Endocrine System. Chapter 18
|
|
|
- Grace Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Endocrine System Chapter 18
2 Learning Outcomes Explain the importance of intercellular communication, describe the mechanisms involved, and compare the modes of intercellular communication that occur in the endocrine and nervous systems. Compare the cellular components of the endocrine system with those of other systems, contrast the major structural classes of hormones, and explain the general mechanisms of hormonal action on target organs. Describe the location, hormones, and functions of the pituitary gland, and discuss the effects of abnormal pituitary hormone production. Describe the location, hormones, and functions of the thyroid gland, and discuss the effects of abnormal thyroid hormone production. Describe the location, hormone, and functions of the parathyroid glands, and discuss the effects of abnormal parathyroid hormone production.
3 Learning Outcomes (contd) Describe the location, structure, hormones, and general functions of the adrenal glands, and discuss the effects of abnormal adrenal hormone production. Describe the location of the pineal gland, and discuss the functions of the hormone it produces. Describe the location, structure, hormones, and functions of the pancreas, and discuss the effects of abnormal pancreatic hormone production. Describe the functions of the hormones produced by the kidneys, heart, thymus, testes, ovaries, and adipose tissue. Explain how hormones interact to produce coordinated physiological responses and influence behavior.
4 Two systems that directly/indirectly control most body functions Nervous System Endocrine System
5 How do these systems work? Nervous System Example: Foot steps on a nail impulse is generated impulse travels to the spinal cord impulses travel to the thigh muscle thigh muscles contract foot is lifted Endocrine System Example: Eat a candy bar blood sugar level goes up pancreas are stimulated to release hormone insulin in blood insulin helps liver and skeletal muscle in taking out access blood sugar and storing as glycogen blood sugar level goes down
6 How do these systems work? Nervous System Sensory system Transmits impulses Impulses go directly to the specific target cells Impulses cause contraction of muscles or secretion from glands Takes a fraction of a second to respond faster system Affect wears off within seconds Endocrine System Chemical system Releases hormones into blood Hormones are sent everywhere but act on specific target cells Hormones affect metabolism, membrane permeability, growth or development Takes minutes, hours, or days to respond.slower system Affect last days, hours or months
7 Endocrine and nervous systems work together and affect each other: Impulses may affect the release of certain hormones. Hormones may affect generation/conduction of impulses.
8 How Cells Communicate with one another Direct communication: is seen between cells of the same type which are in direct contact with one another via gap junctions. Paracrines: Local regulators, Released by body cells Act on neighboring cells Example: Nitric oxide (NO) secreted by endothelial cells lining blood vessels causes vasodilation of the blood vessels Endocrines: True hormones Made by endocrine cells or glands Diffuse into blood Travel to their specific target cells or organs Example: Insulin released by pancreas and act on liver and other cells as target cell. Synaptic communication: Neurons release chemicals called neurotransmitters at junctions close to target cells with specific receptors.
9 Components of the Endocrine System Some endocrine glands secrete hormone as their primary function: Pituitary gland Pineal gland Thyroid gland Parathyroid Adrenal gland Other endocrine glands secrete hormones as their secondary function: Hypothalamus Thymus Pancreas Ovaries Testis Stomach Kidneys Small intestine
10 Functions of Hormones Help maintain homeostasis (water, ph, blood sugar, temperature, minerals). Help regulate metabolism (making/breaking organic chemicals, energy production). Help regulate growth, development and reproduction.
11 Review Time!!! Labeling Activity: Endocrine glands of the body. Answer the following questions to review the material covered so far. What is Hoemostasis? Which two systems of the body maintain homeostasis? What is their mechanism of action? What is the difference between primary and secondary endocrine organs? Give examples of each. Write down the functions of hormones in the body?
12 Characteristics of hormones Over 50 types of hormones produced by human body Hormones are made by endocrine glands Hormones are made in very small amounts Hormones diffuse into blood and are transported by blood to all body parts Only specific target cells or organs recognize and respond to each hormone Target cells have specific receptor proteins
13 Classification of Hormones Based on their chemical structure, hormones can be divided into three groups: Amino acid derivatives: also known as biogenic amines, are derived from amino acids, e.g. thyroid hormones, epinephrine, norepinephrine and melatonin. Peptide hormones: are chains of amino acids, e.g. TSH, LH, FSH, ADH, Oxytocin, GH and PRL. Lipid derivatives: are divided into two classes eicosanoids (signaling molecules, e.g. prostaglandins) and steroid hormones (derived from cholesterol, e.g. estrogen and androgens).
