PILOT STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SPORTING COMPRESSION GARMENTS ON COMPOSITION AND VOLUME OF NORMAL AND LYMPHEDEMA LEGS
|
|
|
- Clifton Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 187 Lymphology 47 (2014) PILOT STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF SPORTING COMPRESSION GARMENTS ON COMPOSITION AND VOLUME OF NORMAL AND LYMPHEDEMA LEGS K. Sierakowski, N. Piller Lymphoedema Research Unit, Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Flinders University Adelaide Australia ABSTRACT Once clinically manifested as a swollen limb, lymphedema can be difficult to manage. Our focus thus must shift from reactive treatment to proactive management and prevention. On the basis of strong evidence in the literature, lymphedema specialists now encourage exercise as it can improve lymphatic drainage through muscle pump action. However, exercise may increase the lymph load on the vulnerable limb. We aimed to examine whether low level sporting compression is a reasonable recommendation for those with early stage lymphedema by measuring whether sporting compression (SC) tights decrease limb extracellular fluid as measured by Bio-impedance Spectroscopy (BIS) and Perometry in legs following exercise in both healthy controls and those with early stage lymphedema. A group of normal subjects (n=10) and a group of Stage 1 (ISL) lymphedema patients (n=9) were enrolled. Efforts were made to match participants in each group. For those with unilateral lymphedema, the non-affected leg was used as a control. All were measured using BIS, Perometry and Indurometry before and after exercise both with and without sporting compression clothing. The exercise regime was standardized and involved treadmill walking at increasing rates within each person s activity limitation. SC tights were shown to significantly decrease the fluid build up caused by exercise in lymphedema-affected limbs as measured with BIS (p=0.0302). Perometry measurements showed that SC caused a significant decrease in limb volume post exercise of the whole cohort (p=0.0081) and of the control Group B (p=0.0348). Our findings support the notion that SC may provide a socially acceptable and effective means of lymphedema control during exercise for early lymphedema management. Keywords: leg lymphedema, sporting compression, leg volumes, bioimpedance spectroscopy, perometry The US National Lymphedema Network recommends appropriate exercise and a general healthy lifestyle as important components of lymphedema management (1). The International Lymphedema Framework (ILF) recommends that those with lymphedema should exercise wearing a compression garment to decrease the fluid build up that is known to occur through stronger forms of exercise (2). During (and immediately after) exercise, the blood supply to skeletal muscles increases. Venous drainage tends to compensate for this increased supply but there remains an increased interstitial fluid load (with a higher concentration of large molecules including cytokines, lymphokines, etc.) that the lymphatic system must remove. When the lymph drainage pathway is hypoplastic (some forms of primary lymphedema) or has been damaged by surgery or
2 188 radiotherapy (secondary lymphedema), this extra fluid can add to an already overloaded system and lead to temporary worsening of symptoms and appearance through the failure of the lymphatics to remove the increased load. The general consensus is that compression alleviates this problem in two ways. Firstly, by wearing compression garments the pressure is transferred to the vessels and tissues within the leg, altering the Starling forces, which ultimately leads to less fluid leaking into the interstitial space. Secondly, the pressure variation through muscular movement against the compressive garment leads to more fluid being loaded into the lymphatics and removed from the area. Many people are reluctant to wear offthe-shelf or made to measure medical compression garments. This is especially the case when exercising as these traditional garments are reported to be hot, uncomfortable and difficult to don and doff. The use of sporting compression (SC) garments has become commonplace in the Australian and world-wide sporting scene with many high level sports people using SC for training and competitions. The sports literature suggests that SC improves peak sporting performance (3), reduces recovery time (4) and reduces postexercise muscle soreness (5). SC is often anecdotally recommended to those with early stage lymphedema or who are at risk of developing lymphedema. To date, no information is available about the effectiveness of SC on the fluid levels of limbs post exercise and particularly whether SC can provide a socially accepted, economically viable alternative to medical compression garments during exercise. This pilot study aimed to evaluate the effect of SC on lower limb volume and composition post-exercise in both healthy volunteers and those with early stage unilateral secondary lymphedema. METHODS The Flinders Medical Centre Clinical Research Ethics Committee, Adelaide, Australia, approved the study, and informed consent was obtained from each participant. A group of 9 healthy subjects (4 males, 5 females) and a group of 9 individuals (4 males, 5 females) with unilateral secondary early stage lymphedema were recruited. Any applicants with underlying lipedema, primary lymphedema, myxedema, uncontrolled hypertension, recurrent cancer, cellulitis or any who had recently (<1 month) undergone surgery or treatment for their lymphedema were excluded from the study. Participants were required to be able to walk on a treadmill and not use any other compressive garments for at least 12 hours prior to each session. They were also required to have relatively normal-shaped limbs to enable good contact and even pressure with the SC tights. The exercise sessions were scheduled as much as practicable for the early morning to minimize difference in activity levels before the session. Care was taken to ensure relatively empty bowels and bladders to ensure all were at a normal state of hydration. Background participant details were collected using a short general questionnaire where those with lymphedema were also asked to disclose the etiology of their lymphedema and other relevant co-morbidities. Each participant then took part in two sessions: the first session involved wearing regular non-compressive clothing, while in the second session the participants wore full length sporting compression tights (provided by SKINs TM ). The SC industry doesn t have a standardized compression scale as the compression offered depends greatly on the fit of the garment to the individual. The tights utilized in this study are similar to those used by Scanlan et al (6) who measured the compression as approximately 19mmHg at the ankle, gradually decreasing to 9mmHg at the buttocks. Measurements of limb volume and composition were taken before and after exercise. Following the exercise, BIS
