Endoscopic Ultrasound in Patients Over 80 Years Old
|
|
|
- Tamsin Young
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI /s ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endoscopic Ultrasound in Patients Over 80 Years Old Tan Attila Douglas O. Faigel Received: 11 January 2011 / Accepted: 8 April 2011 Ó Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011 Abstract Background The data on the safety and utility of EUS in patients over 80 years of age is limited. Objective We investigated the indications, feasibility, safety, and clinical utility of EUS in the management of GI, pancreatobiliary, and mediastinal diseases. Design Retrospective study. Setting A tertiary referral university hospital. Patients Consecutive patients C80 years of age referred over a 9-year period for EUS evaluation. Results A total of 265 EUS scans were performed in 232 patients with a mean age of 83.8 years. The indications for pancreatobiliary EUS were to evaluate a pancreatic mass (n = 60), pancreatic cyst (n = 18), pancreatitis (n = 10), dilated CBD in the setting of jaundice and/or biliary stricture (n = 20), dilated CBD with no jaundice and/or biliary stricture (n = 20). The indications for luminal gastrointestinal EUS were esophageal lesions (n = 21), gastric lesions (n = 30), duodenal lesions (n = 14), rectal lesions (n = 22), and gastrointestinal subepithelial lesions (n = 28). The indications for mediastinal EUS were mass/ lymphadenopathy (n = 14). EUS-guided FNA (EUS-FNA) was performed in 95 (35.8%) cases and results were consistent or suspicious for a malignancy in 62 cases (65.2%). Endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) was performed in 17 cases (6.41%) on the same session following endosonographic evaluation. The procedure was successful in all patients with no complications related to sedation, EUS, or T. Attila D. O. Faigel (&) Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Oregon Health and Science University, 3181 SW Sam Jackson Park Rd (L462), Portland, OR , USA faigeld@ohsu.edu EUS-FNA encountered. One patient had perforation following EMR. Limitation Retrospective study. Conclusions EUS and EUS-FNA are feasible and safe and have a significant impact on the management of GI, pancreatobiliary and mediastinal diseases in extreme elderly. Keywords Endoscopic ultrasound Fine needle aspiration Elderly Introduction As life expectancy increases, the number of older individuals has been increasing in many countries. As a result, this group represents a growing proportion of the total population. According to a US Department of Health and Human Services report in 2007, the older population (65? years) numbered 37.3 million in 2006 [1]. By 2030, the older population is expected to reach 71.5 million (more than twice the number in 2000). As a result of this trend, gastroenterologists are taking care of and performing endoscopic procedures on an increasing number of elderly patients. The role of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is well established in gastrointestinal, pancreatobiliary, and lung cancer diagnosis and staging [2]. The incidence of cancer in the population over 65 years is ten times higher than in those younger than 65 years and the cancer death rate is 16 times greater in patients over 65 years compared to younger patients [3]. Therefore, EUS is expected to play an important role in the care of elderly patients. Patients over 80 years old represent a challenging subgroup of the elderly. In these patients it is important to
2 balance life expectancy, quality of life, and safety concerns against the potential benefits of performing EUS. Unfortunately, there is a lack of data on EUS in the extreme elderly. The aim of this study is to describe clinical and demographic characteristics, indications, feasibility, safety, and impact of EUS in patients over 80 years of age from a tertiary referral center. Materials and Methods Patients All EUS procedures performed from March 1998 to March 2007 at a tertiary referral center (Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, Oregon) were reviewed. Patients 80 years of age or older were identified. The demographics, EUS indications, procedural information (instruments, sedation, American Society of Anesthesiology (ASA) classification, duration of the procedures, findings, interventions, outcome and complications) were retrospectively analyzed. Procedures were performed on both an inpatient and outpatient basis. Equipment and Procedure All EUS procedures were performed by an experienced endosonographer. All patients had a radial endosonographic evaluation (GF-UM160; Olympus, Melville, NY). Curvilinear echoendoscopes (GF-UC140P AL5; Olympus, Melville, NY; or FG36UX: Pentax Precision Medical Orangeburg, NY) were only used after radial endosonographic examination when clinically appropriate to perform EUS-guided FNA (EUS-FNA) or EUS-guided fine needle injection (EUS-FNI). A 19- or 22-gauge needle occluded with a stylet (Wilson Cook Inc, Winston-Salem, NC) was used for EUS-FNA and EUS-FNI. Color Doppler examination was performed before EUS-FNA or EUS-FNI to exclude interposed vascular structures. Intravenous antibiotics were routinely administered only in case of cystic lesion sampling or in patients with jaundice. Ciprofloxacin was the preferred antibiotic. Prophylactic antibiotics were not administered to patients undergoing EUS-FNI. High-frequency ultrasound miniprobe evaluation was performed with a 20-MHz Olympus miniprobe (Olympus Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). A cytopathologist was present during each EUS-FNA procedure. Three different types of sedation were used: moderate (conscious) sedation, deep sedation, and general anesthesia. Fentanyl, midazolam, promethazine, and propofol were used for sedation. Sedation was administered by the endoscopist in cases of moderate sedation and by an anesthesiologist or certified registered nurse anesthetist in case of deep sedation or general anesthesia. The type of sedation was chosen based on comorbidities and previous experience with sedation. Procedures were performed with patients in the left lateral decubitus position. Results Patient Population Over the 9-year period, 265 (8.26%) of 3,205 procedures were performed on 232 patients who were 80 years old or older. Twenty-two