THE REGULATION OF THE FLOW OF BILE
|
|
|
- Julianna York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reprinted from THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY Vol. 74, No. 3, November, ism THE REGULATION OF THE FLOW OF BILE G. E. BURGET From the Department of Physiology, University of Oregon Medical School Received for publication August 12, 1925 The physiology of the gall bladder and the so-called resistance of the sphincter of Oddi have attracted considerable attention largely from a surgical point of view. Because of the pathology often encountered in the gall bladder and ducts, surgeons have been forced to make decisions regarding the functional significance of these structures and perhaps necessarily to draw conclusions with respect to the mechanism involved in the flow of bile into the intestine. The most recent reviews of the literature are those by Mann (1924a) and Chiray and Pavel (1925). I shall only mention here a few papers that embody the more or less common findings. The anatomy of the biliary tract has been studied by Oddi, Hendrickson, Mann, and Auster and Crohn. Oddi (1887) found in the dog near the mouth of the duct a muscular ring which after separation from the fibers that join the intestinal musculature could be considered as an independent sphincter. Hendrickson (1898) found some muscle fibers running around the end of the duct but for the most part the fibers along the duct were continuous with the intestinal musculature. Mann (1920), who studied several species of animals, was able to make out a definite arrangement of muscle fibers which might function as a sphincter. Auster and Crohn (1922) did not see a muscular bundle formation that might be called a sphincter. Microscopic observations upon preparations made from dogs and man indicated that the muscle fibers at the mouth of the common duct were "scanty, widely separated and diffuse and at no time continuous," They gained the impression that the muscular apparatus of the papilla is made up of a fusion of the fibers of the intestinal musculature with the corresponding layer of the duct. Oddi (1888) found this sphincter offered a resistance of 50 mm. Hg to fluids entering the lumen of the intestine. A resistance has been estimated and attributed to the sphincter by many observers since Oddi's work. Archibald (1919) reported similar findings. Mann (1919) ' recorded a minimal resistance in six species of animals possessing a gall bladder of 75 to 100 mm. water. Jacobsen and Gydesen (1922) found a resistance in dogs of 90 to 210 mm. water. Cole (1925) encountered 40 to 100 mm. water resistance in dogs. 583
2 E. BURGET These findings vary widely and would seem to attribute to the sphincter a physiological significance out of proportion to the anatomical structure described. The presence of an uncontrolled factor is indicated. An attempt has been made, therefore, to re-study this resistance under conditions where the tonus of the intestine might be observed and considered in interpreting the results. In the dog and for that matter in most animals including man the duct passes through the intestine in a most oblique manner. The mouth 1 ½ into the wall of the intestine. As a physical arrangement this would constitute an efficient sphincter-like mechanism depending upon the tonicity of the intestine. The duct within the intestinal wall is subject to collapse and consequently would offer a resistance to the passage of fluid in proportion to the state of tonicity of the intestinal musculature. Dogs under ether anesthesia were used for all experiments. An attempt Fig. 1. Effect of adrenalin upon pressure in the common bile duct. The tonus of the intestine was increased by giving 2 cc. of 0.1 per cent eserin intravenously. was made to insert a slender balloon through a slit in the duct into that part of the duct within the intestinal wall so that when filled with water and properly connected with a manometer the tonicity of the duct including the sphincter might be recorded. Practically, this did not work well because it was necessary to use too small a balloon. The usual technic was then utilized of placing a cannula in the duct a little distance from the intestine and pointed toward the lumen of the duct. The animal was kept under light anesthesia and the intestine well protected. The tonicity of the intestine could be observed at any time with the least amount of exposure. The cannula was connected with a manometer and pressure bottle containing water. The pressure withstood or held by the duct in a series of twenty dogs varied from 2 to 12 mm. Hg, depending upon the general condition of the animal and the degree of anesthesia. McWhorter (1921) found that adrenalin increased the tension of the sphincter slightly. Schafer (1924) states that adrenalin causes constriction
3 REGULATION OF BILE FLOW 585 of the bile ducts. This is in accord with Meltzer's (1917) law of contrary innervation of the gall bladder and sphincter. Figure 1 shows the typical effect of adrenalin upon duct pressure. The tonicity of the intestine had been increased by physostigtnine. Adrenalin caused temporary relaxation of the intestine and the duct pressure fell to almost zero. Atropin was used in some experiments and the atony of the intestine produced by it was effective in reducing the duct pressure as may he seen in figure 2. The recovery was less certain and consequently it did not Fig. 2. Effect of atropin upon pressure in the common duct. )f Lt is In rs c- at re et tie )n Fig. 3. After cocainizing the duct and sphincter of Oddi a resistance of 8 mm. Hg was obtained. Following the intravenous injection of eserin the resistance was greatly increased. lend itself well when repeated trials were desired on one animal. Cole (1925) says that intravenous injections of atropin, pilocarpine and physostigmine have no effects on this resistance. His observations were. made with the duodenum laid open which perhaps accounts for his results. Haberland (1924) who has recently made an extensive study of the function of the gall bladder says that atropin dilates the sphincter. However, he states that he believes that the importance of the sphincter has been over-emphasized. In the dog he thinks its action dependent upon the movements of the duodenum.