3 189 measurements were performed at 3-minute intervals for 21 minutes. Indurometry and perometry measurements were taken after the BIS measurements, at approximately minutes post exercise. Total limb fluid volume was measured using Multi frequency Bio-impedance Spectroscopy (BIS) (Inbody Korea). BIS measures total limb fluid from groin/lateral abdominal margin downwards including the foot. As intravascular fluid and intracellular fluid are fairly static, changes in BIS measurement reflect changes of fluid volume in the extracellular compartment (7-9). Opto-electronic Perometry (Pero systems; Germany) was utilized to assess total limb volume (excluding the foot), which includes volumes of fat, fluid, and muscle. However, due to the short time frame over which this study was conducted, changes in perometry measurements would not reflect changes in fat or muscle but just those in total limb fluid between the upper thigh and the malleoli area of the ankle (8). Both the Perometry and BIS measurements therefore reflect changes in limb fluid volume even though the techniques are different. Comparing the outcomes from the two techniques can provide valuable information about fluid accumulation in the groin area as this is measured by BIS only. Tissue hardness was assessed by the Indurometer (previously called a Tonometer) (Biomedical Engineering Flinders Medical Centre) 15cm above the patella anteriorly, 15cm above and below the popliteal crease posteriorly, and at the midline of the limb (8-10). Following the exercise, BIS measurements were performed at 3-minute intervals for 21 minutes. Indurometry and perometry measurements were taken after the BIS measurements, at approximately minutes post exercise. Perceived exertion was scored using a Borg Scale 1-10, where 1 represents very little exhaustion and 10 represents extreme exhaustion that forces the person to rest. The exercise session consisted of a Sub-maximal treadmill exercise test where every 3 minutes either the speed or the percentage of incline increased. The starting pace was 3.2km/hour at 0% incline; the maximal level possible was 7.2km/hour at 15% incline. Heart rate was recorded every minute throughout the exercise, and the exercise was ceased when the participant s heart rate reached 85% of their maximal heart rate as calculated by their age (220 - age x 0.85). RESULTS TABLE 1 Group Demographics The lymphedema cohort (Group A), were significantly older (p<0.05), but similar (n.s.) in their body mass indices to the normal subjects Group B (see Table 1). Bio-Impedance Spectroscopy (BIS) BIS measurements include the whole limb from the toes to the groin and include the lateral groin region. Exercise caused an increased limb volume in all participants with average increase of 253ml ± 138. The whole cohort of 253ml ± 138. The use of SC during exercise decreased the fluid build-up by an average of 35ml per limb. Lymphedema affected limbs and Group B s limbs benefitted the most from SC with average volume decreases of 47 and 49ml, respectively. The non-affected leg of Group A s participants didn t have any reduction in volume as a result of SC; in fact, a very slight average increase in volume of 8ml was noted (see Table 2). Tables 3 and 4 provide individual data for Group A and B, respectively.
4 190 TABLE 2 Mean (Mean ± SD) Measurements of Limb Volume Increase After Exercise TABLE 3 Demographics and Limb Volume Changes After SC in Group A (With Lymphedema)
5 191 TABLE 4 Demographics and Limb Volume Changes After SC in Group B (Without Lymphedema) Analysis of the relative volume change of both legs in Group A participants with and without SC showed no statistically significant decrease in limb volume (p=0.1283). When the analysis was limited to the lymphedemaaffected limb, a significant limb volume decrease when wearing SC to exercise was found (p=0.0302). Group B and the nonaffected limbs only of Group A failed to show a significant benefit of SC (p= and p=0.9088, respectively). The behavior of the non-affected limbs in Group A was compared with that of Group B, as both classes of limbs are supposedly normal and as such should behave in a similar fashion in response to exercise. The limb volumes post exercise were compared (t-test) and without SC these limb subgroups behaved significantly differently (p=0.0032), with the non-affected limbs of Group A accumulating less fluid than the normal legs of Group B. When this same relationship was compared when wearing SC it was found to no longer be the case (p=0.2025), the SC causing the non-affected limbs of Group A to increase in post-exercise volume and in doing so behave similarly to the normal limbs in Group B. Plotting post-exercise relative to preexercise volume with and without the SC was
6 192 Fig. 1. BIS measurements were used to calculate pre-exercise to post-exercise relative volume changes in a normal subject with and without SC use. The top curves display values for the subject without SC use (squares for the left leg and diamonds for the right). The bottom curves display values for the subject with SC use (x for the left leg and triangles for the right). Total limb volume reduction due to SC use averaged 4% over the course of the measurements. used to graphically illustrate changes due to SC use. Fig. 1 displays fluid movement trends post-exercise in a selected representative normal individual. Total limb volume reduction due to SC use averaged 4% over the course of the measurements. Similar though often not as clear outcomes were observed in other participants. Variations between individuals seemed to be linked with the level of induration (as measured by Indurometry). Perometry Perometry measures only from the ankle malleoli to mid upper thigh. Perometry measurements did show a statistically significant decrease in post-exercise limb volumes when wearing SC for Group B (p=0.0152) and when all participants were grouped together (p=0.0036). Group A and its subgroups did not show a significant volume reduction as a result of SC (see Table 2). The mean volume reduction was significantly greater in the thigh region than the calf region (p=0.0053) for all participants. Indurometry Indurometry readings were significantly higher in the limbs with lymphedema when compared to the other non-affected limb (p=0.0226) suggesting that the lymphedema was correlated with epifascial induration. Borg Scale There was a slight trend of participants reaching higher levels of exercise tolerance when wearing SC garments, and participants were often able to reach higher grades on the treadmill while still reporting similar Borg exertion scores. DISCUSSION
7 193 As demonstrated in both Tables 3 and 4, the effectiveness of the SC varied greatly between participants and at times between participant s limbs. This variation calls for a larger study group to gain a true representation of the overall effects of SC. An examination of the data for indications as to why this variation occurred provided no clear associations. Multiple factors contribute to the effectiveness of the SC with likely influence from current and historical lymphedema management, BMI, normal exercise levels, SC fit, etc. One hypothesis is that the effect difference between the participants might be related to varied leg circumferences resulting in variation in compression applied by the SC tights with higher pressure being present on larger limbs. This difference may explain why the unaffected limb of the lymphedema group did not show a decrease in fluid buildup when wearing SC because the garment was necessarily loose on the non-affected limb to enable the affected leg to fit into the garment. Furthermore, one would expect greater compression to lead to larger volume reductions but that was not the case. It has been postulated that lymphedema develops in those with inherently increased capillary filtration rates which puts these people at greater risk of exceeding the maximal sustainable lymphatic flow (11,12). Other factors including tissue hardness, pre-exercise loads of the lymphatic system, and lymphatic filtration rates (11,12) may be contributory. When measured by Perometry, SC generally had their greatest fluid reducing effect in the thigh region, perhaps explaining why BIS failed to show any significant reductions in limb volume in the subgroups other than lymphedema-affected limbs. It appears that the fluid may be shifting from the thigh area into the