14 Measurement of Hormones Hormones are released in blood and transported by blood. Most hormones are measured by taking a blood sample Some hormones are produced in excess and excreted in urine.measured in urine sample
15 Secretion and Distribution of Hormones Hormones are released in blood and transported by blood Some hormones circulate freely in the blood, e.g peptide hormones. These hormones remain functional for a short period of time, minutes to hours. Taken as shots/injections. Examples insulin, growth hormone. Thyroid hormones and steroid hormones travel in the blood bound to a special transport proteins and therefore remain in circulation much longer. Can be administered orally.
16 Hormone Action Hormones are made by an endocrine gland they travel through blood they are recognized by specific receptors present on the target cells a new protein is made or an inactive protein is activated protein could be an enzyme, a transport protein, or a protein hormone There are 2 basic mechanisms of hormone action: Water insoluble/lipid soluble hormone action Water soluble/lipid insoluble hormone action
17 Hormones and Intracellular receptors Hormone diffuses out of the blood capillary to go to its target cell --> Lipid soluble hormone diffuses through the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane --> Hormone binds to the specific cytoplasmic receptor --> OR --> Hormone diffuses through the nuclear membrane to enter the nucleus and bind to nuclear receptor --> Hormone-receptor (HR) complex is formed --> HR complex binds to specific locations on DNA --> Specific genes are activated --> new mrna and proteins are made --> These proteins could be enzymes or transport proteins needed for specific hormone action
18 Hormones and Plasma Membrane Receptors Hormone diffuses out of the blood capillary to go to its target cell --> Peptide hormones cannot pass phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane --> Hormone binds to specific receptor present on plasma membrane --> Hormone receptor (HR) complex is formed on the outer surface of the plasma membrane --> G protein on the inside of the membrane is activated --> leads to the appearance of a second messenger (camp/cgmp/ca) -- > second messenger acts as an enzyme activator, inhibitor, or cofactor --> results in a change in the rate of metabolic reactions
19 Down Regulation: Presence of a hormone triggers decrease in number of hormone receptors. When levels of particular hormone are high, cells become less sensitive to it. Up Regulation: Absence of a hormone triggers increase in number of hormone receptors. When levels of particular hormone are low, cells become more sensitive to it.
20 Stimulation of an Endocrine Gland There are 3 types of signals that stimulate endocrine glands: Nerve impulse stimulation A nerve impulse stimulates an endocrine gland Example: Stress or anxiety generation of nerve impulses impulses travel to adrenal cortex release of epinephrine and norepinepherine increased blood sugar, heart rate, breathing help the body cope with stress Hormonal stimulation A hormone stimulates another endocrine gland to make its hormones Example: Hypothalamus makes thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH*) TRH stimulates anterior pituitary to make thyrotropin thyrotropin* stimulates thyroid gland to make thyroid hormones * TRH and thyrotropin are called tropic hormones Non-hormonal or other chemical stimulation A chemical other than a hormone stimulates an endocrine gland Example: When blood sugar goes up pancreas are stimulated to produce insulin; when blood sugar level goes down insulin secretion goes down
21 Hormone Interaction Most body functions are regulated by two or more hormones hormones often have to interact with each other Permissive interaction When one hormone is required before the target cell can respond to another hormone Example: Estrogen is required for the development of the uterus lining then progesterone maintains this lining during pregnancy Synergistic interaction When two or more hormones complement each other to produce a greater response Example: Estrogen, progesterone, prolactin affect the growth of the mammary gland Antagonistic interaction When two hormones oppose the action of each other Example: Insulin decreases blood sugar while glucagon increases blood sugar
22 Control of Hormone Concentration Hormones are released in short bursts Feedback control mechanism A sequence of events where the end response regulates the secretion of the hormone Negative feedback control most common Where the body s response has an opposite affect on secretion of hormone Positive feedback control not as common Where the body s response has the same affect on the secretion of hormone
23 Review Time!!!! Labeling Activity: three mechanisms of hypothalamic control over endocrine function. Answer the following questions to review the material covered so far. Name the types of hormones based on their structure. Differentiate between the types of hormones based on their solubility, transportation in blood and administration in the body? Discuss the two mechanism of hormone action. Differentiate between up and down regulation. Differentiate between the three types of hormone interaction. Describe the three types of signals that stimulate endocrine secretions. Which hormone diffuses through the plasma membrane and binds to its receptors in the cytoplasm?