patients had more than one procedure. There were 140 (60.3%) female and 92 (39.7%) male patients. Patients ages ranged from 80 to 97 years, with a mean age (standard deviation [SD]) of 83.8 (1.4) years. Anesthesia The ASA classification of each patient for every procedure was determined; two patients were classified as ASA 1, 180 patients were classified as ASA 2, and 83 patients were classified as ASA 3. The majority of the EUS procedures [224 (84.52%)] were performed under conscious sedation. Twenty-eight (10.56%) procedures were performed with the patients under general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation or deep sedation and 13 procedures (4.90%) were performed with no sedation. Average dosage of medications used for conscious sedation were: fentanyl (mean ± standard deviation) 101 ± 43.1 lg (range: ), midazolam 4.6 ± 1.7 mg (range: 1 10). Seventeen patients received promethazine 17.1 ± 8.7 mg (range: ). Procedure Information Two hundred and forty-three (91.7%) upper and 22 (8.3%) lower EUS examinations were performed. Ten patients (3.7%) underwent high-frequency ultrasound miniprobe evaluation. The average procedure (SD) duration was 52 (±18) min. One hundred and twenty-eight patients (48.3%) underwent EUS to evaluate pancreatobiliary pathologies. Indications for pancreatobiliary EUS were to evaluate a pancreatic mass (n = 60), pancreatic cystic lesion (n = 18), pancreatitis (n = 10), dilated common bile duct in the setting of jaundice and/or biliary stricture (n = 20), dilated CBD with no evidence of biochemical cholestasis and/or biliary stricture (n = 20). Eighty-seven patients (30.8%) underwent EUS for luminal gastrointestinal tract pathologies; esophageal (n = 21), gastric (n = 30), duodenal (n = 14), and rectal (n = 22). Twenty-eight patients (10.5%) underwent EUS for gastrointestinal subepithelial pathologies. Fourteen
3 patients (5.2%) underwent EUS for evaluation of mediastinal pathologies. Eight patients (3%) had EUS evaluation for further evaluation of other pathologies. Ninety-five patients (35.8%) had EUS-FNA. No EUS-associated complications occurred. One patient had a perforation complicating EMR of subepithelial lesion (GIST) (see below). Sixty patients were referred for evaluation of pancreatic mass lesions (Table 1). Endosonographic evaluation revealed solid pancreatic mass lesions (n = 29), ampullary mass lesions (n = 13), pancreatic cystic lesions (n = 8), pancreatitis (n = 2), fatty infiltration (n = 2), and normal pancreatic parenchyma (n = 6). Among 29 patients with pancreatic mass lesions; EUS-FNA was performed on the pancreatic mass (16 patients), on the pancreatic mass and associated lymph nodes (eight patients) and on a liver mass (one patient). Cytopathological evaluation of FNA sample of pancreatic mass ± lymph nodes revealed adenocarcinoma (n = 17), suspicion for malignancy (n = 2), renal cell carcinoma (n = 1), and no findings for malignancy (n = 4). Cytopathological evaluation of FNA sample obtained of the liver mass revealed adenocarcinoma and lymph node revealed neuroendocrine tumor. Among 13 patients with an ampullary mass, one patient had EUS-FNA of the ampullary mass, which revealed adenocarcinoma and two patients had EUS-FNA of lymph nodes which were reactive. EUS-FNA was performed on all eight patients with a pancreatic cystic lesion. One patient was diagnosed with a mucinous adenocarcinoma (23 mm in diameter). A carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level could not be measured due to an inadequate amount of fluid obtained to run the test. Another patient who was diagnosed with a mucinous neoplasm with dysplastic features (90 mm in diameter) had a CEA level of 2,887 ng/dl. In the remaining six patients with pancreatic cysts, EUS-FNA samples were negative for a malignancy. Eighteen patients were referred with a primary indication to evaluate pancreatic cystic lesions (Table 2). In 13 patients, cysts did not have any endosonographic evidence of main duct connection. Eleven EUS-FNA performed revealed mucin (n = 3), adenocarcinoma (n = 1), atypical cells (n = 1), pseudocyst (n = 1), and no malignancy (n = 5). CEA was below 192 ng/ml in five patients and above 192 ng/ml in two patients. CEA could not be measured in the rest of the patients due to the inadequate fluid sample. Two patients were found to have cystic lesions with main pancreatic duct connection. EUS-FNA revealed Table 1 Endoscopic ultrasound performed for the evaluation of pancreatic mass lesions (n = 60) FNA fine needle aspiration; LN lymph node; AdenoCA adenocarcinoma Findings No. of patients FNA FNA findings Pancreas mass (mass) AdenoCA (17) 8 (mass?ln) Suspicious for malignancy (2) Renal cell carcinoma (1) Negative for malignancy (4) 1 (liver mass) AdenoCA (1) 1 (LN) Neuroendocrine tumor (1) Ampullary mass 13 1 (mass) AdenoCA (1) 2 (LN) Reactive (2) Cystic lesion 8 8 (mass) Mucinous AdenoCA (1) Mucinous neoplasm with dysplastic features (1) Negative for malignancy (6) Pancreatitis 2 Fatty infiltration 2 No mass 6 Table 2 Endoscopic ultrasound evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions MPD main pancreatic duct; CMPD communicating with main pancreatic duct; NCMPD non-communicating with main pancreatic duct Findings No. of patients FNA FNA findings CEA Isolated MPD dilation 3 (17, 18, 4 mm) Cysts CMPD 2 (34, 42 mm) 2 Mucin: 2 139, 265 Cysts NCMPD 13 (average 24.6 mm) 11 AdenoCA: 1 [192 : 2 Atypical cells 1 Mucin: 3 \192 : 5 Pseudocyst: 1 Negative for malignancy 5
