A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
|
|
|
- Marjory Bailey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS) DipTp (AS) DipTp (SP)
2 KEY NOTES 1. Patients with a pattern of Recurrent, Severe, disabling headaches associated with Nausea and photophobia/phonophobia and who have a normal neurological exam should be considered to have MIGRAINE 2. Oral Triptans for acute treatment of all severities of Migraine if previous attacks were NOT controlled by Analgesics a. NEVER use Opioids for Migraine 3. If aura is a. Purely negative b. Very rapid in onset c. Very short i. Consider TIA 4. Patients with Headaches and Red flag should be referred 5. Patients with FIRST Thunderclap must be referred 6. Intracranial Hypotension should be considered in anyone whose headaches worsen on assuming an upright position (or become worse during the day 7. Conversely intracranial Hypertension should be considered in anyone whose headaches worsen when lying down or bending over 8. Consider Giant Cell Arteritis in anyone over 50 with New or Changed headaches 9. Diagnosis of Tension Type Headache in patients with normal neurological exam with Bilateral, Non-disabling headache 10. Secondary Mimics of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgia so must be referred 11. When patient presents with Frequent, Brief, Unilateral headache with Autosomal features Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgia should be considered 12. When a patient presents with chronic Daily Headache that is purely Unilateral, Hemicrania Continuum should be considered. 13. Hemicrania Continuum secondary mimics so refer
3 14. Anyone presenting with NEW Daily persistent Headache Refer. Secondary causes could be a. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage b. Giant Cell Arteritis c. Raised intracranial Pressure d. Reduced Cerebro-Spinal Pressure e. Post Trauma 15. Patients with Headaches AND Red Flag refer 16. Patients with First headache or Change in headache must have a. Clinical Exam b. Blood pressure c. Neurological exam which includes i. Fundoscopy ii. Cranial Nerve assessments 1. Pupils 2. Fields 3. Ocular movements 4. Facial Power and Sensation 5. Bulbar function Soft Palate, Tongue movement iii. Assessment of all 4 limbs 1. Tone, Power, Reflexes, Coordination iv. Plantar Responses v. Assessment of gait including Heel/Toe walking
4 Characteristics Unilateral Pulsating Moderate to Severe Builds up over minutes to hours Lasts up to 72 hours Disabling Aggravated by physical activity Nausea Photophobia/Phonophobia PRIMARY HEADACHES MIGRAINE Treatment of Acute Presentations 1. NSAIDS (avoid Aspirin and Ibuprofen in Asthma) a. Aspirin b. Paracetamol c. Ibuprofen 2. Oral Triptans a. Oral Triptans for acute treatment of all severities of Migraine if previous attacks were NOT controlled by Analgesics b. NEVER use Opioids for Migraine 3. Oral or Rectal Emetics Prophylaxis 1. B blockers Asthma Anxiety Diabetes Bradycardia Peripheral Vascular Disease Depression 2. Tricyclic Anti-dep Angle Closure Glaucoma Depression TTH Sleep Disturb 3. Topiramate Angle closure glaucoma Obesity Pregnancy Renal Stones 4. Valproate Obesity Depression Pregnancy Liver Disease
5 Characteristics Bilateral Non-disabling Tight or Pressing Not aggravated by physical activity Acute Treatment Paracetamol, Aspirin Prophylaxis Amitripoline TENSION TYPEHEADACHES TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALALGIA Characteristics Unilateral in Trigeminal Distribution Severe Ipsilateral cranial autosomal features Short Duration 15minutes to 3 hours Starts and ceases abruptly There may be background headache between attacks Secondary mimics need to be eliminated so must refer TACS are rare and characterised by attacks of severe UNILATERAL pain in the trigeminal distribution. They are associated with Prominent Ipsilateral cranial autonomic features. Types of TAC 1. Cluster Headaches (1:1000) 2. Paroxymal Hemicrania PH (1:50000) 3. Short Lasting Unilateral Neuralgiform Headache with Conjunctival Injection and Tearing (SUNCT) 4. Short Lasting Unilateral Neuralgiform Headache with Cranial Autonomic Symptoms (SUNA) Cluster Headaches 1. Severe 2. Strictly Unilateral 3. Located in combination of trigeminal roots a. Orbital
