Research Note. Cryptococcal osteomyelitis of the femur: A case report and review of literature
|
|
|
- Ira Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tropical Biomedicine 28(2): (2011) Research Note Cryptococcal osteomyelitis of the femur: A case report and review of literature Zainal, A.I. 1*, Wong, S.L. 2, Pan, K.L. 3, Wong, O.L. 4 and Tzar, M.N. 5 1 Department of Pathology, 2 Radiology and 3 Orthopaedics, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Universiti Malaysia Sarawak, Malaysia 4 Department of Pathology, Sarawak General Hospital, Sarawak, Malaysia 5 Department of Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Center, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia * Correspondence author rzabidin@fmhs.unimas.my Received 15 November 2010; received in revised form 10 April 2011; accepted 11 April 2011 Abstract. Fungal osteomyelitis is a rare opportunistic infection. It exhibits some clinical and radiological similarities to several other bone pathologies. A diagnostic delay may result in significant increase in morbidity. We report a case of a 37-year-old man with underlying hypogammaglobulinaemia presented with isolated cryptococcal osteomyelitis of the femur. INTRODUCTION Fungal infections are more often seen in debilitated patients, particularly among young immunocompromised hosts and the lung is the usual portal of entry (Bullogh, 1997). Very occasionally they cause osteomyelitis and avascular necrosis of bone. The infections may become fatal if not treated promptly; hence an early diagnosis is vital. Gurevitz et al. (1994) reported that fungal infections among immunocompetent patients are rare occasions. The commonly described infections include blastomycosis, coccidoidomycosis, cryptococcosis and rarely actinomycosis (Bullogh, 1997). In this report we highlighted the clinicopathological features of this rare bone infection followed by a literature view on the diagnosis and treatment. Case report A 37-year-old man presented with a slowly enlarging right knee swelling for seven months duration associated with joint stiffness, recurrent fever and significant loss of weight and appetite. On physical examination the mass exhibited surface erythema with limited range of movement. The knee joint was warm and tender on palpation. No discharging sinus or other joint involvement was detected. The man had a previous history of pulmonary tuberculosis and had completed treatment four years prior to this presentation. Radiograph of the knee showed nonexpansile osteolytic lesions with a narrow zone of transition within the distal femur medial condyle (Figure 1). There was a mild marginal sclerosis noted around the lesions. The lesion did not seem to abut the articular surface. There was no regional periosteal reaction noted. Overall radiographic features were suggestive of Brodie s abscess. Subsequently, surgical drainage and curettage of the lesion were performed. Intraoperatively, there was a 2 cm cavity at the medial cortex of distal right femur 2 cm from the joint line. Patchy whitish areas of 444
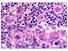
2 Figure 1. The radiograph of the distal femur osteolytic lesions The arrows point at the distal femur lesion. No regional periosteal reaction noted degenerated tissue were seen lining the cavity. Approximately 3 mls of purulent exudates were drained-out. Histological examination of the cavity wall showed fibrocollagenous tissue with scattered clusters of rounded fungal organisms in yeast form. These yeasts were surrounded by aggregates of macrophages (Figure 2). The yeast displayed refractile appearance under polarized light. No hyphae form detected. The organism stained positive with Gomori methanamine silver (GMS) stain. The morphology of the fungus in histology was consistent with Cryptococcus neoformans. Post-operative serum cryptococcal antigen was noted to be positive (1:4096 titres). However, cultures from the tissue fragments and the aspirated pus were negative. No caseating granuloma was seen to suggest tuberculosis. The patient was treated with two weeks course of intravenous amphotericin B 35 mg daily and followed by oral fluconazole 400 mg daily for the following six weeks. Lumbar puncture was performed post-operatively. No fungal element was detected in the cerebrospinal fluid while the culture study was negative. On further investigation, the patient was noted to have low immunoglobulins G, A and M (below the normal levels of an adult). The HIV, hepatitis B and C screenings were non-reactive. The patient was neither neutropaenic nor diabetic. He works as a farmer and denied any direct contact with birds. On follow up, his condition improved with no residual active lesion. He is currently treated for hypogammaglobulinaemia. DISCUSSION Pyogenic bacteria and mycobacteria are among the commonest cause of osteomyelitis. With the emergence of opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients, the diagnosis and treatment of osteomyelitis have become more challenging (Rosenberg, 2004). Cryptococcus neoformans is an uncommon but treatable causal factor of osteomyelitis which may affect both normal and immunocompromised patients (Behrman et al., 1990; McClelland et al., 2007). 445
