Relationship Between Isolated Mild Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation in Second-Trimester Fetuses and Postnatal Congenital Cardiac Disorders
|
|
|
- Malcolm Cecil West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Relationship Between Isolated Mild Tricuspid Valve Regurgitation in Second-Trimester Fetuses and Postnatal Congenital Cardiac Disorders Jizi Zhou, MD, PhD, Yun Zhang, MD, Yonghao Gui, MD, PhD, Chen Chu, MD, PhD, Congcong Zhang, MD, Qiongjie Zhou, MD, Ying Zhang, MD, PhD, Xiaotian Li, MD, PhD, Yingliu Yan, MD Article includes CME test Received August 16, 2013, from the Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China (J.Z., Yu.Z., Q.Z., Yi.Z., X.L., Y.Y.); Children s Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China (Y.G., C.C., C.Z.); and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Female Reproductive Endocrine- Related Diseases, Shanghai, China (X.L.). Revision requested October 17, Revised manuscript accepted for publication January 6, This study was supported by National High Technology Research and Development Program 863 under grant 2007AA02Z442. Drs Jizi Zhou and Yun Zhang are co-first authors. Address correspondence to Xiaotian Li, MD, PhD, or Yingliu Yan, MD, Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Fudan University, 419 Fangxie Rd, Shanghai, China. xiaotianli555@163.com, yan_ying_liu@hotmail.com doi: /ultra Objectives In most cases, the clinical importance of fetal isolated mild tricuspid valve regurgitation is not known. This study evaluated the relationship between fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation in the general obstetric population and postnatal congenital cardiac disorders. Methods Detailed fetal echocardiography was done between 18 and 24 weeks gestation to detect tricuspid regurgitation and to exclude complicated cardiac defects. Routine second-trimester targeted organ scans were also performed to exclude extracardiac defects. Follow-up was done until birth. After birth, the cardiac anatomy of the neonates was examined by echocardiography. The association between fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation and postnatal congenital cardiac disorders was assessed by logistic regression analysis. Results No major cardiac disorders were found postnatally. Some minor disorders were found, including a patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and small ventricular septal defects. Fetuses with isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation had a significantly higher likelihood of having ventricular septal defects (odds ratio, 5.80; P =.027) or a patent foramen ovale with atrial septal defects and a patent ductus arteriosus (odds ratio, 11.61; P =.007). There was no significant association between tricuspid regurgitation and an isolated patent foramen ovale or a patent foramen ovale with atrial septal defects in neonates. Conclusions Fetuses with isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation in the second trimester did not have a higher incidence of major cardiac disorders after birth. The presence of isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation may be an indication of minor postnatal congenital cardiac disorders. Key Words congenital cardiac disorders; echocardiography; fetal; isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation; pediatric ultrasound; postnatal F etal tricuspid valve regurgitation occurs when the right ventricular pressure exceeds the right atrial pressure during systole and results from imperfect coaptation of the tricuspid valve. The development of color Doppler sonographic techniques has enabled relatively frequent detection of tricuspid regurgitation. To date, the evidence has been contradictory as to whether fetal tricuspid regurgitation is predictive of other disorders. In some studies, fetal tricuspid regurgitation during the first trimester was reported to be predictive of chromosomal abnormalities 1 3 or cardiac defects by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
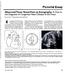
2 Similarly, Anuwutnavin et al 5 found that in women with high-risk pregnancies, fetal tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester was a sonographic marker that identified fetuses with Down syndrome and was associated with cardiac defects in fetuses with normal chromosomes. In addition, tricuspid regurgitation has been reported to be one of the strongest predictors of adverse neonatal outcomes in fetuses with intrauterine growth restriction. 6 However, another study 7 found that fetal tricuspid regurgitation that occurred during the second trimester was benign in fetuses with normal cardiac anatomy. Gembruch and Smrcek 8 reported that tricuspid regurgitation was a frequent finding during Doppler echocardiography, and in most cases, it was an isolated, transient finding with little progression in the severity and breadth of the tricuspid regurgitation jet. However, few studies have been done in the general obstetric population in which the postnatal cardiac anatomy of fetuses with isolated tricuspid regurgitation has been examined in detail. It is not known whether the presence of fetal isolated tricuspid regurgitation alone during the second trimester is a valuable predictor of postnatal cardiac anatomy in the general obstetric population. The purpose of this study was to determine whether there is an association between fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation and postnatal congenital cardiac disorders within the general obstetric population. The clinical importance of fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation was also assessed. Materials and Methods Participants This prospective cohort study was conducted between November 2008 and October 2010 at the Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital affiliated with Fudan University. Target organ sonographic examinations are routinely performed on all pregnant women between 18 and 24 gestational weeks in the Ultrasound Department of the hospital. The gestational age was calculated on the basis of the date of the last menstrual period and corrected by using the crown-rump length at the first-trimester sonographic examination. During this visit, the maternal and gestational ages were recorded. The inclusion criteria for this study were singleton pregnancies with viable fetuses and planned deliveries at our hospital. The exclusion criteria were pregnancies with multiple gestations, major fetal malformations, fetal aneuploidy, and preterm delivery. Follow-up was conducted in all enrolled pregnant women until birth. The neonates underwent echocardiography for examination of cardiac anatomy. In addition, the gestational age at birth and birth weight were recorded. The study cohort was categorized into two groups according to the presence or absence of prenatal tricuspid regurgitation: a tricuspid regurgitation group and control group. