Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
|
|
|
- Georgiana Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016
2 Contents Section Topic Page No 1 Purpose and scope 3 2 Definitions 3 3 Regulatory Background 5 4 Key Responsibilities 6 5 Training 7 6 Monitoring and Assurance 8 7 Step-by-Step Guide for the Management of a Contamination Incident by the Affected Member of Staff 8 Step-by-Step Guide for Contamination Incident Management by the Competent Person 9 Step-by-Step Guide for the Management of a Contamination Incident where a Patient is Contaminated by a Member of Staff - Reverse Incident Appendix A Flowchart - What do I do in the Event of a Contamination Incident? Appendix B Contamination Incident Risk Assessment Form 14 Appendix C Information Leaflet - Source BBV Testing 18 Appendix D HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) 20 Appendix E HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Information Leaflet 22 Appendix F PEP for Hepatitis B 23 Appendix G Appendix H Appendix I Information Leaflet - Members of Staff with a Blood-Borne Virus Assessing Fitness for EPP Work - Staff who are BBV Positive Template letter to patient where a contamination incident has occurred Page 2 of 28
3 Inoculation (Contamination) Incidents incorporating Blood Borne Virus. Standard Operating Procedure 1. Purpose and scope 1.1 PDSE has a duty of care to ensure that any member of staff, patient or visitor who is in receipt of a contamination incident is adequately and efficiently assessed and cared for. 1.2 The Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) covers all staff; to include, contractors; those employed on a fixed term contract, honorary contract, agency or locum staff and students affiliated to educational establishments and volunteers. 1.3 If there is a contamination incident, all staff should follow the procedures in clinic and this policy. 2. Definitions 2.1 Contamination Incident - a generic term which encompasses any percutaneous or mucocutaneous exposure to an object or fluid that has the potential to cause physical injury and possibly transmit a blood-borne virus (BBV). 2.2 Percutaneous Exposure - commonly referred to as a Needlestick injury, is caused by a sharp, the commonest of which is hollow bore needles, particularly following blood sampling (venepuncture). This type of injury carries the greatest risk for the transmission of BBVs in a healthcare setting. 2.3 Mucocutaneous Exposure - occurs as a result of contamination of the mucous membranes of eyes, mouth or nose or of broken skin with infected blood or other infectious material. 2.4 Significant Contamination Incidents - incidents that occur by means of the following High Risk situations: A deep puncture wound Sharps device had been in the Source s artery or vein Sharps device was visibly blood-stained Sharps device has a hollow bore such as a needle A splash of body fluid into member of staff s eyes, mouth or nose A splash of body fluid onto non-intact skin. Page 3 of 28
4 Or contamination with body fluid from a Source, where they: If male, has had sexual relationships with other men Were born outside of Europe, in Australia or the United States Have injected drugs into their veins in the past Have received a blood transfusion or operation outside of Europe, in Australia or the United States Have had a sexual partner who originates from outside of Europe, from Australia or the United States 2.5 High Risk Body Fluid - the following are considered a high risk of transmitting a blood-borne virus: Blood Amniotic Fluid Human breast milk Vaginal secretions or semen Cerebrospinal fluid Peritoneal fluid Pericardial fluid Pleural fluid Saliva in association with dentistry Synovial fluid Exudative or other tissue fluid from burns or skin lesions Unfixed human tissues and organs Visibly blood-stained urine Visibly blood-stained vomit Visibly blood-stained saliva Visibly blood-stained faeces 2.6 Blood Borne Viruses (BBVs) - referred to in this SOP are: Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Transfer of a blood-borne virus can occur when blood, or blood-stained body fluids from the infected individual comes in contact with an uninfected individual s open skin lesions or mucous membranes. 2.7 Sharps - any item having corners, edges, or projections capable of cutting or piercing the skin. Sharps include medical devices such as razors blades, injection needles, suturing needles, lancets and scalpel blades sharp body tissues such as teeth and fragments of bone. 2.8 Exposure Prone Procedures (EPPs) - includes procedures where the member of staff s hands may be in contact with sharp instruments, needle tips, and sharp tissues (teeth or spicules of bone) inside a patient s open body cavity, wound, or confined anatomical space where the hands or fingertips may not be completely visible at all times. Page 4 of 28
5 2.8.1 When there is any doubt about whether a procedure is exposure prone or not, advice should be sought in the first instance from the Staff Health and Wellbeing Department (SH&WB) Consultant Procedures where the hands and fingertips of the worker are visible and outside the patient s body at all times, and internal examinations or procedures that do not involve possible injury to the worker s gloved hands from sharp instruments and/or tissues, are considered not to be exposure prone provided routine infection control procedures are adhered to at all times Examples of procedures that are not exposure prone include: Taking blood (venepuncture) Setting up and maintaining IV lines or central lines (provided any skin tunnelling procedure used for the latter is performed in a non-exposure prone manner i.e. without the operator s fingers being at any time concealed in the patient s tissues in the presence of a sharp instrument) Minor surface suturing The incision of external abscesses Routine vaginal or rectal examinations Simple endoscopic procedures. 2.9 Competent Person - the Competent Person is a Senior Lead Dental Nurse. They are familiar with the epidemiology of BBV infection, the risk of transmission in a health care setting and the management of contamination incidents as outlined in this SOP and related policies Recipient - refers to the person who has been contaminated Source - refers to the origin of the contaminant OPAS - is the Occupational Health Computerised Management System used by the Staff Health & Wellbeing Department (SH&WB). 3 Regulatory Background 3.1 The Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 states that an employer must make provision for securing the health, safety and welfare of persons at work and for protecting others against risks to health or safety in connection with the activities of persons at work. 3.2 The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) Regulations 2002 (as amended) represents the main piece of legislation covering control of the risks to employees and other people arising from exposure to harmful substances generated Page 5 of 28