4 586 G. E. BTJRGET In attempting. to further eliminate the possiblity of a sphincter action the duct was cocainized. Cotton was twisted about a small wire and saturated with a 4 per cent cocaine solution. This was inserted into the duct far enough that the end entered the lumen of the intestine. A second application was made and ample time allowed for the drug to become effective. The cannula was then inserted and resistance measured. Figure 3, for example, shows 8 mm. Hg pressure withstood. Following an intravenous injection of physostigmine the resistance was increased as in previous experiments where the duct was not cocainized. Increased tonus of the duodenum brought about by mechanical irritation increases the amount of pressure that may be held by the duct. Some observers (Cole, 1925) have reported that mechanical irritation of the papilla causes a spasm visible to the naked eye. I have observed a swelling of the papilla when similarly tested but feel that it may be accounted for in part at least by contraction of the muscle fibers of the intestinal wall. In discussing an hypothesis of the function of the gall bladder, Mann (1924b) states that the acid chyme causes a relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi and allows a flow of bile. The only observations made in this connection were upon the effect of a 0.4 per cent solution of HC1 introduced into the duodenum above the entrance of the common duct. In most instances there followed a series of peristaltic waves in the duodenum. These reduced the pressure in the duct by a milking action. It seems probable that this would be an important factor in the flow of bile in digestion. DISCUSSION. The fact that strong inhibition brought about by adrenalin and that brought about by paralysis of the parasympathetic by atropin result equally well in lowering the resistance in the duct would indicate that if there is a reciprocal activity between the gall bladder and the sphincter such a mechanism probably does not play a major role in the regulation of bile flow. All investigators agree that while MgSO4 paralyzes the sphincter it also causes relaxation of the intestinal musculature. Archibald (1919) seldom found a sphincter in dogs that was overcome by less than 600 mm. water. Thinking a tonic sphincter might cause bile to be forced back into the pancreatic duct and cause pancreatitis, he "abolished" the sphincter in dogs and found the resistance reduced to 70 mm. water or less for as long as eight weeks after the operation. Mc- Whorter (1921) attempted to bring about the same end by dilating the sphincter. He says the sphincter was paralyzed by a quite severe dilatation (a small hemostat was used). The resistance was reduced from 180 to 200 mm. water to 25 to 50 mm. water. Of course in such experiments severe damage must have been done to the duodenum and the duct within its fa( sa' du wl bil thr thi Tl 1, an, of th( of the nit stu the fre wa MC ton the she a abl car cc WO fin( ((A Th is 1 clue MO tha of tin' enc inc
5 REGULATION OF BILE FLOW 587 its walls. The extent of injury and the time element would be important factors to be considered in determining the cause of the reduced resistance. Judd and Mann (1917), in a paper on the effect of cholecystectomy, say that following the removal of the gall bladder in the dog or cat the ducts dilated within 60 days. They cite a typical experiment (expt. 469) whereby 113 days after removal of the gall bladder in a dog the common bile duct increased in diameter from 6 mm. to 1 cm. but after entering the intestinal wall the diameter was still 6 mm. They set about to study the mechanism that produced dilatation of the ducts after cholecystectomy. The part played by the sphincter was investigated by three methods: 1, by comparing the pressure withstood by the sphincter in animals before and following the removal of the gall bladder; 2, at the time of removal of the gall bladder, by dissecting the duct free from the muscle fibers of the duodenal wall; 3, by sectioning the mucosal opening and a portion of the sphincter through a duodenal incision. Regarding the first point, they always found the residual pressure after removal of the gall bladder much lower than in normal animals. No explanation is offered. Further study may throw light upon