THE MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE SALAMANDER THYROID GLAND
|
|
|
- Arthur Hopkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VOL. V, No. i SEPTEMBER 1927 THE MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE SALAMANDER THYROID GLAND II. THE ANTERIOR LOBE OF THE HYPOPHYSIS AS A CONTROL MECHANISM OF THE FUNCTION OF THE THYROID GLAND BY EDUARD UHLENHUTH AND SAUL SCHWARTZBACH. (University of Maryland Medical School, Baltimore, and Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole.) {Received ist February 1927.) IN the study of the physiology of the thyroid gland it is becoming more and more evident that the function of this organ is composed of a number of component activities. Only some of them are controlled by intrinsic mechanisms, while the most important of them, the release of the active secretion product of the gland from the follicles into the blood circulation is effected by stimulation through an extrinsic "releasing mechanism." In warm-blooded animals the study of this releasing mechanism has received considerable attention, and although the question cannot by any means be considered a closed chapter of thyroid physiology, the work of O. A. Andersson(i), Leo Asher(z), Cannon and Fitzb), L. B. Wilson(o) and others, is generally credited with having demonstrated that the autonomous nervous system is the path over which the stimuli of the releasing mechanism reach the thyroid in warm-blooded animals. The senior author of this paper has been interested, for some time, in the physiology of the thyroid of cold-blooded animals, and especially in that aspect of it which concerns the nature of the releasing mechanism. This work has now entered an advanced stage and certain definite conclusions are possible. Although the results, together with the records, will be published in a series of more extensive articles, it seems desirable that the chief results be made accessible at once. Morphological as well as experimental work on salamanders, published by the senior author in previous papers (8) indicates that in the urodelan amphibians the thyroid function consists of two main phases, first of the elaboration of the active secretion product of the thyroid, the colloid, in the thyroid cells, of the excretion of the colloid from the cells into the lumen of the follicles and of the storage of the colloid within the follicles, and secondly of the excretion of the colloid from the follicles into the blood-circulation. The presence of two distinct steps of the secretion process is one of the most important characters distinguishing the thyroid from other glands and is the expression of the peculiar structure of this organ. After the secretion product has been excreted from the cells, it lies within the BJEB-vi I
2 2 EDUARD UHLENHUTH and SAUL SCHWARTZBACH completely closed lumen of the follicles, and in order to effect its excretion into the blood-circulation a special releasing mechanism is required. During the larval period the activities of the thyroid are confined entirely to those of the first phase (developmental or storage phase); the second or functional phase develops suddenly at the end of the larval period and is the immediate cause of metamorphosis. The activities of the developmental phase are elementary properties of the thyroid organ and are controlled by factors similar in nature to those controlling the activities of other glands; the display of the functional phase can be effected only by the action of an extrinsic releasing mechanism. Starting from the neuro-secretory hypothesis of the thyroid function in warmblooded animals and upon the basis of the technique employed in the study of the thyroid of mammals, the senior author, while still at the Rockefeller Institute, experimented on salamanders with drugs which are known to stimulate or inhibit the autonomous nervous system. Larvae of Amblystoma tigrinum were kept in solutions of pilocarpine, adrenaline and atropine. It was expected that, if these substances had any effect upon the autonomous nervous system, release of the colloid from the follicles of the thyroid and metamorphosis known to be the direct result of the action of the thyroid hormone should be enforced precociously or inhibited according to whether the particular drug had a stimulating or inhibiting influence upon the excretor-fibres which effect the colloid release in the thyroid gland. These experiments were, however, very disappointing and entirely negative; all larvae underwent metamorphosis at a normal time. It might be suspected that the mere keeping of the larvae in the solutions of the drugs did not permit the drug to come in contact with the nervous system. But various other effects similar to those produced by the same drugs in higher animals were extremely pronounced. Pilocarpine f.i. produced an enormous excretion of slime from the glands of the skin, vomiting, excessive defaecation and visible contractions of the intestinal tract. Adrenaline caused contraction of the melanophores. Nevertheless we repeated these experiments last summer in Woods Hole; this time we injected intraperitoneally pilocarpine and adrenaline (in addition larvae of Amblystoma maculatum were kept in solutions of ergotamine). Again the larvae of Amblystoma tigrinum were employed in many of the experiments with pilocarpine and adrenaline, again they showed a typical and, if the dose was high enough, even violent response to pilocarpine and adrenaline; in case of adrenaline the melanophores remained contracted for 20 hours and more. Yet metamorphosis remained completely uneffected. Before deciding, whether the thyroid, in these experiments, had actually failed to respond by a release of the colloid or whether the colloid had been released, but, in the larval thyroid, does not yet contain the active principle, it was necessary to examine the structure of the thyroid gland. In a previous histological study a very characteristic structural appearance was found to be correlated with the release of the colloid at the time of metamorphosis, indicating an extraordinarily high degree of functional activity of the thyroid cells.