6 out of or in connection with any work activity under the employer's control. 3.3 The Health and Social Care Act 2008 provides a Code of Practice and related guidance for health and adult social care on the prevention and control of infections. 4. Key Responsibilities 4.1 The Director of Community Based Dentistry: Seeking assurance that incidents are managed in accordance with the SOP Ensuring that Competent Persons are appointed and receive training in the requirements of the role. 4.2 All Employees have a responsibility for: Ensuring they are familiar and comply with this SOP and associated policies/guidance. 4.3 The Competent Person has a responsibility for: Ensuring they are competent to undertake the duties required of them. Documenting findings and actions on the PDSE incident report form. Completing the contamination incident risk assessment form immediately after the member of staff has been referred to them. Organising a blood sample from the Member of Staff for Serum Save. Ensuring emotional support is provided to the member of staff. Organising a blood sample from the Source (with consent) and arranging testing for BBVs and informing the Source of the results. Referring members of staff who suffer a significant exposure to the appropriate organisation immediately (see Appendix I). Giving the completed risk assessment form to the Member of Staff if they are to report to ED. Sending the completed risk assessment form to SH&WB in the case of a low risk incident. Informing the member of staff of the Source s Negative blood results within 24hrs of receipt of the results. 4.4 The Staff Health & Wellbeing Department (SH&WB) has responsibility for: Supporting affected members of Staff. Providing advice where appropriate on the risk assessment, clinical management and follow-up care of staff following a contamination incident. Providing confidential advice and support to affected members of staff in the event of a contamination incident. Informing the Health Protection Agency (HPA) where there is a RIDDOR Reportable Contamination Incident (where a Source is positive to a BBV). Organising the health surveillance of an affected member of staff. Providing information and training for staff in the management of contamination incidents. Reviewing and updating this SOP in line with national guidance. 4.5 The Emergency Department (ED) (Plymouth staff only) and Occupational Page 6 of 28
7 Health (Exeter and Truro staff) have responsibility for: Assessment and care of members of staff referred to them following a contamination incident. Administration of Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) if appropriate. Ensuring that adequate stocks of Hepatitis B immunoglobulin and HIV PEP Packs are available. Referring where appropriate to GUM Department and the SH&WB Department. 5. Training 5.1 Mandatory training is concerned with minimising risk and ensuring the organisation meets external standards such as those laid down by The Health and Social Care Act 2008 and the NHS Litigation Authority. 5.2 The importance of training in relation to how a Contamination Incident is managed is recognised by PDSE. 6. Monitoring and Assurance 6.1 Contamination incident reports will be reviewed at the PDSE Clinical Standards and Quality Meetings. 7 Step-by-Step Guide for the Management of a Contamination Incident by the Affected Member of Staff 7.1 In the event of a contamination incident occurring, the following explains the sequence of events that should take place in order to ensure you are cared for appropriately and effectively. A concise flowchart of the management process is shown in Appendix A. 7.2 First Aid should take place immediately as follows: For a Sharps Injury, encourage bleeding at the wound site and wash the site thoroughly with soap and water. Page 7 of 28
8 7.2.2 For a Body Fluid Splash, where skin is exposed - wash the site thoroughly with soap and water For a Body Fluid Splash, where eyes are exposed ensure copious irrigation of the eyes (before and after contact lenses are removed) For a Body Fluid Splash, where mouth or nose is exposed - irrigate with water. 7.3 Report to your Line Manager. If you are not in your usual place of work inform the person in charge of the area you are in as soon as first aid has been administered they will appoint a Competent Person to take you through the process. 7.4 Record the Incident using the PDSE incident report form and process - if you need help with this inform your Line Manager or the person in charge of the area you are in. 7.5 Risk Assessment - The Competent Person must undertake a Contamination Incident Risk Assessment of the incident (Appendix B) this will determine the course of action required (if any) Significant Incident - you must go to ED or Occupational Health as appropriate with the completed risk assessment form within 1 hour of the incident. ED or Occupational Health will be responsible for your immediate care and will be responsible for assessing the need for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP), arranging support as well as referrals as appropriate Non- Significant Incident there is no further immediate action to take. 7.6 Phone the ED or Occupational Health before proceeding. 7.7 Follow-up Care - In every case you must report it to the Staff Health & Wellbeing Department so we can record the incident fully, offer further advice and guidance if you need it and plan your future care including any blood tests you need. Page 8 of 28
9 7.8 Staff Health & Wellbeing Department Contact Details: Plymouth staff (4) Exeter staff Truro staff Step-by-Step Guide for Contamination Incident Management by the Competent Person 8.1 The following guide has been arranged to help you in managing a Contamination Incident and will help you make the right decisions and give the right advice. 8.2 The Competent Person will be a Senior of Lead Dental Nurse. 8.3 Recipient refers to the person who has been contaminated. 8.4 Source refers to the origin of the contaminant. 8.5 Actions of the Competent Person Ensuring they are competent to undertake the duties required of them. Members of staff who do not feel competent must seek appropriate training. Completing the contamination incident risk assessment form (Appendix B) immediately after the member of staff has been referred to them. Organising a blood sample from the Member of Staff for Serum Save. Organising a blood sample from the Source (with consent) and arranging testing for BBVs and informing the Source of the results. Referring members of staff who suffer a significant exposure to ED or Occupational Health as appropriate immediately. Giving the completed risk assessment form to the Member of Staff if they are to report to ED or Occupational Health. Sending the completed risk assessment form to SH&WB in the case of a low risk incident. Informing the member of staff of the Source s blood results within 24hrs of Receipt of the results. 8.6 Care of the Source following a Contamination Incident The Competent Person will coordinate the following sequence of events in the event of a Contamination Incident occurring. This will ensure that the Source will be cared for appropriately and effectively and in a way that maintains their privacy, dignity, and confidentiality during the assessment. 8.7 Explanation An explanation of the incident and the implications of it should be given to the Source (or their Parent/Guardian or next of Kin). The information leaflet (Appendix C) should also be issued and the template letter to patient (Appendix I). The source must be asked to attend their GMP for blood tests. Page 9 of 28
