Teacher Scheme of Work Sarah Outen
|
|
|
- Kristina Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Teacher Scheme of Work Sarah Outen Lesson 1 How can we keep healthy? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What is a healthy lifestyle? Can I think of different things that make my lifestyle healthy or unhealthy? What are the different food groups we need to eat to live healthily? What is a healthy lifestyle? Discuss with pupils. See if pupils can identify healthy and unhealthy behaviour thoughtshower to see what activities they can think of. List a few on board. Can pupils identify what types of food they need to eat to maintain a healthy lifestyle? Starter activity (pair work) compare pictures of healthy and unhealthy lifestyles Video identify healthy activities, identify food types In pairs, put food into different groups Try and identify how much of certain foods we need each day food pyramid Activity 1 What is a healthy lifestyle? Activity 2 What makes a healthy diet? Staying Healthy video Healthy food video Expedition Food photo gallery Plenary: Discussion about healthy living
3 Lesson 2 How does food help the body? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What does each food group provide the body with? What different nutrients are needed for different bodily functions? What vitamins and minerals does the body need to function properly? Starter: Recap from last lesson thought-shower food groups and examples of food from each group. Discuss idea that each food group helps the body to do certain things. Find out what pupils know about vitamins and minerals. Discuss how they are essential for body to function and can be found in different foods Provide ideas for thought-shower Watch video and fill in table to show what types of food belong to different groups, and what each group helps the body to do. Identify what nutrients are needed for heavy exercise. Identify which foods contain vitamins and the important jobs each vitamin does Activity 3 How does food help the body? Worksheet 1 Vitamins and minerals Homework Sheet 1 Food labels Plenary: discuss food myths Lesson 3 How does the body move? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources How does the body move? What do you know about bones? Can you label the bones on a human skeleton? How do joints and muscles work? What do you know about bones? Discuss with pupils what they know about bones and any names they may know thought-shower Help pupils to understand concept of joints and muscles, where bones meet and how this helps movement, and muscles contracting and relaxing Starter activity (pair work) find out what pupils know about bones Label human skeleton Questions about joints think about which joints we use to do different movements Gap fill about muscles and how they work Plenary: The Sarah Challenge Activity 4 How does the body move? Activity 5 How do muscles work? Joints video Use the BBC Learning Zone video ( skeletons/2302.html)
4 Lesson 4 How do your heart and lungs work? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources How does the heart work? Why are lungs so important? What connects the heart to the body? How can we look after our heart and lungs? What do I know about the heart? Thought-shower to find out what pupils know about hearts Discuss idea that heart works as a pump which pumps blood to different parts of body including lungs, and that blood travels through arteries and veins. Starter activity (pair work) find out what pupils know about the heart Watch the video about how heart: circle correct word gap fill True False (pair work) circulatory system Identify things that we can do to look after heart and lungs and compare these with Sarah Activity 6 Why are your heart and lungs important? Activity 7 How can we look after our bodies? Use the Mayo Clinic video ( Use the About Kids Health video ( pages/heart.aspx) Lesson 5 What happens when we exercise? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What happens to our hearts after we do exercise? How do you feel after exercise? How can you measure your heart rate? Why do we exercise? Thoughtshower to find out what are energetic activities and what are not, why we exercise and what effect exercise has on our bodies Elicit how you might measure heart beat pulse Monitor practical activity modelling how to take pulse Provide ideas for thought shower Practical test your pulse rate, record pulse rates after exercise and then plot findings as graph Plenary compare findings with rest of class and interpret findings Extension use graphs to represent the data Activity 8 What happens when we exercise? Activity 9 How do you measure your pulse?
5 Lesson 6 How can we classify living things? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources Why do we classify plants and animals? What are the ways of classifying plants and animals? How do we use a key to classify animals? How are animals and plants different from each other? Thought-shower to think of different animals we find in a zoo and how we can classify different animals size, shape, fur, legs etc. Discuss why it may be a good idea to classify animals Model key questions to start classification key Use the photo sheet and ask pupils to group all the living things there is no right answer Answer the follow-up questions Think about the different characteristics that living things share Use the key to classify the animals and plants on the photo sheet Activity 10 How can we group living things? Activity 11 How do scientists group living things? Photo Sheet 1 How can we group living things? Work Sheet 2 A key for living things Lesson 7 How can we identify organisms? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources How can I design my own classification key? What questions can I use to design my key? Recap discussion about classification keys and how you use them Feedback on starter Participate in recap discussion about classification keys. Starter use key to put trees into correct boxes (pair work) Activity 12 How can we identify organisms? Which keys are useful/not useful for classifying animals? Explain that pupils are going to start on tree and invertebrate keys Create my own key for invertebrates Feedback on keys that have been created Plenary evaluate own key and class discussion Extension: pupils can develop their own keys to be used in the school grounds
6 Lesson 8 What are the connections between living things and their environments? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What is an environment? What is an environment? Provide ideas for thought-shower Activity 13 How have living things adapted? What are the different types of environment? What are the features of different environments? What animals belong to different environments? How do animals and plants adapt to different environments? Thought-shower about what an environment is and what different types of environments exist write list on board Discuss the idea that different environments have their own features and that plants and animals have developed certain features to live in these Identify different environments that Sarah has travelled through (pair work) Match different environments with their features Identify animals and plants that Sarah has seen on her travels See how different animals and plants have adapted to their environments Homework Sheet 2 Living things and environments Use the BBC Learning Zone video ( clips/how-are-camels-adapted-to-live-in-thedesert/6232.html) Lesson 9 How do plants and animals survive? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What do living things need to survive? How do plants and animals rely on each other to survive? What do all living things need to survive? Recap on past knowledge Provide ideas for thought-shower Starter write down things needed for plants and animals to survive Activity 14 How do plants and animals survive? What is a food chain? What is a food web? Discuss the idea that different plants and animals play different roles in their environments and depend on each other for food Ensure pupils become familiar with names for different roles: carnivore, herbivore etc. Complete gap fill and questions about different roles of animals and plants and names for them Decide which roles different animals play Draw 3 food chains and answer questions
7 Lesson 10 How our environments and living things threatened? Enquiry Questions Teacher Input Activities Resources What happens to animals when food chains break down? Why do we need to protect our environment? How do environmental changes affect the animals that live in them? How can we protect our environment? Recap food webs and the idea that plants and animals depend on each other for food Discuss what might happen if certain animals in food webs die and how this might affect others Introduce the idea that environments are changing and human activity is having a negative impact Discuss the idea that we need to look after our environment for future survival of all living things Participate in recap discussion about food webs Starter fill in food web from animals in box Answer questions in pairs about what might happen if certain animals die out True or false exercise about how environments have changed Identify reasons as to why certain organisms are endangered/extinct Plenary discuss need to protect environ Activity 15 What happens when food chains break? Homework Sheet 3 Endangered animals in Britain