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Children s Hospital of Fudan University. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants. Fetal and Neonatal Echocardiography A single operator, with more than 20 years of prenatal diagnostic ultrasound experience, performed fetal echocardiography. A Voluson E8 ultrasound machine (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI) with a 3 6-MHz abdominal probe was used. Efforts were made to minimize excessive fetal movement during image acquisition. The images obtained included a 4-chamber view, views of the left and right ventricular outflow tracts, a 3-vessel and trachea view, a short-axis view, and a view of the abdominal circumference level to localize the aorta and inferior vena cava. Tricuspid regurgitation was recorded during ventricular contraction in the apical or basal 4-chamber view using color Doppler imaging with an angle of 0 to 30 (Figure 1). The size of the color box was set to 60 cm/s when possible. The degree of tricuspid regurgitation was based on the length of the jet into the atrium (ie, the distance from the Figure 1. Sonogram from a fetus with normal heart anatomy at 21.6 weeks gestation. The image shows reversed flow (arrow) across the tricuspid valve at the level of the 4-chamber view. LA indicates left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; and RV, right ventricle J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
3 tricuspid valve to the opposite atrial wall) as follows: mild, less than 1/3; moderate, 1/3 to 2/3; and severe, greater than 2/3. 7 Neonates underwent postnatal echocardiography, done by 2 professional pediatric cardiologists, within 5 days of birth. In this study, ventricular septal defects were defined by visualization of a left-right shunt at the level of the interventricular septum. Deficient areas in the interatrial septum that were 3 mm or greater in size were defined as atrial septal defects. Atrial septal defects that are less than 3 mm in size are reported to close naturally and need not be followed. 9 A patent foramen ovale was defined by visualization of an area of an unclosed foramen ovale of 5 mm or greater with blood flow across it. Two shunts occurring across the interatrial septum was defined as a patent foramen ovale with concomitant atrial septal defects. A patent ductus arteriosus was defined by left-right shunting that passed from the descending aorta through the ductus arteriosus and to the pulmonary artery. Statistical Analysis SPSS version 17.0 software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY) was used for statistical analysis. A t test was used to compare the maternal age, gestational age at diagnosis and birth, and fetal birth weight between the tricuspid regurgitation and control groups. The percentages of neonates with congenital cardiac defects in the tricuspid regurgitation and control groups were compared by a χ 2 test or Fisher exact test. Fetuses with tricuspid regurgitation were compared to those without tricuspid regurgitation, and univariate logistic regression analysis was used to determine odds ratios for various congenital cardiac disorders. P <.05 was considered statistically significant. ages at diagnosis were similar between the tricuspid regurgitation and control groups. Fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester was not associated with gestational age at birth or birth weight. Fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester was identified in 6.71% of fetuses examined (86 of 1281). Only 2 and 8 cases of muscular ventricular septal defects were detected in the tricuspid regurgitation and control groups, respectively. Only 1 case of inlet ventricular septal defects was identified in the tricuspid regurgitation group. The proportion of neonates with ventricular septal defects was significantly higher in the tricuspid regurgitation group than in the control group (3.49% versus 0.67%; P =.027). The deficient area was significantly larger in ventricular septal defect cases in the tricuspid regurgitation group compared to ventricular septal defect cases in the Figure 2. Flowchart of the study population. Results Initially, 1435 singleton pregnancies were enrolled in our study. Of these, 143 cases (9.96%) were excluded because the deliveries took place in other hospitals; 4 cases were eliminated for complex cardiac defects; 2 cases were excluded for extracardiac defects; and 5 cases were excluded for preterm labor. A total of 1281 neonates, including 86 cases in the tricuspid regurgitation group and 1195 cases in the control group, with normal healthy appearances and no obvious abnormalities or chromosomal disorders underwent echocardiography. The acquisition process for the study population is shown in Figure 2. General information regarding the two groups is listed in Table 1. The mean age at which postnatal echocardiography was done was similar between the groups (2.88 versus 2.67 days; P =.62). The mean maternal age and gestational Table 1. General Maternal and Obstetric Characteristics of the Study Population Tricuspid Regurgitation Present Absent Characteristic (n = 86) (n = 1195) P Maternal age, y ± ± Gestational age at diagnosis, wk ± ± Gestational age at birth, wk ± ± Birth weight, kg 3.3 ± ± Age at postnatal examination, d 2.88 ± ± Values were compared by an independent-samples t test and are presented as mean ± SD. J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
4 control group (mean ± SD, 2.50 ± 0.29 versus 1.69 ± 0.13 mm; P =.0142; Table 2). The proportion of patent foramen ovale cases that coexisted with atrial septal defects and a patent ductus arteriosus was significantly higher in the tricuspid regurgitation group than the control group (3.49% versus 0.33%; P=.007); however, there was no significant difference between the tricuspid regurgitation and control groups in the proportion of cases of an isolated patent foramen ovale or a patent foramen ovale that coexisted with atrial septal defects (5.81% versus 2.76%; P =.085; and 1.16% versus 0.42%; P =.316; Table 3 and Figure 3). The deficient area was slightly larger in atrial septal defect cases in the tricuspid regurgitation group compared with atrial septal defect cases in the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (3.95 ± 0.24 versus 3.49 ± 0.10 mm; P =.053; Table 2). Discussion Isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation was observed during the second trimester in 6.71% of the healthy fetuses examined in this cohort study. Postnatal data indicated that isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester was not associated with pregnancy outcomes and was not predictive of major cardiac disorders. However, Table 2. Comparison of Deficient Area Diameters in Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects Between the Tricuspid Regurgitation and Control Groups