10 8.8 Contamination Risk Assessment Form The Contamination Risk Assessment Form (Appendix B) needs to be completed to determine the degree of risk. If the Source is concerned at all about any of the specific questions or declines to answer please take the opportunity to discuss this with them. They may wish to just answer question If the Source has answered yes to any of the questions, the clinician prescribing the PEP should be informed that the source is potentially high risk for HIV, whether the source consents to testing or not. The source should be offered a discussion with one of the GUM Health Advising Team. 8.9 Consent What to do if: Source has been discharged: contact Source (initially by telephone if possible, with a letter following) explaining the situation and requesting that they attend their GMP for blood tests. Source denies consent: medico-legally no further progress can be taken; consider involvement of the GUM Dept. for assistance. Source consents to test but does not want to know result: a referral to the GUM Dept. for advice/assistance is recommended. Source lacks the capacity to consent: follow guidance under the Mental Capacity Act Source has died: the issue of 'best interests in common law does not apply in the case of deceased individuals. Consent for testing in this circumstance could be obtained from the next of kin or where there is no next of kin, a relative or nominated representative. Consent should be sought from the highest ranking individual as laid out in section 27 (4) of the HTA. If there is no such person, then there is no one in law that can consent Full details concerning consent can be found within the PDSE Policy Consent to Treatment. Please discuss with a senior member of the Source s clinical team or GUM Team if you have any queries regarding consent Department Contact Details GUM Dept. Health Advisors: Ext Staff Health & Wellbeing Department: Ext Mon - Fri 8am to 4pm + answer phone out-of-hours plh-tr.occhealth-dutynurse@nhs.net Microbiology Department: Ext Enquiries (Mon - Fri 9am to 5.17pm & Sat 9am to 12.30pm): On call Microbiologist - via switchboard Page 10 of 28
11 9. Step-by-Step Guide for the Management of a Contamination Incident where a Patient is Contaminated by a Member of Staff - Reverse Incident 9.1 The risk that a patient may be exposed to the blood of a member of staff is minimised by ensuring that preventative measures are in place when performing exposure-prone procedures. 9.2 Staff must not rely on their own assessment of risk of transmission to patients. 9.3 Scenarios and Circumstances that may result in a patient being contaminated: I. During an Exposure Prone Procedure (EPP) performed by a member of staff who is not cleared by the SH&WB Department to undertake EPPs. II. During a non-epp performed by a BBV-infected member of staff (e.g. physical assault on the member of staff, spontaneous nosebleed). III. In the event that an invasive device or product contaminated by use on one patient is accidentally re-used on another patient. IV. Visible laceration occurring to a member of staff s hand in circumstances where the patient s open tissues or mucous membranes could be contaminated with the member of staff s blood. V. Visible bleeding of a member of staff from any other site (e.g. nosebleed) leading to significant bleed-back into a patient s open tissues or mucous membranes. VI. An instrument or needle contaminated with the blood of the member of staff is inadvertently introduced into the patient s tissues. 9.4 Immediate Action - Significant Incident I. Report the incident to the Senior Lead Dental Nurse who will co-ordinate the management of the incident and provide advice as required. II. The Senior or Lead Dental Nurse are to contact the ED or Occupational Health as appropriate to site, for advice. Page 11 of 28
12 Flowchart - What do I do in the Event of a Contamination Incident? A Appendix Page 12 of 28
13 Contamination Incident Risk Assessment Form Appendix B Staff Health & Wellbeing Department Contamination Incident Risk Assessment Form Part 1 - This should be completed by the Competent Person. a) Recipient s name: DoB: Employer/Sector: Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise / Medical or Dental School Student / Other Job/Role Title: Time of Incident: Dept. where Incident occurred: b) Incident Factors (Indicate type of injury by placing a or X in the Yes or No columns) Yes No 1 Deep puncture wound 2 Sharps device was in source patient s artery or vein 3 Sharps device was visibly blood stained 4 Sharps device has a hollow bore 5 Visibly blood stained body fluid into eyes, nose or mouth or onto non-intact skin Page 13 of 28
14 c) Body Fluid factors (Indicate type of body fluid by placing a or X in the Yes or No columns) Yes No 1 Blood 2 Amniotic fluid 3 Human breast milk 4 Vaginal secretions or semen 5 Cerebrospinal fluid 6 Peritoneal fluid 7 Pericardial fluid 8 Pleural fluid 9 Saliva in association with dentistry 10 Synovial fluid 11 Unfixed human tissues or organs 12 Exudative or other tissue fluid from burns or skins lesions 13 Any other visibly blood-stained body fluid (urine, saliva, faeces) There is no evidence that BBV can be transmitted by blood contamination of intact skin or inhalation, or by faeco-oral contamination. d) Source known? Yes / No if Yes, please complete this section: Source name: DoB: Patient no: Facility: Page 14 of 28
15 The competent person should explain to the source patient why it is necessary to undergo a risk assessment by asking the questions below whilst maintaining their privacy, dignity, and confidentiality during the assessment. If the source is concerned at all about any of the specific questions or declines to answer please take the opportunity to discuss this with them. Also, they may wish to just answer Yes to Question 6. If the source answers Yes to any of the following the clinician prescribing the PEP should be informed that the source is potentially high risk for HIV, whether the source consents to testing or not. The source should be offered a discussion with one of the GUM Health Advising Team. e) Source Risk factors Yes No 1 2 Was the source born outside of Europe, in Australia or the United States? If the source is male, have they had sexual relationships with other men? 3 Has the source injected drugs into their veins in the past? 4 5 Has the source had a blood transfusion or operation outside of Europe, in Australia or the United States? Has the source had a sexual partner who originates from outside of Europe, from Australia or the United States? 6 One or more of the above applies to the source f) Source Risk factors already known to clinical team Yes No 1 HIV antibody positive 2 Hepatitis C antibody positive 3 HCV RNA positive 4 Hepatitis B surface antigen positive 5 HBeAg positive Page 15 of 28
16 6 HBV DNA > 10 3 copies/ml Please obtain Serum Save from Recipient and send to Microbiology. Obtained: Yes / No If ANY of the questions in sections B, C, E or F are answered as YES the Recipient MUST go to the Emergency Department or Occupational Health as appropriate. Referred to ED/Occ Health? Yes / No - If Yes, Recipient must ring ED Minors Nurse Ext or Occupational Health as appropriate to notify them of their imminent arrival and pass this completed form to the Recipient to take with them. If not referred to ED/Occ Health ~ in order to comply with PDSE policy and to ensure the Recipient s SH&WB records are updated and to plan their future care - please forward this form to: The Nurse Manager, Staff Health and Wellbeing Department, Kingstor House, Derriford Residences, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth. PL6 8DH Signature: Date:.. Time:.am / pm Name in CAPITALS:.. Designation: Part 2 - Emergency Department/ Occupational Health to complete: Time Seen:.. HIV PEP required: Yes / No Prescribed: Yes / Declined HBIG advised / prescribed: Yes / No / Declined Given: Yes / No Hep B Booster advised / prescribed / administered: Yes / No / Declined Referral to GUM advised: Yes / No / Declined In order to comply with PDSE policy and to ensure the Recipient s SH&WB records are updated and to plan their future care this form or a copy of it must be sent to; The Nurse Manager, Staff Health and Wellbeing Department, Kingstor House, Derriford Residences, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth. PL6 8DH Signature:.. Date:.... Time:... Name in CAPITALS:.. Designation:.. Page 16 of 28