this point. Concerning the second point they say, "In those animals in which the muscle fibers were dissected free from the intramural portion of the duct at the time the gall bladder was removed, dilatation of the duct did not occur except when there was mechanical obstruction due to adhesions." This would point strongly toward the seat of the resistance lying in that portion of the duct within the duodenal wall. Judd and Mann did not see this interpretation, as we shall see later. "Section of the mucosal opening and a portion of the sphincter through a duodenal incision after the removal of the gall bladder has given variable results in regard to the effect on the duct and positive conclusions cannot be drawn. However, in one perfect experiment the same dilatation occurred as in animals in which the gall bladder had been removed." This would again indicate the insignificance of the sphincter. They give these findings a different interpretation. In summarizing they say in part, "After the removal of the gall bladder all the ducts outside the liver dilate. The sphincter at the entrance of the common bile duct into the duodenum is the chief factor in producing this dilatation." Certainly such a conclusion is not justifiable by the experimental data presented. For the most part the results support the theory that the seat of resistance is in that portion of the duct within the wall of the duodenum. No great tonicity of the duodenum is necessary to close the small lumen of the duct. The normal tonus is no doubt sufficient to prevent a continuous flow when the gall bladder is present. When the pressure is high enough to overcome this resistance the bile flows into the intestine. The increased mechanical pressure upon the filled gall bladder brought about
6 588 G. E. BURGET by inspiration may easily be conceived to cause bile to spurt into the intestine irrespective of considerable tonus in the duodenum. Coupled with this is the peristalsis of the duodenum in digestion that invariably causes a flow when there is a moderate pressure in the duct. This is brought about partly by a milking action on the duct and probably partly by aspiration due to reduced pressure in the duodenum following the peristaltic wave. :Rost (1923) states that in cholecystectomized dogs there is a continuous flow of bile. In observing the flow in normal dogs under ether through an opening in the duodenum he observed spurts of bile absolutely synchronous with inspiration. In emphasizing the importance of the tonicity of the intestine and intestinal peristalsis in the regulation of bile flow it is not intended to leave the impression that the author feels that the theory is entirely proven. Further evidence is necessary. It may be that the contractions of the gall bladder and the activity of the sphincter play a part. A reciprocal physiological action between the gall bladder and the sphincter has not been satisfactorily demonstrated. This study indicates that such action may not take place and suggests that intra-abdominal pressure, respiration, and tonus and peristalsis of the duodenum are the most important factors in regulating the flow of bile. H; JA Jn M. M: OI.11( Se CONCLUSIONS 1. The normal tonus exhibited by the duodenum offers resistance to pressure in the common bile duct. 2. Drugs that affect the tonus of the intestinal musculature affect this resistance. Pilocarpine and physostigmine greatly increase the amount of pressure withstood in the duct while adrenalin and atropin reduce it to a minimum. 3. Peristalsis of the duodenum is an important factor in emptying the duct. 4. The function of the sphincter of Oddi has been over-emphasized and not enough attention has been given to the tonicity of the intestine in attempting to measure the resistance of this sphincter. 5. This study favors the hypothesis that bile flow is regulated by intraabdominal pressure and tonicity and peristalsis of the duodenum rather than being dependent upon a reciprocal activity between the gall bladder and the sphincter of Oddi. BIBLIOGRAPHY ARCHIBALD, E Surg., Gynec, and Obst., xxiii, 529. AUSTER, L. S. AND B. B. CitonN Amer. Journ. Med. Sci., clxiv, 345. CHIRAY, M. AND I. PAVE L Presse med., xxx, 713. COLE, W. H This Journal, lxxii, 39. HABERLAND. H. F Arch. f. klin. Chir., cxxx, 625.
