Vertebrate Limb Patterning
|
|
|
- Willis Crawford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment of the patterning axes Regulating expression of genes limb enhancers Chris Campbell Nov 8, 2016
2 All tetrapod limbs exhibit the same basic structure but a wide range of morphologies girdle stylopod zeugopod autopod Forelimbs and hindlimbs as well as limbs from different species exhibit the same basic structure but a wide range of morphologies. Historically, the two most common model systems to study limb development have been mouse and chick
3 ive * Ectoderm Skin, hair feathers etc.
4 Lateral Plate Mesoderm * Tbx1 Tanaka (2013) Dev. Growth Diff 55, 149
5 Pathways of limb development are conserved Tetrapod limbs originate as two pairs of limb buds that appear at specific levels of the embryonic flank (species specific). Forelimb buds appear first (~E9 in ~somite 8-9) followed by hindlimb buds ~ 0.5-1day later (@ ~somite 23-24) Each limb bud consists of lateral plate mesoderm (LPM) covered by ectoderm. E10 mouse Duboc (2011) Dev Dyn 240, 1017
6 Scanning EMs of a series of mouse embryos Martin (1990) Int. J. Dev. Biol 34, 323
7 Key events in limb development (1) Specifying limb positioning (Hox genes, Tbxs & Hand2) and identity (forelimb versus hindlimb) (Pitx1 affects hindlimb ; no comparable gene in forelimb) (2)Initiation of limb bud outgrowth (Tbxs and Fgfs) (3)Establishment of the patterning axes PD (AER-Fgfs), DV (BMPs, Wnts, Lmx1, En1) & AP (Hand2 & Gli3 & Shh). There are both positive and negative feedback loops between these proteins that regulate their expression. (4) Maintenance and cessation of growth (Shh-Gre-BMP-Fgfs)
8 Hox genes and specifying limb position Myers (2008) Nat. Ed. In a variety of vertebrates the anterior expression boundaries of a number of Hox genes in the LPM occur exactly at the forelimb level (Oliver et al. 1990, Rancourt et al. 1995, Nelson et al. 1996) Capdevila (2001)
9 Tbx3, Gli3 and Hand2 and limb bud positioning Tbx3 FL * HL Tbx3 misexpression by retrovirus injection shifts limb anteriorly (see above) Hox gene expression is unaltered. Limb position determined by Tbx3, Gli3 and Hand2 expression. Rallis (2005) Dev 132, 1961
10 Specification of limb identity (forelimb versus hindlimb) Tbx4 (and Pitx1) are expressed in hindlimbs and Tbx5 in forelimbs. Do these proteins specify limb identity? cre Tbx4 can rescue forelimb growth in Tbx5 fl/fl Prx1-cre mice. Another gene Pitx1 also expressed in hindlimb cannot. TBX4 DOES NOT SPECIFY HINDLIMB IDENTITY (patterning of skeletal elements) Minguillon (2005) Dev Cell 8, 75
11 Regulation of limb bud outgrowth AER is required for limb bud outgrowth Limb mesenchyme specifies limb identity Inductive interactions between AER and limb mesenchyme similar to the inductive interactions that take place between metanephric mesenchyme and ureteric bud. Gilbert s Developmental Biology
12 Limb bud outgrowth The apical ectodermal ridge (AER) is a specialized epithelium (derived from the ectoderm) that controls limb bud outgrowth. The AER is a transient structure that does not itself contribute cells to the mature limb. (Begins to disappear ~ E in mouse.) E-cadherin