4 mucin and CEA levels of 139 and 265 ng/ml. Three patients were found to have an isolated dilation of the main pancreatic duct. Ten patients were referred for the evaluation of pancreatitis. EUS criteria for chronic pancreatitis described by Catalano et al. [5] were used. One patient fulfilled endosonographic criteria for chronic pancreatitis. Among nine patients with endosonographically normal pancreatic parenchyma, incidental findings were pancreatic cysts in two patients, pancreatic duct stone without other inflammatory changes in one patient, and dilated CBD secondary to ampullary stenosis. Twenty patients were referred for the evaluation of dilated common bile duct (CBD) in the setting of jaundice and/or stricture (Table 3). Eight patients were found to have a pancreatic mass. Seven patients who had EUS-FNA were found to have adenocarcinoma (n = 5), suspicion of malignancy (n = 1), and no malignancy (n = 1). One patient with a pancreatic mass did not have EUS-FNA due to agitation. CBD mass lesions were noted in five patients. EUS-FNA performed on these patients revealed adenocarcinoma (n = 1), metastatic adenocarcinoma (n = 1), atypical cells (n = 1), and no malignancy (n = 2). In the remaining patients, the cause of dilated CBD was found to be pancreatitis (n = 3), ampullary mass (n = 2), retroperitoneal mass (n = 1), and CBD stone (n = 1). Twenty patients were referred for the evaluation of dilated CBD without any biochemical evidence of cholestasis or biliary stricture. Average endosonographic diameter of CBD was 13.7 mm (±3.4 mm). Eight patients had a prior history of cholecystectomy. Seven patients had endosonographic evidence of CBD stones and sludge and were referred to ERCP. The remaining 13 patients had no endosonographic evidence of biliary pathology and the presumed cause of CBD dilation was thought to be secondary to benign ampullary stenosis. Fourteen patients were referred for endosonographic evaluation of mediastinal mass lesions with an average size of 32.7 mm (±15.5 mm) (Table 4). Thirteen EUS-FNA were performed diagnosing adenocarcinoma (n = 3), nonsmall cell lung cancer (n = 3), small cell lung cancer (n = 2), renal cell carcinoma (n = 1), and no evidence of malignancy (n = 4). Three patients with negative EUS- FNA were subsequently diagnosed with locally advanced thymoma, small cell lung cancer on mediastinoscopy, and thymoma on bronchoscopy. Table 3 EUS evaluation of dilated CBD in the setting of jaundice and/or stricture CBD common bile duct; FNA fine needle aspiration; AdenoCA adenocarcinoma; LN lymph node Findings No. of patients Size FNA FNA findings Pancreatic mass 8 29(±7 mm) 5 (mass) AdenoCA (5) 1 (mass? LN) Suspicious for malignancy (1) 1 ascites Negative for malignancy (1) CBD mass 5 20 (±7 mm) 3 (mass) Negative for malignancy (2) 1 (LN) Metastatic adenoca (1) 1 (mass? LN) AdenoCA (1) Atypical cells (1) Pancreatitis 3 1(mass? LN) Pancreatitis (1) 1 (LN) Negative for malignancy (1) Reactive changes (1) Ampullary mass 2 Retroperitoneal mass 1 CBD stone 1 19 Table 4 Endoscopic ultrasound for the evaluation of mediastinal lesions AdenoCA adenocarcinoma; SCLCa small cell lung cancer; NSCLCa non-small cell lung cancer; FNA fine needle aspiration No. of patients FNA FNA findings Intervention AdenoCA (3) SCLCa (2) NSCLCa (3) Renal cell carcinoma (1) Negative for malignancy (4) Mediastinoscopy (2) Locally advanced thymoma SCLCa Bronchoscopy (1) Thymoma
5 Table 5 Esophageal cases Indications No. of patients FNA Outcome Endoscopic Rx Unable to traverse AdenoCA 13 1 LN Neg: 1 EMR 4 2 SCC 5 4 LN Neg: 2 Mets: 2 Dysphagia strictures 2 1 LN Neg: 1 Barrett s esophagus HGD 1 RFA 1 AdenoCA adenocarcinoma; SCC squamous cell carcinoma; HGD high-grade dysplasia; Neg negative; EMR endoscopic mucosal resection; RFA radiofrequency ablation; LN lymph node; N number of Table 6 Endoscopic ultrasound evaluation of gastric lesions Indications No. of patients FNA FNA findings EMR EMR findings Gastric cancer 14 2 AdenoCA (2) Post-EMR f/u 5 3 Inflammatory polyp (1) Lipoma (1) IMD (1) GJA thickening 1 1 (LN) AdenoCA Fundus mass 2 FU 1 Gastric wall thickening 6 (2 normal) Non-healing AU 1 IMD intestinal metaplasia with dysplasia; AdenoCA adenocarcinoma; FNA fine needle aspiration; EMR endoscopic mucosal resection; f/u follow-up; GJA gastrojejunal anastomosis; LN lymph node; FU fundus ulcer; AU antrum ulcer Twenty-one patients were referred for endosonographic evaluation of esophageal lesions (Table 5); adenocarcinoma (n = 13), squamous cell carcinoma (n = 5), stricture (n = 2), and Barrett s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia (n = 1). In two patients, the echoendoscope could not traverse the esophageal narrowing caused by adenocarcinoma. EUS-FNA of five patients with mediastinal lymphadenopathy revealed squamous cell carcinoma metastasis in two patients and no malignancy in the remaining three patients. Following EUS evaluation, four patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma and one patient with Barrett s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia underwent EMR (n = 4) and radiofrequency ablation (n = 1). Thirty patients were referred for endosonographic evaluation of gastric lesions (Table 6). Fourteen patients had EUS for gastric cancer. Two of them subsequently underwent EMR that revealed adenocarcinoma. Five patients had EUS as post-emr follow-up. Three of them subsequently had EMR that revealed an inflammatory polyp, a lipoma and intestinal metaplasia with dysplasia. A patient with a prior history of gastric adenocarcinoma had an EUS for evaluation of gastrojejunal thickening on computerized tomography. A subsequent EUS-FNA of a lymph node showed adenocarcinoma recurrence. The remaining gastric EUS examinations were done for the evaluation of gastric wall thickening (n = 6), fundic mass (n = 2), fundic ulcers (n = 1), and non-healing antral ulcer (n = 1). No endosonographic evidence of a fundic mass was noted. No evidence of gastric wall thickening was noted in four patients. The other patient had an ulcer with wall thickening likely secondary to inflammatory changes. Other patients had normal endosonographic findings. Fourteen patients with duodenal lesions were referred for endosonographic evaluation. Ten patients with duodenal adenoma had high-frequency ultrasound miniprobe evaluation. In nine patients, duodenal adenomas were subsequently ablated with argon plasma coagulation. The other duodenal adenoma was removed with EMR. A patient with a suspicion of duodenal varix was found to have a periduodenal cyst. A patient with a suspicious periduodenal extrinsic compression at previous endoscopic evaluation had normal endosonographic findings. The remaining two patients were referred for endosonographic evaluation of duodenal adenocarcinoma and duodenal polyp (adenoma). Twenty-two patients were referred for endosonographic evaluation of rectal lesions; rectal mass (n = 17), rectal malignancy recurrence (n = 4), and perirectal mass (n = 1). An incidental subepithelial lesion was noted at the endosonographic evaluation for a rectal cancer recurrence follow-up. EUS-FNA of this lesion revealed GIST.
