Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development.
|
|
|
- Janel Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fig. S1. RT-PCR analyses of the expression and distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts during early development. (A) Temporal expression of Xdscr6 at various stages (numbers on the top) and its distribution at stage 35 in the head (He), trunk (Tr) and posterior (P) regions. (B) Schema showing the dissection of different early gastrula tissues including ectoderm (ect), mesoderm, endoderm, dorsal endoderm (DE) and ventral endoderm (VE). (C) RT-PCR analyses of the distribution of Xdscr6 transcripts in different regions of the early gastrula. (D) Induction of Xdscr6 expression in early gastrula ectoderm following overexpression of squint and Wnt8. ODC was used as an input control. Fig. S2. XDSCR6 differentially induces the expression of nodal-related genes. Embryos at the 2-cell stage were injected at the animal pole region with Xdscr6 mrna (0.5 ng), RT-PCR analyses were performed on control embryo and dissected ectoderm explants at the early gastrula stage.
2 Fig. S3. Comparison of sequence and activity between Xenopus and human RIPPLY2 proteins. (A) Sequence alignment. Conserved residues are indicated in red. The amino- and carboxyl-terminal halves of XDSCR6 used for functional analyses are indicated. (B) RT-PCR analyses of the activity of XDSCR6 and human RIPPLY2 in mesoderm gene expression at the early gastrula stage. (C) A control embryo at the stage 33. (D) Induction of a partial secondary axis by human RIPPLY2. The frequency of this induction is similar as XDSCR6 (not shown). Fig. S4. Uniform expression of XDSCR6 suppresses trunk and posterior development. Embryos at the 8-cell stage were radially injected with Xdscr6 mrna (0.4 ng) at the equatorial region and live images of control (A) and injected (B) embryos were taken at larval stage 41. Note that embryos radially injected with Xdscr6 lacks trunk and posterior regions.
3 Fig. S5. XDSCR6 induces chordin and Xbra expression independently of nodal signalling. Embryos at the 2-cell stage were injected at the animal pole region with low amount of Xdscr6 mrna alone or coinjected with VegT-EnR mrna or antivin mrna. They were also injected with VegT mrna (40 pg) or coinjected with VegT-EnR mrna or antivin mrna. RT-PCR analyses on control embryo and dissected ectoderm explants were performed at the early gastrula stage. VegT-EnR and antivin does not block the activity of XDSCR6, but inhibits the activity of VegT. Fig. S6. RT-PCR analyses of Otx2, chordin and Xbra expression in ectoderm explants injected with wild-type Xdscr6 or its mutants, as indicated. Fig. S7. BMI1 inhibits ectopic chordin expression induced by XDSCR6. Embryos at the 4-cell stage were ventrally injected with Xdscr6 mrna alone, BMI1 mrna alone or coinjected with Xdscr6 and BMI1 mrna. In situ hybridization was performed at the early gastrula stage.