7 REGULATION OF BILE FLOW 589 RENDRicxsoN, W. F Johns Hopkins Hosp. Bull., ix, 221. JACOBSON, C. AND C. GYDESEN Arch. Surg., v, 374. Juno, E. S. AND P. C. MANN Surg., Gynec. and Obst., xxiv, 437. MeWHoirmi., G. L Surg., Gynec. and Obst., xxxii, 124. MANN, F. C Journ. Lab. Clin. Med., v, Anat. Rec., xviii, a. Physic!. Reviews, iv, b. Journ. Amer. Med. Assoc., lxxxiii, 829. MELTZER, S. J Amer. Journ. Med. Sci., cliii, 469. Onci, R Arch. Ital. de biol., viii, Arch. per le sci. Med., xii, 333. ROST, F Pathological physiology of surgical diseases. Philadelphia. SCHAFER, E. S The endocrine organs (2nd ed.). London.
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
show-n to give off a branch, and sometimes two or three branches, to
 THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
THE EFFECT OF STIMULATION OF THE VAGI ON THE PYLORIC REGION OF THE STOMACH. BY E. D. McCREA1 AND B. A. McSWINEY. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) THE course taken by the vagus
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
 Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Medical Imaging and Treatment of the Bile and Pancreatic Ducts CIE-02718 Understanding ERCP Brochure Update_F.indd 1 7/11/18 9:51 A Minimally Invasive
STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTRO-ENTEROSTOMY
 STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTRO-ENTEROSTOMY I. THE REGURGITATION OF INTESTINAL CONTENTS IN NORMAL DOGS AND DOGS WITH POSTERIOR. GASTRO-ENTEROSTOMY BY G. E. BURGET AND M. E. STEINBERG Front the Department
STUDIES ON THE PHYSIOLOGY OF GASTRO-ENTEROSTOMY I. THE REGURGITATION OF INTESTINAL CONTENTS IN NORMAL DOGS AND DOGS WITH POSTERIOR. GASTRO-ENTEROSTOMY BY G. E. BURGET AND M. E. STEINBERG Front the Department
Action of various new analgesic drugs on the
 Gut, 1967, 8, 296 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct D. S. HOPTON AND H. B. TORRANCE From Manchester Royal Infirmary EDITORIAL COMMENT There is experimental evidence from
Gut, 1967, 8, 296 Action of various new analgesic drugs on the human common bile duct D. S. HOPTON AND H. B. TORRANCE From Manchester Royal Infirmary EDITORIAL COMMENT There is experimental evidence from
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
(From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
THE INNERVATION OF THE PYLORIC SPHINCTER OF THE RAT. BY M. NAKANISHI. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) WHILST numerous observations have been made on the behaviour of the pyloric region
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS.
 A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS. BY KINGO GOTO, M.D. (From the Department of Surgical Research and the John Herr Musser
A STUDY OF THE NITROGEN METABOLISM AND OF ACIDOSIS AFTER THE TRANSPLANTATION OF A URETER INTO THE DUODENUM IN DOGS. BY KINGO GOTO, M.D. (From the Department of Surgical Research and the John Herr Musser
titration. Thus, Neumeister(ly states that the reaction of bile is
 ON THE REACTION OF BILE. BY SEIZABURO OKADA (Tokyo). (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) WITH regard to the chemical reaction of bile from the gall-bladder there are various
ON THE REACTION OF BILE. BY SEIZABURO OKADA (Tokyo). (From the Institute of Physiology, University College, London.) WITH regard to the chemical reaction of bile from the gall-bladder there are various
Hepatocellular Dysfunction
 www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
www.nuclearmd.com A Normal HIDA Scan Dynamic or Static images of the abdomen are acquired after the IV administration 6-8 mci of Tc99m disofenin or mebrofenin, for one hour. Patients have to be NPO for
3, 4), although its concentration in mixed gastric
 THE VALUE OF THE ACID TEST MEAL: A STUDY OF NORMAL PERSONS AND OF PERSONS WITH DUODENAL ULCER By C. STUART WELCH AND MANDRED W. COMFORT (From The Mayo Foundation and the Division of Medicine, The Mayo
THE VALUE OF THE ACID TEST MEAL: A STUDY OF NORMAL PERSONS AND OF PERSONS WITH DUODENAL ULCER By C. STUART WELCH AND MANDRED W. COMFORT (From The Mayo Foundation and the Division of Medicine, The Mayo