24 Things to learn for each gland Location and Anatomy Hormone/s secreted For each hormone, know Its target tissue and the response of the tissue to the hormone Regulation of the hormone i.e. what controls its release (chemical, neurons, or hormone) Effects of Hyposecretion/Hypersecretion
25 Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus Links nervous system with endocrine system Is anatomically and physiologically connected to pituitary gland by infundibulum
26 Pituitary Gland Made of two lobes: Anterior pituitary An endocrine tissue Makes a variety of hormones Regulated by releasing and inhibitory tropic hormones made by hypothalamus Posterior pituitary A nervous tissue Does not make hormones Houses axon terminals of neurosecretory cells located in hypothalamus Stores and releases hypothalamic hormones in response to nerve impulses
27 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Hypothalamus secretes specific releasing hormones (RH) and inhibiting hormones (IH) Hormones travel via circulatory system hypothalamo hypophyseal portal system. anterior pituitary is stimulated or inhibited to release its hormones hormones are circulated throughout the body.
28 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Human Growth Hormone (hgh) Secretion: - Most actively secreted in early childhood years - Its secretion goes down during puberty Stimulates: Growth of body cells, especially bone, cartilage and muscle cells Protein synthesis, fat metabolism, blood sugar level, ATP production Regulation: chemical control Decreased blood sugar level (hypoglycemia) stimulates GHRH secretion by hypothalamus stimulates anterior pituitary increased hgh secretion Increased blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) stimulates GHIH secretion by hypothalamus inhibits anterior pituitary decreased hgh secretion
29 Growth Hormone (contd) Clinical application: Dwarfism: hyposecretion of hgh during early childhood years Giantism: hypersecretion of hgh during early childhood years Acromegaly: hypersecretion of hgh in an adult after most long bones have sealed thicker jaw bone and forehead, larger hands, feet, tongue, lips Diabetogenic effect of hgh: hypersecretion of hgh symptoms similar to diabetes mellitus (increased blood sugar)
30 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Thyrotropin Tropic hormone Stimulates: Thyroid gland increased secretion of thyroid hormones, T3 and T4 increased metabolism Regulation: Decreased metabolism stimulates Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH) secretion by hypothalamus increased TSH secretion by anterior pituitary Increased metabolism decreased TRH secretion by hypothalamus decreased TSH secretion by anterior pituitary Clinical application: Causes metabolic disorders due to its affect on thyroid hormone secretion
31 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Gonadotropins Tropic hormones: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) Luteinizing Hormone (LH) Stimulate: Ovaries increased secretion of female hormones (estrogen, progesterone) stimulate follicular development and ovulation Testis increased secretion of male hormones (testosterone, inhibin) stimulate sperm formation Regulation: Decreased sex hormones increased Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone (GnRH) secretion by hypothalamus increased FSH and LH secretion by anterior pituitary increased sex hormones by ovaries and testis Increased sex hormones decreased (GnRH) secretion by hypothalamus decreased FSH and LH secretion by anterior pituitary decreased sex hormones by ovaries and testis Clinical application: Cause reproductive disorders due to their affect on secretion of sex hormones
32 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) Tropic hormone Stimulates: Cortex of adrenal gland Secretion of cortisol Regulation: Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH) secretion by hypothalamus increased ACTH secretion by anteriorpituitary increased cortisol secretion by adrenal cortex
33 Anterior Pituitary Hormones Prolactin (PRL) Stimulates: mammary gland milk production Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH) Stimulates: melanin synthesis by melanocytes Darkening of color in the skin
34 Posterior Pituitary Hormones Hypothalamus has neurosecretory cells make two hormones (ADH and OT) hormones are transported through the axons that from the hypothalamic hypophyseal tract hormones are stored in axon terminals hormones are released when a nerve impulse is transmitted by hypothalamus to the axon terminals
35 Posterior Pituitary Hormones Oxytocin (OT) Secretion: - Stimulated by nerve impulses Stimulates: Smooth muscle contraction in mammary duct release of milk Smooth muscle contraction in the wall of the uterus delivery of the baby Regulation: Positive feedback system Clinical application: Low OT during delivery Pitocin (commercial form of OT) shot is given to induce labor
36 Posterior Pituitary Hormones Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Secretion: Stimulated by water levels in blood Stimulates: Water reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct Regulation: Low water intake hypothalamus detects osmolarity of blood neurosecretory cells in hypothalamus generate impulses stimulates release of ADH from axon terminals located in posterior pituitary ADH stimulates water reabsorption in kidneys less urine formed water is conserved High water intake hypothalamus detects osmolarity of blood neurosecretory cells in hypothalamus do not generate impulses less ADH released from axon terminals located in posterior pituitary less water reabsorption in kidneys more urine formed Clinical application: Diabetes insipidus: hyposecretion of ADH symptoms similar to diabetes mellitus (large amounts of urine formed, dehydration, thirst)
37 Summary of Pituitary Hormones
38 Review Time!!!! We have covered a lot of important information in the last few sections. Make sure you spend enough time reviewing this material. Assess your understanding by attempting these questions: Name the two lobes of the pituitary gland? Describe the relationship between hypothalamus and anterior vs posterior pituitary gland. Name the hormones made by the hypothalamus and released by posterior pituitary gland. What is the effect of these hormones in the body. Name the hormones of anterior pituitary gland and their target tissues. What is diabetogenic effect of growth hormone? What are tropic hormones? Give examples.