13 What is the role of the AER? AER functions by providing FGFs required for outgrowth of the limb bud.
14 FGFs and their mechanism of action in mice Fgf4 Fgf8 Fgf9 Fgf17 Fgf10 AER ck/o no effect AER ck/o limb deformities AER k/o no effect AER k/o no effect LPM k/o limb deformities
15 Fgf10 and limb bud outgrowth Fgf10 is expressed in the mesenchyme. In its absence: Fgf10 +/- Fgf10 -/- Fgf10 +/- Fgf10 -/- Fgf8 E9.25 Shh E10.5 H&E E10.5 There is no morphological appearance of an AER There is no Fgf8 expressed in the forelimb bud AER (although Fgf8 is expressed elsewhere in the embryo) There is no Shh in the FL or HL mesenchyme Tbx5 is induced appropriately (E9.5) but expression is rapidly lost. Sekine (1999) Nat Gen 21, 139
16 Fgf8 and Fgf8/Fgf4 and limb bud outgrowth Fgf8 -/- is early embryonic lethal. Therefore conditional k/o made using Msx2-cre (Fgf8 -/- ) Msx2-cre is expressed after Fgf8 expression has initiated in the FL but before expression is initiated in HL. Fgf8 -/- FL are relatively normal while proximal elements of hindlimb (i.e. stylopod) are reduced or missing. Lewandoski (2000) Nat Gen 26,460 +/+ Fgf8-/-/Fgf4-/- Fgf8-/-Fgf4-/- FL are abnormal (zeugopod/autopod) and HL are absent Sun (2002) Nature 418, 501
17 Agarwal et al. (2003) Dev. 130, 623 The role of Tbx5 in forelimb initiation Minguillon (2012) Identification of a limb specific enhancer within intron 2 of Tbx5 Expression of Hox4 and Hox5 PG activate reporter construct containing Tbx5 CREs Hox genes & dhand (Hand2) are still expressed in mutants. Mutation of Hox binding sites causes loss of expression of reporter construct Is Tbx5 expression regulated by Hox genes? HoxPG 4/5 Tbx5
18 The role of Tbx5 in forelimb initiation (cont) Agarwal et al. (2003) Dev. 130, 623 Fgf10 is not expressed in Tbx5-/- Does Tbx5 regulate Fgf10 expression? Tbx5 activates reporter construct containing Fgf10 5 region. Tbx5 and beta-catinin co-operate to activate Fgf10 expression. Sequence conservation identifies several potential Tbx5 binding sites upstream of the Fgf10 promoter
19 Establishing the limb patterning axes The developing limb bud is patterned along three axes : Proximal-Distal Dorsal-Ventral Anterior-Posterior
20 Misexpression of RA affects patterning along the Proximal Distal Axis Meis1 Hoxa11 Hoxa13 RA Retinoic Acid reprograms limb cells to express more proximal markers Mercader (2000) Dev 127, 3961
21 Signaling by the non AER ectoderm controls dorsal ventral patterning Shh Shh normally expressed in ventral ectoderm En-1 Bmp4 & Bmp7 Bmp4 Bmp7 Fgf8 Normally expressed in dorsal ectoderm Wnt7-a dorsal Normally expressed in dorsal mesenchyme Lmx-1 & Shh Normally expressed in AER Fgf8 ventral In situ for Shh (molecular marker for ZPA) & Fgf8 (molecular marker for the AER) Pizette et al. (2001) Dev.128,4463
22 Shh Bmp4 Bmp7 Fgf8 Pizette et al. (2001) Dev.128,4463 Wnt BMP regulate DV patterning Downregulate BMP(v) signaling by misexpression of Noggin (BMP antagonist) by retroviral injections to the ectoderm leads to loss of en1(ve) and expansion of Wnt-7a (de), Lmx1 (dm) & Shh (dm) into ventral region of bud (i.e. dorsalization of bud). Also leads to misexpression of Shh and Fgf8 (AER) (i.e perturb PD & AP patterning) Upregulate BMP(v) signaling by misexpression of a constitutively active Bmp receptor leads to expansion of en1, and loss of Wnt-7a & Lmx1(d) (i.e.ventralization of bud). Also leads to loss of AER Parr (1995) Nature 74, 350 +/+ Wnt7a-/- Wnt7a-/- mouse exhibits formation of dorsal tendons and footpads Loomis (1996) Nature 382, 360 +/+ En-/- En-/- mouse shows loss of ventral pads and formation of nails on both dorsal and ventral side
23 Anterior-posterior patterning is controlled by signals from the mesenchymal cells of the ZPA (zone of polarizing activity) anterior posterior Duplication of posterior digits ZPA
24 Sonic Hedgehog signaling Suzuki(2013) Dev, Growth & Diff 55, 130
25 Shh -/- mice exhibit defects in AP patterning Shh -/- mice form truncated limbs with single digits. A/P patterning is maintained in stylopod but lost in zeugopod and autopod. A number of genes previously shown to be regulated by Shh are either expressed at low levels (Bmps 2&4) or turned on but rapidly downregulated (Gremlin). Gli3 expression (negatively regulated by Shh) is extended (see below). In the absence of SHH, AER formation is initiated but doesn t persist as long as in wt (see Fgf8 expression below) A/P patterning occurs prior to Shh induction but requires Shh to be maintained. Fgf8 Chiang et al. (2001) Dev. Biol. 236,421
26 How SHH regulates digit formation Litingtung (2002) Nat 418, 979
27 Limb bud outgrowth and cessation of outgrowth Tbx2 Gremlin (antagonist of BMP) required to maintain Fgfs in AER Shh required to maintain Gremlin AER-Fgf required to maintain Shh
28 Regulation of Shh expression and the identification of a long range limb bud enhancer (ZRS or MCFS1) E11.5 E12.5 Sharpe (1999) Curr Biol 9, 97 Mouse mutation Ssq causes partial duplication of distal hindlimb, secondary to induction of an anterior Shh expression domain and increased expression of Fgf8. This is caused by the random insertion of a transgene. The site of the transgene insertion was mapped to the vicinity of Shh (within a gene ~ 1Mb distant. The transgene itself showed an expression pattern similar to Shh within the limb bud. Note that Shh is expressed in multiple sites within the developing embryo while the transgene was only expressed within the limb bud. Lettice (2002) Human mutations with similar phenotype were mapped to the homologous region of the human genome (within Lmbr1 gene). No evidence that Lmbr1 transcript or protein were altered. Additional mutations with similar phenotypes were also found in mice and other animals.
