The Glandular System. Approach. Lesson Fifteen. The Pineal, Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenals and Pancreas
|
|
|
- Patrick McDaniel
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson Fifteen The Glandular System The Pineal, Pituitary, Thyroid, Adrenals and Pancreas The body is regulated by the glandular system as well as the nervous system. The glands produce hormones which act as messengers to communicate with the various tissues and organs. Generally, hormones work by negative feedback, reducing or switching off hormone production when a particular condition of the body is sensed. Hormones are substances (created from proteins and fats) that are produced in and secreted from various endocrine glands. Hormones travel through the blood stream, which carries them to the organs and tissues they control. It is a slow but reliable form of transportation that allows hormones to travel a great distance throughout the body. The major glands are the, thyroid, pancreas, adrenals and the gonads. The pineal gland and the thymus gland are also part of the glandular system. The reproductive glands or gonads are covered in Lesson 16, and the thymus is covered under the immune system. The gland is considered the master gland. It is located in the center of the head region, attached to the brain. This gland receives messages from the brain and then secretes various hormones to regulate hormone production in other glands. The thyroid gland is located in the neck just below the larynx. The thyroid s main function is to control metabolism. The four parathyroid glands, located on the back of the thyroid, control levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body. There are two adrenal glands, one on the upper part of each kidney. They work with the kidneys to control fluid and mineral concentrations in the body. The adrenal glands also control the metabolism of glucose and the adrenaline rush we may feel in response to stressful or dangerous situations. The pancreas, as was mentioned during our discussion of the digestive system, is mainly responsible for producing enzymes which break down food particles. It is the head of the pancreas that produces digestive secretions and this aspect of pancreatic function was covered in Lesson Eight. The pancreas also produces insulin, which regulates blood-sugar levels. This is regulated by the tail, which is coverd in this lesson. 119 The + Approach
2 The ABC+D Health System Pituitary/Pineal Thyroid/ Parathyroid Hormones are composed of either amino acids or cholesterol. Low protein diets and low cholesterol levels will disturb glandular function. The is the master gland, and while not listed on the direct aid chart on page 116, is essential to keeping the glandular system in balance. Whenever there are multiple problems with the glands or hormones, work on the pitu- itary. Supplements that can help the include spirulina and alfalfa. can help with General Aids for the Glandular System Thymus Adrenals Kidney Testes Pancreas Ovaries Each hormone has a specific function and acts only on the cells it is supposed affect, much as a key only fits one lock. Because of this, even one dysfunctioning gland can effect the entire body. Some of the results can be serious. The Hormone and Supplement table on pages shows some of the major hormones produced by the various glands. It also lists specific herbs and supplements that can enhance or diminish these hormones. There is much we still need to learn about the glandular system and more specifically, how different herbs affect hormone function, but this table presents the best information my research has uncovered. General Aids to the Glandular System Like the nervous system, the glandular system is aided by obtaining adequate rest and sleep balanced with moderate daily exercise. Stress management is also critical to maintaining healthy gland function. Meditation, relaxation techniques and positive thinking all contribute to healthy glandular function. Specific Direct Aids for the Glandular System When the glandular system is one of the systems in need of direct aid, use the Glandular System direct aid chart on page 116 to help determine what is the most likely direction of imbalance in the glands. Then, select appropriate remedies using the following information. Again, the glandular system chart does not follow the six tissue states. Instead, it is based on patterns of overactive function or underactive function of each gland. Reproductive problems are considered in Lesson Sixteen. High Thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) The most common form of hyperthyroidism is known as Graves disease, in which