Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
|
|
|
- Blaze Lucas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements about the development of the lymphatic system is correct? Question #01 A. The lymphatic system develops independent of the vascular system. B. By the 7 th week of development, there are lymph sacs that become connected to the venous system. C. By the 4 th week of development, there are lymph sacs that become connected to the venous system. D. The thymus gland and spleen are formed by the 3 rd week of development. E. The spleen is completely formed from the cells of the third pharyngeal pouch by the 5 th week. The lymphatic system is derived from the mesoderm, and lymph vessel formation is connected to the formation of the veins in the vascular system. B. Correct! By the 7 th week of development, there are lymph sacs that become connected to the venous system. By the 7 th week of development, there are lymph sacs that become connected to the venous system. The thymus gland and spleen are formed by the 8 th week of development. The spleen, along with the thymus gland, is formed by the 8 th week of development. The lymphatic system is derived from the mesoderm during embryogenesis. Lymph vessel formation is connected to and develops with blood vessels. By the 7 th week of development, there are lymph sacs that become connected to the venous system. The thymus gland and spleen are formed by the 8 th week of development. The thymus gland forms from cells of the third pharyngeal pouch. At birth, the thymus gland takes up the majority of the anterior mediastinal space.
2 Question No. 2 of 10 Which of the following statements is not correct about the thymus gland? Question #02 A. The thymus is formed by the 8 th week of development. B. B-Cells develop in the thymus gland. C. The thymus gland is made up of two lateral lobes that are contained in a capsule. D. The thymus gland normally undergoes involution. E. Inside the thymus gland, positive and negative selection takes place. The thymus is formed by the 8 th week of development. B. Correct! B-Cells develop in the bone marrow, and T-Cells develop in the thymus gland. The thymus gland is made up of two lateral lobes that are contained in a capsule. Involution is a normal process of the thymus gland as we age. T-Cells undergo positive and negative selection in the thymus gland. The thymus gland is made up of 2 lateral lobes, which are enclosed in a capsule. Each lateral lobe is made up of many smaller lobules. The thymus gland lies posterior to the sternum in the superior mediastinum. The thymus reaches its full size during puberty and then gradually decreases in size as we age, a process known as involution. Inside the thymus, lymphocyte precursors mature into T-Cells. To be released into the circulation, the T-Cells must undergo both positive and negative selection.
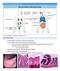
3 Question No. 3 of 10 The lymphatic system, along with the cardiovascular system, includes capillaries. Which of the following statements about lymph capillaries is correct? Question #03 A. The lymph capillaries are located near the major arteries of the vascular system. B. Lymph capillaries permit two-way flow of fluid into and out of the lymphatic system. C. Lymph capillaries are larger than blood capillaries and are structured to allow the collection of lymph fluid. D. Lymphatic capillaries are directly connected to efferent lymph node vessels. E. None of the answers is correct. The lymph capillaries are closely associated with the tissue (blood) capillaries, at the junction of the arterioles and venules. B. Incorrect! Lymphatic capillaries permit one-way flow of fluid, due to their unique valve-like structure. C. Correct! Lymph capillaries are larger than blood capillaries and are structured to allow the collection of lymph fluid. Eventually, the lymphatic capillary becomes the afferent lymphatic vessel at the lymph node. There is one correct answer above. The lymph capillaries are closely associated with the tissue (blood) capillaries, at the junction of the arterioles and venules. The lymph capillaries are larger and are structured to allow the collection of lymph fluid. The wall of the lymphatic capillary is made up of endothelial cells. Similar to certain veins, lymphatic capillaries permit one-way flow of fluid, due to their unique structure. Eventually, the lymphatic capillary becomes the afferent lymphatic vessel at the lymph node. The arrows in the image above indicate the flow of fluid into the lymph capillaries.
