The Syndrome of Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) Infected. by Virus and Bacteria *
|
|
|
- Bertha Watson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VIROLOGICA SINICA, February 2008, 23 (1):63-67 DOI /s CLC number: Q938.8 Document code: A Article ID: (2008) The Syndrome of Sea Cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) Infected by Virus and Bacteria * Huan DENG 1**, Zun-chun ZHOU 1, Nian-bin WANG 1 and Chang LIU 2 (1.Liaoning Marine and Fisheries Science Research Institute, Liaoning Open Lab of Applied Marine Biology, Dalian , China; 2. 89K seven-year system 6 Class,China Medical University, Shenyang ,China) Abstract: A outbreak of disease with symptoms of evisceration and skin ulteration led to mass mortality in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus cultivated in indoor ponds near the Dalian coast from December 2004 to April Spherical virus particles with a diameter of nm were found in the cytoplasm of cells in the water-system, the alimentary canal and in the respiratory trees of the diseased and dying sea cucumber individuals by electron microscopic observation of ultrathin sections. Examination by negative stained samples revealed that all the diseased sea cucumbers were infected by the virus, while the healthly ones cultivated outside the contagious area were not. Two bacterial strains were also isolated from the diseased animals. When exposed to a medium containing the virus particles, regardless of whether the bacterial suspension was added, healthy sea cucumbers exhibited identical disease symptoms as the ones in the indoor ponds, and had a mortality of 90%-100%. However, when exposed to a medium in which there was only one of the two bacterial strains, 30%-80% of the sea cucumbers were infected and nearly 20% died. Negative staining showed that the viral particles were detected only in the bodies of the tested animals that were exposed to the viral medium. Histopathologically, the diseased sea cucumbers are characterized by karyopycnosis, and disintegration of the endoplasmic reticula and mitochondria in the epithelial cells in the water-system, the respiratory tree and the alimentary canal. Key words: Apostichopus japonicus; Virus; Bacteria; Syndrome At present, repeated occurrence of disease has been the bottle-neck for sustainable development of sea Received: , Accepted: Fundation items: Supported by commonweal program of State Oceanic Administration of China ( ), Science and Technology Project of Liaoning Province ( ) and Science and Technology Project of Dlian (2004 BINS030). ** Corresponding author. Tel: , denghuan6@msn.com cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) culture in China, and has been the subject of multiple studies by fishery scientists. Wang et al reported that bacteria, fungi and parasites involved in the skin ulceration and edema in the sea cucumber (7); bacterial diseases in echinoderms, echinoids, holothuroids and asteroids were described by Jangoux (2). Becker et al reported a skin ulceration disease in sea cucumber Holothuria scabra caused by bacterial infection (1). The viruses were
2 64 Virol. Sin. (2008) 23: observed in the body of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus by Wang et al but they did not confirm whether the viruses were pathogens (6). In this paper, for the first time, we show that the virus is a pathogen of the disease in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. A disease with the symptoms of evisceration and skin ulcerations broke out and led to mass mortality in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus cultivated in indoor ponds near the Dalian coast from December 2004 to April 2005, and led to almost 100% mortality. Isolation and identification of the virus as a pathogen and artificial infection was conducted and is described in this paper. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals Healthy sea cucumbers varying from 1.5 to 2.0 cm in body length were collected from the Jinzhou area of Dalian where no contagious disease had occurred, while the diseased ones, eviscerating and dying, were sampled from Dalijia area of the Dalian coast in Liaoning Province, China, where many sea cucumbers suffered from this disease. The animals were acclimatized for one week. The healthy individuals used in this experiment which were not infected by the virus were examined with the negative staining method described below. Preparation and observation of ultrathin sections The diseased animals were first fixed in 3% glutaraldehyde solution for 12 h, then in 1% osmium tetroxide solution. Samples were dehydrated through a graded series of ethanol (50%, 70%, 90% and 100%), then transferred into Epon812 resin and cut with a Leica ultracut UCT. Sections were stained with lead citrate and uranyl acetate and observed with a JEM-1200EX electron microscopy. Preparation and observation of negative stained samples The tissue samples were centrifuged ( r/min, 10 min) twice after homogenizing, freezing and thawing. The supernatant solution was dripped on to a copper net and stained with 2% PTA for 2 min and observed with electron microscopy. In addition, the remaining supernatant was conserved in a low temperature icebox for use in artificial infections. Twenty diseased sea cucumbers