the thyroid gland manufactures an excess of the thyroid hormone thyroxine. Too much thyroxine causes the body s metabolism to speed up. The thyroid gland is located at the base of the neck and is regulated by hormones put out by the gland. Using iodine and other nutrients, the thyroid produces thyroxine, which regulates the body s metabolism rate. While the causes of Graves disease are not known, there are some indications that a tendency towards developing Graves disease may be inherited. Untreated, Graves disease can become very serious. Symptoms of Graves disease include nervousness and tremors of the tongue and hands, heart palpitations, excessive sweating, intolerance to heat, wider than normal high and low end numbers on blood pressure, insomnia, diarrhea, stomach disorders, brittle fingernails, exhaustion, increased appetite often simultaneously with weight loss, swelling at the base of the neck and bulging eyes. Even without developing a full blown case of Grave s disease, the thyroid may tend to be overactive, causing some of the symptoms listed above. There are several herbs that directly inhibit hyperthyroid activity. These include bugleweed, lemon balm, and to a lesser degree motherwort and rosemary. 120
3 Major Hormones Hormone and Supplement Guide 1. Gland Produced By: 2. Target Gland/ Organs: Primary Effects Herbs/Supplements The Glandular System Melatonin 1. Pineal 2. Hypothal-amus Stimulates the secretion of certain hypothalamus releasing factors that affect the secretion of gonadotrophins and ACTH. Melatonin is synthesized from serotonin. Enhanced by: Melatonin, 5-HTP and the essential oils of sage, jasmine, lavender, patchouli, ylang ylang. Oxytocin 1. Posterior 2. Female uterus, mammary glands Uterine contractions during childbirth, lactiferous duct contraction to cause milk letdown. Also released during orgasm. Causes emotional bonding between mother and child and husband and wife. Stimulated by: Blue cohosh, scotch broom, lady s mantle, chocolate, goldenseal, and the essential oils of: clove, cajeput, cinnamon (helps afterbirth pain). Nipple stimulation also increases secretion. Inhibited by: White willow, pasque flower, cramp bark and the essential oils of myrrh, lavender and jasmine. Pituitary Hormones (General) 2. Other glands Regulates the entire glandular system. Aided by: Alfalfa, spirulina, bee pollen, bluegreen algae and Eleuthero. Growth hormone (somatotropin) 2. All body cells Regulates growth; promotes mitotic (cell division) activity IGF-1 is stimulated by growth hormones Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH or thyrotropin) 2. Thyroid gland Regulates hormonal activity of the thyroid gland Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) 2. Adrenal cortex; all body cells Promotes normal functions of the adrenal cortex and assists in the breakdown of fats Stimulated by stress Inhibited by adaptagens: Eleuthero, Suma Combination and schizandra. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) 2. Male - testes; female - ovaries Male-stimulates testes to produce sperm; female-regulates monthly development of follicle and egg and stimulates secretion of estrogen Inhibited by: Chaste tree, white willow, hops, stoneseed, mugwort and sage. 121
4 The ABC+D Health System Luteinizing hormone (LH) 2. Male - testes; female - ovaries Male-stimulates interstitial cells of testes to produce testosterone; female -works with FSH to cause ovulation, also stimulates formation of corpus luteum and production of progesterone. Works with FSH, so together they are called gonadotrophins). Stimulated by: Sarsaparilla, mugwort and wild oat. Inhibited by: Stoneseed, white willow, and hops. Prolactin 2. Mammary glands After childbirth, it assists other hormones in initiating and sustaining milk production Stimulated by: Vervain, fennel. Inhibited by: Periwinkle, sage, clary sage essential oil. Milk flow is inhibited by essential oils of peppermint and geranium. Milk flow is promoted by: Blessed thistle, milk thistle, fenugreek and marshmallow. Thyroxin (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) 1. Thyroid 2. All body cells Controls metabolic rate by increasing protein synthesis, emulsifying and burning fats, and releasing energy from carbohydrates; regulates rate of growth; stimulates sexual maturity and early maturation of nervous system Seaweeds supply iodine to support the thyroid: Kelp, dulse. Also enhanced by: Garlic, black walnut, horseradish, and the essential oil of red myrtle. Inhibited by: Cruciferous vegetables (cabbage, broccoli, etc.), bugleweed, lemon balm or melissa, motherwort, and green myrtle essential oil. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1. Parathyroid 2. Bone, kidneys, intestine Raises blood calcium by stimulating bones to release calcium, kidneys to conserve it and intestines to absorb it Stimulated by the essential oils of: Green myrtle and juniper. Thymosin 1. Thymus 2. T-cells Believed to stimulate T-cells after they leave the thymus Enhanced by: Echinacea, thyme, elecampane, and the essential oils of bergamot, clove, tea tree, oregano, thyme and eucalyptus. Glucagon 1. Pancreas 2. Liver Stimulates liver to convert glycogen to glucose, thus blood sugar levels rise Protein foods stimulate release. It is possible that stevia and licorice root may stimulate this hormone. Insulin 1. Pancreas 2. All body cells; liver Promotes movement of glucose and amino acids into cells, assists in synthesis of proteins and fats; stimulates liver to convert glucose into glycogen, thus lowering blood sugar levels Insulin uptake by cells is enhanced by: Cchromium, zinc, golden seal, cedar berries, nopal, vanadium and vitamin C. Also enhanced by the essential oils of eucalyptus, bergamot, pink grapefruit, rosemary, lemon and geranium. 122
5 The Glandular System Epinephrine 1. Adrenal medulla 2. Various tissues Promotes fight or flight response, improves concentration, accelerates breathing and heart rate, increases energy, tenses muscles, slows digestion Stimulated by: Caffeine (coffee, tea, kola nuts, guarana), ephedra, and the essential oils of basil, lemon, pine, lime, peppermint, rosemary, thyme. Calmed by: Valerian, passion flower, skullcap and ganoderma and the essential oils of clary sage, geranium, and ylang ylang. Aldosterone (example of mineralcorticoids) 1. Adrenal cortex 2. Kidneys Regulates the amount of sodium and potassium eliminated in the urine, promotes water reabsorption and reduces urine output Licorice root helps maintain fluid balance like aldosterone and inhibits destruction of these hormones. These hormones are also stimulated by the essential oils of pine, thyme and rosemary. Inhibited by: Ylang ylang oil. Cortisol or hydrocortisone (example of glucocorticoids) 1. Adrenal cortex 2. All body cells Anti-inflammatory, vasoconstriction, helps the body resist stress. Excess cortisone causes rapid aging by inhibiting adrenal function. Licorice and rehmannia inhibit breakdown. Yucca, licorice and wild yam have a cortisollike constituents and actions. Bupleurum stimulates production. Turmeric improves absorption. Androgens (example of gonadocorticoids) 1. Adrenal cortex 2. Reproductive organs Sex drive Stimulated by: Sage essential oil. Testosterone 1. Reproductive glands and adrenal cortex 2. Male secondary sexual organs Development and function of secondary sexual organs and accessory glands, promotes male secondary sexual characteristics, sex drive Stimulated by: Eleuthero, Korean ginseng, and the essential oils of cinnamon, and lemon. Estrogens Estrais Estrone estradiol 1. Reproductive glands and adrenal cortex 2. Female secondary sexual organs, uterus Development and function of secondary sexual organs, menstrual changes of the uterus, secondary sexual characteristics, sex drive Black cohosh, hops, licorice, soy, white willow, and the essential oils of geranium and clary sage have estrogenic effects. Estrogen is inhibited by chaste tree, wild yam and pasque flower. Progesterone 1. Reproductive glands and adrenal cortex 2. Uterus Prepares uterus for implantation, prevents abortion of fetus Enhanced by: sarsaparilla, yarrow, parsley, lady s mantle.. Wild Yam Creams contain progesterone. 123
6 GLANDULAR SYSTEM Copyright 2003 Tree of Light Publishing All Rights Reserved THYROID PANCREAS ADRENALS OVERACTIVE "HOT" UNDERACTIVE "COLD" OVERACTIVE "HOT" UNDERACTIVE "COLD" OVERACTIVE "HOT" UNDERACTIVE "COLD" Goiter with red skin over thyroid area Nervous anxious, flighty Thin, difficulty gaining weight Protruding or bulging eyes Rapid heart rate and/or heart palpitations Medical diagnosis of Grave's Disease Elevated T3 and/or T4 levels in the blood Low body temperature, skin feels cold to the touch Cold hands and feet Shallow breathing Feeling sluggish and tired Tendency to gain weight easily Dry, dull skin Hair loss Difficulty expressing feelings verbally Loss of libido, especially in women Sugar cravings Sudden fatigue in midafternoon Mood and energy swings Irritability and confusion when food is not eaten regularly Sudden coldness of limbs or nose Weight gain High carbohydrate diets Frequent consumption of refined carbohydrates High cholesterol levels Constant thirst with frequent urination Dizziness or lightheadedness after eating carbohydrates Excess insulin production with cellular resistance to insulin (Type II diabetes) Deficient insulin