3 Thyroid Gland of the Salamander 3 Finally a method was worked out which permits the study of some of these structures (high columnar cells, a conspicuous gathering of the secretion granules at the apical pole of the cells and especially the presence of large, distinctly visible secretion vacuoles "Anderson Vacuoles" within the cells) in the fresh thyroid gland immediately after its removal from the animal. With this method the functional state of the gland can be determined very rapidly and without great loss of time. Ultimately another method was developed which permits the exact counting of the individual follicles composing each thyroid as well as the study of the size and shape of each individual follicle. The thyroids of larvae kept in or injected with solutions of pilocarpine, adrenaline and ergotamine were examined in this fashion, and it was found that they did not show any noticeable difference as compared to the controls. From these experiments it is concluded that in the larval thyroid of salamanders the release of the colloid and the active principle can be neither enforced nor inhibited by drugs known to stimulate or inhibit the sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres in warm-blooded animals. We suspected, and in fact hoped, that these results might mean that in the salamander, during the larval period, the nervous releasing mechanism is not yet established and that it does not become established until immediately before metamorphosis. Such an arrangement would explain the very sudden development of the functional phase at the time of metamorphosis. If this conclusion were correct, drugs stimulating the autonomous nervous system should cause an increased colloid release in the metamorphosed, adult salamander. Adult animals especially of the species Amblystoma tigrinum and Notophthalmus torosus were injected with pilocarpine and adrenaline. But although in both cases a general response to the drugs was very pronounced, just as in the larvae, the thyroids of the injected animals remained entirely unaffected. Evidently then, the thyroid gland cannot be stimulated either in the larval or adult salamander by the drugs employed. It seems to us that this is a very interesting result as it indicates an essential difference between the warm-blooded animals and the cold-blooded salamanders. Apparently in the salamander the thyroid is either not connected up with the autonomous nervous system, or else the latter does not respond to these drugs in the same way as it does in the warm-blooded organism. If now the effect of these drugs is compared with the effect of extracts of the substance of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis, a striking difference is noticed. In 1922 P. E. Smith and I. P. Smith(5) reported experiments showing that fresh anterior hypophyseal extracts retard metamorphosis of the Colorado axolotl. In 1923 Hogben(4) published a paper in which just the opposite effect of anterior lobe substance was claimed; in the Mexican axolotl injected with "Armour's anterior lobe tablets" metamorphosis was enforced. In a recently communicated article Smith (6) maintains that the effect of Armour's anterior lobe tablets, as observed by Hogben, is probably caused by admixtures of thyroid substance; Smith supports his view by experiments which showed that metamorphosis is hastened by feeding the Colorado axolotl on Armour's anterior lobe tablets. Recently Spaulc?)
4 4 EDUARD UHLENHUTH and SAUL SCHWARTZBACH repeated Hogben's experiments in the Mexican axolotl, but used anterior lobe extracts made up freshly in the laboratory. His extracts differed from Smith's extracts in that they were made in acid saline solutions and were kept as free as possible from admixtures of posterior lobe. These extracts had the same effect as Armour's anterior lobe tablets, producing metamorphosis in the Mexican axolotl. We repeated these experiments in the larvae of Amblystoma tigrinum, using Armour's anterior lobe powder and obtained the same result reported by Hogben and by Spaul; metamorphosis of the larvae is distinctly accelerated. Next we examined carefully the thyroids of the control and experimental animals and found that during metamorphosis of the larvae injected with anterior lobe substance the thyroid goes through the whole cycle of functional changes characteristic for the thyroids of the normal metamorphosing larvae. Atfirst the cells increase considerably in height, taking on a high columnar shape, and a massing of the secretion granules at the apical cell end takes place. Finally secretion vacuoles develop within the cells. We repeated this experiment in the Mexican axolotl; unfortunately we had only two larvae at our disposal and no control could be run. Yet as compared with other normal axolotls the behaviour of these two larvae was extremely striking. The first animal died before any metamorphic changes had become visible externally. The second animal was killed at a time at which metamorphosis was in an advanced stage. No other animal of the same stock has ever metamorphosed spontaneously up to the present time. The thyroids of both animals were examined. In the thyroids of animals of the same stock, which the senior author examined previously, all cells are characterised by an extreme flatness; the secretion granules are scattered throughout the whole cell. In the thyroids of both of the two experimental animals the cells were on the contrary conspicuously high columnar and the secretion granules were massed at the apical pole. No secretion vacuoles were found, but the animals were killed at a stage at which the presence of secretion vacuoles could not yet be expected. It is certain that the anterior lobe substance in these animals did not enforce metamorphosis by direct action, but indirectly by the intermediation of the thyroid gland, stimulating it and enforcing its functional activity. Further experiments were carried out to decide whether the action of Armour's anterior lobe powder is the result of the specific principle of the anterior lobe or whether it is caused, as Philip Smith claims, by traces of thyroid substance contained in Armour's preparation. In order to test this point we metamorphosed the larvae of Amblystoma tigrinum by keeping them in solutions of Bayer's iodothyrine and examined their thyroids at various periods after the beginning of the experiment. The thyroids of these animals showed at no time any signs of functional activity; in general it may be said that after the beginning of the iodothyrine administration these thyroids remained at the stage at which they were at the beginning of the experiment. Hence it is evident that thyroid substance administered to the larvae of salamanders enforces metamorphosis directly by its action upon the tissues of the animals, without the intermediation of the animal's own thyroid gland, and therefore behaves entirely differently from the anterior lobe substance. It might still be suspected that the action of Armour's preparation was due to