6 Table 7 Endoscopic ultrasound evaluation of subepithelial lesions Locations No. of patients FNA FNA findings EMR EMR findings Bx Stomach 17 7 GIST (3) 4 Leiomyoma (2) SMN (1) Foveolar polyp (1) Lipoma (1) GIST (1) SCN (2) GEJ 6 1 SMN (1) 3 BE HGD (1) NL (1) Lymphangioma (1) Duodenum 3 1 Carcinoid (1) GIST (1) Esophagus 2 1 B cell lymphoma (1) GIST gastrointestinal stromal tumor; SMN smooth muscle neoplasm; SCN spindle cell neoplasm; NL normal; BE HGD Barrett s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia; GEJ gastroesophageal junction EUS-FNA of a perirectal mass revealed abundant anucleate squamous cells with no evidence of malignancy. These findings raised the possibility of epidermal inclusion cyst. Twenty-eight patients underwent endosonographic evaluation for subepithelial lesions (Table 7) [gastric (n = 17), gastroesophageal junction (n = 6), duodenal (n = 3), and esophageal (n = 2)]. EUS-FNA performed on seven patients with gastric lesions revealed GIST (n = 3), spindle cell neoplasm (n = 2), smooth muscle neoplasm (n = 1), and lipoma (n = 1). Four patients with gastric lesions subsequently underwent EMR, which revealed two leiomyomas, one foveolar polyp, and one GIST. The EMR that was done to remove gastric GIST was complicated with perforation. EUS-FNA that was done on a gastroesophageal junction lesion revealed smooth muscle neoplasm. Three EMRs of gastroesophageal lesions revealed a Barrett s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia, a lymphangioma, and a normal histopathology. An EMR of duodenal lesion revealed a carcinoid tumor. A duodenal GIST was diagnosed with conventional biopsy. An esophageal B cell lymphoma was diagnosed with EUS- FNA. Endosonography of the other esophageal subepithelial lesion revealed a duplication cyst. Four patients who were referred for endosonographic evaluation of suspected upper GI tract pathology had unremarkable EUS findings (a patient with signet ring cell adenocarcinoma on breast biopsy, a patient with abdominal pain, a patient with weight loss, and a patient with lymphoma). Two patients with abnormal liver function tests were endosonographically evaluated for lymphadenopathy. EUS-FNA of a periportal lymph node of a patient with lung mass revealed lung cancer metastasis. A patient with a history of colon cancer was referred for porta hepatis lymphadenopathy. EUS evaluation did not reveal any pathologic lymph nodes but endosonographic findings were consistent with chronic pancreatitis. Discussion Although the role of EUS is well established in adult GI and pancreatobiliary diseases as well as lung cancer diagnosis and staging, there is no specific knowledge in the literature regarding the role of EUS in patients over 80 years of age. The current study illustrates the experience of endoscopic ultrasound at a tertiary referral center evaluating various pancreatobiliary, GI tract and mediastinal lesions in extreme elderly. Given the aging population, gastroenterologists will perform more advanced diagnostic procedures in extremes of ages. Prior studies have reported on the indications and complications of EGD, colonoscopy, and ERCP in patients 80 or older [6]. These studies have generally found these procedures to be safe and effective, and the complications not higher than those in younger patients. Ours is the first study of EUS in this cohort. According to the US Census Bureau s 2007 American Community Survey, individuals over 80 make up 3.6% of the population [4]. However, in our cohort, 8.26% of the EUS procedures were performed on the same age group. This discrepancy is likely due to the higher incidence of malignancies in this age group. Not surprisingly, the vast majority of EUSs were done due for a suspicion of malignancy. EUS-FNA results were consistent with a malignancy or suspicious for a malignancy in 62 out of 95 (65.2%) EUS-FNA performed. Endoscopic mucosal resections were performed in 17 patients (6.41%) upon endosonographic evaluations. All of the EMR results allowed accurate diagnosis and staging of
7 the underlying pathologies. In the extreme elderly seen at our institution, the primary role of EUS was cancer diagnosis and staging. In these older patients with comorbidities, treatment may be more limited, but a diagnosis is important to allow for appropriate counseling. Although only half of the EUS procedures (48.3%) were performed for the evaluation of the pancreatobiliary system in patients over 80, more than two-thirds (67.3%) of the EUS-FNAs were performed to evaluate pancreatobiliary pathologies. Of the 64 patients who underwent pancreatobiliary EUS-FNA, 40 (62.5%) had cytopathologic results consistent with malignancy or suspicious for malignancy. Among the 19 patients with no cytopathologic evidence of malignancy, ten EUS-FNA were obtained from pancreatic cystic lesions. As expected, the yield to demonstrate malignant cells in the fluid obtained from pancreatic cysts is low. Therefore, the presence of mucin and cyst CEA levels plays an important role in risk stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions. The major limitation of this study is the retrospective design. Since a good portion of our practice is based on referral from other institutions, information on surgical pathology as well as clinical outcome of our patients is scarce. Therefore, we cannot comment on the correlation of EUS-FNA results with surgical pathologies. The prereferral evaluations were not standardized. We cannot exclude a referral bias as to why these elderly patients were referred but others may not have been. All patients tolerated the procedure well. No EUS or EUS-FNA-related complications occurred. One patient had a perforation during the EMR that was done following endosonographic evaluation, which was not considered an EUS-related complication. In conclusion, EUS and EUS-FNA are safe and have a significant impact on the management of pancreatobiliary, gastrointestinal, and mediastinal diseases in patients over 80 years of age. EUS allows one to avoid the more-invasive and higher-risk procedures. The primary role appears to be for the diagnosis of malignancy. Conflict of interest The authors (Tan Attila, MD; Douglas O. Faigel, MD) declare that they have no conflicts of interest. References 1. A profile of Older Americans. Administration on aging. US Department of Health and Human Services. prof/statistics/profile/2007/2007profile.pdf; LeBlanc JK, DeWitt J, Sherman S. Endoscopic ultrasound: how does it aid the surgeon? Adv Surg. 2007;41: Berger NA, Savvides P, Koroukian SM, et al. Cancer in the elderly. Trans Am Clin Climatol Assoc. 2006;117: Catalano MF, Lahoti S, Geenen JE, Hogan WJ. Prospective evaluation of endoscopic ultrasonography, endoscopic retrograde pancreatography, and secretin test in the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;48: Qureshi WA, Zuckerman MJ, Adler DG, et al. ASGE guideline: modifications in endoscopic practice for the elderly. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY
 A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
A LEADER IN ADVANCED ENDOSCOPY AND HEPATOBILIARY SURGERY St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center Welcome The St. Peter s Hospital Advanced Endoscopy & Hepatobiliary Center is a leader
Introduction of Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS)
 Introduction of Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) Dr. Yuk Tong LEE MBChB, MD(CUHK), FRCP (Edin), FRCP(Lond), FHKCP, FHKAM Specialist in Gastroenterology and Hepatology Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) ª
Introduction of Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) Dr. Yuk Tong LEE MBChB, MD(CUHK), FRCP (Edin), FRCP(Lond), FHKCP, FHKAM Specialist in Gastroenterology and Hepatology Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) ª
Performing forward-viewing endoscopy at time of pancreaticobiliary EUS and ERCP may detect additional upper gastrointestinal lesions
 E193 Performing forward-viewing endoscopy at time of pancreaticobiliary EUS and ERCP may detect additional upper gastrointestinal lesions Authors Ashby Thomas 1, *, Arunan S Vamadevan 1, *, Eoin Slattery
E193 Performing forward-viewing endoscopy at time of pancreaticobiliary EUS and ERCP may detect additional upper gastrointestinal lesions Authors Ashby Thomas 1, *, Arunan S Vamadevan 1, *, Eoin Slattery
The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic neoplasms
 The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic neoplasms CYSTIC LESIONS AND FLUID COLLECTIONS OF THE PANCREAS Their pathology ranges from pseudocysts and pancreatic necrosis
The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic neoplasms CYSTIC LESIONS AND FLUID COLLECTIONS OF THE PANCREAS Their pathology ranges from pseudocysts and pancreatic necrosis
Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry?
 Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry? President, ASGE Chairman, GI & Hepatology Scottsdale, AZ Faigel.douglas@mayo.edu Case 55 yo male with reflux EGD for Barrett s Screening SET, mucosal
Subepithelial Lesions of the Gut: When Should I Worry? President, ASGE Chairman, GI & Hepatology Scottsdale, AZ Faigel.douglas@mayo.edu Case 55 yo male with reflux EGD for Barrett s Screening SET, mucosal
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical Impact. Giancarlo Caletti. Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna. Caletti
 Clinical Impact Giancarlo Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna AUSL di Imola,, Castel S. Pietro Terme (BO) 1982 Indications Diagnosis of Submucosal Tumors (SMT) Staging of Neoplasms Evaluation of Pancreato-Biliary
Clinical Impact Giancarlo Gastroenterologia Università di Bologna AUSL di Imola,, Castel S. Pietro Terme (BO) 1982 Indications Diagnosis of Submucosal Tumors (SMT) Staging of Neoplasms Evaluation of Pancreato-Biliary
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology
 Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) in gastroenterology. It includes standards for theoretical
Research Article The Utility of Repeat Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Suspected Pancreatic Cancer
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 268290, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/268290 Research Article The Utility of Repeat Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Suspected
Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2010, Article ID 268290, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2010/268290 Research Article The Utility of Repeat Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration for Suspected
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Clinical Study Bedside Endoscopic Ultrasound in Critically Ill patients
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2011, Article ID 529791, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/529791 Clinical Study Bedside Endoscopic Ultrasound in Critically Ill patients Mehdi Mohamadnejad, 1, 2 Julia
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2011, Article ID 529791, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/529791 Clinical Study Bedside Endoscopic Ultrasound in Critically Ill patients Mehdi Mohamadnejad, 1, 2 Julia
Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes
 Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes Evan A. Alston, MD 1 ; Sejong Bae, PhD 2 ; and Isam A. Eltoum, MD, MBA 1 BACKGROUND:
Suspicious Cytologic Diagnostic Category in Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided FNA of the Pancreas: Follow-Up and Outcomes Evan A. Alston, MD 1 ; Sejong Bae, PhD 2 ; and Isam A. Eltoum, MD, MBA 1 BACKGROUND:
EFSUMB EUROPEAN FEDERATION OF SOCIETIES FOR ULTRASOUND IN MEDICINE AND BIOLOGY Building a European Ultrasound Community
 MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography
MINIMUM TRAINING REQUIREMENTS FOR THE PRACTICE OF MEDICAL ULTRASOUND IN EUROPE Appendix 9: Endoscopic Ultrasound in Gastroenterology This curriculum is intended for clinicians who perform endoscopic ultrasonography
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 Pancreatic Cancer- Case #1. Endoscopic management of GI malignancy. Endoscopic approaches in GI malignancy- Agenda
 Slide 1 A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Endoscopic management of GI malignancy Tyler Berzin MD, MS Center for Advanced Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Slide 1 A teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School Endoscopic management of GI malignancy Tyler Berzin MD, MS Center for Advanced Endoscopy Division of Gastroenterology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Original Article. Rattanasupar A Attasaranya S Ovartlarnporn B ABSTRACT
 74 THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal Ultrasound (TUS) for Diagnosed Dyspepsia in Elderly Patients Original Article Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal
74 THAI J GASTROENTEROL 2010 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal Ultrasound (TUS) for Diagnosed Dyspepsia in Elderly Patients Original Article Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) plus Transabdominal
EVALUATION FORM WSGNA 2018 Fall Conference Endoscopy for Malignant and Premalignant Lesions of the GI Tract 10/27/2018
 EVALUATION FORM WSGNA 2018 Fall Conference Endoscopy for Malignant and Premalignant Lesions of the GI Tract 10/27/2018 Please respond to the following items on a scale from 5 (highest) to 1 (lowest). The
EVALUATION FORM WSGNA 2018 Fall Conference Endoscopy for Malignant and Premalignant Lesions of the GI Tract 10/27/2018 Please respond to the following items on a scale from 5 (highest) to 1 (lowest). The
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG 1, Brintha K. Enestvedt, MD, MBA 2, Bryan G. Sauer, MD, MSc, FACG (GRADE Methodologist) 3 and Anne Marie Lennon,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts Grace H. Elta, MD, FACG 1, Brintha K. Enestvedt, MD, MBA 2, Bryan G. Sauer, MD, MSc, FACG (GRADE Methodologist) 3 and Anne Marie Lennon,
Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut
 Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut Moderators: Giuseppe Aliperti, MD Steven Edmundowicz, MD Panelists Douglas O. Faigel, MD Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Oregon
Commonly Encountered Neuro-Endocrine Tumors of the Gut Moderators: Giuseppe Aliperti, MD Steven Edmundowicz, MD Panelists Douglas O. Faigel, MD Professor of Medicine Department of Gastroenterology Oregon
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor
 Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
Barrett s esophagus. Barrett s neoplasia treatment trends
 Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND Furqaan Ahmed Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan. REVIEW ARTICLE : 13-20 Conventional endoscopy has allowed examination and sampling of the mucosal layer of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND Furqaan Ahmed Aga Khan University Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan. REVIEW ARTICLE : 13-20 Conventional endoscopy has allowed examination and sampling of the mucosal layer of the gastrointestinal
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cysts. Introduction
 An Approach to Pancreatic Cysts Nalini M. Guda, MD Aurora St. Luke s Medical Center, Milwaukee Clinical Adjunct Professor of Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Introduction
An Approach to Pancreatic Cysts Nalini M. Guda, MD Aurora St. Luke s Medical Center, Milwaukee Clinical Adjunct Professor of Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Introduction
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Chronic pancreatitis mimicking intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas; Report of tow cases
 Jichi Medical University Journal Chronic pancreatitis mimicking intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas; Report of tow cases Noritoshi Mizuta, Hiroshi Noda, Nao Kakizawa, Nobuyuki Toyama,
Jichi Medical University Journal Chronic pancreatitis mimicking intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas; Report of tow cases Noritoshi Mizuta, Hiroshi Noda, Nao Kakizawa, Nobuyuki Toyama,
Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Be the difference between maybe and definitely.