4 Question No. 4 of 10 Lymph vessels have a unique strucuture and location. Which of the following statements about lymph vessels is correct? Question #04 A. The valve of a lymphatic capillary is made up of endothelial cell overlap. B. All lymphatic vessels are the size of blood capillaries. C. The deep lymphatic vessels accompany the superficial veins and arteries of the body. D. The right lymphatic duct collects blood from the entire upper body. E. The thoracic duct delivers lymph fluid into the aorta. A. Correct! The valve of a lymphatic capillary is made up of endothelial cell overlap. B. Incorrect! The lymphatic vessels range in size from the lymph capillaries to the large diameter collecting vessels that are known as lymphatic ducts. The deep lymphatic vessels accompany the deep arteries and veins of the body. On the right side of the body, the right lymphatic duct collects lymph from the side of the body above the level of the diaphragm. The thoracic duct delivers the lymph into the venous system at the junction of the left subclavian vein and the left internal jugular vein. The lymphatic vessels range in size from the lymph capillaries to the large diameter collecting vessels that are known as lymphatic ducts. The lymphatic capillaries are larger than blood capillaries; they have thinner walls and do not have a continuous basal lamina. The valve of the lymphatic capillary is made up by the endothelial cell overlap at one end of the vessel. There are certain regions of the body that contain numerous lymphatic capillaries, such as: in the connective tissue deep to the dermis, mucosa layer of the digestive tract, and in the small intestine. The lymphatic vessels of the body are divided into the superficial lymphatics and the deep lymphatics. The superficial lymphatic vessels follow the path of the superficial veins and are located deep to the dermis, the lining of the digestive, respiratory, urinary and reproductive tracts. The deep lymphatic vessels accompany the deep arteries and veins of the body. In the thoracic region of the body, the lymphatics form large ducts. On the right side of the body, the right lymphatic duct collects lymph from the side of the body above the level of the diaphragm. This vessel delivers the lymph into the venous system at or near the junction, between the right internal jugular vein and the right subclavian vein. On the left side of the body, the thoracic duct collects lymph from the left side of the body and the right side of the body below the diaphragm. The thoracic duct delivers the lymph into the venous system at the junction of the left subclavian vein and the left internal jugular vein.
5 Question No. 5 of 10 A 47-year-old man is diagnosed with a disorder in which the B-Cells in his body cannot produce antibodies. Based on this information, which of the following statements would be correct? Question #05 A. Plasma cell function would be expected to be normal in this patient. B. All immunity in this individual would be non-functional, rendering him a severely combined immunodeficient person. C. Faulty immunoglobin (Ig) gene rearrangement could be the cause of this patient s disorder. D. Natural killer cell function in this patient would also be abnormal, as these cells are derived directly from B-Cells. E. The positive and negative selection processes that B-Cells normally undergo would be abnormal in this patient. Plasma cells normally produce antibodies in response to antigen; therefore, these cells would not function normally in this patient. B. Incorrect! Cell-mediated immunity through T-Cell function would be expected to be normal in this patient. C. Correct! Faulty immunoglobin (Ig) gene rearrangement could be the cause of this patient s disorder, as this could lead to faulty immunoglobulin (antibody) production. Natural Killer (NK) cells are formed by the same lymphoid stem cells that give rise to T-Cells and B-Cells. T-Cells undergo positive and negative selection in the thymus. Each B-cell produces a single species of antibody, each with a unique antigen-binding site. When a naïve or memory B-cell is activated by antigen with the aid of a helper T-cell, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell. Such cells make and secrete large amounts of soluble antibody, which has the same unique antigen-binding site as the cell-surface antibody that served earlier as the antigen receptor.
6 Question No. 6 of 10 Which of the following statements about the portion of the lymphatic system labelled in the image is correct? Question #06 A. The item labelled in the image is the thoracic duct. B. The organ labelled in the image contains regions known as red pulp and white pulp. C. The inner portion of this gland is known as the cortex. D. The thymus gland is labelled in the image. E. The thymus gland, which is labelled in the image, is made up of 4 major lobes. The thymus gland is labelled in the image. B. Incorrect! The thymus gland is divided into 2 major lobes, each of which is made up of many lobules. The spleen contains red and white pulp. The inner portion of the thymus gland is known as the medulla. D. Correct! The thymus gland is labelled in the image. The thymus gland is made up of 2 lateral lobes, which are enclosed in a capsule. Each lateral lobe is made up of many smaller lobules. The thymus gland is made up of 2 lateral lobes, which are enclosed in a capsule. Each lateral lobe is made up of many smaller lobules. The thymus gland lies posterior to the sternum in the superior mediastinum. The thymus reaches its full size during puberty and then gradually decreases in size as we age, a process known as involution. Inside the thymus, lymphocyte precursors mature into T-Cells. To be released into the circulation, the T-Cells must undergo both positive and negative selection.