were examined to detect the pathogen during the disease epidemic period. Artificial infection Tissue homogenized supernatant solution containing the virus was used as a viral pathogen. The bacterial pathogen was two dominant bacterial strains STT and STW , which were isolated from diseased sea cucumbers, cultivated on 2216E medium and washed down with 0.9% physiological saline. It was confirmed that the solution contained no bacteria. In artificial infection tests, 10 healthy sea cucumbers averaging from 1.5 to 2.0 cm in body length were stocked into a 1L column aquarium (13 cm in diameter; 19cm in height) with three control groups. In the treatment groups the healthy sea cucumbers were cultured in the sea water containing 1 ml of the tissue homogenized supernatant containing the viral particles (Group 1), STT strain (Group 2), STW strain (Group 3), and 1 ml of the tissue homogenized supernatant containing the viral particles and 0.5 ml of STT and STW strains (Group 4). The Control Group 1 contained the test sea cucumbers and 1 ml of 0.9% physiological saline,
3 Virol. Sin. (2008) 23: Control Group 2 contained the test sea cucumbers and 1 ml of tissue homogenized supernatant in which there were no virus and bacteria and Control Group 3 contained the test sea cucumber and 1 ml of physiological saline which was washed down from 2216E medium. The sea water used in the experiment was filtered by sand and water tem-perature was kept at 15.0±0.5. The supernatant contained bacteria at a concentration of CFU/mL. RESULTS Symptoms of the progression of the disease in sea cucumber The infected sea cucumber initially becomes eviscerated, then swelling occurs around the mouth and body wall. The ambulacrum shranks, became flat, thus had no fuction of attachment, and a soft and pale body wall was common. Some individuals had ulcerations from inside to outside the body wall, which became deliquescent when touched. Artificial infection There were no any disease symptoms in the sea cucumbers in the three control groups. On the other hand, the treated individuals exposed to the media containing viruses or viruses plus bacteria particles showed the same disease symptoms as found in naturally diseased individuals. The symptoms were observed from as early as 10 hours to as late as 5 days after administration. One hundred percent mortality occurred in the animals exposed to viruses only or viral and bacterial supernatants. The test animals exposed to the medium containing the two bacterial strains had morbidity from 30% to 80%, with 20% mortality. There was no significant difference in the repeated tests except 80% and 90% mortality in the groups infected with viruses or viruses plus bacteria (the tested individuals used in the negative staining were excluded). Negative staining revealed that the virions were detected only in the specimens in Group 1 and Group 4. Observation under an electron microscope Shape and distribution of virus particle: The electron microscopic examinations revealed that the virus infecting the animals was an enveloped spherical virus with a nuclear capsid which varied from 60 to 110 nm in diameter. A few virions with a nuclear capsid of 200 nm in diameter were also observed. Many naked nuclear capsids and various electronic densities of virion were detected by the negative staining method, some showing almost electron transparency (Fig.1.E). Observation of ultrathin sections showed that the virions with inclusion bodies were distributed throughout the cytoplasm. A large number of virions and inclusion bodies were also detected in the muscular cells of the water-system (such as Polian vesicle), the respiratory tree and the epithelia of the alimentary canal and in the cytoplasm of connective tissue cells in the diseased sea cucumbers. The virons had the same size, but different a electronic density (Fig. 1. F). Infectious extension of the virus detected by negative staining: The electron microscopic examinations of the diseased sea cucumbers from twenty aquaculture firms confirmed that the regions affected by this virus were located in part of Changxingdao island on the Dalian coast. Tissue pathology: The comparison of the organs and tissues of body wall between the normal and diseased sea cucumbers showed that the abundant and clear organelles were distributed evenly and were
4 66 Virol. Sin. (2008) 23: Fig. 1. Electron microscopic observation of ultrathin sections and negative stained samples. A: The intestine epithelia of healthy sea cucumber. B: Showing the healthy sea cucumber coelom cells and connective tissues of Polian vesicle. C:The epithelia of respiratory tree in the healthy sea cucumber. D: The body wall cells in the healthy sea cucumber. E: Viral particles shown by negative staining. F: The inclusion body in the epidermic cells of the digestive canal. G: The disintegrating epithelia tissue of respiratory tree with many viral particles. H: The musclar cells in the water-system, showing karyopycnosis, endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria destroyed. I: The cells in the connective tissue in the affected individual, showing myeloid, electron density material occurred in the cytoplasm. J: The bacteria (white arrow) invaded into the broken tissue where the viruses can be seen (black arrow).
