) Investigator Data Release Data Preparation Guide April 2014
 WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) Investigator Data Release Data Preparation Guide April 2014 1. Introduction This release consists of a single data set from the WHIMS Epidemiology of Cognitive Health Outcomes
WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) Investigator Data Release Data Preparation Guide April 2014 1. Introduction This release consists of a single data set from the WHIMS Epidemiology of Cognitive Health Outcomes
Test review. Comprehensive Trail Making Test (CTMT) By Cecil R. Reynolds. Austin, Texas: PRO-ED, Inc., Test description
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 19 (2004) 703 708 Test review Comprehensive Trail Making Test (CTMT) By Cecil R. Reynolds. Austin, Texas: PRO-ED, Inc., 2002 1. Test description The Trail Making Test
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 19 (2004) 703 708 Test review Comprehensive Trail Making Test (CTMT) By Cecil R. Reynolds. Austin, Texas: PRO-ED, Inc., 2002 1. Test description The Trail Making Test
COGMED CLINICAL EVALUATION SERIES
 COGMED CLIICAL EVALUATIO SERIES Cogmed Working Memory Training Pearson Clinical Assessment Part II Prepared by: Sissela utley, Ph.D. Stina Söderqvist, Ph.D. Kathryn Ralph, M.A. R&D Project Manager R&D
COGMED CLIICAL EVALUATIO SERIES Cogmed Working Memory Training Pearson Clinical Assessment Part II Prepared by: Sissela utley, Ph.D. Stina Söderqvist, Ph.D. Kathryn Ralph, M.A. R&D Project Manager R&D
An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A)
 Netherlands Journal of Psychology / SCARED adult version 81 An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A) Many questionnaires exist for measuring anxiety; however,
Netherlands Journal of Psychology / SCARED adult version 81 An adult version of the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Emotional Disorders (SCARED-A) Many questionnaires exist for measuring anxiety; however,
Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Den Bosch: Boxpress
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Parigger, E.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Language and executive functioning in children with ADHD Parigger, E.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Parigger, E. M. (2012). Language
February 8, Prepared By: Glen M. Doniger, PhD Director of Scientific Development NeuroTrax Corporation
 1 February 8, 2007 Prepared By: Glen M. Doniger, PhD Director of Scientific Development 2...3...3...3...5...6...6...7!" #"...7 ""...8...9 $#%&#$%'#...11!...12 "# $...14!...15 %...18 3 In the following
1 February 8, 2007 Prepared By: Glen M. Doniger, PhD Director of Scientific Development 2...3...3...3...5...6...6...7!" #"...7 ""...8...9 $#%&#$%'#...11!...12 "# $...14!...15 %...18 3 In the following
Levothyroxine Monotherapy Cannot Guarantee Euthyroidism in All Athyreotic Patients
 Levothyroxine Monotherapy Cannot Guarantee Euthyroidism in All Athyreotic Patients Damiano Gullo*., Adele Latina., Francesco Frasca, Rosario Le Moli, Gabriella Pellegriti, Riccardo Vigneri Endocrine Unit,
Levothyroxine Monotherapy Cannot Guarantee Euthyroidism in All Athyreotic Patients Damiano Gullo*., Adele Latina., Francesco Frasca, Rosario Le Moli, Gabriella Pellegriti, Riccardo Vigneri Endocrine Unit,
Clinical Study Depressive Symptom Clusters and Neuropsychological Performance in Mild Alzheimer s and Cognitively Normal Elderly
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Depression Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 396958, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/396958 Clinical Study Depressive Symptom Clusters and Neuropsychological Performance
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Depression Research and Treatment Volume 2011, Article ID 396958, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/396958 Clinical Study Depressive Symptom Clusters and Neuropsychological Performance
Impairments in cognitive abilities are among the. Promising New Approaches to Assess Cognitive Functioning in People with Multiple Sclerosis
 Promising New Approaches to Assess Cognitive Functioning in People with Multiple Sclerosis Heather Becker, PhD; Alexa Stuifbergen, PhD, RN, FAAN; Janet Morrison, MSN, RN Cognitive impairment has a major
Promising New Approaches to Assess Cognitive Functioning in People with Multiple Sclerosis Heather Becker, PhD; Alexa Stuifbergen, PhD, RN, FAAN; Janet Morrison, MSN, RN Cognitive impairment has a major
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. Effects of Evening vs Morning Levothyroxine Intake
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effects of Evening vs Morning Levothyroxine Intake A Randomized Double-blind Crossover Trial Nienke Bolk, MD; Theo J. Visser, PhD; Judy Nijman, BSc; Ineke J. Jongste, RN; Jan G.