3 Figure 2. Tissue biopsy from the lesion (H&E 20X) There were numerous scattered Cryptococcus neoformans organisms (blue arrows) surrounded and engulfed by aggregates of macrophages Several predisposing factors of cryptococcosis have been identified including HIV infection, haematological disorders and several chronic diseases (Chayakulkeeree & Perfect, 2008). Cryptococcosis occurs primarily by inhalation of the infectious propagules, however, direct inoculation into tissue due to trauma or through gastrointestinal tract can be possible portals of entry occasionally (Chayakulkeeree & Perfect, 2008). In healthy individual the infection is commonly cleared or may remain in latent form for a prolong period of time (McClelland et al., 2007). Most fungi are highly immunogenic and induce strong antibody response and T cell-mediated immunity. Cryptococcus neoformans possesses a polysaccharide capsule which inhibits phagocytosis. This protective mechanism can be overcome by host s complement and antibody opsonisation (Male et al., 2006). The capsule is one of the main pathogenic factors as acapsular strains are avirulent (McClelland et al., 2007). Reduced level of immunoglobulin in this case predisposed this patient towards this infection. Deep mycosis typically shows different level of aggressiveness. It most likely depends on the individual and the respective organism involved (Witte et al., 2000). Cyrptococcal osteomyelitis occurs commonly as a complication to chronic meningoencephalitis (Bullogh 1997). An isolated cryptococcal osteomyelitis is an uncommon condition (Witte et al., 2000). The spectrum of clinical presentation extends from asymptomatic with an osteolytic lesion to an infection with signs and symptoms of systemic involvement (Behrman et al., 1990). Sarcoidosis is the most common reported underlying disease in association with this mycosis, followed by tuberculosis and previous steroid treatment (Witte et al., 2000). The vertebra is the commonest reported osteomyelitis site while the other frequent sites include the pelvis, femur, spine and tibia (Bullogh, 1997; Liu, 1998). Radiographically, the osteolytic femoral condyle lesion in especially in this age group displayed non-specific features which are commonly shared by several conditions including giant cell tumor, chondroblastoma, subchondral cyst or infective processes. 446
4 Cryptococcal osteomyelitis commonly exhibits osteolysis with or without local periosteal reaction (Rabia, 2006). An extensive periosteal reaction is an uncommon finding (Witte et al., 2000). With the given history of slow progressive nature of the clinical presentation, the radiographic findings of this patient were more suggestive of tuberculous osteomyelitis or subacute pyogenic osteomyelitis. Clinical and radiological similarity to several other bone pathologies may cause delay in antifungal treatment initiation. The early recognition of the organism by morphology, culture study and serological analysis may potentially improve the prognosis and treatment of this infection (Witte et al., 2000). Histological evaluation is a quick and easy method to identify fungal organism. It is an important adjunct to culture study for diagnosis of fungal infection. Fungi organism can be identified based on their size and distinctive morphology (Haque, 2010). Cryptococcus is a basidiomycete that grows as haploid budding yeast (McClelland et al., 2007). In tissue histology, the yeast cells of Cryptococcus are typically spherical and irregular in size ranging from 5 to 20 µm in diameter. The cells typically exhibit thick polysaccharide capsule (Anselmo et al., 2003). The budding forms appear to be attached by a narrow constriction. Most fungi including Cryptococcus are readily demonstrated with common special stains for fungus including GMS and periodic acid Schiff (Haque, 2010). Fine needle aspiration with Diff-Quick stained slide has been reported to be useful for prompt diagnosis and exclusion of malignant neoplasm (Witte et al., 2000). Hence when a chronic granulomatous inflammation pattern was detected, it is important to perform a direct smear and culture study for acid fast bacilli and also for fungi (Bullogh, 1997). Pre-operative serological cryptococcal antigen may prove to be helpful (Gurevitz et al., 1994). In a properly collected and processed specimen, there are several reasons that might lead to a negative culture study. This includes low sensitivity of culture, host immunocompetence recovery and institution of antifungal agents prior to culture. In this case, visualization of yeast cells during histopathological examination had virtually confirmed the presence of yeasts in the tissue. The only question left was the confirmation of species. Conventional methods of fungal culture have been known to yield unsatisfactory rate of isolation. To our knowledge, there is no published study that looked specifically into the sensitivity of conventional culture methods in isolating Cryptococcus species from clinical specimens. However, Telenti & Roberts (1989) reported that the best blood culture system (the Isolator system) could only detect 73% in a study on autopsy-proven disseminated candidiasis. Therefore, a negative culture does not exclude an active infection. Another possible reason for the negative cultures is recovery of host immunocompetency. In previously treated cases of cryptococcal infection among HIV patients, antiretroviral therapy institution had led to subsequent improvement in CD4+ cell count and immune function. This condition, called