production (Type I diabetes) Excess cortisol and epinephrine production Tendency to hypertension Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) Poor wound healing Poor resistance to disease with lowered immune response Thinning hair Loss of muscle mass with development of abdominal fat Mental obsession, compulsiveness, stress, anxiety Dilated pupils Medical diagnosis of Cushing's disease Deficient production of cortisol and epinephrine Fatigue and lack of stamina with insomnia Pulsing pupils Quivering tongue Dark circles under eyes Tendency to low blood pressure or sudden drop in blood pressure when moving from sitting to standing position Tachycardia and heart palpitations Sensation of pressure in chest (angina) Cravings for sweets and carbohydrates Emotionally sensitive (unreasonable weeping or laughter) Medical diagnosis of Addison's disease Thyroid Irritation Thyroid Depression Pancreatic Irritation Pancreatic Depression Adrenal Irritation Adrenal Depression
7 Hops also has a thyroid-calming effect. The adrenals are usually weak when the thyroid is overactive, so herbs that support the adrenals like eluethero root and licorice may also be beneficial. Finally, raw cruciferous vegetables (cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, etc.) have a slight thyroid inhibiting effect. Avoid all herbs and supplements that feed the thyroid (see Low Thyroid herbs). can help with Hyperthyroidism. Low Thyroid (Hypothyroidism) If the thyroid produces too little thyroxine, then the body s metabolic rate drops significantly. Many Americans suffer from low thyroid output. There are numerous symptoms that arise when the thyroid function is low, but some of the most important are chronic fatigue, variable energy levels, low body temperature (cold hands and feet), dry skin and lack of sex drive. Hypothyroidism causes decreased memory and ability to concentrate and increased difficulties with allergies, asthma, cholesterol, constipation, yeast infections, and abnormal menstrual cycles in women. Goiter, swelling in the glands of the neck, may develop. These conditions can be improved with supplementing the diet with iodine, if that is the reason the thyroid gland is manufacturing too little hormone. Glandular herbs that feed the thyroid with iodine are required. Herbs that feed the thyroid include kelp, dulse, Irish moss and black walnut. Sometimes the real problem with the thyroid is an imbalance in the. SAM-e and MSM can help the liver which also supports better thyroid function. can help with Hypothyroidism. Pancreatic Irritation (Hypoglycemia and Syndrome X) The adrenals and pancreas help to regulate blood sugar levels. When the liver does not store sugar properly and release it gradually into the blood stream, the pancreas and adrenals must work harder and may become stressed and tired. Insulin from the pancreas moves excess sugar from the blood stream into storage. Sugar is first moved into storage in the liver and 125 The Glandular System muscles as glycogen. If there is too much sugar, it will be stored as fat. Later, when blood sugar levels are low, the pancreas secretes another hormone called glucogon that stimulates the release of glycogen stores in the liver to bring blood sugar levels up. The adrenals can also help to mobilize stored sugar for energy. When the blood sugar is too low, it results in hypoglycemia. Hypo meaning low, gly for sugar and cemia referring to the bloodstream. The cells in the body consume vast amounts of sugar for energy. In fact, excluding oxygen and water, sugar is the primary nutrient the body requires. When there is not enough sugar in the bloodstream for cells to do their work, many kinds of health problems can result. When blood sugar levels start to dip below normal, the body gives certain subtle clues that it needs help. These may include suddenly feeling cold or getting a cold nose, strong craving for sweets or caffeine, sudden fatigue or mental confusion, the inability to concentrate, a mild headache or sense of pain around the eyes. If not dealt with soon, the symptoms may worsen into irritability, severe fatigue, dizziness or shakiness. As the above symptoms suggest, hypoglycemia affects far more than the physical body. It also affects our mind and emotions. As the sugar in candy and chocolate rushes into the blood stream, it produces a sugar high. The pancreas hypersecretes insulin to try to remove this excess sugar from the blood. Since insulin depresses glucogon production, this results in a corresponding downer as the blood sugar level falls below normal. The person craves sugar and the cycle begins again, putting the body, and especially the brain, on a blood sugar roller coaster ride. The brain consumes more sugar than any other organ in the human body. So when blood sugar levels drop, the first organ to be affected is the brain. Irritability, depression, fatigue, mental confusion, and even severe behavioral problems like ADD, hyperactivity, juvenile delinquency and mental illness may be caused by blood sugar problems. A person who has a severe problem with hypoglycemia may become very irrational or crazy under stress. When a person is startled, worried or upset, the demand for sugar increases dramatically. Hence, the hypoglycemic may experience a sudden drop in blood