5 Thyroid Gland of the Salamander 5 inorganic iodine contained in it. The senior author showed in previous experiments that, in salamanders, inorganic iodine has no accelerating influence upon metamorphosis. Nevertheless we repeated these experiments, feeding various quantities of inorganic iodine to the larvae of Amblystoma tigrinum. Again the animals failed to show an acceleration of metamorphosis. In addition we examined this time the thyroids of the larvae fed iodine and compared them with control thyroids. We found that the action of inorganic iodine is entirely different from the action of both anterior lobe substance and thyroid substance, and is indeed very specific. In the main it causes an enormous swelling of some follicles, a complete disintegration of other follicles and a conspicuous diminution of the number of follicles. We believe that these experiments permit a further analysis of the physiology of the thyroid gland of salamanders. No nervous control, but a distinct control of the thyroid function by the anterior lobe substance could be demonstrated. The action of the anterior lobe powder (Armour's preparation) is not due to the presence of iodine or thyroid substance in this preparation, but to a specific principle of the anterior lobe of the hypophysis. The anterior lobe of the animal's own hypophysis is an integral component of the peculiar releasing mechanism of the salamander thyroid; it elaborates a specific substance which, in some unknown way, stimulates the thyroid, thereby effecting the release of the thyroid hormone. On the basis of previous findings we propose, as a guide in further experimentation, the hypothesis that this active principle of the anterior lobe is not elaborated during the larval period, and that for this reason release of the colloid and metamorphosis do not take place at an earlier period of life. REFERENCES. (1) ANDERSSON, O. A. (1894). Arch./Or Anat. und Physiol., Anat. Abt., (2) ASHER, L. and FLACK, M. (1910). Zeitsch.f. Biol. 55, (3) CANNON, W. B. and FITZ, R. (1915). Transact. Assn. Amer. Physiol. 30, (4) HOGBEN, L. T. (1923). Proc. Roy. Soc. B, 94, (5) SMITH, P. E. and SMITH, I. P. (1922). Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol. and Med. 20, (6) SMITH, P. E. (1926). Brit, jfourn. Exper. Biol. 3, (7) SPAUL, E. A. (1925). Brit.Journ. Exper. Biol. 2, (8) UHLENHUTH, E. (1927). Arch.f. Enttuicklungsniecltanik der Organismen (in press). (9) WILSON, L. B. (1916). jfourn. Am. Med. Assn. 152, (1916). Transact. Assn. Am. Physiol. 31, (1917). Transact. Assn. Am. Physiol. 32, (1917). Collect. Papers Mayo Clinic, 9, (1917). Journ. Lab. and Clin. Med. 2, (10) WILSON, L. B. and DURANTE, L. (1916). jfourn. Med. Res. 34, (N.S.),
RELATION BETWEEN THYROID GLAND, METAMOR- PHOSIS, AND GROWTH. BY EDUARD IYHLENHUTH. (Received for publication, February 1, 1919.)
 RELATION BETWEEN THYROID GLAND, METAMOR- PHOSIS, AND GROWTH. BY EDUARD IYHLENHUTH. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication, February 1, 1919.)
RELATION BETWEEN THYROID GLAND, METAMOR- PHOSIS, AND GROWTH. BY EDUARD IYHLENHUTH. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication, February 1, 1919.)
ACCELERATED METAMORPHOSIS OF FROG TADPOLES BY INJECTIONS OF EXTRACT OF ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY GLAND AND THE ADMINISTRATION OF IODINE.
 ACCELERATED METAMORPHOSIS OF FROG TADPOLES BY INJECTIONS OF EXTRACT OF ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY GLAND AND THE ADMINISTRATION OF IODINE.* BY E. A. SPAUL, Birkbeck College (University of London). WITH TWO
ACCELERATED METAMORPHOSIS OF FROG TADPOLES BY INJECTIONS OF EXTRACT OF ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY GLAND AND THE ADMINISTRATION OF IODINE.* BY E. A. SPAUL, Birkbeck College (University of London). WITH TWO
THE GROWTH OF THE THYROID AND POSTBRANCHIAL BODY OF THE SALAMANDER, AMBYSTOMA OPACUM. BY EDUARD UHLENHUTH.
 THE GROWTH OF THE THYROID AND POSTBRANCHIAL BODY OF THE SALAMANDER, AMBYSTOMA OPACUM. BY EDUARD UHLENHUTH. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication,
THE GROWTH OF THE THYROID AND POSTBRANCHIAL BODY OF THE SALAMANDER, AMBYSTOMA OPACUM. BY EDUARD UHLENHUTH. (From the Laboratories of The Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research.) (Received for publication,
THE EFFECT OP POSTERIOR LOBE EXTRACT, ADRENALIN, AND PILO CARPINE ON THE RESPONSE OP THE THYROID GLAND TO THE THYREO-
 THE EFFECT OP POSTERIOR LOBE EXTRACT, ADRENALIN, AND PILO CARPINE ON THE RESPONSE OP THE THYROID GLAND TO THE THYREO- ACTIVATOR HORMONE OP THE ANTERIOR LOBE OP THE HYPOPHYSIS fey Harry A* Teitelbaura,
THE EFFECT OP POSTERIOR LOBE EXTRACT, ADRENALIN, AND PILO CARPINE ON THE RESPONSE OP THE THYROID GLAND TO THE THYREO- ACTIVATOR HORMONE OP THE ANTERIOR LOBE OP THE HYPOPHYSIS fey Harry A* Teitelbaura,
during the process. Nevertheless, the small amount of evidence
 CHANGES IN OXYGEN CONSUMPTION DURING METAMORPHOSIS INDUCED BY THYROID ADMINISTRATION IN THE AXOLOTL. BY J. BEILEHRADEK AND J. S. HUXLEY. (Zoological Department, King's College, London.) WHEN we consider
CHANGES IN OXYGEN CONSUMPTION DURING METAMORPHOSIS INDUCED BY THYROID ADMINISTRATION IN THE AXOLOTL. BY J. BEILEHRADEK AND J. S. HUXLEY. (Zoological Department, King's College, London.) WHEN we consider
Since, for many months after section of the right vagus in the neck,
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
published by Hektoen and SchuIhof (1), and since the appearance
 ON THE INNERVATION AND SECRETORY PATH OF THE THYROID GLAND. BY C. S. HICKS (Beit Memorial Fellow). (From the Biochemistry Laboratories, Cambridge, and Physiology Department, University of Adelaide.) IN
ON THE INNERVATION AND SECRETORY PATH OF THE THYROID GLAND. BY C. S. HICKS (Beit Memorial Fellow). (From the Biochemistry Laboratories, Cambridge, and Physiology Department, University of Adelaide.) IN
COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF ACCELERATED AMPHIBIAN METAMORPHOSIS
 22 COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF ACCELERATED AMPHIBIAN METAMORPHOSIS BY E. A. SPAUL, PH.D., B.SC, Birkbeck College, University of London. (Received xytk October 92.) (With Four Text-Figures.) CONTENTS.. Introduction......