4 Table S1. Primers for semi-quantitative PCR. PCR primer pair VegT Krox20 Xdscr6 Xnr1 Xnr2 Xnr4 Xnr5 Xnr6 Goosecoid (promoter) Sequence F: 5'-CAAGTAAATGTGAGAAACCG-3' R: 5'-CAAATACACACACATTTCCC-3' F: 5'-AACCGCCCCAGTAAGACC-3' R: 5'-GTGTACGCCTGTCCTGTTAG-3' F: 5'-GTTCTACTATGGAGCCGAATC-3' R: 5'-CTGTGCAAGATTTAATTTTCAT-3' F: 5'-TAAAAGCAAAGGAAAGGGCAGAG-3' R : 5'-GATGCTTCCTATTGATAAGTGATG-3' F : 5'-ATCTGATGCCGT TCTAAGCC-3' R: 5'-GACCTTCTTCAACCTCAGCC-3' F: 5'-GAAATGGAGGTGATGGTAGAC-3' R: 5'-GACCATCATCACTATCCTGCTG-3' F: 5'-TCACAATCCTTTCACTAGGGC-3' R : 5'-GGAACCTCTGAAAGGAAGGC-3' F : 5'-TCCAGTATGATCCATCTGTTGC-3' R : 5'-GTCAAAGTCAACAATCATGTCGA-3' F: 5'-CCAGAGAAACAAAACAGTCATTCC-3' R: 5'-GCAGACTCTCCCTGTAGTTATTCAC-3'
5 Table S2. Primers for real-time PCR. PCR primer pair Chordin Xbra Wnt8 Sox17α EF1α ODC Goosecoid (promoter) Sequence F: 5'-AGCTGTCAGAAGCGTACCGTG-3' R: 5'-CAGAGGTGGGCACACAATAGG-3' F: 5'-CACCAAGAATGGAAGACGAATG-3' R: 5'-CCCGACATGCTCACCTTCA-3' F: 5'-GCTACCCACAATGGACTTCGA-3' R: 5'-AGCTAATGGCATGCACAAAGG-3' F : 5'-ACAGAACCCCGACCTGCA-3' R : 5'-GGATTTCCATGATTTACCAAGCAT-3' F: 5'-CTTCTCAGGCCGACTGTGC-3' R : 5'-ATTCACCAACACCAGCAGCA-3' F : 5'-GGGCAAAGGAGCTTAATGTGG-3' R: 5'-TGCCAACATGGAAACTCACAC-3' F: 5'-CCAGAGAAACAAAACAGTCATTCC-3' R: 5'-GGTGCAATTTCCTTGCTCTC-3'
6 Table S3. Induction of a secondary embryonic axis by overexpression of XDSCR6. Injection Single axis Secondary axis with head Partial secondary axis Uninjected n Xdscr6 mrna (0.4 ng) (Ventro-vegetal) Xdscr6 mrna (0.4 ng) (Ventro-animal) Xdscr6 DNA (0.4 ng) (Ventro-vegetal) Embryos were injected at the 4-cell stage and the phenotypes were scored when uninjected embryos reached stage 35. The result is presented as percentage, except n, which refers to total embryos scored from three independent experiments.
7 Table S4. XDSCR6 rescues anterior defects produced by dorsal overexpression of BMI1. Injection Normal Anterior defects n Uninjected BMI1 (0.5 ng) Xdscr6 (0.2 ng) BMI1/Xdscr6 (0.5/0.2 ng) Embryos at 4-cell stage were dorsally injected with indicated mrna. They were cultured until stage 32 to score phenotypes. Anterior defects include phenotypes with small head, absence of eye or complete absence of head region as shown in Figure 9C. The results are expressed as percentage, except n, which refers to total embryos scored from three independent experiments.
8 Table S5. BMI1 inhibits secondary axis formation induced by XDSCR6. Injection Normal Secondary axis n Uninjected Xdscr6 (0.1 ng) BMI1 (0.5 ng) Xdscr6/BMI1 (0.1/0.5 ng) Embryos at 4-cell stage were ventrally injected with indicated mrna. They were cultured until stage 35 to score the presence or absence of axis duplication. The results are presented as percentage except n, which refers to total embryos scored from three independent experiments.
9 Table S6. Ectopic chordin expression following overexpression of XDSCR6 or XDSCR6/BMI1. Injection Strong Weak Absence n Uninjected Xdscr6 (0.1 ng) Xdscr6/BMI1 (0.1/0.5 ng) Embryos at 4-cell stage were ventrally injected with indicated mrna and were fixed at early gastrula stage for in situ hybridization. The intensity of ectopic chordin expression was as shown in Figure S7. The results are presented as percentage except n, which refers to total embryos scored from three independent experiments.
Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Formation and Mesoderm Induction October 27, 2005 Amphibian anteroposterior specification polarized eggs animal/vegetal pigment yolk v. clear cytoplasm mitochondrial
Patterning the Embryo
 Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
Patterning the Embryo Anteroposterior axis Regional Identity in the Vertebrate Neural Tube Fig. 2.2 1 Brain and Segmental Ganglia in Drosophila Fig. 2.1 Genes that create positional and segment identity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information included with Nature MS 2008-02-01484B by Colantonio et al., entitled The dynein regulatory complex is required for ciliary motility and otolith biogenesis in the inner ear. This
Supplementary Information included with Nature MS 2008-02-01484B by Colantonio et al., entitled The dynein regulatory complex is required for ciliary motility and otolith biogenesis in the inner ear. This
C. elegans Embryonic Development
 Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Autonomous Specification in Tunicate development Autonomous & Conditional Specification in C. elegans Embryonic Development Figure 8.36 Bilateral Symmetry in the Egg of the Tunicate Styela partita Fig.
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β
 Manuscript EMBOR-2011-35178 Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β Anja Kietzmann, Yingqun Wang, Dominik Weber and Herbert Steinbeisser Corresponding author:
Manuscript EMBOR-2011-35178 Xenopus Paraxial Protocadherin inhibits Wnt/β -catenin signalling via Casein Kinase 2β Anja Kietzmann, Yingqun Wang, Dominik Weber and Herbert Steinbeisser Corresponding author:
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development
 Development 126, 2451-2460 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV2346 2451 Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development Massimiliano Andreazzoli 1,3, Gaia
Development 126, 2451-2460 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV2346 2451 Role of Xrx1 in Xenopus eye and anterior brain development Massimiliano Andreazzoli 1,3, Gaia
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Non-canonical Notch signaling represents an ancestral mechanism to regulate neural differentiation
 Layden and Martindale EvoDevo 2014, 5:30 RESEARCH Non-canonical Notch signaling represents an ancestral mechanism to regulate neural differentiation Michael J Layden 1 and Mark Q Martindale 2* Open Access
Layden and Martindale EvoDevo 2014, 5:30 RESEARCH Non-canonical Notch signaling represents an ancestral mechanism to regulate neural differentiation Michael J Layden 1 and Mark Q Martindale 2* Open Access
Supplementary Figures
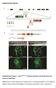 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. nrg1 bns101/bns101 embryos develop a functional heart and survive to adulthood (a-b) Cartoon of Talen-induced nrg1 mutation with a 14-base-pair deletion in
Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural. Neural Development
 Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp 477-506 (sorta) 4 th ed, pp 545-575 (sorta) References : Fainsod, A., Steinbeisser, H., & De Robertis, E. M. (1994).
Lecture IV. Mechanisms of Neural Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings NEUROSCIENCE: 5 th ed, pp 477-506 (sorta) 4 th ed, pp 545-575 (sorta) References : Fainsod, A., Steinbeisser, H., & De Robertis, E. M. (1994).
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION. Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling.
 EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of mitotic cells after perturbation of Notch signalling. Notch activation suppresses the cell cycle indistinguishably both within and outside the neural plate
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
Inhibition of neurogenesis by SRp38, a neurod-regulated RNAbinding
 Research article 1511 Inhibition of neurogenesis by SRp38, a neurod-regulated RNAbinding protein Karen J. Liu* and Richard M. Harland Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California,
Research article 1511 Inhibition of neurogenesis by SRp38, a neurod-regulated RNAbinding protein Karen J. Liu* and Richard M. Harland Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, University of California,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
Wnt signaling. Ramray Bhat.
 Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
Wnt signaling Ramray Bhat ramray@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Starting with animal biology and viral infections The discovery of certain laboratory murine strains that were highly susceptible to mammary gland cancer.
A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
 Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Concept 18.4: A program of differential gene expression leads to the different cell types in a multicellular organism During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types
Bmps and Id2a Act Upstream of Twist1 To Restrict Ectomesenchyme Potential of the Cranial Neural Crest
 Bmps and Id2a Act Upstream of Twist1 To Restrict Ectomesenchyme Potential of the Cranial Neural Crest Ankita Das, J. Gage Crump* Broad CIRM Center, University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine,
Bmps and Id2a Act Upstream of Twist1 To Restrict Ectomesenchyme Potential of the Cranial Neural Crest Ankita Das, J. Gage Crump* Broad CIRM Center, University of Southern California Keck School of Medicine,
Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 5345 Development 138, 5345-5356 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.068908 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
RESEARCH ARTICLE 5345 Development 138, 5345-5356 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.068908 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Novel functions of Noggin proteins: inhibition of Activin/Nodal and Wnt signaling
Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
 Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Wright et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2015) 15:33 DOI 10.1186/s12861-015-0083-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Cooperative and independent functions of FGF and Wnt signaling during early inner ear development
Cell Type Nervous System I. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation. Human issues.