7 Question No. 7 of 10 Interstitial fluid is returned to the cardiovascular system as lymph fluid through the lymphatic system. Which of the following statements about lymph is correct? Question #07 A. Lymph fluid enters a lymph node through the single afferent lymph vessel, attached to each lymph node. B. After entering the lymph node, lymph fluid is exposed to reticular fibers, macrophages and dendritic cells. C. Just prior to exiting the lymph node, lymph fluid passes through the cortex region. D. Lymph fluid does not contain any cells. E. Lymph fluid enters the lymph node at the hilum. There are multiple afferent vessels that deliver lymph into the lymph node. B. Correct! The afferent vessels deliver lymph fluid from the tissues and initially into the subcapsular space of the lymph node. Within the subcapsular space of the lymph node are a network of reticular fibers, macrophages and dendritic cells. Just prior to exiting the lymph node, lymph fluid passes through the medullary cords. Lymph fluid contains lymphocytes and escaped red blood cells. The hilum is the region of a lymph node where the lymph fluid exits. Lymph vessels collect lymphatic fluid (along with escaped red blood cells) from the interstitial space. Lymph fluid is made up of: (1) fluid from the intestines containing proteins and fats, (2) a few red blood cells, and (3) many lymphocytes. Lymph fluid can also contain bacteria, which can lead to the activation of the immune system, through presentation to lymphocytes by antigen-presenting cells.
8 Question No. 8 of 10 Which of the following statements about the tonsil labelled in the image below is correct? Question #08 A. The palatine tonsil is labelled in the image. B. The tonsil labelled in the image is one of a pair of tonsils. C. The tonsil labelled in the image is a pharyngeal tonsil. D. The tonsil labelled in the image is one of four different types of tonsils in the body. E. None of the answers are correct. The lingual tonsil, which is located at the base of the tongue, is labelled in the image. B. Correct! The lingual tonsils, which are labelled in the image, are a pair of tonsils located at the base of the tongue. The lingual tonsil, which is located at the base of the tongue, is labelled in the image. The different types of tonsils are: (1) pharyngeal tonsil, (2) palatine tonsils, and (3) lingual tonsils. There is one correct answer above. Tonsils are specialized lymphoepithelial tissues located in the oropharynx and nasopharynx. Within the tonsils are lymphocytes that gather and remove microorganisms that enter through the respiratory tract or the gastrointestinal tract. These are the first line of defence against inhaled or ingested microorganisms. The different locations and types for tonsils are: (1) pharyngeal tonsil also known as an adenoid, this single tonsil is located in the posterior, superior wall of the nasopharynx. Unlike the other tonsils, adenoids have pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium, (2) palatine tonsils are a pair, located at the posterior margin of the oral cavity. At the boundary of the pharynx and the soft palate, and (3) lingual tonsils are a pair of tonsils that are located at the base of the tongue.
9 Question No. 9 of 10 Which of the following statements about mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) is correct? Question #09 A. MALT is located only in the lymphatic system. B. The mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue contains endothelial cells and red blood cells. C. MALT tissue processes and delivers antigens to the cardiovascular system. D. Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue is populated with lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. E. None of the answers are correct. Along the length of the digestive tract, as well as other regions in the body, are lymphoid nodules, known as mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). B. Incorrect! Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue is populated with lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. MALT tissue encounters and processes antigens that pass through the mucosal epithelium; it also plays a role in regulating mucosal immunity. D. Correct! Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue is populated with lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. There is one correct answer above. Along the length of the digestive tract, as well as other regions in the body, are lymphoid nodules, known as mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Malt tissue includes the following subcategories: gutassociated lymphoid tissues, bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue, and skin-associated lymphoid tissue. These tissues are populated with lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages. MALT tissue encounters and processes antigens that pass through the mucosal epithelium; it also plays a role in regulating mucosal immunity.
10 Question No. 10 of 10 Peyer s patches are part of the lymphatic system that provide immunity to foreign antigens. Which of the following statements is correct? Question #10 A. Peyer s patches are located on the surface of the small intestine. B. Peyer`s patches are typically found in the lower portion of the small intestine, the ileum. C. These structures provide protection for the body, from the spleen where they re located. D. Peyer s patches process antigens that are gathered from inside the body only, via the lymphatic system. E. None of the answers are correct. Peyer`s patches are typically found in the lower portion of the small intestine, the ileum, and are located in the lamina propria in the mucosa and extend to the submucosa. B. Correct! Peyer`s patches are typically found in the lower portion of the small intestine, the ileum. These structures provide immune protection for the body, from the lower portion of the small intestine. Peyer`s patches provide immunological defense to the gastrointestinal tract, which encounter many antigens from the outside world. There is one correct answer above. Peyer`s patches are typically found in the lower portion of the small intestine, the ileum. Histologically, these aggregated lymphoid nodules are oval follicles that are located in the lamina propria in the mucosa and extend to the submucosa. Peyer`s patches provide immunological defense to the gastrointestinal tract, which encounter many antigens from the outside world. Lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and macrophages reside in these specialized nodules and process antigens and provide immunity for the body.