Deficient Area Tricuspid Regurgitation Diameter, mm Present Absent P ASD 3.95 ± 0.24 (n = 4) 3.49 ± 0.10 (n = 9).053 VSD 2.50 ± 0.29 (n = 3) 1.69 ± 0.13 (n = 8).0142 Values were compared by an independent-samples t test and are presented as mean ± SD. ASD indicates atrial septal defects; and VSD, ventricular septal defects. isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation was found to be associated with some minor cardiac disorders, including a patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects and, moreover, the sizes of the deficient areas of atrial and ventricular septal defects. A patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects are congenital cardiac disorders that are often hemodynamically insignificant and not considered cardiac malformations in light of their natural evolution. Most cases of a patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects spontaneously close during childhood, although there is evidence that these defects may be linked to secondary diseases if they persist into adulthood Therefore, although an association between the occurrence of fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester and postnatal cases of a patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects was found in this study, it is of limited clinical importance, since the tricuspid regurgitation was found to be associated with only minor postnatal congenital cardiac disorders. These findings, however, are contrary to results reported in some other studies of cardiac disorders. Pereira et al 4 and Volpe et al 14 found that tricuspid regurgitation was one of the sonographic markers for some major cardiac defects, mainly atrioventricular septal defects. The differing results may be due to the fact that tricuspid regurgitation was detected during the second trimester in our study, and most major cardiac disorders are identified by secondtrimester echocardiography. 15 Furthermore, the severity of the tricuspid regurgitation detected may also have contributed to the differences in results. Table 3. Cardiac Disorders in Neonates in the Tricuspid Regurgitation and Control Groups Tricuspid Regurgitation Present Absent Characteristic (n = 86) (n = 1195) P OR (95%CI) Normal heart anatomy 74 (86) 1145 (95.8) PFO Isolated PFO 5 (5.81) 33 (2.76) ( ) PFO and ASD 1 (1.16) 5 (0.42) ( ) PFO, ASD, and PDA 3 (3.49) 4 (0.33) ( ) VSD 3 (3.49) 8 (0.67) ( ) Values are presented as number (percent) where applicable. P values were analyzed by a Fisher exact test or a χ 2 test, and odds ratios were analyzed by univariate logistic regression analysis. ASD indicates atrial septal defects; CI, confidence interval; OR, odds ratio; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; PFO, patent foramen ovale; and VSD, ventricular septal defects J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
5 The underlying mechanism for the association between fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation and a patent foramen ovale, atrial septal defects, a patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects in neonates is unclear. These benign cardiac disorders represent examples of congenital lesions that are characterized by an abnormal hemodynamic exchange. The abnormal exchange is caused by incomplete closure of the cardiac septum, thus allowing ejection from the right side of the heart into the left side of the heart. We speculate that the presence of fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation may alter the flow dynamics in the right atrium, resulting in delayed closure of the interatrial septum, leading to a patent foramen ovale or atrial septal defects. In cases of ventricular septal defects, we infer that the lack of an interventricular septum might disturb the detachment of the tricuspid valve septum or anterior leaflet, which in turn would increase the chance of tricuspid valve regurgitation. 16 Apart from this situation, it is possible that undiagnosed maternal disease, maternal pharmacologic treatment, and fetal infections at any time during pregnancy could be responsible for the concomitant presence of fetal isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation and postnatal findings of minor cardiac disorders. 17 Although our data were derived from a single center, a relatively large sample size was used. A multicenter study could be conducted in the future to eliminate bias. Other limitations of this study were the relatively early time at which postnatal echocardiography was conducted and the Figure 3. Comparisons of the percentages of various cardiac disorders between the tricuspid regurgitation (TR) and control groups. ASD indicates atrial septal defects; PDA, patent ductus arteriosus; PFO, patent foramen ovale; and VSD, ventricular septal defects. *P <.05. lack of postnatal follow-up. There was still the likelihood of spontaneous closure of many of the minor cardiac disorders that were identified in our study. In conclusion, isolated mild tricuspid regurgitation during the second trimester is common in fetuses with normal heart anatomy, although tricuspid regurgitation may be useful as a prenatal sonographic marker for minor postnatal congenital cardiac disorders. Once a cardiac disorder, such as an atrial or ventricular septal defect, is identified, the necessary follow-up, if any, can be determined according to the type and size of the defect. References 1. Huggon IC, DeFigueiredo DB, Allan LD. Tricuspid regurgitation in the diagnosis of chromosomal anomalies in the fetus at weeks of gestation. Heart 2003; 89: Faiola S, Tsoi E, Huggon IC, Allan LD, Nicolaides KH. Likelihood ratio for trisomy 21 in fetuses with tricuspid regurgitation at the 11 to week scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: Falcon O, Faiola S, Huggon I, Allan L, Nicolaides KH. Fetal tricuspid regurgitation at the to week scan: association with chromosomal defects and reproducibility of the method. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: Pereira S, Ganapathy R, Syngelaki A, Maiz N, Nicolaides KH. Contribution of fetal tricuspid regurgitation in first-trimester screening for major cardiac defects. Obstet Gynecol 2011; 117: Anuwutnavin S, Wanitpongpan P, Chanprapaph P. Specificity of fetal tricuspid regurgitation in prediction of Down syndrome in Thai fetuses at weeks of gestation. J Med Assoc Thai 2009; 92: Makikallio K, Rasanen J, Makikallio T, Vuolteenaho O, Huhta JC. Human fetal cardiovascular profile score and neonatal outcome in intrauterine growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol2008; 31: Messing B, Porat S, Imbar T, Valsky DV, Anteby EY, Yagel S. Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding at various stages of pregnancy. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: Gembruch U, Smrcek JM. The prevalence and clinical significance of tricuspid valve regurgitation in normally grown fetuses and those with intrauterine growth retardation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1997; 9: Radzik D, Davignon A, van Doesburg N, Fournier A, Marchand T, Ducharme G. Predictive factors for spontaneous closure of atrial septal defects diagnosed in the first 3 months of life. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 22: Chang JK, Jien WY, Chen HL, Hsieh KS. Color Doppler echocardiographic study on the incidence and natural history of early-infancy muscular ventricular septal defect. Pediatr Neonatol 2011; 52: Ammash NM, Warnes CA. Ventricular septal defects in adults. Ann Intern Med 2001; 135: Schneider DJ. The patent ductus arteriosus in term infants, children, and adults. Semin Perinatol 2012; 36: J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