29 A cosmid library was created from Ssq genomic DNA. A cosmid containing the transgene plus ~ 8.5kb of flanking sequence at least partially recapitulated the expression pattern of the reporter in the original Ssq mouse. Sequence comparison of mouse and human genomic DNA identified an ~800bp segion of highly conserved sequence most of which was included in the cosmid. Based on this data a transgene was constructed consisting of 1.7kb fragment containing the highly conserved domain, a minimal promoter and a lacz reporter gene. Additional sequence comparisons between mouse and chicken and mouse and fish (fugu) DNA revealed an ~400bp region conserved between all 4 species. This smaller sequence was also introduced into the lacz reporter gene and used to make transgenic mice. Comparison of lacz expression in these plus some additional transgenics indicated that most of the information responsible for regulating appropriate spacial expression of Shh was contained within a 305 bp fragment. Lettice (2003)
30 Multiple mutations within this highly conserved sequence have been found in mice, humans and cats with polydactyly. Ectopic expression is maintained in transgene Lettice (2008)
31 Specificity of the ZRS enhancer Sagai (2005) Dev 132, 797 ΔZRS/ΔZRS ΔZRS/ΔZRS Anderson (2014) Curr Opin Genes & Dev 27, 54 Amano (2009) Dev Cell 16, 47
32 Please Figure Facts before class Thurs for the 5 figures, 1 suppl. figure and tables 1 &2.
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Chapter 2. Genetic interaction between Gli3 and Alx4 during limb and craniofacial development CH Utrecht, The Netherlands
 Genetic interaction between Gli3 and Alx4 during limb and craniofacial development Lia Panman 1, Thijs Drenth 1, Pascal te Welscher 1,3, Aimee Zuniga 1,2, Rolf Zeller 1,2 1 Department of Developmental
Genetic interaction between Gli3 and Alx4 during limb and craniofacial development Lia Panman 1, Thijs Drenth 1, Pascal te Welscher 1,3, Aimee Zuniga 1,2, Rolf Zeller 1,2 1 Department of Developmental
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
The chick oligozeugodactyly (ozd) mutant lacks sonic hedgehog function in the limb
 Development 130, 527-537 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00245 527 The chick oligozeugodactyly (ozd) mutant lacks sonic hedgehog function in the limb Maria A. Ros 1, *, Randall D. Dahn
Development 130, 527-537 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00245 527 The chick oligozeugodactyly (ozd) mutant lacks sonic hedgehog function in the limb Maria A. Ros 1, *, Randall D. Dahn
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs. Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta
 Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Development of the Axial Skeleton and Limbs Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta During the Fourth Week the Embryo Is Segmented. Each segment consists of: a segment of neural
Week 14. Development of the Musculoskeletal System
 Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Week 14 Development of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Derived from: paraxial mesoderm somites and somitomeres sclerotome sclerotome differentiation induced by SHH from notochord and floor plate
Bio Section IV Late Development. Development of the Tetrapod Limb. Pattern Formation. Skeletal pattern formation. Gilbert 9e Chapter 13
 Bio 127 - Section IV Late Development Development of the Tetrapod Limb Gilbert 9e Chapter 13 Pattern Formation Limbs show an amazing aspect of development Similarities: Architectural symmetry in all four
Bio 127 - Section IV Late Development Development of the Tetrapod Limb Gilbert 9e Chapter 13 Pattern Formation Limbs show an amazing aspect of development Similarities: Architectural symmetry in all four
Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem
 86 Review TRENDS in Cell Biology Vol.13 No.2 February 2003 Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem Pao-Tien Chuang 1 and Andrew P. McMahon 2 1 Cardiovascular Research
86 Review TRENDS in Cell Biology Vol.13 No.2 February 2003 Branching morphogenesis of the lung: new molecular insights into an old problem Pao-Tien Chuang 1 and Andrew P. McMahon 2 1 Cardiovascular Research
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development. Lecture 2: Fossil Record
 BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu3onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb Development Lecture 2: Fossil Record Outline Limb Evolution Limb Development Limb Function A Few Definitions Appendicular skeleton girdles & limbs Pectoral
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
Report. Retinoic Acid Promotes Limb Induction through Effects on Body Axis Extension but Is Unnecessary for Limb Patterning
 Current Biology 19, 1050 1057, June 23, 2009 ª2009 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.04.059 Retinoic Acid Promotes Limb Induction through Effects on Body Axis Extension but Is Unnecessary
Current Biology 19, 1050 1057, June 23, 2009 ª2009 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2009.04.059 Retinoic Acid Promotes Limb Induction through Effects on Body Axis Extension but Is Unnecessary
DEVELOPMENT. Lia Panman 1,2, *,, Antonella Galli 1, *, Nadege Lagarde 1, Odysse Michos 1, Gwen Soete 2,, Aimee Zuniga 1, and Rolf Zeller 1,
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3419 Development 133, 3419-3428 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02529 Differential regulation of gene expression in the digit forming area of the mouse limb bud by SHH and gremlin 1/FGF-mediated
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3419 Development 133, 3419-3428 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02529 Differential regulation of gene expression in the digit forming area of the mouse limb bud by SHH and gremlin 1/FGF-mediated
Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling
 Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling Tomomi Fukuchi-Shimogori and Elizabeth A Grove Presented by Sally Kwok Background Cerebral cortex has anatomically and functionally distinct
Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling Tomomi Fukuchi-Shimogori and Elizabeth A Grove Presented by Sally Kwok Background Cerebral cortex has anatomically and functionally distinct
a) They are the most common cause of pediatric kidney failure. b) They are always symptomatic. c) They can be asymmetric.
 Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Gene Expression in the limbless Mutant: Polarized Gene Expression in the Absence of Shh and an AER
 DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 179, 339 346 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0265 Gene Expression in the limbless Mutant: Polarized Gene Expression in the Absence of Shh and an AER Selina Noramly,*, Jacqueline Pisenti, Ursula
DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 179, 339 346 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0265 Gene Expression in the limbless Mutant: Polarized Gene Expression in the Absence of Shh and an AER Selina Noramly,*, Jacqueline Pisenti, Ursula
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development.
 Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
Research Article: Veterinary Anatomy Case Report A case of polydactyly in the hind-limbs of a West African Dwarf goat in South-West Nigeria
 IJAE Vol. 118, n. 3: 298-302, 2013 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article: Veterinary Anatomy Case Report A case of polydactyly in the hind-limbs of a West African Dwarf goat in South-West
IJAE Vol. 118, n. 3: 298-302, 2013 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF ANATOMY AND EMBRYOLOGY Research Article: Veterinary Anatomy Case Report A case of polydactyly in the hind-limbs of a West African Dwarf goat in South-West
Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Pbx1/Pbx2 requirement for distal limb patterning is mediated by the hierarchical control of Hox gene spatial distribution and Shh expression
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 2263 Development 133, 2263-2273 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02395 Pbx1/Pbx2 requirement for distal limb patterning is mediated by the hierarchical control of Hox gene spatial distribution and
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2263 Development 133, 2263-2273 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02395 Pbx1/Pbx2 requirement for distal limb patterning is mediated by the hierarchical control of Hox gene spatial distribution and
Patterning the Embryo
 Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
Hepatogenesis I Liver development
 Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and
 Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Supplementary Figure 1: Signaling centers contain few proliferating cells, express p21, and exclude YAP from the nucleus. (a) Schematic diagram of an E10.5 mouse embryo. (b,c) Sections at B and C in (a)
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification
 Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification Marcus K. Gustafsson, 1,3,4 Hua Pan, 1,3,4 Deborah F. Pinney, 1,3 Yongliang Liu, 1,3 Anna Lewandowski, 1,3
Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification Marcus K. Gustafsson, 1,3,4 Hua Pan, 1,3,4 Deborah F. Pinney, 1,3 Yongliang Liu, 1,3 Anna Lewandowski, 1,3
A New Vocabulary. Secreted Factors. Three Axes of Limb Development 11/9/15. Proteins released from a cell into surrounding area Examples
 Congenital Hand Update Terry R. Light, MD Tampa, FL November 7, 2015 Terminology n Difference rather than Deformity n Cleft Hand rather than Lobster Claw Embryonic period - Events Day 26 - arm bud appears
Congenital Hand Update Terry R. Light, MD Tampa, FL November 7, 2015 Terminology n Difference rather than Deformity n Cleft Hand rather than Lobster Claw Embryonic period - Events Day 26 - arm bud appears
Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most
 Development 125, 2759-2770 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV9597 2759 Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons
Development 125, 2759-2770 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV9597 2759 Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons
Amber Kathleen O Connor. Bradley K Yoder, MENTOR Rosa Serra Robert A. Kesterson Jianbo Wang Stuart J. Frank A DISSERTATION
 NEW MOUSE MODELS TO AID STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF PRIMARY CILIA IN LIMB PATTERNING AND BONE DEVELOPMENT by Amber Kathleen O Connor Bradley K Yoder, MENTOR Rosa Serra Robert A. Kesterson Jianbo Wang Stuart
NEW MOUSE MODELS TO AID STUDIES OF THE ROLE OF PRIMARY CILIA IN LIMB PATTERNING AND BONE DEVELOPMENT by Amber Kathleen O Connor Bradley K Yoder, MENTOR Rosa Serra Robert A. Kesterson Jianbo Wang Stuart
Uncoupling Sonic Hedgehog Control of Pattern and Expansion of the Developing Limb Bud
 Short Article Uncoupling Sonic Hedgehog Control of Pattern and Expansion of the Developing Limb Bud Jianjian Zhu, 1 Eiichiro Nakamura, 1,3,5 Minh-Thanh Nguyen, 1,3,4 Xiaozhong Bao, 1,3 Haruhiko Akiyama,