groin region through wearing the SC tights. The lower lateral groin region is included in the BIS measurements but not in those of Perometry, perhaps underlying apparent inconsistency in measurement findings. Had the BIS measurements been performed post-exercise over a longer period of time and after multiple bouts of exercise, it may have shown the fluid moving from the groin into the abdomen with concomitant significant decreases in limb volume when SC is worn by those without lymphedema, as was found with Perometry. The decreased effectiveness of SC on lymphedema affected limbs as opposed to healthy limbs could be due to the increased tissue hardness that occurs epifascially as lymphedema progresses and is often associated with the surgical and radiotherapy induced scar area. The indurometer measurements were consistently higher in the group with lymphedema (despite its early stage), which indicates that their tissues had already started to undergo induration secondary to lymphedema. Since complex manual therapy and low level laser therapy can soften indurated tissues, the prior treatment of these cases may have improved the outcomes of the SC by freeing up the movement of fluids through the extracellular space. It seems the popularity of SC garments is due to subjective reports of increased performance (13) and decreased muscle soreness following exercise (14,15). The overwhelming majority of subjective feedback from participants wearing SC in this study was very positive. The true value in the use of SC in those affected by lymphedema may be that they help to remove the barriers to healthy exercise. If SC helps to get people with lymphedema up and exercising then that on its own is of great potential benefit. Group A participants who had been exposed to medical grade compression garments in the past reported SC tights as being very comfortable, supportive, and overall enjoyable to wear. Some of the participants struggled with donning the garments but as this was their first attempt it is thought that their technique would improve with practice. Of note, the SC tights are much easier to don and doff than the medical compression grade garments. The increased exercise tolerance observed by the
8 194 Borg Score results is likely due to increased comfort with the exercise regime and treadmill walking in general. It may also reflect increased exercise tolerance as participants reported feeling more athletic and capable when wearing SC. The discrepancy between the demographics of the two groups was not ideal as preferably the participants with lymphedema would be in the early stages of the disease and without or with only minimal fibrotic induration. Prior to commencement of the study, it was thought that those with longstanding lymphedema wouldn t respond well to SC. However, interestingly, there are several who responded very well, e.g., L3 who has suffered with lymphedema of his left leg for 17 years, experienced a 6.9% decrease in his post-exercise Perometry measurement. A future study would include both short term and long-term lymphedema-affected limbs to explore whether the chronicity of the disease affects the response to exercise and SC. There was difficulty in data collection because the measuring techniques cannot be performed simultaneously, and therefore differences in time of acquisition create discrepancies between participants. In addition, the maximum fluid increase seen post exercise is only one way of analyzing the BIS data. It may also be valuable to look at whether there is increased speed of return to pre-exercise volumes when wearing SC garments. This study has shown that SC tights are of some benefit to those with leg lymphedema, however its relative effectiveness in relation to the gold standard medical grade compression remains to be established. Future studies comparing SC to the current medical standard compression garments would be valuable, and also examining more closely both the psychological and physiological effects of SC in the medium to long term. CONCLUSION SC tights may have a role to play in the treatment and prevention of early or latent lower limb lymphedema. Greatest benefits were observed when tissue induration was minimal or normal levels. The garments generally are more acceptable to their users and easy to don and doff compared to medical compression garments. This finding does not suggest that medical compression garments are redundant, but rather that sporting compression garments may have a place in lymphedema management programs when a patient is exercising. SC garments decrease the fluid buildup caused by exercise as measured by BIS and Perometry. Based on this effect, they should be considered in the management options for early stage lymphedema particularly when patients are undertaking any exercise or activity program. REFERENCES 1. Moseley, AL, NB Piller: Exercise for limb lymphedema: Evidence that it is beneficial. J. Lymphoedema, 3 (2008), Cheville, A: Prevention of lymphedema after axillary surgery for breast cancer physiotherapy shows promise in a selected group of women. Br. Med. J. 339 (2009), Sear, JA, TR Hoare, AT Scanlan, et al: The effects of whole body compression garments on prolonged high-intensity intermittent exercise. J. Strength and Conditioning Res. 24 (2010), Jakeman, J, C Byrne, RG Eston: Efficacy of lower limb compression and combined treatment of manual massage and lower limb compression on symptoms of exercise-induced muscle damage in women. J. Strength and Conditioning Res. 24 (2010), Jakeman, J, C Byrne, RG Eston: Lower limb compression garment improves recovery form exercise-induced muscle damage in young, active females. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 109 (2010), Scanlan, A, B Dascombe, P Reaburn, et al: The effects of wearing lower-body compression garments during endurance cycling. Int l. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 3 (2008), Ward, L: Is BIS ready for prime time as the gold standard measure? J. Lymphoedema 4 (2009), Douglass, J, M Immink, N Piller, et al: Yoga
9 195 for women with breast cancer-related lymphoedema: A preliminary 6-month study. J. Lymphoedema, 7 (2012), Moseley, A, N Piller: Reliability of bioimpedance spectroscopy and tonometry after breast conserving cancer treatment. Lymph. Res. Biol. 6 (2004), Mirnajafi, A, A Moseley, N Piller: A new technique for measuring skin changes of patients with chronic postmastectomy lymphoedema. Lymph. Res. Biol. 2 (2008), Stanton, AW, S Modi, B TM Bennett Britton, et al: Lymphatic drainage in the muscle and subcutis of the arm after breast cancer treatment. Breast Cancer Res. Treatment 117 (2009), Modi, S, AW Stanton, WE Svensson, et al: Human lymphatic pumping measured in healthy and lymphoedematous arms by lymphatic congestion lymphoscintigraphy. J. Physiol. 583 (2007), Higgins, T, GA Naughton, D Burgess: Effects of wearing compression garments on physiological and performance measures in a simulated game-specific circuit for netball. J. Sci. Med. Sport, 12 (2009), Duffield, R, M Portus: Comparison of three types of full-body compression garments on throwing and repeat-sprint performance in cricket players. Brit. J. Sports Med. 41 (2007), Gill, N, CM Beaven, C Cook: Effectiveness of post-match recovery strategies in rugby players. Brit. J. Sports Med. 40 (2006), Professor Neil Piller Director Lymphoedema Research Unit Department of Surgery Level 3, Flinders Medical Centre Bedford Park, South Australia 5042 Phone: + 61 (0) Fax : + 61 (0) neil.piller@flinders.edu.au
Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease
 Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease Professor Neil Piller, Director, Lymphoedema Research Unit Flinders Medical Centre Dr Vaughan Keeley, Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Lymphoedema Clinic, Derby
Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease Professor Neil Piller, Director, Lymphoedema Research Unit Flinders Medical Centre Dr Vaughan Keeley, Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Lymphoedema Clinic, Derby
Robert Harris, Neil Piller
 MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE RESEARCH Three case studies indicating the effectiveness of manual lymph drainage on patients with primary and secondary lymphedema using objective measuring tools... Robert Harris,
MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE RESEARCH Three case studies indicating the effectiveness of manual lymph drainage on patients with primary and secondary lymphedema using objective measuring tools... Robert Harris,
Proper Implementation of Compression Garments. John Hobbs Med,RN
 Proper Implementation of Compression Garments John Hobbs Med,RN Working in the complimentary fields of medicine and exercise physiology can provide insight in to new ideas and products. It can also aid
Proper Implementation of Compression Garments John Hobbs Med,RN Working in the complimentary fields of medicine and exercise physiology can provide insight in to new ideas and products. It can also aid
CaresiaTM. Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners
 CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
Lymphedema. Information sheet and exercises
 Lymphedema Information sheet and exercises Lymphedema and its cause Lymphedema may manifest as swelling of one or more limbs and may include the corresponding quadrant of the trunk. Swelling may also affect
Lymphedema Information sheet and exercises Lymphedema and its cause Lymphedema may manifest as swelling of one or more limbs and may include the corresponding quadrant of the trunk. Swelling may also affect
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth
 Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations
 The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
LYMPHOEDEMA Journal of Lymphoedema 2007, Vol 2, N 2,
 LYMPHOEDEMA Journal of Lymphoedema 2007, Vol 2, N 2, 30-36. COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MLD AND LPG TECHNIQUE. MOSELEY A.L. et al. www.lpgsystems.com www.cosire-lpg.com Contact : infomed@lpgsystems.com
LYMPHOEDEMA Journal of Lymphoedema 2007, Vol 2, N 2, 30-36. COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MLD AND LPG TECHNIQUE. MOSELEY A.L. et al. www.lpgsystems.com www.cosire-lpg.com Contact : infomed@lpgsystems.com
LTU-904 Laser Therapy Unit Case Studies
 LTU-904 Laser Therapy Unit Case Studies 2008 case studies These case studies have been provided by Australian therapists who use the Riancorp LTU-904 laser therapy unit. Each therapist selects laser treatment
LTU-904 Laser Therapy Unit Case Studies 2008 case studies These case studies have been provided by Australian therapists who use the Riancorp LTU-904 laser therapy unit. Each therapist selects laser treatment
LYMPHEDEMA GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT. the more you know TEDS. Diuretics. Prescribe compression garments without first reducing edema
 LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
Physiological effects of aquatic physiotherapy in women with lower limb lymphoedema compared to healthy women.
 Griffith Research Online https://research-repositorygriffitheduau Physiological effects of aquatic physiotherapy in women with lower limb lymphoedema compared to healthy women Author Reul-Hirche, Hildegard
Griffith Research Online https://research-repositorygriffitheduau Physiological effects of aquatic physiotherapy in women with lower limb lymphoedema compared to healthy women Author Reul-Hirche, Hildegard
The Lymphatic System. Oedema (Edema) Lymphoedema (Lymphedema)
 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches
 Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
RianCorp. RianCorp. Case Studies Using LLLT: Lymphoedema
 RianCorp RianCorp Case Studies Using LLLT: Lymphoedema If you have a case study that you would like to add to this book- let, please contact sales@riancorp.com case studies These case studies have been
RianCorp RianCorp Case Studies Using LLLT: Lymphoedema If you have a case study that you would like to add to this book- let, please contact sales@riancorp.com case studies These case studies have been
Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema
 Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema Katie Riches Senior Research Nurse Derby Hospitals NHSF Trust Background: Derby Lymphoedema Service Three lymphoedema services based in Acute Hospitals at
Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema Katie Riches Senior Research Nurse Derby Hospitals NHSF Trust Background: Derby Lymphoedema Service Three lymphoedema services based in Acute Hospitals at
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world. Wounds UK Harrogate 2009
 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING
 TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING Debra Doherty is Senior Lecturer, Centre for Research and implementation of Clinical Practice, Thames Valley University Multilayer continues to
TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING Debra Doherty is Senior Lecturer, Centre for Research and implementation of Clinical Practice, Thames Valley University Multilayer continues to
What is Lymphedema? Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels are not formed completely or malformed
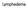 Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Improving customer care in compression hosiery
 Improving customer care in compression hosiery Introduction Within the modern NHS, the Pharmacy Team provides the front line service that most patients have contact with. Compression hosiery has a key
Improving customer care in compression hosiery Introduction Within the modern NHS, the Pharmacy Team provides the front line service that most patients have contact with. Compression hosiery has a key
Submitted by: Date of request: 28 th October 2015
 Submitted by: Frank Vicini, MD, FACR Chief Medical Officer ImpediMed, Inc. 5900 Pasteur Court Suite 125 Carlsbad, CA 92008 Phone: 760 585 2100 Email: fvicini@impedimed.com Date of request: 28 th October
Submitted by: Frank Vicini, MD, FACR Chief Medical Officer ImpediMed, Inc. 5900 Pasteur Court Suite 125 Carlsbad, CA 92008 Phone: 760 585 2100 Email: fvicini@impedimed.com Date of request: 28 th October
Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem
 Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem Screening breast cancer patients for lymphoedema makes it possible to identify problems early and take action to halt
Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem Screening breast cancer patients for lymphoedema makes it possible to identify problems early and take action to halt
Treatment. A Patient s Guide. Patient s Name. Clinician s Name
 Treatment A Patient s Guide Patient s Name Clinician s Name Introduction This booklet has been developed to help patients understand how the Huntleigh Healthcare LymphAssist machine can help in the management
Treatment A Patient s Guide Patient s Name Clinician s Name Introduction This booklet has been developed to help patients understand how the Huntleigh Healthcare LymphAssist machine can help in the management
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders
 Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries. Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA
 Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Sport and compression Improvement of performance or faster recovery phase?