39 Thyroid Gland Located anterior to trachea and inferior to larynx Made of two lobes connected by isthmus Each lobe consists of numerous sacs called follicles Follicles store large amounts of hormones Has a rich blood supply for quick delivery of hormones in the blood stream Secretes: Thyroid hormones - T3 and T4 for maintaining metabolism Calcitonin (CT) for maintaining blood calcium level
40 Thyroid Gland Hormones Thyroid Hormones T3 Triiodothyroxine: tyrosine with 3 iodines T4 Thyroxine: tyrosine with 4 iodines Made by follicular cells Modified and stored inside the follicles with the help of thyroglubulin (TGB) Function: - Regulate carbohydrate and lipid metabolism - Affect growth and development - Increase blood pressure, heart beat, body temperature, and GI tract movement
41 Clinical application Cretinism: hyposecretion of T3 and T4 in infants physical and mental retardation, yellow skin, fat pads, protruding tongue, enlarged belly; hormone therapy Myxedema: hyposecretion of T3 and T4 in adults low metabolism, lethargy, increased weight, decreased body temperature and heart rate, enlarged heart Exophthalmic goiter/graves disease: hypersecretion of T3 and T4 in adults high metabolism, decreased weight, increased body temperature and heart rate, bulging eyes
42 Thyroid Gland Hormones Calcitonin(CT) Calcitonin (CT) Made by parafollicular cells (C Cells) located between the follicles Function: - Decreases blood calcium - Increases bone calcium
43 Parathyroid Gland Four tiny glands on the posterior surface of thyroid gland Made of two types of cells: Chief cells secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) Oxyphil cells function unknown PTH - Increases blood calcium - Decreases bone calcium
44 Calcium Regulation Calcitonin and PTH are antagonistic hormones High blood levels of Ca+2 stimulate Calcitonin Low blood levels of Ca+2 stimulate PTHPTH
45 Review time Assess your understanding of the Thyroid and Parathroid hormones by attempting these questions: Name the hormones of thyroid gland? Which trace element plays an important role in the structure of thyroid hormones? Which thyroid hormone/s are under the regulation of anterior pituitary? Name the hormone/s secreted by the follicular cells and their function in the body. Describe the location of parathyroid glands? Increased blood calcium levels will stimulate the secretion of hormone by the gland.
46 Adrenal Gland Located above the kidneys Consists of: Capsule Adrenal cortex Adrenal medulla
47 Adrenal Gland Capsule Connective tissue protective layer Adrenal cortex Made up of three zones, secrete three types of hormones Adrenal medulla Secretes two types of hormones
48 Adrenal Cortex Hormones Secreted by zona glomerulosa Mineralocorticoids: Mostly aldosterone Regulate minerals Reabsorption of Na+, Cl-, HCO3- and water Excretion of K+ and H+ Affects water level in the body Clinical application: Hypersecretion causes Na+ and water retention hypertension
49 Adrenal Cortex Hormones Secreted by zona fasciculata Glucocorticoids: Mostly cortisol Functions: - Increases blood glucose level - Causes vasoconstriction increases BP - Has anti-inflammatory effects Clinical application: Addison s disease: hyposecretion of aldosterone and cortisol hypoglycemia, lower BP, dehydration Cushing s disease: hypersecretion of cortisol redistribution of fat, spindle legs, moon face, pendulous abdomen
50 Adrenal Cortex Hormones Secreted by zona reticularis Androgens: Insignificant in males (main source is testis) Main source in females Clinical application: Hirsuitism: hypersecretion of androgens excessive hair growth
51 Adrenal Medulla Hormones Epinephrine and norepinephrine: Similar structure and function Released in response to sympathetic nerve Involved in Fight or flight response Increase heart rate, BP, breathing rate, blood sugar, metabolism, and muscle contraction
52 Pancreas Located inferiorly and posteriorly to stomach Consists of Head, Body and Tail Endocrine 1% of the tissue produces hormones that diffuse into blood Exocrine 99% of the tissue produces digestive enzymes that are released through a pancreatic duct into small intestine
53 Pancreas Islet of Langerhans/Pancreatic Islets are the endocrine portion of the pancreas. This region is made up of 3 types of cells: Alpha cells secrete glucagon, which stimulates liver cells to release glucose > causes blood glucose to rise. Beta cells secrete insulin, which stimulates glucose uptake by body cells and increased conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver. Delta cells secrete peptide hormone similar to GHIH, which regulates the secretion of insulin and glucagon.
