The Respiratory System
|
|
|
- Stephany Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Respiratory System EQS 110
2 Table of Contents Click on the different sections of the table of contents to jump through this document Role of the Respiratory System... 3 Anatomy of Respiration... 4 Upper Respiratory Tract... 4 Nostrils & Nasal Cavities... 5 Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea... 6 Breathing & Eating... 7 Flow of the Upper Respiratory Tract... 7 Lower Respiratory Tract... 8 Trachea and Bronchi... 8 Lungs... 8 Gaseous Exchange... 9 Flow of the Lower Respiratory Tract... 9 Respiration & Exercise Management of the Respiratory System - IAD Respiratory Images Upper Airway Respiratory Images Lower Airway Self-Knowledge Checks Answers Glossary... 16
3 Role of the Respiratory System The main function of the respiratory system is to inhale air, which contains oxygen to be delivered to the cells via the circulatory system, and to exhale carbon dioxide; this act of inhaling and exhaling air is better known as respiration. At rest, a healthy adult horse will have a respiration rate of 8 16 breaths per minute. While oxygen is vital for all life processes, for a horse to provide sustained performance, blood must take in oxygen from the lungs and transport it efficiently to the muscles. Therefore, the health and management of a horse s respiratory system is not only crucial for its overall well-being, but for its performance as an equine athlete! Respiratory-related health conditions are the second leading cause of poor performance in athletic horses. Take this into consideration in the Kentucky Derby, a horse respires approximately 4,000 liters of air in and out of the lungs. That equates to two five gallon buckets of air in and out of the lung every second! The ability for the horse to intake enough air and for the blood to get oxygen from the lungs and transport it efficiently to the muscle is key; the more efficient the process, the more stamina the horse will have.
4 Anatomy of Respiration A horse s respiratory system is divided into two parts: Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory Tract The diaphragm, which separates the abdominal and chest cavities, is the primary muscle used for breathing. The abdominal muscles are only used for labored breathing. Upper Respiratory Tract The upper respiratory tract consists of the: Nostrils Nasal cavity Pharynx/Nasopharynx Larynx Trachea We will review the process of respiration within the upper respiratory tract step-by-step, with an emphasis on the structures involved.
5 Nostrils & Nasal Cavities Air is drawn into the nasal cavities through the nostrils as the horse cannot breathe through his mouth. The air that is drawn in through the nostrils is filtered and cleaned in the nasal cavities by moist, mucous membranes and tiny hairs called cilia. Cilia move in a wave-like action, pushing dust, germs, and debris back up into the throat where it either drains out of the nostrils, is swallowed, or coughed up. Horses may typically have a mild degree of translucent/clear, thin nasal discharge if in an environment that is prone to dust or following exercise, but thick, colored mucous discharge is abnormal and an indicator that something is wrong. Evaluating your horse s discharge, or lack thereof, should be a daily task as it could be the first sign of illness or disease. The horse s nasal cavity is separated from the mouth by a structure called the hard palate, a bone that forms the roof of the mouth and the base of the nasal cavity. Respiration in Practice Equine Nasal Strips Taken in part from Flair Equine Nasal Strips Learn Since horses can only breathe through their nose, all the oxygen required for exercise can only come through the nasal passages; a significant portion of which is unsupported by bone or cartilage. This unsupported portion of the nasal passage collapses inward when a horse breathes during exercise reducing the size of the airway and greatly increasing resistance to airflow. This is significant because during exercise over 50% of resistance to air flow to the lungs comes from the nasal passages, with some studies suggesting this percentage can be as high as 80%. In addition, anatomical disorders of the upper airway and the way the horse s head is being held during exercise can create additional increases in the work of breathing. All of these factors can make it difficult to move air into the lungs, reducing the efficiency of the respiratory system.