17 Information Leaflet - Source BBV Testing Appendix C A member of staff involved in your care has sustained a contamination injury (by means of a needle / scratch / bite body fluid splash) during the course of your treatment. The nature of the injury is that there is a risk that the member of staff could have become infected with a virus you might be carrying without your knowledge. How does this affect you? It is PDSE Policy and the Department of Health guidance that we approach you in order to gain consent to screen a sample of your blood for the most common blood borne viruses: Hepatitis B; Hepatitis C and HIV. This will help ensure that the injury sustained by the health care worker can be managed appropriately. If you test negative for these viruses, it will help reduce anxiety in the injured health care worker and assure you. If you test positive for these viruses it will enable appropriate treatment to be given to both you and the injured health care worker as soon as possible. Before having blood taken the following points will be explained: Ways in which Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV viruses are transmitted (can include sexual intercourse, intravenous drug use, receiving a blood transfusion prior to 1991 Seek your agreement to test for Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV Make it clear you have the right to decline the test Management of blood test and results including who will give you the results and how you wish to receive the results. Advantages for testing for you: Identification of previously unknown disease so that treatment can be started as soon as possible Opportunity to be referred to an appropriate specialist Sexual partners may be protected Plans for the future can be made. Disadvantages of testing for you: Anxiety Possible adverse impact on relationships with family Perceived insurance difficulties if the result of testing is positive existing insurance will not be affected; a negative test will not affect future insurance applications. Specialist companies will offer insurance (but exclude the BBV). Blood Test Results The results of the tests will be treated strictly as Medical in Confidence. Only for the purposes of reassurance and determining any appropriate treatment will the results be shared with the affected member of staff. This will be undertaken confidentially via the Senior Dental Nurse. Medical Confidentiality will be maintained at all times Page 17 of 28
18 Many thanks for your co-operation. Page 18 of 28
19 HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Appendix D This is a combination of vaccines and oral medicines that are prescribed when an individual suffers a contamination incident in which the Source is actually or potentially HIV positive. Headings Sharps Guidelines and protocol (24-hour cover) Key points Risk assessment of exposure to determine if significant. Immediate access to advice on HIV PEP 24 hours, 7 days a week. Baseline member of staff serum stored for 2 years. Source patient Universal approach to source patient testing for antibodies to HIV. Source patient should be consented and a blood sample obtained, and consider risk for HBV and HCV. Guidelines clarify the implications of the Human Tissue Act 2004 and the Mental Capacity Act 2005 with regard to testing incapacitated source (adult) patients for serious communicable diseases without consent. Recommended good practice is that hospitals should have the capacity to obtain a source patient HIV test result within 8 hours (ideally) and no longer than 24 hours after blood is obtained. Factors influencing transmission Transmission rate: Low Drugs (starter pack triple therapy HIV PEP) Deep injury. Visible blood on the device. Needle from source patient s artery or vein. Terminal HIV-related illness in source patient. 3:1000 percutaneous. <1:1000 mucocutaneous. No risk where intact skin is exposed to HIV-infected blood. One Truvada tablet (300mg tenofovir and 200mg emtricitabine- FTC) once a day. Plus- Two Kaletra film-coated tablets (200mg Lopinavir and 50mg Ritonavir) twice a day. No antiretroviral drug has been licensed for HIV PEP, so must be prescribed on an off-label basis only. Timing of HIV PEP Initiated as soon as possible after the exposure, ideally within an hour following a careful risk assessment. PEP is now not generally recommended after 72 hours post-exposure. Follow-up Recommended follow-up period after occupational exposure to HIV, as a minimum, is now for at least 12 weeks after the HIV exposure, or if PEP was taken, for at least 12 weeks from when PEP was stopped. Longer follow-up with additional testing may be indicated in complex cases; e.g. member of staff is immunocompromised, member of staff experiences illness compatible with acute retroviral syndrome, or the source patient is dually infected. Where the Source is the member of staff, PEP for HIV should only be offered following a positive test in the member of staff. This recognises that member of staff who are following the DH Page 19 of 28
20 guidance are at low-risk for HIV infection and that there are considerable practical difficulties to administering PEP in the immediate post-operative period (e.g. obtaining valid consent, possible need for parenteral administration and toxicity of PEP for sick patients). Only in exceptional circumstances would it be warranted to initiate PEP in the absence of a positive HIV test result e.g. high likelihood of HIV infection in the member of staff and/or refusal of the member of staff to be tested. A 28-day course of treatment with a triple combination of antiretroviral drugs is normally used and needs to be commenced rapidly for maximum efficacy. Particular consideration will need to be paid to the risk/benefit ratio of PEP for sick patients whose ability to tolerate antiretroviral therapy may be compromised. A higher threshold for commencing PEP may be appropriate because of the high incidence of side effects. Advice from GUM consultant on the best combination to use may be necessary for patients with systemic organ failure/organ insufficiencies. In patients who are nil-by-mouth, antiretroviral drugs are available in a number of formulations suitable for naso-gastric or intravenous administration. If a patient is unconscious, PEP should not be withheld on the grounds that they are unable to consent, if clinical judgement deems it to be in their best clinical interests. If a child is exposed, specialist advice from a paediatrician with experience in HIV should be sought. Page 20 of 28
21 HIV Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Information Leaflet Appendix E This leaflet is to help you decide whether to take post exposure prophylaxis (PEP) following an actual or potential exposure to a BBV (blood borne virus). Is the service confidential? All information discussed between you and the doctor is confidential. What risk assessment is required? The doctor will discuss the risks of you becoming infected with you. This is based on the source (the person whose blood or other body fluid you were exposed to), and the type of injury. Are there risks with PEP? The doctor will go through your medical history with you. They will also discuss the medication you re taking, to ensure there are no drug interactions. What if I m pregnant? This does not preclude use of PEP, but if this is the case, the GU consultant will discuss this with you in detail. What are the risks of developing HIV? The worst case scenarios are that, following a needlestick-type injury, your risk is 1:300. Following a splash-type injury, the risk is about 1:1000. The risk is reduced by about 80% if you take PEP. What are the side effects? The PEP can make you feel unwell, and a significant number of people stop the medication because of this. The main symptoms are nausea and diarrhoea. Less commonly, there can be problems with your liver and kidneys, bone marrow suppression, or pancreatitis. When should I start PEP? The ideal time is within 1-4 hours, but it can be used up to 72 hours after the exposure. What is the blood test for? You have an initial blood test done. This is only stored. If subsequently you do become HIV positive, this blood will be tested, to clarify whether you were HIV positive before the incident. Can I work on PEP? If you feel well, you can continue to work normally. There is no need to restrict you from any work, including exposure prone procedures. If you don t feel well on the medication, the time off sick will not be recorded as normal sickness absence. What about safe sex? You are advised to practise safe sex until the follow up period is complete. Likewise, you are advised not to try and fall pregnant, or to breast feed. You should not donate blood. When will I be reviewed? You will be seen every week for 4 weeks. You will then be reviewed at 6-8 weeks, and weeks. If the HIV after 12 weeks is negative, it is unlikely that you will become HIV positive. Page 21 of 28