6 b. Supraorbital c. Temporal Region 4. Ipsilateral autonomic features MUST occur with an attack 5. Starts and ceases abruptly 15 minutes to 3 hours 6. Patient Restless 7. Frequency 1 every second day to 8 per day 8. May be background headache between attacks and migranous symptoms may be present 9. There is often a striking circadian rhythm a. Attacks same time each day b. Clusters same time each year Paroxymal Hemicrania, SUNCT and SUNA have similar characteristics to Cluster Headaches but the duration of attacks vary. WHEN A PATIENT PRESENTS WITH FREQUENT, BRIEF UNILATERAL HEADACHES WITH AUTONOMIC FEATURES A TRIGEMINAL AUTONOMIC CEPHALALGIA HEADACHE SHOULD BE CONSIDERED. PATIENTS WITH NEW SUSPECT TAC SHOULD BE REFERRED FOR ASSESSMENT. Acute Treatment Subcutaneous injection of sumatriptan Nasal sumatriptan Prophylaxis Verapamil
7 Other Primary and Pseudo Primary Headaches Characteristics Continuous Purely Unilateral Waxes and Wanes but NEVER goes May also have brief stabs HEMICRANIA CONTINUUA Secondary mimics are common so refer Treatment Indomethacine NEW DAILY PERSISTENT HEADACHES Remember that this is not a diagnosis but a description. Can be Primary or Secondary. Must consider Secondary aetiologies Must allow 3/12 before diagnosis is made (really chronic) MEDICINE OVERUSE HEADACHE This is not a primary headache but is often misdiagnosed as such. Must be excluded particularly in (New) Daily Persistent Headaches All medications can produce MOH
8 SECONDARY HEADACHES Consider in a patient with 1. NEW headache 2. CHANGE in headache patterns Neurological exam which includes 1. Fundoscopy 2. Cranial Nerve assessments a. Pupils b. Fields c. Ocular movements d. Facial Power and Sensation e. Bulbar function Soft Palate, Tongue movement 3. Assessment of all 4 limbs a. Tone, Power, Reflexes, Coordination 4. Plantar Responses 5. Assessment of gait including Heel/Toe walking Secondary headaches should be considered in patients with NEW onset headaches or headaches that differ from their usual headaches. RED FLAG features should be considered. The mnemonic SNOOP T helps.
9 RED FLAG Features : 1. S Systemic Symptoms or Secondary Risk Factors a. FEVER, WEIGHT LOSS, KNOWN CANCER, HIV, IMMUNOSUPPRESSION, PATIENTS WITH RISK FACTORS FOR CEREBRAL THROMBOSIS, JAW CLAUDICATION, VISUAL DISTURBANCE 2. N Neurological Symptoms or Abnormal Neurological Signs in Examination a. Symptoms : CONFUSION, IMPAIRED ALERTNESS, DROWSINESS, LIMB WEAKNESS, COGNITIVE DISTURBANCE b. Optometry Based Signs : Neurological Screen, Fundoscopy, Pupils, Colour Perception, Ocular Motility 3. O Onset a. FIRST AND WORST HEADACHE, THUNDERCLAP HEADACHE, SUDDEN OR ABRUPT FROM SLEEP (but remember that migraine is the most frequent cause of morning HAs), PROGRESSIVELY WORSENING.NEW ONSET HEADACHES IN PATIENTS OVER 50,PARIENTS WITH KNOWN CANCER, PATIENTS WITH HIV. 4. O Older a. NEW ONSET OR PROGRESSIVE IN OVER 50s. (Temporal Arteritis could also be associated with jaw claudication and temporal tenderness) 5. P Previous Headache History a. FIRST HEADACHE OR FUNDAMENTALLY DIFFERENT FROM EXISTING HEADACHE (Significant change in features, frequency, severity, associated symptoms) 6. T Triggered Headaches a. HEADACHE PRECIPITATED BY PHYSICAL EXERTION OR VALSALVA ACTIVITIES(coughing, straining, sneezing) HEADACHE THAT CHANGES WITH POSTURE
10 The following are warning signs or "red flags" for potential secondary headache: 1. New headache in a patient aged over 50 consider Temporal Arteritis 2. First presentation of thunderclap onset. Refer immediately to hospital for exclusion of subarachnoid haemorrhage. intracranial haemorrhage, meningitis, cerebral thrombosis. 3. For patients with headache and features suggestive of infection of the central nervous system(such as fever, rash), refer immediately to hospital. 4. Headache with features suggestive of raised intracranial pressure : changing with posture; valsalva headache (triggered by coughing, sneezing, bending, heavy lifting, straining); Fever; History of HIV or cancer; Focal or non-focal symptoms or signs; papilloedema. Refer urgently. 5. Consider MRI for patients presenting with a trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia. 6. Consider intracranial hypotension in all patients with headache developing or worsening after assuming an upright posture. Refer such patients to a neurologist or headache clinic.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS
 HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
HEADACHES THE RED FLAGS FAYYAZ AHMED CONSULTANT NEUROLOGIST HON. SENIOR LECTURER HULL YORK MEDICAL SCHOOL SECONDARY VS PRIMARY HEADACHES COMMON SECONDARY HEADACHES UNCOMMON BUT SERIOUS SECONDARY HEADACHES
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly North West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0
 Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Headache Pain Generators
 Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Headache. Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016
 Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine. Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital
 Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Managing Headache in Acute Medicine Ben Lovell Consultant Physician in Acute Medicine University College London Hospital Some ED headache stats Arrive by ambulance 31% Median age 39 Worst ever headache
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Headache and Facial Pain. Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology
 Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017
 Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES
 GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
GENERAL APPROACH AND CLASSIFICATION OF HEADACHES CLASSIFICATION Headache is one of the most common medical complaints. Most of the population will have experienced headache, and over 5% will seek medical
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline. Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford
 Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Reflections on NICE Headache Guideline Dr Kay Kennis GPwSI in Headache, Bradford Overview The process of guideline development illustrated with the headache guideline Reflections on the process Key recommendations
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton. September Headache
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Pause for thought. Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist
 Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
Pause for thought Dr Jane Anderson Consultant Neurologist Which is the top cause of years lived with disability worldwide? 1. COPD 2. Low Back pain 3. Diabetes 4. Migraine with medication overuse headache
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. No relevant financial relationships
 Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
25/09/2018 HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
Diagnosing headache. The clinician should approach the diagnosis of. Secondary headache. Primary headache. Blue and red flag headaches
 Headache THEME Diagnosing headache BACKGROUND A systematic approach to the diagnosis of primary and secondary headache disorders requires the measurement of the frequency and the duration of headache.
Headache THEME Diagnosing headache BACKGROUND A systematic approach to the diagnosis of primary and secondary headache disorders requires the measurement of the frequency and the duration of headache.
July 2012 Target Population. Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings.
 Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND
 MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
2) Headache - Dr. Hawar
 2) Headache - Dr. Hawar Headache is caused by traction, displacement, inflammation, vascular spasm, or distention of the painsensitive structures in the head or neck. Isolated involvement of the bony skull,
2) Headache - Dr. Hawar Headache is caused by traction, displacement, inflammation, vascular spasm, or distention of the painsensitive structures in the head or neck. Isolated involvement of the bony skull,
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
Migraine Management. Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital
 Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Migraine Management Dr Helen Brown Director of Neurology and Stroke The Princess Alexandra Hospital Referral Criteria for Migraine Migraine Management Migraine Diagnosis Spot on Health Migraine pathway
Overview INTRODUCTION 3/15/2018. Headache Emergencies. Other way to differentiate between them? Is there an easy way to differentiate between them?
 Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
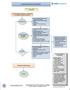 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
PRIORITIES AND CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS FORUM MANAGEMENT OF ADULT HEADACHE
 PRIORITIES AND CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS FORUM MANAGEMENT OF ADULT HEADACHE o This is a new guideline produced jointly by GPs and Consultant Neurologists. o The aim is to reduce referrals to Consultants for
PRIORITIES AND CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS FORUM MANAGEMENT OF ADULT HEADACHE o This is a new guideline produced jointly by GPs and Consultant Neurologists. o The aim is to reduce referrals to Consultants for
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care
 Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology)
 Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
Headaches. Mini Medical School. November 10, 2016 A. Laine Green MSc, MD FRCP(C) Assistant Professor Department of Medicine (Neurology) Artist Agnes Cecile Disclosures I have received an honorarium from
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist
 Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist Wednesday 10 th of April 2019 Summary Why does it matter? Classification and diagnosis Who to refer / scan? Serious
Headache Management in Primary Care Dr Niranjanan Nirmalananthan Consultant Neurologist Wednesday 10 th of April 2019 Summary Why does it matter? Classification and diagnosis Who to refer / scan? Serious
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Headache. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Classification and WHO ICD-10NA Codes
 Classification and WHO ICD-10NA Codes IHS WHO Diagnosis ICHD-II ICD-10NA [and aetiological ICD-10 code for secondary headache disorders] code code 1. [G43] Migraine 1.1 [G43.0] Migraine without aura 1.2
Classification and WHO ICD-10NA Codes IHS WHO Diagnosis ICHD-II ICD-10NA [and aetiological ICD-10 code for secondary headache disorders] code code 1. [G43] Migraine 1.1 [G43.0] Migraine without aura 1.2
Measure Components Numerator Statement
 MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
MEASURE #5: OVERUSE OF OPIOID CONTAINING MEDICATIONS FOR PRIMARY HEADACHE DISORDERS Headache For Quality Improvement Only. Not to be used for Public Reporting or Accountability Measure Description Percentage
HEADACHE. Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit}
 F:M=3:1 Affects 15% adults HEADACHE Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit} Primary: Migraine (with aura 1/3, without aura 2/3) Tension Cluster Other Secondary Neuralgia
F:M=3:1 Affects 15% adults HEADACHE Summary of British Association on the Study of Headaches {click to visit} Primary: Migraine (with aura 1/3, without aura 2/3) Tension Cluster Other Secondary Neuralgia
11/10/2017. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives
 THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
HEADACHE P of o. G. G Z u Z l u iani
 HEADACHE Prof. G. Zuliani General Statistics Everyone has headaches (HA) Second most common complain after back pain in the population More than 80 million Emergency Room visits in USA per year Frequency
HEADACHE Prof. G. Zuliani General Statistics Everyone has headaches (HA) Second most common complain after back pain in the population More than 80 million Emergency Room visits in USA per year Frequency
Managing Headache in General Practice 2nd Edition
 1 Managing Headache in General Practice 2nd Edition Dr Raeburn Forbes Consultant Neurologist November 2012 Email: elaine.johnston@southerntrust.hscni.net Department of Neurology Craigavon Area Hospital
1 Managing Headache in General Practice 2nd Edition Dr Raeburn Forbes Consultant Neurologist November 2012 Email: elaine.johnston@southerntrust.hscni.net Department of Neurology Craigavon Area Hospital
Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description
 Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC. Associate Director New York Headache Center
 Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers
 Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Brain and Central Nervous System Cancers NICE guidance link: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta121 Clinical presentation of brain tumours History and Examination Consider immediate referral Management
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes. Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Goals Distinguish primary from secondary headaches Recognize typical histories
Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Goals Distinguish primary from secondary headaches Recognize typical histories
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Headache. Karen Thaxter
 Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture
 Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Cluster headache (CH): epidemiology, classification and clinical picture Toomas Toomsoo, M.D. Head of the Center of Neurology East Tallinn Central Hospital 1 INTRODUCTION Cluster headache - known as trigeminal
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION. Headaches HEADACHE DISORDERS. R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP
 Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
Patient with Lots of NTERNATIONAL CLASSIFICATION Headaches of R. Allan Purdy, MD, FRCPC,FACP HEADACHE DISORDERS Professor of Medicine (Neurology) Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada 2nd edition (ICHD-II)
6/4/2018. Headache. Headaches. Headache. Migraine Headaches. Headache. Red Flag signs and symptoms. Imaging CT without contrast.
 Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster?
 HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster? Hussien H. Rizk, MD Cairo University Medical School ١ Headache Second most common o symptom (after pain) Migraine alone afflicts 12
HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster? Hussien H. Rizk, MD Cairo University Medical School ١ Headache Second most common o symptom (after pain) Migraine alone afflicts 12
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias
 Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
Chapter 2 Diagnosis of Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Mark J. Stillman Introduction The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) refer to a specific group of primary headaches characterized by unilaterality,
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
How to remove the headache of dealing with headaches. Dr. Stefan Schumacher Consultant Neurologist Salford Royal Hospital
 How to remove the headache of dealing with headaches Dr. Stefan Schumacher Consultant Neurologist Salford Royal Hospital Case 30 y old woman Sudden headache Vomiting, dizziness, photophobia Recurrent migraines
How to remove the headache of dealing with headaches Dr. Stefan Schumacher Consultant Neurologist Salford Royal Hospital Case 30 y old woman Sudden headache Vomiting, dizziness, photophobia Recurrent migraines
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS:
 CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS: 1. Have any of you heard of cluster headaches? 2. Do you know someone who suffers from cluster headaches? 1 WHAT ARE CLUSTER HEADACHES? A neurological
CLUSTER HEADACHES: THE WORST PAIN POSSIBLE? QUESTIONS: 1. Have any of you heard of cluster headaches? 2. Do you know someone who suffers from cluster headaches? 1 WHAT ARE CLUSTER HEADACHES? A neurological
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Primary Headache Prevalence % (95% CI) Migraine without aura 9 (7-9) Migraine with aura 6 (5-8)
 Primary Headache Prevalence % (95% CI) Migraine without aura 9 (7-9) Migraine with aura 6 (5-8) Episodic tension-type headache 66 (62-69) Chronic tension-type headache 3 (2-5) Cluster headache 0.1 (0 1)
Primary Headache Prevalence % (95% CI) Migraine without aura 9 (7-9) Migraine with aura 6 (5-8) Episodic tension-type headache 66 (62-69) Chronic tension-type headache 3 (2-5) Cluster headache 0.1 (0 1)
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
The trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) are a group of. Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias By Mark Burish, MD, PhD
 Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Downloaded from https://journals.lww.com/continuum by SruuCyaLiGD/095xRqJ2PzgDYuM98ZB494KP9rwScvIkQrYai2aioRZDTyulujJ/fqPksscQKqke3QAnIva1ZqwEKekuwNqyUWcnSLnClNQLfnPrUdnEcDXOJLeG3sr/HuiNevTSNcdMFp1i4FoTX9EXYGXm/fCfrbTavvQSUHUH4eazE11ptLzgCyEpzDoF
Improving Headache Care
 Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre Improving Headache Care (without breaking the bank) Implementation of useful referral guidelines Scale of the problem Over 10% population suffer from headache 2%
Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre Improving Headache Care (without breaking the bank) Implementation of useful referral guidelines Scale of the problem Over 10% population suffer from headache 2%
PREVALENCE BY HEADACHE TYPE
 CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
CLINICAL CLUES AND CLINICAL RULES: PRIMARY VS SECONDARY HEADACHE * Based on a presentation by David W. Dodick, MD ABSTRACT Headache is a common condition, accounting for many specialist office visits annually.
Neuralgias tend to be sudden, brief, intermittent severe, stabbing or lightning pains or electric shock sensations.
 Neuralgia is the term used to describe pain arising from a nerve. There are many different neuralgias which have been described in the medical literature, but I will only touch upon a few more common ones.
Neuralgia is the term used to describe pain arising from a nerve. There are many different neuralgias which have been described in the medical literature, but I will only touch upon a few more common ones.
Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease?
