HIV-1 genome organization
|
|
|
- Hubert Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HIV-1 genome organization Gag encodes for a polyprotein that is cleaved into 4 proteins by HIV-1 protease. Gag is present in 2 transcripts: Gag polyprotein precursor and GagPol polyprotein precursor (5%). web.stanford.edu Cleavage occurs during virus maturation, after viral budding.
2 Late stage of HIV-1 replication Gag recruits viral RNA and is targeted to inner leaflet of plasma membrane. Virus budding involves assembly of Gag into lattice, evagination of bud, and scission of bud. P6 of Gag is necessary for budding. After virion is released, it undergoes maturation associated with cleavage of Gag and morphological change (radially symmetric to containing a conical capsid core). Freed (2015) Nat Rev Microbiology
3 Tsg101 is essential for HIV-1 virion release sirna: against Tsg101 sirna INV : inverted sirna (control) Tsg*: sirna resistant Tsg101 Knockdown of Tsg101 prevents release of virions into supernatant of 293T cells. This effect can be rescued with sirna-resistant Tsg101 construct. In other experiments, knockdown of Tsg101 did not affect MLV virion production. Garrus et al (2001) Cell
4 Inhibition of Vps4 blocks HIV-1 virion release K173Q (blocks ATP binding) and E228Q (blocks ATP hydrolysis) are dominant negative mutants. PTAP- is a mutant Gag (p6) that cannot be interact with Tsg101; used as control for defective virion production. Expression of WT Vsp4 reduced virion production several fold. Garrus et al (2001) Cell
5 Arrested budding intermediates (Tsg101 sirna) In cells lacking Tsg101 or Vsp4, late budding intermediates were found by EM. Immature viral particles connected to plasma membrane by membrane stalks. Similar to defect found in PTAP- mutant. Garrus et al (2001) Cell
6 Model of ESCRT-III in HIV-1 budding and virion release The p6 protein of Gag interacts with Tsg101, a component of ESCRT-I. Gag also interacts with ALIX, which interacts with Tsg101 and ESCRT-III. This leads to recruitment of ESCRT-III/Vps4. ESCRT-III polymerization at the bud neck causes scission. Freed (2015) Nat Rev Microbiology
7 Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) Lodish et al. EGFR is a receptor tyrosine kinase. Binding of EGF activates EGFR kinase activity. This leads to MAPK signal transduction cascade for cell growth regulation. Receptor down regulation: Activation of EGFR causes reduction in EGFR numbers; the EGF/EGFR complexes are endocytosed and delivered to the lysosome. Failure to downregulate can result in dysregulated growth.
8 EGFR is delivered to multivesicular bodies EGFR was labeled with anti-egfpr conjugated with gold particles. MVBs EGF was added. Chase 1 hour. Futter et al (1996) JCB
9 Sorting of cargo into MVBs is selective Some surface receptors, like LDL receptor and transferrin receptor, go through many rounds of internalization and recycling; they stay in the limiting membrane of the lysosome and get resorted to the plasma membrane. Proteins destined for the lysosomal membrane do not get sorted into lumenal vesicles. Sorting of EGFR: Cytosolic tail Kinase activity Ubiquitin added to cytosolic tail
10 Receptor downregulation by the multivesicular body EGFR is normally distributed uniformly on cell surface. Addition of EGF causes clustering of EGFR at clathrincoated pits. Within 1-2 min, the EGF- EGFR complexes are internalized. Some are recycled to the cell surface. Katzmann et al., 2002 Some go to the MVB and are degraded in the lysosome this is a major mechanism for regulating cell surface EGFR levels. Requires ubiquitination by Cbl.
11 Downregulation of Ste2 in yeast by MVB sorting Ste2 is a receptor (expressed in a cells) that binds to a-factor (peptide mating hormone) expressed by a cells. Ste2 activates MAPK cascade. Ste2 is downregulated by endocytosis and sorting to MVBs. Mutation of lysines from Ste2 impairs downregulation, showing importance of ubiquitylation. Mono-ubiquitination Katzmann et al., 2002
12 The multivesicular body delivers cargo to the lysosome MVBs deliver cargo to lysosome lumen for degradation. Endosomes form invaginating buds that pinch off and form internal vesicles within the endosome. The MVB are progressively acidified and fuse with lysosomes. Mono-ubiquitin targets certain cell surface receptors for downregulation via MVB formation and fusion with lysosome. ESCRT (endosomal sorting complex required for transport) proteins recognize ubiquitinated cargo and sort them into MVBs for degradation by the lysosome. ESCRT-III and Vps4 mediate the scission of lumenal vesicles.