6 13. Calvert PA, Rana BS, Kydd AC, Shapiro LM. Patent foramen ovale: anatomy, outcomes, and closure. Nat Rev Cardiol 2011; 8: Volpe P, Ubaldo P, Volpe N, et al. Fetal cardiac evaluation at weeks by experienced obstetricians in a low-risk population. Prenat Diagn2011; 31: Volpe P, De Robertis V, Campobasso G, Tempesta A, Volpe G, Rembouskos G. Diagnosis of congenital heart disease by early and second-trimester fetal echocardiography. J Ultrasound Med2012; 31: Said SM, Burkhart HM, Dearani JA. Surgical management of congenital (non-ebstein) tricuspid valve regurgitation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu 2012; 15: Smrcek JM, Gembruch U. Longitudinal observations in normally grown fetuses with tricuspid valve regurgitation: report of 22 cases. Prenat Diagn 1999; 19: J Ultrasound Med 2014; 33:
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding at various stages of pregnancy
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 606 610 Published online 7 October 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1999 Mild tricuspid regurgitation: a benign fetal finding
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
Summary. HVRA s Cardio Vascular Genetic Detailed L2 Obstetrical Ultrasound. CPT 76811, 76825, _ 90% CHD detection. _ 90% DS detection.
 What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
ISUOG Basic Training. Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA. Basic training. Editable text here
 ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
ISUOG Basic Training Obtaining & Interpreting Heart Views Correctly Alfred Abuhamad, USA Learning Objectives 6, 7 & 8 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe how to assess cardiac situs
Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram
 JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
JDMS 23:143 149 May/June 2007 143 Fetal Echocardiography and the Routine Obstetric Sonogram SHELLY ZIMBELMAN, RT(R)(CT), RDMS, RDCS ASAD SHEIKH, MD, RDCS Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Objectives. Introduction 11/2/2015
 Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Systematic approach to Fetal Echocardiography. Pediatric Echocardiography Conference, JCMCH November 7, 2015 Rajani Anand Objectives Fetal cardiology pre-test Introduction Embryology and Physiology of
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
Anatomy & Physiology
 1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
1 Anatomy & Physiology Heart is divided into four chambers, two atrias & two ventricles. Atrioventricular valves (tricuspid & mitral) separate the atria from ventricles. they open & close to control flow
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome
 Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Journal of American Science 2014;10(9) http://www.jofamericanscience.org Congenital Heart Disease in Pediatric with Down's Syndrome Jawaher Khalid Almaimani; Maryam Faisal Zafir; Hanan Yousif Abbas and
Coarctation of the aorta: difficulties in prenatal
 7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
Disclosures. Outline. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Introduction. Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart
 Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
Sonographic Screening Examination of the Fetal Heart Lami Yeo, MD Director of Fetal Cardiology Perinatology Research Branch of NICHD / NIH / DHHS Bethesda, MD and Detroit, Michigan, USA Professor, Division
HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
ORIGINAL RESEARCH HDlive Silhouette Mode With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation for Assessment of the Fetal Heart Toshiyuki Hata, MD, PhD, Mohamed Ahmed Mostafa AboEllail, MD, Suraphan Sajapala, MD, Mari
Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley Lee, MD, Fernando Viñals, MD, Josep Maria Martinez, MD, PhD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Collaborative Study of 4-Dimensional Fetal Echocardiography in the First Trimester of Pregnancy Jimmy Espinoza, MD, Wesley Lee, MD, Fernando Viñals, MD, Josep Maria Martinez, MD, PhD,
Editorial. Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 1 9 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1096 Editorial Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: 1 9 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1096 Editorial Color and pulsed Doppler in fetal echocardiography A. ABUHAMAD
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT
 ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHIC APPROACH TO CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: THE UNOPERATED ADULT Karen Stout, MD, FACC Divisions of Cardiology University of Washington Medical Center Seattle Children s Hospital NO DISCLOSURES
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation
 First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function
 CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
Deok Young Choi, Gil Hospital, Gachon University NEONATES WITH EBSTEIN S ANOMALY: PROBLEMS AND SOLUTION
 Deok Young Choi, Gil Hospital, Gachon University NEONATES WITH EBSTEIN S ANOMALY: PROBLEMS AND SOLUTION Carpentier classification Chauvaud S, Carpentier A. Multimedia Manual of Cardiothoracic Surgery 2007
Deok Young Choi, Gil Hospital, Gachon University NEONATES WITH EBSTEIN S ANOMALY: PROBLEMS AND SOLUTION Carpentier classification Chauvaud S, Carpentier A. Multimedia Manual of Cardiothoracic Surgery 2007
Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different
 Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different methods with echocardiography Ying Zhang 1* * Corresponding author Email: baogoubei@hotmail.com Ai-Lu Cai 1 Email: caial_us@hotmail.com
Accuracy of prenatal diagnosis of fetal congenital heart disease by different methods with echocardiography Ying Zhang 1* * Corresponding author Email: baogoubei@hotmail.com Ai-Lu Cai 1 Email: caial_us@hotmail.com
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Screening for Critical Congenital Heart Disease Caroline K. Lee, MD Pediatric Cardiology Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships or conflicts of interest 1 Most Common Birth Defect Most