the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS), may sometimes cause clinical deterioration as a result of rapid and dysregulated immune response recovery. These cases usually presented with negative cryptococcal cultures (Bicanic & Harrison, 2010). Another study by Manfredi et al. (2003) showed that after the introduction of highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART), episodes of HIV-related cryptococcosis characterized by persistently negative cultures rose from 10.3% of years to 87.5% after They concluded that the apparent absence of viable organisms might be explained by the increased immune response against a latent infection due to HAART use, the co-administration of suppressive antifungal therapy and the proinflammatory role played by cryptococcal antigen, even in the absence of active fungal replication. However in this case, the patient was neither diagnosed as HIV-positive nor did he receive any antifungal agents prior to sample collection for the culture studies. The possibility of the cryptococcal antigen test being false positive is remote. The false positive rate of cryptococcal 447
5 capsular polysaccharide antigen testing is only 0% to 0.4% (Kauffman et al., 1981). In addition, a titre of 4096 in this case was too high to be ignored. Most of the false positive results of latex agglutination testing for cryptococcal polysaccharide antigen have initial reciprocal titers of 8 or less (Tanner et al., 1994). Antifungal treatment and surgery are the two common therapeutic choices (Raftopoulos et al., 1998). Most cases of cryptococcal osteomyelitis were successfully treated with medical treatment alone or in combination with surgical debridement (Liu, 1998). The reported effective antifungal agents include amphotericin B and fluconazole as proven in this case (Behrman et al., 1990). Cryptococcal osteomyelitis may lead to significant morbidity and mortality. It should be considered as one of the differential diagnoses of osteolytic osseous lesions particularly in immunocompromised or even in immunocompetent hosts. Acknowledgements. The authors wish to thank Dr. Mohd Zulkarnaen A Narihan and Angela Chia Yin Yin for her assistance in writing this case. REFERENCES Anselmo, C., Lee, K., Lia, J.Y., Bergunio, R., Lum, A., Viduya, P., Jang, J., Goodman, C.D., Warner, S.L., Roemer, M. & Haller, B. (2003). A resident s fungal morphology [Online]. Available from: ucsf.edu/education (Accessed 7 November 2010) Behrman, R.E., Masci, J.R. & Nicholas, P. (1990). Cryptococcal skeletal infections: case report and review. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 12(2): Bicanic, T. & Harrison, T. (2010). Cryptococcus. In: Spectrum of Disease and Treatment in Pathogenic Yeasts, the Yeast Handbook. Ashbee HR and Bignell EM (editors) Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg: Bullogh, P.G. (1997). Bullogh and Vigoritta s Orthopaedic Pathology 3 rd edition. Mosby-Wolfe: Chayakulkeeree, M. & Perfect, J.R. (2008). Cryptococcosis. In: Infectious Disease: Diagnosis and Treatment of Human Mycoses. Hospenthal DR and Rinaldi MG Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ: Gurevitz, O., Goldschmied-Reuven, A., Block, C., Kopolovic, J., Farfel, Z. & Hassin, D. (1994). Cryptococcus neoformans vertebral osteomyelitis. Journal of Medical and Veterinary Mycology. 32(4): Haque, A. (2010). Special stains use in fungal infections. Connection: Kauffman, C.A., Bergman, A.G., Severance, P.J. & McClatchey, K.D. (1981). Detection of cryptococcal antigen. Comparison of two latex agglutination tests. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 75: Liu, Y.F. (1998). Cryptococcal osteomyelitis: Case report and review. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 30(1): Male, D., Brostoff, J., Roth, D.B. & Roitt, I. (2006). Immunology 7th edition. Mosby: Manfredi, R., Calza, L. & Chiodo, F. (2003). AIDS-associated cryptococcus infection before and after the highly active antiretroviral therapy era: Emerging management problems. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 22: McClelland, E.E., Casadevall, A. & Eisenman, H.C. (2007). New Insight in Medical Mycology. Springer Netherlands: Rabia, A. (2006). Cryptococcal osteomyelitis of the humeral head initially diagnosed as avascular necrosis. Southern Medical Journal [Online]. Available from: (Accessed 7 November 2011) Raftopoulos, I., Mellerab, J.L., Harris, V. & Reyesab, H.M. (1998). Cryptococcal rib osteomyelitis in a pediatric patient. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 33(5):
6 Rosenberg, A.E. (2004). Bone, joints and soft tissue tumours. In: Robbins and Contran Pathologic Basis of Disease 7 th edition. Elsevier Saunders Philadelphia: Tanner, D.C., Weinstein, M.P., Fedorciw, B., Joho, K.L., Thorpe, J.J. & Reller, L. (1994). Comparison of commercial kits for detection of cryptococcal antigen. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 32: Telenti, A. & Roberts, G.D. (1989). Fungal blood cultures. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 8: Witte, D.A., Chen, I., Brady, J., Ramzy, I., Truong, L.D. & Ostrowski, M.L. (2000). Cryptococcal osteomyelitis. Report of a case with aspiration biopsy of a humeral lesion with radiologic features of malignancy. Acta Cytologica 44(5):
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
OSTEOMYELITIS. If it occurs in adults, then the axial skeleton is the usual site.
 OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
OSTEOMYELITIS Introduction Osteomyelitis is an acute or chronic inflammatory process of the bone and its structures secondary to infection with pyogenic organisms. Pathophysiology Osteomyelitis may be
Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I
 BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
Common Fungi. Catherine Diamond MD MPH
 Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit
 ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
ECMM Excellence Centers Quality Audit Person in charge: Department: Head of Department: Laboratory is accredited according to ISO 15189 (Medical Laboratories Requirements for quality and competence) Inspected
Definition. Paracoccidioidmycosis. History. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Epidemiology
 Definition Paracoccidioidmycosis Hillary Howard Carlisle Heinselman Sarah Maher Arjun Vikuntam A systematic endemic disease produced by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Primarily a pulmonary disease Disseminated
Definition Paracoccidioidmycosis Hillary Howard Carlisle Heinselman Sarah Maher Arjun Vikuntam A systematic endemic disease produced by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Primarily a pulmonary disease Disseminated
General History. 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : ~ Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious 5 minutes in the morning.
 General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
General History 林陳 珠 Female 69 years old 住院期間 : 93.5.8~93.5.15 Chief Complaint : sudden loss of conscious for 2-52 5 minutes in the morning. General History DM under regular medical control for 10 years.
Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming Yeh, Jung-Chung Lin, Ning-Chi Wang, Ming-Yieh Peng, Feng-Yee Chang
 J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 9;:-6 Cryptococcal disease in patients with or without human immunodeficiency virus: clinical presentation and monitoring of serum cryptococcal antigen titers Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming
J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 9;:-6 Cryptococcal disease in patients with or without human immunodeficiency virus: clinical presentation and monitoring of serum cryptococcal antigen titers Te-Yu Lin, Kuo-Ming
HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM
 HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Hanoi, Vietnam, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan, Bach Mai hospital, Vietnam, Military
HISTOPLASMOSIS - LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS IN VIETNAM National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Hanoi, Vietnam, National Institute of Infectious Diseases, Tokyo, Japan, Bach Mai hospital, Vietnam, Military
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis
 Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis Identify the structures neutrophils macrophages x40 Organisms 8 30 micron in size, with variable capsule
Impression smear from a nasal mass on a 2 year old cat Presented with: one month duration of epistaxis Identify the structures neutrophils macrophages x40 Organisms 8 30 micron in size, with variable capsule
Enzyme Immunoassay versus Latex Agglutination Cryptococcal Antigen Assays in Adults With non-hiv-related Cryptococcosis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 24 September 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02017-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 24 September 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02017-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Case Report Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis and Prevention of Cryptococcal Meningitis Using a Novel Point-of-Care Lateral Flow Assay
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 640216, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/640216 Case Report Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis and Prevention of Cryptococcal Meningitis Using a Novel Point-of-Care
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2013, Article ID 640216, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/640216 Case Report Diagnosis of Cryptococcosis and Prevention of Cryptococcal Meningitis Using a Novel Point-of-Care
Cryptococcosis*,** *usually considered to be an opportunistic mycosis that often becomes systemic.
 Cryptococcosis*,** Definition - a chronic, subacute or rarely acute pulmonary, systemic or meningitic infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans - the encapsulated Blastomycetes anamorph of Filobasidiella
Cryptococcosis*,** Definition - a chronic, subacute or rarely acute pulmonary, systemic or meningitic infection caused by Cryptococcus neoformans - the encapsulated Blastomycetes anamorph of Filobasidiella
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens
 Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
Pathogens with Intermediate Virulence Dermatophytes opportunistic Pathogens Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Aspergillus species Pneumocystis carinii 1 Dermatophytes Named for derma skin Cause
RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE PULMONARY CRYPTOCOCCOSIS WITH CAVITATION IN AN IMMUNOCOMPETENT WOMAN: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW
 RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE PULMONARY CRYPTOCOCCOSIS WITH CAVITATION IN AN IMMUNOCOMPETENT WOMAN: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Junyan Qu, Xiaohui Wang, Yanbin Liu and Xiaoju Lv Center of Infectious Disease,
RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE PULMONARY CRYPTOCOCCOSIS WITH CAVITATION IN AN IMMUNOCOMPETENT WOMAN: A CASE REPORT AND LITERATURE REVIEW Junyan Qu, Xiaohui Wang, Yanbin Liu and Xiaoju Lv Center of Infectious Disease,
Mycology. BioV 400. Subcutaneous Mycoses. Ecological associations. Geographic distribution World-wide
 BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
BioV 400 Mycology Handout 8 Subcutaneous Mycoses Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Chromoblastomycosis Phaeohyphomycosis Zygomycosis Mycetoma Lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis Sporothrix schenckii Chronic infection
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Chifu, Sadamu; Sakata, Shuji; Hayas. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 2003, 48
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Skull Cryptococcal Osteomyelitis Co Tuberculosis Yoshida, Shintaro; Nakazaki, Kiyosh Chifu, Sadamu; Sakata, Shuji; Hayas Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Skull Cryptococcal Osteomyelitis Co Tuberculosis Yoshida, Shintaro; Nakazaki, Kiyosh Chifu, Sadamu; Sakata, Shuji; Hayas Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Fungal Meningitis. Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse Bern
 Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation
 Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
Topics. Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities. Detection of Infection. Role of Imaging in Extremity Infection. Detection of Infection
 Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
Topics Musculoskeletal Infection Extremities Nuttaya Pattamapaspong M.D. Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand Role of imaging in extremity infection
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues. Introduction. Histochemical Stains Used to Detect Fungi. Histopathologic Diagnoses
 The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
The Differentiation of Yeast and Yeast-Like Forms in Human Tissues Gary W. Procop, MD Chair, Clinical Pathology Staff, Anatomic Pathology Director, Molecular Microbiology, Mycology, and Parasitology Cleveland
CMV. Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone.