54 Pancreas Insulin and Glucagon Regulation Low blood glucose stimulates release of glucagon High blood glucose stimulates secretion of insulin Diabetes mellitus Type I childhood diabetes - decrease in beta cells decrease in insulin secretion high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) excretion of glucose (glucosuria) and large amounts of water (polyuria) low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) and dehydration excessive thirst. - Treatment insulin shots Type II Non-insulin dependent diabetes - Obese or older adults fewer insulin receptors on target cells lesser response symptoms as above - Treatment diet, exercise, insulin shots Hyperinsulinism - Overdoze of insulin sudden drop in glucose coma and death
55 Role of Insulin in blood Sugar Homeostasis
56 Role of Glucagon in blood Sugar Homeostasis
57 Review time!!! Assess your understanding of the Thyroid and Parathroid hormones by attempting these questions: Describe the location of adrenal gland. Identify the two regions of an adrenal gland? List the three zones of adrenal cortex. What effect will elevated cortisol levels have on blood glucose levels? Which hormone/s are responsible for the fight or flight response of the body? Identify the types of cells in the pancreatic islet and the hormones produced by each. The secretion of which hormone lowers blood glucose concentration. Describe diabetes mellitus. Identify the two types of diabetes mellitus.
58 Ovaries and Testis Primary function: Gamete formation eggs and sperms Secondary function: Hormone production - Ovaries produce estrogen, progesterone, relaxin, inhibin - Testis produce testosterone, inhibin Regulation: Hypothalamus secretes GnRH anterior pituitary secretes gonadotropins (FSH and LH) stimulate ovaries (follicular and oocyte development, hormone production) and testis (sperm and hormone production)
59 Pineal Gland Located posterior to thalamus Has neuroglial cells and secretory cells Secretes hormone, melatonin secretion is regulated by light impulses affects secretion of gonadotropins regulates internal cycle
60 Thymus Large organ in infants but atrophied as adult 2 lobed organ located in mediastinum superior to the heart Primary function maturation of T lymphocytes Secondary function secretion of hormone thymosin to aid maturation process
61 Other Endocrine Glands Stomach: secretes gastrin to regulate secretion of gastric juices Small intestine: secretes secretin, cholecystokinin that stimulate pancreas and gall bladder but inhibit stomach Placenta: secretes several hormones to support pregnancy Kidneys: secrete erythropoietin to stimulate RBC production by red bone marrow
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. The body has two kinds of glands, exocrine
Endocrine System. Chapter 18. Introduction. How Hormones Work. How Hormones Work. The Hypothalamus & Endocrine Regulation
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 18 The endocrine system consists of cells, tissues, & organs that secrete into the blood Hormone an organic substance secreted by a cell that has an effect on the
Chapter 11. Endocrine System
 Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Chapter 11 Endocrine System 1 Introduction A. The endocrine system is made up of the cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones into body fluids. B. Hormones diffuse into the bloodstream to act target
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System. Modified by M. Myers
 Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
Endocrine System Modified by M. Myers 1 The Endocrine System 2 Endocrine Glands The endocrine system is made of glands & tissues that secrete hormones. Hormones are chemicals messengers influencing a.
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.45 - ENDOCRINE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
!! www.clutchprep.com Chemical signals allow cells to communicate with each other Pheromones chemical signals released to the environment to communicate with other organisms Autocrine signaling self-signaling,
Endocrine System. Endocrine vs. Exocrine. Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Endocrine System Bio 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Endocrine vs. Exocrine Endocrine glands secrete their products called hormones into body fluids (the internal environment) Exocrine glands secrete their
Major endocrine glands and their hormones
 Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
Chapter 18 Major endocrine glands and their hormones Endocrine glands Pituitary gland Has two major parts Anterior lobe called the adenohypophysis is epithelial in origin Posterior lobe called the neurohypophysis
The Endocrine System. I. Overview of the Endocrine System. II. Three Families of Hormones. III. Hormone Receptors. IV. Classes of Hormone Receptor
 The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
The Endocrine System I. Overview of the Endocrine System A. Regulates long term metabolic processes B. Releases hormones from endocrine cells 1. Hormones are chemicals 2. Alter metabolism of cells 3. Release
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
The Endocrine System. Endocrine System. 1
 The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System The Endocrine System Second-messenger system of the body Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes Reproduction
The Endocrine System 7/6/2015. Outline. Function of the Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
The Endocrine System Biology 105 Lecture 13 Chapter 10 Outline I. Function of endocrine system II. Hormones and neurotransmitters III. Types of hormones and their actions IV. Endocrine glands/organs and
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1
 Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Unit 9 - The Endocrine System 1 I. Unit 9: The Endocrine System A. The Endocrine System 1. Second-messenger system of the body 2. Uses chemical messengers (hormones) that are released into the blood 3.