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues
 The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues The peripheral (secondary) lymphoid tissues : are the lymph nodes, spleen, Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). All secondary lymphoid organs have one
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Functions of the Lymphatic System Fluid Balance Drains excess fluid from tissues Lymph contains solutes from plasma Fat Absorption Lymphatic system absorbs
3/17/2014. The Lymphatic System. Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs
 The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System Overview Lymphatic Vessels and Flow of Lymph Lymphoid Cells, Tissues, and Organs Overview of the Lymphatic System Slide 2 Major Components of the Lymphatic System
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
Chapt 21: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Goals 1. Discuss the organization of the lymphatic system, including the vessels, principal lymph nodes, thymus, and spleen 2. Explain the relationship between
The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R 21 Part 1 The Lymphatic and Immune Systems The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Lymphatic system Main function
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue. nur
 8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
8: Lymphatic vessels and lymphoid tissue nur Lymphatic vascular system Functions return to the blood extracellular fluid (Lymph) from connective tissue spaces. ensures the return of water, electrolytes
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Lymphatic System. Chapter 14. Introduction. Main Channels of Lymphatics. Lymphatics. Lymph Tissue. Major Lymphatic Vessels of the Trunk
 Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
Lymphatic System Chapter 14 Components Lymph is the fluid Vessels lymphatics Structures & organs Functions Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
The Lymphatic System
 الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
الكلية االسالمية الجامعة قسم تقنيات التحليالت المرضية االسم التدريسي: ا.د.عبد الهادي صالل المرحلة الثانية المادة : التشريح / النظري 2018-2017 م. م. عباس حسين عبيد The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system
Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts
 Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Lymphatic System Returns fluids that leaked from blood vessels back to blood Consists of three parts 1. Network of lymphatic vessels (lymphatics) 2. Lymph fluid in vessels 3. Lymph cleanse lymph 1 Lymphoid
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream (fluid balance) Immunity. Transport fats from the digestive tract to the bloodstream
 Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Lymphatic System L Y M P H A T I C C O M P O N E N T S What is a Lymphatic System? The lymphatic system is a complex system of fluid drainage and transport, immune response, and disease resistance. Fluid
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Immune - lymphatic system
 Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
Immune system - organisation: Immune - lymphatic system - histology & embryology organised lymphoid structures cell components lymphocytes event. lymphatic follicles accessory cells monocytes-macrophages
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
 GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
GENERAL ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM 1 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM - A SYSTEM WHICH CONTROLS PRESERVE GENETIC INTEGRITY OF THE ORGANISM. BODILY FUNCTIONS PROTECTION OF ANTIGENS CALLED IMMUNITY (FROM THE LATIN WORD
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Lymphatic Vessels & Lymph lymphatic vessels. 20 The Lymphatic System. They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System. Keeps us healthy!
 They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
They can't all be superstars! The Lymphatic System Lymphatic System: 1. lymphatic vessels 2. lymph 3. irculation, P, Supports immune & clotting, etc... cardiovascular system! Lymphoid Organs & Tissues:
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS. Has a pump (heart)
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS Cardiovascular Derived from mesoderm Transport System Has a pump (heart) Arteries Veins for return Veins have valves Carries RC, WBC, plasma Lymphatic Derived from mesoderm Transport
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
Overview of the Lymphoid System
 Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Overview of the Lymphoid System The Lymphoid System Protects us against disease Lymphoid system cells respond to Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells, such as cancers Overview of the Lymphoid
Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
Lymphatic and Immune www.vastaccess.com 2 Specialized component of circulatory system Lymphatic system functions: Maintenance of internal fluid balance Immunity Lymph derived from blood and tissue fluid
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
12 PART A The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
The Lymphatic System. General Functions of Lymphatic System:
 The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
The Lymphatic System network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc without
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 7 Lymphatic System & Immune System Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions and Structure of the lymphatic
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
Chapter 12- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses I. The Lymphatic System a. Consists of two semi-independent parts i. Lymphatic vessels and Lymphoid tissues and organs b. Lymphatic system functions i.