 CMV Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone. CMV inclusions are often present in a very patchy distribution Carefully examine all levels CMV CMV
CMV Inclusions predominantly in endothelial cells. Immunostaining greater sensitivity than H&E alone. CMV inclusions are often present in a very patchy distribution Carefully examine all levels CMV CMV
Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2013 1 Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV Deepak Nayak M *. Sushma V. Belurkar **, Chethan Manohar ***,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 3, Issue 3, March 2013 1 Cryptococcal Meningitis: Looking beyond HIV Deepak Nayak M *. Sushma V. Belurkar **, Chethan Manohar ***,
ACCEPTED. Title: False Positive Culture Results from Patient Tissue Specimens Due to. Contamination of RPMI Medium with Cryptococcus albidus
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 February 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02447-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 February 2007 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.02447-06 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Aspergillus species. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis
 Pentalfa 3 maart 2016 The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis Pascal Van Bleyenbergh, Pneumologie UZ Leuven Aspergillus species First described in 1729 * >250 species * ubiquitous Inhalation of
Pentalfa 3 maart 2016 The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis Pascal Van Bleyenbergh, Pneumologie UZ Leuven Aspergillus species First described in 1729 * >250 species * ubiquitous Inhalation of
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION
 CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration often for months, years or even indefinitely. Its prolonged course is proved by persistence of the causative
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery
 Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
Prof Oluwadiya KS FMCS (Orthop) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon / Associate Professor Division of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Department of Surgery College of Health Sciences Ladoke Akintola University
KAP conference 19 th March 2008: Dr Mohamed Hussein Jin.
 SENSITIVITY PATTERNS, SEROTYPES OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS AND DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF INDIA INK IN PATIENTS WITH CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL. KAP conference 19 th March 2008: Dr
SENSITIVITY PATTERNS, SEROTYPES OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS AND DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF INDIA INK IN PATIENTS WITH CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS AT KENYATTA NATIONAL HOSPITAL. KAP conference 19 th March 2008: Dr
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in an HIV-infected Patient
 Case Report Vol. 28 No. 3 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis:- Wongkulab P, et al. 203 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in an HIV-infected Patient Panuwat Wongkulab, M.D., Nontakan Nuntachit, M.D., Romanee Chaiwarith, M.D.,
Case Report Vol. 28 No. 3 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis:- Wongkulab P, et al. 203 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in an HIV-infected Patient Panuwat Wongkulab, M.D., Nontakan Nuntachit, M.D., Romanee Chaiwarith, M.D.,
Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract
 Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Before you start: You must read the slides! The Dr. did not bother to explain them all Mycobacteria and fungal infections of the respiratory tract - TB is a global problem that the WHO is trying to combat.
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis
 Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: granulomatous inflammation, including tuberculosis These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System
 Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
PREVALENCE OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS AMONGST HIV SEROPOSITIVE CASES FROM A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL
 IJCRR Vol 06 issue 14 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 25/05/14 Revised on: 21/06/14 Accepted on: 12/07/14 PREVALENCE OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS AMONGST HIV SEROPOSITIVE CASES FROM A
IJCRR Vol 06 issue 14 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 25/05/14 Revised on: 21/06/14 Accepted on: 12/07/14 PREVALENCE OF CRYPTOCOCCAL MENINGITIS AMONGST HIV SEROPOSITIVE CASES FROM A
Tuberculosis. By: Shefaa Q aqa
 Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Tuberculosis By: Shefaa Q aqa Tuberculosis is a communicable chronic granulomatous disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It usually involves the lungs but may affect any organ or tissue in the
Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report
 Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
Volume 2 Issue 3 2012 ISSN 2250-0359 Actinomycosis and aspergillosis in the nose of a diabetic: A case report 1 Meenu Khurana Cherian 1*, Rajarajeswari 2 1 Department of ENT, Gulf Medical College Hospital
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data
 2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
2046: Fungal Infection Pre-Infusion Data Fungal infections are significant opportunistic infections affecting transplant patients. Because these infections are quite serious, it is important to collect