 7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
Nodal and BMP2/4 Signaling Organizes the Oral-Aboral Axis of the Sea Urchin Embryo
 Developmental Cell, Vol. 6, 397 410, March, 2004, Copyright 2004 by Cell Press Nodal and BMP2/4 Signaling Organizes the Oral-Aboral Axis of the Sea Urchin Embryo Véronique Duboc, Eric Röttinger, Lydia
Developmental Cell, Vol. 6, 397 410, March, 2004, Copyright 2004 by Cell Press Nodal and BMP2/4 Signaling Organizes the Oral-Aboral Axis of the Sea Urchin Embryo Véronique Duboc, Eric Röttinger, Lydia
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set.
 Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Supplementary Figure 1. A microarray screen of organizers compared to non-organizer tissue reveals a putative organizer gene set. (a, b) Venn diagrams of 31 enriched (a) and 17 depleted (b) genes significantly
Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4493 4498, April 1997 Developmental Biology Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development (signal transduction
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 4493 4498, April 1997 Developmental Biology Expression of mutated Nck SH2 SH3 adaptor respecifies mesodermal cell fate in Xenopus laevis development (signal transduction
The lefty-related factor Xatv acts as a feedback inhibitor of Nodal signaling in mesoderm induction and L-R axis development in Xenopus
 Development 127, 1049-1061 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4264 1049 The lefty-related factor Xatv acts as a feedback inhibitor of Nodal signaling in mesoderm
Development 127, 1049-1061 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4264 1049 The lefty-related factor Xatv acts as a feedback inhibitor of Nodal signaling in mesoderm
Hepatogenesis I Liver development
 Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Hepatogenesis I Liver development HB 308 George Yeoh Room 2.59 MCS Building yeoh@cyllene.uwa.edu.au Topics Early liver development Tissue interaction - role of morphogens and cytokines Liver enriched transcription
Members of the transforming growth factor- (TGF- ) family
 Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase Ying Zhang*, Chenbei Chang, Daniel J. Gehling*, Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou, and Rik Derynck *Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular
Regulation of Smad degradation and activity by Smurf2, an E3 ubiquitin ligase Ying Zhang*, Chenbei Chang, Daniel J. Gehling*, Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou, and Rik Derynck *Laboratory of Cellular and Molecular
Consistent Left-Right Asymmetry Cannot be Established by Late Organizers in Xenopus Unless the Late Organizer is a Conjoined Twin
 University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Laura Vandenberg April 1, 2010 Consistent Left-Right Asymmetry Cannot be Established by Late Organizers in Xenopus Unless the Late Organizer
University of Massachusetts Amherst From the SelectedWorks of Laura Vandenberg April 1, 2010 Consistent Left-Right Asymmetry Cannot be Established by Late Organizers in Xenopus Unless the Late Organizer
Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus mesoderm induction
 Development 128, 35-44 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2656 35 Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus
Development 128, 35-44 (2001) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV2656 35 Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase acts in parallel to the ERK MAP kinase in the FGF pathway during Xenopus
Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling
 Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling Tomomi Fukuchi-Shimogori and Elizabeth A Grove Presented by Sally Kwok Background Cerebral cortex has anatomically and functionally distinct
Emx2 patterns the neocortex by regulating FGF positional signaling Tomomi Fukuchi-Shimogori and Elizabeth A Grove Presented by Sally Kwok Background Cerebral cortex has anatomically and functionally distinct
Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between
 Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between Myod +/ or Myod / females and Myod +/ ;Igf2 +/ males and
Fig. S1. Weight of embryos during development. Embryos are collected at different time points (E12.5, E14.5, E16.5 and E18.5) from matings between Myod +/ or Myod / females and Myod +/ ;Igf2 +/ males and
A secreted splice variant of the Xenopus frizzled-4 receptor is a biphasic modulator of Wnt signalling
 Gorny et al. Cell Communication and Signaling 2013, 11:89 SHORT REPORT Open Access A secreted splice variant of the Xenopus frizzled-4 receptor is a biphasic modulator of Wnt signalling Anne-Kathrin Gorny
Gorny et al. Cell Communication and Signaling 2013, 11:89 SHORT REPORT Open Access A secreted splice variant of the Xenopus frizzled-4 receptor is a biphasic modulator of Wnt signalling Anne-Kathrin Gorny
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at
 Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Supplementary Figure 1. EC-specific Deletion of Snail1 Does Not Affect EC Apoptosis. (a,b) Cryo-sections of WT (a) and Snail1 LOF (b) embryos at E10.5 were double-stained for TUNEL (red) and PECAM-1 (green).