13 ESCRT-III processes have topology opposite traditional budding events ESCRT-III processes bud away from cytosol. ESCRT-III protein assemble inside vesicle. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
14 Two types of ubiquitin signals Ub is a 76 aa polypeptide Mono-Ub Poly-Ub Attached to lysine residues by isopeptide bond between C-term of Ub and e-amino group (NH3 + ) of lysine on substrate. Requires E1 (ubiquitin-activating enzyme) E2 (ubiquitinconjugating enzyme) E3 (ubiquitin ligase) Ubiquitylation can reversed by de-ubiquitylating enzymes. Ub has 7 lysines; K48 polyubiquitylation is classic degradation signal for 26S proteasome. Katzmann et al., 2002
15 Identification of ubiquitylation sites by mass spectrometry Trypsin is an endopeptidase that cleaves after R and K. Trypsin digestion of a protein creates an array of tryptic peptides that can be identified by mass spectrometry. In the case of a ubiquitylated protein, some of these tryptic peptides will have gly-gly signatures. The C-terminal sequence of Ub is: RGG* Udeshi et al (2013) Nature Protocols
16 Inability to downregulate EGFR can lead to cancer Cbl is a Ring Finger E3 ubiquitin ligase (RF is the largest class of E3s) Cbl is recruited to activated EGFR and conjugates ubiquitin to it. Loss of Cbl E3 ligase activity is associated with myeloid cancers in humans and mouse. Note: Cbl has both positive and negative roles for EGFR activity. Kales et al (2010) Cancer Research
17 ESCRT complexes mediate MVB sorting and scission Mechanism of ESCRTs not fully understood. ESCRT-0, I, II act early to sort cargo and recruit ESCRT-III. ESCRTI plays a major role in cargo recognition: several components (Vps23/Tsg101, Vps27) bind Ub. ESCRTIII assembles into spiral filaments that likely mediate scission. A key component of ESCRT- III is Chmp4/Snf7, which constitute the bulk of the filament. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal Disassembly of ESCRT-III requires the AAA ATPase Vps4.
18 Model of ESCRT-III scission ESCRT-III forms spiral filaments on lipid membranes. The diameters of these spirals can change; a small enough diameter may lead to membrane merger. Vps4 is usually thought to mediate disassembly of ESCRT-III after scission, so that the proteins can be used again; however, it may also contribute to the scission process. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
19 AAA ATPases AAA (ATPases Associated with various cellular Activities); also called AAA+ family. A large family of ATPases characterized by certain sequence motifs. Typically form oligomeric rings that use the power from ATP hydrolysis to undergo conformational changes and perform work on substrates. Examples: Protein unfolding and degradation (ClpXP, ClpAP, Lon, 26S proteasome) Protein disassembly (NSF, Vps4, VCP/p97) Solubilization of protein aggregates (Hsp104) Hexameric AAA domain from NSF Hanson & Whiteheart (2005) NRMCB
20 Examples of protein remodeling by AAA ATPases AAA domain unfolds protein and delivers it to proteolytic chamber. Protein aggregates are solubilized by 104 kd heat shock protein. NSF, together with SNAP, disassemble 4-helix bundle SNARE complexes so that they can perform additional rounds of membrane fusion. Hanson & Whiteheart (2005) NRMCB
21 p97/vcp is a AAA ATPase with many functions p97/vcp (valosincontaining protein), Cdc48 in yeast Highly homologous to NSF. D2 has higher ATPase activity than D1. p97 operates with many adaptors/co-factors. Mutations in p97 cause IBMPFD (inclusion body myopathy associated with Paget disease of the bone and frontotemporal dementia) Meyer et al (2012) Nat Cell Biol
22 p97 often functions between ubiquitylation and the 26S proteasome p97 associates with ubiquitylated substrates that need remodeling before delivery to the 26S proteasome. Substrates might be in stable complexes or associated with surface. Meyer et al (2012) Nat Cell Biol
23 Additional functions of ESCRT-III pathway Exosomes: MVBs can fuse with plasma membrane, releasing vesicles to the extracellular space nm diameter. Ectosomes are microvesicles ( nm) that are shed directly from the plasma membrane. Tsg101 often used as a marker Some are independent of ESCRT. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
24 Exosomes may function in intercellular communication Exosomes contain RNA, mirna, and protein, and have been proposed to facilitate intercellular communication. Many proposed functions: Waste removal Antigen presentation Tumor promotion Signal transduction Raposo & Stoorvogel (2013) JCB
25 Additional functions of ESCRT-III pathway Near the end of cytokinesis, the daughter cells are separated by the midbody. Midbody contains bundles of microtubules from the mitotic spindle. Cleavage at the midbody is termed abscission. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
26 Additional functions of ESCRT-III pathway Neuronal processes no longer needed can be pruned to remodel neurons. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
27 Additional functions of ESCRT-III pathway Holes in the plasma membrane can be caused by physical trauma or bacterial toxins. Such damage leads to recruitment of ESCRT-III proteins to injury site. By budding part of the plasma membrane, the damage can be repaired. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