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS. Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA. University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014
 SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
SEPTIC ARTHRITIS Dr Ahmed Husam Al Ahmed Rheumatologist SYRIA University of Science and technology Hospital Sanaa Yemen 18/Dec/2014 Objectives be able to define Septic Arthritis know what factors predispose
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A CASE REPORT Babu B. Hundekar 1
 TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
TUBERCULOUS OSTEOMYELITIS OF PATELLA: A Babu B. Hundekar 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Babu B. Hundekar. Tuberculous Osteomyelitis of Patella: A Case Report. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
number Done by Corrected by Doctor د.حامد الزعبي
 number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
number Fungi#1 Done by نرجس الس ماك Corrected by مهدي الشعراوي Doctor د.حامد الزعبي Introduction to Mycology -Terms: -Medical Mycology: The study of mycosis and their etiological agents -Mycosis: Disease
Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case
 Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case Nanda Patil 1, Avinash Mane 2, Rashmi L. Sonawane 3, Suchi Gadhiya 4 Abstract: Introduction: Actinomycosis is a chronic suppurative infection caused by Actinomyces
Actinomycosis of Thoracic Spine A Rare Case Nanda Patil 1, Avinash Mane 2, Rashmi L. Sonawane 3, Suchi Gadhiya 4 Abstract: Introduction: Actinomycosis is a chronic suppurative infection caused by Actinomyces
Fungi. Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy:
 MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
MYCOLOGY Mycology I Fungi Eucaryotic Rigid cell wall(chitin, glucan) Cell membrane ergosterol Unicellular, multicellular Classic fungus taxonomy: Morphology Spore formation FFungi Yeast Mold Yeastlike
Cryptococcal Meningitis in Patients with or without Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Experience in a Tertiary Hospital
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.3.482 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 52(3):482-487, 2011 Cryptococcal Meningitis in Patients with or without Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Experience
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2011.52.3.482 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 52(3):482-487, 2011 Cryptococcal Meningitis in Patients with or without Human Immunodeficiency Virus: Experience
Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1168 1172 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.119 Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1168 1172 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.119 Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
Fungal Infections. Fungal Infections
 Fungal Infection in the Immune Competent Host Steven L. Primack, MD Fungal Infection in the Immune Competent Host Steven L. Primack, MD Department of Radiology Oregon Health & Science University Fungal
Fungal Infection in the Immune Competent Host Steven L. Primack, MD Fungal Infection in the Immune Competent Host Steven L. Primack, MD Department of Radiology Oregon Health & Science University Fungal
Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of the Knee
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 1961287, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1961287 Case Report Sacral Emphysematous Osteomyelitis Caused by Escherichia coli after Arthroscopy of
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~ 1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Bone necrosis. Cross section.
 Bone necrosis. Cross section. Note the large area of necrosis (N) seen as pale discolored bone (beneath physeal cartilage). The texture of the necrotic bone is also changed. Necrotic bone becomes friable
Bone necrosis. Cross section. Note the large area of necrosis (N) seen as pale discolored bone (beneath physeal cartilage). The texture of the necrotic bone is also changed. Necrotic bone becomes friable
TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY
 CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
CASE REPORT TUBERCULOSIS OF THE RIB IN A 20 MONTH S OLD BOY El Mouhtadi Aghoutane, Tarik Salama, Redouane El Fezzazi Pediatric surgery department, Kadi Ayyad University, Marrakech, Morocco Abstract Primary
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
ACCME/Disclosures. Two Patients and a Caveat 4/13/2016. Patient #1: 13 y/o boy with IPEX syndrome; s/p BMT
 Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
Two Patients and a Caveat The Use and Misuse of Molecular Methods in Mycobacterial Infections Gary W. Procop, MD Director, Molecular Microbiology Infectious Disease Pathologist Cleveland Clinic ACCME/Disclosures
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE RHINOCEREBRAL MUCORMYCOSIS DUE TO RHIZOPUS IN A RECENTLY DIAGNOSED DIABETIC FEMALE: A CASE REPORT KULKARNI KV 1, PATHAK NP 2 1. Assistant
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE RHINOCEREBRAL MUCORMYCOSIS DUE TO RHIZOPUS IN A RECENTLY DIAGNOSED DIABETIC FEMALE: A CASE REPORT KULKARNI KV 1, PATHAK NP 2 1. Assistant
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Cryptococcal Meningitis
 Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 CASE REPORT Disseminated Cryptococcosis Complicated with Bilateral Pleural Effusion and Ascites during Corticosteroid Therapy for Organizing Pneumonia with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Hiroyuki Kamiya 1, Rie