6 One way to combat this is through the use of an equine nasal strip, such as a FLAIR Strip. Nasal strips can gently support the nasal passages and reduce soft tissue collapse that can cause narrowing of the airways during exercise. Pharynx, Larynx, Trachea Once air is filtered by the nasal cavities it makes its way to the pharynx (also called the nasopharynx), a chamber lined with mucous membranes that connects the nasal passages to the larynx. Horses can get pharyngitis (commonly known as a sore throat), which is an inflammation of the pharyngeal airway. This issue often follows a respiratory infection or may be due to a heavily contaminated environment (dust, debris, etc.). After passing through the pharynx, air reaches the larynx, a structure located on top of the trachea, the horse s windpipe. The larynx is responsible for directing air into the trachea, controlling airflow into the lungs during breathing, and producing vocal noises. The larynx is protected by five rings of cartilage that can be felt between the two lower jawbones. The rings provide areas for muscle attachments which open and close the epiglottis and arytenoid cartilages. The epiglottis and arytenoid cartilages both serve similar roles in that they help close the airway when a horse is swallowing so that foreign bodies do not enter the trachea. The arytenoid cartilages are located on each side of the horse s larynx whereas the epiglottis sits on top of the soft palate, a structure that is responsible for separating the larynx from the esophagus. Epiglottis The Larynx & Its Components (Epiglottis, Arytenoids, and Soft Palate)
7 Horses can have anatomical issues with their arytenoid cartilages, epiglottis, and soft palate, resulting in restrictive airflow that can cause poor performance. Dorsal Displacement of the Soft Palate (DDSP) and Laryngeal Hemiplegia ( Roaring ) are two of the most common anatomical respiratory disorders seen in racehorses. A dynamic endoscope allows us to evaluate the anatomy and function of the larynx during exercise Breathing & Eating While the focus of this lecture is respiration, keep in mind another activity that is often going on in the mouth eating. In order to make sure the right things go down the right pipes, the soft palate, epiglottis, and arytenoid cartilages work together in opening and closing the correct junctions. By doing this, air is allowed to pass into the trachea to the lungs while food is allowed to pass into the esophagus to the stomach. Click here to see a visual representation of this process. Breathing Eating Flow of the Upper Respiratory Tract Nostrils Nasal Cavities Pharynx Larynx Trachea
8 Lower Respiratory Tract The lower respiratory tract consists of the: Trachea (continuation from the upper respiratory tract) Bronchi Lungs Similar to our discussion of the upper respiratory tract, we will continue the process of respiration within the lower respiratory tract step-by-step, with an emphasis on the structures involved. Trachea and Bronchi Bronchi The trachea, a cartilaginous ringed tube, goes from jaw to chest. Just above the heart, the trachea divides into two tubes called bronchi. Each bronchi enters into a lung a horse has a right and left lung. Lungs The lungs of a horse are an amazing piece of engineering. Consisting of an enormous surface area of spongy, elastic tissue that increases and decreases as the horse breathes, the lungs, as well as the heart and spleen, fill the horse s thorax. Within the lungs, the bronchi continue to divide and subdivide, like the branches of a tree. The smallest branches are called the bronchioles, which are scarcely larger than a hair. Each bronchiole ends in millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
9 Gaseous Exchange A thin membrane, called the blood-gas barrier, surrounds each alveolus and this is where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs. Deoxygenated blood (blood without oxygen) flows into the lungs through the capillaries embedded in the semi-permeable walls of the alveoli. Carbon dioxide is then extracted and exhaled as waste. Inhalation brings in fresh, dry air high in oxygen. This reaches the alveoli where it is extracted by the blood, which then returns back to the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body where it is absorbed and used. This complex process is known as gaseous exchange. Flow of the Lower Respiratory Tract Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli
10 Respiration & Exercise Even in a race lasting less than a minute, the majority of energy generated must come from using oxygen to burn fuel, such as carbohydrates. The oxygen absorbed by the lungs is used to perform a process called aerobic metabolism, which was discussed briefly in the lecture on the Muscular System. Remember that slow and fast twitch muscle fibers produce energy via two forms of metabolism aerobic and anaerobic. Of the total amount of energy the racehorse needs to get from the starting gate to the finish line in a 5 furlong race, around 70% of this will come from aerobic metabolism. This underlies the importance of a well-functioning respiratory system. The remaining energy comes from anaerobic metabolism, which is a fast, but inefficient source of energy production. The respiratory system is one equine body system that training will actually not improve. While you might have heard that certain training regimens can build a strong respiratory system, numerous scientific studies have shown the reverse. The amount of air moved in and out by an unfit horse at a fixed speed will be the same when the horse is fully fit. What we as equine caretakers do have an impact on is the health of the respiratory structures. Unfortunately, respiratory stress and ailments are often human caused poor ventilation, dusty bedding or forage, and lack of turnout are often the root causes of respiratory distress. Management of the Respiratory System - IAD Inflammatory Airway Disease (IAD) is a common issue among stabled horses, especially those that are young. Common signs and symptoms of this ailment include: Persistent cough that lingers more than one month No fever Poor performance, taking longer to return to a normal resting respiration following exercise Mild, watery, or white nasal discharge, especially after exercise Most horses suffering from IAD maintain a good appetite and appear bright and alert, which can help you differentiate this issue from other infectious, and sometimes contagious, respiratory ailments. While diagnosis of IAD can be apparent from clinical signs, your veterinarian may choose to perform an endoscopic examination, which involves passing a small camera through the airways after exercise to see if mucous is present. Swabbing mucous may also be performed to rule out any bacterial or viral infections.