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Effects of Evening vs Morning Levothyroxine Intake A Randomized Double-blind Crossover Trial Nienke Bolk, MD; Theo J. Visser, PhD; Judy Nijman, BSc; Ineke J. Jongste, RN; Jan G.
Construct and predictive validity of the Comprehensive Neurodiagnostic Checklist 10/20 (CNC)
 Construct and predictive validity of the Comprehensive Neurodiagnostic Checklist 10/20 (CNC) BSc. N. A. H. Helgers, University of Leiden, M.Ed. T. S. Brownback, Brownback, Mason and Associates Drs. D.
Construct and predictive validity of the Comprehensive Neurodiagnostic Checklist 10/20 (CNC) BSc. N. A. H. Helgers, University of Leiden, M.Ed. T. S. Brownback, Brownback, Mason and Associates Drs. D.
Pilot study on the assessment of the setpoint of the hypothalamus pituitary thyroid axis in healthy volunteers
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2010) 162 323 329 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Pilot study on the assessment of the setpoint of the hypothalamus pituitary thyroid axis in healthy volunteers N Benhadi,
European Journal of Endocrinology (2010) 162 323 329 ISSN 0804-4643 CLINICAL STUDY Pilot study on the assessment of the setpoint of the hypothalamus pituitary thyroid axis in healthy volunteers N Benhadi,
Case reports. Computerised cognitive assessment of concussed Australian Rules footballers
 354 Br J Sports Med 1;35:354 360 Case reports Centre for Sports Medicine Research Education, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, Australia M Makdissi P McCrory K Bennell Neuropsychology Laboratory,
354 Br J Sports Med 1;35:354 360 Case reports Centre for Sports Medicine Research Education, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria, Australia M Makdissi P McCrory K Bennell Neuropsychology Laboratory,
Multiple sclerosis : how cognitive performance relates to quality of life, depression, and perception of deficits
 Oregon Health & Science University OHSU Digital Commons Scholar Archive May 2011 Multiple sclerosis : how cognitive performance relates to quality of life, depression, and perception of deficits Rebecca
Oregon Health & Science University OHSU Digital Commons Scholar Archive May 2011 Multiple sclerosis : how cognitive performance relates to quality of life, depression, and perception of deficits Rebecca
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED YEARS
 CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
CHAPTER 2 CRITERION VALIDITY OF AN ATTENTION- DEFICIT/HYPERACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) SCREENING LIST FOR SCREENING ADHD IN OLDER ADULTS AGED 60 94 YEARS AM. J. GERIATR. PSYCHIATRY. 2013;21(7):631 635 DOI:
Mild deficits in attentional control in patients with the IGSF1 deficiency syndrome
 Clinical Endocrinology (2016) 84, 896 903 doi: 10.1111/cen.12947 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mild deficits in attentional control in patients with the IGSF1 deficiency syndrome S.D. Joustra*,, C.D. Andela*, W. Oostdijk,
Clinical Endocrinology (2016) 84, 896 903 doi: 10.1111/cen.12947 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mild deficits in attentional control in patients with the IGSF1 deficiency syndrome S.D. Joustra*,, C.D. Andela*, W. Oostdijk,
Concurrent validity of WAIS-III short forms in a geriatric sample with suspected dementia: Verbal, performance and full scale IQ scores
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 20 (2005) 1043 1051 Concurrent validity of WAIS-III short forms in a geriatric sample with suspected dementia: Verbal, performance and full scale IQ scores Brian L.