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
OBJECTIVES. The Amazing Immune System
 The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
The Amazing Immune System Graphic source: (l) Jeanne Kelly, NIAID; (r) Wikimedia Commons OBJECTIVES Describe at least three components of the immune system Describe the role in our immune response of at
Chapter 14. Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
Chapter 14 Lymphatic System and Immunity 1 Introduction A. The lymphatic system is comprised of a network of vessels that transport body fluids, the cells and chemicals in those vessels and the organs
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
CHAPTER VI PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Lymphatic System: Lymphatic System which consists of vessels and organs plays two vital roles in our lives: 1) The vessels
1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50%
 BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
BIOL2030 Huaman A&P II -- Exam 3 -- XXXX -- Form A Name: 1. Lymphatic vessels recover about of the fluid filtered by capillaries. A. ~1% C. ~25% E. ~85% B. ~10% D. ~50% 2. Special lymphatic vessels called
The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 14 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 14 Learning Outcomes 14-1 14-2 14-3 14-4 Distinguish between innate
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 14 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 14 Learning Outcomes 14-1 14-2 14-3 14-4 Distinguish between innate
Lymphoid tissue. 1. Central Lymphoid tissue. - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus.
 1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
1. Central Lymphoid tissue Lymphoid tissue - The central lymphoid tissue (also known as primary) is composed of bone morrow and thymus. Bone Morrow - The major site of hematopoiesis in humans. - Hematopoiesis
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
General Biology. A summary of innate and acquired immunity. 11. The Immune System. Repetition. The Lymphatic System. Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.
 A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
A summary of innate and acquired immunity General iology INNATE IMMUNITY Rapid responses to a broad range of microbes Course No: NG00 Credits:.00 External defenses Invading microbes (pathogens). The Immune
Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Immunity- ability to resist infection and disease through the activation of specific defenses These defenses can be found in the lymphatic system Lymphatic
the liver and spleen. There they will proliferate and differentiate along the various leucocyte lines. Later, bone marrow becomes the predominant
 Chapter 10 Lymphatic System 10.1. General Comments The primary functions of lymphoid organs are protective or immunologic in nature. They are the source of immunocompetent cells which are capable of neutralizing
Chapter 10 Lymphatic System 10.1. General Comments The primary functions of lymphoid organs are protective or immunologic in nature. They are the source of immunocompetent cells which are capable of neutralizing
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Lymphatic System. Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph. Organs and structures involved. similar to interstitial fluid
 Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Lymphatic System Organs, vessels and a fluid called lymph similar to interstitial fluid Organs and structures involved red bone marrow thymus spleen lymph nodes diffuse lymphatic tissue tonsils, adenoids
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 28 The Immune System Lesson 1: The Immune System Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson,
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Matthew Velkey, 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
3- Antigen-presenting cells, which are found, in addition to lymphoid tissue, in skin.
 Lymphoid System Dr.firdous It consists of organs, whose tissues and cells play an important role in immunity; a protective response of the internal environment of the body against microorganisms and foreign
Lymphoid System Dr.firdous It consists of organs, whose tissues and cells play an important role in immunity; a protective response of the internal environment of the body against microorganisms and foreign
Cardiovascular & lymphatic system both are supply fluid flow in to the body. but bothe are deferent type of fluid..
 Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
The Lymphatic System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
The Lymphatic System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Lymphatic System Lymphatic capillaries reabsorb excessive tissue fluid and transport the fluid through the lymphatic pathway, and ultimately dispose
Lymphatic System. The most important functions of the lymphatic system are: Maintenance of fluid balance in the internal environment
 Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
1. Lymph, the fluid of the lymphatic system, is collected from nearly every tissue and organ and transported to.
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Lymphatic and Immune Systems Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about pathogens is true? Question #01 (A) Both viruses and bacteria need to infect
Lymphatic System & Immunity
 Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
Lymphatic System & Immunity Arteriole Venule Tissue Blood Lymph cells capilla capillaries ries Lymphatic System -closely related to cardiovascular system -conducting system that carries fluid from extracellular
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Lymphatic System. Where s your immunity idol?
 Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Lymph Parts of the Lymphatic Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Organs System Functions of the Lymphatic Fluid Balance System Drains excess fluid
Lymphatic System Where s your immunity idol? Lymph Parts of the Lymphatic Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Organs System Functions of the Lymphatic Fluid Balance System Drains excess fluid
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying.