22 COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF ACCELERATED AMPHIBIAN METAMORPHOSIS BY E. A. SPAUL, PH.D., B.SC, Birkbeck College, University of London. (Received xytk October 92.) (With Four Text-Figures.) CONTENTS.. Introduction......
MELANOPHORES OF FISHES. Spaeth (1918) reported that the melanophores on isolated scales of
 VOL. 19, 1933 ZOOLOGY: J. M. ODIORNE other 8 subjects enough were tabulated (800 for two, 1200 for three, 2400 for one and 3800 for two) to satisfy all requirements. In all cases, the first two sets of
VOL. 19, 1933 ZOOLOGY: J. M. ODIORNE other 8 subjects enough were tabulated (800 for two, 1200 for three, 2400 for one and 3800 for two) to satisfy all requirements. In all cases, the first two sets of
THE EFFECT OF EXTRACTS OF SUPRARENAL CORTEX ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM
 35 THE EFFECT OF EXTRACTS OF SUPRARENAL CORTEX ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) (Received 12th February 1929.) INTRODUCTION.
35 THE EFFECT OF EXTRACTS OF SUPRARENAL CORTEX ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) (Received 12th February 1929.) INTRODUCTION.
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
hypophysectomized rat. Marenzi & Gerschman [1934] studied six of the University and Royal Infirmary, Glasgow (Received 13 December 1937)
![hypophysectomized rat. Marenzi & Gerschman [1934] studied six of the University and Royal Infirmary, Glasgow (Received 13 December 1937) hypophysectomized rat. Marenzi & Gerschman [1934] studied six of the University and Royal Infirmary, Glasgow (Received 13 December 1937)](/thumbs/96/129025719.jpg) 124 J. Physiol. (I938) 92, I24-130 6i2.492.5:6I2.I26 THE EFFECT OF HYPOPHYSECTOMY ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM AND PHOSPHORUS OF THE RAT BY A. B. ANDERSON AND E. G. OASTLER From the Biochemical Laboratory, Department
124 J. Physiol. (I938) 92, I24-130 6i2.492.5:6I2.I26 THE EFFECT OF HYPOPHYSECTOMY ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM AND PHOSPHORUS OF THE RAT BY A. B. ANDERSON AND E. G. OASTLER From the Biochemical Laboratory, Department
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
Endocrine system consists of organs that produce and secrete hormones "endocrine" = internal secretion into capillaries Hormones carried by the blood to another organ; exert effects Hormones manipulate
hypoglycoemic reaction to insulin is greater in sheep after thyroidectomy, BY J. (The National Institute for Medical Research, London.
 THE RELATION OF THE THYROID GLAND TO THE ACTION OF INSULIN. BY J. H. BURN AND H. P. MARKS. (The National Institute for Medical Research, London.) AN experimental investigation of the connection between
THE RELATION OF THE THYROID GLAND TO THE ACTION OF INSULIN. BY J. H. BURN AND H. P. MARKS. (The National Institute for Medical Research, London.) AN experimental investigation of the connection between
following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
 612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
Nervous and chemical regulation heart
 Nervous and chemical regulation heart Myogenic heart when separated out from the body keep on beating on their own but when in the body the rate of heart beat is modified through various stimuli such as
Nervous and chemical regulation heart Myogenic heart when separated out from the body keep on beating on their own but when in the body the rate of heart beat is modified through various stimuli such as
however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation.
![however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation. however, reduced after parasympathetic denervation [Nordenfelt et al., 1960]. opposite to those caused by parasympathetic denervation.](/thumbs/90/101412039.jpg) CHOLINE ACETYLASE IN SALIVARY GLANDS OF THE CAT AFTER SYMPATHETIC DENERVATION. By IVAR NORDENFELT. From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden. (Received for publication 20th April 1964)
CHOLINE ACETYLASE IN SALIVARY GLANDS OF THE CAT AFTER SYMPATHETIC DENERVATION. By IVAR NORDENFELT. From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden. (Received for publication 20th April 1964)
THE IODINE CONTENT OF THE THYROID OF THE FOWL WITH REFERENCE TO AGE AND SEX
 66 THE IODINE CONTENT OF THE THYROID OF THE FOWL WITH REFERENCE TO AGE AND SEX BY A. C. CHAUDHURI, B.SC. (AGRIC). Animal Breeding Research Department, University of Edinburgh. {Received ist January 98.)