5 Virol. Sin. (2008) 23: observed in the cells of the intestines, the Polian vesicle, the respiratory tree, the body wall and the karyoplasm in normal individuals(fig. 1. A, B, C, D). However, karyopycnosis, endoplasmic reticulum atrophy and the disintegration of the outer membrane and cristae in mitochondria were observed in the diseased sea cucumber. The number of ribosomes was reduced greatly or even disappeared in the cytoplasm in the diseased sea cucumber. Sometimes, virions with high electron densities appeared in the mitochondria of diseased sea cucumber. With the disintegration of organelles, the marrow presented in the cytoplasm and the cell ultimately disaggregated (Fig. 1. H, I). Many viral particles filled the disintegrating tissue (Fig.1. G). The bacteria invasion into the tissue was expedited due to the ruptured epidermis (Fig. 1. J). DISCUSSION Artificial infection indicated that a spherical virus was a pathogen causing the disease found in the sea cucumber and resulted in high mortality. There was lower infection rate in the two strains of bacteria than that observed for the virus. With a mixture of bacteria and viruses, however, the diseased sea cucumber showed an earlier onset of symptoms, indicating that these bacteria played a synergism role in the epidemiological spread of the disease. However, it is still unclear whether the virus or the bacteria, represents the original pathogen and which is present as a secondary affliction. The serious disease in sea cucumber culture is attributed to the over-culturing and ignoring scientific management of the farms. According to present conditions, water supply, feed and larvae all could be the carriers of the pathogen. In a virtual study, control of the diseases in sea cucumber culture can be best achieved by a program of good management. Most of the viruses found in the sea cucumber are less than 140 nm in diameter, and others which were observed with a diameter of 200 nm, may belong to another genus, which need further study. Several marine animals have been reported to be infected by a virus in the past few years, such as scallop (4, 5), and abalone (3). But the virus infecting the sea cucumber was different from the others previously identified in shellfish. This paper reports only the primary studies and the purification, identification, culture of virus and more detail research is needed to clarify the problem. References 1. Becker P, Gillan D, Lanterbecq D, et al The skin ulceration disease in cultivated juveniles of Holothuria scabra (Holothuroidea, Echinodermata). Aquaculture, 242: Jangoux M Diseases of echinodermata. In: Diseases of Marine Animals (Kinne O. ed). Vol. 3. Biologische Anstalt Helgoland, Hamburg, Germany, p Li X, Wang B, Liu S F Studies on pathogen and histopathology of crack shell disease of Haliotis discus hanni. Journal of Fisheries of China, 22 (1): (in Chinese) 4. Li X, Wang B, Liu S F, et al The infection to a few kinds of shellfish inshore by a kind of virus. J Dalian Fish Univ, 15 (2): (in Chinese) 5. Wang C M, Wang X H, Song X L, et al Purification and ultrastructure of a spherical virus in cultured scallop Chlamys farreri. J Fish China, 26 (2): (in Chinese) 6. Wang P H, Chang Y Q, Xu G R, et al Isolation and ultrastructure of an enveloped virus in cultured sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka). J Fishery Sci China, 12 (6): (in Chinese) 7. Wang Y G, Rong X J, Zhang C Y, et al Main diseases of cultured Apostichopus japonicus: prevention and treatment. Marine Sci, 29 (5): 1-7. (in Chinese).