11 Prevention and good stable management practices are the best ways to manage this issue. Your first step should be identifying any contaminants/irritants that may be the cause of IAD. For example, horses suffering from IAD do better on paper or wood shavings rather than straw. While you may be limited on what you can change in a racing environment, you can implement the following to help reduce dust and contaminant exposure: Remove horses from the stall prior to cleaning stalls Minimize sweeping, raking, and other measures that can increase dust in the air Water down shedrows if raking is necessary Keep stall windows and barn doors open to increase airflow Pick up clutter in the barn and tack room to decrease areas where dust can settle Turnout as much as possible In addition to environmental adjustments, horses suffering from IAD are often treated with an anti-inflammatory medication to help treat airway inflammation and/or prescribed a bronchodilator, which is a category of medication that can help expand the airways and loosen mucous.
12 Respiratory Images Upper Airway
13 Respiratory Images Lower Airway
14 Self-Knowledge Checks 1. At rest, the normal respiration rate of a healthy adult horse is: a. 2 4 breaths per minute b breaths per minute c breaths per minute d breaths per minute 2. A horse that is having an issue with their pharynx would be having an issue with their: a. Upper respiratory tract b. Lower respiratory tract 3. Inhaled air will be filtered and cleaned in the: a. Hard Palate b. Epiglottis c. Nasal cavities d. Larynx % of resistance to airflow comes from the nasal passages. a. True b. False 7. Just above the heart the trachea divides into two tubes called: a. Bronchioles b. Alveoli c. Bronchi d. Larynx 8. This structure is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. a. Bronchi b. Alveoli c. Pharynx d. Cilia 9. The equine respiratory system can improve with training. a. True b. False 10. What management strategies can help reduce dust and contaminant exposure, reducing the risk of IAD? 5. The larynx is responsible for: a. Directing air into the trachea b. Producing vocal noises c. Controlling airflow into the lungs d. All the above 6. Which of the following are components of the larynx? (Circle all that apply) a. Pharynx b. Epiglottis c. Soft palate d. Bronchi e. Arytenoids
15 Answers 1. At rest, the normal respiration rate of a healthy adult horse is: b breaths per minute A healthy adult horse s normal respiration rate (the inhalation and exhalation of air) is 8 16 breaths per minute (bpm) 2. A horse that is having an issue with their pharynx would be having an issue with their: a. Upper respiratory tract The pharynx is part of the horse s upper respiratory tract 3. Inhaled air will be filtered and cleaned in the: c. Nasal cavities Air that is drawn into the nasal cavities through the nostrils is filtered and cleaned by moist, mucous membranes and tiny hairs called cilia % of resistance to airflow comes from the nasal passages. a. True A significant portion of the horse s nasal passages is unsupported by bone or cartilage this means when a horse s breathes during exercise, the nasal passages collapse inward, reducing the size of the airway and increasing resistance to airflow. It would be like it if you tried to take a deep breath in and someone placed pressure on the unsupported tissue of your nose (give it a try!). Research has shown that over 50%, with up to 80%, of airflow resistance comes from the nasal passages 5. The larynx is responsible for: d. All the above The larynx is responsible for all three functions listed 6. Which of the following are components of the larynx? (Circle all that apply) b. Epiglottis c. Soft palate e. Arytenoids The larynx is comprised of numerous structures that assist with main functions the epiglottis, soft palate, and arytenoids 7. Just above the heart the trachea divides into two tubes called: c. Bronchi The bronchi each enter into a lung 8. This structure is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. b. Alveoli Alveoli are tiny air sacs found at the end of each bronchiole. Around each alveolus is a thin membrane that allows for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide 9. The equine respiratory system can improve with training. b. False Training has not shown to improve the equine respiratory system the amount of air move in and out by an unfit horse at a fixed speed will be the same when the horse is fully fit. Equine caretakers can unfortunately do more harm than good to the respiratory system because of poor stable conditions 10. What management strategies can help reduce dust and contaminant exposure, reducing the risk of IAD? There are many management strategies one can implement to help reduce dust and contaminant exposure - removing horses prior to stall cleaning, minimizing sweeping or raking, watering down shedrows, opening windows and doors, picking up clutter, and turning out when possible
16 Glossary Aerobic Metabolism Is dependent on oxygen to break down fuel stores inhaled oxygen during aerobic exercise is carried to the muscles and liver to metabolize (utilize) carbohydrates and fats for the production of ATP, the energy source for muscle contraction. Exercise is classified as aerobic if the heart rate is less than 150 beats per minute. The waste products of aerobic metabolism are carbon dioxide, water, and heat Alveoli Tiny air sacs that form on the end of each bronchiole, allows for the gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide Anaerobic Metabolism Is not dependent on oxygen to break down fuel stores, provides a rapid means of producing a limited supply of energy during anaerobic exercise. Exercise is classified as anaerobic if the heart rate is greater than 150 beats per minute. In the absence of oxygen, only carbohydrates can be metabolized for ATP production and the waste products of anaerobic metabolism are heat and lactic acid Arytenoid Cartilages Located on each side of the horse s larynx, closes