CASE REPORT Disseminated Cryptococcosis Complicated with Bilateral Pleural Effusion and Ascites during Corticosteroid Therapy for Organizing Pneumonia with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Hiroyuki Kamiya 1, Rie
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
CRYPTOCOCCOSIS IN HIV-INFECTED CHILDREN
 CRYPTOCOCCOSIS IN HIV-INFECTED CHILDREN Surachai Likasitwattanakul, Boonsom Poneprasert and Virat Sirisanthana Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
CRYPTOCOCCOSIS IN HIV-INFECTED CHILDREN Surachai Likasitwattanakul, Boonsom Poneprasert and Virat Sirisanthana Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
Case Presentation. Intern Tutor VS 2007/01/26
 Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
Case Presentation Intern 8931150 Tutor VS 2007/01/26 About The Patient 38 years old worker ID: M120794700 Admission date: 2006/12/28 C.C.: Fever with headache for 2 days Present Illness Smoker, alcoholism
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient. Dr Kirsty Dodgson
 Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
Fungal infection in the immunocompromised patient Dr Kirsty Dodgson Aims Discuss different types of fungi Overview of types of clinical infections Clinical Manifestations Fungus Includes Moulds Aspergillus
LUNG FUNGUS PRESENTED WITH NODULES- A CASE REPORT
 LUNG FUNGUS PRESENTED WITH NODULES- A CASE REPORT Dr Ujwal Thakur 1, Prof. Dr Huang Jinbai 2 and Prof. Dr Ren Boxu 3 1Department of radiology, the first affiliated Hospital of Yangtze University, Jingzhou,
LUNG FUNGUS PRESENTED WITH NODULES- A CASE REPORT Dr Ujwal Thakur 1, Prof. Dr Huang Jinbai 2 and Prof. Dr Ren Boxu 3 1Department of radiology, the first affiliated Hospital of Yangtze University, Jingzhou,
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 2.417, ISSN: , Volume 3, Issue 11, December 2015
 MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
MANAGEMENT OF PATHOLOGICAL FRACTURE SHAFT HUMERUS SECONDARY TO BACTERIAL OSTEOMYELITIS: A CASE REPORT DR. NARENDRA SINGH KUSHWAHA* DR.SHAH WALIULLAH** DR.VINEET KUMAR*** DR.VINEET SHARMA**** *Asst. Professor,
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification. Taxonomic Systems for Identification of the Anamorphs of Conidiogenous Fungi
 Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Hyphomycetes & Coelomycetes Identification Saccardo ~1880 devised the first practical scheme for identifying fungi based on structure (morphology) of the conidium. "Sylloge Fungorum IV" Vuillemin ~ 1910
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient
 Clin Drug Investig (2013) 33 (Suppl 1):S47 S50 DOI 10.1007/s40261-012-0021-5 CASE REPORT Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient Ricardo Louro Rui Ferreira Catarina Pinheiro Helena Parada Domitília
Clin Drug Investig (2013) 33 (Suppl 1):S47 S50 DOI 10.1007/s40261-012-0021-5 CASE REPORT Fungal Meningitis in an Immunocompetent Patient Ricardo Louro Rui Ferreira Catarina Pinheiro Helena Parada Domitília
Too Competent for Cryptococcus Starr Steinhilber, MD Victoria Johnson, MD
 SGIM Clinical Vignettes Session F May 12, 2012 Too Competent for Cryptococcus Starr Steinhilber, MD Victoria Johnson, MD 48 yo healthy AAM Sx Fevers Chills Headache Back pain Vomiting Headache Back pain
SGIM Clinical Vignettes Session F May 12, 2012 Too Competent for Cryptococcus Starr Steinhilber, MD Victoria Johnson, MD 48 yo healthy AAM Sx Fevers Chills Headache Back pain Vomiting Headache Back pain
Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease
 Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Non-TB Mycobacterial Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, MD Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Jeffrey P. Kanne, M.D. Consultant Disclosures Perceptive Informatics Royalties (book author) Amirsys, Inc. Wolters
Paracoccidioidomycosis
 Paracoccidioidomycosis Paracoccidioidomycosis refers to the infectious, endemic disease caused by the fungi pathogen, paracoccidioides Phylum: Ascomycota Genus: Paracoccidioides Wide spectrum of disease
Paracoccidioidomycosis Paracoccidioidomycosis refers to the infectious, endemic disease caused by the fungi pathogen, paracoccidioides Phylum: Ascomycota Genus: Paracoccidioides Wide spectrum of disease
Types of bone/joint infections. Bone and Joint Infections. Septic Arthritis. Pathogenesis. Pathogenesis. Bacterial arthritis: predisposing factors
 Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
Bone and Joint Infections Types of bone/joint infections Arthritis (infective/septic) Osteomyelitis Prosthetic bone and joint infections Septic Arthritis Common destructive athroplasty Mono-articular Poly-articular
Management of fungal infection
 Management of fungal infection HKDU symposium 17 th May 2015 Speaker: Dr. Thomas Chan MBBS (Hons), MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Synopsis Infection caused by fungus mycoses Skin infection by fungus is common in general
Management of fungal infection HKDU symposium 17 th May 2015 Speaker: Dr. Thomas Chan MBBS (Hons), MRCP, FHKCP, FHKAM Synopsis Infection caused by fungus mycoses Skin infection by fungus is common in general
Update from the Laboratory: Clinical Identification and Susceptibility Testing of Fungi and Trends in Antifungal Resistance 13
 Fungal Infections Preface: Fungal Infections Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner and Jack D. Sobel xiii The Global Burden of Fungal Diseases 1 Snigdha Vallabhaneni, Rajal K. Mody, Tiffany Walker, and Tom Chiller Fungal
Fungal Infections Preface: Fungal Infections Luis Ostrosky-Zeichner and Jack D. Sobel xiii The Global Burden of Fungal Diseases 1 Snigdha Vallabhaneni, Rajal K. Mody, Tiffany Walker, and Tom Chiller Fungal