66 THE IODINE CONTENT OF THE THYROID OF THE FOWL WITH REFERENCE TO AGE AND SEX BY A. C. CHAUDHURI, B.SC. (AGRIC). Animal Breeding Research Department, University of Edinburgh. {Received ist January 98.)
ON THE ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY
 49 ON THE ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY BY E. A. SPAUL. (From the Department of Zoology, Birkbeck College, University of London.) (Received $thjuly 1929.) (With One Text-figure.) CONTENTS. PAGE
49 ON THE ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY BY E. A. SPAUL. (From the Department of Zoology, Birkbeck College, University of London.) (Received $thjuly 1929.) (With One Text-figure.) CONTENTS. PAGE
(From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
616 EDUARD UHLENHUTH
 The Golgi Apparatus in the Thyroid Gland of Amphibians, in its relation to Excretion Polarity. By Eduard Uhlenhuth, University of Maryland, Medical School. With Plate 36. IN 1923 Nassonov reported observations
The Golgi Apparatus in the Thyroid Gland of Amphibians, in its relation to Excretion Polarity. By Eduard Uhlenhuth, University of Maryland, Medical School. With Plate 36. IN 1923 Nassonov reported observations
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
ANTERIOR PITUITARY AND GROWTH IN THE AXOLOTL (AMBLYSTOMA TIGRINUM (GREEN) NEOTENIC FORM)
 54 1 ANTERIOR PITUITARY AND GROWTH IN THE AXOLOTL (AMBLYSTOMA TIGRINUM (GREEN) NEOTENIC FORM) I. THE EFFECTS OF INJECTION OF GROWTH-PROMOTING EXTRACTS OF THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY BY D. I. CLEMENTS AND N.
54 1 ANTERIOR PITUITARY AND GROWTH IN THE AXOLOTL (AMBLYSTOMA TIGRINUM (GREEN) NEOTENIC FORM) I. THE EFFECTS OF INJECTION OF GROWTH-PROMOTING EXTRACTS OF THE ANTERIOR PITUITARY BY D. I. CLEMENTS AND N.
Jolly(l), Halpenny and Thompson(2) supported this view, but. during secretory activity and can be traced to the tubes of the parathyroid.
 EFFECT OF PARATHYROID FEEDING ON THE THYROID. BY DOROTHY WOODMAN. (From the Department of Physiology, London (R.F.H.) School of Medicine for Women.) Two hypotheses have been put forward to explain the
EFFECT OF PARATHYROID FEEDING ON THE THYROID. BY DOROTHY WOODMAN. (From the Department of Physiology, London (R.F.H.) School of Medicine for Women.) Two hypotheses have been put forward to explain the
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
THE DIABETOGENIC HORMONE OF THE PITUITARY GLAND
 VOL. XIII, i JANUARY, 96 THE DIABETOGENIC HORMONE OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BY DAVID SLOME. (From the Department of Social Biology, the University of London, and the Buckston Browne Research Farm, Royal College
VOL. XIII, i JANUARY, 96 THE DIABETOGENIC HORMONE OF THE PITUITARY GLAND BY DAVID SLOME. (From the Department of Social Biology, the University of London, and the Buckston Browne Research Farm, Royal College
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS
![[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS](/thumbs/90/101209894.jpg) [485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
[485] THE BREAKDOWN OF THE THORACIC GLAND IN THE ADULT INSECT, RHODNIUS PROLIXUS BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge (Received 3 November 1954) The thoracic or ' prothoracic'
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES
 HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION
 Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
CHARA CTERS* nearly sterile. As in other similar combinations the sex glands are reduced ZOOLOGY: E. WITSCHI
 ZOOLOGY: E. WITSCHI VOL. 23, 1937 35 STIMULATIVE AND INHIBITIVE INDUCTION IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SEX CHARA CTERS* By EMIL WITSCHI DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY, STATE UNIVERSITY OF IOWA Read
ZOOLOGY: E. WITSCHI VOL. 23, 1937 35 STIMULATIVE AND INHIBITIVE INDUCTION IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY SEX CHARA CTERS* By EMIL WITSCHI DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY, STATE UNIVERSITY OF IOWA Read
THE GOITRE CYCLE AND ITS ANATOMIC FINDINGS*
 THE GOITRE CYCLE AND ITS ANATOMIC FINDINGS* A REPORT OF 1028 SECTIONED GOITRES B. MARKOWITZ During the past thirty years vast contributions have been made to the study of the etiology of goitre. These
THE GOITRE CYCLE AND ITS ANATOMIC FINDINGS* A REPORT OF 1028 SECTIONED GOITRES B. MARKOWITZ During the past thirty years vast contributions have been made to the study of the etiology of goitre. These
1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis.
 ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
ENDOCRINE Objectives 1. To describe the gross structure of the pituitary gland and be able to identify the pars nervosa, pars intermedia and pars distalis. 2. Identify and describe the histological features
Title. Author(s)HANAOKA, Kin-Ichiro. Citation 北海道帝國大學理學部紀要, 3(4): Issue Date Doc URL. Type. File Information
 Title A SEMIDIFFERENTIATED RACE OF URODELANS WITH REGARD T Two Plates and Three Text-figures) Author(s)HANAOKA, Kin-Ichiro Citation 北海道帝國大學理學部紀要, 3(4): 247-253 Issue Date 1934-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/26972
Title A SEMIDIFFERENTIATED RACE OF URODELANS WITH REGARD T Two Plates and Three Text-figures) Author(s)HANAOKA, Kin-Ichiro Citation 北海道帝國大學理學部紀要, 3(4): 247-253 Issue Date 1934-12 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/26972
however, to have been directly studied in any of the numerous observations
 ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT AND THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY
 44 THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT AND THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY BY E. A. SPAUL AND W. W. MYDDLETON. (Received zyth May 1930.) (With Two Text-figures.) QUALITATIVE and quantitative studies
44 THE PHOSPHATE CONTENT AND THE BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF THE ANTERIOR LOBE PITUITARY BY E. A. SPAUL AND W. W. MYDDLETON. (Received zyth May 1930.) (With Two Text-figures.) QUALITATIVE and quantitative studies
Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology
 Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology 1 2 : Positive feedback control of labor contractions during birth of a baby. The solid return arrow symbolizes positive feedback. If the response
Medical Endocrinology / Introduction 4 Medical Endocrinology 1 2 : Positive feedback control of labor contractions during birth of a baby. The solid return arrow symbolizes positive feedback. If the response
Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology LECTURE NO (-) Hypothalamus. Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology
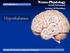 LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
LECTURE NO (-) Neuro-Physiology Kamal Mohammed Lecturer Of Physiology Hypothalamus Faculty Of Medicine Dept.Of Physiology Hypothalamus Less than 1% of the brain mass Many connect the hypothalamus to the
glands are reported to have no antidiuretic action) produce a principle gland of some lower vertebrates (teleost fishes, amphibians, reptiles), has
 246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
(Foulerton Student of the Royal Society).
 6I2.62I:6I2.OI8 STUDIES ON OVULATION. VI. Relative importance of concentration and absolute amount of the ovulation-producing hormone. BY F. W. ROGERS BRAMBELL AD A. S. PARKES (Foulerton Student of the
6I2.62I:6I2.OI8 STUDIES ON OVULATION. VI. Relative importance of concentration and absolute amount of the ovulation-producing hormone. BY F. W. ROGERS BRAMBELL AD A. S. PARKES (Foulerton Student of the
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Cannon(3) and Elliott(4). The action of these fibres has thrown a new
 ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
ON THE PART PLAYED BY THE SUPRARENALS IN THE NORMAL VASCULAR REACTIONS OF THE BODY. BY G. VON ANREP. (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) THE existence of secretory nerves to
Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with
![Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with Franklin, 1933; Waterman, 1933]; indeed, the only negative findings, [Waterman, 1933]. Inasmuch, then, as Donegan was misled with](/thumbs/91/106294335.jpg) 381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
381 6I2.I34:6I2.893 THE CONSTRICTOR RESPONSE OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA TO STIMULATION OF THE SPLANCHNIC NERVE BY K. J. FRANKLIN AND A. D. McLACHLIN (From the University Department of Pharmacology, Oxford)
Fig. 1. The reverse change is shown in Fig. 3. fluid, and then when activity was re-established the fluid replaced by a
 CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
CARDIAC TETANUS. By W. BURRID GE, M.B. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Oxford.) WALTHER(13) gives complete references to the experiments on cardiac tetanus and in his discussion concludes that superposition
Hormones and the Endocrine System
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids
 Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System Organs and Tissues: Pituitary Adrenals Pancreas Thyroid Parathyroids Bruce A. Fenderson, Ph.D. Pathology, Anatomy & Cell Biology Sidney Kimmel Medical College Bruce.Fenderson@Jefferson.edu
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
King's College, London.)
 THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
THE EFFECT OF THE CIRCULATION ON THE ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE OF THE SKIN. BY F. AVELING AND R. J. S. McDOWALL. (From the Departments of Physiology and Psychology, King's College, London.) OF recent years,
A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA
 J. Exp. Biol. (197a), 57. 737-743 737 ^Vith 5 text-figures WPrinted in Great Britain A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA BY ALBERT D. CARLSON Department
J. Exp. Biol. (197a), 57. 737-743 737 ^Vith 5 text-figures WPrinted in Great Britain A COMPARISON OF TRANSMITTER AND SYNEPHRINE ON LUMINESCENCE INDUCTION IN THE FIREFLY LARVA BY ALBERT D. CARLSON Department
PSYCHE THE FUSED THORACIC GANGLIA OF THE FIBER TRACTS OF THE ADULT EPHESTIA KUEHNIELLA ZELLER (LEPIDOPTERA: PYRALIDZE) BY ROBEttT W.