22 PEP for Hepatitis B Appendix F PEP for Hepatitis B may be recommended following exposure to Hepatitis B and consists of a course of immunoglobulin with or without a booster dose of Hepatitis B vaccine. *An accelerated course of vaccine consists of doses spaced at 0, 1 and 2 months. A booster dose may be given at 12 months to those at continuing risk of exposure to HBV Page 22 of 28
23 Information Leaflet - Members of Staff with a Blood-Borne Virus Appendix G Being informed that you have tested positive to a blood borne virus (BBV) can be devastating; involve psychological effects, emotional trauma; hardship and inconveniences to you, your family and friends. The impact cannot be underestimated and in view of the seriousness of a positive result, the SH&WB Team will ensure that a support mechanism is in place to support you. You will see or have seen an Occupational Physician to discuss your own situation, and it is important that you read these notes carefully and keep them for later reference. Obligations to your Patients There is a risk that Healthcare workers who are infected with a BBV may pass the infection to a patient. You have an overriding ethical and legal duty to protect the health and safety of patients and colleagues. You must consider your personal accountability as set out in the codes of professional bodies such as the NMC, GMC and GDC and also the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act You must keep yourself informed and updated on the codes of professional conduct and guidelines with reference to BBV infected staff. You must not rely on your own assessment of the risks you pose to patients or others. You must have appropriate medical supervision of your clinical condition and take advice regarding risks to close family members and also regarding the need to inform your dentist or surgeon of your condition when undergoing procedures. You must also attend appointments with the Occupational Physician as deemed appropriate. When applying for new jobs you must declare your condition confidentially to the Occupational Health Department of your new employer. You must take particular care to observe good practice in control of infection matters including regular hand washing, wearing gloves where appropriate, covering existing wounds or skin lesions with waterproof dressings and avoiding contamination injuries. Always dispose of sharps correctly. Exposure Prone Procedures (EPPs) Health Care Workers with certain BBVs must not undertake EPPs. These are procedures where there is a risk that an injury to the worker may result in the patient s open tissues being exposed to the worker s blood. This is where the worker s gloved hands may be in contact with sharp instruments or spicules of bone or teeth inside a patient s open body cavity or wound where the hands and fingertips may not be completely visible at all times. The Occupational Physician will explain to you whether or not you are permitted to do exposure prone procedures, and will give you specific advice regarding what procedures in your own workplace you are permitted to do. Procedures which are not usually classified as exposure prone and may be undertaken even by workers whose practice is restricted include: Internal examinations where sharp instruments are not involved Giving injections, taking blood, inserting venflons Page 23 of 28
24 Wound dressings, draining superficial abscesses Lumbar puncture, paracentesis Urethral catheterisation Cardiac and respiratory resuscitation including mouth-to-mouth resuscitation (if you are the only person available to do this), endotracheal intubation. Internal direct cardiac massage is excluded. Reverse Incidents In exceptional circumstances a patient may be exposed to your blood despite all precautions. In these circumstances you must stop the procedure immediately. The incident must immediately be reported to both SH&WB and to one of the Infectious Diseases Consultants or to the Consultant Microbiologist on call. These doctors will assess the risk to the patient and whether further action is necessary. You must not rely on your own assessment of the risk posed to the patients. Failure to report potential hazardous incidents may breach the duty of care to patients. Confidentiality You have a right to confidentiality regarding your condition. In certain circumstances where a change of duties is necessary (for example to avoid exposure prone procedures) advice will be given to your manager with regard to your duties but the diagnosis will not be divulged. In these circumstances, the need to provide such advice, how it will be given and the wording used will be discussed beforehand with you. In rare cases when it is thought that patients may have been exposed to blood borne viruses from a health care worker, a look back exercise may need to be discussed with public health doctors and senior managers. In these circumstances the health care worker s right to confidentiality is vigorously protected but inevitably certain senior professionals would need to know the diagnosis. The SH&WB Team will never divulge your diagnosis to your manager or employer without your knowledge. Health Surveillance & Review The SH&WB Team will keep you under review at appropriate intervals. You must attend these appointments. The purpose of this is to: Review your general health and liaise with your clinician as necessary. Review your duties and the tasks you are required to perform, and to identify any aspects of your job that are a potential risk to patients or colleagues. Ensure your work is not putting you at risk, e.g. if you are unwell or immunosuppressed. Discuss any other problems in your workplace regarding confidentiality or difficulties arising because of the need to avoid certain activities. Give advice regarding career progression and to discuss proposed moves to new areas of work. Give you an opportunity to discuss any wider implications of your condition that you have not otherwise had a chance to discuss with a physician. We may be able to refer you for further specialist advice. Page 24 of 28
25 Assessing Fitness for EPP Work - Staff who are BBV Positive Appendix H Page 25 of 28
26 Template letter to patient where a contamination incident has occurred Appendix I ENTER DEF ADDRESS Dear A student/staff member sustained an inoculation injury today from an instrument which had been used during your treatment. In order to assess the possible risk of the staff/student having been infected with a Blood Borne Virus (BBV) we hereby request that you attend your General Medical Practitioner as soon as possible to arrange for a blood test for BBVs. On receipt of the results of this test please would you send a copy of the results to the Senior Dental Nurse (marked confidential), at the above address. Please take this letter with you to your General Medical Practitioner, to explain the need for this blood test. Many thanks for your assistance with this matter. Page 26 of 28