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
Electron Microscopic Evidence of Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus)
 Electron Microscopic Evidence Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) Yukinori Takahashi*1, Toshiaki Itami*1, Masakazu Kondo*2, Minoru Maeda*1, Reiko Fujii*3, Susumu Tomonaga3,
Electron Microscopic Evidence Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) Yukinori Takahashi*1, Toshiaki Itami*1, Masakazu Kondo*2, Minoru Maeda*1, Reiko Fujii*3, Susumu Tomonaga3,
PMT. Contains ribosomes attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Genetic material consists of linear chromosomes. Diameter of the cell is 1 µm
 1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
1. (a) Complete each box in the table, which compares a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell, with a tick if the statement is correct or a cross if it is incorrect. Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell Contains
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Discovery of. 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes. 1931: first images of viruses obtained using
 Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral structures. Just how small are viruses? Workbook Lesson 1.4 1
 Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Phylum Echinodermata
 Phylum Echinodermata Spiny Skin Echinodermata Radially symmetrical in five ways (pentamerous) Echinodermata No head, right or left side, or top or bottom, so we refer to the oral surface (mouth side) and
Phylum Echinodermata Spiny Skin Echinodermata Radially symmetrical in five ways (pentamerous) Echinodermata No head, right or left side, or top or bottom, so we refer to the oral surface (mouth side) and
Cells & Cell Transport. Cells
 Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Cells & Cell Transport Cells Cell Membrane Cell membrane (plasma membrane): a phospholipid bilayer surrounding the cell Each phospholipid has a polar phosphate head and lipid tails Selectively permeable:
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level
 Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
47 (5) : , ( Haliotis discus hannai Ino) (microvilli),, ( : 2, 3) (cisternae wit h elect ron2dense cores) , 7 cm, 215 % ,, L KB28800
 47 (5) :583 586, 2001 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 (, 315211),,,,,,,, ( Haliotis discus hannai Ino), 211,, (microvilli),, ( : 2),, 6 (, ), (apical granules), 1 1997, 7 cm 215 % (cisternae wit h elect ron2dense
47 (5) :583 586, 2001 A cta Zoologica S inica 3 (, 315211),,,,,,,, ( Haliotis discus hannai Ino), 211,, (microvilli),, ( : 2),, 6 (, ), (apical granules), 1 1997, 7 cm 215 % (cisternae wit h elect ron2dense
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Coronaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
Coronaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Spherical enveloped particles studded with clubbed spikes Diameter 120-160 nm Coiled helical
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Chapter 3 - The Immune System
 Chapter 3 - The Immune System What are germs? We all have heard that washing your hands helps stop the spread of germs What are germs exactly? Germs are disease-causing invaders or organisms, also called
Chapter 3 - The Immune System What are germs? We all have heard that washing your hands helps stop the spread of germs What are germs exactly? Germs are disease-causing invaders or organisms, also called
Dr. Gary Mumaugh. Viruses
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Some living things are made of ONE cell, and are called. Other organisms are composed of many cells, and are called. (SEE PAGE 6)
 Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
psittaci by Silver-Methenamine Staining and
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS*
 Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
Onderstepoort J. vet. Res. (1968), 35 (1), 139-150 Printed in the Repub. of S. Afr. by The Government Printer, Pretoria ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE FORMATION OF BLUETONGUE VIRUS* G. LECATSAS, Veterinary
KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans.