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration
 Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Correspondence: mirna regulation of Sdf1 chemokine signaling provides genetic robustness to germ cell migration Alison A. Staton, Holger Knaut, and Antonio J. Giraldez Supplementary Note Materials and
Prolonged FGF signaling is necessary for lung and liver induction in Xenopus
 Shifley et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2012, 12:27 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prolonged FGF signaling is necessary for lung and liver induction in Xenopus Emily T Shifley 1, Alan P Kenny 2, Scott A
Shifley et al. BMC Developmental Biology 2012, 12:27 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prolonged FGF signaling is necessary for lung and liver induction in Xenopus Emily T Shifley 1, Alan P Kenny 2, Scott A
Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin, Kazumi Fukatsu, and Paul Grossfeld
 Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Evidence That Deletion of ETS-1, a Gene in the Jacobsen Syndrome (11q-) Cardiac Critical Region, Causes Congenital Heart Defects through Impaired Cardiac Neural Crest Cell Function 52 Maoqing Ye, Yan Yin,
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Supplementary Fig. 1 Blocking shh function at the protein level confirms its role as a guidance cue for postcommissural axons. As an alternative method to demonstrate the role of shh as a guidance cue
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Transcription assay of nine ABA-responsive PP2C genes. Total RNA was isolated from 7 day-old seedlings treated with or without
Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes
 Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Objectives: Testing the ABC floral-organ identity model: expression of A and C function genes To test the validity of the ABC model for floral organ identity we will: 1. Use the model to make predictions
Urogenital Development
 2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
2-5-03 Urogenital Development Greg Dressler Assoc. Professor Dept. of Pathology x46490 Dressler@umich.edu The Origin of the Kidney In the vertebrate embryo, the first stage of kidney development occurs
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos
 S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
S. S. SUMIDA BIOLOGY 340 Comparative Embryology Introduction Laboratory Exercise 1 Laboratory Examination of a Basal Deuterostome: Sea Urchin Embryos Many laboratories that examine sea urchin embryos do
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation
 A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
A study of cilia density in sea urchin embryos during gastrulation Steve Das Independent Research Project Report Bio 254 Developmental Biology May 3, 2012 Introduction Embryo growth and development is
Further studies on the melanophores of periodic albino mutant of Xenopus laevis
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 91, 65-78 (1986) 65 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 Further studies on the melanophores of periodic albino mutant of Xenopus laevis T. FUKUZAWA AND
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 91, 65-78 (1986) 65 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 Further studies on the melanophores of periodic albino mutant of Xenopus laevis T. FUKUZAWA AND
Tetrapod Limb Development
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular and Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development February 11, 2008 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Patterning
The Nervous System PART D. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART D PNS: Spinal Nerves There is a pair of spinal nerves at the level of each
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Supplemental Information. Figures. Figure S1
 Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
Supplemental Information Figures Figure S1 Identification of JAGGER T-DNA insertions. A. Positions of T-DNA and Ds insertions in JAGGER are indicated by inverted triangles, the grey box represents the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Glucosylceramide synthase (GlcT-1) in the fat body controls energy metabolism in Drosophila Ayako Kohyama-Koganeya, 1,2 Takuji Nabetani, 1 Masayuki Miura, 2,3 Yoshio Hirabayashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of the AA5x. a, Camera lucida drawing of embryo at 48 hours post fertilization (hpf, modified from Kimmel et al. Dev Dyn. 1995 203:253-310). b, Confocal microangiogram