8 activity 1 what is a healthy lifestyle? Follow Sarah on her amazing journey around the world and find out what it takes to lead a healthy lifestyle. starter Compare the images and fill in the table listing what is healthy behaviour and what is unhealthy? Unhealthy Healthy Q1 Meet Sarah... Can you identify from the video the things that Sarah does to lead a healthy lifestyle? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET ONE I PAGE 1
9 activity 2 what makes a healthy diet? Find out what Sarah eats on her expedition and learn how to make sure you eat a healthy diet. starter What types of food do we need to stay healthy? Watch the video of Sarah talking about what she eats each day. Can you list what she eats and drinks? Q1 What are the different types of food that we eat? From the list above can you arrange the foods into different types? Look at the photos to remind you. Bread & cereals Meat & fish Milk & cheese Sugary & fatty foods Fruit Vegetables SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TWO I PAGE 1
10 Q2 How much of the different types of food do we need each day? Fill in the food pyramid thinking about the different foods we need to eat. The bigger the box, the more we need to eat of that type of food. Word choices Bread and cereals Milk and cheese Meat and fish Fruit Vegetables Sugary and fatty foods Q3 Discuss in pairs and then make a short list of all the things that you eat. Are they healthy or unhealthy? Healthy Unhealthy SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TWO I PAGE 2
11 activity 3 how does food help the body? In the last lesson we learned how there are different kinds of food and about a balanced diet. This lesson looks at grouping different foods based on what they do for our bodies. starter Why do we need to eat food? Try to come up with as many reasons as you can. Why eat?! info Introducing the different food groups These different food groups are based on the different chemicals they are made from. The different chemicals help our bodies in different ways. Carbohydrate Fat Protein Fibre Carbohydrates come mainly from foods like bread, rice and pasta. They can also be found in vegetables, fruit and sugary foods. Fats come from foods like butter, cheese and nuts, as well as different kinds of oils. Proteins come from meat and fish as well as cheese, eggs and lentils. Fibre comes from fruit and vegetables, as well as granary bread and brown rice. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET THREE I PAGE 1
12 Q1 Can you complete the first column of this table? Then we are going to see a video from Sarah about how these different food groups help us. Food Group Example of food How they help the body Carbohydrate Fat Protein Sausage Fibre Q2 Watch the video clip again. Which two food groups do you think Sarah needs to eat most of? Why do think this is? 1. I think that Sarah needs to eat a lot of, because 2. Q3 Vitamins and Minerals As well as the four main food groups, there are two other important groups - vitamins and minerals. Can you sort the different lists of vitamins and minerals, their jobs and where you might find them? 1. Which vitamin can you find in fruits like oranges and lemons? 2. Which mineral is important to strengthen bones? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET THREE I PAGE 2
13 Work Sheet 1 vitamins and minerals Cut the lists of vitamins and minerals, their functions, and where you would find them into strips (along the dotted lines). Hand out a set to groups and see if they can match them up. Vitamin A Vitamin B Vitamin C Helps maintain eyesight Helps body make protein Heals skin and prevents colds Carrots Green leafy vegetables Oranges, lemons, blackcurrants Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin F Strengthen bones Strengthen cells Healthy blood Milk, sunlight Vegetables and oils Green leafy vegetables Iron Calcium Magnesium Good for blood Good for bones Good for nervous system Meat and baked beans Milk and cheese Wheat and barley SARAH OUTEN WORK SHEET ONE I PAGE 1
14 Homework SHEET 1 food labels Q1 What are the labels on food supposed to tell us? Why is it important to read the labels on food? Q2 What are calories? Q3 How many calories are we meant to eat in a day? Is it different for adults and children? If it is, why do you think this might be? Q4 During the expedition, Sarah eats about 6,000 calories a day. Is this more than the average adult woman needs to eat? Why might she need to eat this much? SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET ONE I PAGE 1
15 Q5 Find five different food items at home with food labels and find out how many calories they contain and also the amount of carbohydrates in them Name of food Calories per 100g Carbohydrates per 100g Q6 Is there anything that you found surprising? Remember to give details and reasons for your answer. SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET ONE I PAGE 2
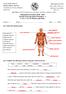
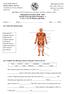
16 activity 4 how does the body move? In this lesson, it s all about movement and as you can imagine Sarah needs to move a lot on her journey. starter What do you know about bones? In pairs, try and answer the questions below. What is the name for all the bones in your body? What does your skull do? Are your bones bendy or straight? Are bones rough or smooth? Where do you think the longest bone in your body is? Can you draw a picture of what a bone looks like? Q1 Watch the BBC clip on bones. Can you link the names of the bones with the right place on this skeleton? pelvis knee cap arm bones collar bone thigh bone ribs backbone hand bones skull foot bones SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FOUR I PAGE 1
17 Q2 Watch the video of Sarah talking about some very important parts of her body called joints. Joints are where your bones meet. What would our body be like if we didn t have joints? Which joint is shown in the picture? Where would you find it? Q3 In pairs discuss which joints Sarah uses when doing different movements and tick the correct joints in the table below. Hint: try acting out the movement first with your partner Joint Talk Walk Run Cycle Row Eat Ankle Knee Hip Jaw Wrist Shoulder Elbow SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FOUR I PAGE 2
18 activity 5 how do muscles work? In the previous activity you learned about bones and joints, now we are going to look at muscles and how they work. starter Now that we have seen how bones help Sarah move we need to look at her muscles. Check these facts out in pairs and circle the correct answer. There are over 150 / 450 / 650 muscles in the human body. They make up nearly 25% / 40% / 80% of your body weight. In your face there are over 10 / 50 / 90 different muscles to help you smile, frown, show that you are cross, surprised or sad. Eye muscles are the busiest muscles in the body. Scientists estimate they move more than 1,000 / 10,000 / 100,000 times a day. Q1 How do muscles function? Clench your fist and bend your arms like you are doing weightlifting. Notice how the muscles in your arm change, and now try to complete the sentences below. Humans and animals have skeletons with attached. Each muscle is attached to a different set of. All muscles work in. While one muscle tightens up and, the other muscles. When muscles contract they get and and when they relax they get and. Word choices fatter relax bones thinner contracts longer muscles shorter pairs SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FIVE I PAGE 1
19 Q3 Some muscles are called voluntary muscles. This means that they only move when you want them to. Other muscles move automatically without you thinking. These are called involuntary muscles. Decide if the movements below are voluntary or involuntary. 1. Raising your arm 2. Bending your knee 3. Your heart beating 4. Clapping your hands 5. Blinking your eyes 6. Breathing in and out Q4 So, you can see that moving maybe isn t as simple as you thought it was. After travelling all those miles, what do you think happens to Sarah s muscles? activity To see what happens to our muscles after exercise, we are going to shorten all the different activities that Sarah is doing in the 877 days of her expedition into just 5 minutes. Step 1 As a class think of a different action for kayaking, cycling, resting and rowing. Step 2 Now do each action for the following amounts of time... Action Time (seconds) Kayak 2 Cycle 62 Kayak 7 Rest 34 Row 68 Cycle 3 You would only have to do this another 105,240 times to complete the same amount of exercise as Sarah will during the entire expedition. Phew!! SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FIVE I PAGE 2
20 activity 6 Why are your heart and lungs important? Today we are going to find out about other key body parts and their functions. Without them, it would be impossible to do anything at all. starter Let s see what you know already. In pairs discuss the questions and then write down your answers. How big is your heart? Why does your heart beat? On the picture draw where you think the heart is. Q1 What does your heart do? Watch the video and see if you can select the correct answers below. The heart is a bone / muscle. The heart is protected by the ribs / skull and is located slightly to the left / right of the centre of your chest. The heart acts like a pump / cleaner pushing blood filled with carbon dioxide / oxygen around your body. When the heart pumps, it beats. We measure the heartbeat using temperature / pulse. You can check your heartbeat easily at your neck or wrist. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET SIX I PAGE 1