Short Article Uncoupling Sonic Hedgehog Control of Pattern and Expansion of the Developing Limb Bud Jianjian Zhu, 1 Eiichiro Nakamura, 1,3,5 Minh-Thanh Nguyen, 1,3,4 Xiaozhong Bao, 1,3 Haruhiko Akiyama,
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
Segmentation. Serial Homology. Hox genes
 Segmentation Hox genes Serial Homology William Bateson 1861-1926 Homeosis: a variation in which something has been changed into the likeness of something else Calvin Bridges at Columbia bithorax 1923 1
Segmentation Hox genes Serial Homology William Bateson 1861-1926 Homeosis: a variation in which something has been changed into the likeness of something else Calvin Bridges at Columbia bithorax 1923 1
Skeletal System. Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section
 Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Skeletal System Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Department of Anatomy/Embryology Section Learning objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the embryonic origin of skeletal
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
The role of HoxA11 and HoxA13 in the evolution of novel fin morphologies in a representative batoid (Leucoraja erinacea)
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13227-017-0088-4 EvoDevo RESEARCH Open Access The role of HoxA11 and HoxA13 in the evolution of novel fin morphologies in a representative batoid (Leucoraja erinacea) Shannon N.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13227-017-0088-4 EvoDevo RESEARCH Open Access The role of HoxA11 and HoxA13 in the evolution of novel fin morphologies in a representative batoid (Leucoraja erinacea) Shannon N.
evolution and development of primate teeth
 evolution and development of primate teeth diversity of mammalian teeth upper left molars buccal mesial distal lingual Jernvall & Salazar-Ciudad 07 trends in dental evolution many similar single-cusped
evolution and development of primate teeth diversity of mammalian teeth upper left molars buccal mesial distal lingual Jernvall & Salazar-Ciudad 07 trends in dental evolution many similar single-cusped
Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling
 Short Article Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling Danyi Li, 1,2 Rui Sakuma, 1 Niki A. Vakili, 1,2 Rong
Short Article Formation of Proximal and Anterior Limb Skeleton Requires Early Function of Irx3 and Irx5 and Is Negatively Regulated by Shh Signaling Danyi Li, 1,2 Rui Sakuma, 1 Niki A. Vakili, 1,2 Rong
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 334 (2009) 133 141 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Aberrant FGF signaling, independent of ectopic
Developmental Biology 334 (2009) 133 141 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Aberrant FGF signaling, independent of ectopic
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma. Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD
 Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
Developing Molecularly Targeted Therapies for Basal Cell Carcinoma Ivor Caro, MD, FAAD Disclosures Genentech, Inc Medical Director, Dermatology (employee) Stock holder Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Fundamental
CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES
 CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES Lisa Lattanza, MD Chief Division of Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery UCSF Medical Center Amy L Ladd MD, Chief, Chase Hand Center Stanford University CONGENITAL DEFORMITIES Upper
CONGENITAL HAND DIFFERENCES Lisa Lattanza, MD Chief Division of Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery UCSF Medical Center Amy L Ladd MD, Chief, Chase Hand Center Stanford University CONGENITAL DEFORMITIES Upper
Name _ AP Biology Your Inner Fish not NOT DUE DATE: March 17, 2015
 Name _ AP Biology Your Inner Fish Below are reading questions based on Your Inner Fish by Neil Shubin. As part of your 6 th six weeks test average for AP Biology, you will read the book and answer all
Name _ AP Biology Your Inner Fish Below are reading questions based on Your Inner Fish by Neil Shubin. As part of your 6 th six weeks test average for AP Biology, you will read the book and answer all
Heart Development. Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells. Robert G. Kelly
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences Heart Development 19th June 2013 Origins of congenital heart defects Properties of cardiac progenitor cells Robert G. Kelly Animal models of heart development
Positional signalling and the development of the humerus in the chick limb bud