 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness KEY CONCEPT Germs cause many diseases in humans. 31.1 40.1 Pathogens Infectious Diseases and Human Illness Germ theory states that microorganisms
CHAPTER 3 1/21/2016. Typical Bacteria Cell. The Cell
 CHAPTER 3 The Cell Chapter 3 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why surface area-to-volume ratios constrain cell size. Contrast light microscopy
CHAPTER 3 The Cell Chapter 3 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why surface area-to-volume ratios constrain cell size. Contrast light microscopy
The World of Cells. Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both
 The World of Cells Name Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CHROMATIN SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
The World of Cells Name Organelle Description Function Animal, Plant or Both CELL WALL CELL MEMBRANE CYTOPLASM NUCLEUS NUCLEAR MEMBRANE NUCLEOLUS CHROMATIN SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC
Immune System and Disease. Chapter 31
 Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Date. Student Name. Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses.
 Student Name Characteristics of Viruses--Part I Level High School - Science Date _ Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses. Similarities and Differences Between Viruses
Student Name Characteristics of Viruses--Part I Level High School - Science Date _ Prompt: This passage is called Characteristics of Viruses. It is about viruses. Similarities and Differences Between Viruses
Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy uridine in Human Lymphoblastoid Cells F ro m a Rhabdom yosarcom a*
 A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Diversity. Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include:
 Echinoderms Diversity Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include: Sea stars Brittle stars Sand dollars Sea cucumbers
Echinoderms Diversity Echinodermata means spiny skin Echinoderms usually inhabit shallow coastal waters and ocean trenches organisms in this class include: Sea stars Brittle stars Sand dollars Sea cucumbers
Virology. *Viruses can be only observed by electron microscope never by light microscope. The size of the virus: nm in diameter.
 Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Viruses. Picture from:
 Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Mitigation of pathogens and marine biotoxins contamination in shellfish
 Safety and Security Engineering V 691 Mitigation of pathogens and marine biotoxins contamination in shellfish P. Fajardo 1, M. Atanassova 1, J. Cotterill 2, T. Wontner-Smith 2, J. Vieites 1 & A. Cabado
Safety and Security Engineering V 691 Mitigation of pathogens and marine biotoxins contamination in shellfish P. Fajardo 1, M. Atanassova 1, J. Cotterill 2, T. Wontner-Smith 2, J. Vieites 1 & A. Cabado
FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION
 FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION 1. True or false: because enzymes are produced by living organisms and because they allow chemical reactions to occur that would not otherwise occur, enzymes represent an exception
FIRST MIDTERM EXAMINATION 1. True or false: because enzymes are produced by living organisms and because they allow chemical reactions to occur that would not otherwise occur, enzymes represent an exception
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 (ii) Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1
 1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
1. (a) (i) Ability to distinguish points (close together); 1 Electrons have a shorter wavelength; 1 (b) (i) Golgi / nucleus / mitochondrion / endoplasmic reticulum / chromosome / larger ribosomes; R Membrane
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Reoviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
Cell Theory. Two Types of Cells. Cells: The Basic Unit of Life. 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells
 Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things 3. All cells are produced from other
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things 3. All cells are produced from other
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Wednesday, October 19, 16. Viruses
 Viruses Image of an animal cell More realistic size of a virus compared to an animal cell Cells can fulfill all characteristics of life Viruses on their own can be considered lifeless chemicals, unless?
Viruses Image of an animal cell More realistic size of a virus compared to an animal cell Cells can fulfill all characteristics of life Viruses on their own can be considered lifeless chemicals, unless?
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR
 ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
ISOLATION OF A SARCOMA VIRUS FROM A SPONTANEOUS CHICKEN TUMOR Shigeyoshi ITOHARA, Kouichi HIRATA, Makoto INOUE, Masanori Veterinary Pathology, Faculty of Agriculture, Yamaguchi University* HATSUOKA, and
Classification of Diseases
 Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
The Immune System it protects your health. Who are the invaders? Viruses tiny protein shells filled with DNA or RNA
 The Immune System it protects your health Who are the invaders? Bacteria Viruses Pathogens Bacteria are very small and mostly harmless Single-celled organisms Only a few cause disease Extremely small,
The Immune System it protects your health Who are the invaders? Bacteria Viruses Pathogens Bacteria are very small and mostly harmless Single-celled organisms Only a few cause disease Extremely small,
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Domoic Acid Toxicity Toxic Algae Poisoning
 The Marine Mammal Center began doing research on marine mammal diseases almost from its inception in 1975. Because animals in the Center s care offer a unique opportunity to perform blood and tissue analyses,
The Marine Mammal Center began doing research on marine mammal diseases almost from its inception in 1975. Because animals in the Center s care offer a unique opportunity to perform blood and tissue analyses,
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics. AP Biology
 Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
SEPUP ITEM BANK. Item Banks TR-253. Multiple choice. Circle the best answer.
 Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Paris, 8-10 August 2006
 1 Original: English August 2006 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE AD HOC GROUP ON THE OIE LIST OF AQUATIC ANIMAL DISEASES - MOLLUSC TEAM - FOR THE OIE AQUATIC ANIMAL HEALTH CODE Paris, 8-10 August 2006
1 Original: English August 2006 REPORT OF THE MEETING OF THE OIE AD HOC GROUP ON THE OIE LIST OF AQUATIC ANIMAL DISEASES - MOLLUSC TEAM - FOR THE OIE AQUATIC ANIMAL HEALTH CODE Paris, 8-10 August 2006
18.2. Viral Structure and Reproduction. Viruses differ in shape and in ways of entering
 18.2 Viral Structure and Reproduction VOCABULARY bacteriophage lytic infection lysogenic infection prophage compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role
18.2 Viral Structure and Reproduction VOCABULARY bacteriophage lytic infection lysogenic infection prophage compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role
Part I. Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents.
 Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x
 J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE
 CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
CELL (PLASMA) MEMBRANE Separates cell from its environment Controls substances that enter and leave the cell Selectively permeable allows certain substances to pass COMPOSITION Composed of 2 layers of
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
SNEEZE ZONE BACKGROUND INFORMATION MATERIALS TO RUN THE ACTIVITY. Teacher s notes
 BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many diseases are airborne and can spread in tiny droplets of water or aerosols that people cough or sneeze into the air. Aerosols in a sneeze can travel at more than 100 kilometres
BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many diseases are airborne and can spread in tiny droplets of water or aerosols that people cough or sneeze into the air. Aerosols in a sneeze can travel at more than 100 kilometres
the structure of their ducts has been
 Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Tza JOURNAL 0? INVEa'riGATrVN DEBMATOLOOT Copyright t 1966 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 46, No. I Printed in U.S.A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF THE ADULT HUMAN APOCRINE DUCT* KEN HASHIMOTO,
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*)
 Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Hiroshima Journal of Medical Sciences Vol. 31, No. 1, March, 1982 HJIM 31-6 31 Ultrastructural Study of Human Natural Killer CNK) Cell*) Yoshinori KAWAGUCHI, Eishi KITTAKA, Yoshito TANAKA, Takeo TANAKA
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function
 7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
VIRAL AGENTS CAUSING GASTROENTERITIS
 VIRAL AGENTS CAUSING GASTROENTERITIS VIRAL AGENTS CAUSING GASTROENTERITIS Pathogens discussed in our lectures 1. Rotavirus 2. Enteric adenoviruses 3. Caliciviruses 4. Astroviruses 5. Toroviruses Viruses
VIRAL AGENTS CAUSING GASTROENTERITIS VIRAL AGENTS CAUSING GASTROENTERITIS Pathogens discussed in our lectures 1. Rotavirus 2. Enteric adenoviruses 3. Caliciviruses 4. Astroviruses 5. Toroviruses Viruses
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability
 Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Wellcome Research Laboratories, Beckenham, Kent, England. Royal Postgraduate Medical School, London, England. (Accepted 27 January I972)
 J. gen. ViroL (I972), I5, 227-234 22 7 Printed in Great Britain Interaction of Sendai (HVJ) Virus with Human Erythrocytes: a Morphological Study of Haemolysis Cell Fusion By K. APOSTOLOV Wellcome Research
J. gen. ViroL (I972), I5, 227-234 22 7 Printed in Great Britain Interaction of Sendai (HVJ) Virus with Human Erythrocytes: a Morphological Study of Haemolysis Cell Fusion By K. APOSTOLOV Wellcome Research
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Cells. Cell as a basic unit of life. Activity: Observing onion cells. Cells
 1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
Farm-level biosecurity (TiLVD prevention and management)
 Session 5 Win Surachetpong DVM, PhD, CertAqV, DTBVP Farm-level biosecurity (TiLVD prevention and management) Outlines: What is biosecurity? Identify risks causing the introduction and spread of disease