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation
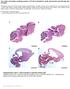 The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
The coiled-coil domain containing protein CCDC40 is essential for motile cilia function and left-right axis formation Anita Becker-Heck#, Irene Zohn#, Noriko Okabe#, Andrew Pollock#, Kari Baker Lenhart,
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
College of Arts and Sciences Grants for Undergraduate Scholars
 Background The Wnt signaling pathway is responsible for many different developmental processes such as cell proliferation, cell-fate determination, and tissue pattering (Nakamure et al., 2008). Prior studies
Background The Wnt signaling pathway is responsible for many different developmental processes such as cell proliferation, cell-fate determination, and tissue pattering (Nakamure et al., 2008). Prior studies
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE. Thomas Marino, Ph.D.
 BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
BRAIN DEVELOPMENT I: ESTABLISHMENT OF BASIC ARCHITECTURE Thomas Marino, Ph.D. Development of the Brain I. Competencies: Upon completion of this section of the course, the student must be able to: 1. Understand
FGF-20 and DKK1 are transcriptional targets of b-catenin and FGF-20 is implicated in cancer and development
 The EMBO Journal (2005) 24, 73 84 & 2005 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/05 www.embojournal.org FGF-20 and DKK1 are transcriptional targets of b-catenin and FGF-20
The EMBO Journal (2005) 24, 73 84 & 2005 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 0261-4189/05 www.embojournal.org FGF-20 and DKK1 are transcriptional targets of b-catenin and FGF-20
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Publisher statement: None
 University of Warwick institutional repository This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please refer to the repository
University of Warwick institutional repository This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please refer to the repository
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
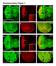 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Protocol: specimen preparation (brain dissection and region extraction) for using RT-qPCR to examine gene expression in brain regions of a fish
 HOST LAB: DR. LAUREN O'CONNELL, CENTER FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY, HARVARD UNIVERSITY Protocol: specimen preparation (brain dissection and region extraction) for using RT-qPCR to examine gene expression in brain
HOST LAB: DR. LAUREN O'CONNELL, CENTER FOR SYSTEMS BIOLOGY, HARVARD UNIVERSITY Protocol: specimen preparation (brain dissection and region extraction) for using RT-qPCR to examine gene expression in brain
tom tom 24hpf tom tom 48hpf tom 60hpf tom tom 72hpf tom
 a 24hpf c 48hpf d e 60hpf f g 72hpf h i j k ISV ISV Figure 1. Vascular integrity defects and endothelial regression in mutant emryos. (a,c,e,g,i) Bright-field and (,d,f,h,j) corresponding fluorescent micrographs
a 24hpf c 48hpf d e 60hpf f g 72hpf h i j k ISV ISV Figure 1. Vascular integrity defects and endothelial regression in mutant emryos. (a,c,e,g,i) Bright-field and (,d,f,h,j) corresponding fluorescent micrographs
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture. Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu
 Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
Title: Chapter 5 Recorded Lecture Speaker: Title: What Anthony is the title Berger/Angela of this lecture? Williams Speaker: Amit Dhingra Created by: (remove if same as speaker) online.wsu.edu Chapter
Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
 Development 130, 2225-2238 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00443 2225 Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
Development 130, 2225-2238 2003 The Company of Biologists Ltd doi:10.1242/dev.00443 2225 Notch activates sonic hedgehog and both are involved in the specification of dorsal midline cell-fates in Xenopus
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin
 Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Baf60c and baf180 are induced during cardiac regeneration in zebrafish. RNA in situ hybridization was performed on paraffin sections from sham-operated adult hearts (a and i) and