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS
 Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Appendix II: ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY ANALYSIS Two-Dimensional (2D) imaging was performed using the Vivid 7 Advantage cardiovascular ultrasound system (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee) with a frame rate of 400 frames
Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program
 DOI: 10.1002/pd.4372 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program Jodi I. Pike, Anita
DOI: 10.1002/pd.4372 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Early fetal echocardiography: congenital heart disease detection and diagnostic accuracy in the hands of an experienced fetal cardiology program Jodi I. Pike, Anita
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease by Fetal Echo M Selvarani Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiology,
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
 Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Early fetal echocardiography: Experience of a tertiary diagnostic service
 Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2015; 55: 552 558 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12379 Original Article Early fetal echocardiography: Experience of a tertiary diagnostic service Ritu
Australian and New Zealand Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2015; 55: 552 558 DOI: 10.1111/ajo.12379 Original Article Early fetal echocardiography: Experience of a tertiary diagnostic service Ritu
Natural history of innocent heart murmurs in newborn babies: controlled echocardiographic study
 F166 Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1998;78:F166 F170 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Natural history of innocent heart murmurs in newborn babies: controlled echocardiographic study Romaine Arlettaz, Nicholas Archer,
F166 Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 1998;78:F166 F170 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Natural history of innocent heart murmurs in newborn babies: controlled echocardiographic study Romaine Arlettaz, Nicholas Archer,
Congenital heart disease. By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics
 Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Congenital heart disease By Dr Saima Ali Professor of pediatrics What is the most striking clinical finding in this child? Learning objectives By the end of this lecture, final year student should be able
Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus*
 Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Br Heart J 1981; 46: 358-62 Identification of congenital cardiac malformations by echocardiography in midtrimester fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, ROBERT H ANDERSON From Guy's Hospital;
Complete atrioventricular septal defect identified during routine 19 week fetal anomaly ultrasound
 CASE REPORT Complete atrioventricular septal defect identified during routine Mark Hare Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital, Herston, QLD, Australia doi:10.1002/sono.12014 Introduction Complete atrioventricular
CASE REPORT Complete atrioventricular septal defect identified during routine Mark Hare Royal Brisbane and Women s Hospital, Herston, QLD, Australia doi:10.1002/sono.12014 Introduction Complete atrioventricular
Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study
 J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
J. Fetal Med. (March 2015) 2:27 32 DOI 10.1007/s40556-015-0038-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Fetal Pulmonary Veins During Early Gestation by Pulsed Doppler Ultrasound: A Feasibility Study Aldo L. Schenone
Methods PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
1805 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Trends and Outcomes After Prenatal Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Malformations by Fetal Echocardiography in a Well Defined Birth Population, Atlanta, Georgia, 1990 1994 EDUARDO
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Surgical Repair of Ventricular Septal Defect; Contemporary Results and Risk Factors for a Complicated Course
 Pediatr Cardiol (2017) 38:264 270 DOI 10.1007/s00246-016-1508-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical Repair of Ventricular Septal Defect; Contemporary Results and Risk Factors for a Complicated Course Maartje Schipper
Pediatr Cardiol (2017) 38:264 270 DOI 10.1007/s00246-016-1508-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical Repair of Ventricular Septal Defect; Contemporary Results and Risk Factors for a Complicated Course Maartje Schipper
Paediatrica Indonesiana. Echocardiographic patterns in asphyxiated neonates. Maswin Masyhur, Idham Amir, Sukman Tulus Putra, Alan Roland Tumbelaka
 Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 49 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Echocardiographic patterns in asphyxiated neonates Maswin Masyhur, Idham Amir, Sukman Tulus Putra, Alan Roland Tumbelaka Abstract Background
Paediatrica Indonesiana VOLUME 49 July NUMBER 4 Original Article Echocardiographic patterns in asphyxiated neonates Maswin Masyhur, Idham Amir, Sukman Tulus Putra, Alan Roland Tumbelaka Abstract Background
"Lecture Index. 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development.
 "Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
"Lecture Index 1) Heart Progenitors. 2) Cardiac Tube Formation. 3) Valvulogenesis and Chamber Formation. 4) Epicardium Development. 5) Septation and Maturation. 6) Changes in Blood Flow during Development.
Cardiac ultrasound protocols
 Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Cardiac ultrasound protocols IDEXX Telemedicine Consultants Two-dimensional and M-mode imaging planes Right parasternal long axis four chamber Obtained from the right side Displays the relative proportions
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus*
 Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
Br Heart J 1980; : 51 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlates in the fetus* LINDSEY D ALLAN, MICHAEL J TYNAN, STUART CAMPBELL, JAMES L WILKINSON, ROBERT H ANDERSON From King's College Hospital, and
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
The Fetal Cardiology Program
 The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Fetal Cardiology Program at Texas Children s Fetal Center About the program Since the 1980s, Texas Children s Fetal Cardiology Program has provided comprehensive fetal cardiac care to expecting families
The Impacts of Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) on Fetal Hearts *
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2012; 25(1): 15 22 15 Original Article The Impacts of Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) on Fetal Hearts * CHU Chen 1, GUI Yong Hao 1,#, REN Yun Yun 2, and SHI Li Ye 3 1.