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 20 (2005) 1043 1051 Concurrent validity of WAIS-III short forms in a geriatric sample with suspected dementia: Verbal, performance and full scale IQ scores Brian L.
The Context and Purpose of Executive Function Assessments: Beyond the Tripartite Model
 The Context and Purpose of Executive Function Assessments: Beyond the Tripartite Model Janina Eberhart & Sara Baker Neuroscience & Education Conference 4 th June 2018 Executive Function (EF) EF is important
The Context and Purpose of Executive Function Assessments: Beyond the Tripartite Model Janina Eberhart & Sara Baker Neuroscience & Education Conference 4 th June 2018 Executive Function (EF) EF is important
Thyroid profile in geriatric population
 Original article: Thyroid profile in geriatric population Dr. Abhijit Pratap, Dr. Mona A. Tilak, Dr. Pradnya Phalak Dept of Biochemistry, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune 18 Corresponding
Original article: Thyroid profile in geriatric population Dr. Abhijit Pratap, Dr. Mona A. Tilak, Dr. Pradnya Phalak Dept of Biochemistry, Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune 18 Corresponding
The Neuropsychological Impairment Scale (NIS) Self-Report Form
 The Neuropsychological Impairment Scale (NIS) Self-Report Form A WPS TEST REPORT by William E O Donnell, PhD, MPH Copyright 1999 by Western Psychological Services wwwwpspublishcom Version 1110 ID Number:
The Neuropsychological Impairment Scale (NIS) Self-Report Form A WPS TEST REPORT by William E O Donnell, PhD, MPH Copyright 1999 by Western Psychological Services wwwwpspublishcom Version 1110 ID Number:
Carmen Inoa Vazquez, Ph.D., ABPP Clinical Professor NYU School of Medicine Lead Litigation Conference Philadelphia May 19, 2009 Presentation
 Carmen Inoa Vazquez, Ph.D., ABPP Clinical Professor NYU School of Medicine Lead Litigation Conference Philadelphia May 19, 2009 Presentation Neuropsychological Tests Battery The following List represents
Carmen Inoa Vazquez, Ph.D., ABPP Clinical Professor NYU School of Medicine Lead Litigation Conference Philadelphia May 19, 2009 Presentation Neuropsychological Tests Battery The following List represents
Risk factors for symptoms after traumatic stress: a 5-year longitudinal study in general practice
 Risk factors for symptoms after traumatic stress: a 5-year longitudinal study in general practice Bellis van den Berg, C. Joris Yzermans, Linda Grievink, Rebecca K. Stellato, Peter G. van der Velden, Bert
Risk factors for symptoms after traumatic stress: a 5-year longitudinal study in general practice Bellis van den Berg, C. Joris Yzermans, Linda Grievink, Rebecca K. Stellato, Peter G. van der Velden, Bert
Effects of severe depression on TOMM performance among disability-seeking outpatients
 Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 21 (2006) 161 165 Effects of severe depression on TOMM performance among disability-seeking outpatients Y. Tami Yanez, William Fremouw, Jennifer Tennant, Julia Strunk,
Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology 21 (2006) 161 165 Effects of severe depression on TOMM performance among disability-seeking outpatients Y. Tami Yanez, William Fremouw, Jennifer Tennant, Julia Strunk,
Decoding Your Thyroid Tests and Results
 Decoding Your Thyroid Tests and Results Wondering about your thyroid test results? Learn about each test and what low, optimal, and high results may mean so you can work with your doctor to choose appropriate
Decoding Your Thyroid Tests and Results Wondering about your thyroid test results? Learn about each test and what low, optimal, and high results may mean so you can work with your doctor to choose appropriate
The Five-Point Test: Reliability, Validity and Normative Data for Children and Adults
 The Five-Point Test: Reliability, Validity and Normative Data for Children and Adults Lara Tucha 1 *, Steffen Aschenbrenner 2, Janneke Koerts 1, Klaus W. Lange 3 1 Department of Clinical and Developmental
The Five-Point Test: Reliability, Validity and Normative Data for Children and Adults Lara Tucha 1 *, Steffen Aschenbrenner 2, Janneke Koerts 1, Klaus W. Lange 3 1 Department of Clinical and Developmental
Meniere s Disease Case. Suzanne Beason-Hazen, Ph.D.