8 The ABC+D Health System sugar levels in stressful situations. If the drop is severe enough, the higher functions of the brain tend to shut down. The person descends into the animal mode of fight or flight behavior. That means they are no longer in a rational state. The only options perceived are fight or flee. Therefore, they may lash out in uncontrolled rage, retreat into a shell, or even babble in an irrational manner. In the book, Low Blood Sugar and You, Carlton Fredricks and Herman Goodman suggest that hypoglycemia may also be a factor in allergies, asthma, rheumatic fever, neurosis, epilepsy and even ulcers. Of course, many of these illnesses may not be directly linked to hypoglycemia, but the same dietary patterns that cause hypoglycemia probably contribute to a host of other illnesses as well. When insulin production is too high, it results in hyperinsulinemia or syndrome X. This problem causes obesity, heart disease and eventually diabetes. For reducing pancreatic irritation, avoid the whites, especially refined sugar and flours. Also avoid all stimulants, especially cola drinks. Carbohydrates in the diet should be whole fruits, vegetables and grains. Protein stimulates glucogon production so spirulina or bee pollen can be used to bring blood sugar levels to normal. Licorice root can help to stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce cravings for sweets. Other supplements that may help include bilberry, stevia, and-l-glutamine. can help with Hypoglycemia and Syndrome X. Pancreatic Depression Diabetes mellitus is a chronic degenerative disease caused by either a lack of insulin (Type I diabetes) or a cellular resistance to insulin (Type II diabetes). Insulin is essential for metabolizing glucose. In a normal person, after a meal the glucose level in their blood rises, causing the pancreas to produce insulin to return the blood sugar level to normal. People with diabetes either cannot produce insulin, or their cells have become resistant to insulin. As a result, they are unable to maintain normal blood glucose levels by moving glucose from the bloodstream to the cells. This causes an excess of sugar in the blood which can spill into the urine. 126 Diabetes can result in increased appetite, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, mood swings, vaginal infections in women, leg cramps or sensation of pins and needles in the fingers and toes, blurred vision, impotence in men and slow healing of wounds. Uncontrolled, diabetes can cause blindness, loss of limbs to amputation, coma and death. There are more than 10 million diagnosed cases in the United States alone, with an estimation that at least 5 million more have diabetes and don t know they have it. Diabetes should be diagnosed by a medical doctor. However, Type II often can be controlled or even cured with diet and herbs, especially if caught in the early stages. Type II diabetes is by far the most common, and occurs mostly in middle age. Symptoms are the same as Type I, except there is weight gain, not weight loss. Most often, Type II diabetes is caused by being overweight and poor diet laden with sugars and empty calories. The most effective treatment is correct and healthy dietary management, healthy lifestyle with exercise, weight loss and herbs for blood sugar stabilization. Type I diabetes usually begins in childhood, but may occur later in life if the pancreas is damaged from illness or injury. Only 5-10 percent of diabetics have Type I, which can be brought on by viral infection, or some extreme stress that damages the pancreas. There can be a genetic predisposition, but this is not always the case. Injections of insulin must be given to help control the condition. Herbs and supplements can reduce the need for insulin, but I have encountered no dependable protocol for regenerating the pancreatic cells. Stevia makes a great sugar substitute for diabetics. It is a safe, non-caloric sweetener that helps to balance blood sugar levels. The minerals chromium and zinc are also beneficial for diabetics. Herbs that can be used to overcome cellular resistance to insulin include anamu, fenugreek, goldenseal, noni (morinda), nopal, cedar berries and gymnema. Effective natural therapy for Type II diabetes must include dietary modification. Simple sugars and starches must be avoided in favor of foods with a low glycemic index (primarily non-starchy vegetables, essential fatty acids and protein). Exercise is also very important for diabetics. Combined with lifestyle changes, many people have been able to use supple-