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION. Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics
 BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
BONE AND JOINT INFECTION Dr.Jónás Zoltán Dept.of Orthopaedics www.ortopedia.dote.hu Order of verbal exams: The students are able to register for the exam on the Neptun system. The students pick two titles,
North American Endemic Fungi
 North American Endemic Fungi Boni Elizabeth Elewski, MD Chair Department of Dermatology University of Alabama at Birmingham James Elder Professor of Graduate Medical Education DISCLOSURE OF FINANCIAL RELATIONSHIPS
North American Endemic Fungi Boni Elizabeth Elewski, MD Chair Department of Dermatology University of Alabama at Birmingham James Elder Professor of Graduate Medical Education DISCLOSURE OF FINANCIAL RELATIONSHIPS
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST
 ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Dr J Garbino University Hospital Geneva ASPERGILLOSIS IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST INTRODUCTION SWISS ASPERGILLOSIS SURVEY IN THE NON-NEUTROPENIC HOST Introduction
Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
 Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, Vol 4(2) 2008, pp. 11-14 http://dx.doi.org/10.21161/mjm.11508 Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, Vol 4(2) 2008, pp. 11-14 http://dx.doi.org/10.21161/mjm.11508 Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
and the Working Group from the EMBO-AIDS Related Mycoses Workshop Institute of Infectious Disease and Molecular Medicine, University of Cape Town,
 1 AIDS-related mycoses: the way forward Gordon D. Brown 1,2*, Graeme Meintjes 1, Jay K. Kolls 3, Clive Gray 1, William Horsnell 1 and the Working Group from the EMBO-AIDS Related Mycoses Workshop 1 Institute
1 AIDS-related mycoses: the way forward Gordon D. Brown 1,2*, Graeme Meintjes 1, Jay K. Kolls 3, Clive Gray 1, William Horsnell 1 and the Working Group from the EMBO-AIDS Related Mycoses Workshop 1 Institute
Isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis in an immunocompetent patient presenting with right shoulder pain: a case report and review of the literature
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis in an immunocompetent patient presenting with right shoulder pain: a case report and review of the literature RKH Cheung, F Ng,
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Isolated pulmonary cryptococcosis in an immunocompetent patient presenting with right shoulder pain: a case report and review of the literature RKH Cheung, F Ng,
A CASE REPORT OF: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS CANDIDIASIS INDUCED BY LONG TERM SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS THERAPY
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 A CASE REPORT OF: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS CANDIDIASIS INDUCED BY LONG TERM SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS THERAPY Ziad Salim Abdul
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 A CASE REPORT OF: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS CANDIDIASIS INDUCED BY LONG TERM SYSTEMIC CORTICOSTEROIDS THERAPY Ziad Salim Abdul
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease
 Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
Histopathology Description:
 2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
2013-2-1 CANINE HEART Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION : The Royal Veterinary college, Dept. of Pathology and Biology Signalment: 11-month-old male Border Collie dog (Canis familiaris)
Scottish Surveillance of Healthcare Associated Infection Programme (SSHAIP) Health Protection Scotland (HPS) SSI Surveillance Protocol 7th Edition
 1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
1 Contents Female reproductive system operations (Abdominal hysterectomy and Caesarean section)... 3 Intra-abdominal infections... 3 Endometritis... 4 Other infections of the female reproductive tract...
Case Report Coccidioides immitis Cervical Lymphadenitis Complicated by Esophageal Fistula
 Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2016, Article ID 8715405, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8715405 Case Report Coccidioides immitis Cervical Lymphadenitis Complicated by Esophageal Fistula
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases Volume 2016, Article ID 8715405, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8715405 Case Report Coccidioides immitis Cervical Lymphadenitis Complicated by Esophageal Fistula
8/2/10. Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer Demler, Jeremy King. Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system.
 Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system. Type of chronic respiratory infection http://www.eregimens.com/regimens/antifungal%20general.htm Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer
Histoplasmosis is an intracellular mycotic infection of the reticuloendothelial system. Type of chronic respiratory infection http://www.eregimens.com/regimens/antifungal%20general.htm Sanaz Jalali, Jennifer
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases
 Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases Healthcare Focus on: - individual - diagnosis - treatment Public Health Focus on: - population - prevention The nature of fungi Kingdom Fungi (lat. fungus, -i)
Epidemiology and ecology of fungal diseases Healthcare Focus on: - individual - diagnosis - treatment Public Health Focus on: - population - prevention The nature of fungi Kingdom Fungi (lat. fungus, -i)