 (EUS) Be the difference between maybe and definitely. Maybe? Definitely. EUS lets you be certain in uncertain cases. Why EUS? EUS combines ultrasound technology with endoscopy to gain an internal vantage
(EUS) Be the difference between maybe and definitely. Maybe? Definitely. EUS lets you be certain in uncertain cases. Why EUS? EUS combines ultrasound technology with endoscopy to gain an internal vantage
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam
 Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Safe Answers For The American Board of Surgery Certifying Exam & Recertifying Exam By Sarmad Aji, MD., FACS. A comprehensive review of the most commonly asked questions on the American Board of Surgery
Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Malignancies
 Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Malignancies Gareth Eeson MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist and General Surgeon Kelowna General Hospital Interior Health Consultant, Surgical Oncology BC Cancer Agency Centre
Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Malignancies Gareth Eeson MD MSc FRCSC Surgical Oncologist and General Surgeon Kelowna General Hospital Interior Health Consultant, Surgical Oncology BC Cancer Agency Centre
ENDOSCOPY IN COMPETITION DIAGNOSTICS. Dr. med. Dirk Hartmann Klinikum Ludwigshafen
 Falk Symposium 166 GI Endoscopy Standards and Innovations Mainz, 18. 19. September 2008 ENDOSCOPY IN COMPETITION DIAGNOSTICS Dr. med. Dirk Hartmann Klinikum Ludwigshafen ENDOSCOPY IN COMPETITION Competing
Falk Symposium 166 GI Endoscopy Standards and Innovations Mainz, 18. 19. September 2008 ENDOSCOPY IN COMPETITION DIAGNOSTICS Dr. med. Dirk Hartmann Klinikum Ludwigshafen ENDOSCOPY IN COMPETITION Competing
Faculty Disclosure. Objectives. State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) 24/11/2014
 State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) Dr. Amy Morse November 2014 Faculty: Amy Morse Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
State of the Art #3: Referrals for Gastroscopy (focus on common esophagus problems) Dr. Amy Morse November 2014 Faculty: Amy Morse Faculty Disclosure Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research
Barrett s Esophagus Burn, Resect, Freeze, or Just Watch Strategies for Evaluation and Surveillance of Barrett s Amitabh Chak, MD OBJECTIVES: NOTES:
 Speaker 1 Barrett s Esophagus Burn, Resect, Freeze, or Just Watch Strategies for Evaluation and Surveillance of Barrett s Amitabh Chak, MD 1. List the epidemiology of Barrett s esophagus. 2. Review the
Speaker 1 Barrett s Esophagus Burn, Resect, Freeze, or Just Watch Strategies for Evaluation and Surveillance of Barrett s Amitabh Chak, MD 1. List the epidemiology of Barrett s esophagus. 2. Review the
The Pancreas. Basic Anatomy. Endocrine pancreas. Exocrine pancreas. Pancreas vasculature. Islets of Langerhans. Acinar cells Ductal System
 SGNA: Back to Basics Rogelio G. Silva, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Advocate Christ Medical Center GI
SGNA: Back to Basics Rogelio G. Silva, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Advocate Christ Medical Center GI
The current tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:573 579 Influence of the Number of Malignant Regional Lymph Nodes Detected by Endoscopic Ultrasonography on Survival Stratification in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:573 579 Influence of the Number of Malignant Regional Lymph Nodes Detected by Endoscopic Ultrasonography on Survival Stratification in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Endoscopic ultrasonography in suspected pancreatic malignancy and indecisive CT
 O r i g i n a l a r t i c l e Endoscopic ultrasonography in suspected pancreatic malignancy and indecisive CT O.L.M. Meijer 1, R.K. Weersma 1, E.J. van der Jagt 2, H.M. van Dullemen 1 * Departments of
O r i g i n a l a r t i c l e Endoscopic ultrasonography in suspected pancreatic malignancy and indecisive CT O.L.M. Meijer 1, R.K. Weersma 1, E.J. van der Jagt 2, H.M. van Dullemen 1 * Departments of
Evaluation of AGA and Fukuoka Guidelines for EUS and surgical resection of incidental pancreatic cysts
 Evaluation of AGA and Fukuoka Guidelines for EUS and surgical resection of incidental pancreatic cysts Authors Alexander Lee 1, Vivek Kadiyala 2,LindaS.Lee 3 Institutions 1 Texas Digestive Disease Consultants,
Evaluation of AGA and Fukuoka Guidelines for EUS and surgical resection of incidental pancreatic cysts Authors Alexander Lee 1, Vivek Kadiyala 2,LindaS.Lee 3 Institutions 1 Texas Digestive Disease Consultants,
Expect Endoscopic Ultrasound Aspiration Needle
 Expect Endoscopic Ultrasound Aspiration Needle GLOBAL TECHNIQUE SPOTLIGHT CASES PRESENTED BY: Krishnavel V. Chathadi, MD Therapeutic Endoscopist, BJC Medical Group Missouri Baptist Medical Center St. Louis,
Expect Endoscopic Ultrasound Aspiration Needle GLOBAL TECHNIQUE SPOTLIGHT CASES PRESENTED BY: Krishnavel V. Chathadi, MD Therapeutic Endoscopist, BJC Medical Group Missouri Baptist Medical Center St. Louis,
Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines
 Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Pancreas Case Scenario #1
 Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors
 2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
2014 CPT COD1NG UPDATES Gastroenterology CPT Advisors Joel V. Brill, MD, AGA CPT Advisor Daniel C. DeMarco, MD, ACG CPT Advisor Glenn D. Littenberg, MD, ASGE CPT Advisor The American College of Gastroenterology
WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights
 WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights OPEN TO THE POSSIBILITIES SEAN E. McGarr, do Kennebec Gastrointestinal Associates Maine General Medical Center, Augusta, ME 04330, United States Director of Gastrointestinal
WallFlex Stents Technique Spotlights OPEN TO THE POSSIBILITIES SEAN E. McGarr, do Kennebec Gastrointestinal Associates Maine General Medical Center, Augusta, ME 04330, United States Director of Gastrointestinal
The Risk Factors for Acute Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Biopsy
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 72 No. 3, 135-140 https://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.72.3.135 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Risk Factors for Acute Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Ultrasound
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 72 No. 3, 135-140 https://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2018.72.3.135 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Risk Factors for Acute Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Ultrasound
High-frequency miniprobe endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of indeterminate esophageal strictures
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-5 High-frequency miniprobe endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of indeterminate esophageal strictures Surinder Singh Rana a, Ravi Sharma a,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (2018) 31, 1-5 High-frequency miniprobe endoscopic ultrasonography for evaluation of indeterminate esophageal strictures Surinder Singh Rana a, Ravi Sharma a,
Gastroenterology Fellowship Program
 Gastroenterology Fellowship Program Outpatient Clinical Rotations I. Overview A. Three Year Continuity Clinic Experience All gastroenterology fellows will be required to have a ½ day continuity clinic
Gastroenterology Fellowship Program Outpatient Clinical Rotations I. Overview A. Three Year Continuity Clinic Experience All gastroenterology fellows will be required to have a ½ day continuity clinic
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case 1- B.N. 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids.