Biomed Environ Sci, 2012; 25(1): 15 22 15 Original Article The Impacts of Maternal Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) on Fetal Hearts * CHU Chen 1, GUI Yong Hao 1,#, REN Yun Yun 2, and SHI Li Ye 3 1.
Fetal echocardiography. Ahmeabad. to neonatal series due to high SB rate. Prenatal detection can improve the fetal outcome. (4, 5) 60% 40% 20%
 Guidelines for Fetal Echocardiography 1 Fetal echocardiography Introduction Dr Jayprakash Shah MD; FICOG Chairman Imaging science committee FOGSI Fetal Medicine expert Rajni Hospital, Ahmedabad, Ex sonologist
Guidelines for Fetal Echocardiography 1 Fetal echocardiography Introduction Dr Jayprakash Shah MD; FICOG Chairman Imaging science committee FOGSI Fetal Medicine expert Rajni Hospital, Ahmedabad, Ex sonologist
Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early second trimester by enhanced-flow (e-flow) echocardiography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
The Normal Offset of the Tricuspid Septal Leaflet in the Fetus
 Article The Normal Offset of the Tricuspid Septal Leaflet in the Fetus Ivana M. Vettraino, MD, Raywin Huang, PhD, Christine H. Comstock, MD Objective. To quantify the normal distance between the insertion
Article The Normal Offset of the Tricuspid Septal Leaflet in the Fetus Ivana M. Vettraino, MD, Raywin Huang, PhD, Christine H. Comstock, MD Objective. To quantify the normal distance between the insertion
Data Collected: June 17, Reported: June 30, Survey Dates 05/24/ /07/2010
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Pediatric Echocardiography Data Collected: June 17, 2010 Reported: Analysis Summary For: Pediatric Echocardiography Exam Survey Dates 05/24/2010-06/07/2010 Invited Respondents
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
The incidence and follow-up of isolated ventricular septal defect in newborns by echocardiographic screening
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 223-227 Original The incidence and follow-up of isolated ventricular septal defect in newborns by echocardiographic screening Filiz Ekici, Ercan Tutar, Semra
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2008; 50: 223-227 Original The incidence and follow-up of isolated ventricular septal defect in newborns by echocardiographic screening Filiz Ekici, Ercan Tutar, Semra
Fetal Echocardiography
 Marie M. Gleason, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pediatrics The Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Director of Outpatient and Community Cardiology and Cardiac Outreach Associate
Marie M. Gleason, M.D. Clinical Professor of Pediatrics The Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Director of Outpatient and Community Cardiology and Cardiac Outreach Associate
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15 weeks gestation with later cardiac evaluation
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 679 686 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12517 Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013; 42: 679 686 Published online in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.12517 Comparison of echocardiographic findings in fetuses at less than 15
Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!!
 Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!! Abha'Khandelwal,'MD,'MS' 'Stanford'University'School'of'Medicine'
Clinicians and Facilities: RESOURCES WHEN CARING FOR WOMEN WITH ADULT CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE OR OTHER FORMS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE!! Abha'Khandelwal,'MD,'MS' 'Stanford'University'School'of'Medicine'
Pediatric Cardiology. Spontaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in Premature vs Full-Term Neonates
 Pediatr Cardiol 21:129 134, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002469910020 Pediatric Cardiology Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2000 Spontaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in Premature vs Full-Term Neonates T. Riggs,
Pediatr Cardiol 21:129 134, 2000 DOI: 10.1007/s002469910020 Pediatric Cardiology Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2000 Spontaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defects in Premature vs Full-Term Neonates T. Riggs,
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES. PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU
 CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
CYANOTIC CONGENITAL HEART DISEASES PRESENTER: DR. Myra M. Koech Pediatric cardiologist MTRH/MU DEFINITION Congenital heart diseases are defined as structural and functional problems of the heart that are
ISOLATED ANOMALOUS DEVELOPMENT OF MYOCARDIUM DURING FETAL LIFE: EXPERIENCE OF OUR CENTRE
 Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata Verona ISOLATED ANOMALOUS DEVELOPMENT OF MYOCARDIUM DURING FETAL LIFE: EXPERIENCE OF OUR CENTRE C.Sandrini *, L.Rossetti *, M.Rebonato *, M.A.Prioli *, F.Bettinazzi,
Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata Verona ISOLATED ANOMALOUS DEVELOPMENT OF MYOCARDIUM DURING FETAL LIFE: EXPERIENCE OF OUR CENTRE C.Sandrini *, L.Rossetti *, M.Rebonato *, M.A.Prioli *, F.Bettinazzi,
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by this history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy.
 HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
HISTORY 18-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Heart murmur present since early infancy. PRESENT ILLNESS: Although normal at birth, a heart murmur was heard at the six week check-up and has persisted since
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Recent technical advances and increasing experience
 Pediatric Open Heart Operations Without Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization Jean-Pierre Pfammatter, MD, Pascal A. Berdat, MD, Thierry P. Carrel, MD, and Franco P. Stocker, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology,
Pediatric Open Heart Operations Without Diagnostic Cardiac Catheterization Jean-Pierre Pfammatter, MD, Pascal A. Berdat, MD, Thierry P. Carrel, MD, and Franco P. Stocker, MD Division of Pediatric Cardiology,
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
AOGS ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE
 AOGS ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Ventricular outputs, central blood flow distribution and flow pattern through the aortic isthmus of fetuses with simple transposition of the great arteries JULIE BLANC 1,2,
AOGS ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Ventricular outputs, central blood flow distribution and flow pattern through the aortic isthmus of fetuses with simple transposition of the great arteries JULIE BLANC 1,2,
UPDATE FETAL ECHO REVIEW
 UPDATE 1 FETAL ECHO REVIEW Study Alert for RDCS Candidates D A V I E S P U B L I S H I N G I N C. Fetal Echo Review Study Alert U P D A T E D A U G U S T 1, 2 0 1 2 Nikki Stahl, RT(R)(M)(CT), RDMS, RVT
UPDATE 1 FETAL ECHO REVIEW Study Alert for RDCS Candidates D A V I E S P U B L I S H I N G I N C. Fetal Echo Review Study Alert U P D A T E D A U G U S T 1, 2 0 1 2 Nikki Stahl, RT(R)(M)(CT), RDMS, RVT
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso
 2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
2) VSD & PDA - Dr. Aso Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Most common cardiac malformation 25-30 % Types of VSD: According to position perimembranous, inlet, muscular. According to size small, medium, large.
Prevalence of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect and Associated Findings
 Prevalence of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect and Associated Findings 3 Mark D. Reller Oregon Health & Science University, USA 1. Introduction The goal of this chapter is to review data regarding the current
Prevalence of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect and Associated Findings 3 Mark D. Reller Oregon Health & Science University, USA 1. Introduction The goal of this chapter is to review data regarding the current
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation
 Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Basic Fetal Cardiac Evaluation Mert Ozan Bahtiyar, MD Director, Fetal Care Center Division of Maternal Fetal Medicine Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Sciences S L I D E 1 Background
Congenital heart disease in twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome treated with fetoscopic laser surgery
 Chapter 10 Congenital heart disease in twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome treated with fetoscopic laser surgery Enrico Lopriore MD Regina Bökenkamp MD Marry Rijlaarsdam MD Marieke Sueters MD Frank PHA Vandenbussche
Chapter 10 Congenital heart disease in twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome treated with fetoscopic laser surgery Enrico Lopriore MD Regina Bökenkamp MD Marry Rijlaarsdam MD Marieke Sueters MD Frank PHA Vandenbussche
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease
 5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
5.8 Congenital Heart Disease Congenital heart diseases (CHD) refer to structural or functional heart diseases, which are present at birth. Some of these lesions may be discovered later. prevalence of Chd
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems. Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven
 Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Foetal Cardiology: How to predict perinatal problems Prof. I.Witters Prof.M.Gewillig UZ Leuven Cardiopathies Incidence : 8-12 / 1000 births ( 1% ) Most frequent - Ventricle Septum Defect 20% - Atrium Septum
Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation
 Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation Ivan Romero Rivera, Maria Alayde Mendonça da Silva, José Maria Gonçalves Fernandes, Ana Claire
Congenital Heart Diseases in the Newborn: from the Pediatrician s Request to the Cardiologist s Evaluation Ivan Romero Rivera, Maria Alayde Mendonça da Silva, José Maria Gonçalves Fernandes, Ana Claire
Evaluating Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Technology as a Tool for Training Nonexpert Sonographers to Perform Examinations of the Fetal Heart
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluating Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Technology as a Tool for Training Nonexpert Sonographers to Perform Examinations of the Fetal Heart Hagai Avnet, MD, Eyal Mazaaki, MD, Ori
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluating Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Technology as a Tool for Training Nonexpert Sonographers to Perform Examinations of the Fetal Heart Hagai Avnet, MD, Eyal Mazaaki, MD, Ori
Accuracy of the Fetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right Ventricle
 Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USACHDCongenital Heart Disease 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing, Inc.? 200723237Original ArticleFetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right
Blackwell Publishing IncMalden, USACHDCongenital Heart Disease 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 Blackwell Publishing, Inc.? 200723237Original ArticleFetal Echocardiogram in Double-outlet Right
September 28-30, 2018
 September 28-30, 2018 Course Director Optimizing Detection of Congenital Heart Disease: Important Anatomic Cardiac Regions The Top 5 Critical Anatomic Regions in Fetal Cardiac Imaging Alfred Abuhamad,
September 28-30, 2018 Course Director Optimizing Detection of Congenital Heart Disease: Important Anatomic Cardiac Regions The Top 5 Critical Anatomic Regions in Fetal Cardiac Imaging Alfred Abuhamad,
The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 340 345 The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac Blackwell Science, Ltd scanning S. YAGEL*, R. ARBEL, E. Y. ANTEBY*, D. RAVEH and R. ACHIRON *Department
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2002; 20: 340 345 The three vessels and trachea view (3VT) in fetal cardiac Blackwell Science, Ltd scanning S. YAGEL*, R. ARBEL, E. Y. ANTEBY*, D. RAVEH and R. ACHIRON *Department
C ongenital heart disease accounts for the majority of
 387 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Improving the effectiveness of routine prenatal screening for major congenital heart defects J S Carvalho, E Mavrides, E A Shinebourne, S Campbell, B Thilaganathan... See end
387 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Improving the effectiveness of routine prenatal screening for major congenital heart defects J S Carvalho, E Mavrides, E A Shinebourne, S Campbell, B Thilaganathan... See end
T wo dimensional and Doppler echocardiography is being
 F287 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of echocardiography on the neonatal unit S Moss, D J Kitchiner, C W Yoxall, N V Subhedar... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Subhedar,
F287 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of echocardiography on the neonatal unit S Moss, D J Kitchiner, C W Yoxall, N V Subhedar... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Subhedar,
Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016
 1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
1 Adult Congenital Heart Disease: What All Echocardiographers Should Know Sharon L. Roble, MD, FACC Echo Hawaii 2016 DISCLOSURES I have no disclosures relevant to today s talk 2 Why should all echocardiographers
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view.