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands
 Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Chapter 18: Endocrine Glands I. Functions of the Endocrine System A. List and describe the eight major functions of the endocrine system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Page 1 of 19 C II. Pituitary Gland and
Anatomy and Physiology. The Endocrine System
 Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Anatomy and Physiology The Endocrine System The endocrine system includes anything that secretes hormones directly into body fluids. Endocrine glands include: the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, kidney,
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = coordinate and control the body with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with
Ch45: Endocrine System
 Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Ch45: Endocrine System Endocrine System Homeostasis is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. Function = with hormones to maintain homeostasis Works with nervous system Anatomy Location:
Endocrine System. Chemical Control
 Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Chemical Control Endocrine System - the system that secretes hormones in the body - hormones can last for minutes or for hours - a major gland, once called the master gland, is the pituitary
Endocrine System Hormones. AP Biology
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? u chemical messages from one body part to another u communication needed to coordinate whole body u daily homeostasis & regulation
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells.
 BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
BIOL 2458 A&P II CHAPTER 18 SI 1 1. Both the system and the endocrine system affect all body cells. 2. Affect on target cells by the system is slow. Affect on target cells by the system is fast. INTERCELLULAR
The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
The Endocrine System Like nervous system, endocrine system provides communication and control. Messages are relayed from one cell to another via chemical messengers (hormones). Unlike nervous system which
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45)
 Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
Endocrine System Hormones (Ch. 45) Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large
2/28/18. Endocrine System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Comparing Endocrine and Nervous System Functions
 Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
Introduction Endocrine System Chapter 24 Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions - Nervous system uses impulses and neurotransmitters - Endocrine system uses hormones Many
The Endocrine System Pearson Education, Inc.
 19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
19 The Endocrine System Introduction The nervous system and the endocrine system work together to monitor the body s activities The nervous system: produces short-term, very specific responses The endocrine
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System
 Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Chapter 17 The Endocrine System Endocrine Systems n Endocrine system Hormone mediator molecule released in 1 part of the body but regulates activity of cells in other parts Slower responses, effects last
Human Biochemistry. Hormones
 Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Human Biochemistry Hormones THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The ENDOCRINE SYSTEM = the organ system that regulates internal environment conditions by secreting hormones into
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs
 9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
9.2: The Major Endocrine Organs ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Major Endocrine Organs Below is a list of the major endocrine organs that we will worry about for this class We will look at hormones associated
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Page 1. Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System. Target Cells: Cells specialized to respond to hormones
 Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Chapter 37: Chemical Control of the Animal Body - The Endocrine System Endocrine System: Hormones and the various cells that secrete and receive them Types of Glands: 1) Endocrine Glands: Release substances
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Chapter 20. Endocrine System Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chemical signals coordinate body functions. !
 26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
26.1 Chemical signals coordinate body functions Chapter 20 Endocrine System! Hormones Chemical signals Secreted by endocrine glands Usually carried in the blood Cause specific changes in target cells Secretory
Endocrine System. Chapter 24. Copyright 2012, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
Endocrine System Chapter 24 1 Introduction (p. 638) Endocrine system works with nervous system to coordinate body functions Nervous system uses neural impulses Endocrine system uses hormones 2 Comparing
3. The function of that hormone. In other words, what change does that hormone facilitate.
 Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
Slide 2 The endocrine operates to regulate internal functions. It does so, via the use of hormones, or chemical messengers. Hormones travel in the blood from the site of production to distant target cells
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES The endocrine system is a collection of glands that secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system to be carried toward a distant target organ. These hormones will be
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Endocrine
 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Endocrine Function Help regulate internal functions Use chemical messengers Recall: Endocrine vs. Exocrine glands Nervous System vs Endocrine System Target Specificity Lock n Key action
Endocrine Control. Chapter 35
 Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
Endocrine Control Chapter 35 Impacts, Issues Hormones in Balance Many chemicals we release into the environment (such as the herbicide atrazine) have disruptive hormonal effects 35.1 Introducing the Vertebrate
The Endocrine System
 C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
C H A P T E R 1 2 The Endocrine System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. List the functions of hormones. 2. Classify hormones into their major chemical categories. 3. Describe
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Chapter 12 Endocrine System (export).notebook. February 27, Mar 17 2:59 PM. Mar 17 3:09 PM. Mar 17 3:05 PM. Mar 17 3:03 PM.
 Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Endocrine System Hormones Chemical messengers released directly into the bloodstream Regulate: *May have wide spread effect or only affect certain tissues ** : cells with receptors that respond to specific
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Endocrine System Hormones
 Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
Endocrine System Hormones 2007-2008 Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body homeostasis & regulation metabolism
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
 HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM The human endocrine system consists of ductless glands which releases hormones directly to the bloodstream. Glands are any tissue or organ which secretes chemical compounds useful
Human Anatomy, First Edition. Endocrine System. Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System. McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 20 Lecture Outline: Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System Endocrine system and the nervous system often work together to bring about homeostasis.