21 Q2 Watch the video a second time to learn more about how the heart works. Your heart is divided into two parts. The right side receives blood oxygen from your and pumps it to your. The left side receives blood oxygen from the and pumps it to your. This pumping happens because the in the walls of your heart regularly. This movement of blood around your body is called. Word choices without with lungs body circulation muscles contract body lungs activity How much oxygen do you get when you breathe? The heart is only useful if it receives oxygen from the air. The way we do this is by breathing air into our lungs. Do you know how big your lungs are? Take a big breath in and then try blowing up a balloon using just this one breath. All the air that was in your lungs is now in the balloon. Now you have a rough idea about how big they are. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET SIX I PAGE 2
22 Q3 You are now going to see an animation about how the heart and lungs work together to take oxygen around the body and take carbon dioxide away from muscles. While you are watching the animation select True or False for the statements below. Blood cells are like little delivery trucks for your body. True False The circulatory system is made up of your heart and blood vessels. True False Your heart stops when you go to sleep. True False There is only one red blood cell in your entire body. True False Blood cells pick up oxygen from your lungs. True False Blood cells only go to your feet. True False Blood with oxygen in it is blue. True False Q4 Here s a diagram of the circulatory system in your body. It s quite hard to see from the outside! Roll up your sleeves and turn your left hand over so you can see your wrist and lower arm. Clench your hand then open it again. Repeat this 5 to 10 times. Arteries are the blood vessels that take blood with oxygen from the lungs. This blood is red. Veins are blood vessels that take blood without oxygen from the body to the lungs. Now see if you can answer the questions below. Which blood vessels begin to appear on your forearm and wrist? What colour are they and why? Can you explain why you cannot see your arteries? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET SIX I PAGE 3
23 starter activity 7 how can we look after our bodies? As you learned, your heart, lungs and blood vessels are vital for your circulatory system to work properly. Let s see how we can keep them healthy. Can you think of thing that healthy and unhealthy for hearts and lungs. Try to remember some of things that Sarah does to stay healthy. Healthy for heart and lungs Unhealthy for heart and lungs Q1 What do you do to look after your heart and lungs? info By doing exercise regularly, our hearts get fitter and bigger and our lungs get stronger and increase in size. We also feel healthier. Did you know that an adult has nearly 60,000 miles of blood vessels in their body and over 9 pints of blood? That s a lot to keep healthy! SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET SEVEN I PAGE 1
24 activity 8 what happens when we exercise? Today we are going to investigate what happens to our hearts after we do exercise. Sarah s doing quite a lot of exercise at the moment and we will see how this affects her. starter Before we begin, have a discussion in pairs and write down as many ideas as you can. Why exercise? Q1 Can you think of activities that just need a little energy and activities that need a lot of energy? A little energy A lot of energy SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET EIGHT I PAGE 1
25 Q2 How do you feel when you exercise? Q3 What happens to your body during and after exercise? Q4 Think about what happens when you exercise and then look below to see if you can select the correct word from each sentence. When you exercise parts of your body need a decreased / normal / increased blood supply (more carbon dioxide / oxygen / nitrogen and nutrients) so your heart beats at the same pace / faster / slower. You also breathe slower / faster / less deeply - to get more oxygen into your kidneys / stomach / lungs, and to get rid of the nitrogen / carbon dioxide / oxygen. You also get cold / hot / shivery and sometimes flushed (or red faced). SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET EIGHT I PAGE 2
26 Garden Town Desert SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET TWO I PAGE 2
27 activity 9 how do you measure your pulse? As we have seen, Sarah has to do lots of exercise every day, as she makes her way across the world. starter This lesson is an investigation and before we start we are going to look at some possible questions: What happens to your pulse rate when you exercise? How can you raise your pulse rate? How can you drop your pulse rate? Q1 Extension: Can you think of any other possible investigation questions? activity The first thing we are going to do is to learn how to measure our pulse. The easiest place to feel your pulse is at your wrist. 1. Place two fingers on your wrist and move them gently until you can feel your pulse. 2. First of all count how many heartbeats you can feel in one minute. Beats per minute 3. How many was it? Was it more or less than the person sitting next to you? 4. Now count how many heartbeats you can feel in 10 seconds. 5. Now you need to do some maths to work out how many beats per minute this would be. Beats per 10 secs x 6 = Beats per minute SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET NINE I PAGE 1
28 Q2 Now we re going to gather some data. You are going to try some of the activities Sarah does to get your pulse rate moving. You will need to think of an action you can do for each activity. Do each activity for two minutes. In the table below fill in the beats per minute for each activity at three stages. Before the activity Straight afterwards 2 minutes after Kayak Cycle Row Q3 In the table below, you can see Sarah s pulse for each of the activities. Before the activity Straight afterwards 2 minutes after Kayak Cycle Row Compare your results with Sarah s. What differences do you notice? Why might Sarah s pulse rate be different to yours? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET NINE I PAGE 2
29 activity 10 How can we group living things? On her journey, Sarah sees a lot of different living things from forests in Europe to camels in China and a wolverine in Russia. In this lesson we learn how to group living things. starter The scientific word for grouping living things is classification. Can you you classify the living things on the photo sheet by putting them in six different groups? Write the names in the boxes below. Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 Group 5 Group 6 Q1 Why did you choose to classify or group the living things in this way? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TEN I PAGE 1
30 Q2 Can you think of all the different ways to classify different living things? size colour Ways to classify Q3 A useful way of classifying living things is by asking ourselves key questions. In pairs decide which of the living things on the photo sheet have webbed feet. Q4 Now decide which of the living things on the photo sheet lay eggs. There may be more than you think. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TEN I PAGE 2
31 activity 11 How do scientists group living things? Organism is the scientific word for living things. Scientists develop key questions to classify and identify different organisms. Starter A key is a series of key questions that scientists use to sort organisms into different groups. Keys use the fact that different organisms share characteristics. Can you remember any characteristics or ways to classify you came up with last lesson? Q1 What characteristics do eagles and ducks share? Q2 What characteristics do dogs and sheep share? Q3 What characteristics do oak trees and tulips share? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET ELEVEN I PAGE 1
32 Q4 For each organism on the photo sheet, decide how it should be classified and write its name in the correct box below. Flowering plant Non-flowering plant Mollusc Insect Arachnid Mammal Bird Fish Reptile Amphibian Q5 Can you complete the following sentences using the information from the key? A snail is a mollusc because A dog is a mammal because An oak tree is a flowering plant because A snake is a reptile because SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET ELEVEN I PAGE 2
33 Photo sheet 1 how can we group living things? platypus dog snail oak bee shark snake eagle chicken duck sheep tulip spider seaweed frog SARAH OUTEN PHOTO SHEET ONE I PAGE 1
34 Work Sheet 2 a key for living things SARAH OUTEN WORK SHEET ONE I PAGE 1
35 activity 12 how can we identify organisms? In the last lessons, we looked at classifying or grouping different living things. Now we are going to see how keys might be able to identify different organisms. Starter As she was cycling through Russia, Sarah posted this tweet on her twitter page. What questions could you ask Sarah to help you identify this animal? Q1 Use the key below to identify these different trees from their leaves. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TWELVE I PAGE 1
36 Q2 Your challenge is now to make your own key. In groups decide on the key questions that will help anyone identify the organisms in the photos below. Remember that your key questions need to be about characteristics and have yes or no answers. Hint: you may need to practise on some spare paper first. Slug Ant Snail Bee Woodlouse Spider EXTENSION So you reckon you can make a key. Why don t you have fun at home or in the school grounds and make a key to identify the creepycrawlies, flowers or trees? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET TWELVE I PAGE 2