 Case 1- B.N 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids. Reports retching to clear esophagus. Case 1- B.N EGD: Stricture in the distal
Case 1- B.N 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids. Reports retching to clear esophagus. Case 1- B.N EGD: Stricture in the distal
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master
 Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Making ERCP Easy: Tips From A Master Raj J. Shah, M.D., FASGE Associate Professor of Medicine University of Colorado School of Medicine Co-Director, Endoscopy Director, Pancreaticobiliary Endoscopy Services
Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers. Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD
 Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD Panelists Axel Grothey, MD Professor of Oncology Division of Medical Oncology
Imaging techniques in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of GI cancers Moderators: Banke Agarwal, MD and Paul Schultz, MD Panelists Axel Grothey, MD Professor of Oncology Division of Medical Oncology
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE
 GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
GASTROINTESTINAL IMAGING STUDY GUIDE Pharynx Diverticula Foreign bodies Trauma o Motility Disorders Esophagus Diverticula Trauma Esophagitis Barrett esophagus Rings, webs, and strictures Varices Benign
Quiz Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been increasing in the last 20 years. a. True b. False
 Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
Quiz 1 1. Which of the following are risk factors for esophagus cancer. a. Obesity b. Gastroesophageal reflux c. Smoking and Alcohol d. All of the above 2. Adenocarcinoma of the distal stomach has been
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
Intraoperative staging of GIT cancer using Intraoperative Ultrasound
 Intraoperative staging of GIT cancer using Intraoperative Ultrasound Thesis For Fulfillment of MSc Degree In Surgical Oncology By Abdelhalim Salah Abdelhalim Moursi M.B.B.Ch (Cairo University ) Supervisors
Intraoperative staging of GIT cancer using Intraoperative Ultrasound Thesis For Fulfillment of MSc Degree In Surgical Oncology By Abdelhalim Salah Abdelhalim Moursi M.B.B.Ch (Cairo University ) Supervisors
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 4 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Topics to be covered Peptic ulcer disease Hiatal hernia Gastric neoplasms Peptic ulcer disease (PUD)= chronic gastric ulcer Causes H pylori
Original article. Introduction!
 382 Original article Peritoneal seeding in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: The PIPE Study Authors Won
382 Original article Peritoneal seeding in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration: The PIPE Study Authors Won
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases
 Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases Lynn WR 1, Vadhwana B 1, Borgstein R 2, Demetriou G 1, Nair MS 1, Meleagros L 1, Bell DJ 2 1 Department
Are extra-colonic findings on CT colonogram clinically significant? A review of 758 consecutive cases Lynn WR 1, Vadhwana B 1, Borgstein R 2, Demetriou G 1, Nair MS 1, Meleagros L 1, Bell DJ 2 1 Department
Results III. Results IV
 Comparing Polyp And Cancer Detection Rate Between Asymptomatic Patients With A Positive Family History Of Colon Cancer Or Polyps And Asymptomatic Patients Of A Similar Age Range Who Have Average Risk Of
Comparing Polyp And Cancer Detection Rate Between Asymptomatic Patients With A Positive Family History Of Colon Cancer Or Polyps And Asymptomatic Patients Of A Similar Age Range Who Have Average Risk Of
Current status of gastric ESD in Korea. Jun Haeng Lee. Department of Medicine Sungkyunkwanuniversity School of Medicie, Seoul, Korea
 Current status of gastric ESD in Korea Jun Haeng Lee. Department of Medicine Sungkyunkwanuniversity School of Medicie, Seoul, Korea Contents Brief history of gastric ESD in Korea ESD/EMR for gastric adenoma
Current status of gastric ESD in Korea Jun Haeng Lee. Department of Medicine Sungkyunkwanuniversity School of Medicie, Seoul, Korea Contents Brief history of gastric ESD in Korea ESD/EMR for gastric adenoma
Title: EUS-GUIDED FNA: HOW DO I INCREASE THE YIELD? Session No.: 7
 Title: EUS-GUIDED FNA: HOW DO I INCREASE THE YIELD? Session No.: 7 Name: Tomas Hucl Institution: Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Institute of Clinical and Experimental Medicine Country: Czech
Title: EUS-GUIDED FNA: HOW DO I INCREASE THE YIELD? Session No.: 7 Name: Tomas Hucl Institution: Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Institute of Clinical and Experimental Medicine Country: Czech
The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:S53 S57 The Use of Pancreatoscopy in the Diagnosis of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Tumor Lesions of the Pancreas KENJIRO YASUDA, MUNEHIRO SAKATA, MOOSE
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer
 Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Tumors of the Stomach Gastric adenocarcinoma Incidence and Epidemiology Incidence mortality rates USA High incidence: Japan, China, Chile, Ireland risk lower socioeconomic
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples. VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė
 Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of Gastric Subepithelial Tumors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2017;50:64-68 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.094 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2017;50:64-68 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.094 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Mucosal Incision and Forceps Biopsy for Reliable Tissue Sampling of
Appendix 4: WHO Classification of Tumours of the pancreas 17
 S3.01 The WHO histological tumour type must be recorded. CS3.01a The histological type of the tumour should be recorded based on the current WHO classification 17 (refer to Appendices 4-7). Appendix 4:
S3.01 The WHO histological tumour type must be recorded. CS3.01a The histological type of the tumour should be recorded based on the current WHO classification 17 (refer to Appendices 4-7). Appendix 4:
Evaluation of Suspected Pancreatic Cancer
 Evaluation of Suspected Pancreatic Cancer October 15, 2015 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-779-3239 Toll
Evaluation of Suspected Pancreatic Cancer October 15, 2015 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-779-3239 Toll
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
Radiology Pathology Conference Nadia F. Yusaf, M.D. PGY-3 1/29/2010 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2010 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 90 Case 1 60 year- old man presents
40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016
 40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016 EUS FNA of abdominal organs: An approach to reporting and triage for ancillary testing Date and time: Sunday 2 nd October 2016 15.00-16.30
40th European Congress of Cytology Liverpool, UK, 2-5 th October 2016 EUS FNA of abdominal organs: An approach to reporting and triage for ancillary testing Date and time: Sunday 2 nd October 2016 15.00-16.30
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Case 1. Case 1: EUS Report 5/1/2017. Interesting Cases of Pancreatic Masses
 Interesting Cases of Pancreatic Masses Martha Bishop Pitman, MD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Cytopathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL PHYSICIANS
Interesting Cases of Pancreatic Masses Martha Bishop Pitman, MD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Cytopathology Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA MASSACHUSETTS GENERAL PHYSICIANS
Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma?