 Sport and compression Improvement of performance or faster recovery phase? G. Willscheid, Orthopedics, Sports medicine Zürich, Switzerland Effects of compression garments (CG) - During sports - In recovery
Sport and compression Improvement of performance or faster recovery phase? G. Willscheid, Orthopedics, Sports medicine Zürich, Switzerland Effects of compression garments (CG) - During sports - In recovery
COURSE INFORMATION. Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
 Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT) Post Graduate Certificate in MLD & CDT COURSE INFORMATION Jan Douglass CONTENTS
Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT) Post Graduate Certificate in MLD & CDT COURSE INFORMATION Jan Douglass CONTENTS
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
Welcome to Pulmonary Rehab
 Patient Education Welcome to Pulmonary Rehab This handout is designed to help you get started in our program. We encourage you to read it before coming to your first class. Feel free to ask questions or
Patient Education Welcome to Pulmonary Rehab This handout is designed to help you get started in our program. We encourage you to read it before coming to your first class. Feel free to ask questions or
Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh)
 Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh) Quadriceps contusion or a cork thigh, as it is commonly known, is the result of a severe impact to the thigh which consequently compresses against the
Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh) Quadriceps contusion or a cork thigh, as it is commonly known, is the result of a severe impact to the thigh which consequently compresses against the
Estrid and Emil Vodder, originators of Manual Lymph Drainage with Gunther Wittlinger, founder of the Dr Vodder School, Walchsee, Austria
 Estrid and Emil Vodder, originators of Manual Lymph Drainage with Gunther Wittlinger, founder of the Dr Vodder School, Walchsee, Austria Hildegard Wittlinger, Director of the Dr Vodder School, Walschee,
Estrid and Emil Vodder, originators of Manual Lymph Drainage with Gunther Wittlinger, founder of the Dr Vodder School, Walchsee, Austria Hildegard Wittlinger, Director of the Dr Vodder School, Walschee,
Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June Policy No: 82 Effective Date: September 1, 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Date of Origin: April 2011 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 82 Effective
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Date of Origin: April 2011 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 82 Effective
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema. Sue Lawrance
 Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA. John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA
 When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs
 Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs How to Warm-up and Cool-down Appropriate warm-ups and cool-downs are important parts of any physical activity. The greater the speed of the movements required during the
Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs How to Warm-up and Cool-down Appropriate warm-ups and cool-downs are important parts of any physical activity. The greater the speed of the movements required during the
Dear Medical Professional,
 www.solarismed.com Dear Medical Professional, My co-workers and I would like to take this opportunity to thank you for partnering with us in providing a comprehensive lymphedema management program for
www.solarismed.com Dear Medical Professional, My co-workers and I would like to take this opportunity to thank you for partnering with us in providing a comprehensive lymphedema management program for
Impact of BIS Technology
 Skilled nursing leaders know that the number of women surviving breast cancer is rising. While this is good news, survivorship care has grown more complex and challenging for clinicians in skilled nursing
Skilled nursing leaders know that the number of women surviving breast cancer is rising. While this is good news, survivorship care has grown more complex and challenging for clinicians in skilled nursing
Power - Q1000. Digital 4 tiered rippling compressive limb and circulation therapy system
 Power - Q1000 Digital 4 tiered rippling compressive limb and circulation therapy system Mode D1 Mode D2 Mode A Mode B Mode C Mode D3 Mode D4 Easy in exploitation compressive limb therapy and lymphatic
Power - Q1000 Digital 4 tiered rippling compressive limb and circulation therapy system Mode D1 Mode D2 Mode A Mode B Mode C Mode D3 Mode D4 Easy in exploitation compressive limb therapy and lymphatic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 manual lymphatic drainage massage manual lymphatic drainage massage pdf manual lymphatic drainage massage Manual Lymphatic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 manual lymphatic drainage massage manual lymphatic drainage massage pdf manual lymphatic drainage massage Manual Lymphatic
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
6. Increased fat mass 2. Decreased anaerobic capacity
 The Importance of Resistance Training for the Aging Competitive Swimmer Peter Reaburn PhD Introduction Research has consistently shown that competitive swim performance decreases with increasing age. This
The Importance of Resistance Training for the Aging Competitive Swimmer Peter Reaburn PhD Introduction Research has consistently shown that competitive swim performance decreases with increasing age. This
Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland. Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema
 Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema Conditions related to increased risk of developing lymphoedema: High risk referral criteria Do you have any of
Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema Conditions related to increased risk of developing lymphoedema: High risk referral criteria Do you have any of
Robert Harris Senior instructor Dr. Vodder School - International
 Robert Harris Senior instructor Dr. Vodder School - International www.vodderschool.com Acknowledgements / Affiliations Animations and Movie clips Prof. Neil Piller, Flinders University: Vital Essence CD
Robert Harris Senior instructor Dr. Vodder School - International www.vodderschool.com Acknowledgements / Affiliations Animations and Movie clips Prof. Neil Piller, Flinders University: Vital Essence CD
Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions
 Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions page 1 of 6 TRAINING INSTRUCTIONS CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ AND ADJUST THE PELVIC AND FOOT-UNIT BELTS PER "ADJUSTING THE PELVIC PULL" INSTRUCTIONS ON THE FOLLOWING
Posture Pump PENTAVEC Model 2500 Instructions page 1 of 6 TRAINING INSTRUCTIONS CAUTION: CAREFULLY READ AND ADJUST THE PELVIC AND FOOT-UNIT BELTS PER "ADJUSTING THE PELVIC PULL" INSTRUCTIONS ON THE FOLLOWING
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet
 PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 2.01.82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection Effective Date January 30, 2015 Original Policy Date July 2, 2010 Next Review Date January 2015 Medical
2.01.82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection Effective Date January 30, 2015 Original Policy Date July 2, 2010 Next Review Date January 2015 Medical
Educating Yourself; Athletically. By Ben Wisbey
 Educating Yourself; Athletically By Ben Wisbey When you set yourself a goal to complete a particular event or do a particular time for a given distance, it is not just about getting yourself to peak physical
Educating Yourself; Athletically By Ben Wisbey When you set yourself a goal to complete a particular event or do a particular time for a given distance, it is not just about getting yourself to peak physical
Compression Garments for Lipoedema Patients. Friend or Foe?