37 activity 13 how have living things adapted? Sarah has travelled through many different environments during her journey. In this lesson, we will investigate how living things have adapted. Starter There are many different environments across our planet and Sarah has travelled through a lot of them. Watch the video and make a list of the environments that she has passed through. Environments that Sarah has passed through Environments that Sarah has not passed through Word choices Forest Polar Ocean Desert Swamp Lake Rainforest Mountains Grassland Q1 Can you match these environments with some of their features? Cold, salt water, many predators Very cold, snow and ice and no shelter Very damp and hot and many plants Lots of trees and can be cold in winter Little shelter and lots of grass to eat Damp and marshy with many different plants Very dry and hot in the day and cold at night Water is calm and sheltered SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET THIRTEEN I PAGE 1
38 info Introducing adaptation All living things have to be suited to their environment if they are to survive. Fish have streamlined bodies, fins and specially shaped tails to help them move quickly and easily through the water. Squirrels have sharp, strong claws for gripping tree trunks and strong teeth for eating nuts. Q2 When Sarah was travelling through Kazakhstan and China, she saw a lot of camels. Sarah found cycling through the desert very tough, but camels have adapted well to live in this environment. Watch the video to find out why camels are better at living in the desert than Sarah. How many adaptations can you remember? Make a note of them below. info Did you know that a camel with one hump is called a dromedary and a camel with two humps is called a Bactrian camel. Sarah saw Bactrian camels when she was in Kazakhstan and China. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET THIRTEEN I PAGE 2
39 Q1 Homework SHEET 2 LIVING THINGS AND environments Have a look at these five environments in the table below. Write the names of the plants and animals in the correct columns. Ocean Woodland Garden Town Desert Word choices Seaweed Snail Woodlouse Camel Tulip Squirrel Butterfly Dandelion Eagle Deer Oak tree Mouse Pigeon Shark Crab Q2 Choose one plant or animal from each column and find out how it is adapted to its environment Ocean Woodland SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET TWO I PAGE 1
40 Garden Town Desert SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET TWO I PAGE 2
41 activity 14 how do animals and plants survive? Last lesson we looked at how different animals and plants have adapted to their environments. In this lesson we are going to see how different plants and animals, including humans, rely on each other to survive starter Can you think of the different things that plants and animals need to survive? Plants Animals info Plants and animals are called different things depending on what they eat to survive. Carnivores are animals and plants that eat animals. Herbivores are animals that eat plants. Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. Q1 Complete the sentences using the words below. Plants are because they make their own food using. are animals that other animals. Animals that are and by other animals are called. Word choices prey predators sunlight moonlight eat producers plants animals farmed hunted eaten supper SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FOURTEEN I PAGE 1
42 Q2 In pairs decide whether the following animals are carnivores, herbivores or omnivores and whether they are predators, prey or both. Fill in the table by choosing the correct term and add characteristics that each animal has. Example: Lion - Carnivore - Predator - Characteristics: claws, sharp teeth, strong carnivore herbivore omnivore predator prey carnivore herbivore omnivore predator prey carnivore herbivore omnivore predator prey both both both Characteristics Characteristics Characteristics info About food chains Living things in their environments are dependent on each other for food. Food chains show which animals eat other animals or plants. A food chain starts with what gets eaten and the arrows point towards the animal that is doing the eating. Food chains only go in one direction. SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FOURTEEN I PAGE 2
43 Q3 Can you draw three more food chains using these plants and animals? Write the names of the organisms in the boxes below. Rabbit Eagle Plant Fox Slug Bird Berries Mouse Q4 Can you answer the questions below about food chains? Why do you think that the arrows only point in one direction? What do you think being at the end of the food chain means? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FOURTEEN I PAGE 3
44 activity 15 what happens when food chains break? Last lesson we looked at how different animals and plants adapted to their environments. In this lesson we are going to see how different plants and animals including humans rely on each other to survive starter In the last lesson we looked at simple food chains, but nature is more complicated. Below you can see a food web showing the more complicated links between animals and plants. Can you complete it? Word choices Blackbird Mouse Slug Fox Q1 Now think about these questions. What would happen to the eagle population if all the rabbits were killed by disease? What would happen to the blackbird population if all the slugs were killed by farmers and gardeners? How would this affect the rest of the food web? SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FIFTEEN I PAGE 1
45 Q2 Fill in the missing words to make the sentences make sense. If one part of a food chain dies out or is greatly, the consumers have to find alternative, move away, or. This then affects more. Word choices consumers food starve increased kill reduced Q2 Now circle the correct words in the sentences below. The number of people in the world is rapidly shrinking / growing / staying the same. But this is not the case for all cars / mountains / animals. In some cases, there are only a few of certain animals left in the wild / zoo / circus. These animals are plentiful / endangered / lost. If they die out completely, they will become extinct / unhappy / reduced. Q3 Here are some pictures of the endangered animals in the countries that Sarah is travelling through. In pairs, can you think why they might be threatened? Panda Wild camel Tuna Grey wolf SARAH OUTEN ACTIVITY SHEET FIFTEEN I PAGE 2
46 Q1 Homework SHEET 3 ENDANGERED ANIMALS IN BRITAIN Environmental damage and threats to plants and animals also happen closer to home. For your homework research find the names of three animals in Britain that are endangered. Then describe what the problems are and what we can do to protect them. Name of animal: Why is this animal threatened? What can be done to protect it? Name of animal: Why is this animal threatened? What can be done to protect it? Name of animal: Why is this animal threatened? What can be done to protect it? SARAH OUTEN HOMEWORK SHEET THREE I PAGE 1
47
activity 3 how does food help the body?
 activity 3 how does food help the body? In the last lesson we learned how there are different kinds of food and about a balanced diet. This lesson looks at grouping different foods based on what they do
activity 3 how does food help the body? In the last lesson we learned how there are different kinds of food and about a balanced diet. This lesson looks at grouping different foods based on what they do
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
GRADE 2 Human Body 2012 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems and explain their connection to personal health. State Standard Descriptive Statement function of the cardiovascular system.
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
GRADE 2 Human Body Revised 6/16 2.1 The student will identify the major body systems, healthy food and beverage choices, emotions, and social skills, and explain how each is connected to personal health.
ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES
 ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS (Lesson 1:1) Living things need Micro habitats Macro habitats Animals Difference? Plants Name: Class: Date: COMPARING ANIMALS
ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS: KS2 STUDENT RESOURCES ANIMALS AND THEIR HABITATS (Lesson 1:1) Living things need Micro habitats Macro habitats Animals Difference? Plants Name: Class: Date: COMPARING ANIMALS
Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy
 Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy A Healthy Diet and Our Body If our bodies are human machines food is our fuel. How well we eat, affects how well our bodies work, and how long we live. It is especially
Healthy Eating & Staying Healthy A Healthy Diet and Our Body If our bodies are human machines food is our fuel. How well we eat, affects how well our bodies work, and how long we live. It is especially
Matter and Energy Transfer
 Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants back.
Imagine for a moment that you stay after school one day to clean up the classroom. While cleaning, you move some plants away from the sunny windows. A week later, you remember to move the plants back.