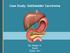 Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma? By: Megan Wyatt K. SON Wyatt 225 2B1 RDMS, RVT Patient: Male 85 YOA Caucasian Indication: Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase History Annual physical showed elevated alkaline
Case Study: #3: Gallbladder Carcinoma? By: Megan Wyatt K. SON Wyatt 225 2B1 RDMS, RVT Patient: Male 85 YOA Caucasian Indication: Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase History Annual physical showed elevated alkaline
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Performance of novel tissue harmonic echo imaging using endoscopic ultrasound for pancreatic diseases
 E Performance of novel tissue harmonic echo imaging using endoscopic ultrasound for pancreatic diseases Authors Kazuyuki Matsumoto, *, Akio Katanuma, *, Hiroyuki Maguchi, Kuniyuki Takahashi, Manabu Osanai,
E Performance of novel tissue harmonic echo imaging using endoscopic ultrasound for pancreatic diseases Authors Kazuyuki Matsumoto, *, Akio Katanuma, *, Hiroyuki Maguchi, Kuniyuki Takahashi, Manabu Osanai,
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Genetics of Pancreatic Cancer. October 6, If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation:
 Genetics of Pancreatic Cancer October 6, 2016 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-229-3239 Toll Only: 1-408-435-7088
Genetics of Pancreatic Cancer October 6, 2016 If you experience technical difficulty during the presentation: Contact WebEx Technical Support directly at: US Toll Free: 1-866-229-3239 Toll Only: 1-408-435-7088
Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone?
 Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Greetings from UNC,
Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Barrett s Esophagus: Ablate Everyone? Nicholas J. Shaheen, MD, MPH, FACG Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Greetings from UNC,
Endoscopic ultrasound: what is it and when should it be used?
 CLINICAL PRACTICE Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 6: 539 43 Endoscopic ultrasound: what is it and when should it be used? Yogananda Reddy and Robert P Willert ABSTRACT Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is
CLINICAL PRACTICE Clinical Medicine 2009, Vol 9, No 6: 539 43 Endoscopic ultrasound: what is it and when should it be used? Yogananda Reddy and Robert P Willert ABSTRACT Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology
 Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology Faculty representative: David L. Burns, MD, CNSP Resident representative: Tom Castiglione, MD Revision date: March 6, 2006
Lahey Clinic Internal Medicine Residency Program: Curriculum for Gastroenterology Faculty representative: David L. Burns, MD, CNSP Resident representative: Tom Castiglione, MD Revision date: March 6, 2006
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
EUS. Endoscopic Ultrasonography In clinical practice. THAWEE Ratanachu-ek, M.D. Surgical Endoscopy Unit, Department of Surgery, Rajavithi Hospital
 EUS Endoscopic Ultrasonography In clinical practice THAWEE Ratanachu-ek, M.D. Surgical Endoscopy Unit, Department of Surgery, Rajavithi Hospital Endoscopic ultrasound(eus) What is endoscopic ultrasonography?
EUS Endoscopic Ultrasonography In clinical practice THAWEE Ratanachu-ek, M.D. Surgical Endoscopy Unit, Department of Surgery, Rajavithi Hospital Endoscopic ultrasound(eus) What is endoscopic ultrasonography?
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C.
 Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Research Grants: Disclosures
Endoscopic UltraSound (EUS) Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Research Grants: Disclosures
Navigators Lead the Way
 RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
RN Navigators Their Role in patients with Cancers of the GI tract Navigators Lead the Way Nurse Navigator Defined Nurse Navigator A clinically trained individual responsible for the identification and
Original Article. Key words: Cytology, fine-needle aspiration (FNA), pancreatic cancer
 Original Article Effect of the time of day and queue position in the endoscopic schedule on the performance characteristics of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing pancreatic
Original Article Effect of the time of day and queue position in the endoscopic schedule on the performance characteristics of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for diagnosing pancreatic
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
A Single-Center Experience of Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Enlarged Pancreas on Computed Tomography
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:98 103 A Single-Center Experience of Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Enlarged Pancreas on Computed Tomography SAMMY HO,* ROBERT J. BONASERA, BONNIE J. POLLACK,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:98 103 A Single-Center Experience of Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Enlarged Pancreas on Computed Tomography SAMMY HO,* ROBERT J. BONASERA, BONNIE J. POLLACK,
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions
 ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
ROSE in EUS guided FNA of Pancreatic Lesions Guy s Hospital, London, 16 April 2018 Laxmi Batav Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College NHS Trust Cytology Workload Cervical Cytology 57,500 (decreases
Types of IPMN. Pancreas Cysts: An Incidental Finding or Harbinger of Malignancy. Cysts: Early Neoplasia. Mucinous Cystic Lesions. EUS-guided FNA EUS
 Pancreas Cysts: An Incidental Finding or Harbinger of Malignancy EUS-guided FNA William R. Brugge,, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Massachusetts General
Pancreas Cysts: An Incidental Finding or Harbinger of Malignancy EUS-guided FNA William R. Brugge,, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Director, GI Endoscopy Unit Massachusetts General
Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients
 Original Article on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients Ting Jiang, Jinghua Yu, Lihua Chen, Hongtan Chen, Guodong Shan, Ming
Original Article on Endoscopic Ultrasonography Clinical value of endoscopic ultrasonography for esophageal leiomyoma in elder patients Ting Jiang, Jinghua Yu, Lihua Chen, Hongtan Chen, Guodong Shan, Ming
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role
 Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
Principles of diagnosis, work-up and therapy The Gastroenterologist s role Dr. Christos G. Toumpanakis MD PhD FRCP Consultant in Gastroenterology/Neuroendocrine Tumours Hon. Senior Lecturer University
EGD Data Collection Form
 Sociodemographic Information Type Zip Code Gender Height (in inches) Race Ethnicity Inpatient Outpatient Male Female Birth Date Weight (in pounds) American Indian (Native American) or Alaska Native Asian
Sociodemographic Information Type Zip Code Gender Height (in inches) Race Ethnicity Inpatient Outpatient Male Female Birth Date Weight (in pounds) American Indian (Native American) or Alaska Native Asian
American Journal of Gastroenterology. Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma
 Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Case Scenario year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux.
 Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Case Scenario 1 57-year-old white male presented to personal physician with dyspepsia with reflux. 7/12 EGD: In the gastroesophageal junction we found an exophytic tumor. The tumor occupies approximately
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation. See specific types, e.g., Thermal ablation Achalasia, 53 75 described, 53 features of, 53 management of past options, 54 POEM
EUS in the Management of
 EUS in the Management of Pancreaticobiliary Cancers Frank Gress, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology State University of New York Downstate Medical Center Brooklyn,
EUS in the Management of Pancreaticobiliary Cancers Frank Gress, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology State University of New York Downstate Medical Center Brooklyn,
Information Technology Solutions
 2016 2014 CPT Esophagoscopy Changes - Gastroenterology CPT Changes Information Technology Solutions ASGE LOGO AND INFO Esophagogastroduodenoscopy CPT Codes 43235-43270 The American Society for Gastrointestinal
2016 2014 CPT Esophagoscopy Changes - Gastroenterology CPT Changes Information Technology Solutions ASGE LOGO AND INFO Esophagogastroduodenoscopy CPT Codes 43235-43270 The American Society for Gastrointestinal