27 Information Leaflet - Source BBV Testing A member of staff involved in your care has sustained a contamination injury (by means of a needle / scratch / bite body fluid splash) during the course of your treatment. The nature of the injury is that there is a risk that the member of staff could have become infected with a virus you might be carrying without your knowledge. How does this affect you? It is PDSE Policy and the Department of Health guidance that we approach you in order to gain consent to screen a sample of your blood for the most common blood borne viruses: Hepatitis B; Hepatitis C and HIV. This will help ensure that the injury sustained by the health care worker can be managed appropriately. If you test negative for these viruses, it will help reduce anxiety in the injured health care worker and assure you. If you test positive for these viruses it will enable appropriate treatment to be given to both you and the injured health care worker as soon as possible. Before having blood taken the following points will be explained: Ways in which Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV viruses are transmitted (can include sexual intercourse, intravenous drug use, receiving a blood transfusion prior to 1991 Seek your agreement to test for Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV Make it clear you have the right to decline the test Management of blood test and results including who will give you the results and how you wish to receive the results. Advantages for testing for you: Identification of previously unknown disease so that treatment can be started as soon as possible Opportunity to be referred to an appropriate specialist Sexual partners may be protected Plans for the future can be made. Disadvantages of testing for you: Anxiety Possible adverse impact on relationships with family Perceived insurance difficulties if the result of testing is positive existing insurance will not be affected; a negative test will not affect future insurance applications. Specialist companies will offer insurance (but exclude the BBV). Blood Test Results The results of the tests will be treated strictly as Medical in Confidence. Only for the purposes of reassurance and determining any appropriate treatment will the results be shared with the affected member of staff. This will be undertaken confidentially via the PDSE s Senior Dental Nurse. Medical Confidentiality will be maintained at all times Many thanks for your co-operation. Page 27 of 28
28 All policies are required to be electronically signed by the Director of Community Based Dentistry The proof of signature for all policies is stored in the policies database. The Director of Community Based Dentistry approves this document and any attached appendices. Signed: Title: Director of Community Based Dentistry Date: 17 October 2013 Page 28 of 28
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS. All clinical areas of the Trust. Prevent spread of Hepatitis B virus
 Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses
 Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP:
 Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy
 Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS
 TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions
 Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
B. Tasks and Procedures where employees, students or contractors can be exposed to bloodborne pathogens:
 Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
Page 1 of 6 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM INTRODUCTION The intended purpose of this document is to comply with OSHA s Occupational Exposures to Bloodborne Pathogens in Title 29 Code of Federal Regulations
PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy
 PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy 1 Policy title Protection from Occupational Acquired /Transmitted Communicable Diseases Policy COR 60 reference Policy category
PROTECTION FROM OCCUPATIONAL ACQUIRED/TRANSMITTED COMMUNICABLE DISEASES Policy 1 Policy title Protection from Occupational Acquired /Transmitted Communicable Diseases Policy COR 60 reference Policy category
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES
 NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
Bloodborne Pathogens. Montclair Kimberley Academy 1
 Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Bloodborne Pathogens Montclair Kimberley Academy 1 Introduction! Approximately 5.6 million workers in health care and other facilities are at risk of exposure to bloodborne pathogens such as human immunodeficiency
Colgate University. Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines
 Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust)
 A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC20 VACCINATION PROGRAMME FOR STAFF AND
A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC20 VACCINATION PROGRAMME FOR STAFF AND
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS
 HUMAN RESOURCES (WITH OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH) HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS DOCUMENT REF: PHRMHEPAB (Version No. 5.0) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee,
HUMAN RESOURCES (WITH OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH) HEPATITIS B VIRUS: PROTECTING EMPLOYEES AND PATIENTS DOCUMENT REF: PHRMHEPAB (Version No. 5.0) Name and designation of policy author(s) Approved by (committee,
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP)
 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
COLLEGE'S RESPONSE TO AN INDIVIDUAL'S INABILITY TO WORK OR STUDY WITH A PERSON WITH A BLOOD-BORNE COMMUNICABLE DISEASE #2-01
 Policy & Procedures Manual COLLEGE'S RESPONSE TO AN INDIVIDUAL'S INABILITY TO WORK OR STUDY WITH A PERSON WITH A BLOOD-BORNE COMMUNICABLE DISEASE #2-01 Approved: June 23, 1993 by: Board of Governors Effective:
Policy & Procedures Manual COLLEGE'S RESPONSE TO AN INDIVIDUAL'S INABILITY TO WORK OR STUDY WITH A PERSON WITH A BLOOD-BORNE COMMUNICABLE DISEASE #2-01 Approved: June 23, 1993 by: Board of Governors Effective:
INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES
 Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
Sharps Injuries Management
 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
El Paso - Ambulatory Clinic Policy and Procedure
 Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
A. Background for Trainer: B. What OSHA Requires: Bloodborne Pathogens. Lesson Plan 6080a
 Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1
 PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
PROCEDURE TITLE: BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN PROCEDURE NO.: 5.21:1 RELATED POLICY: 5.21REV PAGE NO.: 1 OF 9 RESPONSIBLE ADMINISTRATOR(S): VPF&A/EHS EFECTIVE DATE: 07/11/14 NEXT REVIEW DATE:
Village By Village HIV/AIDS Policy
 The Old Sweet Shop Teme Street, Tenbury Wells, Worcs. WR15 8BB Phone: 07887 870090 Web: villagebyvillage.org.uk Email: neil@villagebyvillage.org.uk Registered Charity Number 1116952 18/9/07 Village By
The Old Sweet Shop Teme Street, Tenbury Wells, Worcs. WR15 8BB Phone: 07887 870090 Web: villagebyvillage.org.uk Email: neil@villagebyvillage.org.uk Registered Charity Number 1116952 18/9/07 Village By
EU Directive for Safer Sharps. Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant
 EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
SHARPS MANAGEMENT AND INOCULATION INJURIES
 Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
Community Infection Prevention and Control Guidance for Health and Social Care Sharps Management and Inoculation Injuries Version 1.01 May 15 Harrogate and District NHS Foundation Trust Sharps Management
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS.
 SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
Bloodborne Pathogens Training
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
Bloodborne Pathogens Training OSHA S Bloodborne Pathogen Standard 29CFR 1910.1030 Employers must: Develop an Exposure Control Plan (ECP) that details their Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Program Provide employees
Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected?
 Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected? Dr Alison Rimmer Consultant Occupational Physician and Clinical Director Sheffield Occupational Health Service Serious communicable
Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected? Dr Alison Rimmer Consultant Occupational Physician and Clinical Director Sheffield Occupational Health Service Serious communicable
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy
 Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C)
 Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
Management of Healthcare Workers Infected With A Blood-borne Virus (HIV, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
AIDS, HIV, and Hepatitis B. To outline a plan for the prevention of exposure of hospital personnel to patients with AIDS, HIV, or Hepatitis B.
 Audience: Purpose: Policy: AIDS, HIV, and Hepatitis B All personnel in the. To outline a plan for the prevention of exposure of hospital personnel to patients with AIDS, HIV, or Hepatitis B. The University
Audience: Purpose: Policy: AIDS, HIV, and Hepatitis B All personnel in the. To outline a plan for the prevention of exposure of hospital personnel to patients with AIDS, HIV, or Hepatitis B. The University
ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICES MANUAL
 1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
1 of 10 Purpose Scope University of Alaska Anchorage departments will develop plans and procedures to limit occupational exposure to blood and other potentially infectious materials (PIM) in compliance
Drew University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan and Procedures
 PURPOSE To provide a written plan for preventing and/or minimizing exposure to bloodborne pathogens for those Drew University personnel who may be involved in the handling of human blood, blood products,
PURPOSE To provide a written plan for preventing and/or minimizing exposure to bloodborne pathogens for those Drew University personnel who may be involved in the handling of human blood, blood products,
Goldenrod Hills Community Action. Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR
 Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
Goldenrod Hills Community Action Bloodborne Pathogen (BBP) Training according to OSHA Standard 29 CFR 1910.1030 Welcome to GHCA s Bloodborne Pathogen Training based upon the Occupational Safety and Health
I. PROCEEDINGS AFTER EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (OPIM) WHICH MIGHT TRANSFER AN INFECTION WITH HAEMATOGENOUS VIRUSES
 Annex no. 1 to the enactment No. 13/XIV R/2010 of the Rector of the Medical University in Wrocław dated April 12, 2010 Proceedings after occupational exposure to HIV, HBV and HCV 1 LEGAL GROUNDS: 1. The
Annex no. 1 to the enactment No. 13/XIV R/2010 of the Rector of the Medical University in Wrocław dated April 12, 2010 Proceedings after occupational exposure to HIV, HBV and HCV 1 LEGAL GROUNDS: 1. The
Bloodborne Pathogens. Post-Exposure Incident Packet. An Informational Guide
 Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet An Informational Guide Faribault Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet This packet has been developed as an informational
Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet An Informational Guide Faribault Public Schools Bloodborne Pathogens Post-Exposure Incident Packet This packet has been developed as an informational
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts)
 SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
May Safety Subject. Bloodborne Pathogens
 May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
May Safety Subject Bloodborne Pathogens Everyone is at risk to contact bloodborne pathogens. Some more than others. Universal precautions means treating all objects as potentially contaminated Personal
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
 Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps Version: 8 Status: Owner: In review Infection Prevention
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
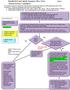 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Blood borne Pathogen Exposure Policy for Students
 Blood borne Pathogen Exposure Policy for Students A University of Rhode Island (URI) student or intern who sustains an exposure from a needle stick, instrument stick, or mucous membranes to non-intact
Blood borne Pathogen Exposure Policy for Students A University of Rhode Island (URI) student or intern who sustains an exposure from a needle stick, instrument stick, or mucous membranes to non-intact
Blood-borne Virus Infections in Health Care Workers: Victorian Lookback Experiences
 Blood-borne Virus Infections in Health Care Workers: Victorian Lookback Experiences Dr Jessica Rotty, Dr Brett Sutton, Dr Mihaela Ivan, Adam Hamilton, Jay Healy, Nasra Higgins, Rachel Coutts, Rachel M
Blood-borne Virus Infections in Health Care Workers: Victorian Lookback Experiences Dr Jessica Rotty, Dr Brett Sutton, Dr Mihaela Ivan, Adam Hamilton, Jay Healy, Nasra Higgins, Rachel Coutts, Rachel M
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Nursing and Midwifery students only. Section 1: Information
 Nursing and Midwifery students only. Section 1: Information Students enrolled in programs offered by our School are REQUIRED to provide evidence of their immunisation status for the diseases listed in
Nursing and Midwifery students only. Section 1: Information Students enrolled in programs offered by our School are REQUIRED to provide evidence of their immunisation status for the diseases listed in
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005
 Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
Sharps Management, Needle-Stick Injuries and Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Procedure ICPr005 Version Date Date of Next Reason for Change (eg. full rewrite, No. Ratified/ Implementation Review amendment
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure STUDENT. Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure. Student. Rev:
 Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Blood Borne Pathogen Exposure Student INSTRUCTIONS 1. Student: Get name, DOB and, if available, health record number of source patient Obtain form and assist your supervisor with providing information
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Sue Sebazco, Arlington, Texas A Webber Training Teleclass
 Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Health and Social Care Workers and Pandemic Influenza
 Health and Social Care Workers and Pandemic Influenza Information for staff who are pregnant or in DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning / Clinical Document Purpose Gateway