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES
 Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES General points about this talk: This is a fun interactive talk which includes the opportunity to touch some reptiles. This talk generally lasts 30 minutes
Special Educational Needs (SEN) HANDS-ON REPTILES General points about this talk: This is a fun interactive talk which includes the opportunity to touch some reptiles. This talk generally lasts 30 minutes
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Name Surname..Date..Class. Science Test. 1. Take a look at this chart. These people answered a survey on their lifestyle. (3)
 Name Surname..Date..Class. Science Test Marks: 50/50 1. Take a look at this chart. These people answered a survey on their lifestyle. (3) Fast food restaurant HEALTHY DIET EXERCISE John Yes No No Emma
Name Surname..Date..Class. Science Test Marks: 50/50 1. Take a look at this chart. These people answered a survey on their lifestyle. (3) Fast food restaurant HEALTHY DIET EXERCISE John Yes No No Emma
East Park Academy Science Year 3: Animals including humans Overview of the Learning: In this unit children will
 Science Year 3: Animals including humans Overview of the Learning: In this unit children will identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot
Science Year 3: Animals including humans Overview of the Learning: In this unit children will identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot
GRADE 4 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i
 GRADE 4 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i TEACHER SCRIPT: Keep your eyes on me and I will tell you the directions for this survey. We are going to read each question and all of the possible
GRADE 4 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i TEACHER SCRIPT: Keep your eyes on me and I will tell you the directions for this survey. We are going to read each question and all of the possible
A HEALTHY DIET. Healthy food is necessary for your body. We need to eat the right food:
 1 Name: _ A HEALTHY DIET Your body needs a good diet to stay healthy. Many people eat too much or eat unhealthy food. Fast food is an example of a kind of unhealthy food. Healthy food is necessary for
1 Name: _ A HEALTHY DIET Your body needs a good diet to stay healthy. Many people eat too much or eat unhealthy food. Fast food is an example of a kind of unhealthy food. Healthy food is necessary for
Interactive Notebooks
 Grade 4 Interactive Notebooks CD-104908 Interactive Notebooks: Science Interactive notebooks are a fun new way to teach and reinforce effective note taking for students of all ages. Students are able to
Grade 4 Interactive Notebooks CD-104908 Interactive Notebooks: Science Interactive notebooks are a fun new way to teach and reinforce effective note taking for students of all ages. Students are able to
PENTOUCH TRANSLATION & EDUCATION Utility Vehicles States of Matter
 States of Matter A. For many years, people did not know what matter was made of. The ancient Greeks tried to figure out what would happen if a rock were broken into smaller and smaller pieces. B. They
States of Matter A. For many years, people did not know what matter was made of. The ancient Greeks tried to figure out what would happen if a rock were broken into smaller and smaller pieces. B. They
GRADE 5 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i
 GRADE 5 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i TEACHER SCRIPT: Keep your eyes on me and I will tell you the directions for this survey. We are going to read each question and all of the possible
GRADE 5 SURVEY PART 1: School Garden Knowledge Questions i TEACHER SCRIPT: Keep your eyes on me and I will tell you the directions for this survey. We are going to read each question and all of the possible
Warm-Up 92. The Importance of Good Health. A eating good food B exercising. C playing video games D getting good sleep
 Name: Warm-Up 92 The Importance of Good Health Your health is very important. It is what lets you play and think and sleep. You feel great when your body is healthy. What can you do to stay healthy? There
Name: Warm-Up 92 The Importance of Good Health Your health is very important. It is what lets you play and think and sleep. You feel great when your body is healthy. What can you do to stay healthy? There
EatHealthy. SUBJECTS: Health Science English Language Arts listening, speaking, and writing Math. Healthy
 Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
Bee you eat, think about what goes on your plate or in your cup or bowl. steps to build a healthy plate: Make half your plate Switch to skim or 1% milk Make at least half your Vary your protein food choices
Lesson #5 Get the Beat
 PROPS: 5-lbs. fat model 5-lbs. muscle model MATERIALS DISPOSABLES: Sticky notes or scrap paper LESSON PREP Write vocabulary words on board Review heart diagram (see end of lesson) Options to track heart
PROPS: 5-lbs. fat model 5-lbs. muscle model MATERIALS DISPOSABLES: Sticky notes or scrap paper LESSON PREP Write vocabulary words on board Review heart diagram (see end of lesson) Options to track heart
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
To meet the expectations of this unit, students should already be able to describe the skeleton s role in movement, support and protection.
 GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
GRADE 9: Life science 4 Movement UNIT 9L.4 4 hours About this unit This unit is the fourth of six units on life science for Grade 9. This unit is designed to guide your planning and teaching of lessons
HEALTHY BLOOD PARENT AND CAREGIVER RESOURCE
 HEALTHY BLOOD PARENT AND CAREGIVER RESOURCE PARENT AND CAREGIVER RESOURCE NOTES RESOURCES MENU 1. Your Kidney Health Team 2. Meet Your Kidneys! 3. Balance 4. Connections 5. Healthy Eating 6. Being Active
HEALTHY BLOOD PARENT AND CAREGIVER RESOURCE PARENT AND CAREGIVER RESOURCE NOTES RESOURCES MENU 1. Your Kidney Health Team 2. Meet Your Kidneys! 3. Balance 4. Connections 5. Healthy Eating 6. Being Active
Supporting Material 3D model of the Food Pyramid
 Module 3 Supporting Material 3D model of the Food Pyramid Supporting Material: 3D model of the Food Pyramid The PORTION PLATE Worksheet 1 Draw a pyramid with an internal subdivision in five layers. Colour
Module 3 Supporting Material 3D model of the Food Pyramid Supporting Material: 3D model of the Food Pyramid The PORTION PLATE Worksheet 1 Draw a pyramid with an internal subdivision in five layers. Colour
FALL GRADE. Edible SCHOOL GARDEN. Program WORKBOOK STUDENT: VERSION: AUGUST 2016 JHU CAIH
 4 FALL GRADE Edible SCHOOL GARDEN Program WORKBOOK STUDENT: VERSION: AUGUST 2016 JHU CAIH The Champion Cheer! We drink WATER cause it s fun, feels good, and makes us strong! We enjoy FRUITS AND VEGGIES
4 FALL GRADE Edible SCHOOL GARDEN Program WORKBOOK STUDENT: VERSION: AUGUST 2016 JHU CAIH The Champion Cheer! We drink WATER cause it s fun, feels good, and makes us strong! We enjoy FRUITS AND VEGGIES
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1
 Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
Food Chains and Food Webs
 Program Support Notes by: Spiro Liacos B.Ed. Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producers: Edwina Baden-Powell B.A, CVP. Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. You
Program Support Notes by: Spiro Liacos B.Ed. Produced by: VEA Pty Ltd Commissioning Editor: Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. Executive Producers: Edwina Baden-Powell B.A, CVP. Sandra Frerichs B.Ed, M.Ed. You
DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan
 1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
1 DAIRY 2 nd Grade Lesson Plan Goal: The goal is to for students to recognize the importance of a diet rich in calcium to support bone and dental health. Objectives: 1. Students will state that calcium
FOOD AND DIET The study of food is called nutrition.
 Try-out lesson material for schools in Belarus FOOD AND DIET The study of food is called nutrition. Why do we need food? We need food for four main reasons: it serves as a fuel, giving us energy and warmth.