 Development 100, 333-338 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 333 Positional signalling and the development of the humerus in the chick limb bud L. WOLPERT and AMATA HORNBRUCH
Development 100, 333-338 (1987) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1987 333 Positional signalling and the development of the humerus in the chick limb bud L. WOLPERT and AMATA HORNBRUCH
Cholesterol Modification of Sonic Hedgehog Is Required for Long-Range Signaling Activity and Effective Modulation of Signaling by Ptc1
 Cell, Vol. 105, 599 612, June 1, 2001, Copyright 2001 by Cell Press Cholesterol Modification of Sonic Hedgehog Is Required for Long-Range Signaling Activity and Effective Modulation of Signaling by Ptc1
Cell, Vol. 105, 599 612, June 1, 2001, Copyright 2001 by Cell Press Cholesterol Modification of Sonic Hedgehog Is Required for Long-Range Signaling Activity and Effective Modulation of Signaling by Ptc1
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
The Evolution and Development of the Gut. Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department
 The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
The Evolution and Development of the Gut Dr Mike Wride School of Natural Sciences Zoology Department email: wridem@tcd.ie The gut? Gut Function and Regulation (Dr. Alan Tuffery) Absorption of nutrients
Heart Development. Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy
 ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
ESC CBCS Summer School on Cardiovascular Sciences 15th June 2011 Heart Development Robert G. Kelly Developmental Biology Institute of Marseilles - Luminy Animal models of heart development Tinman/Nkx2.5
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Independent regulation of Dlx2 expression in the epithelium and mesenchyme of the first branchial arch
 Development 127, 217-224 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV2450 217 Independent regulation of Dlx2 expression in the epithelium and mesenchyme of the first branchial
Development 127, 217-224 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV2450 217 Independent regulation of Dlx2 expression in the epithelium and mesenchyme of the first branchial
An unusual case of radial polydactyly, (tetraplication of the thumb, duplication of the radial carpal bones and bifurcation of the radius)
 Case Report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences An unusual case of radial polydactyly, (tetraplication of the thumb, duplication of the radial carpal
Case Report Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran (MJIRI) Iran University of Medical Sciences An unusual case of radial polydactyly, (tetraplication of the thumb, duplication of the radial carpal
Supplementary Figures
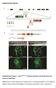 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor
 BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
BCL11B Regulates Epithelial Proliferation and Asymmetric Development of the Mouse Mandibular Incisor Kateryna Kyrylkova 1, Sergiy Kyryachenko 1, Brian Biehs 2 *, Ophir Klein 2, Chrissa Kioussi 1 *, Mark
ROLE OF CANONICAL WNT-SIGNALLING IN JOINT FORMATION
 D European Später et Cells al. and Materials Vol. 12. 2006 (pages 71-80) DOI: 10.22203/eCM.v012a09 Role of canonical Wnt-signalling in ISSN joint 1473-2262 formation ROLE OF CANONICAL WNT-SIGNALLING IN
D European Später et Cells al. and Materials Vol. 12. 2006 (pages 71-80) DOI: 10.22203/eCM.v012a09 Role of canonical Wnt-signalling in ISSN joint 1473-2262 formation ROLE OF CANONICAL WNT-SIGNALLING IN
Sonic hedgehog acts cell-autonomously on muscle precursor cells to generate limb muscle diversity
 Sonic hedgehog acts cell-autonomously on muscle precursor cells to generate limb muscle diversity Claire Anderson, 1,6,7 Victoria C. Williams, 2,6 Benjamin Moyon, 3 Philippe Daubas, 4 Shahragim Tajbakhsh,
Sonic hedgehog acts cell-autonomously on muscle precursor cells to generate limb muscle diversity Claire Anderson, 1,6,7 Victoria C. Williams, 2,6 Benjamin Moyon, 3 Philippe Daubas, 4 Shahragim Tajbakhsh,
How is digit identity determined during limb development?
 The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (203) 55, 30 38 doi: 0./dgd.2022 Review Article How is digit identity determined during limb development? Takayuki Suzuki * Division
The Japanese Society of Developmental Biologists Develop. Growth Differ. (203) 55, 30 38 doi: 0./dgd.2022 Review Article How is digit identity determined during limb development? Takayuki Suzuki * Division
Cell Type Nervous System I. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation. Human issues.