 When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 12 The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses Slides 12.1 12.22 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Lymphatic
Anatomy. Lymph: Tissue fluid that enters a lymphatic capillary (clear fluid that surrounds new piercings!)
 Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
Lymphatic System Anatomy Lymphatic vessels: meet up in capillaries of of tissues to collect extra water, and have an end point of meeting up with lymphatic ducts that empty fluid into large veins in the
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
The Lymphatic System
 94 The Lymphatic System Lymph Lymph is the name for tissue fluid that enters lymph capillaries. Filtration in capillaries creates tissue fluid, most of which returns almost immediately to the blood in
94 The Lymphatic System Lymph Lymph is the name for tissue fluid that enters lymph capillaries. Filtration in capillaries creates tissue fluid, most of which returns almost immediately to the blood in
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout. Secondary lymphoid organs. Dr H Awad
 Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Immunology 2017: Lecture 12 handout Secondary lymphoid organs Dr H Awad INTRODUCTION So far we discussed the cells of the immune system and how they recognize their antigens and get stimulated. The number
Paper No.: 10: Immunology Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and structure of immune system.
 Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
Paper No.: 10: Module : 04: Phylogeny and Ontogeny of immune system: Organization and Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer:
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE.
 CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
CELLS, ORGANS, AND MOLECULES: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM THE CELLS OF THE BLOOD FROM AN IMMUNOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE. Erythrocytes: Red blood cells (~5 x 10 6 / L) (~5 x 10 12 /L) of blood.
Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS; Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD; and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 2 (pages 22 33): Cells and
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, Dan Stetson
 Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Introduction to Immunology Part 2 September 30, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #2 Slide 1 of 26 CLASS ANNOUNCEMENT PLEASE NO TREE NUTS IN CLASS!!! (Peanuts, walnuts, almonds, cashews, etc)
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
You see it every rainy day water, water everywhere, rushing along gutters and down
 Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
Chapter 11 Keeping Up Your Defenses: The Lymphatic System In This Chapter Delving into lymphatic ducts Noodling around with nodes Exploring the lymphatic organs You see it every rainy day water, water
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
Ch. 22 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Above: macrophage (gray), T lymphocyte (pink), and bacteria (orange) The lymphatic system General functions: It acts with other organ systems to help provide immunity
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Peripheral Circulation
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Immunity or Resistance Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Ability to ward off damage or disease through our defenses 2 types of immunity Innate or nonspecific immunity present at birth No specific
Immunity or Resistance Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity Ability to ward off damage or disease through our defenses 2 types of immunity Innate or nonspecific immunity present at birth No specific
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
The Respiratory System:
 The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
The Respiratory System: Respiration Involves both the respiratory and the circulatory systems Four processes that supply the body with O 2 and dispose of CO 2 Respiration Pulmonary ventilation (breathing):
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Portal System & Lymphatic System. When the vein of any organ of the body does not open in the caval vein or heart.
 1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
Chapter 22. The Lymphatic System. AP2 Chapter 22 1
 Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Chapter 22 The Lymphatic System AP2 Chapter 22 1 Chapter 22 Outline I. Lymphatic System II. Immunity III. Innate Immunity IV. Adaptive Immunity V. Immune Interactions VI. Immunotherapy VII. Acquired Immunity
Small Intestine -- Peyer s Patch. Appendix. Afferent Lymphatic High Endothelial Venule. Germinal Center. Cortex Paracortex
 Supplement to The Art of Getting Well How the Immune System Works Anthony di Fabio Copyright 998 All rights reserved by the The Roger Wyburn-Mason and Jack M.Blount Foundation for Eradication of Rheumatoid
Supplement to The Art of Getting Well How the Immune System Works Anthony di Fabio Copyright 998 All rights reserved by the The Roger Wyburn-Mason and Jack M.Blount Foundation for Eradication of Rheumatoid
The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
CHAPTER 1 The Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System Sagittal Section of Upper Airway Fig. 1-1. Sagittal section of upper airway. Structure of the Nose Fig. 1-2. Structure of the nose. Sagittal
Lymphatic System and Immune System. Blood capillaries. Lymphatic vessels/ lymph nodes. Then, identify by labeling these specific structures in part B.
 Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
Name: Date: Period: Lymphatic System and Immune System 1. Figure 21.1 provides an overview of the lymphatic vessels. In part A the relationship between lymphatic vessels and the blood vessels of the cardiovascular