Try-out lesson material for schools in Belarus FOOD AND DIET The study of food is called nutrition. Why do we need food? We need food for four main reasons: it serves as a fuel, giving us energy and warmth.
in food Nutrients Unit 2 Nutrients in food Functions of food Different types of food Carbohydrates Proteins Natural food Fats and oils
 Unit 2 Nutrients in food Nutrients in food Functions of food Different types of food Carbohydrates Natural food Proteins Fats and oils Vitamins and minerals Processed food Why is food processed? Food labels
Unit 2 Nutrients in food Nutrients in food Functions of food Different types of food Carbohydrates Natural food Proteins Fats and oils Vitamins and minerals Processed food Why is food processed? Food labels
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES. THE HEART Student Pages. Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile
 CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES THE HEART Student Pages Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile The heart is the most important muscle in the body! Heart Activity I Just beat it! The heart is the most important muscle
CLASSROOM ACTIVITIES THE HEART Student Pages Designers Brianne Miller, Molly Bugaile The heart is the most important muscle in the body! Heart Activity I Just beat it! The heart is the most important muscle
New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1
 Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. THURSDAY, 12 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
Surname Other Names Centre Number 0 Candidate Number New GCSE 4461/01 SCIENCE A FOUNDATION TIER BIOLOGY 1 ADDITIONAL MATERIALS A.M. THURSDAY, 12 January 2012 1 hour In addition to this paper you may require
SU228R Grades 4-8. Hayes FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY
 Hayes SU228R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY Fast Facts & Dazzling Data The Human Body This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc., Grand
Hayes SU228R Grades 4-8 FAST FACTS & DAZZLING DATA THE HUMAN BODY Fast Facts & Dazzling Data The Human Body This book was developed for Hayes School Publishing Co., Inc. by Good Neighbor Press, Inc., Grand
Activity Breaks. Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities
 Activity Breaks Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities Studies show students can benefit both physically and academically from physical activity breaks*: Helps meet recommended daily physical
Activity Breaks Quick & Easy Classroom-Based Physical Activities Studies show students can benefit both physically and academically from physical activity breaks*: Helps meet recommended daily physical
Welcome & Review Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 3 Lesson 4: Vitamins, Minerals and Water Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 3 Lesson 4: Vitamins, Minerals and Water Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. :
 1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
1 (v) science 1 st Term Worksheet Subject Science Class V Name : Sec. : Chapter 2 [Bones and Muscles] Keywords: [30] Tendons: Ligaments: Exercise: [31-33] [A] Fill in the boxes with the names of the main
Supported by. A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science.
 Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out how your body processes food. Mouth The teeth in your mouth are involved in the first stage of digestion. Teeth are used
Supported by A seven part series exploring the fantastic world of science. Find out how your body processes food. Mouth The teeth in your mouth are involved in the first stage of digestion. Teeth are used
Session 13. Fitness and Exercise. Teacher Notes. Physical Fitness. Aerobics (Cardio) Muscular Strength. Stretching. Stability (Balance)
 Session 13 Fitness and Exercise Teacher Notes Physical Fitness Physical fitness is a crucial component of living a healthy lifestyle. Exercise is necessary for maintaining a healthy weight and is particularly
Session 13 Fitness and Exercise Teacher Notes Physical Fitness Physical fitness is a crucial component of living a healthy lifestyle. Exercise is necessary for maintaining a healthy weight and is particularly
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2013 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon-transforming
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement. Educator(s) Name (s): Sub-Contractor: Region: County: Date of Lesson:
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Marty Moose: Lesson 4 Where s Your Moosetache? Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment Fidelity
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Marty Moose: Lesson 4 Where s Your Moosetache? Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment Fidelity
Information for Parents/Carers SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST
 SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY EVS Practice Worksheet
 GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY 2017 EVS Practice Worksheet Ch1: It is me! Ch2: Inside my body Remember: Our body is like a temple, we should take proper care of all our body parts. Q1. Name the following
GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY 2017 EVS Practice Worksheet Ch1: It is me! Ch2: Inside my body Remember: Our body is like a temple, we should take proper care of all our body parts. Q1. Name the following
5. Which word describes the tone of
 Name: Date: WEEK 14 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Have you ever wondered about where we get our food? All living things require energy to survive. They receive that energy from food. All
Name: Date: WEEK 14 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Have you ever wondered about where we get our food? All living things require energy to survive. They receive that energy from food. All
Digestion and Excretion
 Digestion and Excretion Nutrition What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or
Digestion and Excretion Nutrition What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or
Unit 2 Packet Nutrition and Fitness
 First Name Last Name Period Unit 2 Packet Nutrition and Fitness If you are ever absent go on to the class website and use the power points to guide your notes. POINTS ASSIGNMENT / 10 pts Daily Food Log
First Name Last Name Period Unit 2 Packet Nutrition and Fitness If you are ever absent go on to the class website and use the power points to guide your notes. POINTS ASSIGNMENT / 10 pts Daily Food Log
2. Cheese is a source of calcium. Why do we need calcium? Draw a line from each nutrient to a good source of that nutrient in our diet.
 St. Mary s Catholic High School-Dubai Name. Year6. Science revision (2) Date 27-12-17 1. a) Green beans contain vitamin C? Which other food is a good source of vitamin C? Put a cross to show the correct
St. Mary s Catholic High School-Dubai Name. Year6. Science revision (2) Date 27-12-17 1. a) Green beans contain vitamin C? Which other food is a good source of vitamin C? Put a cross to show the correct
Diet, digestion and excretion
 WORKSHEET 5.1 1. Circle the hidden nutrients. efats proteinssts lecarbohydratesfg femineralsbn 2. Solve the clues to write the words. Find the secret word. Clues 1 1. You have this on your head. 2 2. Eating
WORKSHEET 5.1 1. Circle the hidden nutrients. efats proteinssts lecarbohydratesfg femineralsbn 2. Solve the clues to write the words. Find the secret word. Clues 1 1. You have this on your head. 2 2. Eating
The Big Six Nutrients on Our Plate
 The Big Six Nutrients on Our Plate Grade: Kindergarten Goal Objectives Students will understand that fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, and dairy as the essential parts of a healthy diet. Students will
The Big Six Nutrients on Our Plate Grade: Kindergarten Goal Objectives Students will understand that fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, and dairy as the essential parts of a healthy diet. Students will
Welcome & Introduction Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 2: Serve up Your Dairy and Protein Foods Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 4 Lesson 2: Serve up Your Dairy and Protein Foods Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor
Unit 5L.4: Food. Know that humans require food as an energy source. Know that a balanced diet must contain proteins, fats,
 Unit 5L.4: as an energy source Balanced diet Requirements for different lifestyles Science skills: Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should: Know that humans require food as an energy source.
Unit 5L.4: as an energy source Balanced diet Requirements for different lifestyles Science skills: Observing Classifying By the end of this unit you should: Know that humans require food as an energy source.