 7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
9/16/2009. Fast and slow twitch fibres. Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 335 (2009) 396 406 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Essential mesenchymal role of small GTPase
Developmental Biology 335 (2009) 396 406 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Essential mesenchymal role of small GTPase
SONIC HEDGEHOG (Shh) is a secreted glycoprotein
 Role of Sonic Hedgehog in the Development of the Trachea and Oesophagus By Adonis S. Ioannides, Deborah J. Henderson, Lewis Spitz, and Andrew J. Copp London, England and Newcastle, England Backround/Purpose:
Role of Sonic Hedgehog in the Development of the Trachea and Oesophagus By Adonis S. Ioannides, Deborah J. Henderson, Lewis Spitz, and Andrew J. Copp London, England and Newcastle, England Backround/Purpose:
Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2
 Development 128, 5161-5172 (2001) Printed in Great ritain The Company of iologists Limited 2001 DEV4578 5161 Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2 Chunyang rian ai 1 and Alexandra L. Joyner 1,2,
Development 128, 5161-5172 (2001) Printed in Great ritain The Company of iologists Limited 2001 DEV4578 5161 Gli1 can rescue the in vivo function of Gli2 Chunyang rian ai 1 and Alexandra L. Joyner 1,2,
Interaction between the Signaling Molecules WNT7a and SHH during Vertebrate Limb Development: Dorsal Signals Regulate Anteroposterior Patterning
 Cell, Vol. 80, 939-947, March 24, 1995, Copyright 1995 by Cell Press Interaction between the Signaling Molecules WNT7a and SHH during Vertebrate Limb Development: Dorsal Signals Regulate Anteroposterior
Cell, Vol. 80, 939-947, March 24, 1995, Copyright 1995 by Cell Press Interaction between the Signaling Molecules WNT7a and SHH during Vertebrate Limb Development: Dorsal Signals Regulate Anteroposterior
Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
 Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Subject Index. AXIN2, cleft defects 24, 26
 Subject Index ADAMTS, mouse mutants and palate development 37, 38 Africa, cleft lip and palate prevalence 6, 7 Alcohol dependence, pregnancy risks for cleft 25, 61 Altitude, pregnancy risks for cleft 25,
Subject Index ADAMTS, mouse mutants and palate development 37, 38 Africa, cleft lip and palate prevalence 6, 7 Alcohol dependence, pregnancy risks for cleft 25, 61 Altitude, pregnancy risks for cleft 25,
Analysis of Variation in Clubfoot Candidate Genes
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-2010 Analysis of Variation in Clubfoot Candidate Genes Audrey R.
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 5-2010 Analysis of Variation in Clubfoot Candidate Genes Audrey R.
Review From fruitflies to mammals: mechanisms of signalling via the Sonic hedgehog pathway in lung development Minke van Tuyl* and Martin Post*
 Review From fruitflies to mammals: mechanisms of signalling via the Sonic hedgehog pathway in lung development Minke van Tuyl* and Martin Post* *Hospital for Sick Children Research Institute, Toronto,
Review From fruitflies to mammals: mechanisms of signalling via the Sonic hedgehog pathway in lung development Minke van Tuyl* and Martin Post* *Hospital for Sick Children Research Institute, Toronto,
Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons by multidirectional repulsion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
The role of mechanical stimuli induced by prenatal movements in skeletal development
 The role of mechanical stimuli induced by prenatal movements in skeletal development Niamh Nowlan, PhD Department of Bioengineering, Imperial College London Mechanobiology of Bone Mechanoregulation of
The role of mechanical stimuli induced by prenatal movements in skeletal development Niamh Nowlan, PhD Department of Bioengineering, Imperial College London Mechanobiology of Bone Mechanoregulation of
Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University
 Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
Development of the skin and its derivatives
 Development of the skin and its derivatives Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School
Development of the skin and its derivatives Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School
Dynamic Changes in the Response of Cells to Positive Hedgehog Signaling during Mouse Limb Patterning
 Cell, Vol. 118, 505 516, August 20, 2004, Copyright 2004 by Cell Press Dynamic Changes in the Response of Cells to Positive Hedgehog Signaling during Mouse Limb Patterning Sohyun Ahn 1,2 and Alexandra
Cell, Vol. 118, 505 516, August 20, 2004, Copyright 2004 by Cell Press Dynamic Changes in the Response of Cells to Positive Hedgehog Signaling during Mouse Limb Patterning Sohyun Ahn 1,2 and Alexandra
Sonic Hedgehog in Feather Morphogenesis: Induction of
 DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 207:57-70 (996) Sonic Hedgehog in Feather Morphogenesis: Induction of Mesenchymal Condensation and Association With Cell Death SHEREE A. TING-BERRETH AND CHENG-MING CHUONG Department
DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 207:57-70 (996) Sonic Hedgehog in Feather Morphogenesis: Induction of Mesenchymal Condensation and Association With Cell Death SHEREE A. TING-BERRETH AND CHENG-MING CHUONG Department
Development of the Pharyngeal Arches
 Development of the Pharyngeal Arches Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Recall the
Development of the Pharyngeal Arches Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Recall the
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Douglas J. Epstein 1, *, Andrew P. McMahon 2 and Alexandra L. Joyner 1,3, SUMMARY
 Development 126, 281-292 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV4093 281 Regionalization of Sonic hedgehog transcription along the anteroposterior axis of the mouse central
Development 126, 281-292 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV4093 281 Regionalization of Sonic hedgehog transcription along the anteroposterior axis of the mouse central