Endocrine Notes Mrs. Laux AP Biology I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones
 I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
I. Endocrine System consists of endocrine glands (ductless), cells, tissues secrete hormones regulates metabolism, fluid balance, growth, reproduction A. Hormones 1. chemical signals-cell to cell communication
Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands. Adrenal Glands 4/12/2016. Controlled by both nerves and hormones.
 Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Glands http://www.hawaiilife.com/articles/2012/03/good-news-vacation-rental-owners/ 70 Figure 10.14a gland Glands cortex Mineralocorticoids Gonadocorticoids Glucocorticoids medulla Epinephrine Norepinephrine
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology
 Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
Ch 8: Endocrine Physiology Objectives 1. Review endocrine glands of body. 2. Understand how hypothalamus controls endocrine system & sympathetic epinephrine response. 3. Learn anterior pituitary hormones
CHAPTER 12. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
CHAPTER 12 QUICK CHECK Page 311 1. Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. 2. Nonsteroid hormones are whole proteins, shorter chains of amino acids, or simply versions of single amino
Endocrine System Worksheet
 Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Endocrine System Worksheet Name Section A: Endocrine vs. Nervous Systems The endocrine and nervous systems function to regulate body activities. Since both systems are involved in regulation, how does
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System Nervous and Endocrine Systems Act together to coordinate functions of all body systems Nervous system Nerve impulses/ Neurotransmitters Faster responses, briefer effects,
Page 1. Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following statements about hormones is incorrect? A) They are produced by endocrine glands. B) They are modified amino
Chapter 18, Part 2! Chapter 18, Part 2 Endocrine system! The Endocrine System!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to know for each hormone we cover:! 1. Name
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 16: The Endocrine System Question No. 1 of 10 The endocrine system is made up of a number of organs and glands. Which one of the following is not an organ or
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones!
 Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 18, Part 2! The Endocrine System! Know at the level covered in these notes! SECTION 18-3! The bilobed pituitary gland is an endocrine organ that releases nine peptide hormones! What you need to
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
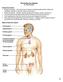 The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
The Endocrine System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Endocrine System Endocrine system the body s second great controlling system which influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Endocrine glands pituitary,
BIOLOGY. CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition. Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor. CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation
 BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
BIOLOGY CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS Fourth Edition Neil A. Campbell Jane B. Reece Lawrence G. Mitchell Martha R. Taylor CHAPTER 26 Chemical Regulation Modules 26.1 26.5 From PowerPoint Lectures for Biology:
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Chapter 26. Hormones and the Endocrine System. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture
4/23/2018. Endocrine System: Overview. Endocrine System: Overview
 Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
Endocrine System: Overview With nervous system, coordinates and integrates activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities via hormones transported in blood Response slower but longer lasting than
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System
 I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
I. Endocrine System & Hormones Figure 1: Human Endocrine System Endocrine System: a) Endocrine glands are ductless since they lack specific vessels for the transport of hormones throughout the body. Instead,
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION
 CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
CHEMICAL COORDINATION & INTEGRATION 1. The hormone responsible for Fight and Flight response is a) Adrenalin** b) Thyroxine c) ADH d) Oxytocin 2. The primary androgen produced by males is. a) Epinephrine
The Endocrine System
 9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
9 The Endocrine System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Endocrine System Second controlling system of the body Nervous system is the fast-control system Uses chemical messengers
Chapter 13 worksheet
 Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
Name: Chapter 13 worksheet The Endocrine System Please label the: hypothalamus pineal gland pituitary gland thyroid gland parathyroid gland thymus heart stomach liver adrenal glands kidneys pancreas small
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System What is the system? 1. Made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical messengers) 2. Regulation of growth, metabolism, sexual development 3. Responses to stress and
The Endocrine System
 The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
The Endocrine System Glands are modified epithelium which produces certain secretions. TYPES OF GLANDS: Exocrine Gland/Duct Gland Secretions of these Glands are carried to the site of action through fine
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine System Functions
 Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Chapter 13 Endocrine System Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System. Simple Hormone Pathways
 Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 45-Hormones and the Endocrine System Simple Hormone s Low ph in duodenum Hormones are released from an endocrine, travel through the bloodstream, and interact with the receptor or a target to cause
Chapter 13 Endocrine System. Endocrine System. Endocrine Glands. Comparison of Nervous System and Endocrine System
 Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
Endocrine glands are ductless Exocrine glands have ducts Chapter 13 Endocrine System 1 Endocrine System composed of cells, tissues and organs that secrete substances into the internal environment Hormones
HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 13 Notes OBJECTIVES HOLE S HA&P CHAPTER THIRTEEN 1. Define hormone. 2. Distinguish between endocrine and exocrine glands. 3. Explain what makes a cell