 APPENDIX 1 Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease? 1. Does the patient have one or more of these? Bulbar features Limb features Respiratory features Cognitive features (rare)
APPENDIX 1 Painless, progressive weakness Could this be Motor Neurone Disease? 1. Does the patient have one or more of these? Bulbar features Limb features Respiratory features Cognitive features (rare)
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After
 Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
Headaches in Pregnancy Before, During, and After Robert Kaniecki, MD Director, UPMC Headache Center Assistant Professor of Neurology University of Pittsburgh Headaches and Pregnancy Pre-pregnancy counseling
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Secondary Headaches: A Strategic Approach. Emerg Med 40(4):18, 2008
 Secondary Headaches: A Strategic Approach Emerg Med 40(4):18, 2008 Headaches are common complaints in the emergency department, but the causes of secondary headaches are often misdiagnosed. The authors
Secondary Headaches: A Strategic Approach Emerg Med 40(4):18, 2008 Headaches are common complaints in the emergency department, but the causes of secondary headaches are often misdiagnosed. The authors
Classification of headaches
 Classification of headaches Primary headaches OR Idiopathic headaches Secondary headaches OR Symptomatic headaches THE HEADACHE IS ITSELF THE DISEASE NO ORGANIC LESION IN THE BEACKGROUND TREAT THE HEADACHE!
Classification of headaches Primary headaches OR Idiopathic headaches Secondary headaches OR Symptomatic headaches THE HEADACHE IS ITSELF THE DISEASE NO ORGANIC LESION IN THE BEACKGROUND TREAT THE HEADACHE!
Controlling Migraine Pain
 Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present
 23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
23 How Cluster Headache and Other Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Present Henrik Winther Schytz 1. Cristina Tassorelli 2. Messoud Ashina 1 1 Glostrup Hospital, University of Copenhagen, Glostrup, Copenhagen,
Pearls in Child Neurology. Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida
 Pearls in Child Neurology Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida Outline 1. Autism 2. Bell s Palsy 3. First unprovoked seizure in children 4. Migraine headache Objectives 1.
Pearls in Child Neurology Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida Outline 1. Autism 2. Bell s Palsy 3. First unprovoked seizure in children 4. Migraine headache Objectives 1.
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD
 CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept
 Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Migraine in Children. Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014
 Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
florida child neurology
 Headaches florida child neurology You re sitting at your desk, working on a difficult task, when it suddenly feels as if a belt or vice is being tightened around the top of your head. Or you have periodic
Headaches florida child neurology You re sitting at your desk, working on a difficult task, when it suddenly feels as if a belt or vice is being tightened around the top of your head. Or you have periodic
Headache. Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine
 Headache Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine SOURCE OF HEAD PAIN (NOCICEPTIVE STRUCTURES) Intracranial Extracranial arteries of circle of Willis dura, dural arteries
Headache Anna Morenkova, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Neurology UC Irvine SOURCE OF HEAD PAIN (NOCICEPTIVE STRUCTURES) Intracranial Extracranial arteries of circle of Willis dura, dural arteries
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Treatments for migraine
 Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Treatments for migraine Information for patients and carers Department of Neurology Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Contents Page About this leaflet Abortive medication for migraine Painkillers Antisickness medication
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Teeth and supporting tissues, e.g. dental. Maxillary sinus, salivary gland
 MJDF Facial Pain. Patricia Thomson Always start with SOCRATES S site O onset C character R radiation A associated features T timing E exacerbating/relieving factors S severity Examine the cranial nerves
MJDF Facial Pain. Patricia Thomson Always start with SOCRATES S site O onset C character R radiation A associated features T timing E exacerbating/relieving factors S severity Examine the cranial nerves
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b
 UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011
 Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine
 GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
GUIDELINES SIGN on the pharmacological management of migraine STEVE CHAPLIN In February 2018, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) published a new guideline on the pharmacological management
The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache Key Words
 Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
Paper Eur Neurol 1994;34(suppl 2):35-39 P.J. Peter J. Goadsby Department of Neurology, The Prince Henry Hospital, Little Bay, Sydney, NSW, Australia The Clinical Profile of Sumatriptan: Cluster Headache