9 ments to overcome Type II diabetes, and to reduce insulin requirements in Type I diabetes. can help with Pancretic Depression, Diabetes I & II. Adrenal Stress The adrenals are the home of the fight or flight response. When we are subjected to stress, they fire off hormones that put the body on alert. Excess stress causes overactivity of the adrenals which results in an excess production of the stress hormones cortisol and epinephrine. This can cause lowered immune response, high blood pressure, poor wound healing, abdominal fat, mental obsession, compulsive thoughts and behaviors, stress and anxiety. In its most severe form, this is called Cushing s disease. Adaptagens are the primary means of reducing adrenal stress. Examples of adaptagenic herbs include eleuthero root, schizandra, rhodiola, ginseng and suma. Nervine herbs that calm the nervous system may also be beneficial. These include blue vervain, chamomile, kava kava, passion flower and valarian. The adrenals need B complex vitamins and vitamin C to function properly. The essential oils of lavender, lemon, Roman chamomile and rose can also be used to calm excess adrenal activity. Other products or formulas that can be helpful for adrenal stress include borage. can help with Adrenal Stress. Adrenal Fatigue The adrenals are under a great deal of stress in modern culture. Not only do we tend to lead lives of high pressure and constant busy-ness, we also abuse the adrenals with refined carbohydrates and stimulants (especially caffeine). The adrenals play a major role in creating stamina and endurance. Hence, when the adrenals become tired, we lose staying power and are more easily fatigued or run down. If this The Glandular System condition lasts long enough, we become enervated and exhausted. Low adrenal function also increases mental confusion and the inability to concentrate. It increases levels of inflammation in the body, since the adrenals produce hormones to dampen the inflammatory response. Most diseases where there is chronic inflammation and pain involve some loss of adrenal function, including auto-immune diseases. Asthma is another illness where low adrenal function plays a role. Asthma attacks are stopped medically by use of the adrenal hormone epinephrine (more commonly known as adrenaline). Specific symptoms of adrenal fatigue include increased thirst, increased urination in frequency and amount, weight loss, low blood pressure, dark circles under the eyes, quivering tongue, emotional sensitivity and cravings for sweets and carbohydrates. Serious adrenal deficiency creates a medical condition called Addison s disease. Generally speaking, adaptagens, which help the body cope better with stress, are herbs that aid adrenal function. Some of the better choices include Korean ginseng, American ginseng, eleuthero root and schizandra. Licorice root reduces sugar cravings and has a sparing effect on adrenal hormones. Other products that may help here are Ho Shou Wu, B-Complex vitamins (particularly pantothenic acid), vitamin C, Roman chamomile essential oil. Since caffeine stimulates (i.e. whips) the adrenals, it is important to avoid all caffeinated beverages when the adrenals become depleted. can help with SAdrenal Fatigue. 127
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
The ABC+D Approach to Natural Healing Webinar: Session 7, The Respiratory System
 ABC+D Approach Lesson Eleven: The Glandular System The Control System of the Body Endocrine Glands Types of Hormones Pineal Pituitary Thyroid Thymus Pancreas Adrenals Ovaries/Testes Amine (Amino Acid Based)
ABC+D Approach Lesson Eleven: The Glandular System The Control System of the Body Endocrine Glands Types of Hormones Pineal Pituitary Thyroid Thymus Pancreas Adrenals Ovaries/Testes Amine (Amino Acid Based)
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
The Endocrine System 2
 The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
The Endocrine System 2 Continuing on from the previous instalment, we will now look at the adrenal glands, the pancreas and the gonads as parts of the endocrine system. Adrenal Glands The adrenal glands
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes?
 Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Do Now: 1. Turn in your exit ticket that was due for homework 2. Pg 91: How did they use to test people for Diabetes? Diabetes a disease in which the pancreas stops producing insulin, the hormone that
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS
 BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
BODY CONTROL SYSTEMS THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - 1 of the 2 chemical control systems of the human body - function of the endocrine system: regulate body functions = maintain homeostasis ie. physical and mental
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Target cells only respond to specific signals Different target cells have different kinds of receptors in their membranes or cytoplasm
 1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIO 1102 Lec. 9 (Guided): Chapter 13 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Controls many body functions through chemical signals Hormones Carried in blood stream Affect target cells Composed
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Lesson 1. Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms
 Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Lesson 1 Nervous & Endocrine Comparison Endocrine Glands diagram Feedback Mechanisms Nervous System Endocrine System 1. Uses neurons to transmit electrochemical messages (neurotransmitters) Regulation
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the
 Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
Chapter 6 Hormones and the Endocrine System Introduction In lions, the hormone testosterone promotes the development and maintenance of male traits including growth and maintenance of the mane and increased
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
OpenStax-CNX module: m58003 1 Human Biology Chapter 11: The Endocrine System * Willy Cushwa Based on Endocrine System by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Endocrine Glands System. Agha Zohaib Khan
 Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Endocrine Glands System Agha Zohaib Khan Introduction Endocrine means secreting internally. Indeed, the endocrine system is made up of glands whose secretions enter the blood stream. Hence these glands
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL?
 Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System WHO IS IN CONTROL? Objectives Explain how the endocrine and nervous system work together to regulate bodily functions Describe the basic anatomy of the endocrine system Describe the functions
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
Endocrine System. The Endocrine Glands
 Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
Endocrine System Working together with the nervous system, the endocrine system helps maintain homeostasis in the body. Where the nervous system uses electric signals, the endocrine system uses chemical
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Regula'ng Body Func'on
 Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
Chapter 10 Regula'ng Body Func'on Working closely with your nervous system is the endocrine system, a chemical communication system that regulate many body functions. Exocrine vs Endocrine Exocrine Glands
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System R. Cummins 1 The Endocrine System Body Coordination This is controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems. The endocrine system is, 1. Slow acting 2. Based on hormones 3. Has a slow
The Endocrine System R. Cummins 1 The Endocrine System Body Coordination This is controlled by the nervous and endocrine systems. The endocrine system is, 1. Slow acting 2. Based on hormones 3. Has a slow
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System The nervous system allows the body to respond to various stimuli in a quick manner and this allows for homeostasis. The endocrine system, using hormones also allows the body to respond
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW
 THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM: AN OVERVIEW Functions: 1. Reproduction 2. Growth & development 3. Maintenance of electrolytes, water and nutrient balance of the blood 4. Regulation of cell metabolism and energy
The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo
 The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care
The Intricate Web Of Hormone Relationships Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
The Adrenals Are a key factor in all hormonal issues Because the adrenals can convert one hormone to another they play a role like no other in the bod
 The Players Part II The Adrenals Are a key factor in all hormonal issues Because the adrenals can convert one hormone to another they play a role like no other in the body Can affect all hormone systems
The Players Part II The Adrenals Are a key factor in all hormonal issues Because the adrenals can convert one hormone to another they play a role like no other in the body Can affect all hormone systems
The Players. Liver Thyroid Adrenals Pancreas Reproductive System Pituitary Gut Bacteria
 The Players Part I Quick Review Understanding some of the key systems and their relationship to hormones is the best place to start It will help with some of the hormone interconnections Key to understanding
The Players Part I Quick Review Understanding some of the key systems and their relationship to hormones is the best place to start It will help with some of the hormone interconnections Key to understanding
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
The Endocrine System Endocrine Glands Glands that secrete their products (HORMONES) into extracellular spaces around cells. The hormones then enter into the bloodstream by diffusing into the capillaries
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System. A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body.
 Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Endocrine System A system that consists of glands that transmit chemical messengers throughout the body. HORMONES: chemical that circulates throughout the blood stream and influence the activity of distant
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones
 Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
Student Worksheet Additional Case Study: Glands and Hormones LSM 8.5-2 This activity can be done individually or in pairs. Prepare the pieces ahead of time. Materials For each student (or pair): one copy
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
The ABC+D Approach to Natural Healing Webinar: Session 12: The Reproductive System
 ABC+D Approach Lesson Twelve: The Reproductive System Reproductive Hormones FSH - Follicle Stimulating Hormone LH - Luteinizing Hormone Oxytocin Prolactin Testosterone Estrogens Progesterone 1 Follicle-Stimulating
ABC+D Approach Lesson Twelve: The Reproductive System Reproductive Hormones FSH - Follicle Stimulating Hormone LH - Luteinizing Hormone Oxytocin Prolactin Testosterone Estrogens Progesterone 1 Follicle-Stimulating
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Pages
 NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
NOTES 11.5: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pages 1031-1042 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Communication system that controls metabolism, growth, and development with hormones Maintains homeostasis Hormones: chemical messengers released
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M
 C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
C H A P T E R 1 3 : T H E E N D O C R I N E S Y S T E M U N I T 1: MAINTA I N I N G DYNAMIC EQ UILIBR IUM II NERVOUS SYSTEM VS. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses
Welcome! The Glandular System. Rachel Rauch. How the adrenal glands affect the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary, hypothalamus and sex hormones.
 Welcome! The Glandular System How the adrenal glands affect the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary, hypothalamus and sex hormones. Rachel Rauch July 9 th, 2013 This NSPWebinar will begin at 11:00 am MDT A recording
Welcome! The Glandular System How the adrenal glands affect the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary, hypothalamus and sex hormones. Rachel Rauch July 9 th, 2013 This NSPWebinar will begin at 11:00 am MDT A recording
Welcome! Type in Your Questions! 7/9/2013. A recording of this webinar will be available at
 Welcome! The Glandular System How the adrenal glands affect the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary, hypothalamus and sex hormones. Rachel Rauch July 9 th, 2013 This NSPWebinar will begin at 11:00 am MDT A recording
Welcome! The Glandular System How the adrenal glands affect the thyroid, pancreas, pituitary, hypothalamus and sex hormones. Rachel Rauch July 9 th, 2013 This NSPWebinar will begin at 11:00 am MDT A recording
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System 26.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Hormones are chemicals produced by the endocrine system that
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions)
 ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
ANAT113: Endocrine System Practice Exam Answer Key (42 questions) 1. While the nervous system functions very slowly, the endocrine system works very quickly. a. True b. False 2. Hormones that act locally
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books)
 Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
Bell Work Day 1 Write the Standard in your notes. Explain the difference between endocrine and exocrine glands. (page 197 in small books) 1 Standard Day 1 24) List the structures of the, explain the functions
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 11 The Human Endocrine System. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 11-1 through 11-18. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 11-1. Given a hormone, identify
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Hormones by location
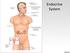 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Biology 30. Morinville Community High School. Unit 2: Endocrine System. Name:
 Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
Biology 30 Morinville Community High School Unit 2: Endocrine System Name: 2 Endocrine System Unit Outline Chapter 13 text p. 434-471 Key Concept A: The endocrine system and nervous system both mediate
The Endocrine System - An Overview. 32 Darcy Road, St Osyth, Clacton on Sea, Essex CO16 8QF. Registered Charity Number:
 Last Updated: 23.04.12 Review Date: 25.05.12 Thyroid UK Source materials available on request. If you would like to confirm that this is the latest version of this document please contact: THYROID UK Registered
Last Updated: 23.04.12 Review Date: 25.05.12 Thyroid UK Source materials available on request. If you would like to confirm that this is the latest version of this document please contact: THYROID UK Registered
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
Pancreas. Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin
 Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Glands of the Endocrine System
 Glands of the Endocrine System Key Questions What are the functions of the major endocrine glands? How are endocrine glands controlled? Vocabulary pituitary gland releasing hormone corticosteroid epinephrine
Glands of the Endocrine System Key Questions What are the functions of the major endocrine glands? How are endocrine glands controlled? Vocabulary pituitary gland releasing hormone corticosteroid epinephrine
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