Physiologic Anatomy and Nervous Connections of the Bladder
 Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION
 Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
Brit. J. Pharmnacol. (1952), 7, 665. THE ACTION OF NICOTINE ON THE CILIARY GANGLION BY BRENDA M. SCHOFIELD From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Oxford (Received June 7, 1952) The existing
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES. tube along with several
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CLASS NOTES Digestion Breakdown of food and the of nutrients in the bloodstream. Metabolism Production of for and cellular activities. The digestive system is composed of the canal which
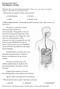
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD)
 SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
SPHINCTER OF ODDI DYSFUNCTION (SOD) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to structural or functional disorders involving the biliary sphincter that may result in impedance of bile and pancreatic juice
A PHARMACOLOGICAL AND CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF BENZYL MANDELATE
 A PHARMACOLOGICAL AND CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF BENZYL MANDELATE DAVID I. MACHT From the Pharmacological Laboratory, the John8 Hopkins University Received for publication July 13, 1923 In a study of the
A PHARMACOLOGICAL AND CLINICAL EXAMINATION OF BENZYL MANDELATE DAVID I. MACHT From the Pharmacological Laboratory, the John8 Hopkins University Received for publication July 13, 1923 In a study of the
striking difference between these two animals in respect of the sympathetic
 THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
THE PART PLAYED BY THE DUCTS IN THE PANCREATIC SECRETION. BY L. K. KOROVITSKY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, University of Odessa.) THE first object of this work was to compare the secretory innervation
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
University College, Cork.)
 612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
612. 893 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE GREAT SPLANCHNIC NERVES. BY D. T. (From the Department of Physiology, BARRY. University College, Cork.) "ON no subject in physiology do we meet with so many discrepancies
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Pfluiger's Archiv, LXIV
 THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
THE PHYSIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF THE PITUITARY BODY. BY E. A. SCHAFER, F.R.S., AND SWALE VINCENT, M.B. (Six Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College, London.) Results
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine.
 Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
Function of the ileocecal valve: 1-It is to prevent back flow of fecal content from colon into small intestine. 2-The wall of the ileum for several centimeters preceding valve has a thickened muscular
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
University of Leeds.)
 6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
6I2.328:6I2.89 THE SYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE STOMACH. I. The effect on the stomach of stimulation of the thoracic sympathetic trunk. BY G. L. BROWN, B. A. McSWINEY AND W. J. WADGE. (Department of
Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy
 1 Monterey County Surgical Associates 2 Upper Ragsdale Drive, Bldg B, Suite 230 Monterey, CA 93940 Phone: (831) 649-0808 Fax: (831) 649-8795 Mark Vierra, MD Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy Introduction
1 Monterey County Surgical Associates 2 Upper Ragsdale Drive, Bldg B, Suite 230 Monterey, CA 93940 Phone: (831) 649-0808 Fax: (831) 649-8795 Mark Vierra, MD Achalasia and Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy Introduction
Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2009) 394:209 213 DOI 10.1007/s00423-008-0330-6 CURRENT CONCEPT IN CLINICAL SURGERY Congenital dilatation of the common bile duct and pancreaticobiliary maljunction clinical implications
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests. Amelyn R.
 Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
interstitium at pressures below the maximum secretory pressure of the pancreas. The ink
 Gut, 1970, 11, 69-73 Effect of pressure on the integrity of the duct-acinar system of the pancreas R. C. PIROLA1 AND A. E. DAVIS From the Department of Medicine, Prince Henry Hospital, Sydney, Australia
Gut, 1970, 11, 69-73 Effect of pressure on the integrity of the duct-acinar system of the pancreas R. C. PIROLA1 AND A. E. DAVIS From the Department of Medicine, Prince Henry Hospital, Sydney, Australia
following its stimulation. joined each superior thyroid artery and was found just cephalad to
 612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
612.44: 612.817 THE THYROID NERVE IN THE DOG AND ITS FUNCTION. By W. DONALD Ross 1 and V. H. K. MOORHOUSE. From the Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Manitoba. (Received for
GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA*
 JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
JUNE, 1974 GIANT DUODENAL DIVERTICULA* By JACK R. MILLARD, M.D., FRED M. H. ZITER, JR., M.D., and WILLIAM P. SLOVER, M.D. HARTFORD, D UODENAL diverticula are common incidental findings on barium examinations
THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER PRESSOR AGENTS* BY RICHARD G. ABELL, ProD., ~
 Published Online: 1 March, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.3.305 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER
Published Online: 1 March, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.3.305 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Asma Karameh. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة -
 -2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
-2 Asma Karameh -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد خطاطبة - 1 P a g e Gastrointestinal motilities Chewing: once you introduce the first bolus to the mouth you started what we call chewing reflex appears by muscle
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
Why would fatty foods aggravate the patient s RUQ pain? What effect does cholecystokinin (CCK) have on gastric emptying?
 CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
CASE 28 A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with the acute onset of abdominal pain. Her pain is located to the right upper quadrant (RUQ) and radiates to the right shoulder. She reports
THE RECEPTIVE RELAXATION OF THE STOMACH,
 THE RECEPTIVE RELAXATION OF THE STOMACH, I BY W, B. CANNON AND C. W. LLEB. [From tk Lubordury of Physiology in Ihe Hamad Medicat School. N 1898 Langley described the action of inhibitory fibres for the
THE RECEPTIVE RELAXATION OF THE STOMACH, I BY W, B. CANNON AND C. W. LLEB. [From tk Lubordury of Physiology in Ihe Hamad Medicat School. N 1898 Langley described the action of inhibitory fibres for the
QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY
 612.337:612.013.88 "e ra4 78D QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY AND COGNATE MEDICAL SCIENCES FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MOTILITY OF THE PERFUSED HORSE INTESTINE. By FRANK ALEXANDER. From the Department
612.337:612.013.88 "e ra4 78D QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY AND COGNATE MEDICAL SCIENCES FACTORS INFLUENCING THE MOTILITY OF THE PERFUSED HORSE INTESTINE. By FRANK ALEXANDER. From the Department
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
(From the Physiological Laboratory, University College.)
 ON THE UNIFORMITY OF THE PANCREATIC ME- CHANISM IN VERTEBRATA. BY W. M. BAYLISS AND E. H. STARLING. (Nine Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College.) In a previous paper'
ON THE UNIFORMITY OF THE PANCREATIC ME- CHANISM IN VERTEBRATA. BY W. M. BAYLISS AND E. H. STARLING. (Nine Figures in Text.) (From the Physiological Laboratory, University College.) In a previous paper'
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction)
 SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
SOD (Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction) SOD refers to the mechanical malfunctioning of the Sphincter of Oddi, which is the valve muscle that regulates the flow of bile and pancreatic juice into the duodenum.
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Topics and aims. Introduction. Metabolism and Excretion
 Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
Topics and aims Introduction This section contains instructions that are applicable to all material, irrespective of your specific course. Please take note and make sure to comply. Failure to comply could
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Experimental Recanalization of the Fallopian Tubes in the Macacus Rhesus Monkey
 Experimental Recanalization of the Fallopian Tubes in the Macacus Rhesus Monkey Mario A. Castallo, M.D. with the technical assistance of JoHN M. STACK, M.D., AND AMos S. WAINER, M.D. THis PAPER REPORTS
Experimental Recanalization of the Fallopian Tubes in the Macacus Rhesus Monkey Mario A. Castallo, M.D. with the technical assistance of JoHN M. STACK, M.D., AND AMos S. WAINER, M.D. THis PAPER REPORTS
ON THE EXPULSION OF BILE BY THE GALL BLADDER; AND A RECIPROCAL RELATIONSHIP WITH THE SPHINCTER ACTIVITY.