Hox genes. Discovered in Drosophila in 1923 by Bridges and Morgan Antennapaedia complex ANT-C Bithorax complex BX-C
 Hox genes Establish body plan during development Specify head to tail axis of animal embryos Head Hox genes, abdomen hox genes. Mutations can cause one body part to transform to another 39 transcription
Hox genes Establish body plan during development Specify head to tail axis of animal embryos Head Hox genes, abdomen hox genes. Mutations can cause one body part to transform to another 39 transcription
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
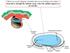 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Meeting Report. From December 8 to 11, 2012 at Atlanta, GA, U.S.A
 Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases
 Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases Aug. 21, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Bone Development Mouse embryo, E14.5 Mouse embryo, E18.0
Jilin University School of Stomatology Skeletogenesis Lecture 3: Skeletogenesis and diseases Aug. 21, 2015 Yuji Mishina, Ph.D. mishina@umich.edu Bone Development Mouse embryo, E14.5 Mouse embryo, E18.0
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
Sonic hedgehog is a survival factor for hypaxial muscles during mouse development
 Development 128, 743-752 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2654 743 Sonic hedgehog is a survival factor for hypaxial muscles during mouse development Marcus Krüger
Development 128, 743-752 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2654 743 Sonic hedgehog is a survival factor for hypaxial muscles during mouse development Marcus Krüger
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2
 ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
/06/ PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 3, 2006 Copyright 2006 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc.
 0031-3998/06/5903-0349 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 3, 2006 Copyright 2006 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. ARTICLES Sonic Hedgehog Is Essential for First Pharyngeal
0031-3998/06/5903-0349 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 59, No. 3, 2006 Copyright 2006 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. ARTICLES Sonic Hedgehog Is Essential for First Pharyngeal
Islets of Langerhans consist mostly of insulin-producing β cells. They will appear to be densely labeled
 Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Are adult pancreatic beta cells formed by self-duplication or stem cell differentiation? Introduction Researchers have long been interested in how tissues produce and maintain the correct number of cells
Wnt signaling and PKA control Nodal expression and left-right determination in the chick embryo
 Development 128, 3189-3195 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV9773 3189 Wnt signaling and PKA control Nodal expression and left-right determination in the chick embryo
Development 128, 3189-3195 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV9773 3189 Wnt signaling and PKA control Nodal expression and left-right determination in the chick embryo
Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2 mutation
 Development 127, 1593-1605 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4314 1593 Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2
Development 127, 1593-1605 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4314 1593 Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2
Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors. Implications for adrenal diseases. Gary D.
 Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors Implications for adrenal diseases Gary D. Hammer Condensation of the Ventral Intermediate Mesoderm Forms the
Adrenocortical Stem and Progenitor cells: Growth factors, signaling and transcription factors Implications for adrenal diseases Gary D. Hammer Condensation of the Ventral Intermediate Mesoderm Forms the
WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
DBS: Project Seminar Guidelines
 DBS: Project Seminar Guidelines Updated on 19 January 2011 Project Area Review Seminar ( Project I ) Content: This is a comprehensive review of the literature in the area the student has selected for their
DBS: Project Seminar Guidelines Updated on 19 January 2011 Project Area Review Seminar ( Project I ) Content: This is a comprehensive review of the literature in the area the student has selected for their
MCB140: Second Midterm Spring 2010
 MCB140: Second Midterm Spring 2010 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 11 pages including this page. You will have 150 minutes
MCB140: Second Midterm Spring 2010 Before you start, print your name and student identification number (S.I.D) at the top of each page. There are 11 pages including this page. You will have 150 minutes
Current Model for how cells become neural. Double Inhibition Model for Neural fate. Neural Development. How do cells become neurons?
 Current Model for how cells becoe neural 1) Default state is neural 2) Local secretion of BMPs by epideris inhibits neural fate 3) Local secretion of noggin, chordin by dorsal lip or esoder inhibits BMP
Current Model for how cells becoe neural 1) Default state is neural 2) Local secretion of BMPs by epideris inhibits neural fate 3) Local secretion of noggin, chordin by dorsal lip or esoder inhibits BMP
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Lecture 1: Embryology of the Limbs (Development of Skeletal and Muscular Systems)
 Lecture 1: Embryology of the Limbs (Development of Skeletal and Muscular Systems) Musculoskeletal Block Editing file Colour Index: Red: Important Gray: Notes Green: Dr. s notes After this lecture you should
Lecture 1: Embryology of the Limbs (Development of Skeletal and Muscular Systems) Musculoskeletal Block Editing file Colour Index: Red: Important Gray: Notes Green: Dr. s notes After this lecture you should