the opening of the trachea when swallowing Bronchi Two tubes that subdivide from the trachea, enters into each lung Bronchioles Smallest branches of bronchi that go all throughout the lungs Cilia Tiny hairs found in the nasal cavities, move in a wave-like action to help filter air Diaphragm Primary muscle used for breathing, separates the abdominal and chest cavities Endoscope An instrument used to visually examine internal parts of the horse Epiglottis Elastic cartilaginous structure that prevents food from entering the trachea, sits on top of the soft palate Esophagus Soft walled muscular tube that takes food from the mouth to the stomach Gaseous Exchange The removal of carbon dioxide to be exhaled and extraction of oxygen by the blood from inhaled air Hard Palate A bone that forms the roof of the mouth and base of the nasal cavity, separates the nasal cavity and mouth Inflammatory Airway Disease (IAD) Inflammation of the airway due to airway contaminants, such as dust and debris Larynx Directs air into the trachea, controls airflow into the lungs during breathing, and produces vocal sounds Lower Respiratory Tract Consists of the trachea (lower portion), bronchi, and lungs Lungs Spongy, elastic tissue that increases and decreases as the horse breathes
17 Nasal Cavities Contains sinuses, mucous membranes, and cilia to filter dust, germs, and debris Nasopharynx See pharynx Nostrils Soft-walled, cartilaginous structure that allows for air to be drawn in Pharynx Chamber lined with mucous membranes that connect the nasal passages to the larynx Soft Palate Continuation of the hard palate, responsible for separating the larynx from the esophagus Trachea A structure comprised of cartilaginous rings, takes air to the lungs Upper Respiratory Tract Consists of the nostrils, nasal passages, pharynx (nasopharynx), larynx, and trachea (upper portion)
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
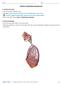 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
NAME PER DATE. membrane
 NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
NAME PER DATE Chapter 9, Section 1 Review Matching: 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae 6. epiglottis 7. larynx 8. mediastinum 9. nares 10. olfactory
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body
 In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
The Respiratory System Respiration Includes Pulmonary ventilation Air moves in and out of lungs Continuous replacement of gases in alveoli (air sacs) External respiration Gas exchange between blood and
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
Nasal Cavity. The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the. (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!)
 Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Structures Nasal Cavity The air breathed in the nose is filtered in the Nasal Cavity (It is also used to smell and to resonate the voice!) Nasal Cavity Then, it exits the naval cavity to the pharynx through
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Circulatory and Respiratory System. By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu
 Circulatory and Respiratory System By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu Content Standards 34.5 Gas exchange occurring in the respiratory system 34.1 Open and Closed circulatory systems linking
Circulatory and Respiratory System By: Kendall Taomoto, Czaresse Piano, and Lynn Luu Content Standards 34.5 Gas exchange occurring in the respiratory system 34.1 Open and Closed circulatory systems linking
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 1 Review of the Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 1-1 through 1-6. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 1-1. Identify
Lecture Overview. Respiratory System. Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition. Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11
 Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Martini s Visual Anatomy and Physiology First Edition Martini Ober Chapter 20 - Respiratory System Lecture 11 1 Lecture Overview Overview of respiration Functions of breathing Organs of the respiratory
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Respiration & Circulation
 Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
Objectives. Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology. Function of the Lungs/Heart. The lung is for gas exchange. Failure of the Lungs/Heart
 Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Module A2: Upper Airway Anatomy & Physiology Objectives Classify epithelial tissue based on cell type and tissue layers. Identify location of tissue epithelium in the respiratory system. Describe the major
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
Anatomy of the Lungs. Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy
 Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy of the Lungs Dr. Gondo Gozali Department of anatomy 1 Pulmonary Function Ventilation and Respiration Ventilation is the movement of air in and out of the lungs Respiration is the process of gas
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Circulatory and Respiratory
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Respiratory System. All I need is the air that I breathe
 Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
Respiratory System All I need is the air that I breathe Men go abroad to wonder at the heights of mountains, at the huge waves of the sea, at the long courses of the rivers, at the vast compass of the
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human body systems Questionnaires, coding schemes, analysis and results
 Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
Homi Bhabha Centre for Science Education Tata Institute of Fundamental Research V.N. Purav Marg, Mankhurd, Mumbai 400088 Sindhu Mathai PhD project on Visual and Verbal literacies in the context of human
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