Strength, any two: curl-ups/crunches, push-ups, step-ups; heart and lung endurance, any two:
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Materials Photo copied food labels and worksheet available Understanding Food Labels & Claims (take home handout)
 Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
Reading Food Labels Grade Level: Grades 4-8 Objectives: Student will learn the key components of the food label Students will identify which nutrient values should be low and which values should be high
JIGSAW READING CARBOHYDRATES
 Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
Chapter 1: Food Guide Pyramid
 Chapter 1: Food Guide Pyramid Goals 1. When given a list of the five food groups on the USDA Food Guide Pyramid, student will read the name of each group and write the name in the appropriate place on
Chapter 1: Food Guide Pyramid Goals 1. When given a list of the five food groups on the USDA Food Guide Pyramid, student will read the name of each group and write the name in the appropriate place on
My Senses 1.1. Diabetes Education in Tribal Schools Health Is Life in Balance. Copymaster 1.1 Grades 1 2 Unit 4, Lesson 1
 1.1 My Senses Community, Prevention, Lifestyle, Education Diabetes Education in Tribal Schools Health Is Life in Balance Copymaster 1.1 Grades 1 2 Unit 4, Lesson 1 My Senses My Science Journal Name The
1.1 My Senses Community, Prevention, Lifestyle, Education Diabetes Education in Tribal Schools Health Is Life in Balance Copymaster 1.1 Grades 1 2 Unit 4, Lesson 1 My Senses My Science Journal Name The
Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs
 Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chains All living things need food. It gives them energy as well as substances they need to build up their body. The sun is the starting point of every food
Chapter 4.3: Food Chains and Food Webs Food Chains All living things need food. It gives them energy as well as substances they need to build up their body. The sun is the starting point of every food
Focusing on the Fundamental Movement Skill of Balancing in a Gymnastics lesson
 Sample Lesson Plan Focusing on the Fundamental Movement Skill of Balancing in a Gymnastics lesson Class Level Strand Strand Unit Curriculum Objectives Learning outcomes Fundamental Movement Skill Resources
Sample Lesson Plan Focusing on the Fundamental Movement Skill of Balancing in a Gymnastics lesson Class Level Strand Strand Unit Curriculum Objectives Learning outcomes Fundamental Movement Skill Resources
TE Activity: Cereal Magnets
 TE Activity: Cereal Magnets Summary In this activity, students will design a process that removes the most iron from the cereal. This activity is meant for the students to experiment with different materials
TE Activity: Cereal Magnets Summary In this activity, students will design a process that removes the most iron from the cereal. This activity is meant for the students to experiment with different materials
GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY EVS Practice Worksheet
 GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY 2018 EVS Practice Worksheet Ch1: It is me! Ch2: Inside my body Remember: Our body is like a temple, we should take proper care of all our body parts. Q1. Name the following
GD GOENKA PUBLIC SCHOOL APRIL-MAY 2018 EVS Practice Worksheet Ch1: It is me! Ch2: Inside my body Remember: Our body is like a temple, we should take proper care of all our body parts. Q1. Name the following
To help students gain familiarity with the health benefits of foods contained in each group of MyPlate
 : Lesson for Third Grade Purpose To help students gain familiarity with the health benefits of foods contained in each group of MyPlate Desired Outcomes The learner will develop enabling strategies and
: Lesson for Third Grade Purpose To help students gain familiarity with the health benefits of foods contained in each group of MyPlate Desired Outcomes The learner will develop enabling strategies and
SAFI NUTRITION OUTREACH AND EDUCATION PROGRAM
 SAFI NUTRITION OUTREACH AND EDUCATION PROGRAM Title Strong Bones, Healthy Family Target Audience Elementary aged children Terminal Objective Students will be able to explain what calcium is and its function
SAFI NUTRITION OUTREACH AND EDUCATION PROGRAM Title Strong Bones, Healthy Family Target Audience Elementary aged children Terminal Objective Students will be able to explain what calcium is and its function
Matter and Energy: What foods to eat for a healthy body
 Matter and Energy: What foods to eat for a healthy body By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.03.17 Word Count 585 Level 560L Fruit and vegetables at a farmers market in Dallas, Texas.
Matter and Energy: What foods to eat for a healthy body By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.03.17 Word Count 585 Level 560L Fruit and vegetables at a farmers market in Dallas, Texas.
Teacher Pages. Grade Level 3-5
 Grade Level 3-5 Activity Summary: The Happening Heart Students will explore by demonstration the heart s pumping action with the use of a bucket of water and their hands. Time 30-40 minutes Activity Summary:
Grade Level 3-5 Activity Summary: The Happening Heart Students will explore by demonstration the heart s pumping action with the use of a bucket of water and their hands. Time 30-40 minutes Activity Summary:
YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION
 YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
YEAR 9 FOOD PREPARATION At the end of this unit you will have an assessment. 50% = The quality of your dishes cooked, with regard to hygiene and safety. 50% = The information you have learnt. Knowledge
DeltaScience. Content Readers. Summary. Science Background. Objectives. Reading Comprehension Skills. Supporting English Learners
 DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
DeltaScience Content Readers TM Red Edition Grade 3 4 reading level Purple Edition Grade 4 5 reading level Objectives Describe cells, the basic units of all living things. List the four main kinds of tissue
Weight and heart and circulatory diseases
 Weight and heart and circulatory diseases YOUR UNDERSTANDING WEIGHT This leaflet is for people who are at increased risk of heart and circulatory diseases because of their weight. Heart and circulatory
Weight and heart and circulatory diseases YOUR UNDERSTANDING WEIGHT This leaflet is for people who are at increased risk of heart and circulatory diseases because of their weight. Heart and circulatory
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A. Fall, 2012
 DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2012 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon- transforming
DRK-12 Carbon Assessment, Form A Fall, 2012 Please don t include this first sheet in student copies. This assessment is designed to elicit middle school or high school students accounts of carbon- transforming
Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer
 Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer This leaflet is for men who want to find out more about healthy eating and physical activity. A healthy diet and regular exercise are important
Diet, physical activity and your risk of prostate cancer This leaflet is for men who want to find out more about healthy eating and physical activity. A healthy diet and regular exercise are important
Be Fit for Life Series. Key Number Five Increase Metabolism
 Key #5 Increase Metabolism Page 1 of 9 Be Fit for Life Series Key Number Five Increase Metabolism Sit or lie in a safe and comfortable position I want you to close your eyes keep them closed until I ask
Key #5 Increase Metabolism Page 1 of 9 Be Fit for Life Series Key Number Five Increase Metabolism Sit or lie in a safe and comfortable position I want you to close your eyes keep them closed until I ask
Healthy. Fit. Living with FH. life. Having means we can still grow up the same as anyone else and live a
 FH me & Living with FH Having means we can still grow up the same as anyone else and live a Fit & Healthy life. There are just a few things we need to pay attention to. So let's take a closer look at what
FH me & Living with FH Having means we can still grow up the same as anyone else and live a Fit & Healthy life. There are just a few things we need to pay attention to. So let's take a closer look at what
Lesson Two Nutrients and the Body
 Lesson Two Nutrients and the Body Objectives After participating in this lesson, students will Be able to identify key nutrients the body needs and describe their function and importance. Understand that
Lesson Two Nutrients and the Body Objectives After participating in this lesson, students will Be able to identify key nutrients the body needs and describe their function and importance. Understand that
Group Session 3. Physical Fitness instructor or video
 Group Session 3 at a Glance Key Behavioral Strategies Participant Behavioral Strategies Process Objectives & Session Content Handouts Other Materials Suggested Partnerships Topics/Agenda (2 hours) Calorie
Group Session 3 at a Glance Key Behavioral Strategies Participant Behavioral Strategies Process Objectives & Session Content Handouts Other Materials Suggested Partnerships Topics/Agenda (2 hours) Calorie
Healthy Eating for Kids
 Healthy eating and being active are very important for your child to grow up in a proper way. The food plate is a guide to help you and your child know what and how much should be eaten every day. The
Healthy eating and being active are very important for your child to grow up in a proper way. The food plate is a guide to help you and your child know what and how much should be eaten every day. The
HEART HEALTH. Anjanette Fraser. The Natural Alternative Health & Wellbeing Ltd
 HEART HEALTH Anjanette Fraser The Natural Alternative Health & Wellbeing Ltd AGENDA 1 Heart conditions 2 Blood pressure 3 Diabetes 4 Cholesterol 5 Smoking 6 Alcohol 7 Exercise 8 Weight UK STATISTICS Chronic
HEART HEALTH Anjanette Fraser The Natural Alternative Health & Wellbeing Ltd AGENDA 1 Heart conditions 2 Blood pressure 3 Diabetes 4 Cholesterol 5 Smoking 6 Alcohol 7 Exercise 8 Weight UK STATISTICS Chronic
S.No. Chapters Page No. 1. Plants Animals Air Activities on Air Water Our Body...