Homeostasis Through Chemistry. The Endocrine System Topic 6.6
 Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Homeostasis Through Chemistry The Endocrine System Topic 6.6 Comparing NS & ES Animals have two systems of internal communication and regulation The nervous system Response time: Fast, quick Signals: electrical
Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid
 Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Animal Hormones Concept 30.1 Hormones Are Chemical Messengers Endocrine secretion cells secrete substances into the extracellular fluid Exocrine secretion cells secrete substances into a duct or a body
Lab Activity 21. Endocrine System Glucometer. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
Lab Activity 21 Endocrine System Glucometer Portland Community College BI 232 2 Hormone Functions ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) Regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland TSH (thyroid
The Endocrine System Part II
 The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
The Endocrine System Part II Thyroid gland Parathyroid glands Regulation of blood Calcium level Adrenal gland Exocrine part of pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) Thyroid Gland Located in the anterior neck
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Robert Wadlow and his father
 Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Robert Wadlow and his father 1 Robert Wadlow Wadlow reached 8 ft 11.1 in (2.72 m) in height and weighed 485 lb (220 kg) at his death at age 22. Born in Illinois. His great size and his continued growth
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System and Hormone Activity Overview Coordinates and directs the activity of cells. Interacts with the nervous system Uses chemical messengers called hormones released by organs
Endocrine System. A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine. Endocrine: Exocrine:
 Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
Endocrine System Endocrine System A gland is any organ that produces a secretion 2 types: endocrine and exocrine Endocrine: Organized groups of tissue that use materials from the blood to make hormones
The Endocrine System/Hormones
 The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
The Endocrine System/Hormones Controls many body functions exerts control by releasing special chemical substances into the blood called hormones Hormones affect other endocrine glands or body systems
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 16 - Endocrine System Lecture 16 1 Lecture Overview The Adrenal Glands The Pancreas Other Endocrine Tissues Stress and its effects
Hormones. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
 Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System Hormones Hormones are chemical substances created by the body that control numerous body functions. They actually act as "messengers" to coordinate functions of various body parts. Follicle
Endocrine System. Part 2
 Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Endocrine System Part 2 Thyroid Gland Saddle bag shaped gland Largest endocrine gland in the body 3 hormones Throxin Triiodothyronine Calcitonin Thyroid hormone Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland
Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes
 Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
Operation of the Endocrine System Biology 3201Unit 1 Endocrine System Notes What is the Endocrine System? The endocrine system is comprised of the hormone producing glands and tissues of the body. Hypothalamus
8/26/13. Announcements
 Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
Announcements THM questions will start for points on Wednesday. Make sure you are registered correctly! Problems registering for BioPortal? Make sure you are using the link from the syllabus or FAQ. 30
The Endocrine System PART B
 9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
9 The Endocrine System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Thyroid Gland Found
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11
 The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
The Endocrine System - Chapter 11 Around age 12, as they enter puberty, boys and girls start to develop striking differences in physical appearance and behavior. Chemical messages originating from the
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Understand the functions and disorders of the endocrine system
 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the 4.04 Understand the Functions and Disorders of the What are the functions of the endocrine system? What are some disorders of the endocrine system? How
Endocrine Glands: Hormone-secreting organs are called endocrine glands
 University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
University of Jordan Department of Physiology and Biochemistry Nursing students, Academic year 2017/2018. ******************************************************************* Ref: Principles of Anatomy
The endocrine system -- a brief overview.
 The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction - the endocrine system is an integration system that influences the metabolic activities of cells. - acts via hormones, chemical messengers produced
Summary The Endocrine System The Reproductive System Human Endocrine Glands. Endocrine and Reproductive Systems.
 Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Name Class Date Chapter 39 Summary Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 39 1 The Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands that release secretions
Endocrine system. Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones
 Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Endocrine system Coordination & regulation Glands Hormones Endocrine system structures Anatomy - Dispersed system of glands that communicate with each other & all body cells via hormones. Endocrine glands:
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
11/26/2007. The Endocrine System. The Endocrine System. NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEM. Lecture Series
 The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
The Endocrine System Lecture Series Principles of Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11e 1 The Endocrine System The nervous and endocrine systems act as a coordinated interlocking supersystem, the neuroendocrine
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System
 Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
Unit Eleven - The Endocrine System I. Introduction A. Overview: the endocrine system and nervous system work to control homeostasis within the body. The endocrine system operates at a much pace but the
/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1. Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