 Meniere s Disease Case Suzanne Beason-Hazen, Ph.D. IDENTIFYING INFORMATION 64-year-old man, 15 years of education (three years of college, did not complete a degree) Employed as airline transport pilot
Meniere s Disease Case Suzanne Beason-Hazen, Ph.D. IDENTIFYING INFORMATION 64-year-old man, 15 years of education (three years of college, did not complete a degree) Employed as airline transport pilot
Relationships Between Traumatic Life Events, Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies, and Somatic Complaints
 DOI 10.1007/s10880-017-9494-y Relationships Between Traumatic Life Events, Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies, and Somatic Complaints Nadia Garnefski 1 Yanda van Rood 2 Carlijn de Roos 3 Vivian Kraaij
DOI 10.1007/s10880-017-9494-y Relationships Between Traumatic Life Events, Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies, and Somatic Complaints Nadia Garnefski 1 Yanda van Rood 2 Carlijn de Roos 3 Vivian Kraaij
The Use of Brief Assessment Batteries in Multiple Sclerosis. History of Cognitive Studies in MS
 This is the html version of the file http://wwwvagov/ms/library/managing/robert_kane_brief_assessment_batteries_in_msppt Google automatically generates html versions of documents as we crawl the web 1
This is the html version of the file http://wwwvagov/ms/library/managing/robert_kane_brief_assessment_batteries_in_msppt Google automatically generates html versions of documents as we crawl the web 1
Neurocognitive and psychosocial outcomes of obstructive sleep apnoea in Hong Kong Chinese
 HEALTH AND HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH FUND Neurocognitive and psychosocial outcomes of obstructive sleep apnoea in Hong Kong Chinese EYY Lau *, MSM Ip, TMC Lee K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Patients with obstructive
HEALTH AND HEALTH SERVICES RESEARCH FUND Neurocognitive and psychosocial outcomes of obstructive sleep apnoea in Hong Kong Chinese EYY Lau *, MSM Ip, TMC Lee K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Patients with obstructive
 alternate-form reliability The degree to which two or more versions of the same test correlate with one another. In clinical studies in which a given function is going to be tested more than once over
alternate-form reliability The degree to which two or more versions of the same test correlate with one another. In clinical studies in which a given function is going to be tested more than once over
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28958 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Keurentjes, Johan Christiaan Title: Predictors of clinical outcome in total hip
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/28958 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Keurentjes, Johan Christiaan Title: Predictors of clinical outcome in total hip
Neuropsychological Performance in Cannabis Users and Non-Users Following Motivation Manipulation
 University at Albany, State University of New York Scholars Archive Psychology Honors College 5-2010 Neuropsychological Performance in Cannabis Users and Non-Users Following Motivation Manipulation Michelle
University at Albany, State University of New York Scholars Archive Psychology Honors College 5-2010 Neuropsychological Performance in Cannabis Users and Non-Users Following Motivation Manipulation Michelle
 Your choice of SVTs is fundamental to the Slick et al criteria Paul Green Ph.D. paulgreen@shaw.ca www.wordmemorytest.com Central to the criteria is the presence of cognitive symptom exaggeration or feigning
Your choice of SVTs is fundamental to the Slick et al criteria Paul Green Ph.D. paulgreen@shaw.ca www.wordmemorytest.com Central to the criteria is the presence of cognitive symptom exaggeration or feigning
Current evidence for the treatment of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine/levotriiodothyronine combination therapy versus levothyroxine monotherapy
 Received: 28 September 2017 Accepted: 22 December 2017 DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.13062 REVIEW ARTICLE Current evidence for the treatment of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine/levotriiodothyronine combination therapy