 Published Online: 1 August, 1926 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.44.2.173 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 ON THE EXPULSION OF BILE BY THE GALL BLADDER; AND A RECIPROCAL RELATIONSHIP
Published Online: 1 August, 1926 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.44.2.173 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on November 7, 2018 ON THE EXPULSION OF BILE BY THE GALL BLADDER; AND A RECIPROCAL RELATIONSHIP
INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Anatomy Journal of Africa. 2014, 3 (1): 223 227. TERMINATION PATTERN OF THE MAIN AN ACCESSORY PANCREATIC UCTS AMONG TANZANIANS *Gabriel J. Mchonde, Ainory Peter Gesase Correspondence
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Anatomy Journal of Africa. 2014, 3 (1): 223 227. TERMINATION PATTERN OF THE MAIN AN ACCESSORY PANCREATIC UCTS AMONG TANZANIANS *Gabriel J. Mchonde, Ainory Peter Gesase Correspondence
The sympathetic nerve fibres which originate in the thoracic part of. postganglionic but does not affect preganglionic nerve fibres, Langley has
 532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
532 PHYSIOLOGY: S. J. MELTZER PROC. N. A. S. ARE THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANLIA INDISPENSABLE TO THE MAINTENANCE OF LIFE? By S. J. MULTZUR ROCKUPSLLUR INSTITUTh FOR MUDICAL RuSZARCH Read before the Academy,
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
mainly due to variability of the end-inspiratory point, although subjectively
 376 J. Physiol. (I950) III, 376-38I 6I2.2I7 THE NATURE OF THE LIMITATION OF MAXIMAL INSPIRATORY AND EXPIRATORY EFFORTS BY J. N. MILLS, Fellow of Jesus College, Cambridge From the Department of Physiology,
376 J. Physiol. (I950) III, 376-38I 6I2.2I7 THE NATURE OF THE LIMITATION OF MAXIMAL INSPIRATORY AND EXPIRATORY EFFORTS BY J. N. MILLS, Fellow of Jesus College, Cambridge From the Department of Physiology,
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER
 SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
6I :6I2.I83 BY ALISON S. DALE. concluded that the apparent vaso-constriction obtained by F r6 hli c h and
 6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY
 EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY HANS SELYE Fro,m the Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada Received for publication May
EXPERIMENTAL EVIDENCE SUPPORTING THE CONCEPTION OF ADAPTATION ENERGY HANS SELYE Fro,m the Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada Received for publication May
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
Case Report (1) Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction. Case Report (3) Case Report (2) Case Report (4) Case Report (5)
 Dr David Westaby Imperial NHS Trust Imperial College Medical School London Case Report (1)! TD 33yr old male! Feb May 2010: Recurrent episodes of abdominal pain! June 2010 Episode severe abdominal pain
Dr David Westaby Imperial NHS Trust Imperial College Medical School London Case Report (1)! TD 33yr old male! Feb May 2010: Recurrent episodes of abdominal pain! June 2010 Episode severe abdominal pain
gland, the tongue and the sweat glands of the cat. The submaxillary
 306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE.
 ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE. BY JAMES L. GAMBLE, M.D., AND MONROE A. McIVER, M.D. WI~r ~a~ ASSlSTANC~ OF PAULINE MARSII AND MAURICE M. TOL~.N. (From the Departments of Pediatrics
ACID-BASE COMPOSITION OF PANCREATIC JUICE AND BILE. BY JAMES L. GAMBLE, M.D., AND MONROE A. McIVER, M.D. WI~r ~a~ ASSlSTANC~ OF PAULINE MARSII AND MAURICE M. TOL~.N. (From the Departments of Pediatrics
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic agent.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 9 Cholinergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 9-1 through 9-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 9 Cholinergic Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 9-1 through 9-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES 9-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes the term cholinergic
ESSENTIAL QUESTION. What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the structures of the digestive system? THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM DIGESTIVE SYSTEM, AKA. ALIMENTARY CANAL digestive tract or gastrointestinal tract (GI Tract). A 30 ft. tube from
THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM
 55 THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) {Received 12th February 1929.) IT has long been
55 THE EFFECT OF TESTICULAR EXTRACTS ON THE BLOOD CALCIUM BY L. MIRVISH AND L. P. BOSMAN. (From the Department of Biochemistry, University of Cape Town.) {Received 12th February 1929.) IT has long been
however, to have been directly studied in any of the numerous observations
 ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
ON SOME CARDIAC REFLEXES. BY F. A. BAINBRIDGE. (From the University of Durhamt College of Medicine.) BAYLISS(3) has demonstrated the existence of reciprocal innervation in vaso-motor reflexes, and it is
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
 Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Patient Information published on: 03/2004 by the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) PATIENT INFORMATION FROM YOUR SURGEON & SAGES Laparoscopic Anti-Reflux (GERD) Surgery
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
of circular fibres. The bundle passes down on each side of the lesser sling." SEBER (3) has also demonstrated the "horse shoe sling" in the
 THE STRUCTURE AND MOVEMENTS OF THE CARDIA. By B. A. M'SWINEY. From the Department of Physiology, University of Leeds. (With one Plate.) (Received for publication 16th November 1928.) ON examination of
THE STRUCTURE AND MOVEMENTS OF THE CARDIA. By B. A. M'SWINEY. From the Department of Physiology, University of Leeds. (With one Plate.) (Received for publication 16th November 1928.) ON examination of
*1 p.c. NaOH, 75 p.c. alcohol and 75 p.c. acetone. Further, it has been
 THE SECRETION OF PANCREATIC JUICE. By J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) SINCE 1902 the secretin hypothesis of Bayliss and Starling(l) for the secretion of
THE SECRETION OF PANCREATIC JUICE. By J. MELLANBY. (From the Physiological Laboratory, St Thomas's Hospital, London.) SINCE 1902 the secretin hypothesis of Bayliss and Starling(l) for the secretion of
in gastric emptying' of the stomach was recorded by an electronic transducer (T1) attached by an air-filled tube to the second limb of
 Gut, 1963, 4, 174 Function of the pylorus and pyloric antrum in gastric emptying' A. K. ARMITAGE AND A. C. B. DEAN From the Department of Surgery, King's College Hospital Medical School, London EDITORIAL
Gut, 1963, 4, 174 Function of the pylorus and pyloric antrum in gastric emptying' A. K. ARMITAGE AND A. C. B. DEAN From the Department of Surgery, King's College Hospital Medical School, London EDITORIAL
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The Human Digestive System We will divide the Human Digestive System into two main topics: 1. Nutrition and what our body needs 2. How the human body breaks down food and makes
CHOLECYSTECTOMY CONSENT FORM
 1 of 6 Patient Name: I, have been asked to carefully read all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described
1 of 6 Patient Name: I, have been asked to carefully read all of the (name of patient or substitute decision-maker) information contained in this consent form and to consent to the procedure described
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
In The Name of God. Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis.
 In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
In The Name of God (A PROJECT OF NEW LIFE HEALTH CARE SOCIETY, KARACHI) Advanced Concept of Nursing- II UNIT- V Advance Nursing Management of GIT diseases. Cholecystitis. Shahzad Bashir RN, BScN, DCHN,MScN
Autonomic Nervous System. Part of the nervous system that controls most of the visceral functions of the body ( Automatically?
 Autonomic Response? Autonomic Nervous System Part of the nervous system that controls most of the visceral functions of the body ------ ( Automatically?) Classification Of CNS Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic Response? Autonomic Nervous System Part of the nervous system that controls most of the visceral functions of the body ------ ( Automatically?) Classification Of CNS Autonomic Nervous System
satisfactorily as a means of altering experimentally the ph of the upper
 THE REACTION QF HUMAN DUODENAL CONTENTS TO ACID AND ALKALINE MEAT MIXTURES By STACY R. METTIER (From I1e Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
THE REACTION QF HUMAN DUODENAL CONTENTS TO ACID AND ALKALINE MEAT MIXTURES By STACY R. METTIER (From I1e Thorndike Memorial Laboratory, Boston City Hospital, and the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical
Digestion and Absorption. Food:
 Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
Digestion and Absorption Food: Food is a basic requirement of all living beings. Food provides energy for different activities in the body. Food also provides organic materials for growth and repair. Carbohydrates,