 PSYCHE VOL. XLVIII DECEMBER, 1941 No. 4 THE FIBER TRACTS OF THE FUSED THORACIC GANGLIA OF THE ADULT EPHESTIA KUEHNIELLA ZELLER (LEPIDOPTERA: PYRALIDZE) BY ROBEttT W. PYLE Biological Laboratories, Harvard
PSYCHE VOL. XLVIII DECEMBER, 1941 No. 4 THE FIBER TRACTS OF THE FUSED THORACIC GANGLIA OF THE ADULT EPHESTIA KUEHNIELLA ZELLER (LEPIDOPTERA: PYRALIDZE) BY ROBEttT W. PYLE Biological Laboratories, Harvard
Embryos of Amblystoma punctatum were used for the majority of the. Conclusions.-A method of resolution of tertiary carbinols of the aromatic
 218 ZOOLOG Y: R. F. BLO UNT Conclusions.-A method of resolution of tertiary carbinols of the aromatic series containing an asymmetric carbon atom has been described by means of which an optically active
218 ZOOLOG Y: R. F. BLO UNT Conclusions.-A method of resolution of tertiary carbinols of the aromatic series containing an asymmetric carbon atom has been described by means of which an optically active
CHOLINE AS A FACTOR IN THE ELABORATION OF ADRENALINE
 CHOLINE AS A FACTOR IN THE ELABORATION OF ADRENALINE R. L. STEHLE, K. I. MELVILLE AND FRANCES K. OLDHAM Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal Received for publication January 31, 1936
CHOLINE AS A FACTOR IN THE ELABORATION OF ADRENALINE R. L. STEHLE, K. I. MELVILLE AND FRANCES K. OLDHAM Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal Received for publication January 31, 1936
Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online
 Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online Chapter Title Copyright Year 2015 Copyright Holder Thyroxine-Induced Metamorphosis in the Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) Springer Science+Business
Metadata of the chapter that will be visualized online Chapter Title Copyright Year 2015 Copyright Holder Thyroxine-Induced Metamorphosis in the Axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) Springer Science+Business
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
blood-vessels of the isolated perfused lungs of the rat. Both Hirakawa
 547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
Cardiac muscle is different from other types of muscle in that cardiac muscle
 6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
6 E X E R C I S E Cardiovascular Physiology O B J E C T I V E S 1. To define autorhythmicity, sinoatrial node, pacemaker cells, and vagus nerves 2. To understand the effects of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
indirectly through its nerve, its contraction is not simultaneous all over but
 466 J. Physiol. (I957) I39, 466-473 ALTERNATING RELAXATION HEAT IN MUSCLE TWITCHES BY A. V. HILL AND J. V. HOWARTH From the Physiological Laboratory, University College London (Received 31 July 1957) When
466 J. Physiol. (I957) I39, 466-473 ALTERNATING RELAXATION HEAT IN MUSCLE TWITCHES BY A. V. HILL AND J. V. HOWARTH From the Physiological Laboratory, University College London (Received 31 July 1957) When
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
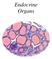 Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis) Function o Production of hormones Location o Connected to the hypothalamus via an infundibulum situated within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone Structure
IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS.
 CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
CULTIVATION IN VITRO OF MALIGNANT TUMORS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL AnD MONTROSE T. BURROWS. (From the Laboratories of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York.) Pr~AT~ LXXVII. The growth of malignant
THE RELATIVE INCIDENCE OF OOPHORECTOMY IN WOMEN WITH AND WITHOUT CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST'
 THE RELATIVE INCIDENCE OF OOPHORECTOMY IN WOMEN WITH AND WITHOUT CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST' WALLACE E. HERRELL, M.D. (Fellow in Medicine, The Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota) In the past two decades numerous
THE RELATIVE INCIDENCE OF OOPHORECTOMY IN WOMEN WITH AND WITHOUT CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST' WALLACE E. HERRELL, M.D. (Fellow in Medicine, The Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota) In the past two decades numerous
Overton,1 who has worked exhaustively at the subject, looked upon. considered by some to be due to the state of the fluid originally in the
 THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE ON THE OSMOTIC PROPER- TIES OF MUSCLE. By D. H. DE SOUZA. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Sheffield.) (With six diagrams in the text.) (Received for publication
investigated. According to the current hypothesis fat is completely hydrolysed
 306 J. Physiol. (I943) I02, 3o6-3I2 6i2. 322 73 DIFFERENTIATION IN THE ABSORPTION OF OLIVE OIL *0 AND OLEIC ACID IN THE. RAT By A. C. FRAZER,* From the Physiology Department, St Mary's Hospital Medical
306 J. Physiol. (I943) I02, 3o6-3I2 6i2. 322 73 DIFFERENTIATION IN THE ABSORPTION OF OLIVE OIL *0 AND OLEIC ACID IN THE. RAT By A. C. FRAZER,* From the Physiology Department, St Mary's Hospital Medical
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
(Sherrington School of Physiology, St Thomas's Hospital, London.)