Fertilization. mitosis. N sperm pronucleus. fertilization. N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) 2N zygote nucleus
 Fertilization 2N pronucleus (suspended in meiotic metaphase) N polar body reduction division N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) mitosis 2N zygote nucleus N polar bodies (2): disintegrate membrane formation
Fertilization 2N pronucleus (suspended in meiotic metaphase) N polar body reduction division N pronucleus (after sperm enters egg) mitosis 2N zygote nucleus N polar bodies (2): disintegrate membrane formation
Localization of Shh expression by Wnt and Eda affects axial polarity and shape of hairs
 Developmental Biology 305 (2007) 246 261 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Localization of Shh expression by Wnt and Eda affects axial polarity and shape of hairs Brigitte Hammerschmidt, Thomas Schlake Max-Planck
Developmental Biology 305 (2007) 246 261 www.elsevier.com/locate/ydbio Localization of Shh expression by Wnt and Eda affects axial polarity and shape of hairs Brigitte Hammerschmidt, Thomas Schlake Max-Planck
In canonical Wnt signaling, Dishevelled (Dvl) is a critical
 Published Online: 17 March, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200710050 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 11, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Nuclear Dvl, c-jun, -catenin, and TCF form a complex
Published Online: 17 March, 2008 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200710050 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 11, 2018 JCB: ARTICLE Nuclear Dvl, c-jun, -catenin, and TCF form a complex
A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines
 Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Supplemental Data A Cxcl12-Cxcr4 Chemokine Signaling Pathway Defines the Initial Trajectory of Mammalian Motor Axons Ivo Lieberam, Dritan Agalliu, Takashi Nagasawa, Johan Ericson, and Thomas M. Jessell
Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification
 Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification Marcus K. Gustafsson, 1,3,4 Hua Pan, 1,3,4 Deborah F. Pinney, 1,3 Yongliang Liu, 1,3 Anna Lewandowski, 1,3
Myf5 is a direct target of long-range Shh signaling and Gli regulation for muscle specification Marcus K. Gustafsson, 1,3,4 Hua Pan, 1,3,4 Deborah F. Pinney, 1,3 Yongliang Liu, 1,3 Anna Lewandowski, 1,3
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4)
 Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Identification and characterization of multiple splice variants of Cdc2-like kinase 4 (Clk4) Vahagn Stepanyan Department of Biological Sciences, Fordham University Abstract: Alternative splicing is an
Supplemental Information. Spatial Auxin Signaling. Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis
 Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Current Biology, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Spatial Auxin Signaling Controls Leaf Flattening in Arabidopsis Chunmei Guan, Binbin Wu, Ting Yu, Qingqing Wang, Naden T. Krogan, Xigang Liu, and Yuling
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Mouse Lefty2 and Zebrafish Antivin Are Feedback Inhibitors of Nodal Signaling during Vertebrate Gastrulation
 Molecular Cell, Vol. 4, 287 298, September, 1999, Copyright 1999 by Cell Press Mouse Lefty2 and Zebrafish Antivin Are Feedback Inhibitors of Nodal Signaling during Vertebrate Gastrulation Chikara Meno,
Molecular Cell, Vol. 4, 287 298, September, 1999, Copyright 1999 by Cell Press Mouse Lefty2 and Zebrafish Antivin Are Feedback Inhibitors of Nodal Signaling during Vertebrate Gastrulation Chikara Meno,
Multi-site phosphorylation regulates NeuroD4 activity during primary neurogenesis: a conserved mechanism amongst proneural proteins
 Hardwick and Philpott Neural Development (215) 1:15 DOI 1.1186/s1364-15-44-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-site phosphorylation regulates NeuroD4 activity during primary neurogenesis: a conserved
Hardwick and Philpott Neural Development (215) 1:15 DOI 1.1186/s1364-15-44-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-site phosphorylation regulates NeuroD4 activity during primary neurogenesis: a conserved
Tetrapod Limb Development
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Tetrapod Limb Development July 29, 2009 Tetrapod Limbs Merlin D. Tuttle Vicki Lockard and Paul Barry Father Alejandro Sanchez Anne Fischer Limb Development - Overview
Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates
 Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates L. Cheng, A. Arata, R. Mizuguchi, Y. Qian, A. Karunaratne, P.A. Gray, S. Arata, S. Shirasawa, M. Bouchard,
Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates L. Cheng, A. Arata, R. Mizuguchi, Y. Qian, A. Karunaratne, P.A. Gray, S. Arata, S. Shirasawa, M. Bouchard,
Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN
 UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
UNC-6/Netrin mediates dendritic self-avoidance Cody J. Smith 1, Joseph D. Watson 1,4,5, Miri K. VanHoven 2, Daniel A. Colón-Ramos 3 and David M. Miller III 1,4,6 1 Department of Cell and Developmental
More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection of Activin into Xenopus Neurula Embryos
 Developmental Biology 221, 321 336 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9666, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection
Developmental Biology 221, 321 336 (2000) doi:10.1006/dbio.2000.9666, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on More Than 95% Reversal of Left Right Axis Induced by Right-Sided Hypodermic Microinjection
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Divergent effects of intrinsically active MEK variants on developmental Ras signaling Yogesh Goyal,2,3,4, Granton A. Jindal,2,3,4, José L. Pelliccia 3, Kei Yamaya 2,3, Eyan Yeung
E-selectin ligand 1 regulates growth plate homeostasis in mice by inhibiting the intracellular processing and secretion of mature TGF-β
 Research article E-selectin ligand 1 regulates growth plate homeostasis in mice by inhibiting the intracellular processing and secretion of mature TGF-β Tao Yang, 1 Roberto Mendoza-Londono, 1 Huifang Lu,
Research article E-selectin ligand 1 regulates growth plate homeostasis in mice by inhibiting the intracellular processing and secretion of mature TGF-β Tao Yang, 1 Roberto Mendoza-Londono, 1 Huifang Lu,
WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Publicly Accessible Penn Dissertations 1-1-2012 WNT2 and WNT7B Cooperative Signaling in Lung Development Mayumi Miller University of Pennsylvania, mayumimiller@gmail.com
Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons by multidirectional repulsion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:697-716. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Shh signaling guides spatial pathfinding of raphespinal tract axons
Essential role for b-arrestin 2 in the regulation of Xenopus convergent extension movements
 The EMO Journal (2007) 26, 2513 2526 & 2007 European Molecular iology Organization ll Rights Reserved 0261-4189/07 www.embojournal.org Essential role for b-arrestin 2 in the regulation of Xenopus convergent
The EMO Journal (2007) 26, 2513 2526 & 2007 European Molecular iology Organization ll Rights Reserved 0261-4189/07 www.embojournal.org Essential role for b-arrestin 2 in the regulation of Xenopus convergent
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance
 Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Investigating the role of EphAl ephrin-a signalling during trigeminal ganglion axon guidance A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Molecular and Biomedical Science (Discipline of Genetics),
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Supporting Information
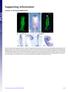 Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Supporting Information Creuzet 10.1073/pnas.0906072106 Fig. S1. Migrating CNC cells express Bmp inhibitors. (A) HNK1 immunolabeling of migrating CNC cells at 7 ss. (B) At this stage, Fgf8 is strongly expressed
Supplemental Data. Wu et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Figure 1. FIM5 is preferentially expressed in stamen and mature pollen. The expression data of FIM5 was extracted from Arabidopsis efp browser (http://www.bar.utoronto.ca/efp/development/),
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
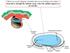 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
Otx1 and Otx2 activities are required for the normal development of the
 Development 126, 2335-2343 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV1416 2335 Otx1 and Otx2 activities are required for the normal development of the mouse inner ear Hakim
Development 126, 2335-2343 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 DEV1416 2335 Otx1 and Otx2 activities are required for the normal development of the mouse inner ear Hakim