Session 5 Win Surachetpong DVM, PhD, CertAqV, DTBVP Farm-level biosecurity (TiLVD prevention and management) Outlines: What is biosecurity? Identify risks causing the introduction and spread of disease
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses. Virus Characteristics. Viral Host Range
 Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION
 M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville
M I C R O B I O L O G Y WITH DISEASES BY TAXONOMY, THIRD EDITION Chapter 14 Infection, Infectious Diseases, and Epidemiology Lecture prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, University of Tennessee, Knoxville
1.3 - Cells. Chapter 3 - Cells
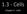 1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
1.3 - Cells Chapter 3 - Cells Cells Cytology = the study of cells All animal cells have 3 main parts: Nucleus Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semipermeable Cytoplasm (cytosol): where remaining organelles
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
 1. (a) An electron microscope has a much greater resolving power than an optical microscope. (i) Explain the meaning of the term resolving power. Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
1. (a) An electron microscope has a much greater resolving power than an optical microscope. (i) Explain the meaning of the term resolving power. Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1975, p. 1332-1336 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and Canine Cell Lines
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Nov. 1975, p. 1332-1336 Copyright i 1975 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 16, No. 5 Printed in U.S.A. Temperature-Sensitive Mutants Isolated from Hamster and Canine Cell Lines
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Acta Medica Okayama. Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON. Zensuke Ota DECEMBER 1970
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 24, Issue 6 1970 Article 3 DECEMBER 1970 Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON Zensuke Ota Okayama University, Copyright c 1999
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 24, Issue 6 1970 Article 3 DECEMBER 1970 Electron microscopic demonstration of a new virus isolated from a patient with SMON Zensuke Ota Okayama University, Copyright c 1999
Offending agents like: 1. Infectious agents: 2. toxic agents(toxins) Micro-organisms Bacteria Viruses Parasites Fungi
 Immunity Dr.Talar Immunity: is the ability of the human body to resist almost all types of offending agents that tend to damage the tissues and organs or it s a special system for combating different infectious
Immunity Dr.Talar Immunity: is the ability of the human body to resist almost all types of offending agents that tend to damage the tissues and organs or it s a special system for combating different infectious
CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
 THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
THS JOURNAL OF INVEBTIOATIVR DERMATOLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 93, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. CELLS CONTAINING LANGERHANS GRANULES IN HUMAN LYMPH NODES OF DERMATOPATHIC LYMPHADENOPATHY*
CONTENTS. 1. Introduction. 4. Virology. 2. Virus Structure. 5. Virus and Medicine. 3. Virus Replication. 6. Review
 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 4. Virology 2. Virus Structure 5. Virus and Medicine 3. Virus Replication 6. Review We have all gotten viruses from bacteria, plants to animals. Viruses cause colds, flu, warts
CONTENTS 1. Introduction 4. Virology 2. Virus Structure 5. Virus and Medicine 3. Virus Replication 6. Review We have all gotten viruses from bacteria, plants to animals. Viruses cause colds, flu, warts
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
Name: INTRODUCTION TO THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Introduction: If you missed the microscope lab we did in class, you will need to make it up by using a "virtual microscope" which can be accessed on the internet.
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
18.2 Viruses and Prions
 KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
UNIT 6: PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 31: Immune System and Disease
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be stamped after each assigned
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