Received: 28 September 2017 Accepted: 22 December 2017 DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.13062 REVIEW ARTICLE Current evidence for the treatment of hypothyroidism with levothyroxine/levotriiodothyronine combination therapy
Trail making test A 2,3. Memory Logical memory Story A delayed recall 4,5. Rey auditory verbal learning test (RAVLT) 2,6
 NEUROLOGY/2016/790584 Table e-1: Neuropsychological test battery Cognitive domain Test Attention/processing speed Digit symbol-coding 1 Trail making test A 2,3 Memory Logical memory Story A delayed recall
NEUROLOGY/2016/790584 Table e-1: Neuropsychological test battery Cognitive domain Test Attention/processing speed Digit symbol-coding 1 Trail making test A 2,3 Memory Logical memory Story A delayed recall
Reliability and Validity of the Divided
 Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 12:89 98 Copyright 2005 Taylor & Francis, Inc. ISSN: 1382-5585/05 DOI: 10.1080/13825580590925143 Reliability and Validity of the Divided Aging, 121Taylor NANC 52900
Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition, 12:89 98 Copyright 2005 Taylor & Francis, Inc. ISSN: 1382-5585/05 DOI: 10.1080/13825580590925143 Reliability and Validity of the Divided Aging, 121Taylor NANC 52900
Life stress and hysterectomy-oophorectomy
 Maturitas, 6 (1984) 319-325 Elsevier 319 MAT 00323 Life stress and hysterectomy-oophorectomy loor W. Kraaimaat and Arend T. Veeninga Academic Hospital, Utrecht, The Netherlands (Received 18 April 1984;
Maturitas, 6 (1984) 319-325 Elsevier 319 MAT 00323 Life stress and hysterectomy-oophorectomy loor W. Kraaimaat and Arend T. Veeninga Academic Hospital, Utrecht, The Netherlands (Received 18 April 1984;
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Stefanie Fendrick Pacific University. Recommended Citation. Notice to Readers
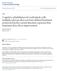 Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2009 Cognitive rehabilitation for individuals with multiple sclerosis does not have defined treatment protocols
Pacific University CommonKnowledge Physical Function CATs OT Critically Appraised Topics 2009 Cognitive rehabilitation for individuals with multiple sclerosis does not have defined treatment protocols
NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT S A R A H R A S K I N, P H D, A B P P S A R A H B U L L A R D, P H D, A B P P
 NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT S A R A H R A S K I N, P H D, A B P P S A R A H B U L L A R D, P H D, A B P P NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXAMINATION A method of examining the brain; abnormal behavior is linked to
NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT S A R A H R A S K I N, P H D, A B P P S A R A H B U L L A R D, P H D, A B P P NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL EXAMINATION A method of examining the brain; abnormal behavior is linked to
A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI I AT MĀNOA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF
 PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFICACY OF CLINICALLY PRACTICAL DUAL-TASK TESTS AS A CONCUSSION ASSESSMENT TOOL: A COMPARISON OF SINGLE- AND DUAL-TASK TESTS ON HEALTHY YOUNG ADULTS A THESIS SUBMITTED
PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFICACY OF CLINICALLY PRACTICAL DUAL-TASK TESTS AS A CONCUSSION ASSESSMENT TOOL: A COMPARISON OF SINGLE- AND DUAL-TASK TESTS ON HEALTHY YOUNG ADULTS A THESIS SUBMITTED
3 Moniek ter Kuile, Philomeen Weijenborg and Philip Spinhoven.
 Adapted from J Sex Med 2009, Aug 12 [Epub ahead of print] Sexual functioning in women with chronic pelvic pain: the role of anxiety and depression 3 Moniek ter Kuile, Philomeen Weijenborg and Philip Spinhoven.
Adapted from J Sex Med 2009, Aug 12 [Epub ahead of print] Sexual functioning in women with chronic pelvic pain: the role of anxiety and depression 3 Moniek ter Kuile, Philomeen Weijenborg and Philip Spinhoven.