28 Additional functions of ESCRT-III pathway During late anaphase, the nuclear envelope must be re-formed; ESCRT-III is important for this process. Repair of defective nuclear pore complexes. Adell et al (2016) The FEBS Journal
There are approximately 30,000 proteasomes in a typical human cell Each proteasome is approximately 700 kda in size The proteasome is made up of 3
 Proteasomes Proteasomes Proteasomes are responsible for degrading proteins that have been damaged, assembled improperly, or that are of no profitable use to the cell. The unwanted protein is literally
Proteasomes Proteasomes Proteasomes are responsible for degrading proteins that have been damaged, assembled improperly, or that are of no profitable use to the cell. The unwanted protein is literally
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I
 01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
01.25.10 Lecture 6 - Intracellular compartments and transport I Intracellular transport and compartments 1. Protein sorting: How proteins get to their appropriate destinations within the cell 2. Vesicular
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #2 March 22, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) In the
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008
 Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008 Guys, The average on the test was 69.9. Before you start reading the right answers please do me a favor and remember till the end of your life that GLUCOSE TRANSPORT
Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008 Guys, The average on the test was 69.9. Before you start reading the right answers please do me a favor and remember till the end of your life that GLUCOSE TRANSPORT
Chapter 6. Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
The ubiquitin-proteasome system. in bone biology. University of Nottingham. ECTS PhD Training July 5 th Dr Rob Layfield
 The ubiquitin-proteasome system in bone biology Dr Rob Layfield University of Nottingham ECTS PhD Training July 5 th 2009 Images reproduced from: http://www.bostonbiochem.com/overview.php?prod=ubchains
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in bone biology Dr Rob Layfield University of Nottingham ECTS PhD Training July 5 th 2009 Images reproduced from: http://www.bostonbiochem.com/overview.php?prod=ubchains
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Cellular functions of protein degradation
 Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, Please print your name: Instructions:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Proteasomes. When Death Comes a Knock n. Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001
 Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
PROTEIN TRAFFICKING Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview Proteins are synthesized either on free ribosomes or on ribosomes bound to endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The synthesis of nuclear, mitochondrial and peroxisomal
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 October 3, 2013 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Virus Entry/Uncoating
 Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands
 CHA P T E R F IVE Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands Shinya Yamamoto, *,1 Wu-Lin Charng, *,1 and Hugo J. Bellen *,,, Contents 1. Notch Signaling and its Regulation by Endocytosis
CHA P T E R F IVE Endocytosis and Intracellular Trafficking of Notch and Its Ligands Shinya Yamamoto, *,1 Wu-Lin Charng, *,1 and Hugo J. Bellen *,,, Contents 1. Notch Signaling and its Regulation by Endocytosis
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014
 Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17
 Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
Chapter 2: Exocytosis and endocytosis Biochimica cellulare parte B 2016/17 Exocytosis and endocytosis Transport from the trans-golgi network to the cell exterior: exocytosis. All eukaryotic cells continuously
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003
 7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
7.06 Spring 2003 Exam 3 Name 1 of 8 7.06 Cell Biology EXAM #3 April 24, 2003 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes. Please write your answers to the questions in the
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Overview of virus life cycle
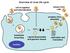 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/122889
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/122889
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting
 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
Intracellular Compartments and Protein Sorting Intracellular Compartments A eukaryotic cell is elaborately subdivided into functionally distinct, membrane-enclosed compartments. Each compartment, or organelle,
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH INTRACELLULAR PROTEIN TRANSPORT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Molecular Trafficking
 SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
SCBM 251 Molecular Trafficking Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th Lecture outline 1. What is molecular trafficking? Why is it important?