 An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
An update on technique of fetal echocardiography with emphasis on anomalies detectable in four chambered view. Dr. Ranjitha.G Specialist Radiologist NMC-SH Al ain, UAE Fetal echocardiography is an essential
Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 964-968 Personal practice Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities L D ALLAN Guy's Hospital, London The feasibility of cross sectional imaging of the structure
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 964-968 Personal practice Diagnosis of fetal cardiac abnormalities L D ALLAN Guy's Hospital, London The feasibility of cross sectional imaging of the structure
Congenital Heart Disease
 Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Screening Programmes Fetal Anomaly Congenital Heart Disease Information for health professionals Publication date: April 2012 Review date: April 2013 Version 2 67 Congenital Heart Disease Information for
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs)
 Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
Making Sense of Cardiac Views and Imaging Characteristics for 13 Congenital Heart Defects (CHDs) Manny Gaziano, MD, FACOG obimages.net obimages.net@gmail.com Acknowledgements: Krista Wald, RDMS, sonographer,
AbnormalThree-VesselView on Sonography: A Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus
 rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
rt Pictorial Essay bnormalthree-vesselview on Sonography: Clue to the Diagnosis of Congenital Heart Disease in the Fetus screening tool for major congenital heart diseases [I. 2J. However, anomalies of
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE
 By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
By Dickens ATURWANAHO & ORIBA DAN LANGOYA MAKchs, MBchB CONGENTAL HEART DISEASE Introduction CHDs are abnormalities of the heart or great vessels that are present at birth. Common type of heart disease
Uptofate Study Summary
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Uptofate Study Summary Acyanotic Atrial septal defect Ventricular septal defect Patent foramen ovale Patent ductus arteriosus Aortic coartation Pulmonary stenosis Cyanotic Tetralogy
Fetal Ductus Arteriosus: The Good, Bad, and the Ugly. Tet Abs Valve syndrome With PDA. Fetal Ductus Arteriosus. James C. Huhta, M.D.
 Fetal Ductus Arteriosus: The Good, Bad, and the Ugly Tet Abs Valve syndrome With PDA James C. Huhta, M.D. Perinatal Cardiology Tampa, Florida 7 th Annual Fetal Echocardiography Course Friday, November
Fetal Ductus Arteriosus: The Good, Bad, and the Ugly Tet Abs Valve syndrome With PDA James C. Huhta, M.D. Perinatal Cardiology Tampa, Florida 7 th Annual Fetal Echocardiography Course Friday, November
Failing right ventricle
 Failing right ventricle U. Herberg 1, U. Gembruch 2 1 Pediatric Cardiology, 2 Prenatal Diagnostics and Fetal Therapy, University of Bonn, Germany Prenatal Physiology Right ventricle dominant ventricle
Failing right ventricle U. Herberg 1, U. Gembruch 2 1 Pediatric Cardiology, 2 Prenatal Diagnostics and Fetal Therapy, University of Bonn, Germany Prenatal Physiology Right ventricle dominant ventricle
Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal
 Br Heart J 1984; 52: 542-8 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal congenital heart disease LINDSEY D ALLAN, DIANE C CRAWFORD, ROBERT H ANDERSON,* MICHAEL J TYNAN From Guy's Hospital, London;
Br Heart J 1984; 52: 542-8 Echocardiographic and anatomical correlations in fetal congenital heart disease LINDSEY D ALLAN, DIANE C CRAWFORD, ROBERT H ANDERSON,* MICHAEL J TYNAN From Guy's Hospital, London;
Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias
 1386 JACC Vol 7. No 6 June 19X6 I3Xh-91 Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias JANETTE F. STRASBURGER, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, FACC, ROBERT J. CARPENTER,
1386 JACC Vol 7. No 6 June 19X6 I3Xh-91 Doppler Echocardiography in the Diagnosis and Management of Persistent Fetal Arrhythmias JANETTE F. STRASBURGER, MD, JAMES C. HUHTA, MD, FACC, ROBERT J. CARPENTER,
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Case Report by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2004; 23: /04/$3.50
 Case Report A Systematic Approach to Prenatal Diagnosis of Transposition of the Great Arteries Using 4-Dimensional Ultrasonography With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza,
Case Report A Systematic Approach to Prenatal Diagnosis of Transposition of the Great Arteries Using 4-Dimensional Ultrasonography With Spatiotemporal Image Correlation Luís F. Gonçalves, MD, Jimmy Espinoza,
Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural congenital heart diseases
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 21: 19 25 Published online 12 December 2002 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7 Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2003; 21: 19 25 Published online 12 December 2002 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.7 Factors influencing the prenatal detection of structural
D iagnosis of congenital heart defects by fetal echocardiography
 1070 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Timing of presentation and postnatal outcome of infants suspected of having coarctation of the aorta during fetal life C E G Head, V C Jowett, G K Sharland, J M Simpson...
1070 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Timing of presentation and postnatal outcome of infants suspected of having coarctation of the aorta during fetal life C E G Head, V C Jowett, G K Sharland, J M Simpson...
Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
 Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
Reprinted with permission from ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY, Volume 18, No. 1, January 2001 Copyright 2001 by Futura Publishing Company, Inc., Armonk, NY 1004-0418 Quantitative Assessment of Fetal Ventricular Function:
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