Health and Social Care Workers and Pandemic Influenza Information for staff who are pregnant or in DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning / Clinical Document Purpose Gateway
Student Immunisation Record Faculty of Medicine. Section 1: Information. Notes
 Student Immunisation Record Faculty of Section 1: Information Students enrolled in programs offered by the Faculty of are REQUIRED to provide evidence of their immunisation status for the diseases listed
Student Immunisation Record Faculty of Section 1: Information Students enrolled in programs offered by the Faculty of are REQUIRED to provide evidence of their immunisation status for the diseases listed
COMMONWEALTH SCAFFOLD Quality Scaffolding Across New England
 Prepared by Allied Insurance Brokers, Inc. Commonwealth Scaffold, LLC Bloodborne Pathogens Program and Training Materials Effective Date: 12/14/2012 Revision #: Table of Contents Bloodborne Pathogens Program
Prepared by Allied Insurance Brokers, Inc. Commonwealth Scaffold, LLC Bloodborne Pathogens Program and Training Materials Effective Date: 12/14/2012 Revision #: Table of Contents Bloodborne Pathogens Program
Naval Support Activity Monterey / Naval Postgraduate School
 Background: Bloodborne pathogens are viruses present in human blood and body fluids that can cause disease in humans. Diseases like the hepatitis B virus (HBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and others
Background: Bloodborne pathogens are viruses present in human blood and body fluids that can cause disease in humans. Diseases like the hepatitis B virus (HBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and others
POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG.
 POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG. Reference Number: PPG CUH CUH Revision No: 1 Review Cycle: 2 Years Author (Lead): Dr Colm Kerr, Infectious Owner: Dr A Jackson, Infectious
POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG. Reference Number: PPG CUH CUH Revision No: 1 Review Cycle: 2 Years Author (Lead): Dr Colm Kerr, Infectious Owner: Dr A Jackson, Infectious
MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS)
 MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS) INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY NO. 4 Applies to: Staff employed
MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURE TO HEALTH CARE ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS (HCAI) AND INOCULATION INCIDENTS (INCLUDING SAFE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS) INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY NO. 4 Applies to: Staff employed
BAY-ARENAC BEHAVIORAL HEALTH AUTHORITY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES MANUAL
 Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard. The OSHA Standard
 Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
Bloodborne Pathogen Training 1 What are Bloodborne Pathogens? We already have learned that pathogens are infectious agents that can cause us to get sick like viruses or bacteria or germs or parasites.
SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS
 SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS Version 10. Feb 2017 First issued Oct 2008 Reviewed Feb 2017 Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
SHARPS POLICY: SAFE HANDLING AND DISPOSAL OF SHARPS Version 10. Feb 2017 First issued Oct 2008 Reviewed Feb 2017 Document Control Sheet Name of document: Sharps Policy: Safe Handling and Disposal of Sharps
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Training (OHS_BIO500) Course Material
 Introduction (OHS_BIO500) Course Material Welcome to the Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Training Course (OHS_BIO500). UAB Campus Employees whose job duties put them at increased risk for exposure to bloodborne
Introduction (OHS_BIO500) Course Material Welcome to the Bloodborne Pathogens (BBP) Training Course (OHS_BIO500). UAB Campus Employees whose job duties put them at increased risk for exposure to bloodborne
Kingdom of. Bahrain FOR
 Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Health Public Health Directorate Diseases Control Section POLICY FOR IMMUNIZATION AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES SCREENING FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL, NURSING, AND PHYSIOTHERAPY STUDENTS
Kingdom of Bahrain Ministry of Health Public Health Directorate Diseases Control Section POLICY FOR IMMUNIZATION AND INFECTIOUS DISEASES SCREENING FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL, NURSING, AND PHYSIOTHERAPY STUDENTS
City of Montpelier, Vermont The Smallest Capital City in the United States BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN AND PROCEDURES
 City of Montpelier, Vermont The Smallest Capital City in the United States BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN AND PROCEDURES Last Updated June 19, 2003 1 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
City of Montpelier, Vermont The Smallest Capital City in the United States BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN AND PROCEDURES Last Updated June 19, 2003 1 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
Doc No: BLOOD Midland Engineering Co., Inc. Initial Issue Date 12/04/15 Safety Management System
 Revision Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: President Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has a variety of regulations that all
Revision Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: President Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 15 INTRODUCTION The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has a variety of regulations that all
Infection Control Program (ICP) ICP Components 1. Exposure Determination 2. Control Methods A. Universal Precautions
 Compliance Assistance Guideline for the February 27, 1990, OSHA Instruction CPL 2 2.44B Enforcement Procedures for Occupational Exposure to Hepatitis B Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus from the U.S.
Compliance Assistance Guideline for the February 27, 1990, OSHA Instruction CPL 2 2.44B Enforcement Procedures for Occupational Exposure to Hepatitis B Virus and Human Immunodeficiency Virus from the U.S.
Bloodborne Pathogens
 Bloodborne Pathogens Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper
Bloodborne Pathogens Disclaimer This training material presents very important information. Your organization must do an evaluation of all exposures, applicable codes and regulations, and establish proper
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: NON- OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOOD-BORNE PATHOGENS (HIV, Hepatitis B, AND Hepatitis C)
 General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
June 4, Page 1 of 5 POLICY STATEMENT
 POLICY STATEMENT This policy has been written to inform all staff, clients, relatives and other visitors to the homes of service users about the risks associated with MRSA, AIDS and HIV hazards in the
POLICY STATEMENT This policy has been written to inform all staff, clients, relatives and other visitors to the homes of service users about the risks associated with MRSA, AIDS and HIV hazards in the