Molecular Graphics Perspective of Protein Structure and Function
 Molecular Graphics Perspective of Protein Structure and Function VMD Highlights > 20,000 registered Users Platforms: Unix (16 builds) Windows MacOS X Display of large biomolecules and simulation trajectories
Molecular Graphics Perspective of Protein Structure and Function VMD Highlights > 20,000 registered Users Platforms: Unix (16 builds) Windows MacOS X Display of large biomolecules and simulation trajectories
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking
 Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking Chi-Kuang Yao (IBC, Academia Sinica) 11-6-2017 ckyao@gate.sinica.edu.tw 1 Compartmentalization makes difference between bacteria and yeast 1. More compartments with specific
Intracellular Vesicle Trafficking Chi-Kuang Yao (IBC, Academia Sinica) 11-6-2017 ckyao@gate.sinica.edu.tw 1 Compartmentalization makes difference between bacteria and yeast 1. More compartments with specific
General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class.
 General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class. 1 Exam 1 Lecture 2: Discussed intracellular killing mechanisms Important maturation steps Rapid development into a microbicidal
General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class. 1 Exam 1 Lecture 2: Discussed intracellular killing mechanisms Important maturation steps Rapid development into a microbicidal
Chapter 31. Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing and Degradation. Biochemistry by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham
 Chapter 31 Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing and Degradation Biochemistry by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham Essential Question How are newly synthesized polypeptide chains transformed
Chapter 31 Completing the Protein Life Cycle: Folding, Processing and Degradation Biochemistry by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham Essential Question How are newly synthesized polypeptide chains transformed
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Virus Entry. Steps in virus entry. Penetration through cellular membranes. Intracellular transport John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Virus Entry Steps in virus entry Penetration through cellular membranes Intracellular transport Steps in virus entry How do virions get into cells? Viruses of bacteria, archaea, algae and plants use different
Virus Entry Steps in virus entry Penetration through cellular membranes Intracellular transport Steps in virus entry How do virions get into cells? Viruses of bacteria, archaea, algae and plants use different
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
7.012 Quiz 3 Answers
 MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
MIT Biology Department 7.012: Introductory Biology - Fall 2004 Instructors: Professor Eric Lander, Professor Robert A. Weinberg, Dr. Claudette Gardel Friday 11/12/04 7.012 Quiz 3 Answers A > 85 B 72-84
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins
 Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
Posttranslational Modification and Targeting of Proteins Graduate Biochemistry Term 2/2016 Assist. Prof. Dr. Panida Khunkaewla School of Chemistry, Institute of Science Suranaree University of Technology
Complexity DNA. Genome RNA. Transcriptome. Protein. Proteome. Metabolites. Metabolome
 DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18
 Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Cells. 1. Smallest living structures. 2. Basic structural and functional units of the body. 3. Derived from pre-existing cells. 4. Homeostasis.
 Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
Cells The Cell The human body has about 75 trillion cells All tissues and organs are made up of cells Smallest functional unit of life Cytology Histology Cytology Epithelial cells Fibroblasts Erythrocytes
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004
 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004 Ubiquitous Quality Control of Life C S Karigar and K R Siddalinga Murthy The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2004 is shared by Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004 Ubiquitous Quality Control of Life C S Karigar and K R Siddalinga Murthy The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2004 is shared by Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
Peptide hydrolysis uncatalyzed half-life = ~450 years HIV protease-catalyzed half-life = ~3 seconds
 Uncatalyzed half-life Peptide hydrolysis uncatalyzed half-life = ~450 years IV protease-catalyzed half-life = ~3 seconds Life Sciences 1a Lecture Slides Set 9 Fall 2006-2007 Prof. David R. Liu In the absence
Uncatalyzed half-life Peptide hydrolysis uncatalyzed half-life = ~450 years IV protease-catalyzed half-life = ~3 seconds Life Sciences 1a Lecture Slides Set 9 Fall 2006-2007 Prof. David R. Liu In the absence
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral structures. Just how small are viruses? Workbook Lesson 1.4 1
 Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis
 Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. Cell 7.5
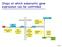 Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
Steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled Cell 7.5 Protein Variability and Protein Activity Control Aminoacid sequence Three-dimensional shape (conformation) Function Protein processing
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cellular control of cholesterol. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
Cellular control of cholesterol Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Brief overview of cholesterol s biological role Regulation of cholesterol synthesis Dietary and cellular uptake of cholesterol
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses
 Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Chapter 13B: Animal Viruses 1. Overview of Animal Viruses 2. DNA Viruses 3. RNA Viruses 4. Prions 1. Overview of Animal Viruses Life Cycle of Animal Viruses The basic life cycle stages of animal viruses
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
ALG-2 activates the MVB sorting function of ALIX through relieving its intramolecular interaction
 OPEN Citation: Cell Discovery (2015) 1, 15018; doi:10.1038/celldisc.2015.18 2015 SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 2056-5968/15 www.nature.com/celldisc ALG-2 activates the MVB sorting function of ALIX through
OPEN Citation: Cell Discovery (2015) 1, 15018; doi:10.1038/celldisc.2015.18 2015 SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 2056-5968/15 www.nature.com/celldisc ALG-2 activates the MVB sorting function of ALIX through
2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. PROTEIN SORTING. Lecture 10 BIOL 266/ Biology Department Concordia University. Dr. S.
 PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
PROTEIN SORTING Lecture 10 BIOL 266/4 2014-15 Dr. S. Azam Biology Department Concordia University Introduction Membranes divide the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells into distinct compartments. The endomembrane
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs
 Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Types of cells. Cell size comparison. The Jobs of Cells 10/5/2015. Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Types of cells Prokaryote Cells & Cell Organelles bacteria cells Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes 2009-2010 animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most bacteria (prokaryotic)
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Organization of ATPases
 The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
The Primary Active Transporter II: The ATPase Objectives: Organization P type with NPA domains Proton pumps of the rotary V type ATPase 1 Organization of P type, solute transport, found in plasma membranes
Cell biology of AB toxins
 Cell biology of AB toxins Gisou van der Goot, EPFL Lausanne EMBO/FEBS Advanced course at Spetses, Greece, September 1-9, 2010 Bacterial protein toxins Definition: Proteins released by bacteria into the
Cell biology of AB toxins Gisou van der Goot, EPFL Lausanne EMBO/FEBS Advanced course at Spetses, Greece, September 1-9, 2010 Bacterial protein toxins Definition: Proteins released by bacteria into the
Protein and membrane trafficking
 Protein and membrane trafficking Lodish et al, 2000 The secretory pathway cisternal progression Lodish et al, 2000 Cells can be specialized for the secretion of specific proteins Lodish et al, 2000 The
Protein and membrane trafficking Lodish et al, 2000 The secretory pathway cisternal progression Lodish et al, 2000 Cells can be specialized for the secretion of specific proteins Lodish et al, 2000 The
Section 6. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
Section 6 Junaid Malek, M.D. The Golgi and gp160 gp160 transported from ER to the Golgi in coated vesicles These coated vesicles fuse to the cis portion of the Golgi and deposit their cargo in the cisternae
Picornaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport
 Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Structural biology of viruses
 Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
17/01/2017. Protein trafficking between cell compartments. Lecture 3: The cytosol. The mitochondrion - the power plant of the cell
 ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Cellular compartments
 Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Cellular compartments 1. Cellular compartments and their function 2. Evolution of cellular compartments 3. How to make a 3D model of cellular compartment 4. Cell organelles in the fluorescent microscope
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