 Compression Garments for Lipoedema Patients. Friend or Foe? Denise Hardy; RGN BSc (Hons) Nurse Consultant - Kendal Lymphology Centre Nurse Advisor LSN & LipoedemaUK Compression for Lipoedema - Introduction
Compression Garments for Lipoedema Patients. Friend or Foe? Denise Hardy; RGN BSc (Hons) Nurse Consultant - Kendal Lymphology Centre Nurse Advisor LSN & LipoedemaUK Compression for Lipoedema - Introduction
August 2015 Newsletter
 1 August 2015 Newsletter www.coretherapy.co.uk CONTENTS: Stretch of the month Exercise of the month Education Section: Where have I been? STRETCH OF THE MONTH Overdeveloped and tight hip flexors can contribute
1 August 2015 Newsletter www.coretherapy.co.uk CONTENTS: Stretch of the month Exercise of the month Education Section: Where have I been? STRETCH OF THE MONTH Overdeveloped and tight hip flexors can contribute
The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is :
 The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is : Badminton is well known and widely recognised by the public as an ideal, healthy activity, part of a lifelong healthy lifestyle; and as a well-organised and serious
The BADMINTON England Brand Vision is : Badminton is well known and widely recognised by the public as an ideal, healthy activity, part of a lifelong healthy lifestyle; and as a well-organised and serious
Yoga therapy and breast cancer
 Yoga therapy and breast cancer Yoga is being utilized with positive results in breast cancer patients as an intervention for lymphedema. This treatment has some medical and psychological benefits to offer.
Yoga therapy and breast cancer Yoga is being utilized with positive results in breast cancer patients as an intervention for lymphedema. This treatment has some medical and psychological benefits to offer.
BELLISSE COMFORTABLE, SUPPORTIVE TREATMENT FOR BREAST OEDEMA THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND.
 BELLISSE COMFORTABLE, SUPPORTIVE TREATMENT FOR BREAST OEDEMA THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. BELLISSE INNOVATIVE APPROACH TO BREAST AND CHEST WALL OEDEMA FOLLOWING BREAST CANCER TREATMENT The welcomed integration
BELLISSE COMFORTABLE, SUPPORTIVE TREATMENT FOR BREAST OEDEMA THERAPIES. HAND IN HAND. BELLISSE INNOVATIVE APPROACH TO BREAST AND CHEST WALL OEDEMA FOLLOWING BREAST CANCER TREATMENT The welcomed integration
LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT
 LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT Dear Health Practitioner, The level one lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT program at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals only (such
LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT Dear Health Practitioner, The level one lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT program at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals only (such
10 Week ADVANCED 5KM TRAINING PLAN
 RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 1 10 Week ADVANCED 5KM TRAINING PLAN RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 2 The NSPCC has teamed up with RG Active to
RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 1 10 Week ADVANCED 5KM TRAINING PLAN RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 2 The NSPCC has teamed up with RG Active to
2007 ICL SHANGHAI 24/03/2013
 Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
Background Intradermal Lymphoscintigraphy: Technical Improvement and an Interpretation of the Pathological Patterns on Clinical Management of Severe Stage Lymphoedema. Girolamo Tartaglione, MD Department
EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
 EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Dragana Bojinović-Rodić MD, PhD Institute of Physical Medicine
EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Dragana Bojinović-Rodić MD, PhD Institute of Physical Medicine
Training Outline. History of medi. Circulation in the body. Medical Conditions. Athletic Conditions. Compression in Sports. Compression for recovery
 Compression 101 1 Training Outline History of medi Circulation in the body Medical Conditions Athletic Conditions Compression in Sports Compression for recovery Tips 2 History of medi medi began in the
Compression 101 1 Training Outline History of medi Circulation in the body Medical Conditions Athletic Conditions Compression in Sports Compression for recovery Tips 2 History of medi medi began in the
Fitness for Players & Referees
 Handout: Fitness for Players & Referees By Wayne Grant, TFA High Performance Manager & Andrew Lees, NSWTA Development Officer, for NSW Touch Association 2009 State Conference. 1. Strength and Conditioning
Handout: Fitness for Players & Referees By Wayne Grant, TFA High Performance Manager & Andrew Lees, NSWTA Development Officer, for NSW Touch Association 2009 State Conference. 1. Strength and Conditioning
Phlebo Press. Use In: Phlebo Press
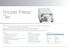 Phlebo Press Use In: Phlebo Press is a sequential pneumatic compression system specially designed for efficient reduction and management of peripheral edema, such as lymphedema and ulceration associated
Phlebo Press Use In: Phlebo Press is a sequential pneumatic compression system specially designed for efficient reduction and management of peripheral edema, such as lymphedema and ulceration associated
Stretching. Knees: Rotate your knees in a circle, keeping them together and bending down slightly.
 Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Diagnosis and Classification: How to Investigate Lymphoedema
 Diagnosis and Classification: How to Investigate Lymphoedema Professor Neil Piller, Director Lymphoedema Assessment Clinic and Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Flinders University and Flinders
Diagnosis and Classification: How to Investigate Lymphoedema Professor Neil Piller, Director Lymphoedema Assessment Clinic and Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Flinders University and Flinders
ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION
 ALL ABOUT EXERCISE ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION BODY MASS INDEX Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a person s height and weight. BMI is an indicator of total body fat and is used to screen
ALL ABOUT EXERCISE ASSESSING BODY COMPOSITION BODY MASS INDEX Body Mass Index (BMI) is a number calculated from a person s height and weight. BMI is an indicator of total body fat and is used to screen
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure
 When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations
 IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD, Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale Florida mayrovit@nova.edu ICC
IPC Use in Lymphedema: Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD, Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences, Nova Southeastern University Ft. Lauderdale Florida mayrovit@nova.edu ICC
Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Muscles are unique in their ability to relax, contract, and produce force. In addition, this metabolically
Chapter 8: Muscular Strength & Endurance ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Muscles are unique in their ability to relax, contract, and produce force. In addition, this metabolically
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
 Module 3 Progressive Muscle Relaxation Introduction 2 Progressive Muscle Relaxation 3 Preparing for Relaxation 3 Relaxation Technique 4 The Calming Technique: Body and Breath 6 Difficulties with Relaxation
Module 3 Progressive Muscle Relaxation Introduction 2 Progressive Muscle Relaxation 3 Preparing for Relaxation 3 Relaxation Technique 4 The Calming Technique: Body and Breath 6 Difficulties with Relaxation
Does the Time Frame Between Exercise Influence the Effectiveness of Hydrotherapy for Recovery?
 Brief Review International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 147-159 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Does the Time Frame Between Exercise Influence the Effectiveness of Hydrotherapy for
Brief Review International Journal of Sports Physiology and Performance, 2011, 6, 147-159 2011 Human Kinetics, Inc. Does the Time Frame Between Exercise Influence the Effectiveness of Hydrotherapy for
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY
 PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
Priorities Forum Statement
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 5 Subject Lymphoedema Date of decision November 2015 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 GUIDANCE Lymphoedema is the result of accumulation of fluid
Priorities Forum Statement Number 5 Subject Lymphoedema Date of decision November 2015 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 GUIDANCE Lymphoedema is the result of accumulation of fluid
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION. UNIT 2 Lesson 5 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION
 LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 2 Lesson 5 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION MUSCULAR ENDURANCE Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance Trainer
LIFETIME FITNESS HEALTHY NUTRITION MUSCULAR STRENGTH AEROBIC ENDURANCE UNIT 2 Lesson 5 FLEXIBILITY LEAN BODY COMPOSITION MUSCULAR ENDURANCE Created by Derek G. Becher B.P.E., B. Ed., AFLCA Resistance Trainer
Turning into a pear shape? Then you could have 'painful fat' syndrome
 dailymail.co.uk ORIGINAL PAGE Turning into a pear shape? Then you could have 'painful fat' syndrome by JILL FOSTER AUG. 1, 2011 By Jill Foster UPDATED: 02:15 EST, 2 August 2011 Louise Farquharson was gaining
dailymail.co.uk ORIGINAL PAGE Turning into a pear shape? Then you could have 'painful fat' syndrome by JILL FOSTER AUG. 1, 2011 By Jill Foster UPDATED: 02:15 EST, 2 August 2011 Louise Farquharson was gaining
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2017 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2017 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Case study: Young athlete suffering from PTS recovers from traumatic foot ulcer, following use of the geko TM device.
 Case study: Young athlete suffering from PTS recovers from traumatic foot ulcer, following use of the geko TM device.... Subject 34-year-old male, ex professional rugby player. Wound Type Lower left leg
Case study: Young athlete suffering from PTS recovers from traumatic foot ulcer, following use of the geko TM device.... Subject 34-year-old male, ex professional rugby player. Wound Type Lower left leg
Lymphoedema reducing its risk though early detection and treatment
 Lymphoedema reducing its risk though early detection and treatment Professor Neil Piller, Lymphologist, Director Lymphoedema Assessment Clinic and Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Flinders University
Lymphoedema reducing its risk though early detection and treatment Professor Neil Piller, Lymphologist, Director Lymphoedema Assessment Clinic and Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Flinders University
LX7 (Luxury) New automatic system
 LX7 Product Introduction RevitaPump LX7 Sequential Compression Therapy Solutions LX7 (Luxury) New automatic system 2 Compression modes Pressure: 20~250mmHg Optional care (foot, calf, knee, thigh) Automatic
LX7 Product Introduction RevitaPump LX7 Sequential Compression Therapy Solutions LX7 (Luxury) New automatic system 2 Compression modes Pressure: 20~250mmHg Optional care (foot, calf, knee, thigh) Automatic
Obesity and Lymphoedema : a clinical dilemma
 Obesity and Lymphoedema : a clinical dilemma Professor Christine Moffatt CBE Professor of Clinical Nursing Research & Nurse consultant Royal Derby Hospital Foundation Trust Lymphoedema Service Chair ILF
Obesity and Lymphoedema : a clinical dilemma Professor Christine Moffatt CBE Professor of Clinical Nursing Research & Nurse consultant Royal Derby Hospital Foundation Trust Lymphoedema Service Chair ILF
Five for Life Student Portfolio
 Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
Five for Life Student Series 1, Student Edition Table of Contents Student Essential Question: How do my current behaviors and fitness affect my health now and in the future? Over the course of this portfolio,
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment
 Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Planning a Training Program
 Planning a Training Program Planning a training program Devising and implementing a training program requires a carefully considered, step-bystep approach in which the coach and/or athlete incorporates
Planning a Training Program Planning a training program Devising and implementing a training program requires a carefully considered, step-bystep approach in which the coach and/or athlete incorporates
Training 1. Training c Training. For AQA
 Training 1 Training Training 2 What you will learn about in this topic: 1. Methods of training 2. What each training method develops 3. How each method works Training 3 Learning objectives By the end of
Training 1 Training Training 2 What you will learn about in this topic: 1. Methods of training 2. What each training method develops 3. How each method works Training 3 Learning objectives By the end of
1. Skin care: Cleansing, lubrication, debriding and administration of antimicrobial therapy.
 Lymphedema Treatment Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.05aC9 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider
Lymphedema Treatment Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.05aC9 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider
Sports Med Critical Question 3.notebook May 05, Critical Question 3
 Critical Question 3 What role do preventative actions play in enhancing the wellbeing of the athlete? Syllabus Apr 21 5:37 PM Big Heading: Critical Questions 2: What role do preventative actions play in
Critical Question 3 What role do preventative actions play in enhancing the wellbeing of the athlete? Syllabus Apr 21 5:37 PM Big Heading: Critical Questions 2: What role do preventative actions play in
Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Programs Diabetic Management & Weight Loss Exercise Programs
 Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Programs Diabetic Management & Weight Loss Exercise Programs Information for participants Welcome to our cardiac rehabilitation, diabetic & weight loss exercise programs.