 1 Contents S.No. Chapters Page No. 1. Plants... 1 2. Animals... 7 3. Air... 14 4. Activities on Air... 16 5. Water... 18 6. Our Body... 21 7. Food & Nutrition... 25 8. Safety and First Aid... 28 9. Up
1 Contents S.No. Chapters Page No. 1. Plants... 1 2. Animals... 7 3. Air... 14 4. Activities on Air... 16 5. Water... 18 6. Our Body... 21 7. Food & Nutrition... 25 8. Safety and First Aid... 28 9. Up
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Welcome & Introduction Yes No Comments and/or Changes
 Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 5 Lesson 8: Go Lean with Protein Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
Washington State Snap-Ed Curriculum Fidelity for Continuous Improvement Lesson Assessment Tool for Show Me Nutrition: Grade 5 Lesson 8: Go Lean with Protein Educator Self-Assessment Supervisor Assessment
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3
 Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie. Overview of the Book
 Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie Overview of the Book Five friends go on a quest to find out where food comes from and to gather
Maryland Agricultural Education Foundation s 8 h Annual Ag Literacy program See What We Eat by Scot Ritchie Overview of the Book Five friends go on a quest to find out where food comes from and to gather
1 What Are the Different Food Groups?
 1 What Are the Different Food Groups? 1. Match the food items below to where they are found in the supermarket. The first one has been done for you. Food item Section Oil Meat Fruits and vegetables Grains
1 What Are the Different Food Groups? 1. Match the food items below to where they are found in the supermarket. The first one has been done for you. Food item Section Oil Meat Fruits and vegetables Grains
Wriggle and Crawl Medium Term Plan
 Wriggle and Crawl Medium Term Plan Subject/ Topic: Science living things, habitats, animals including humans Year Group: 1/2 Date: Summer II 2017 Key questions are differentiated - orange = basic, turquoise
Wriggle and Crawl Medium Term Plan Subject/ Topic: Science living things, habitats, animals including humans Year Group: 1/2 Date: Summer II 2017 Key questions are differentiated - orange = basic, turquoise
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. Video Quiz
 1 Video Quiz At the conclusion of the videotape, there will be a short quiz with these questions. Write your answers in the space provided. Use the back of this sheet if necessary. Question 1: What is
1 Video Quiz At the conclusion of the videotape, there will be a short quiz with these questions. Write your answers in the space provided. Use the back of this sheet if necessary. Question 1: What is
New Food Label Pages Diabetes Self-Management Program Leader s Manual
 New Food Label Pages The FDA has released a new food label, so we have adjusted Session 4 and provided a handout of the new label. Participants use the handout instead of looking at the label in the book
New Food Label Pages The FDA has released a new food label, so we have adjusted Session 4 and provided a handout of the new label. Participants use the handout instead of looking at the label in the book
Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
 Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Created by Dr. Maria-Carmen Adamuz, Consultant Cardiologist. Aug 2017. WHAT IS HYPERTENSION? Blood pressure (BP) is the
Medical Advice for Athletes with High or Normal-High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) Created by Dr. Maria-Carmen Adamuz, Consultant Cardiologist. Aug 2017. WHAT IS HYPERTENSION? Blood pressure (BP) is the
TRACKS Lesson Plan. Sodium Cut the Salt! Grade: 5-8
 TRACKS Lesson Plan Sodium Cut the Salt! Grade: 5-8 I. Lesson Objectives: A. Students will explain the health benefits of reducing sodium in their diets. B. Students will identify common sources of sodium
TRACKS Lesson Plan Sodium Cut the Salt! Grade: 5-8 I. Lesson Objectives: A. Students will explain the health benefits of reducing sodium in their diets. B. Students will identify common sources of sodium
TKT CLIL LESSON PLAN
 TKT CLIL LESSON PLAN Teacher s name Date Agostini Samanta 19 th May Time 9.00 10.00 (Activity 1 and 2) The observer will be present during this lesson. I will develop activity 2 and 3 in the next two lessons.
TKT CLIL LESSON PLAN Teacher s name Date Agostini Samanta 19 th May Time 9.00 10.00 (Activity 1 and 2) The observer will be present during this lesson. I will develop activity 2 and 3 in the next two lessons.
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH
 eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
eat well, live well: EATING WELL FOR YOUR HEALTH It may seem like information on diet changes daily, BUT THERE IS ACTUALLY A LOT WE KNOW ABOUT HOW TO EAT WELL. Eating well can help you improve your overall
A. Reading Comprehension 20 marks. Facts about Seals. Seals bark like a dog, have whiskers like a cat and swim like a fish.
 A. Reading Comprehension 20 marks A. 1. Read the following text carefully. Facts about Seals Seals bark like a dog, have whiskers like a cat and swim like a fish. Seals have special qualities that allow
A. Reading Comprehension 20 marks A. 1. Read the following text carefully. Facts about Seals Seals bark like a dog, have whiskers like a cat and swim like a fish. Seals have special qualities that allow
Circulatory System. Date. Name Sunday, March 10. By Sharon Fabian
 Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System By Sharon Fabian Blood circulates through your body all the time through a complicated system of large and small pathways. Your heart pumps day and night to transport
Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System By Sharon Fabian Blood circulates through your body all the time through a complicated system of large and small pathways. Your heart pumps day and night to transport
The Circulatory System
 Science Unit: Lesson 3: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Circulatory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Science Unit: Lesson 3: Human Anatomy How Do We Move? The Circulatory System School year: 2007/2008 Developed for: Developed by: Grade level: Duration of lesson: Henderson Annex Elementary School, Vancouver
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Switch from Sugary Drinks to Water
 5Ways to Healthy Grow 1 Switch from Sugary Drinks to Water Goal: Switch from sugary drinks (like soda, sports, and fruit drinks) to water. Did You Know? The following count as sugary drinks: Powder drink
5Ways to Healthy Grow 1 Switch from Sugary Drinks to Water Goal: Switch from sugary drinks (like soda, sports, and fruit drinks) to water. Did You Know? The following count as sugary drinks: Powder drink
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY
 Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
LER Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation!
 LER 1902 Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation! The human heart is one of the most important parts of the body. It is responsible for moving blood and other
LER 1902 Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation! The human heart is one of the most important parts of the body. It is responsible for moving blood and other
Living Things Need Energy
 2 Living Things Need Energy Key Concept Energy and matter flow between organisms and their environment. What You Will Learn Producers, consumers, and decomposers have specific functions in an ecosystem.
2 Living Things Need Energy Key Concept Energy and matter flow between organisms and their environment. What You Will Learn Producers, consumers, and decomposers have specific functions in an ecosystem.
Name of Activity Making My Plate Great
 Name of Activity Making My Plate Great Submitted by Melanie Lynch National Standard(s) Standard 7 Grade Level Outcome High School or Performance S3.H13 Nutrtion Indicator Cognitive: By completing this
Name of Activity Making My Plate Great Submitted by Melanie Lynch National Standard(s) Standard 7 Grade Level Outcome High School or Performance S3.H13 Nutrtion Indicator Cognitive: By completing this
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1
 Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
Physical Fitness - Exercises 1 1 Answer the following questions in your own words! Why is being physically active important? What does strength training do to your body? Why won t girls get bigger muscles
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID: GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment
 TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
TEST NAME:Cells and Health TEST ID:1326431 GRADE:08 - Eighth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: School Assessment Cells and Health Page 1 of 15 Student: Class: Date: 1. Which best