 6I2.352.I7:6II-0I3.85 MATERNAL CONTROL OF THE PLACENTAL GLYCOGEN. BY A. ST G. HUGGETT. (Sherrington School of Physiology, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) CLAUDE BERNARD(1), in 1859, showed that glycogen
6I2.352.I7:6II-0I3.85 MATERNAL CONTROL OF THE PLACENTAL GLYCOGEN. BY A. ST G. HUGGETT. (Sherrington School of Physiology, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) CLAUDE BERNARD(1), in 1859, showed that glycogen
Systemic The study of anatomy by body systems
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
Chapter 1: Introduction to Structural Units Video Worksheet Anatomy Terms: What should you do to learn the terms in this class??? Buy notecards Anatomy The study of the body o Identification of the body
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
OBSERVATIONS ON PIGMENTARY CO-ORDINATION IN ELASMOBRANCHS
 460 OBSERVATIONS ON PIGMENTARY CO-ORDINATION IN ELASMOBRANCHS BY URSULA WYKES (Laboratory of the Marine Biological Association, Plymouth) (With One Text-figure) (Received February 27, 1936) I. INTRODUCTION
460 OBSERVATIONS ON PIGMENTARY CO-ORDINATION IN ELASMOBRANCHS BY URSULA WYKES (Laboratory of the Marine Biological Association, Plymouth) (With One Text-figure) (Received February 27, 1936) I. INTRODUCTION
Babkin, Savitsch) that pancreatic secretion is due, in part, to reflex
 THE MECHANISM OF PANCREATIC DIGESTION-THE FUNCTION OF SECRETIN. BY J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) A SECRETION of pancreatic juice may be evoked by appropriate
THE MECHANISM OF PANCREATIC DIGESTION-THE FUNCTION OF SECRETIN. BY J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) A SECRETION of pancreatic juice may be evoked by appropriate
Thyroid Gland. Chapter 18 Part 2. Thyroid gland. Thyroid Gland. Thyroid Gland. Parathyroid Gland. Adrenal Gland. Pancreas
 Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Thyroid Gland Chapter 18 Part 2 Synthesis and function of Thyroid hormone Calcitonin and Calcium regulation Parathyroid Gland PTH and Calcium regulation Adrenal Gland The corticosteroids Pancreas Regulation
Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 528-532, March 1971 Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections in Frogs after Visual Deprivation or Disparate
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Vol. 68, No. 3, pp. 528-532, March 1971 Absence of Adaptive Modification in Developing Retinotectal Connections in Frogs after Visual Deprivation or Disparate
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR
 SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
Columbia University, New York.)
 15 6I2.62I:6I2.4 THE EFFECT OF OVARIAN HORMONE ON THE PITUITARY, THYROID, AND ADRENAL GLANDS OF SPAYED FEMALE RATS. BY DOROTHY H. ANDERSEN. (From the Department of Pathology, College of Physicians and
15 6I2.62I:6I2.4 THE EFFECT OF OVARIAN HORMONE ON THE PITUITARY, THYROID, AND ADRENAL GLANDS OF SPAYED FEMALE RATS. BY DOROTHY H. ANDERSEN. (From the Department of Pathology, College of Physicians and
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
Endocrine system. Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to:
 Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
Name: 1.4 Responses to Stimuli Objectives At the end of this sub section students should be able to: 3.5.3 Responses in the Human -- Endocrine System 1. Say what an Endocrine system is 2. Define the term
The Emotional Nervous System
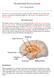 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
nyx4edema; that is to say, in no case was there any appreciable swelling 1 Proc. Roy. Soc., vol. xxxviii., 1884, p. 5; ibid., vol. xl., 1886, p. 6.
 NOTE ON EXTIRPATION OF THE THYROID GLAND IN MONKEYS. By JASPER HALPENNY and JOHN A. GUNN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.) (Received for publication 22nd May 1911.)
NOTE ON EXTIRPATION OF THE THYROID GLAND IN MONKEYS. By JASPER HALPENNY and JOHN A. GUNN. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.) (Received for publication 22nd May 1911.)
DURING the past ten years it has been suggested that the classical form
 163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
PITUITARY HYPERPLASIA IN A MALE MOUSE AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF OESTRIN
 PITUITARY HYPERPLASIA IN A MALE MOUSE AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF OESTRIN HAROLD BURROWS (From The Research Institute of the Royal Cancer Hospital (Free), London, S.W.3) Several observers have noticed
PITUITARY HYPERPLASIA IN A MALE MOUSE AFTER THE ADMINISTRATION OF OESTRIN HAROLD BURROWS (From The Research Institute of the Royal Cancer Hospital (Free), London, S.W.3) Several observers have noticed
LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
THE sebaceous glands of the rabbit consist of clusters of about ten cells
 79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
79 On the Relationship between Mammary, Sweat, and Sebaceous Glands By D. B. CARLISLE (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, Oxford, and the Plymouth Laboratory of the Marine Biological
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I. different, but most of them appear to be satisfactory from a qualitative
 442 612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I SIZE CHANGES IN THE SEMINAL VESICLES OF THE MOUSE DURING DEVELOPMENT AND AFTER CASTRATION. BY RUTH DEANESLY AND A. S. PARKES'. (From the National Institute for Medical Research,
442 612.6I7.5:612.6I6.I SIZE CHANGES IN THE SEMINAL VESICLES OF THE MOUSE DURING DEVELOPMENT AND AFTER CASTRATION. BY RUTH DEANESLY AND A. S. PARKES'. (From the National Institute for Medical Research,
Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis
 Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis The maintenance of a constant internal environment By maintaining a relatively constant environment (of the tissue fluid) for their cells, organisms can limit the
Section 12.1 Principle of homeostasis The maintenance of a constant internal environment By maintaining a relatively constant environment (of the tissue fluid) for their cells, organisms can limit the
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the
 Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Nicole Rodi Bio 235: Animal Physiology Heart Muscle Lab Report 10/24/2014 Effects of Temperature, Stretch, and Various Drug Treatments on the Cardiac Muscle Activity of Rana pipiens Abstract Mechanical
Histology of the Thyroid Gland
 Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Histology of the Thyroid Gland A Introduction The thyroid hormone is derived The thyroid gland is responsible for the secretion of the from the amino acid tyrosine thyroid hormone that controls the basal
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels
 17.6 The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels Partially embedded in the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland
17.6 The Parathyroid Glands Secrete Parathyroid Hormone, which Regulates Calcium, Magnesium, and Phosphate Ion Levels Partially embedded in the posterior surface of the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES To state the function of the Nervous system. To describe the structure and workings of the nervous system. To name the major parts of the nervous system. To describe