Cardiac Rehabilitation Exercise Programs Diabetic Management & Weight Loss Exercise Programs Information for participants Welcome to our cardiac rehabilitation, diabetic & weight loss exercise programs.
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust. Your guide to breast and chest wall swelling after breast cancer treatments. Issued by the Breast Team
 Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Your guide to breast and chest wall swelling after breast cancer treatments Issued by the Breast Team This leaflet is to give you information on the treatment
Northumbria Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Your guide to breast and chest wall swelling after breast cancer treatments Issued by the Breast Team This leaflet is to give you information on the treatment
9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!
 1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
Fitter, Faster, Stronger, Longer: Precor Cardio Development Program
 Fitter, Faster, Stronger, Longer: Precor Cardio Development Program The Precor Cardio Development Program is a 3 phase training program that progressively guides your clients towards aerobic fitness and
Fitter, Faster, Stronger, Longer: Precor Cardio Development Program The Precor Cardio Development Program is a 3 phase training program that progressively guides your clients towards aerobic fitness and
Personal Training Initial Packet
 Personal Training Initial Packet ****Please complete and return to the reception desk at least 2 days prior to your scheduled Fitness Assessment**** Name: D.O.B: Today s Date: Member or Non-member (circle
Personal Training Initial Packet ****Please complete and return to the reception desk at least 2 days prior to your scheduled Fitness Assessment**** Name: D.O.B: Today s Date: Member or Non-member (circle
A Protocol for Establishing Critical Power in Running
 A Protocol for Establishing Critical Power in Running A Working Paper Prepared by The Stryd Team 27 September 201 1 Introduction One of the primary reasons for considering one s power consumption during
A Protocol for Establishing Critical Power in Running A Working Paper Prepared by The Stryd Team 27 September 201 1 Introduction One of the primary reasons for considering one s power consumption during
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling
 A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS CHRONIC SWELLING? As a normal part of your blood circulation, your vascular system leaks fluid into the surrounding tissues. Your
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS CHRONIC SWELLING? As a normal part of your blood circulation, your vascular system leaks fluid into the surrounding tissues. Your
22 Week ADVANCED MARATHON TRAINING PLAN
 RG Active 22 Week Advanced Marathon Training Plan Page 1 22 Week ADVANCED MARATHON TRAINING PLAN [Type www.bloodwise.org.uk here] Introduction Below is a 22 week advanced marathon training plan to help
RG Active 22 Week Advanced Marathon Training Plan Page 1 22 Week ADVANCED MARATHON TRAINING PLAN [Type www.bloodwise.org.uk here] Introduction Below is a 22 week advanced marathon training plan to help
Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients
 Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients Name Date of diagnosis Date Name of physician making diagnosis Do you also have lymphedema? What areas of the body are affected? Outside of thighs Inner thighs Knees
Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients Name Date of diagnosis Date Name of physician making diagnosis Do you also have lymphedema? What areas of the body are affected? Outside of thighs Inner thighs Knees
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
SHS FITNESS ACROSS THE P.E. CURRICULUM
 SHS FITNESS ACROSS THE P.E. CURRICULUM Five Health-Related Fitness components: Flexibility the ability to move a joint through a full range of motion A regular program of stretching may incorporate dynamic
SHS FITNESS ACROSS THE P.E. CURRICULUM Five Health-Related Fitness components: Flexibility the ability to move a joint through a full range of motion A regular program of stretching may incorporate dynamic
Exercise on Dialysis. Instruction Manual
 Exercise on Dialysis Instruction Manual i Bennett, PN., Lingard, B. & Maxwell, E. (2015). Exercise on Dialysis: Instruction Manual. Published by Copyright 2015 www.cambridgemedia.com.au First published
Exercise on Dialysis Instruction Manual i Bennett, PN., Lingard, B. & Maxwell, E. (2015). Exercise on Dialysis: Instruction Manual. Published by Copyright 2015 www.cambridgemedia.com.au First published
6 WEEK TRAINING PROGRAM
 CLIMB FOR CANCER 2015 810 Steps & 37 Floors STAIR CLIMBING INFORMATION: In the training program, where we mention using stairs as your equipment, Kangaroo Point is the perfect place to train with the bonus
CLIMB FOR CANCER 2015 810 Steps & 37 Floors STAIR CLIMBING INFORMATION: In the training program, where we mention using stairs as your equipment, Kangaroo Point is the perfect place to train with the bonus
The management of patients with lymphoedema
 Juxta-Fit compression garments in lymphoedema management Julie Mullings Julie Mullings, Tissue Viabilty Specialist Nurse, University Hospital of South Manchester - Community Services Email: Julie.mullings@uhsm.nhs.uk
Juxta-Fit compression garments in lymphoedema management Julie Mullings Julie Mullings, Tissue Viabilty Specialist Nurse, University Hospital of South Manchester - Community Services Email: Julie.mullings@uhsm.nhs.uk
14 Week BEGINNER HALF MARATHON (21km) TRAINING PLAN
 RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 1 14 Week BEGINNER HALF MARATHON (21km) TRAINING PLAN RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 2 The NSPCC has teamed up with
RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 1 14 Week BEGINNER HALF MARATHON (21km) TRAINING PLAN RG Active 14 Week Beginner Half-Marathon Training Plan Page 2 The NSPCC has teamed up with
